Selling and Sales management - Chapter 5: Understanding Prospective customers
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Ideal customer profile (ICP)
Helps the salesperson focus on the needs of potential customers as well as which customers are most likely to purchase as well as craft an effective value proposition
The three ways to profile a customer
Demographics
Psychographics
Behavioural characteristics
Demographics
The visible and measurable traits of a consumer
e.g. A firm’s number of employees, industry, revenue, etc
B2C demographics
Income, marital status, age
B2B demographics
Number of employees, the firm’s revenue, industry, location
Psychographics
A customer’s psychological traits.
e.g. Desires, habits, hobbies, etd
Behavioural characteristics
Traits which define how someone behaves; are usually observed through measuring the customer’s behaviour with data and analytics
e.g. How long a customer stays on a website, how many price quotes they get before making a purchase, etc
Critical questions about ICP
What does my typical customer need and want?
What are my customers’ attitudes and desires?
Is my customer price-conscious? What can they afford?
Will they buy immediately? Or will they think on it more?
Does the customer prefer to communicate by email or phone calls?
How should sellers focus on the right prospects?
Sellers should focus on customers who match their ICP
How should sellers focus on the right prospects? (con’t)
Which type of customers offer the highest MRR (monthly recurring revenue)?
Do medium or large businesses use our product the most?
Which type of customers offer the most referrals?
Value proposition
Discovering the problem(s) faced by customers that they hope to solve with what’s being offered
Post-purchase research
To find out what aspects of the offering solve the consumer’s problem the best, by figuring out the main competitive advantage and understanding what features they find appealing, their motives, etc
Retaining the prospect’s attention
Focus on 2-4 main selling points at a time as the average person can only hold 3-4 items in their memory at a time
Feature-advantage-benefit
Turning product features into concepts prospects will care about
e.g. A medical supply company’s knee braces being light and flexible, thus allowing the patient to live an easier and normal life while in rehab
Value proposition (con’t)
A statement (or set of statements) which highlights how the offering gives value to customers
The best practices for a value proposition
Give proof, such as statistics or testimonials
Keep it simple and stay focused on the main advantages
Be specific about what exactly the product is
Focus on the customer by keeping statements focused on them instead of the product
Focus on the outcome(s)
Personalizing the ICP
Tailoring the ICP to the specific prospect’s needs by collecting as much info as possible
AI tools for research and personalization
Tools like Crystal Knows can help identify customer personality types, while 6sense and Apollo can help identify buyer intent
Sales cadence
A series of actions/touch points executed by a seller over a time period to engage with a prospect; can be dynamic and changing based on what happened
Sales cadence (con’t)
Helps a sales professional deliver proper communication (e.g. phone calls, emails, in person visits, etc) over the right period of time
Sales cadence (III)
Helps a sales professional remember to follow up with the prospect the appropriate number of times as communications are planned and scheduled in advance
Scheduling the cadence
Ensures communication is as natural as possible
Preferred communication means for different age demographics
Older people: Email or phone call
Younger people: LinkedIn or social media
How to schedule the cadence
Begin with a LinkedIn Connection to use as a reference point, then follow up with a very personalized email, and then going from there

Sales cadence for re-engaging prospects
Developing a type of sales cadence different from the usual cadence
Cadence automation tools
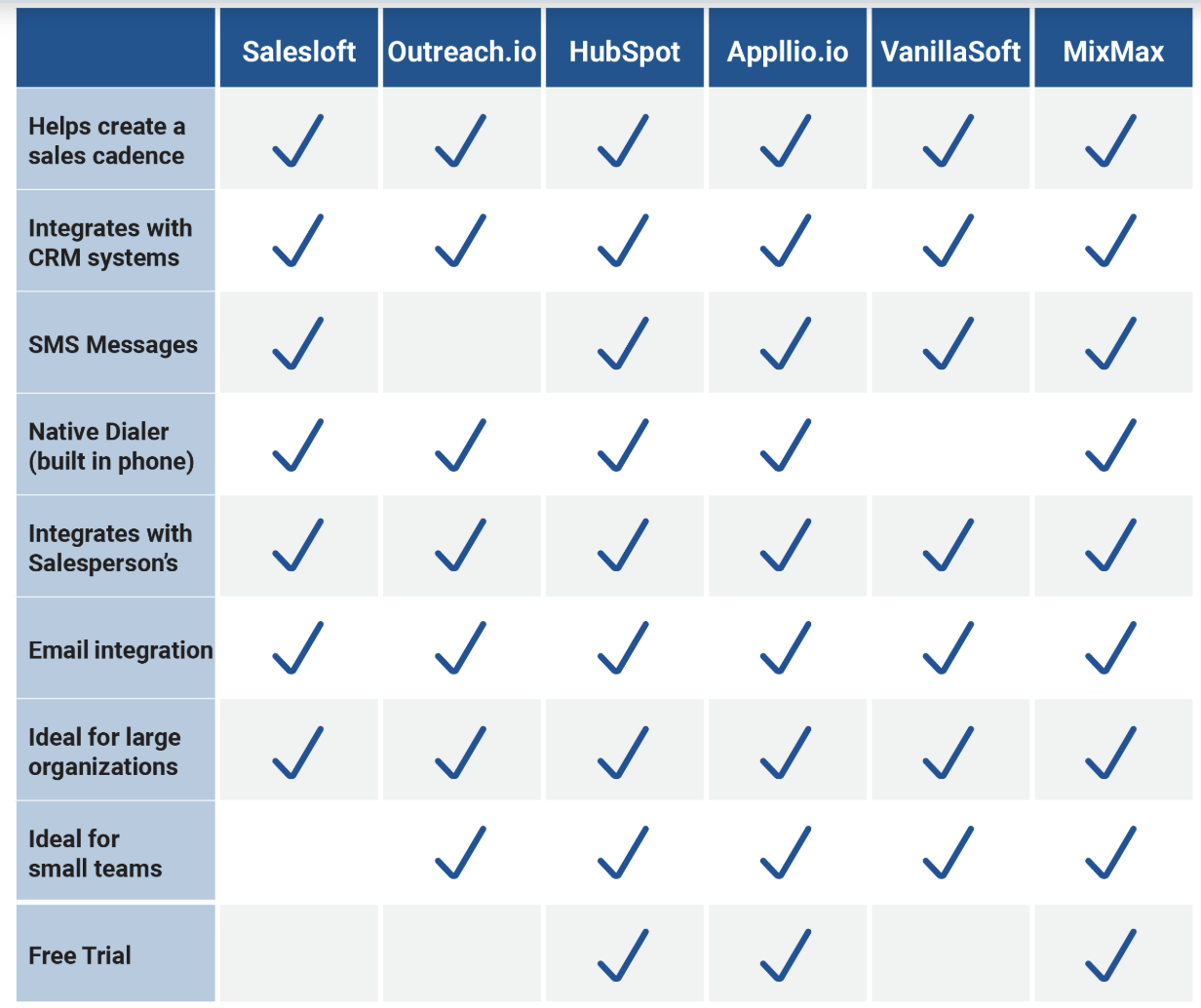
Offering value beyond the product
Offering the prospect resources like blog posts, podcasts, or educational videos
Webinars
Online trainings and seminars which are often open to the public
Connecting on multiple platforms
Engaging with prospects on more than one platform, which will enable learning about the prospect and their organization
e.g. Commenting on something the prospect shared on LinkedIn instead of sending a generic email
Things to NOT do during the follow-up process
Not taking no for an answer
Getting too personal
Trying to circumvent the prospect and contact other decision makes other than the primary contact
Not being authentic