Lecture 9: Protein Sorting (Gated Transport, Transmembrane transport)
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Gated Transport, Transmembrane Transport To mitochondria, chloroplasts, peroxisomes
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Animal Specific Cell-Component - Lysosome Matrix
Degradation of cellular components that are no longer necessary
Plant-Specific Cell Component - Vacuole
For storage and degradation (like animal’s lysosome)
Animal Specific Cell-Component: Peroxisome
Contain enzymes for oxidative reactions (some of these reactions can be done by mitochondria as well)
Post-Translational Protein Sorting
Protein are fully synthesized in the cytosol before sorting
Post-Translational Protein Sorting: Which ones remain unfolded and which ones remain folded?
Unfolded: mitochondria, chloroplasts
Folded: Nucleus, Peroxisomes
Co-Translational Protein Sorting
Proteins with ER Signal Sequence → associated with ER during protein synthesis
Gated Transport
Proteins moving to and from nucleus and cytosol
Transmembrane Transport
Requires protein translocators (proteins usually unfolded, except for peroxisomes)
Transport of protein across membrane
What is a Nuclear Pore Complex?
Transport of cargo go through NPC, transport in both directions (export and import)
Selective transport and free diffusions for small molecules
What is the Nuclear Pore Complex made up of?
made up of nucleoporin (many proteins)
What does cargo proteins have in order to help them get imported?
Nuclear Localization Signal → which binds with the Nuclear Import Receptor
For Import: NLS is rich in Lys and Arg
What does the Nuclear Import Receptor do?
Binds to the NLS of the cargo protein → binds to nucleoporins of NPC → transport into the nucleus
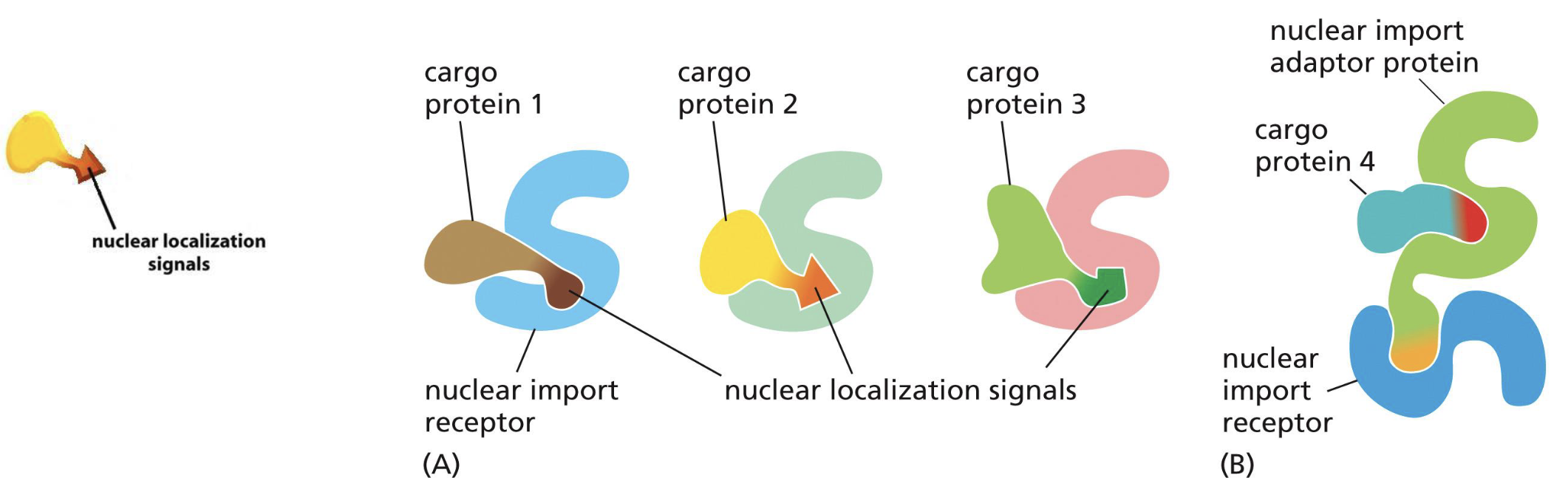
What is the use of the adaptor proteins?
Sometimes, some cargo proteins have a sequence that binds to the adaptor protein, and the adaptor proteins have the NLS, which binds to the Nuclear Import Receptor
What do the cargo proteins that want to be exported have?
Nuclear Export Signal → Nuclear Export Receptor binds to this part of the cargo
What does the Nuclear Export Receptor do?
binds to the NES of the cargo protein → binds to nucleoporins of NPC → transport into cytosol
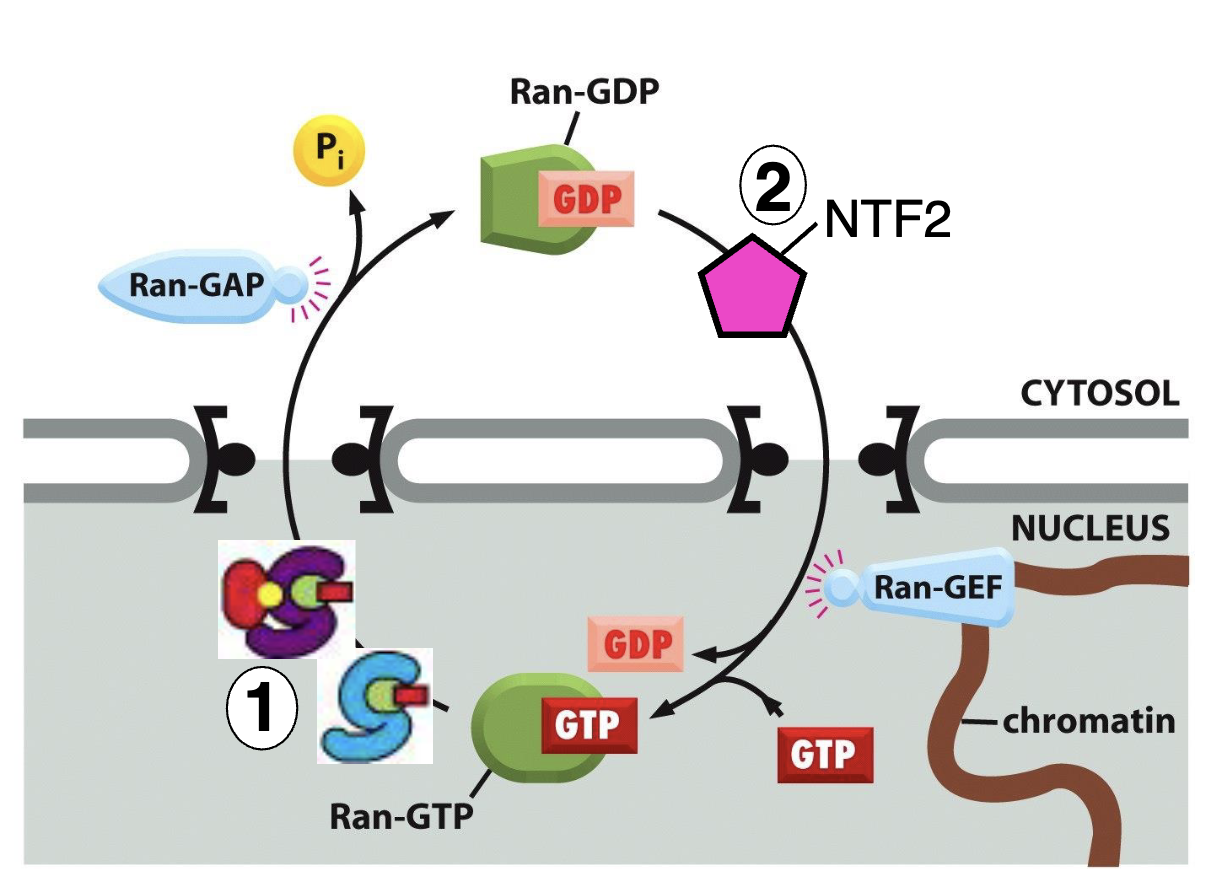
Ran GTP and Ran GDP, where are they found?
Ran GTP (bound by GTP) - found in nucleus
Ran GDP (bound by GDP) - found in the cytosol
Ran GEF and Ran GAP what do they do?
Ran GAP: GTPase Activating Protein
in the cytosol
Cuts Ran GTP to Ran GDP
Ran GEF: Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factor
in the nucleus
Exchanges Ran GDP to Ran GTP
NTF2 function?
Nuclear Transport Factor 2
transports Ran-GDP into the nucleus
Ran-GTP and Ran-GDP Circulating
Ran GTP in the nucleus → goes to cytosol → Ran GAP cuts the GTP into GDP → becomes Ran GDP
Ran GDP is brought back into nucleus via NTF2 → Ran GEF exchanges GDP to GTP → becomes Ran GTP
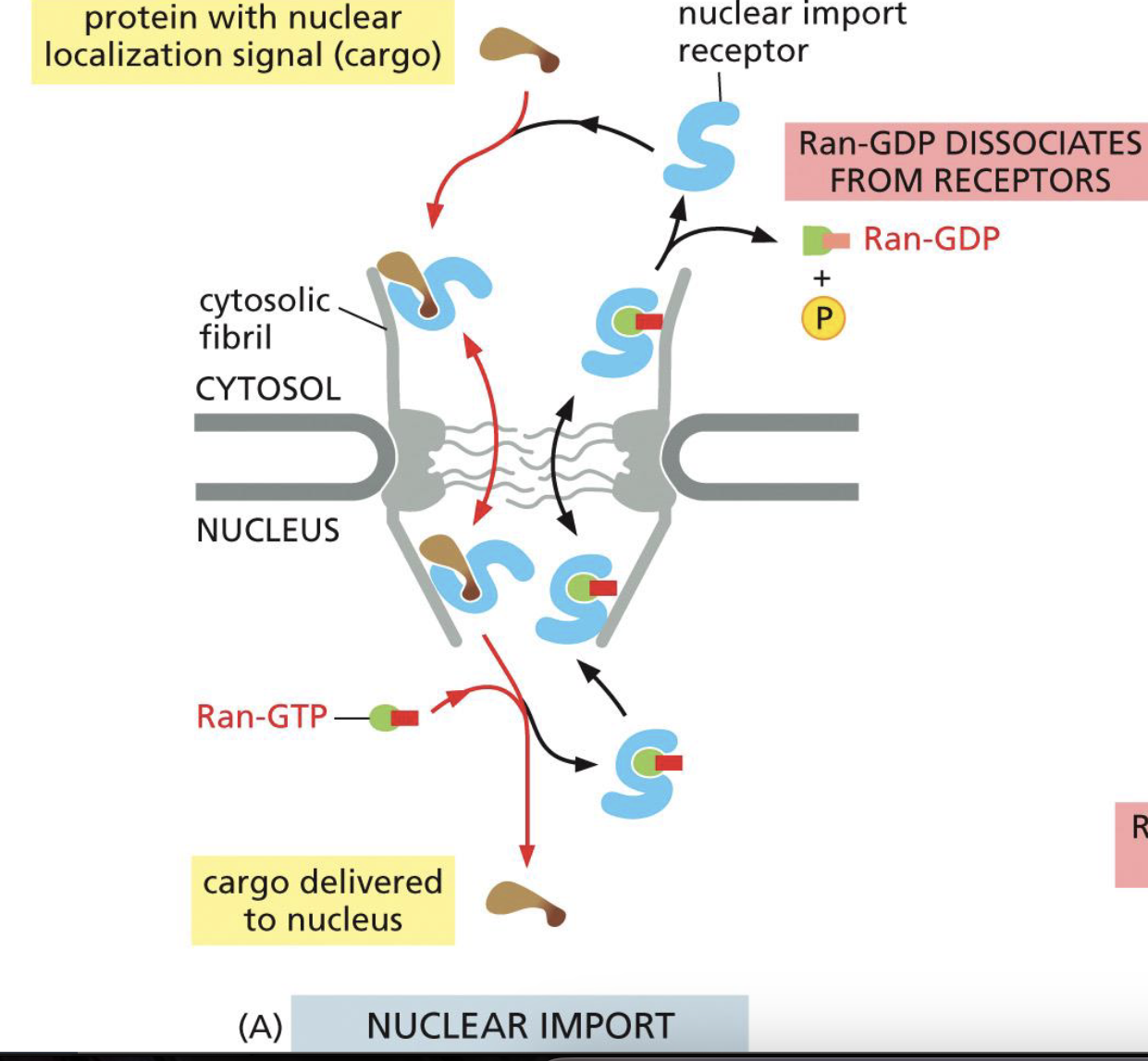
Nuclear Import Mechanism
Cargo Protein’s NLS binds with Nuclear Import Receptor
Nuclear Import Receptor binds to nucleoporins in the NPC, and transports cargo into the nucleus
Bound by Ran-GTP → causes a release in cargo
Empty import receptor and Ran-GTP goes to cytosol
Ran-GTP is cleaved into Ran-GDP by Ran-GAP and Ran Binding Protein
Ran-GDP gets transported back into nucleus with NTF2
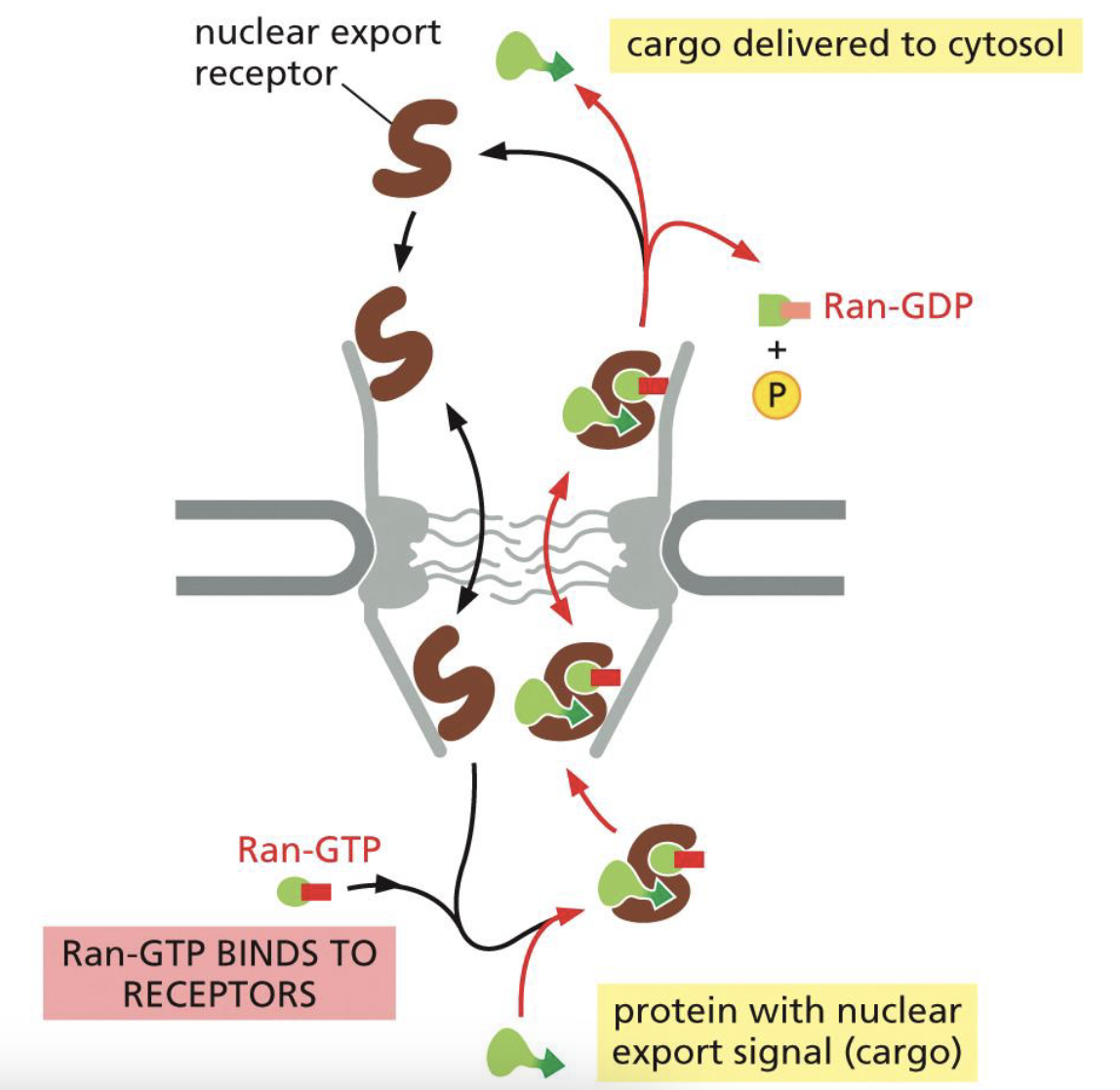
Nuclear Export Mechanism
Nuclear Export Receptor binds to cargo NES and Ran-GTP
Nuclear Export Receptor binds to nucleoporins of the NPC, and goes to cytosol
Ran-GTP is cut by Ran-GAP and Ran Binding Proteins (becomes Ran-GDP), where the cargo is released into cytosol
Empty nuclear export receptor gets transported back to nucleus
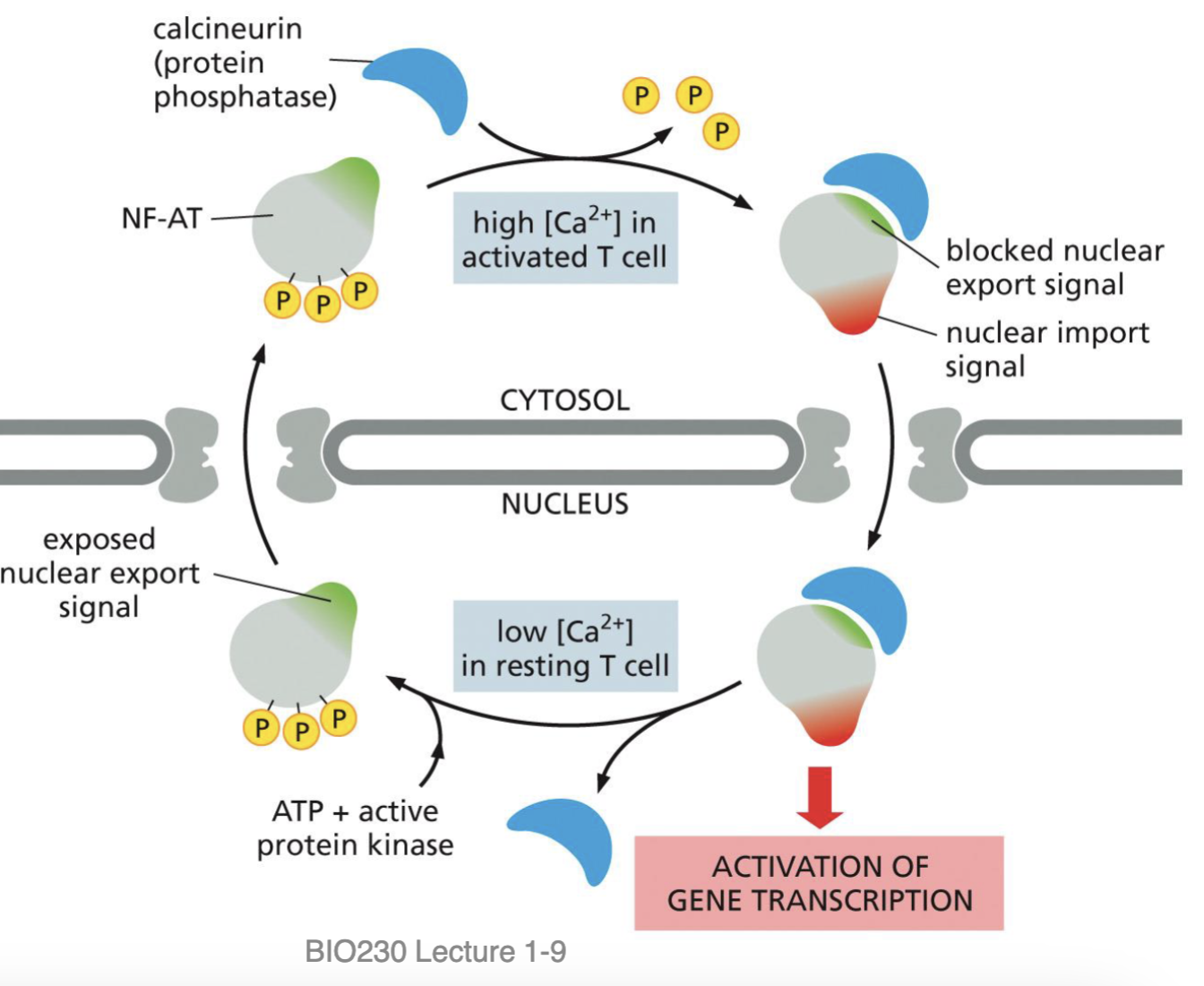
Example of Nuclear Import/Export - What is NFAT?
Nuclear Factor of Activated T Cells
Example of Nuclear Import/Export - NFAT: Import
high Calcium ions = encountered bacteria/virus: Nuclear Import to enable transcription
Phosphatase cuts 3 Phosphates and blocks the export signal → this enables the import signal
Imported into the cell = gene transcription activated
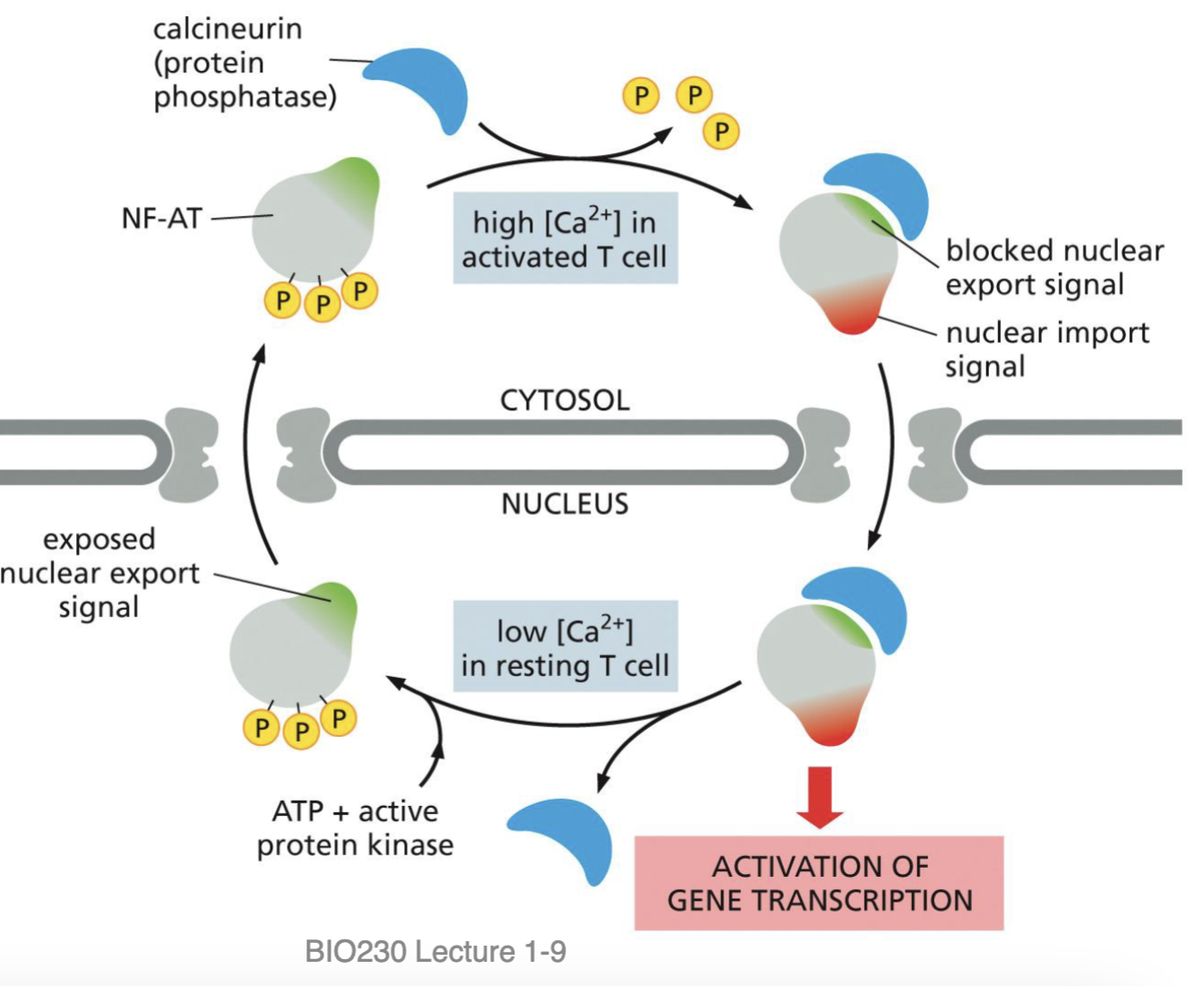
Example of Nuclear Import/Export - NFAT: Export
low Calcium ions = nothing to attack: Nuclear Export
Protein kinase adds three Phosphates → changes shape
This exposes nuclear export signal
Leaves nucleus
Transmembrane Transport: Sorting to Mitochondria and Chloroplasts - Protein is translated ____ and is folded or unfolded?
Protein is fully translated in the cytosol, and when importing into organelle, it is unfolded
Transmembrane Transport: Sorting to Mitochondria and Chloroplasts - How do proteins remain unfolded?
hsp70 chaperones bind onto the unfolded proteins in the cytosol, and prevent it from folding
What do proteins that need to be transported to mitochondria and chloroplasts have?
N-terminus amphipathic alpha-helix → to bind to the transmembrane receptor
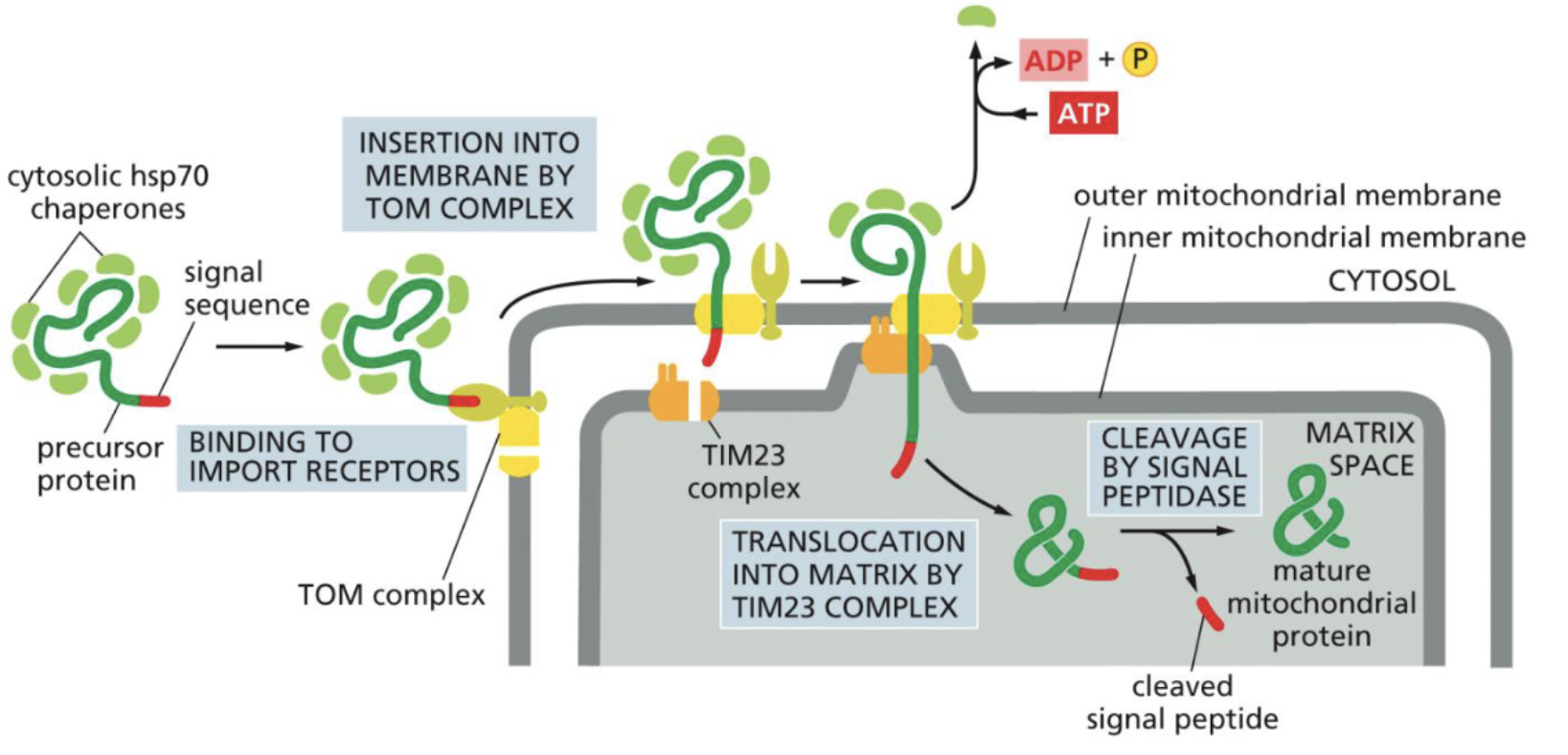
Transporting into Mitochondria mechanism
TOM (Translocase of outer membrane) and TIM23 (Translocase of the Inner membrane) used
protein’s N terminal amphipathic alpha helix sequence is recognized by TOM
Binds to TOM → moves to TIM23
Protein moves into matrix
N-terminal amphipathic alpha helix sequences are cleaved by signal peptidase
Protein further folded
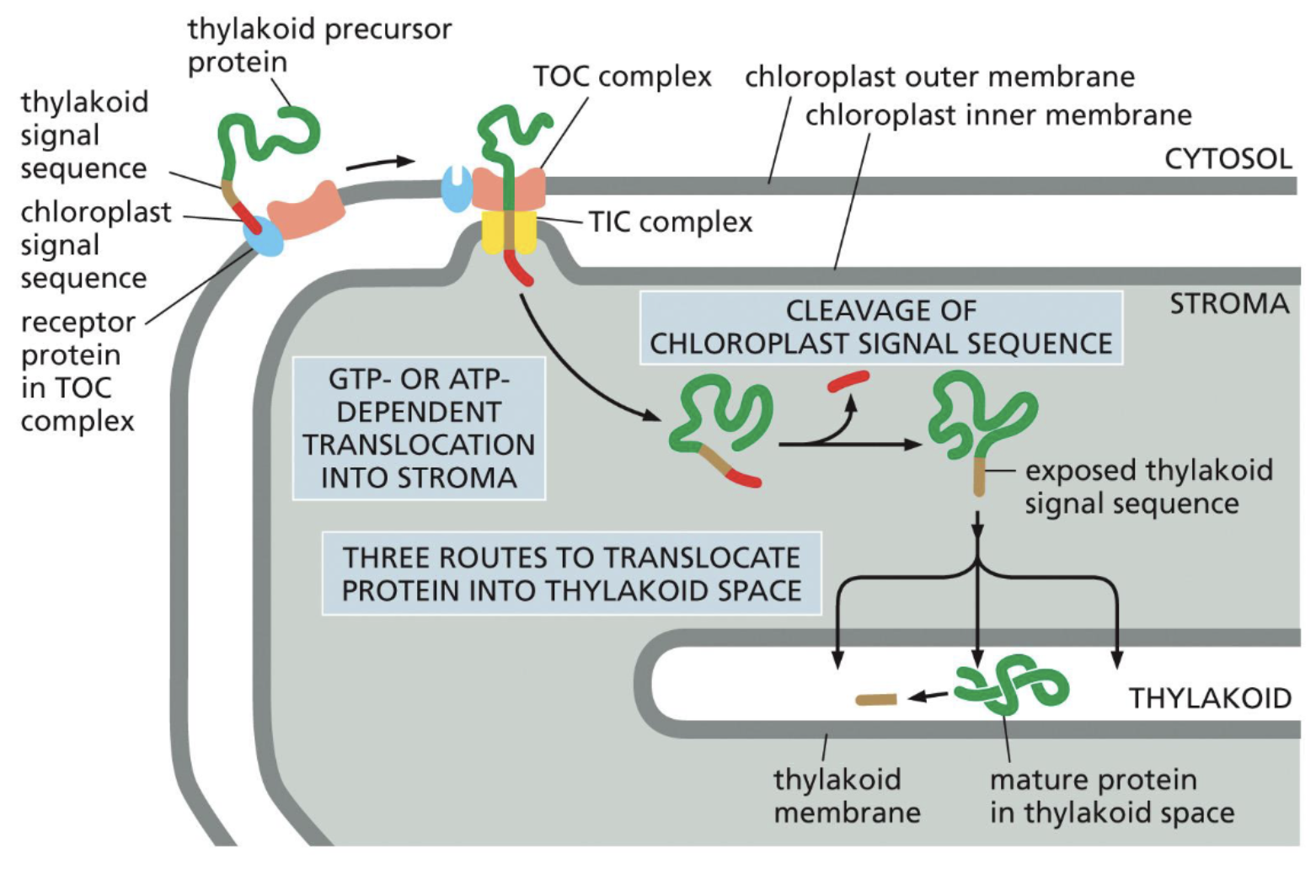
Transporting into Chloroplast mechanism
TOC (Translocase of outer chloroplast membrane) and TIC (Translocase of the inner chloroplast membrane) used
Precursor protein has a N-terminal amphipathic alpha helix that is recognized by TOC
TOC passes protein onto TIC, protein is now inside the stroma
The N-terminus amphipathic alpha helix is cleaved off
Once cleaved off, exposes thylakoid signal sequence
Transported into the thylakoid → cleave off sequence
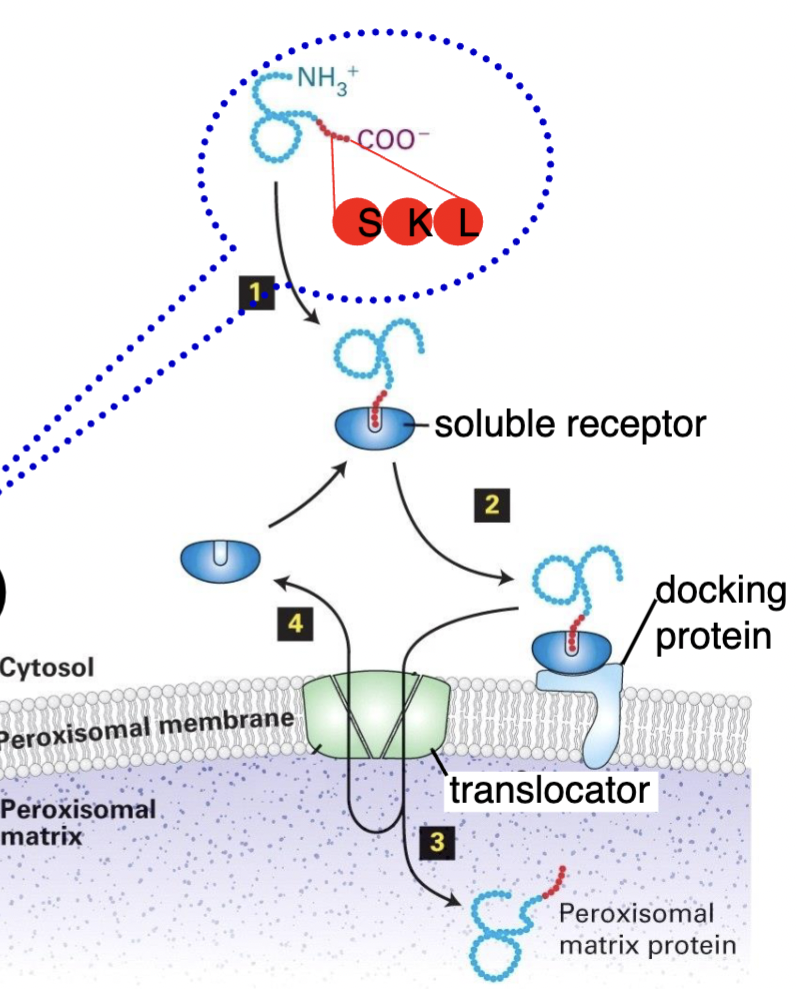
Are proteins folded for peroxisomal proteins? What target signals do they have?
Proteins for transporting into peroxisome is folded
Peroxisomal targeting signal = 3 amino acids (SKL) in the C terminus
Transporting into Peroxisome mechanism
Protein’s C terminus SKL sequence binds to soluble receptor → goes to docking protein
Docking protein tranferrs protein to translocator
Translocator brings the protein in
Does not cut the SKL sequence