Physiological implications in PK - Pregnancy and Obesity
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
What physiological changes occur during pregnancy?
1. Changes in total BW and body fat composition.
2. Delayed gastric emptying and prolonged GI transit time.
3. Increase in extra cellular fluid and total body water.
4. Increased cardiac output, increased stroke volume, and elevated maternal heart rate.
5. Decreased albumin concentration with reduced protein binding.
6. Increased blood flow.
7. Increased glomerular filtration rate.
8. Changed hepatic enzyme activity (phase I, phase II metabolic pathways).
What changes occur in pregnancy which affect absorption?
There is no evidence to show a difference in absorption between patients who are and aren't pregnant.
- this is shown by a study which administered antibacterial medication in patients in their 2nd or 3rd trimester compared to those 6 weeks postpartum.
What changes occur in pregnancy which affect distribution?
1. Increased volume of distribution
2. Decreased protein binding due to decrease albumin concentration
What is the effect of an increased Vd in pregnant patients?
1. It could lead to a decrease in concentration after loading dose and a decrease in Cmax after multiple-dose administration.
The effect of Vd increasing also depends on clearance.
Cl = Vd x k
2. If clearance remains the same or decreases, then an increase in Vd will lead to a decrease in k, which means t1/2 (half-life) increases.
OR
If clearance increases, then an increase in Vd will lead to an unknown effect on t1/2. This is because it depends on the magnitude of the increase in Vd or Cl.
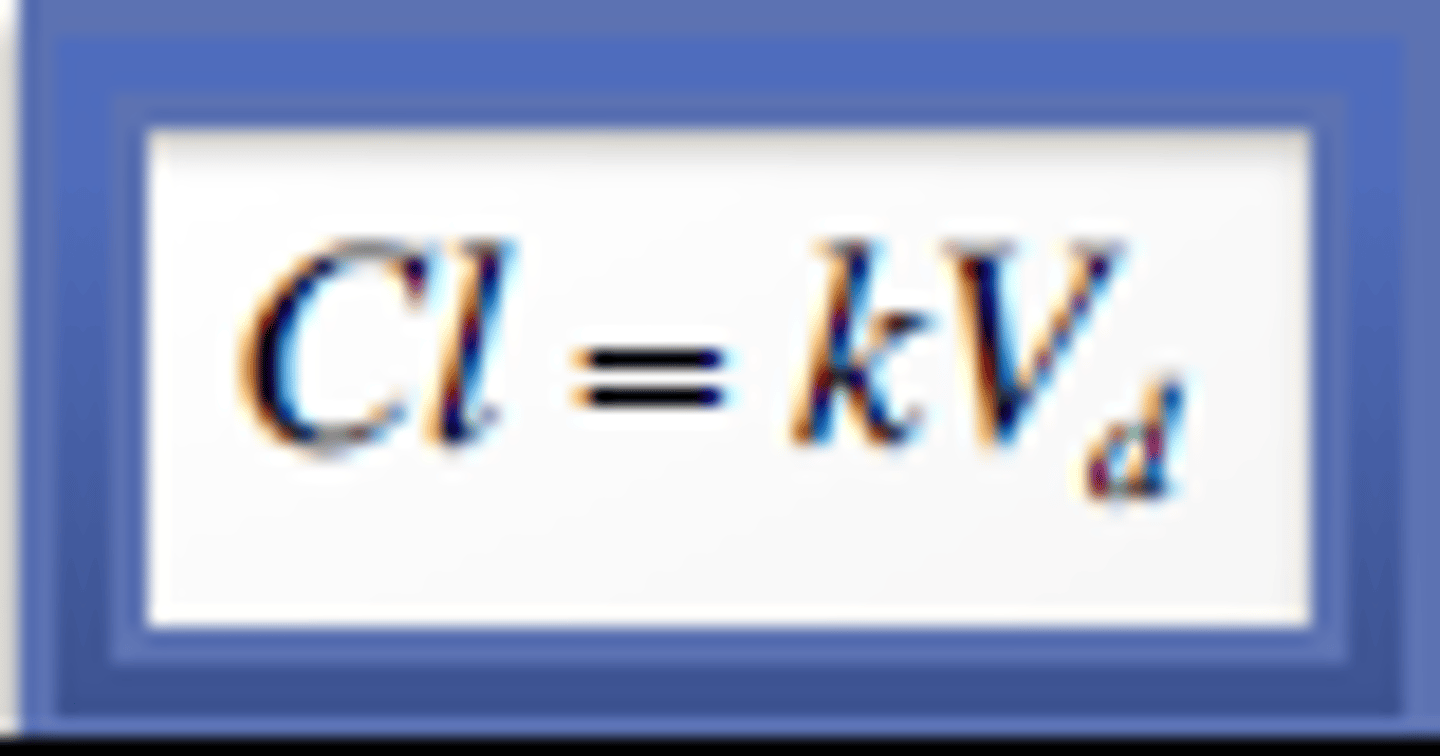
What is the effect of a decrease in plasma protein binding?
It depends on whether the drug has a high or low extraction ratio:
Low extraction ratio:
- Doses were monitored using total Cp
- Total Cp underestimates unbound or active Cp of drug
High extraction ratio:
- Decreased plasma protein binding increases the amount of unbound drug significantly. This increases the pharmacological effect of the drug
What changes occur in pregnancy which affect metabolism?
1. Increase activity of CYP3A4
2. Decrease of activity of CYP1A2
What is the effect of an increase/decrease in CYP enzymes in pregnancy?
- Increased drug metabolism therefore we need to increase the dose for efficacy and toxicity management.
- If there is a decrease in activity of CYP1A2, then we must decrease the dose to prevent accumulation of the drug.
What changes occur in pregnancy which affect excretion?
1. Increased renal excretion of drug (GFR increases by 50%)
2. Unknown effect on tubular secretion and reabsorption,
What is the effect of an increase in renal excretion in pregnancy?
There is a faster filtration rate which means there is faster elimination of the drug.
We know secretion and reabsorption are related to transport proteins or efflux transporters. We need to consider how to change dose as the effects aren't known.
What are the limitations of predictions of pregnancy on ADME?
1. Observational studies, only seen in small number of women
2. Don't effect on transport proteins
3. We don't know effect on drug eliminated by non-CYP or non-UGT pathways
4. Ethical issues of studies on pregnant women and foetus
5. The effect of pregnancy on only one drug for some isoenzymes has been discovered.
What BMI is considered overweight?
BMI ≥25 to 29.9 kg/m2
What BMI is considered obese?
BMI ≥30 kg/m2
- moderate (BMI 30.0 to 34.9)
- severe (BMI 35.0 to 39.9)
- morbid (BMI ≥ 40.0
What changes occur in obesity which affect absorption?
There is no evidence to show a difference in absorption between patients who are and aren't obese.
What changes occur in obesity which affect distribution?
1. Higher percentage of body fat
2. Lower percentage of lean tissue and body water
3. Effects on AAG (R1-acid glycoprotein) binding
What is the effect of a higher body fat percentage in obesity?
There is more fat, therefore obese patients have a greater affinity for lipophilic drugs (compared to hydrophilic compounds).
Lipophilic compounds have increase Vd in obesity.
What is the effects of obesity on AAG plasm protein binding?
AAG is a plasma protein (like albumin).
For AAG there can be an increase, decrease or no change in free fraction of drug depending on the type of drug.
e.g. increase in AAG decreases free fraction of propranolol
BUT
increase in AGG causes no change in the free fraction of triazolam
There may be changes in affinity to the proteins even if the free fraction of the drug doesn't change. We need to consider what % of the drug is free or bound. This defines dosing schedule.
What changes occur in obesity which affect metabolism?
1. Higher cardiac output and liver blood flow
2. Enlarged liver with altered histologic status
What is overall effect on metabolism by liver in obese patients?
There is little evidence.
Obesity can cause NAFLD (non-alcoholic fatty liver disease). This could reduce the body's ability to metabolise drugs.
There is evidence to suggest increased glucuronidation in obesity.
What changes occur in obesity which affect elimination?
1. Higher renal blood flow
2. Higher glomerular filtration rate
What is the effect of a greater glomerular filtration rate in obese patients?
There is differing evidence on effect of obesity on elimination.
There is a greater creatinine clearance between obese patients compared to normal bodyweight patients (for vancomycin). But this depends on the type of drug.
Safe therapeutic protocol is: to use existing therapeutic information and monitor the patient.