Exam 2
1/206
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
207 Terms
summary of decarboxylase test
name of medium: decarboxylase broth
substrate: lysine/ornithine
bacterial enzyme: LDC/ODC
end products: cadaverine/putrescine
positive result: purple/alkaline
negative result: yellow/acidic
reagent: n/a
pH indicator: bromocresol purple
summary of phenylamine deaminase
name of medium: phenol alanine slant
substrate: phenylamine
bacterial enzyme: phenylamine deaminase
end products: phenyl pyruvic
positive result: green
negative result: yellow
reagent: Ferric chloride
pH indicator: n/a
summary of casein hydrolysis
name of medium: skim milk agar
substrate: casein
bacterial enzyme: casease (exoenzyme)
end products: amino acids and polypeptides
positive result: milk becomes clear
negative result: no clearing, but still growing
reagent: n/a
pH indicator: n/a
summary of urease test
name of medium: urease broth
substrate: urea
bacterial enzyme: urease (exoenzyme)
end products: ammonia and carbon dioxide
positive result: pink
negative result: yellow
reagent: n/a
pH indicator: phenol red
summary of the triple sugar iron test (sulfur reduction)
name of medium: triple sugar agar
substrate: cysteine and sodium thio sulfate
bacterial enzyme: cysteine desulfurize and thiosulfate reductase (various endoenzymes)
end products: h2S + ferrous ammonium sulfate → black
positive result: black for sulfur reduction
negative result: not black
reagent: ferrous ammonium sulfate
pH indicator: n/a
summary of triple sugar iron (sugar)
name of medium: triple sugar agar
substrate: glucose/ lactose/ sucrose
bacterial enzyme: various endoenzymes
end products: acids and gas
positive result: yellow
negative result: pink/orange
reagent: n/a
pH indicator: phenol red
purpose of decarboxylase test
to determine whether bacteria can decarboxylate lysine or ornithine (amino acid)
peptones, beef extract in decarboxylase test
food for general growth
glucose in decarboxylase test
for fermentation ( bacteria use glucose 1st at a low concentration to lower pH)
pyridoxyl in decarboxylase test
vitamin B6 - required coenzyme
l-lysine or l-ornithine in carboxylase test
amino acid substrate
negative result meaning in decarboxylase
bacteria metabolized used a produced acid sugar that lowered the pH
purpose of deaminase
to determine whether bacteria can deaminate phenylaline
yeast extract in phenylalanine deaminase
general growth
Aspartame (nutrasweet & equal)
artificial sweetener that is a dipeptide of phenylamine and aspartic acid with methanol, 180x times sweeter than sugar
Why can’t you use a pH indicator as a readout
ammonia is a base and phenyl pyruvic acid is an acidic → cancel each other out
negative result of deaminase
stays yellow and no phenylpyruvic acid produced
positive result of deaminase
turn green and phenylpyruvic acid present
aerobic in deaminase
proteins are deanimated
anaerobic in deaminase
proteins are carboxylase
purpose of casein hydrolysis
to determine whether bacteria can hydrolyze casein
pancreatic digest of casein and yeast extract in casein hydrolysis
general growth
non-fat milk in casein hydrolysis
source of casein (substrate)
glucose in casein hydrolysis
added nutrients for growth
why peptones instead of intact proteins in casein hydrolysis
peptones are small and already digested. They’re ready to go for bacteria in terms of general growth
one type of organism in urease test
Proteus mirabilis
purpose of urease test
to determine whether bacteria can hydrolyze urea
yeast extract in urease test
general growth
urea in urease test
substrate found in urine
phenol red in urease test
pH indicator
purpose of TSI agar
to differentiate bacteria on the basis of glucose fermentation, lactose fermentation, sucrose fermentation, and sulfur reduction
peptones in TSI agar
general growth
glucose in TSI agar
low glucose concentration as substrate for fermentation to produce acids
lactose and sucrose in TSI agar
substrate (disaccharide) for fermentation to produce acid
ferrous ammonium sulfate in TSI agar
H2S detector reagent - turns black
sodium thiosulfate in TSI agar
source of reducible sulfur
phenol red in TSI agar
phenyl red
interpretation and organism of pink slant and yellow butt
glucose only fermenter
as glucose is exhausted, the organism will break down protein and cause reversion in the aerobic slant
proteus Alcofacies
interpretation and organism of yellow slant and yellow with gas butt
ferments glucose and lactose and/or glucose
Eserichia coli
interpretation and organism of pink slant and orange butt
non-fermenter, used peptones aerobically
obligate aerobe (peptone used aerobically only)
n/a
interpretation and organism of pink slant and pink butt
nonfermented, used peptones anaerobically too
non-saccharolytic
pseundoneas aeroginosa & alicligenes faecalis
interpretation and organism of yellow slant and black butt
H2S production and all sugar fermentation
hydrolyzes into H2S by acidic
pseudomonas vulgaris
interpretation and organism of pink slant and black butt
H2S production and glucose only fermenter
Proteus mirabilis & salmonella underaesis
purpose of motility test
to determine whether bacteria are motile (can move)
purpose of gelatin hydrolysis test
to determine whether bacteria can hydrolyze gelatin
gelatin
protein extract from bones, cartilage, connective tissue, etc.
collagen is the most abundant protein in the body
it is a protein food source for bacteria
organism in gelatinase hydrolysis test (+ bacteria)
Clostridium perfringens
has collagenase (a type of gelatinase) activity
causes gangrene: skin becomes black and dies. Blood can’t get to it so it can’t be treated with antibiotics
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
most common cause of death in burn victims
gram negative rod that loves water and if it gets into wound and get trapped in the dressing, almost no antibiotics work
purpose of anaerobic jar
to determine the oxygen requirements of an organism
O2 indicator and interpretations
resazurin (O2 indicator)
pink = oxidized/aerobic
clear = reduced/anaerobic
how microbes process oxygen

Aerobes and the different types
use molecular O2 as a final electron acceptor
obligate aerobe
microaerophiles
obligate aerobes and example
require O2
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
superoxide dismutase = +
catalase = +
microaerophiles and examples
require low O2 concentration
helicobacter pylori
superoxide dismutase = - (a little)
catalase = - (a little)
anaerobes and types
don’t use O2 or it is toxic to them
obligate anaerobes
facultative anaerobes
aerotolerant anaerobes
obligate anaerobes and example
cease growth or die in O2
clostridium
superoxide dismutase = -
catalase = -
facultative anaerobes and example
grow with or without O2, but grow best with O2
eserichia coli
superoxide dismutase = +
catalase = +
aerotolerant anaerobes and example
can grow in O2, but don’t use it as final electron acceptor
streptococcus
superoxide dismutase = +
catalase = -
purpose of thioglycollate medium
to determine the O2 requirements of an organism
yeast extract, peptones in thioglycolate medium
general growth
glucose/dextrose in thioglycolate medium
fermentation
sodium thioglycolate and L-cystine in thioglycolate medium
reduce O2 into water (make anaerobic
resazurin in thioglycolate medium
O2 indicator
pink = oxidized, O2 present
colorless = reduced, O2 absent
pseudomonas aeruginosa (gram - rod) in anaerobic jar
aerobic = +
anaerobic = -
O2 requirement = strict/obligate aerobic
disease = skin infection in burn victim, ear infection, lung infection in cystic fibrosis patients
additional notes = pyocyanin pigment; interfaces with air

staphylococcus aureus (gram + coccus) in anaerobic jar
aerobic = +
anaerobic = +
O2 requirement = facultative oxygen
disease = skin infection, skin boil, abscesses, sepsis, food poisoning, pneumonia
additional notes = staphyloxanthin pigment; no flagella

clostridium sporogenes (gram + rod)
aerobic = -
anaerobic = +
O2 requirement = strict/obligate anaerobe
disease = other clostridium, botulism, tetanus, gangrene, colitis
additional notes = nitrate reducer, doesn’t interface with air; has flagella

neisseria meningitidis or N. gonorrhoeae (Gram - coccus) in anaerobic jar
aerobic = -
anaerobic = -
O2 requirement = microaerophile (little air lover), requires low O2
disease = meningitis, gonorrhea

purpose of oxidase test
to test bacteria for the oxidase enzyme
positive and negative result of oxidase
positive = blue/purple; using O2 as FEA
negative = colorless; does not use O2 as FEA (within 20 seconds)
purpose of catalase test
to test bacteria for the catalase enzyme (produced by organisms that use O2 as FEA in the ETC → neutralize hydrogen peroxide (H2O2))
positive and negative result of catalase test
positive result = bubbles when H2O2 is added (O2 produced
negative result = no bubbles when H2O2 is added (no O2 produced)
summary of gelatin hydrolysis
name of medium: gelatin
substrate: gelatin
Bacterial enzyme: gelatinase (exoenzyme)
End products: polypeptides and amino acids
positive result: blue
negative result: green
reagent: n/a
pH indicator: n/a
liquification
turning to liquid
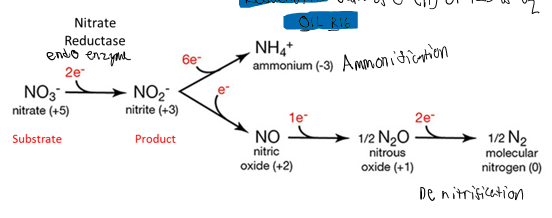
purpose of nitrate reduction test
to determine whether bacteria can use nitrate (NO3) as the final electron acceptor (FEA) during anaerobic respiration
ammonification
the production of ammonium
denitrification
loss of biologically available nitrogen; occurs by release of nitrogenous gases
oxidation
loss of e (H) or gain of O2
reduction
gain of e (H) or less of O2
nitrate reduction substrate
NO3 (nitrate)
bacterial enzyme in nitrate reduction test
Nitrate reductase (endoenzyme)
product of nitrate reduction test
NO2 (nitrite)
complete process of nitrate reduction test
Color results in nitrate reduction test
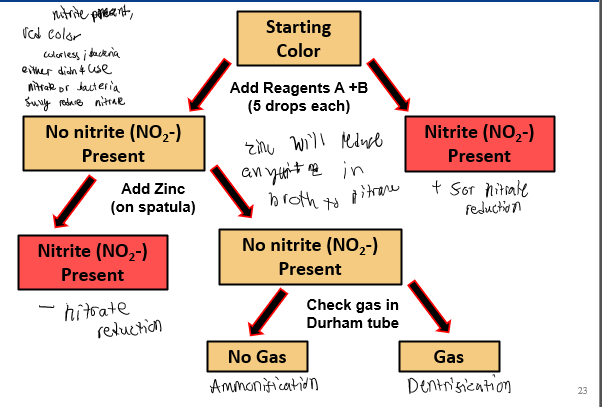
zinc in nitrate reduction test
a reducing agent, will cause nitrate to gain electrons
turns red = bacteria don’t use nitrate
remains clear = full reduction of nitrate occurred
reagent in nitrate reduction test
reagent A and B
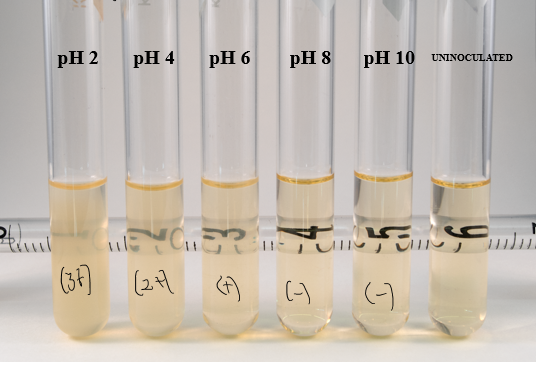
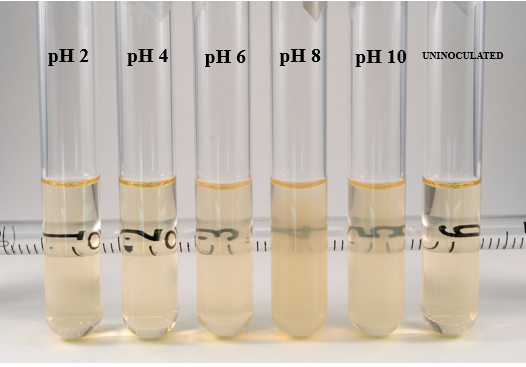
Picture of pH effect on Lactobacillus
acid = more murky
base = more clear
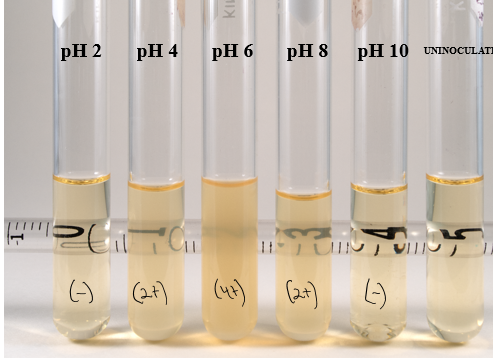
pH effect of S Aureus
mostly murky around neutral
pH effect of A faecalis
acid = more clear
base = more murky
effect of staphylococcus epidermidis in osmotic pressure
grew at all concentrations of salt (from 2-11%)

effect of Escherichia coli in osmotic pressure
can only grow at certain salt concentrations; lives in gut and can’t tolerate changes in salt
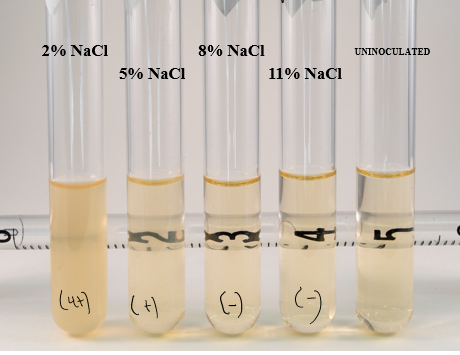
osmotolerant
lives on skin and salt concentration can change
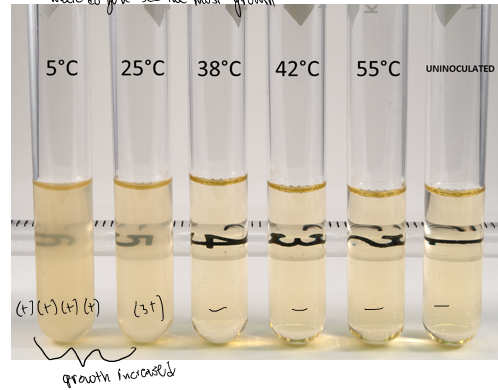
Chart of effect of temperature on microbial growth
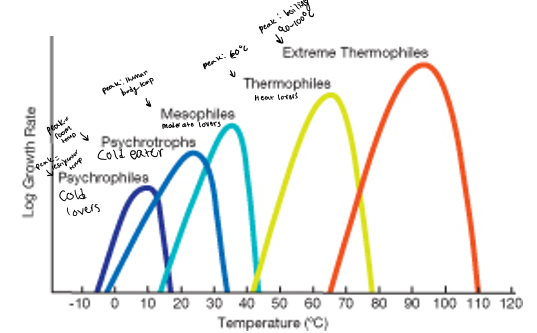
temperature microbial growth chart
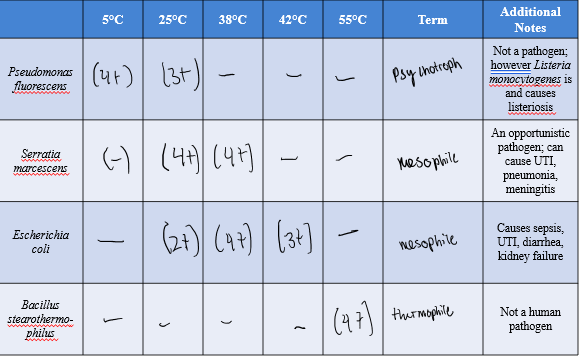
temperature effect on P. fluorescens
most growth around 5 C (psychotroph)
purpose of steam serilization
to determine if the autoclave is working properly to sterilize instruments, media, etc.
sterilization
killing all living organisms
sanition
reduce amount of micorobes
bacillus stearothermophilus endospores in steam steralization
heat resistant
bromocresol purple in steam sterilization
pH indicator
glucose = acidic
purple = alkaline
glucose in steam sterilization
fermentation if organisms survive, but will ferment glucose and produce acidic products; decrease pH
purpose of kirby bauer method
to perform a culture and antibiotic sensitivity test on an organism