Reporting financial performance
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
What are the types of accounting abuses?
• Reserve accounting
• Extraordinary items
• Earnings management
• Big bath accounting
• Recognising income too early
• Deferring recognition of expenses/costs
• Pro forma earnings
What is reserve accounting?
Excluding certain items from profit and loss account, and reporting them as reserve movements
What are exraordinary and exceptional items?
• The term “outside the ordinary course of business” was vague and open to interpretation
As a result:
• Many one-off material losses were classified as extraordinary
– Excluded from EPS
• Many one-off material profits were classified as exceptional
– Included in EPS
What is earnings management?
• No single accepted definition
– Accounting choice
– Income smoothing
– Earnings management
– Earnings manipulation (violate GAAP)
• Information perspective
– Better communicating inside information to external stakeholders
• Opportunistic perspective
– Managers manipulate earnings to achieve personal gains
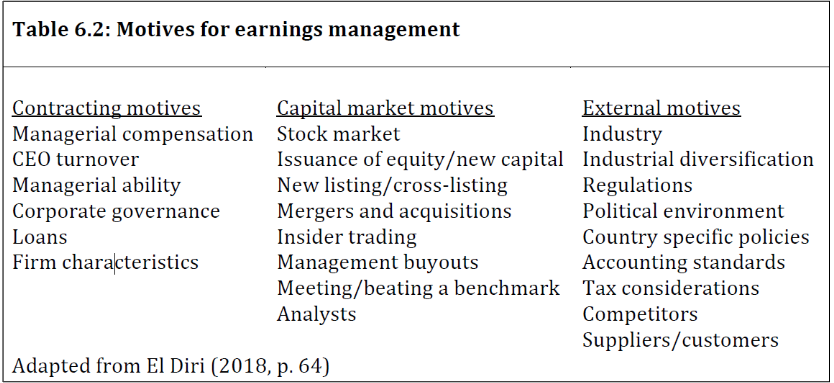
what are the motivations for Earnings Management?
What is big bath?
one time large write-offs
to boost future profits
What is anticipating income?
Recognising income before it is earned.
What is delaying recognition?
Choosing to delay your recognition of costs/expenses
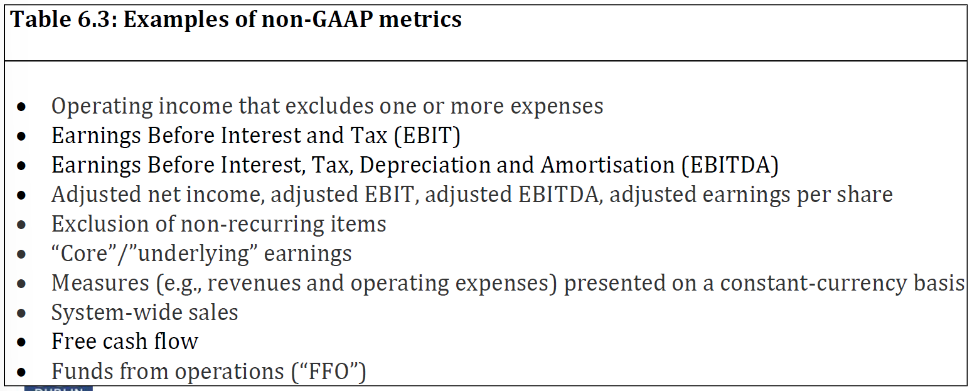
What is Alternative Performance Measures?
not audited
“earnings without the bad stuff”
Examples of non-GAAP metrics
FRS 3 Reporting Financial Performance
• Extraordinary items were eliminated
• Most items previously classed as extraordinary now treated as exceptional
• Up to three exceptional items permitted to be highlighted on face of profit and loss account
• Other exceptional items to be disclosed in notes
• All realised gains and losses to be shown in profit and loss account
What items need to be seperately disclosed?
Write downs of inventory to net realisable value (and reversals)
Write downs of property, plant, equipment to recoverable amount (and reversals)
Costs of, provisions for, restructuring (and reversals)
Profit / loss on disposal of property, plant and equipment
Profit / loss on disposal of investments
Profit / loss on discontinued operations
Litigation settlements
Other reversals of provisions
What is material?
Information is material if omitting, misstating or obscuring it could reasonably be expected to influence the decisions of primary users.
The size or nature of the item, or a combination of both, could be the determining factor
Users are assumed to have reasonable knowledge of business and economic activities and accounting and a willingness to study the information with reasonable diligence.