9- Genes and Protein synthesis
1/54
Earn XP
Description and Tags
relevant topics= pack 21 + 22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
What is a gene?
a section/ sequence of DNA that codes for 1 polypeptide, and in turn determine the nature and development of organisms
What is an allele?
a different form of a gene
What is the fixed position a gene occupies called?
a locus
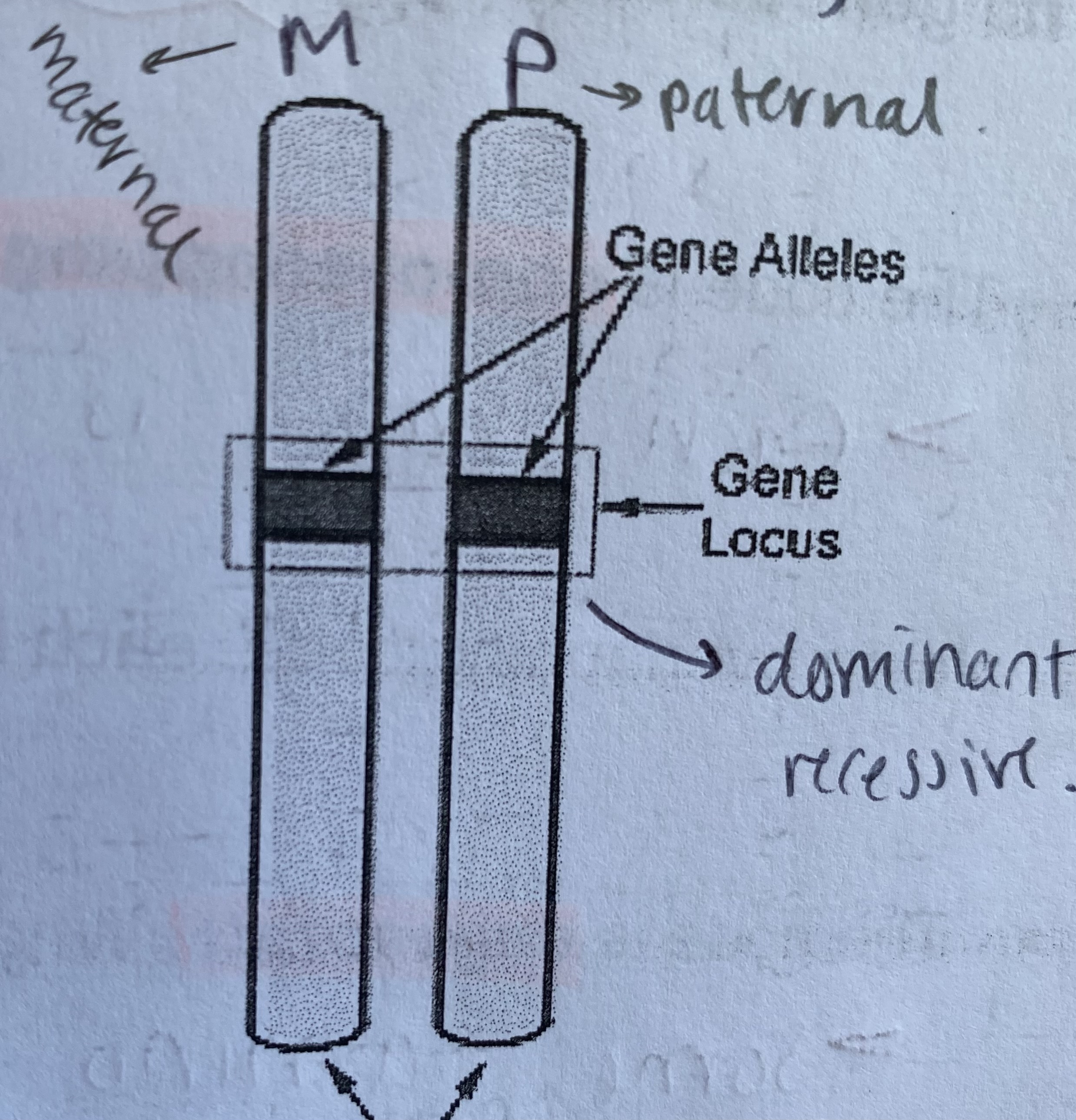
What is a pair of chromosomes called?
homologous pair
What genotype is BB?
homozygous (dominant)
What genotype is Bb?
heterozygous
What genotype is bb?
homozygous (recessive)
What does DNA carry?
the genetic code to allow the cell to make proteins
as enzymes are proteins, and enzymes control all the chemical processes going on inside cells, proteins are vital to a cell’s functions
What is the only difference between DNA strands?
length
sequence of bases
What is a triplet code?
3 base code for 1 amino acid
What are the 3 important features of genetic code?
non-overlapping
degenerate
universal
What does it mean if the genetic code is non-overlapping?
each base is part of only 1 triplet
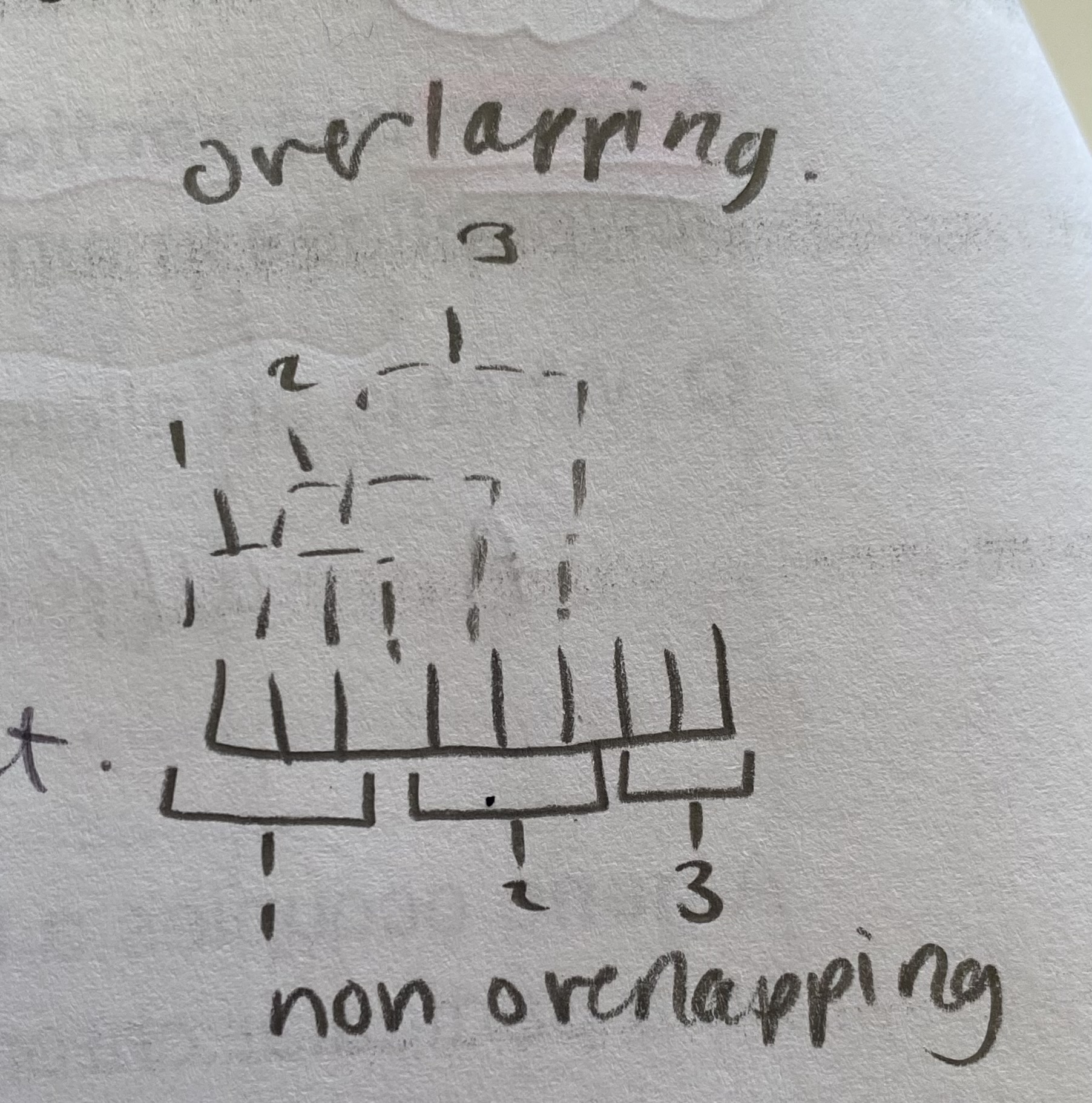
What would happen in an overlapping code?
each base would be part of 3 triplets
What does it mean if the genetic code is degenerate?
some amino acids are coded by for more than one triplet
Why is the genetic code degenerate?
there are 64 different triplet codes but only 20 amino acids
What does it mean if the genetic code is universal?
a given triplet specifies the same amino acid in all organisms
How does the gene code informationWhat does it mean if the genetic code is non-overlapping?
the specific sequence of bases on 1 strand of DNA controls the sequence of amino acids in polypeptide chains/ proteins (e.g. primary structure) that are made by a cells ribosomes, and therefore the tertiary structure and function of that protein
What does RNA stand for?
ribonucleic acid
What are the 3 main types of RNA?
ribosomal RNA
messenger RNA
transfer RNA
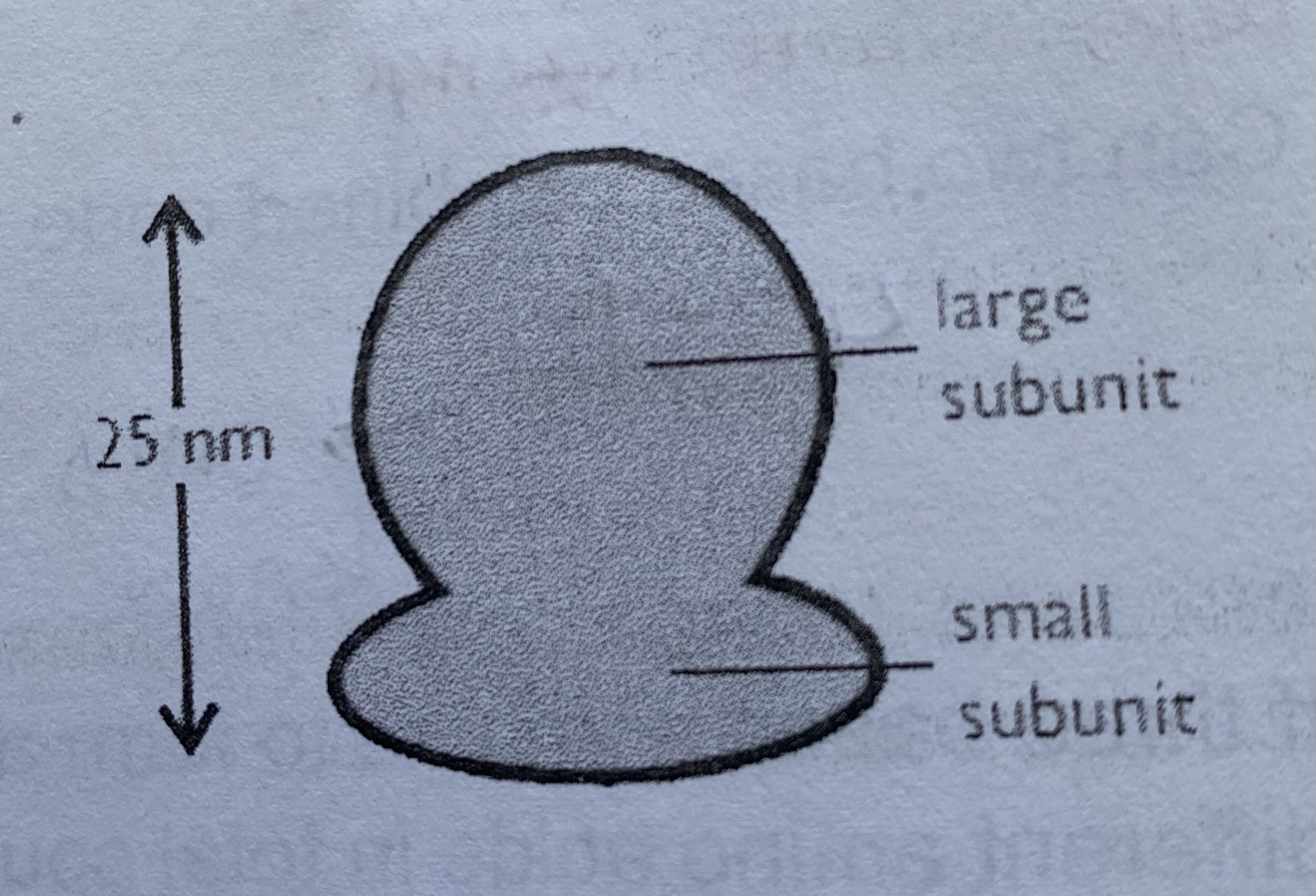
What is ribosomal RNA?
rRNA + proteins= a ribosome
site of mRNA translation and protein synthesis
rRNA is coded for by numerous genes in many different chromosomes
What is messenger RNA?
formed by transcription in the nucleus
is complementary to the DNA of its base sequence
molecules consist of thousands of nucleotides in a single linear strand
amino acid is coded by a triplet of bases on mRNA called a codon
has many unpaired bases so is easily broken down in cytoplasm- only needs to exist temporarily until protein is manufactured
What is transfer RNA?
shortest RNA molecule- made from around 80 nucleotides
single strand which folds back on itself
forms hydrogen bonds within complementary sections so causes the folding
not linear
has an anticodon
longer end holds the amino acid
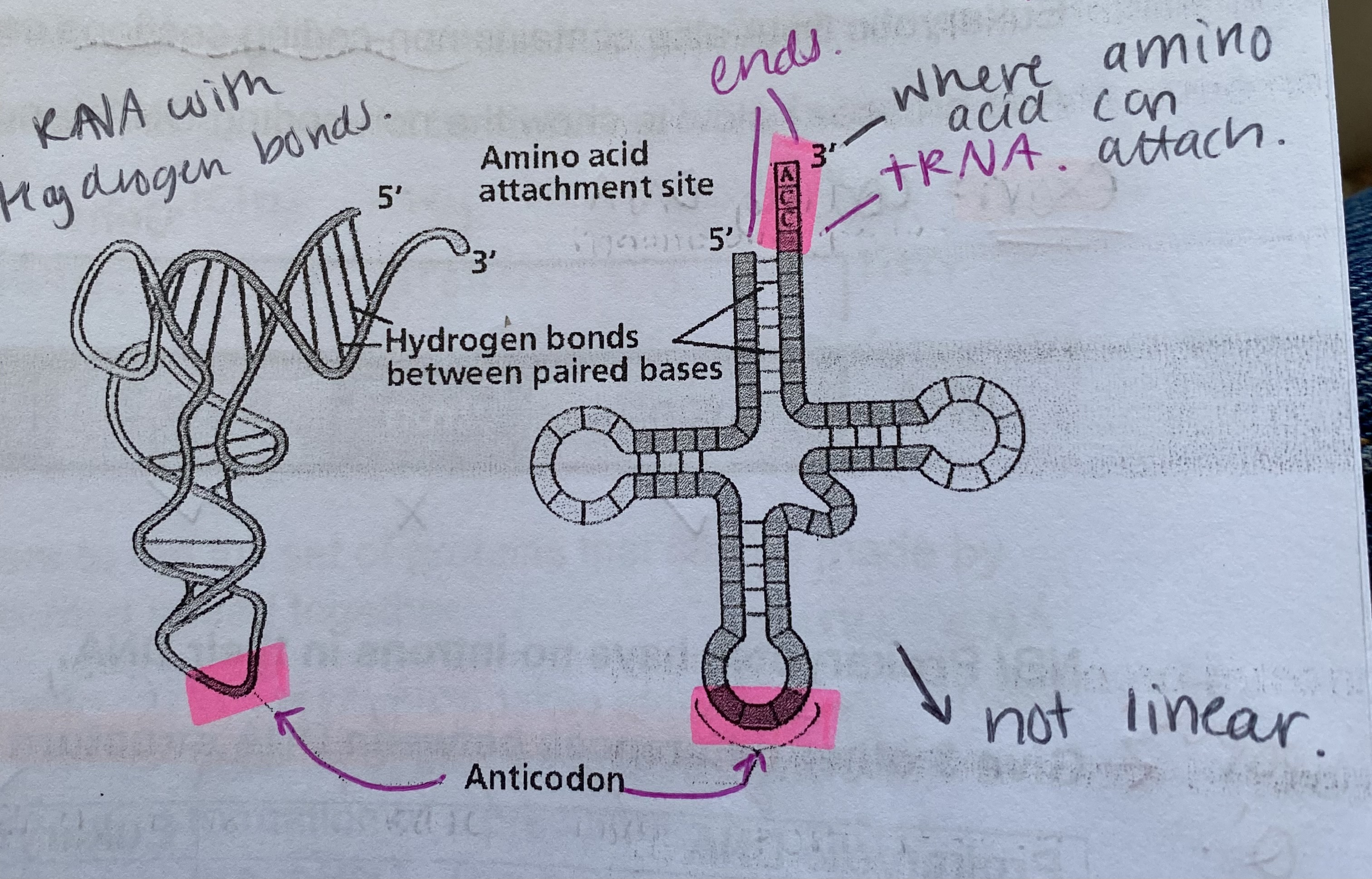
What is the role of the many hydrogen bonds in tRNA?
help stabilise the molecule
Tell me about the end of the chain that attaches to the amino acid in tRNA
each carry a single specific amino acid
at the base of the tRNA molecule is a sequence of 3 bases called the anticodon
in RNA, thymine is replaced by uracil
What is non-coding DNA?
between genes
doesn’t code for protein synthesis
contains multiple repeats called Variable Number Tandem Repeats (VNTRs) and are important in genetic fingerprinting
What are the non-coding sections called?
introns
What are the coding sections called?
exons
Give differences between DNA structure in prokaryotes and eukaryotes
PROKARYOTE DNA
circular
no protein (histones associated)
shorter
no introns
free within cytoplasm (not on MS)
EUKARYOTE DNA
linear
associated with protein (histones)
longer
has introns
What is the genome?
the complete set of genes in a cell
What is the proteome?
the full range of proteins that a cell is able to produce
Both pancreas and liver cells contain the gene that codes for the insulin protein. However, only pancreas cells produce insulin.
Would the genome of a pancreas cell and liver cell be the same?
yes as contain identical genes due to mitosis
Both pancreas and liver cells contain the gene that codes for the insulin protein. However, only pancreas cells produce insulin.
Why would the proteomes be different?
genes to make some proteins may be switched off so the cell never produces that protein e.g. in the liver cells, insulin would be part of the proteome of the pancreatic cell but not the liver cell
What is the order of protein synthesis?
DNA—transcription—> pre-mRNA—splicing—> mRNA—translation—> polypeptide chain (protein)
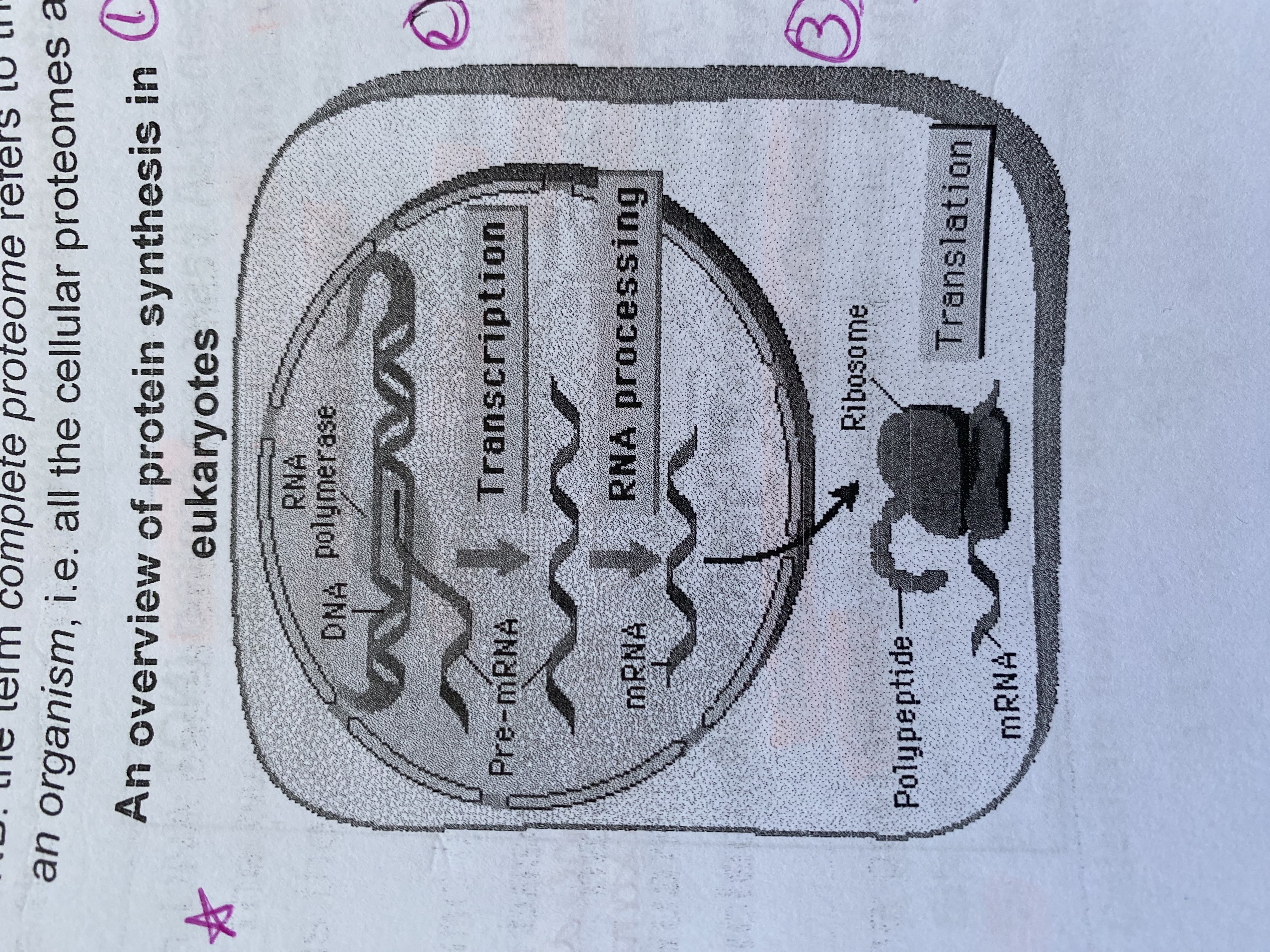
What is transcription?
takes place in the nucleus
involves the formation of pre-mRNA
has a complementary sequence of bases to the DNA
What is RNA processing?
takes place in the nucleus
non-functioning sequences of bases are spliced from pre-mRNA to form mRNA
mRNA then leaves the nucleus via nuclear pores and attaches to a ribosome
What is translation?
occurs on ribosomes
involves translation of mRNA into a specific sequence of amino acids to form a polypeptide
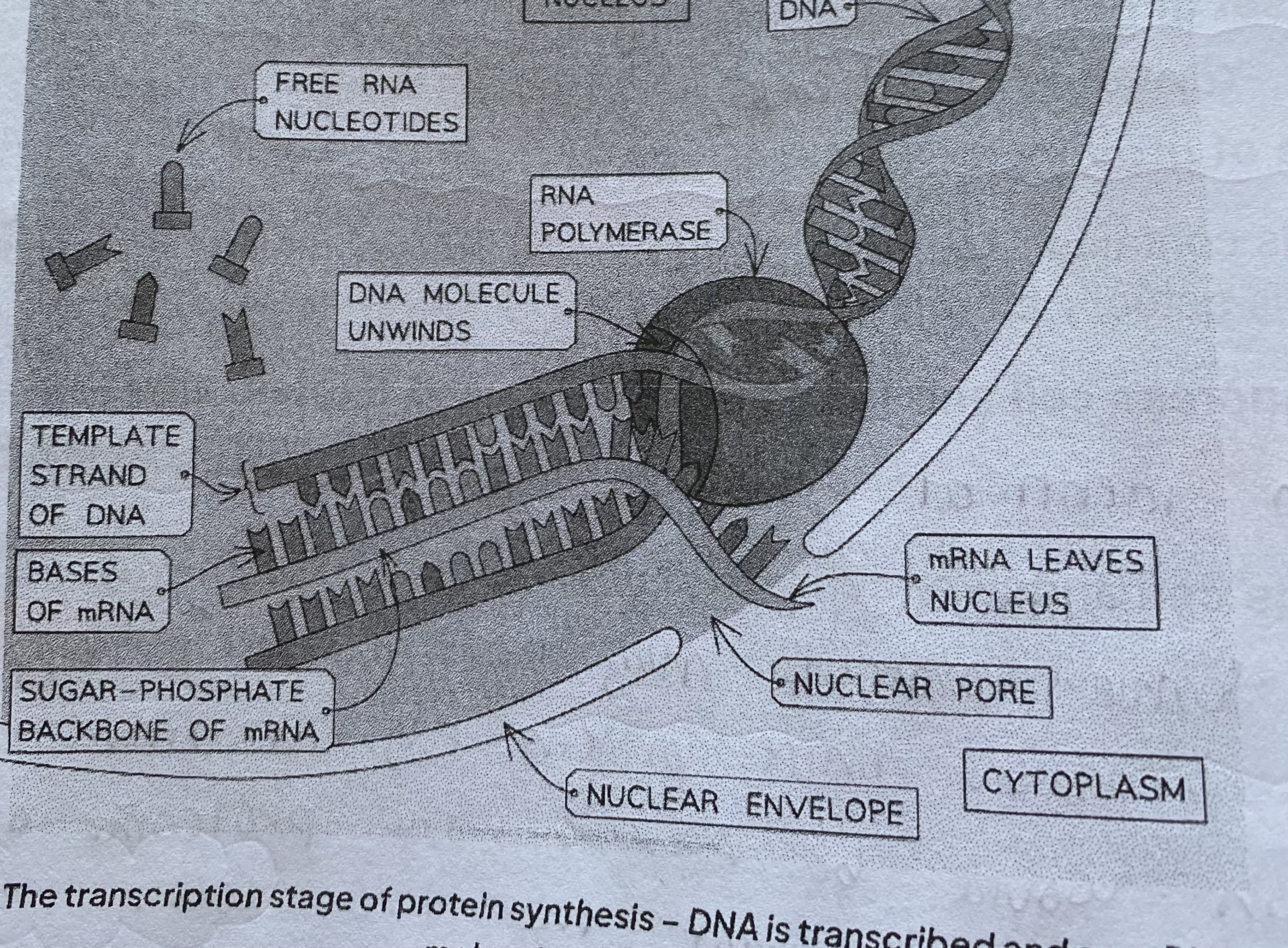
What is the 5 marker for transcripton?
the hydrogen bonds between DNA bases are broken which separates the 2 strands of DNA
1 strand of the DNA acts as the template strand upon which pre-mRNA is built
free RNA nucleotides are found in the nucleoplasm. They are attracted to exposed DNA bases on the DNA template strand and align by complementary base pairing
uracil= adenine, guanine= cytosine
RNA polymerase join RNA nucleotides together to make an RNA polynucleotide chain via phosphodiester bonds
introns are removed from the pre-mRNA and the exons spliced back together
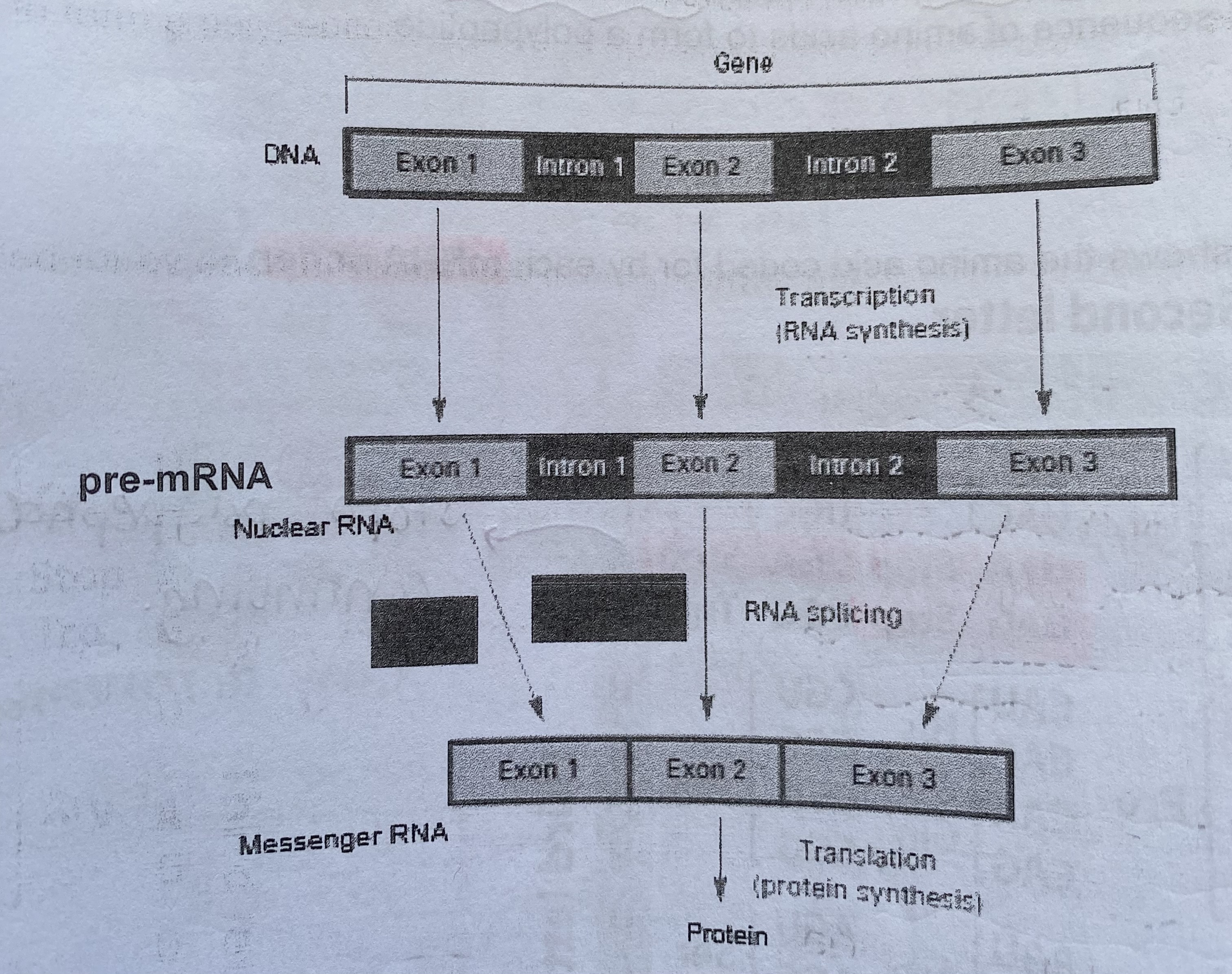
What is splicing of pre-mRNA? (eukaryotes only)
DNA is made from sections called exons and introns
exons are expressed to produce proteins
in pre-mRNA, the introns are removed by enzymes before the mRNA moves into the cytoplasm
remaining exons are joined together= splicing
mRNA molecules leave the nucleus through the nuclear pores
Tell me about protein synthesis in prokaryotes
transcription—> translation
do not contain non-coding sections, therefore do not produce pre-mRNA that requires splicing
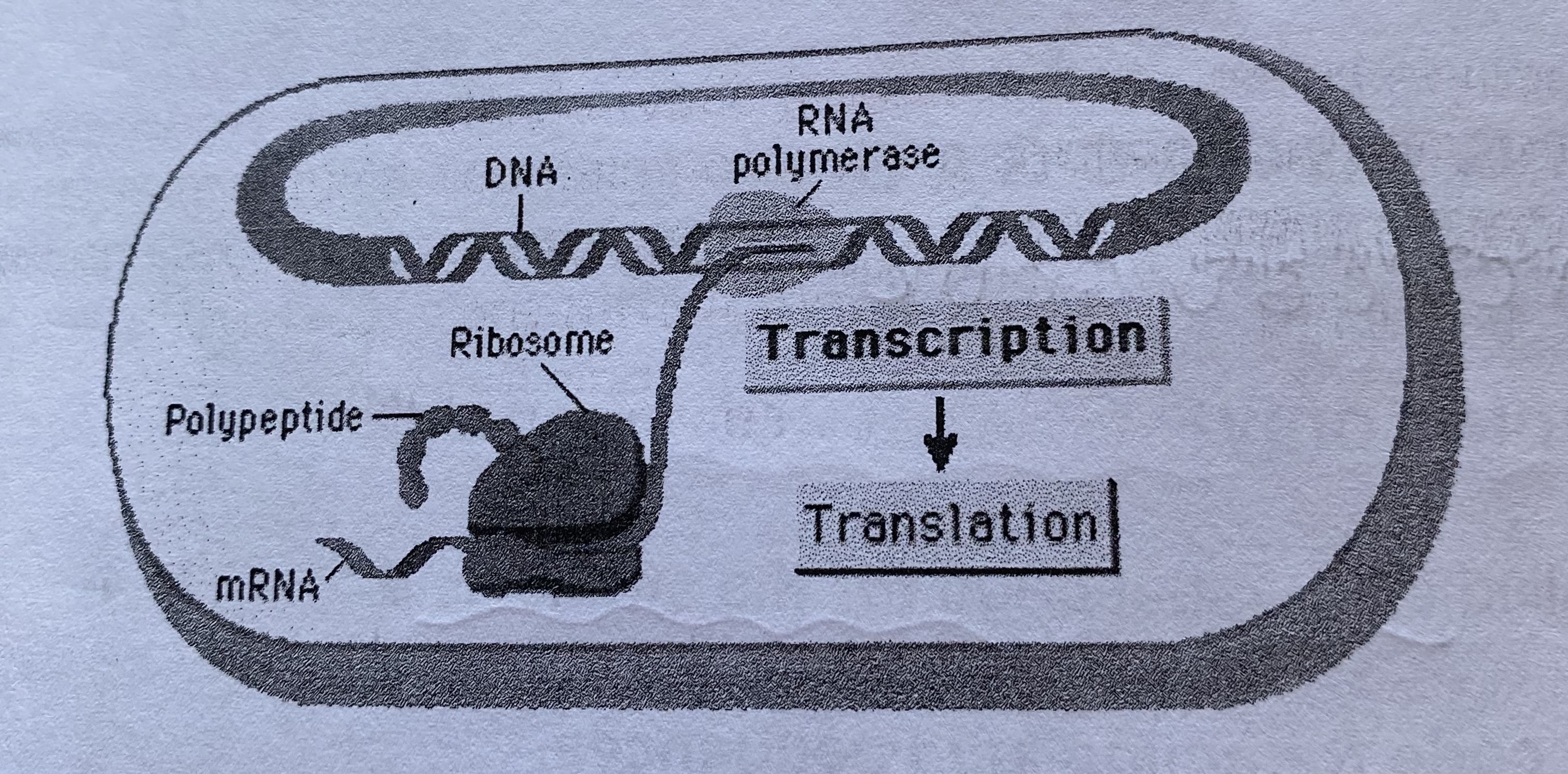
What is transcription in a prokaryote?
takes place in cytoplasm
involves the formation of functional mRNA that is a complementary sequence of bases to the DNA
What is translation in a prokaryote?
occurs on ribosomes
involves the translation of the mRNA message into a specific sequence of amino acids to form a polypeptide chain
How can you work out what amino acid the mRNA codon is coding for?
the codon dictionary

What is the start codon/ amino acid?
AUG= Methionine (Met)
How many stop codons are there?
3
What are the stop mRNA codons?
UAA
UAG
UGA
How many bases of the codon code for the amino acid?
the first 2 of the triplet
Why don’t all the bases code for a specific amino acid?
reduces the chance that a change in the bases will alter the function of the polypeptide
What is the 5 marker for translation?
mRNA attaches to ribosomes
tRNA anticodons bind to mRNA codons by complementary base pairing
each tRNA brings a specific amino acid
2 tRNA molecules are held together at a ribosomes at any one time
a peptide bond forms between adjacent amino acids. This requires the use of ATP
tRNA molecules are released after their amino acids have been joined to the growing polypeptide chain
the ribosome moves along the mRNA forming the polypeptide until a stop codon is reached, at which point the ribosome and mRNA dissociate
What is similar to the DNA triplet code?
the tRNA anticodon
TTC= UUC
AGG= AGG
GCC= GCC
What does the mRNA codon code for?
the amino acid
What are the comparison points for DNA?
double polynucleotide chain
longest molecule of the 3
double helix shape
pentose sugar is deoxyribose
bases found are A T C G
found mostly in the nucleus (doesn’t want to get damaged)
chemically stable
What are the comparison points for mRNA?
single polypeptide chain
shorter than DNA, longer than tRNA
single linear strand (single helix)
pentose sugar is ribose
bases found are A U C G
manufactured in nucleus but found throughout the cell
less stable than DNA or tRNA. Usually broken down within a few days
What are the comparison points for tRNA?
single polynucleotide chain
shortest
clover leaf shaped molecule (single strand folded back on itself and forms hydrogen bonds within complementary sections)
pentose sugar is ribose
bases found are A U C G
maufactured in the nucleus but found throughout the cell
more stable than mRNA, less stable than DNA (due to H bonds)
Give an advantage of mRNA being broken down relatively quickly
mRNA is used in protein production
a protein only needs to be produced when it is needed
mRNA breaks down once used and is made again when protein production is required
Describe how mutations affect the protein
different base sequence leads to a different amino acid sequence (primary structure), which leads to bonds forming in different places, so there is a different tertiary structure in the protein coded for by that gene
if the protein is an enzyme, the active site will change shape, the substrate will not fit so fewer/ no enzyme-substrate complexes will form