Medical Terminology
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
104 Terms
Anatomy
is the study of the structures of the body,
Physiology
is the study of the functions of those structures of the body.
pathophysiology
When anatomical structures malfunction, then healthcare professionals examine their pathophysiology, the study of disease.
Anatomical Position
When describing a particular location, position, or direction of the body, healthcare professionals reference the body’s anatomical position. In anatomical position, a person is standing upright with the head and feet facing forward, the arms at the sides, and the palms of the hands facing forward
Anatomical Planes
In anatomy, the human body is divided into three imaginary, flat sections called
Frontal/Coronal Plane
is a vertical plane that divides the body into front and back sections
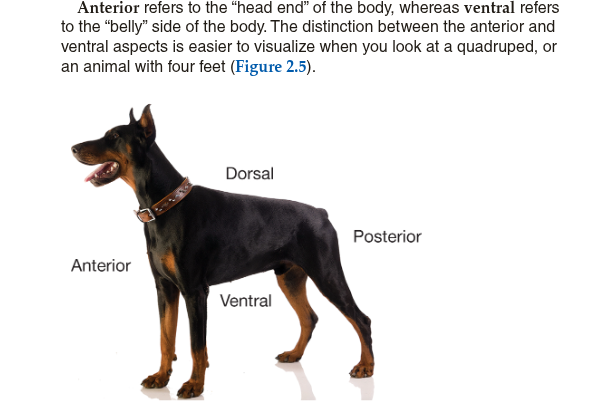
Anterior/Ventral
The front of the body
Dorsal/Posterior
The back of the body
Difference between anterior/ventral and posterior/dorsal
Anterior refers to the “head end” of the body, whereas ventral refers to the “belly” side of the body. The word posterior refers to the tail end, or rear, of the body. The word dorsal refers to the back of the body or the spinal column.
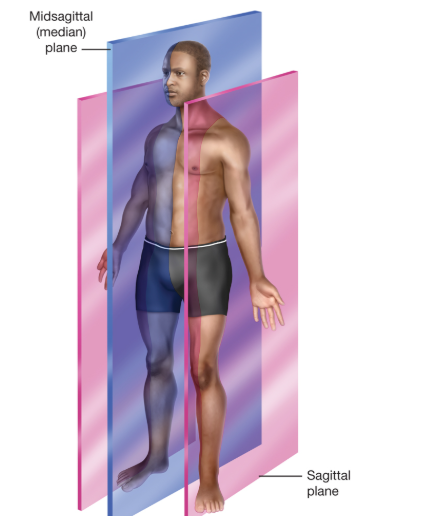
Midsagittal Plane
is a vertical plane that divides the body into equal left and right halves
Sagittal Plane
When the midsagittal plane is visualized on any part of the body other than the center.
Medial
Near the midline, or center, of the body.
Lateral
Near the side of the body; farther from the midline (center) of the body.
Proximal
Near the point of origin.
Point of origin
It means “the point at which something starts” or “the point from which something is derived.”( torso )
Distal
Away from the point of origin.
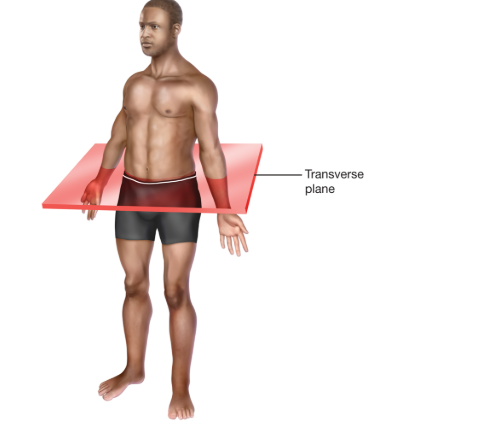
Transverse Plane
is a horizontal plane that divides the body into upper (superior) and lower (inferior) sections
Superior
Located closer to the top of the head in relation to a specific reference point on the body; situated above another body part.
Inferior
Located near the soles of the feet in relation to a particular reference point on the body; situated below another body part.
Cephalic
Relating to the cranium (head), or situated near the head.
Caudal
Relating to, or situated near, the tail or inferior end of the body.
Erect
Normal standing position and Chest X-rays; assessment for neurological issues and sudden rise in blood pressure upon standing.
High Fowler’s Position
A sitting position with the head of the bed elevated 75 to 90 degrees; knees raised slightly used in Mealtime, oral care, X-rays, and breathing treatments.
Knee-Chest
Lying facedown with knees bent while resting on the knees and chest used in Rectal and pelvic exams.
Lateral
Left or right side; lying position and used in It is used as a “recovery position” for illness, injury, and surgery
Low Fowler’s Position
A semi-sitting position with the head of the bed elevated 15 to 30 degrees; knees raised slightly used for Rest and relief of pressure off the hips and shoulders.
Prone
Lying flat with the face down and used in Cutting-edge treatment in breast cancer care; bedsore treatment; sleeping/resting position in children.
Semi Fowler’s position
A semi-sitting position with the head of the bed elevated 30 to 45 degrees; knees bent for comfort used in Rest during childbirth and lung expansion.
Sim’s Positon
Lying on the side with the hip and knee straight, and the other hip and knee bent or flexed used in Rectal exams
Supine
Lying flat with the face up used in CT (computed tomography) and MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) scans; X-rays.
Body Cavity
is a space within the body that contains and protects internal organs and other body structures. There are two main cavities in the human body: the dorsal and ventral cavities
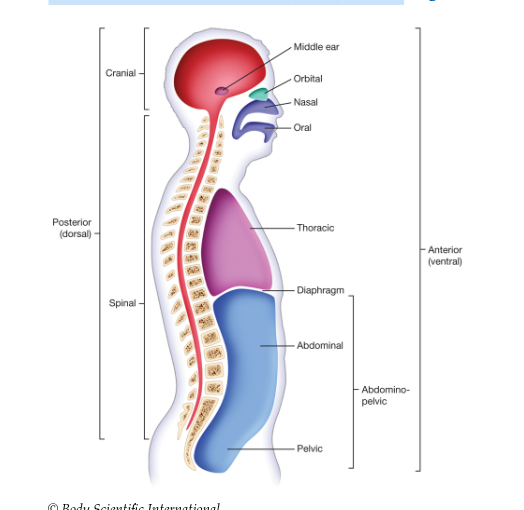
Dorsal Cavity
protects the organs and tissues within the back side of the body. The dorsal cavity is divided into two separate cavities: the cranial and spinal cavities.
Cranial Cavity
is located within the skull. It protects the brain.
Spinal Cavity
is located within the spinal column. As its name implies, it protects the spinal cord.
Ventral Cavity
protects the organs and tissues within the front side of the body. The ventral cavity is divided into three separate cavities: the thoracic, abdominal, and pelvic cavities.
thoracic cavity also called chest cavity
protects the heart, lungs, esophagus, and major blood vessels that run through the chest. The thoracic cavity is separated from the abdominal cavity below it by the diaphragm. Inside the chest cavity is the pleural cavity, the space between the outside of the lungs and the interior of the chest wall.
Abdominal Cavity
contains the stomach, liver, spleen, gallbladder, pancreas, and parts of the large intestine. The abdominal cavity is separated from the pelvic cavity below it by an imaginary horizontal line drawn from the right iliac (IL-ee-ak) crest to the left iliac crest. The iliac crests form the upper borders of the largest bone in the pelvis.
pelvic Cavity
contains the urinary bladder, urethra, portions of the large intestine, and the reproductive organs. Together, the abdominal and pelvic cavities make up the abdominopelvic (ab-DAH-mih-noh-PEL-vik) cavity.
abdominopelvic cavity
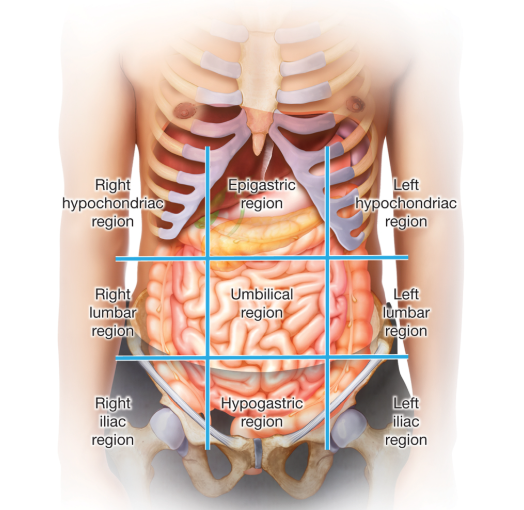
For anatomical purposes, it is divided according to one of two methods: quadrants or regions.
Quadrants
The belly button serves as the intersection point for a horizontal and a vertical line, dividing the area into. The terms used to describe the quadrants refer to the left and right sides of the patient’s body, not the left and right sides from another person’s viewpoint.
RUQ
contains the liver (right lobe), gallbladder, part of the pancreas, and portions of the small and large intestines.
LUQ
contains the liver (left lobe), stomach, spleen, part of the pancreas, and parts of the small and large intestines.
RLQ
contains parts of the small and large intestines; the right ovary, right fallopian tube, and right side of the uterus in females; the right ureter; the right side of the bladder; and the right side of the reproductive organs in males.
LLQ
contains portions of the small and large intestines; the left ovary, left fallopian tube, and left side of the uterus in females; the left ureter; the left side of the bladder; and the left side of the reproductive organs in males.
Right and left hypochondriac regions
the upper part of the abdomen on both sides of the epigastric region and beneath the cartilage (connective tissue) of the lower ribs. the term hypochondriac means “pertaining to below the cartilage.”
Epigastric Region
the area above the stomach. The word epigastric means “pertaining to (lying or being located) above the stomach.”
Right and Left Lumbar regions
the two regions of the back that are lateral to the lumbar spine (the lower back). The term lumbar means “pertaining to the lower back.”
Umbilical region
the area surrounding the umbilicus (um-BIL-ih-kus), or belly button.
Right and left iliac regions, also called the inguinal (ING-gwih-nuhl) regions—
the lower part of the abdomen, which starts with an imaginary line drawn between the iliac crests on the front upper tips of both hip bones. The ilium is the broad bone of the pelvis.
Hypogastric
the area of the abdomen below the umbilical region; also called the pelvic region. The term hypogastric means “pertaining to (lying or being located) below the stomach.”
Cell
is the basic structural unit of the body.
Tissue
is a combination of similar cells.
Organ
is a collection of tissues working together to perform a particular function.
Body system
consists of a group of organs that work together to perform a specific function.
organism
is a life form made up of interdependent parts (cells, tissues, organs, and body systems), all of which work together to maintain life.
Cytology
is the study of the formation, structure, and function of cells.
organelles
specialized structures that enable specific functions. Most cells have certain organelles in common.
Cell membrane
also called a plasma membrane, surrounds every cell. The cell membrane separates the cell from its external environment. Because the membrane is responsible for what enters and leaves the cell,
Nucleus
is the controlling structure of the cell. It is responsible for the main function and reproduction of the cell. The nucleus of every human cell (except for the sex cells, the egg and sperm) contains 46 chromosomes arranged into 23 pairs, 22 of which are identical. The final pair of chromosomes are the XX and XY chromosomes. Each chromosome contains genes composed of a chemical called deoxyribonucleic (dee-AHK-see-RIGH-boh-noo-KLEE-ik) acid (DNA). DNA is responsible for each person’s unique genetic makeup.
Cytoplasm
is a sticky, semifluid material between the nucleus and the cell membrane. The cytoplasm contains organelles that the cell needs to function properly. It is the area of the cell in which all chemical reactions occur.
Electrolytes
compounds made up of charged particles called ions
ions
can conduct electrical currents in water or in the cytoplasm of the cell.
cation
A positive-charge ion and creates an acid.
Acids
are chemical substances that taste sour and neutralize bases.
bases
are substances that react with acids to form salts.
Anion
A negatively charged ion and creates a base.
pH
of a fluid is a measurement of how much acid or base is present. The cells and tissues in your body function at different pH levels. They do not function properly if their normal pH is not maintained. Many conditions and diseases cause, and are affected by, an electrolyte imbalance in the body.
Body cells contain certain types of organelles that allow those cells to carry out specialized functions.
Muscle cells, Epithelial, Fat cells, Nerve Cells
Muscle Cells
for example, are long, slender cells within muscle tissue. Muscle cells contain fibers that allow muscular tissue to contract and relax.
Epithelial cells
are typically flat, square cells that cover the skin and line the digestive tract and other hollow organs.
Fat Cells
contain large, empty spaces for fat storage in the body.
Nerve Cells
which tend to be long, have several fibrous extensions that carry nerve impulses. Blood cells vary in shape and size according to their function.
Fascinating Fact
The largest cell in the human body is the ovum, or egg—the female sex cell. The sperm, the male sex cell, is the smallest.
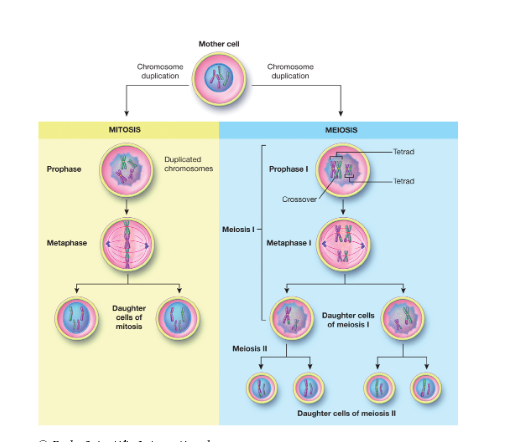
Cell division
serves a twofold purpose: growth and development of cells and replacement of old, dead, or damaged cells. Most cells divide through a process known as mitosis. Sex cells, which are involved in the reproduction of an organism, require a different process called meiosis (migh-OH-sis).
Genetics
is the study of the ways in which genes are transferred from individuals to their offspring and of the role that genes play in the health of offspring.
Genetic disorder
is a disease or condition caused by a defective gene. Genetic disorders, while present at birth, may not manifest until later in life. There are more than 2,000 known human genetic disorders.
Tissues
is a group of similar cells that work together to perform a specific function.
Histology
is the study of the structure and function of tissues.
Pathologist
a physician who specializes in the study of disease, examines the tissue or sections of the organ under a microscope.
Epithelial Tissue
forms the skin covering the surface of the body. Two characteristics affect how epithelial tissues are described: the number of cell layers within the tissue and the shape of the tissue’s cells.
Isotonic solution
If concentration is equal on both sides, water will move back and forth, but it will not have any result on the overall amount of water on either side. The combining form is/o means “same” or “equal.”
Hypotonic Solution
The prefix hypo- means “below.” If the concentration of solute is lower outside the cell, and the concentration of water is greater outside the cell, water will move into the cell. The cell will gain water and grow larger. The cell may be in danger of bursting.
Hypertonic Solution
The prefix hyper- means “above.” If the concentration of solute is greater outside the cell, and the concentration of water is lower outside the cell, water will be sucked in that direction. The cells shrink and may die.
Connective Tissue
supports and connects organs and other body tissues.
Muscle tissue
has the specialized function of contracting (shortening) to produce bodily movement. There are three major types of muscle tissue: Skeletal muscle, Cardiac muscle, Smooth muscle
Skeletal muscle
also called voluntary muscle, is attached to bones. Skeletal muscle works with the bones of the skeletal system and other structures of the muscular system to generate movement at will.
Cardiac Muscles
is found only in the heart. It is responsible for the pumping action of the heart.
Smooth Muscle
also called visceral (VIS-uh-ruhl) muscle or involuntary muscle, is found in the walls of hollow organs, such as those of the digestive tract
Visceral
means “pertaining to body organs.”) This type of muscle cannot be consciously controlled.
Peristalsis
Smooth muscle enables alternating contraction and stretching motions
nervous tissue
as the name indicates, makes up the nervous system of the body. It is composed of cells called neurons, which receive and conduct electrochemical impulses between the brain and other parts of the body.
organ
is a structure composed of several kinds of tissue that work together to perform a specific function.
System
is a group of organs that work together to perform a complex function.
Integumentary system
Protects the body by acting as a physical barrier against microorganisms that cause disease, harmful chemicals, and the ultraviolet rays of the sun; regulates temperature and fluid control; produces vitamin D, which is essential for calcium absorption; provides sensory information to the brain through nerve receptors in the skin, which conduct messages about touch, pressure, pain, and temperature.
Skeletal
Provides support and shape for the body; protects the internal organs and
Muscular System
Allows voluntary and involuntary body movement; produces body heat through energy generated by the muscles.
Nervous System
Transmits messages about sensory stimuli between the brain and the other parts of the body.
Endocrine System
Produces hormones and regulates body functions, including metabolism, mood, growth and development of cells and tissues, and reproductive development and function.
Respiratory System
Transports life-sustaining oxygen through the blood to the organs and tissues of the body; expels carbon dioxide through the lungs; filters airborne pollutants and some microorganisms from the respiratory tract; regulates pH (acid-base) levels in the body.
Cardiovascular System
Pumps blood containing oxygen and nutrients throughout the body; carries carbon dioxide to the lungs and other chemical waste products to the kidneys and lungs, which eliminate them from the body.