Urine formation T2 W9
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
Nephron
Structural and functional unit of kidneys
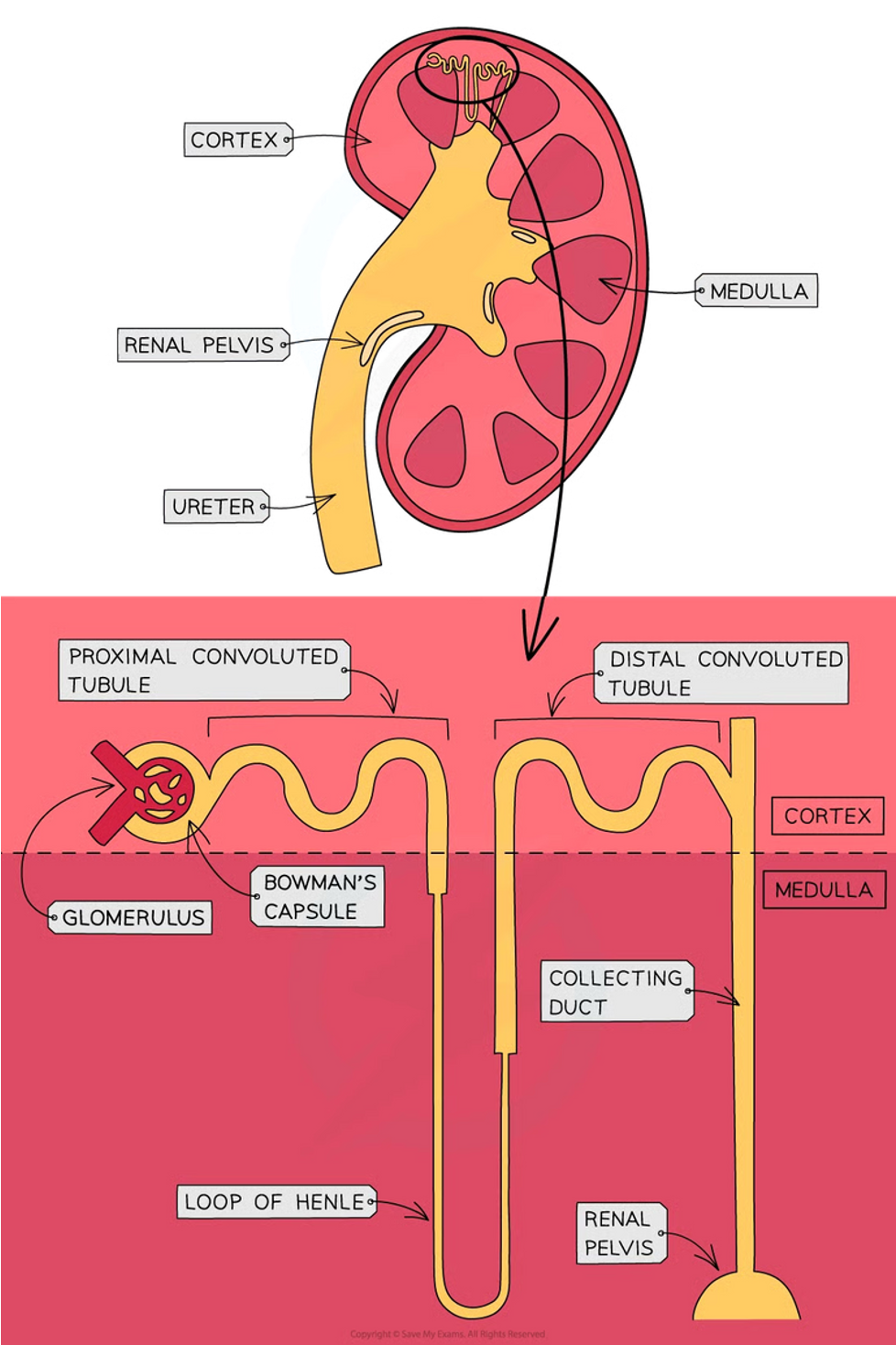
How many nephrons per kidney
1 million per kidney (thus high surface area)
3 major processes for urine formation in nephrons
Glomerular filtration
Selective reabsorption
Tubular secretion
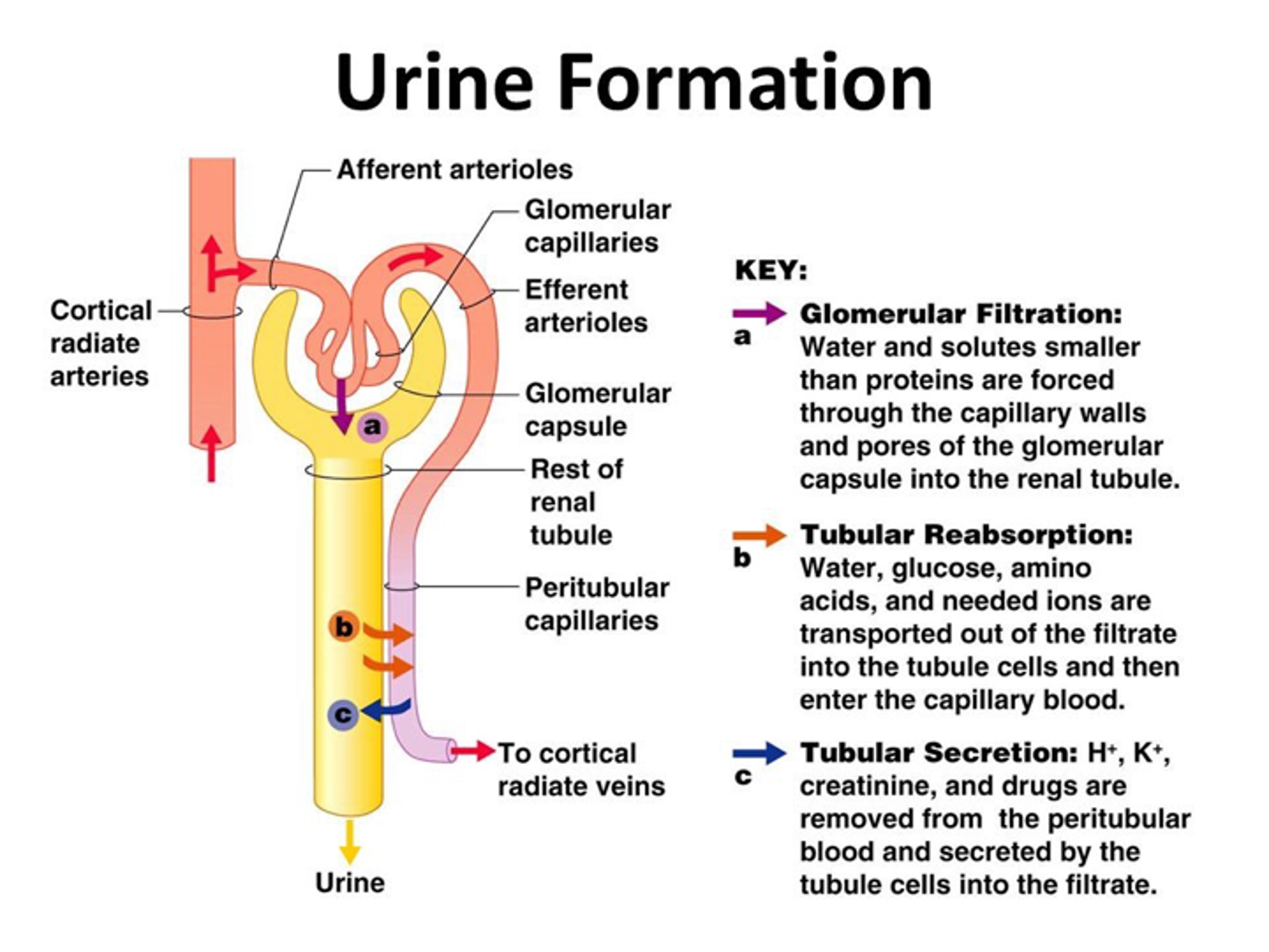
Summary of Glomerular filltration
Water + solute that are smaller than proteins are forced out through capillary walls and pores of glomerular capsule into the renal tubule.
Summary of selective (tubular) reabsorption
Water, glucose, amino acids, and needed ions are transported out of the filtrate into the tubule cells and then enters the capillary bed.
Summary of tubular secretion
Creatinine and drugs removed from peritubular blood and and secreted by tubule cells into filtrate.
What happens after urine processing
•Once the processing of filtrate ends in the collecting duct, the fluid is now called urine.
•The presence of hydrogen ions and ammonium ions lowers the pH of the urine (pH 4.5-6.0).
•Urine droplets travel down the collecting duct to the papilla of the renal pyramid.
•These urine droplets are collected by the minor calyx, which then empties into the major calyx and then the renal pelvis.
•The urine will then enter the ureter, down to the bladder for storage and then leaves the body via the urethra.
How much of urine is produced daily
approx 1.5L
What makes up urine
Water, urea, various ions and smaller quantities of other substances
What does it mean for your kidneys when there are amino acids and glucose present
Kidney dysfunction