Overview of Animal Sensory Systems and Mechanisms (3)
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
Sensory receptors
Cells responding to specific stimuli, transmitting signals.
Thermoreceptors
Sense heat and cold temperatures.
Electromagnetic receptors
Detect light and electromagnetic fields.
Mechanoreceptors
Detect sound, touch, and motion. Hair cells
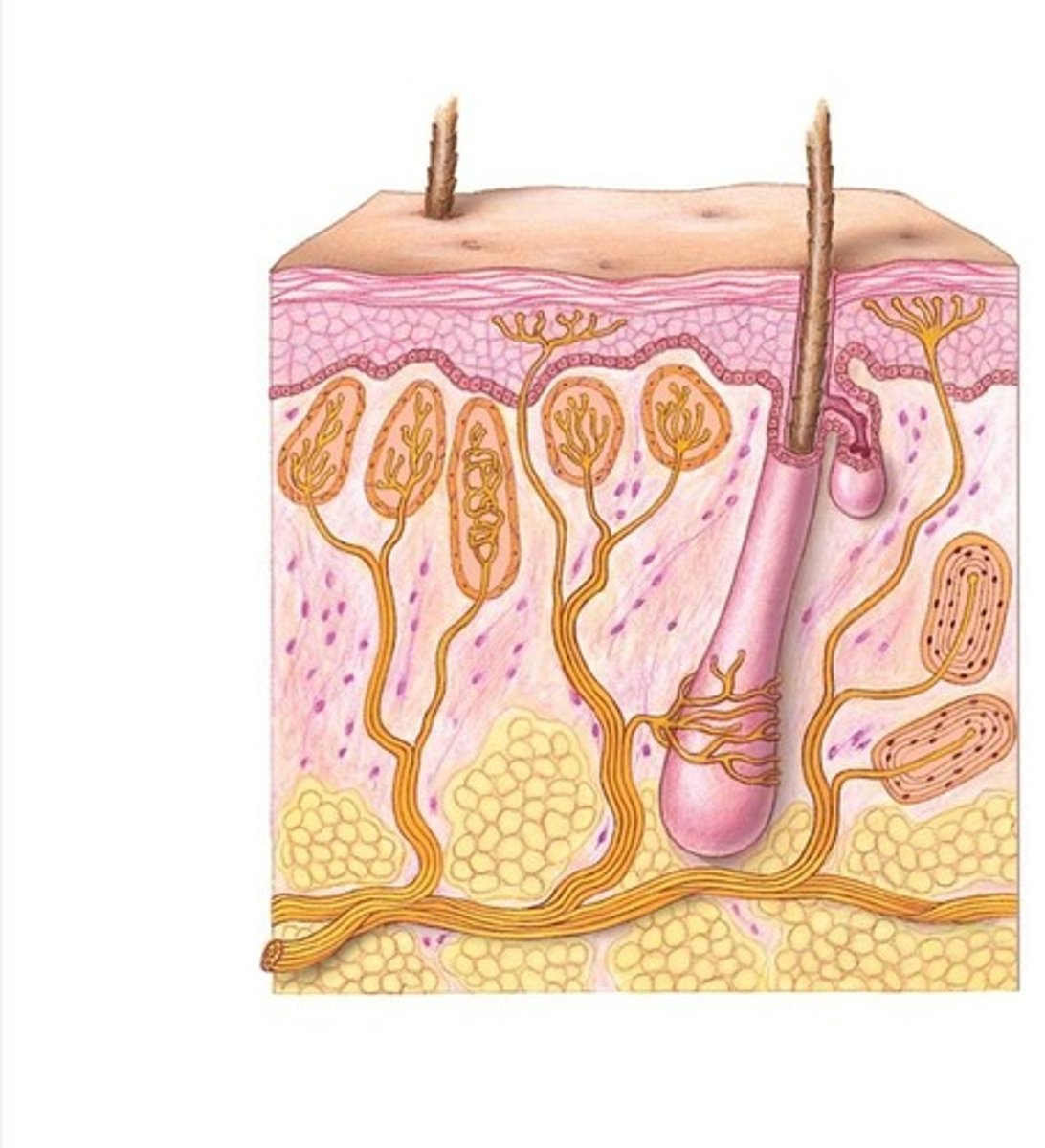
Pain receptors
free nerve endings transmit ___ in response to thermal and mechanical stimuli or molecules released by injured cells
Vibrations from sounds
transmitted from the tympanic membrane through the three middle ear bones to the cochlea
Volume and pitch
detected by the number of hair cells stimulated
the position of the stimulated cells along the cochlea
Lateral line
system of aquatic vertebrates that is used to detect vibrations and currents in water
Chemoreceptors
Detect solutes, tastes, and smells.
Oldest and most universal sense
Important in identifying food, mates, predators, noxious chemicals, CO2, H2O
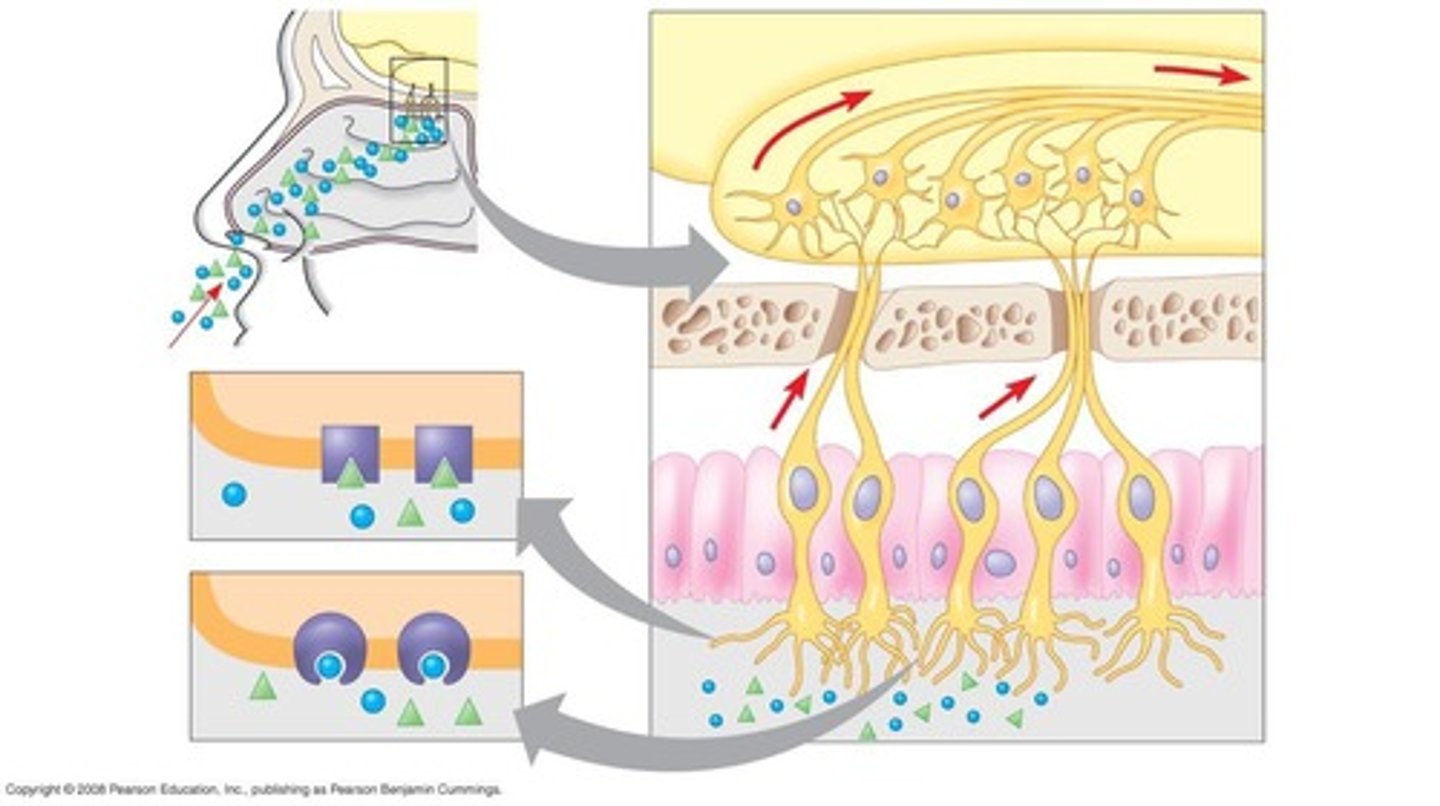
Olfactory cells
chemoreceptors providing a sense of smell. Detect signals that are far, and at low threshold
Pheromones
chemicals used for communication among same species
Vomeronasal organ
in the roof of the mouth of some vertebrates for chemoreception, in response to pheromones
Flehmen response
the pulling back of the lips draw molecules towards the organ increasing effectiveness
Electroreception
detect the electric field produced by the muscle activity of living organisms. Well developed in sharks and for prey detection. Platypus has them on their bills
Gustation cells
the receptors of taste
in humans, receptor cells for taste are organized as taste buds
Afferent neuron
Transmits sensory information to the CNS.
Motor commands
Signals sent from CNS to muscles or glands.
Neuronal receptors
Afferent neurons acting as sensory receptors.
Non-neuronal receptors
Regulate afferent neurons without direct transmission.
Free nerve endings
Transmit pain signals from thermal and mechanical stimuli.
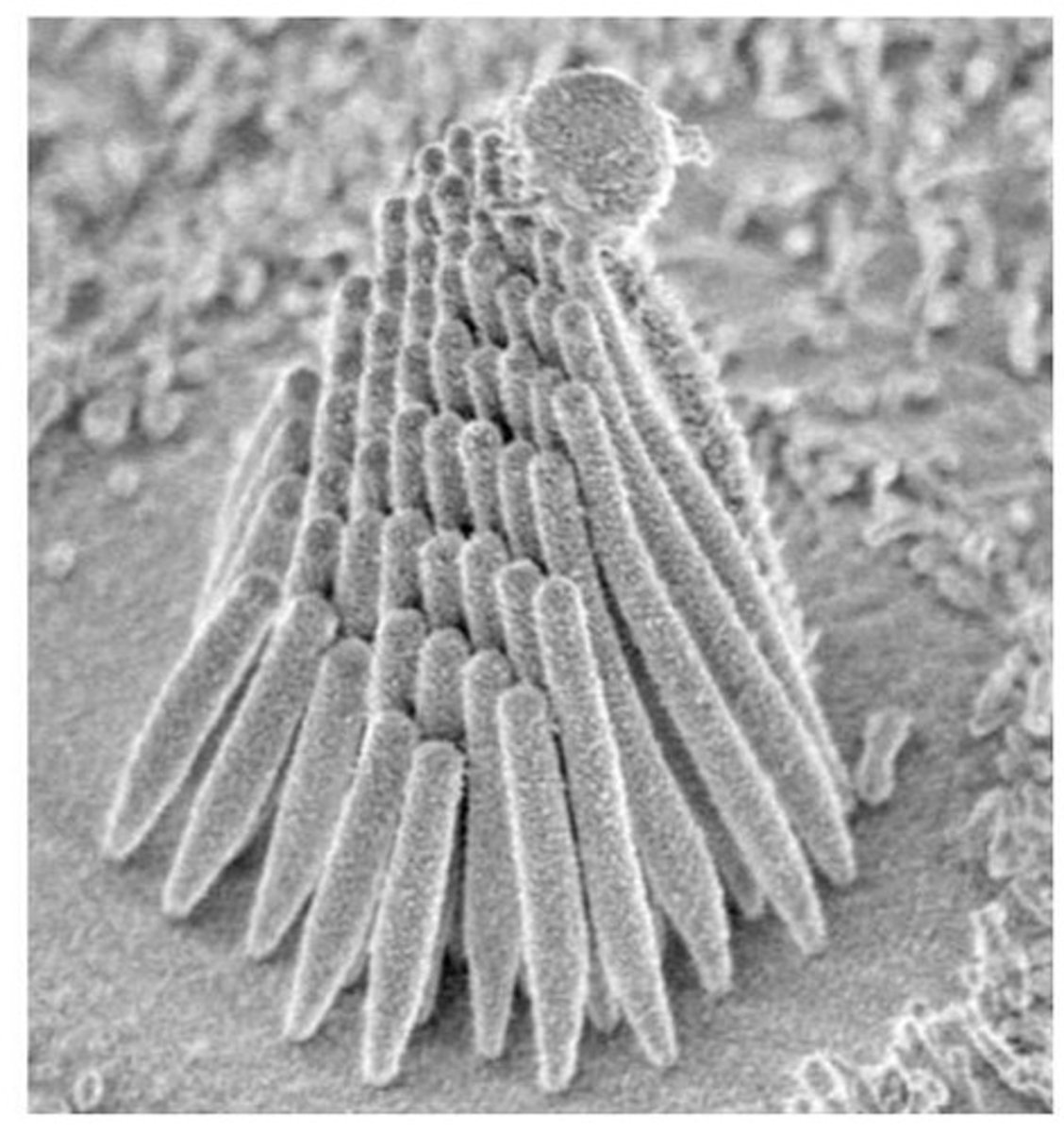
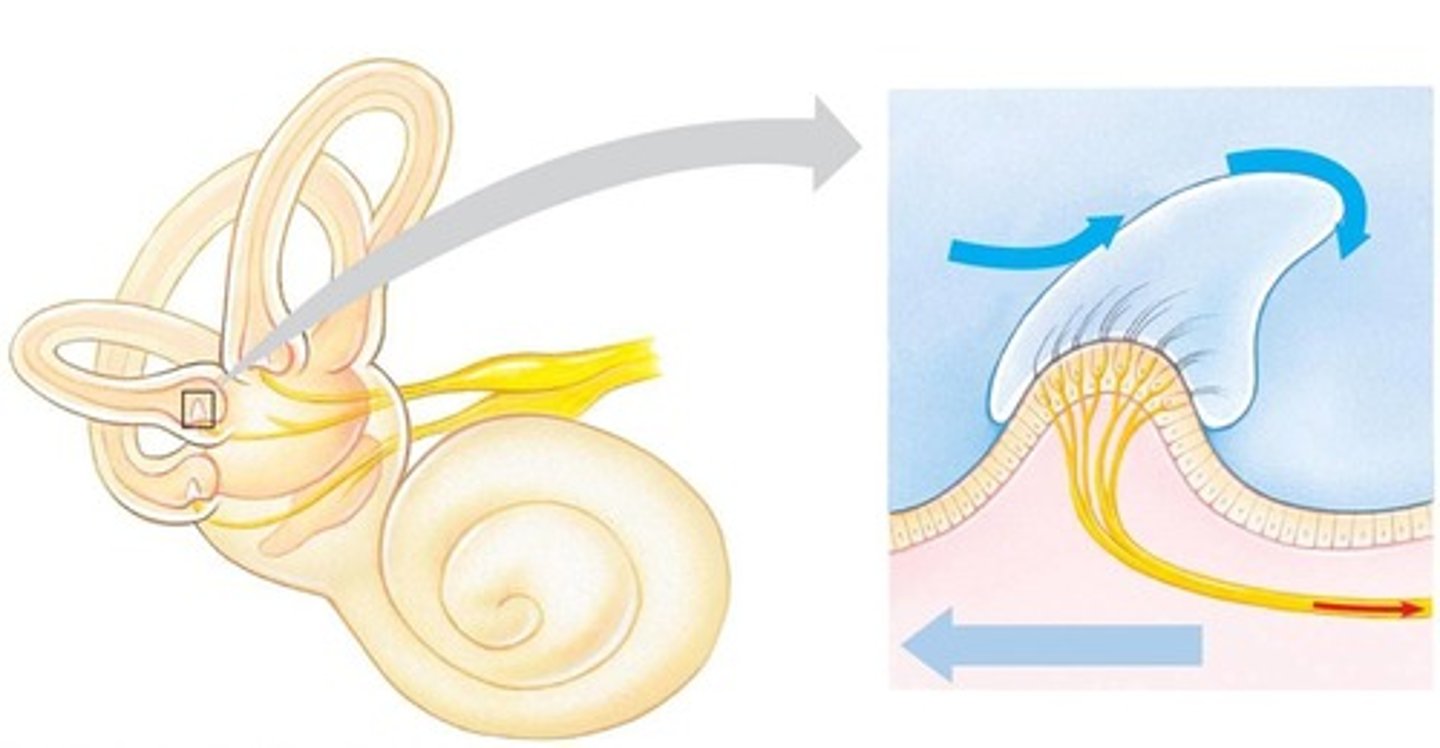
Hair cells
Mechanoreceptors for hearing and equilibrium.
Cochlea
Inner ear structure for sound processing.
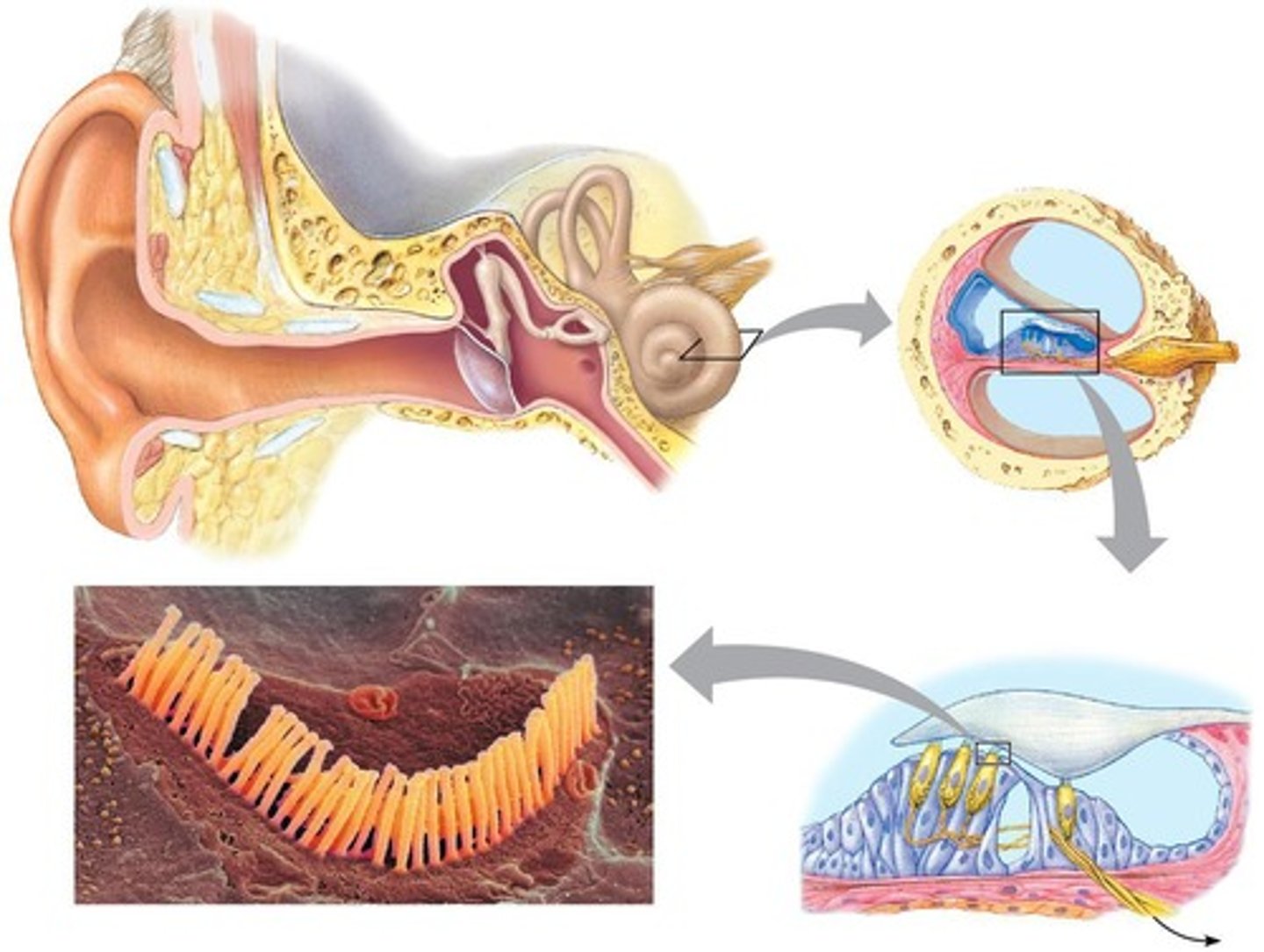
Basilar membrane
Vibrates in response to sound frequencies.
Tectorial membrane
Interacts with hair cells in the cochlea.
Olfaction
Sense of smell via olfactory cells.
Gustation
Sense of taste through gustatory cells.
Papillae
Structures on the tongue housing taste buds.

Photoreceptors
Cells responding to light in the retina.
Rhodopsin
Pigment changing configuration in light response and trigger a reaction that stimulates nerves
Rod photoreceptors
are sensitive to low light
Cone photoreceptors
sensitive to specific frequencies of light
Single-lens eyes
Focus light on photoreceptors in the retina.
Statolith
Granules aiding balance in inner ear.
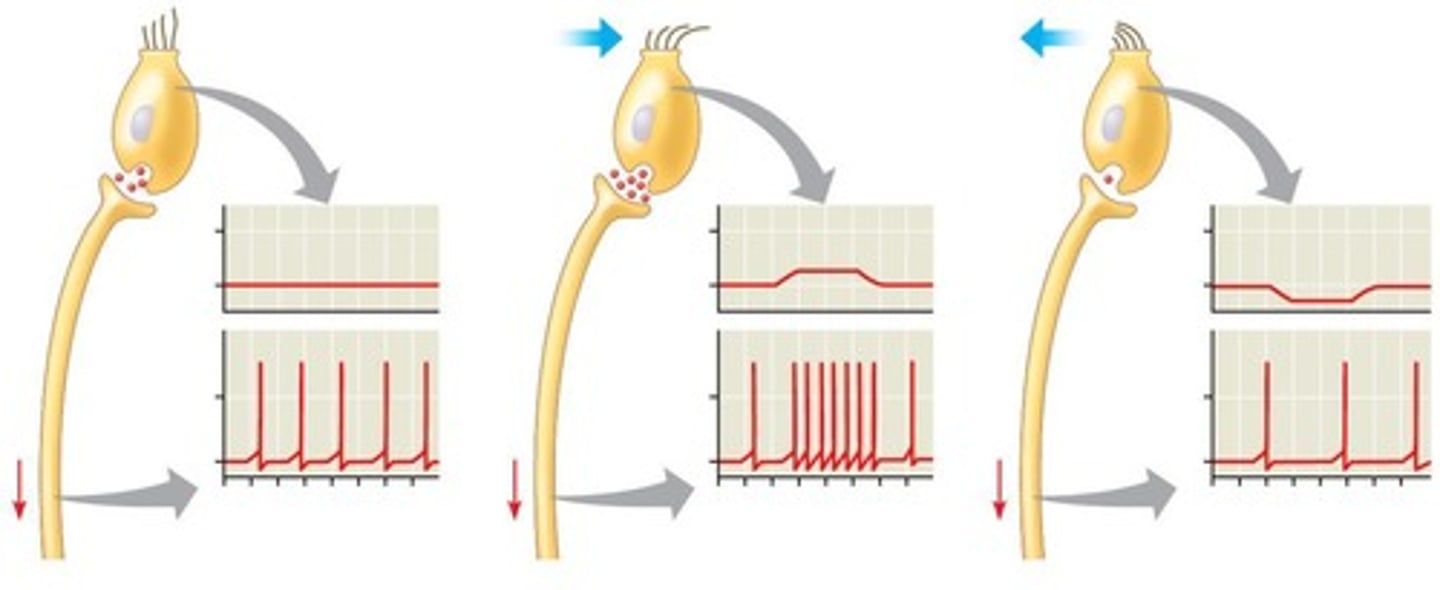
Action potentials
Electrical signals transmitting information along neurons.
Lateral inhibition
Neuronal interaction enhancing image contrast.
Pit organs
detect infrared radiation and function in thermal imaging