Art history exam 1 (in progress)
1/248
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
249 Terms
Upper Paleolithic Period
period of human history from 40,000 to 10,000 BCE, when distinct human cultures first developed (also called the old stone age)
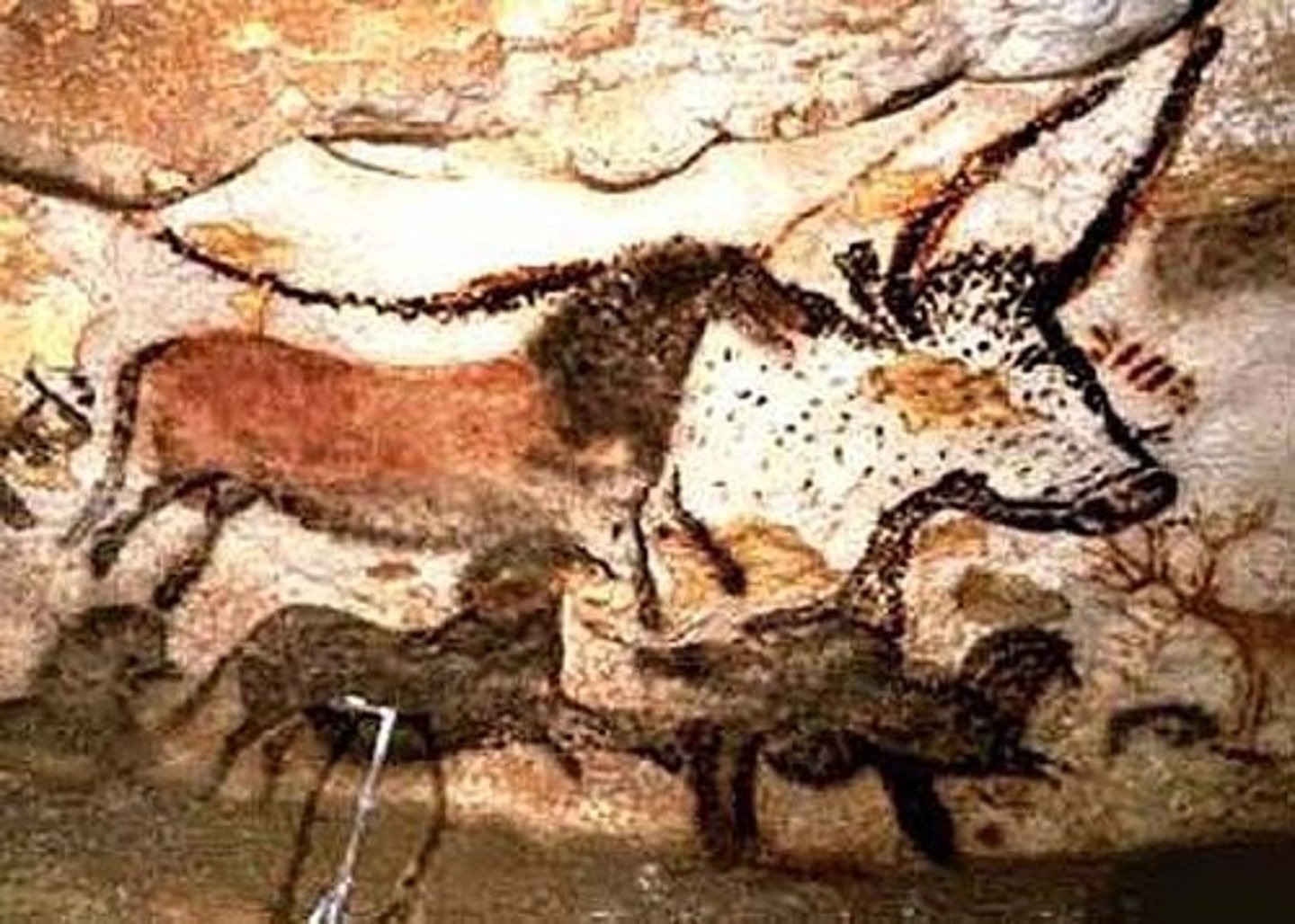
Hall of Bulls, Lascaux Cave, Paleolithic, c. 15,000 BCE

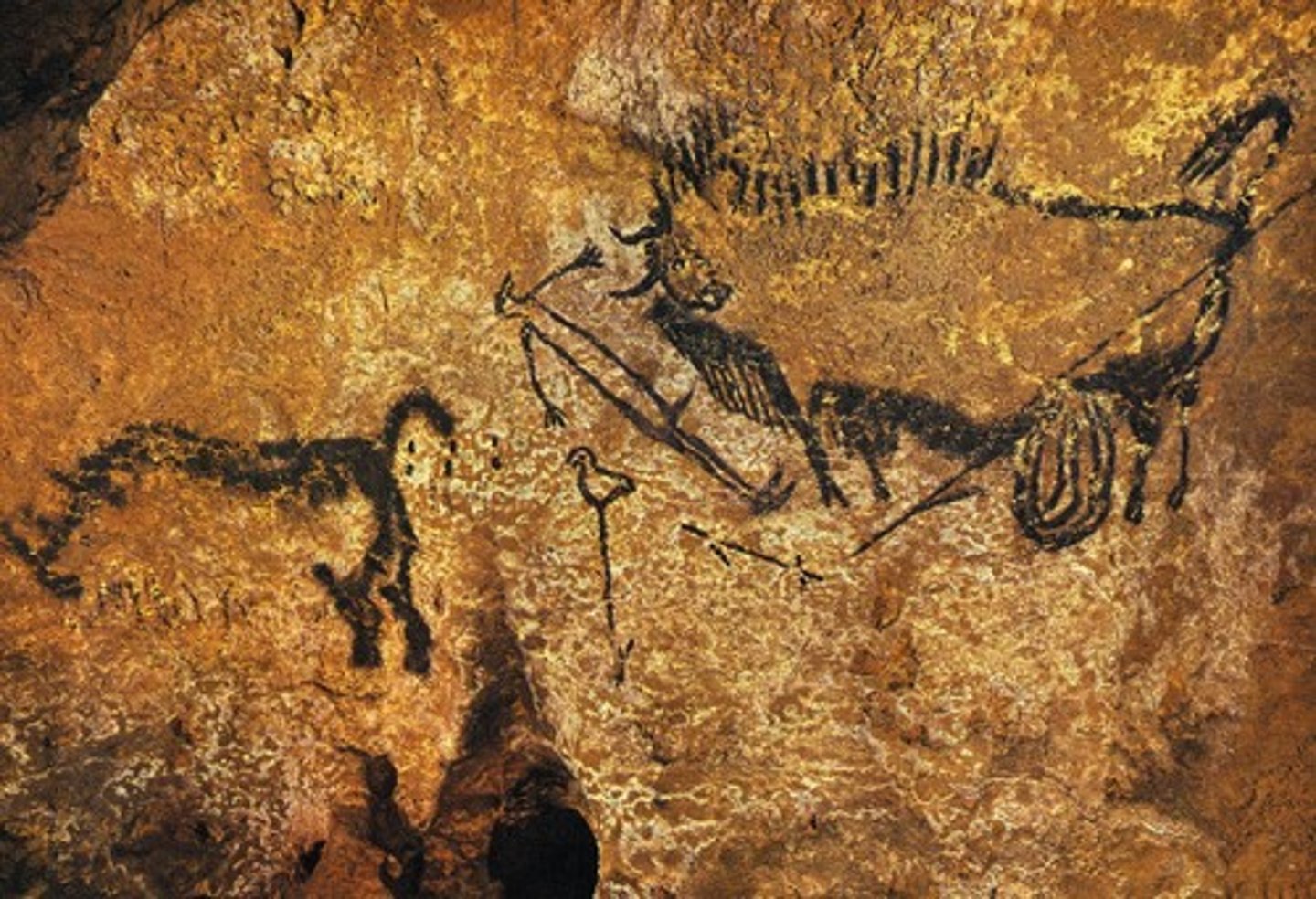
Bird-headed Man with Bison, Lascaux Cave, Paleolithic, c. 15,000 BCE

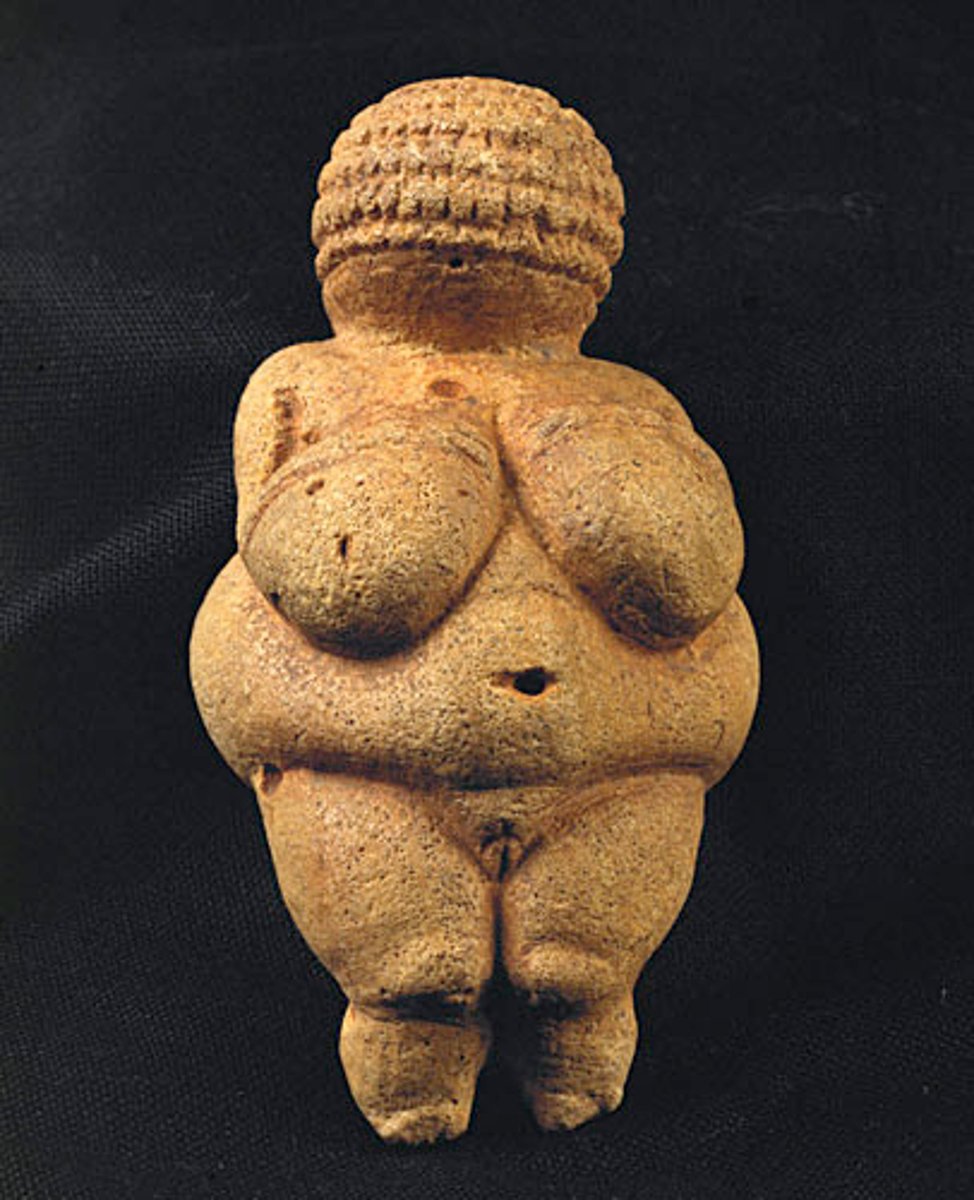
Woman from Willendorf, Paleolithic, c. 25,000 BCE

Neolithic Period
the final era of prehistory, which began about 9000 B.C.; also called the New Stone Age
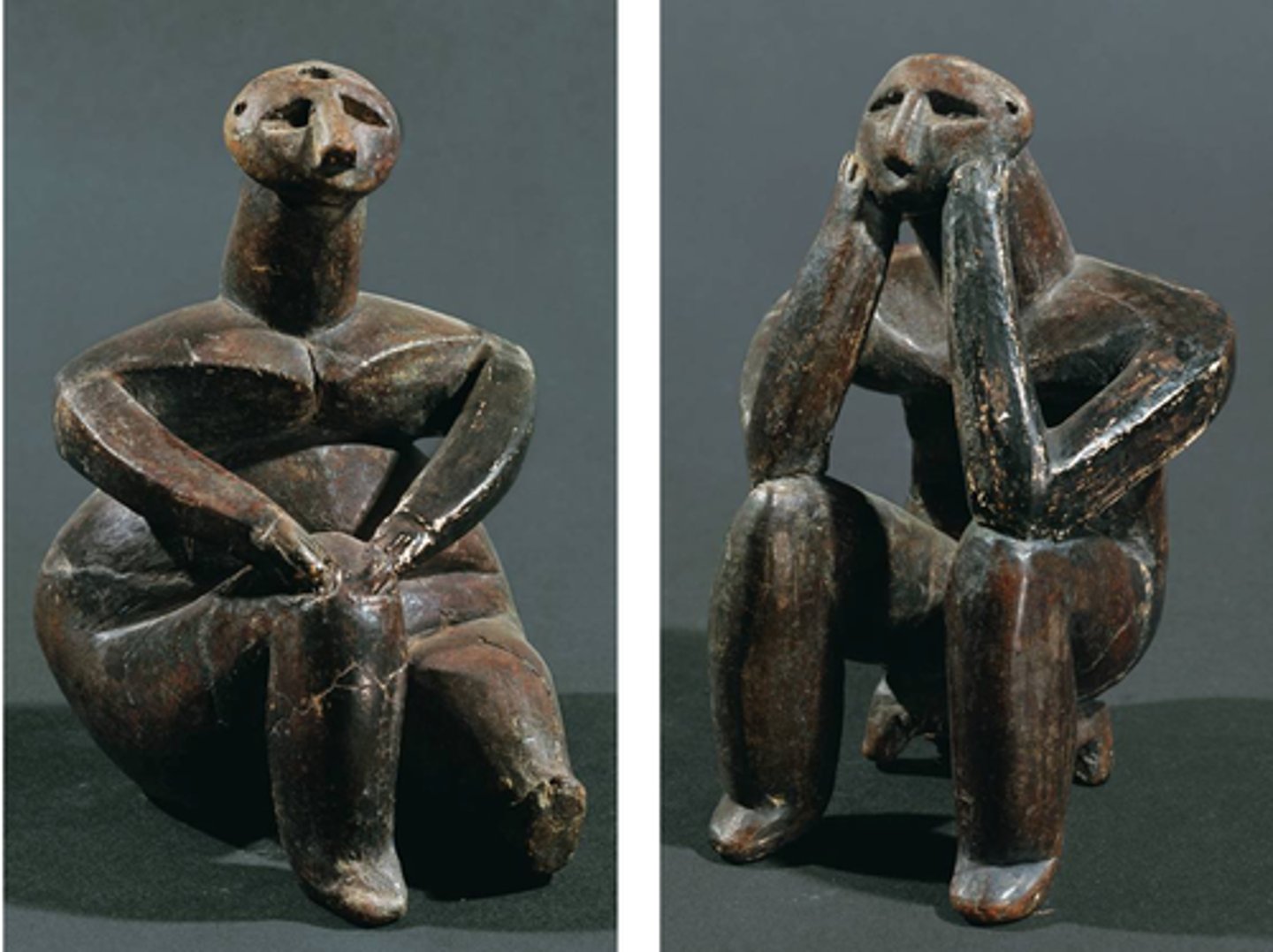
Female and Male Figures, Neolithic, ***c. 3,500 BCE

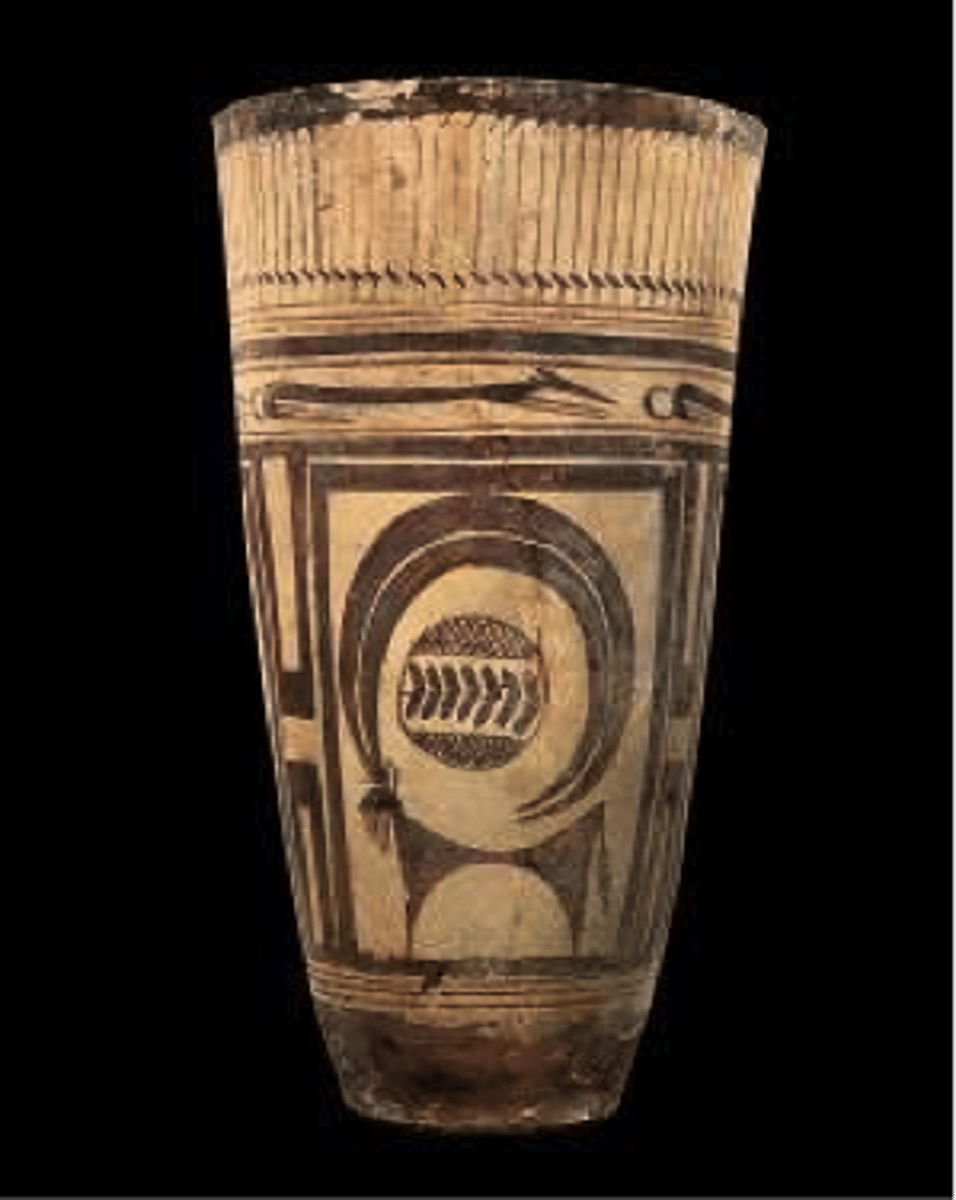
Painted Beaker with Animals, Neolithic, c. 5,000 BCE

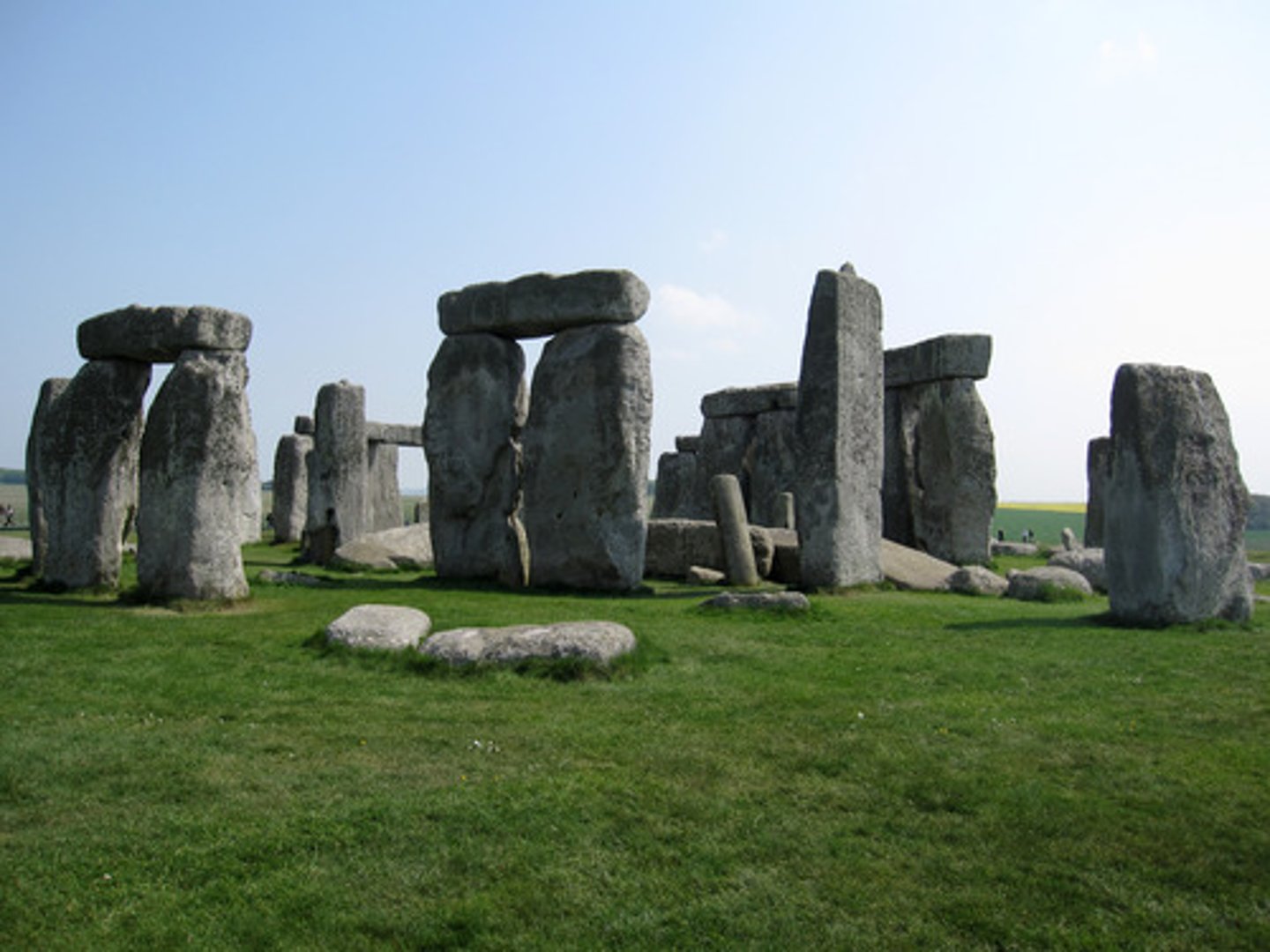
Stonehenge, England, Neolithic, c. 2,500BCE (post & lentil construction)

Ancient Egypt
A civilization concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River. Its history occurred in a series of stable Kingdoms, separated by periods of relative instability known as Intermediate Periods: the Old Kingdom, Middle Kingdom, and New Kingdom.
When was the Predynastic Period?
c. 5,000 BCE
When was the Old Kingdom?
c. 2,500 BCE
When was the Middle Kingdom?
c. 2,000 BCE
When was the New Kingdom?
c. 1,500 BCE
What was the Amarna period (***c. 1,350 BCE )?
Amarna Period during and just after the reign of Akhenaten -- gave Akhenaten very feminine qualities

What was the Ptolemaic Period (***332-30 BCE)?
Ptolemy took the title of King and he founded the Ptolemaic dynasty that was to rule Egypt for nearly 300 years.

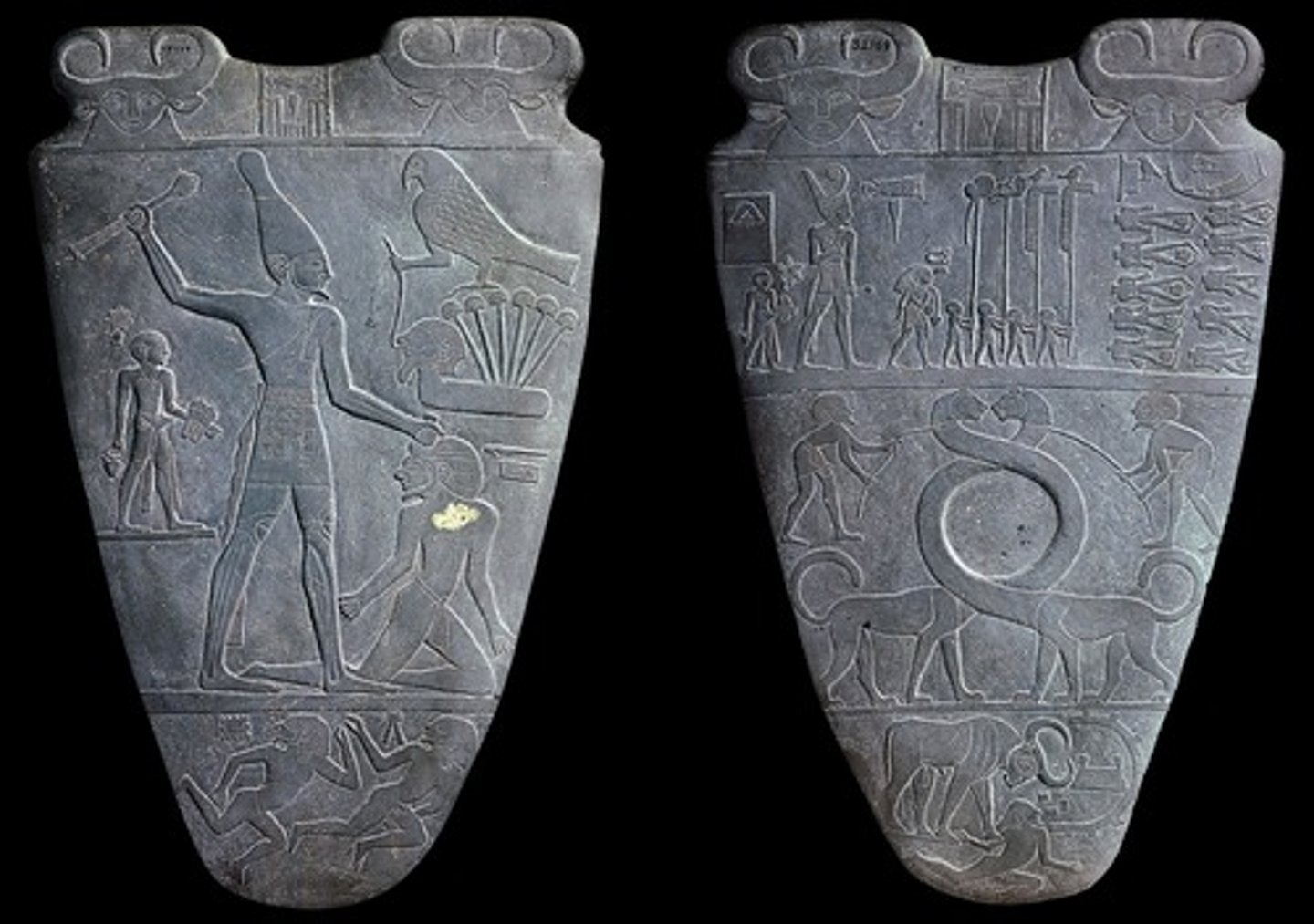
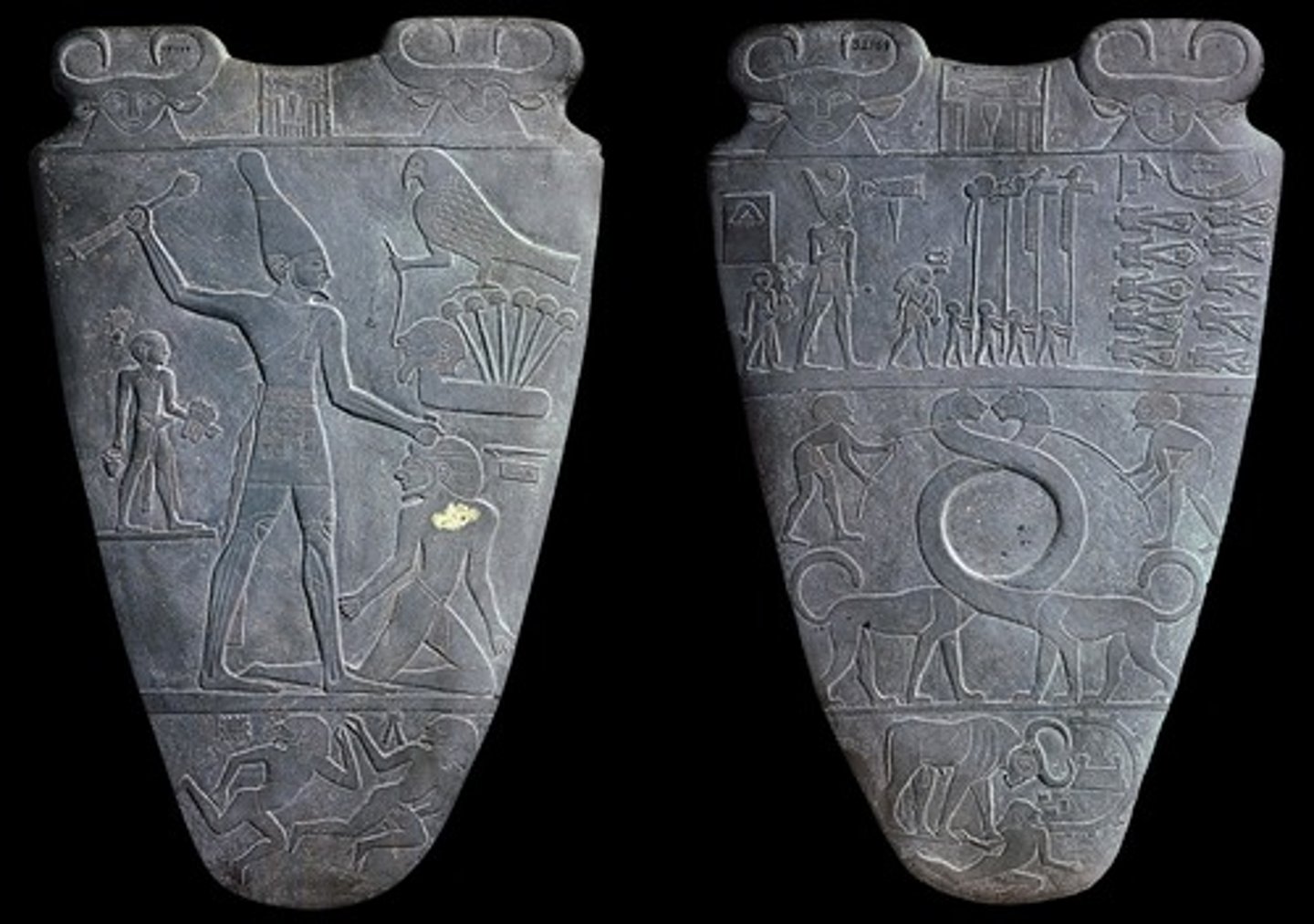
Palette of King Narmer (front & back), Predynastic, ***c. 3,000 BCE

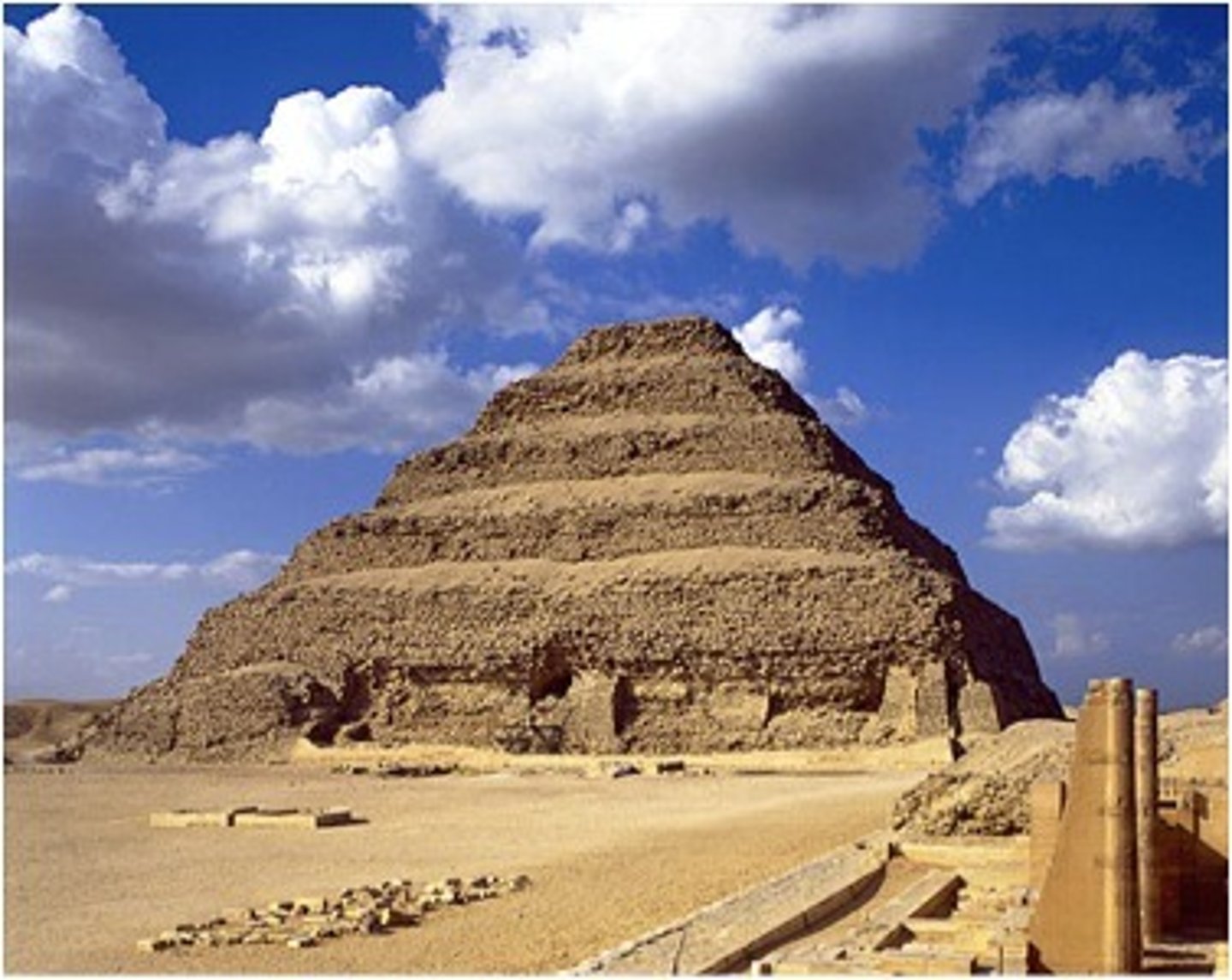
Imhotep, Step Pyramid of King Djoser, Old Kingdom, ***c. 2,500 BCE

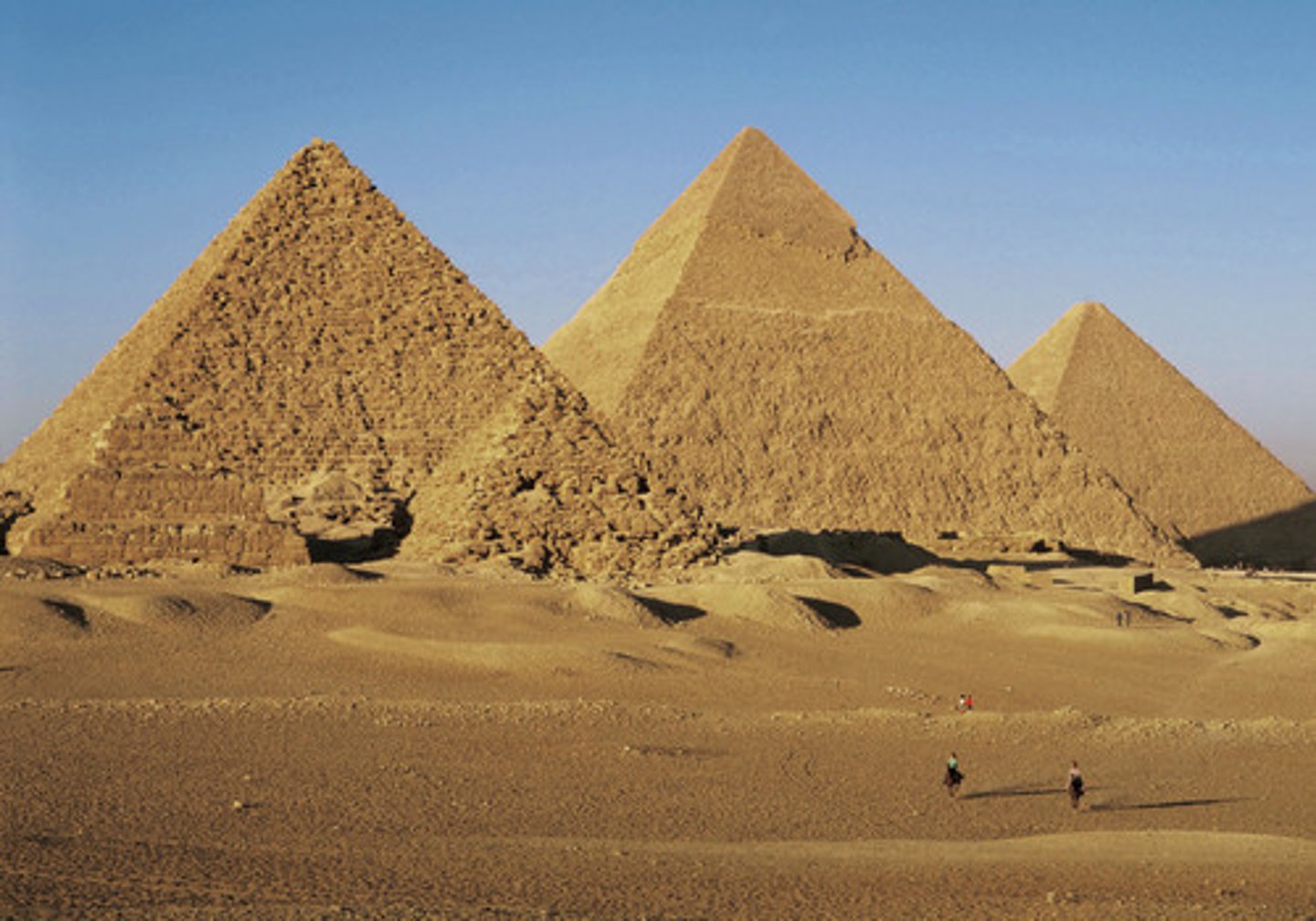
The Great Pyramids (Giza), Old Kingdom, ***c. 2,500 BCE

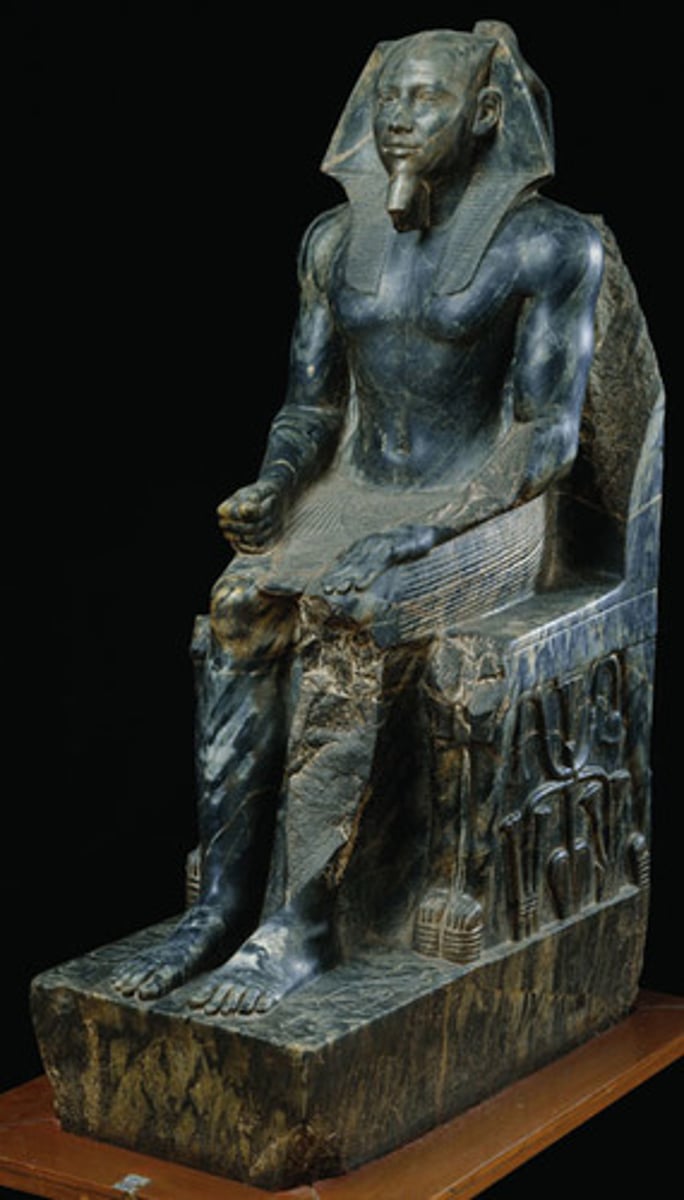
Khafre, Old Kingdom, ***c. 2,500 BCE

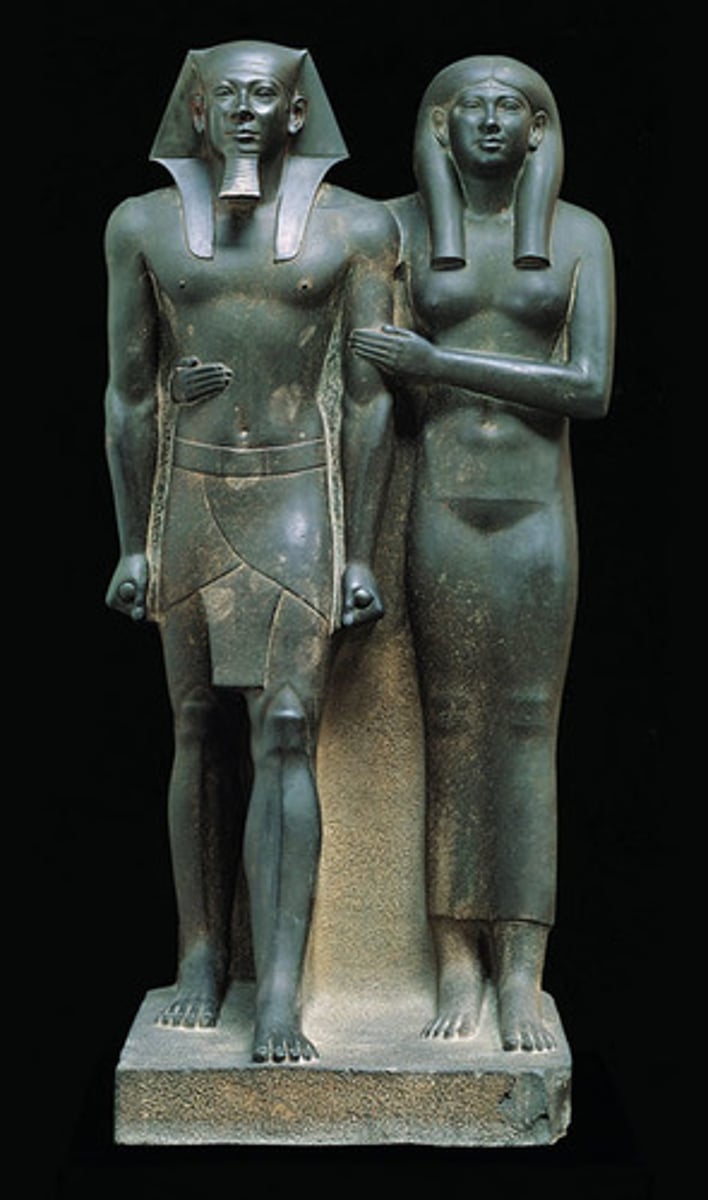
Mycerinus & his Wife, Old Kingdom, ***c. 2,500 BCE

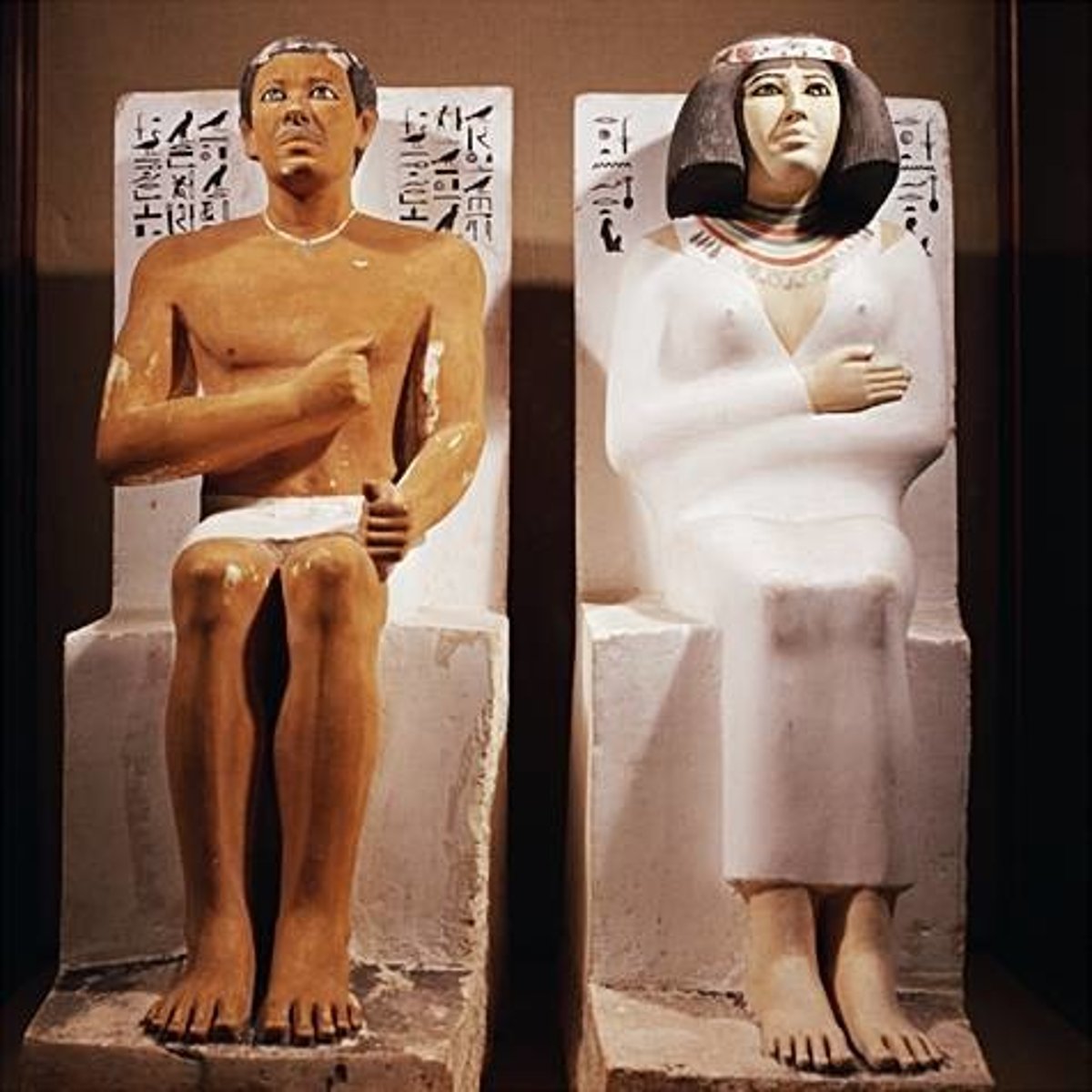
Prince Rahotep and his Wife Nofret, Old Kingdom, ***c. 2,500 BCE

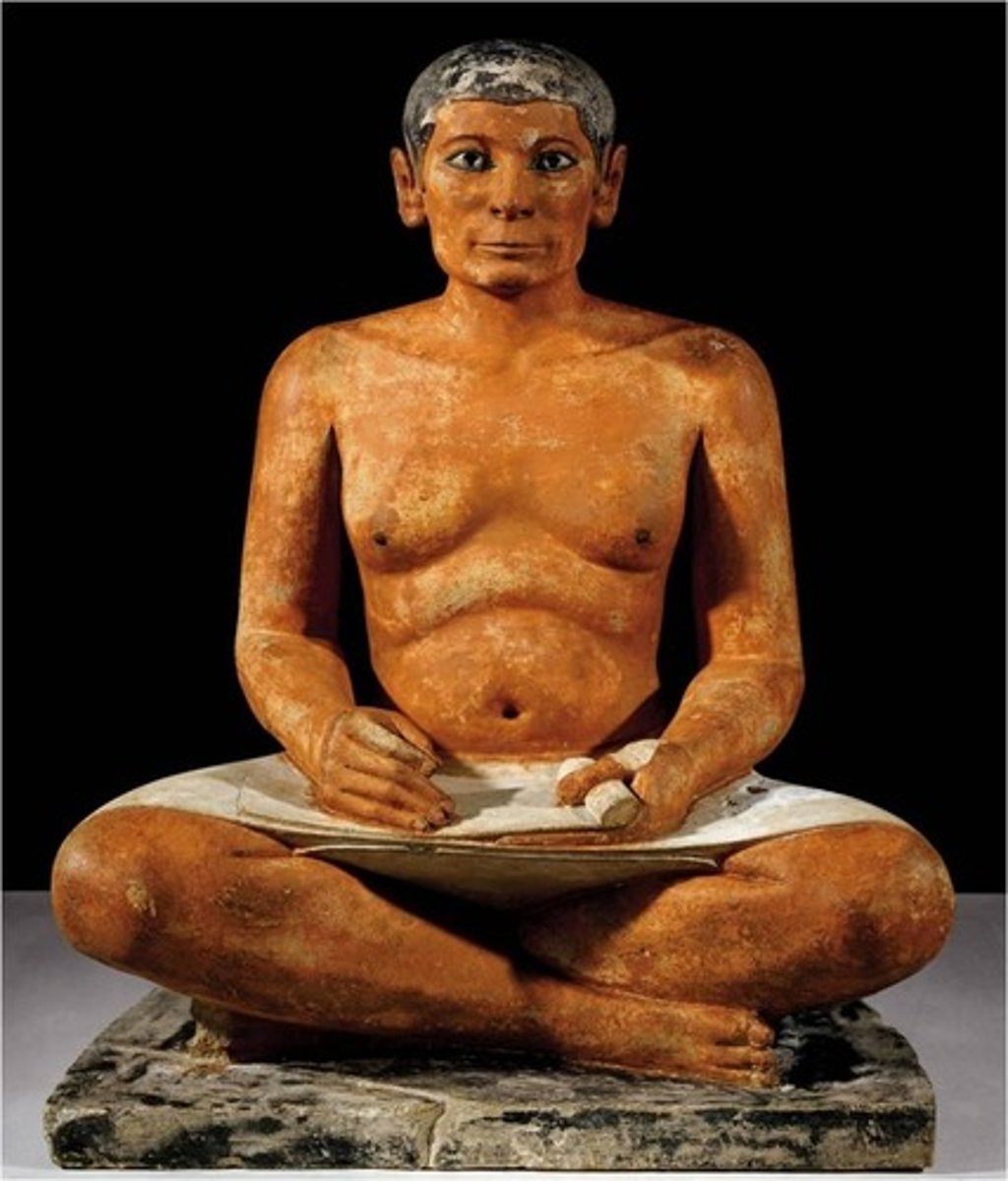
Seated Scribe, Old Kingdom, ***c. 2,500 BCE

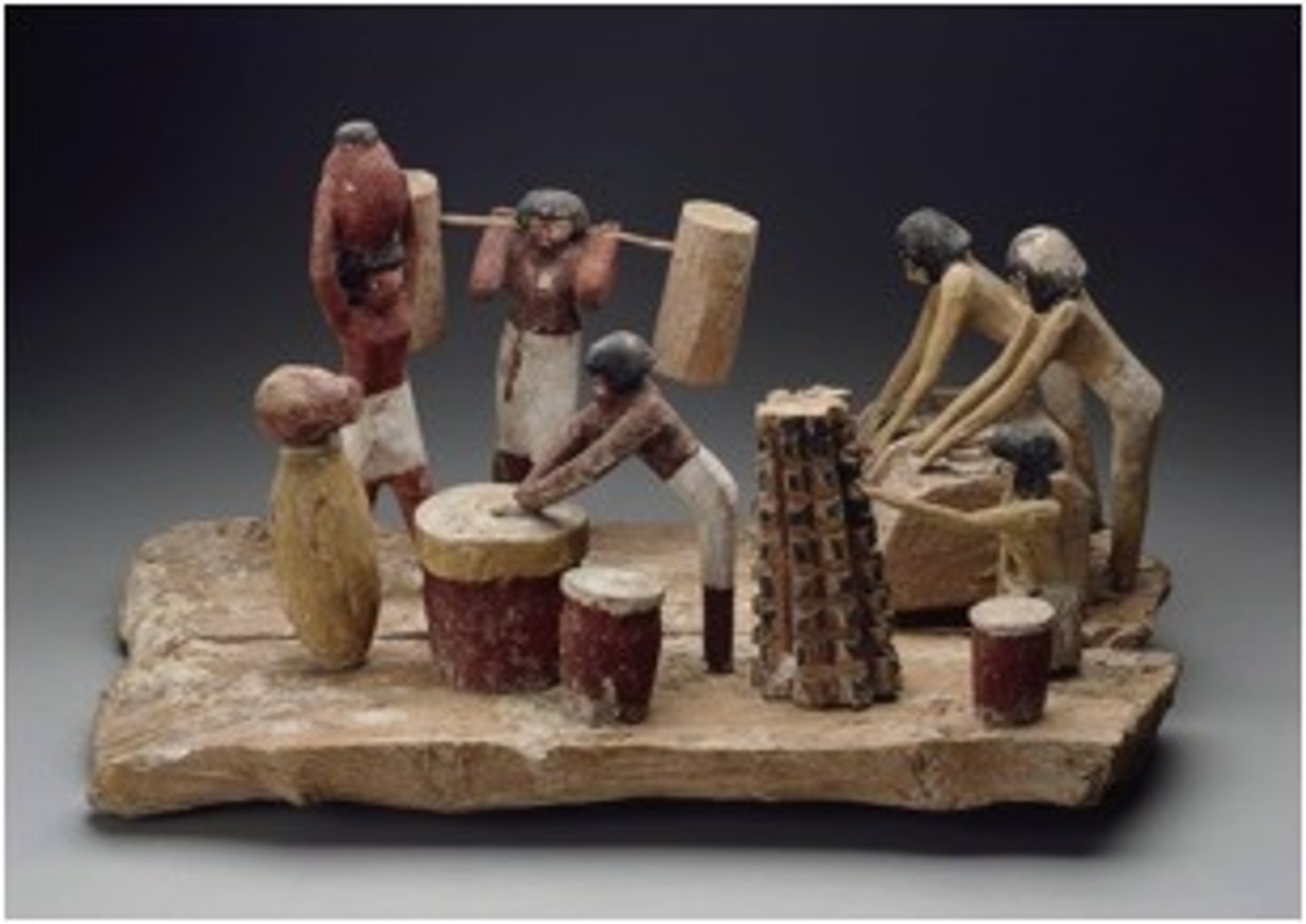
Model of People Making Beer, Middle Kingdom, ***c. 2,000 BCE

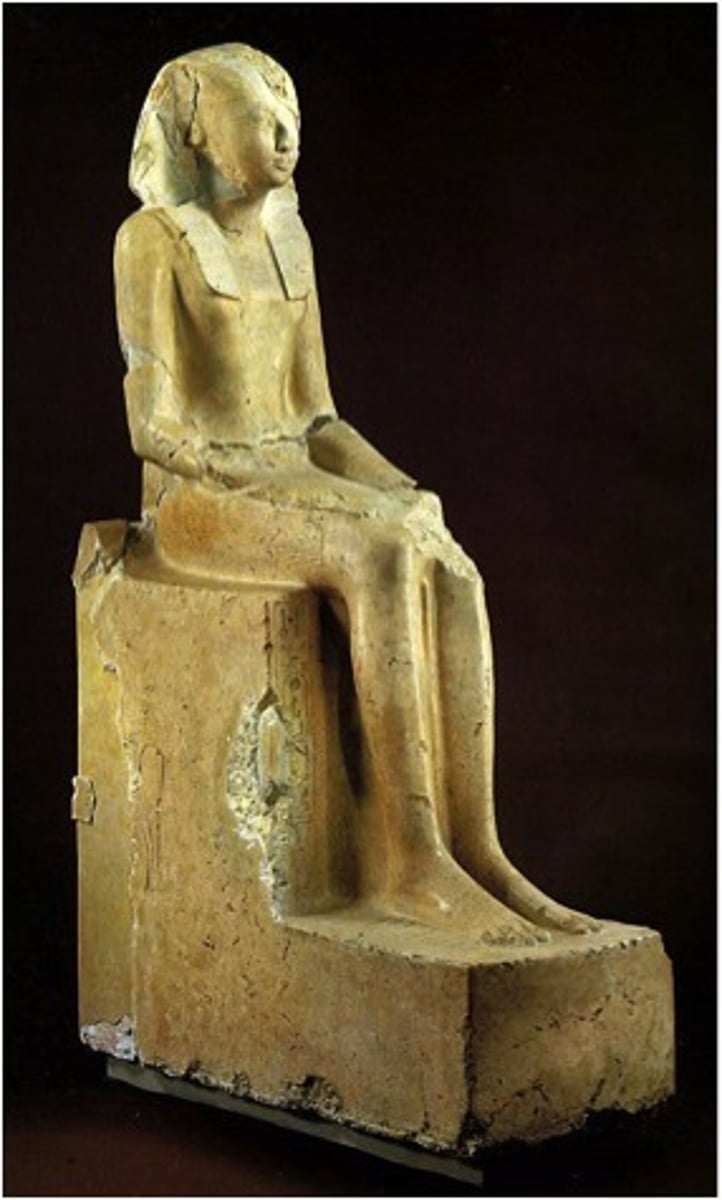
Hatshepsut Enthroned, New Kingdom, ***c. 1,500 BCE

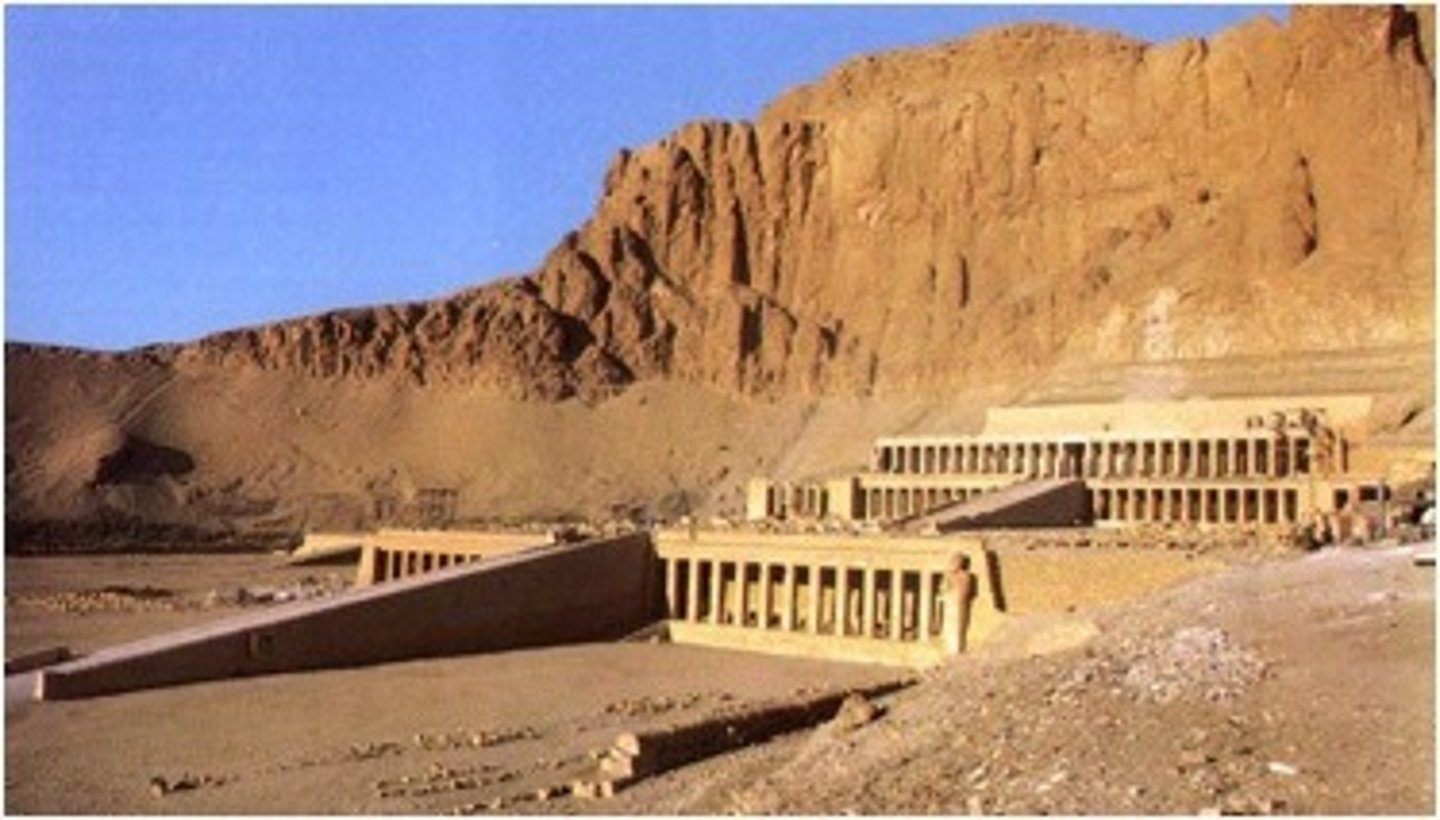
Funerary Temple of Hatshepsut, New Kingdom, ***c. 1,500 BCE

Akhenaten, New Kingdom - Amarna Period, ***c. 1,350 BCE
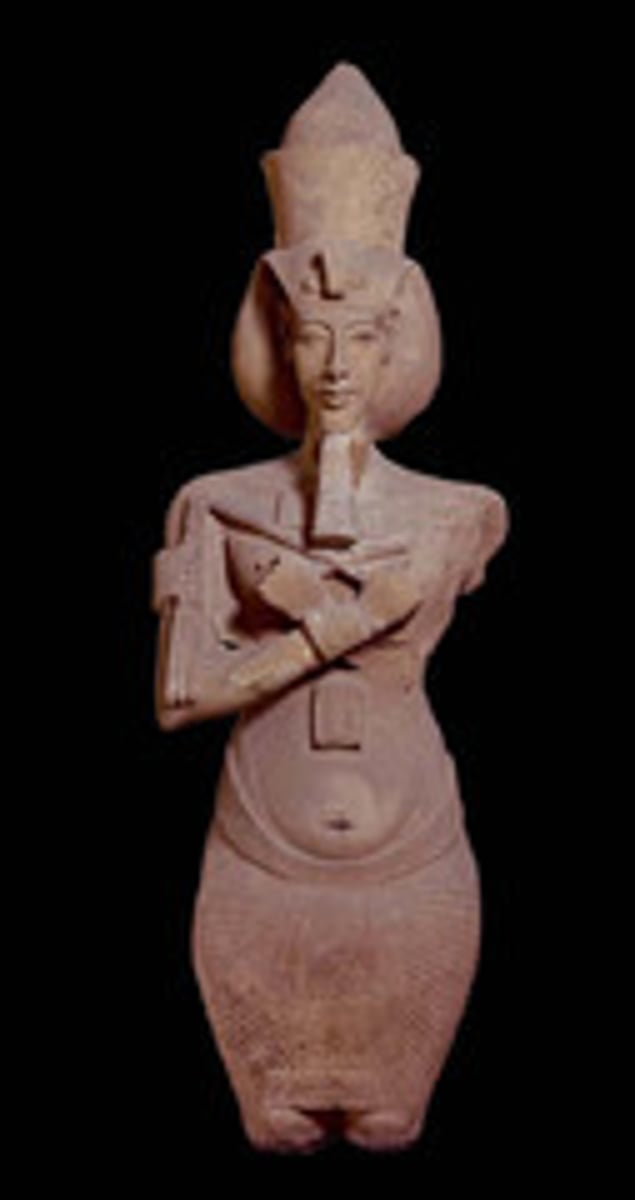

Akhenaten and His Family, New Kingdom - Amarna Period, ***c. 1,350 BCE

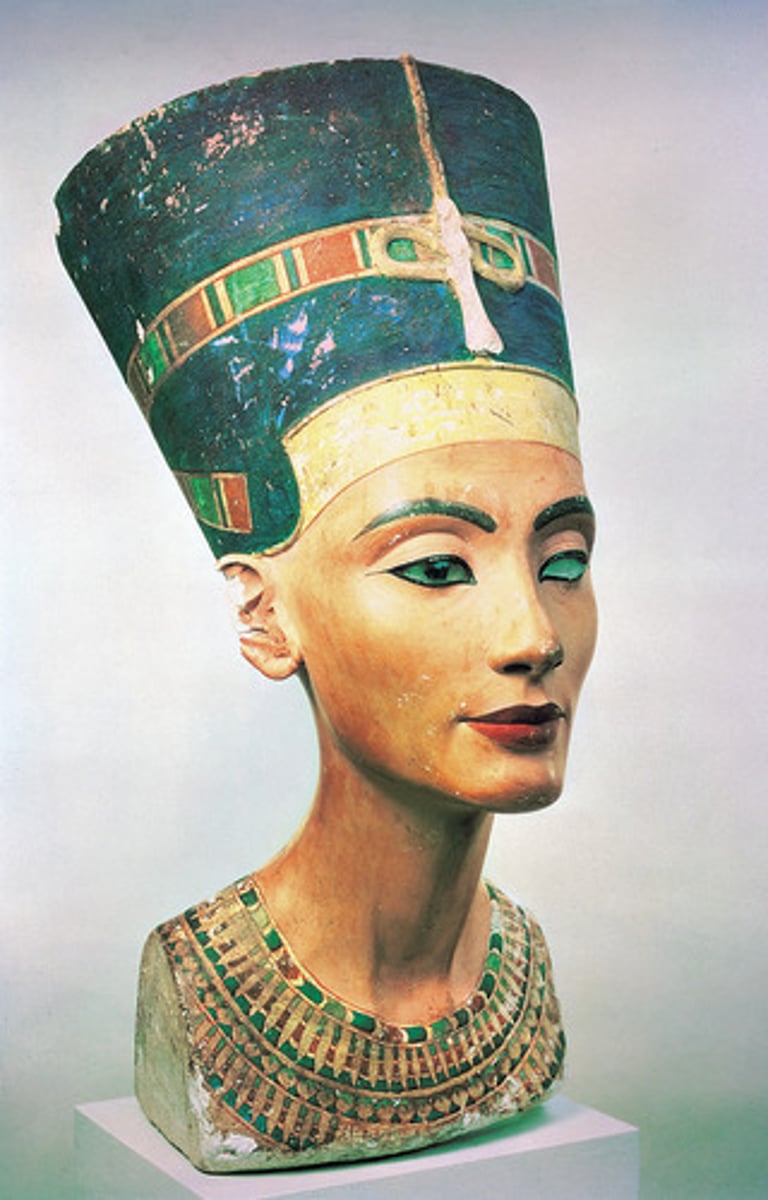
Nefertiti, New Kingdom - Amarna Period, ***c. 1,350 BCE

Funerary Mask of King Tutankhamen, New Kingdom, ***c. 1,300 BCE

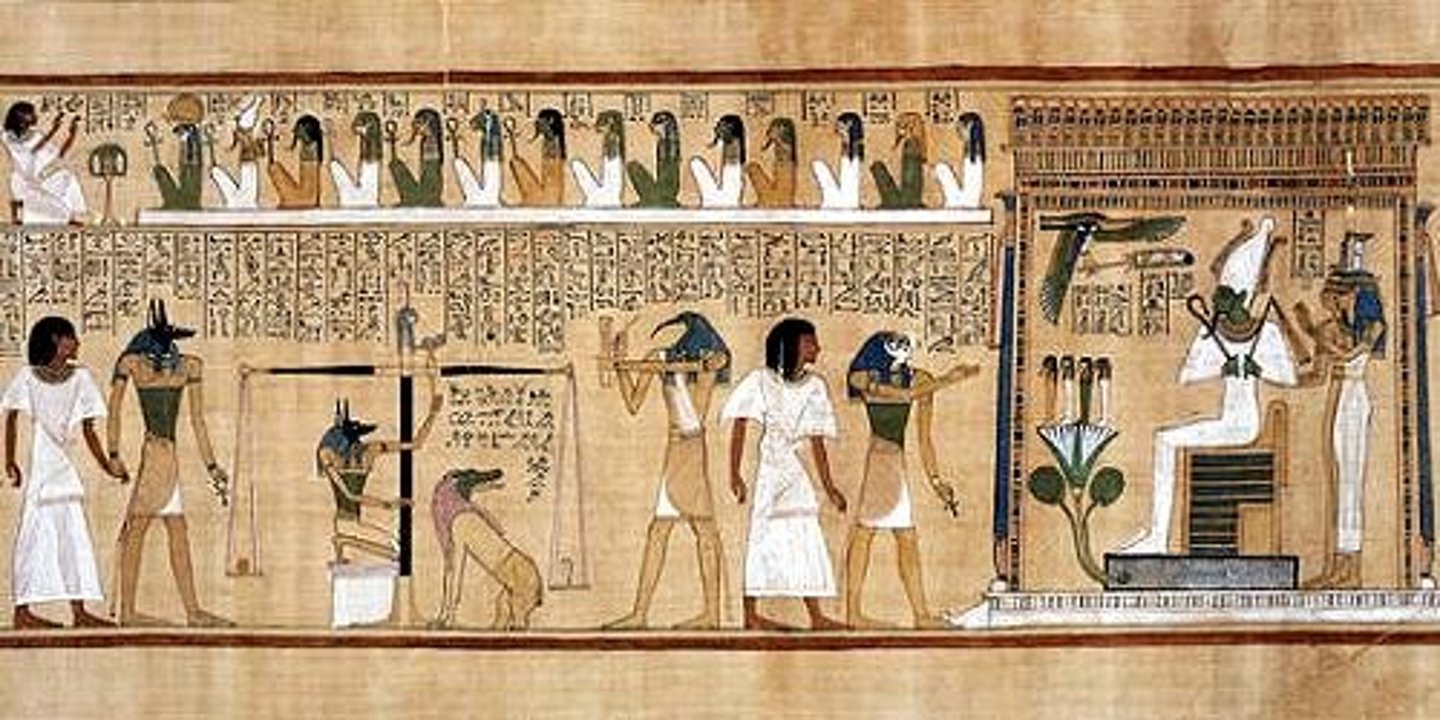
Judgement Before Osiris, New Kingdom, ***c. 1,300 BCE
Mesopotamia
A region between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers that developed the first urban societies. Included Sumer and the Akkadian, Babylonian and Assyrian empires as well as by the Neo-Assyrian and Neo-Babylonian empires. Also known as the "land between two rivers."
Sumer
The world's first civilization, founded in Mesopotamia, which existed for over 3,000 years, c. 3,300 BCE
Akkad
Mesopotamian city-state; world's first empire, c. 2,250 BCE
Neo Sumer (***c. 2,100 BCE)
The Third Dynasty of Ur, also called the Neo-Sumerian Empire, refers to a 22nd to 21st century BC Sumerian ruling dynasty based in the city of Ur and a short-lived territorial-political state which some historians consider to have been a nascent empire.
When was the Persian Empire?
c. 500 BCE
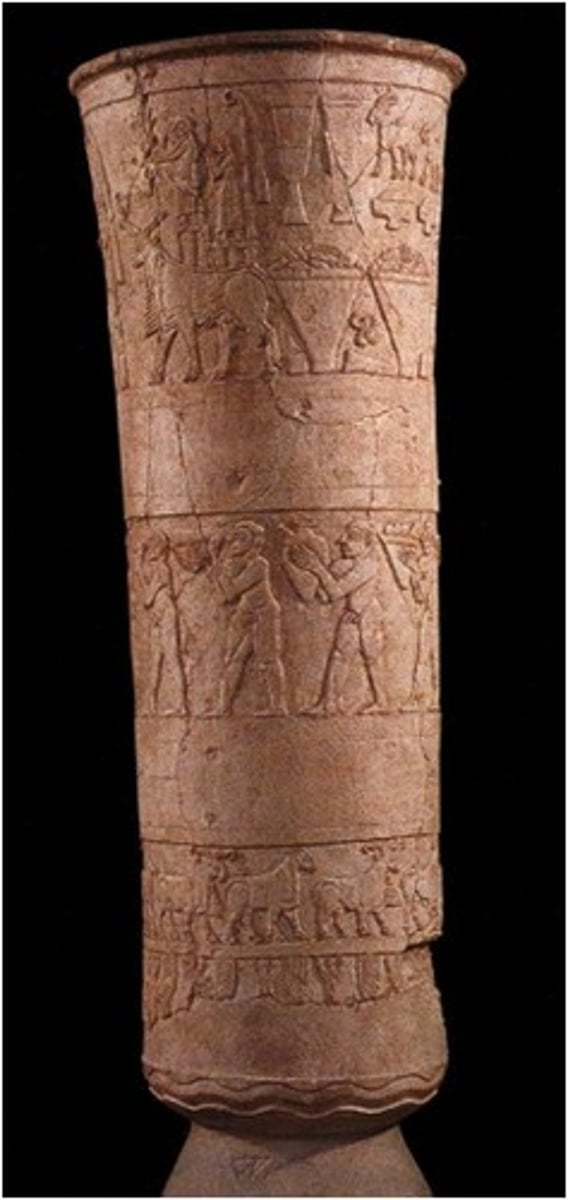
The Uruk Vase, Sumerian, ***c. 3,300 BCE

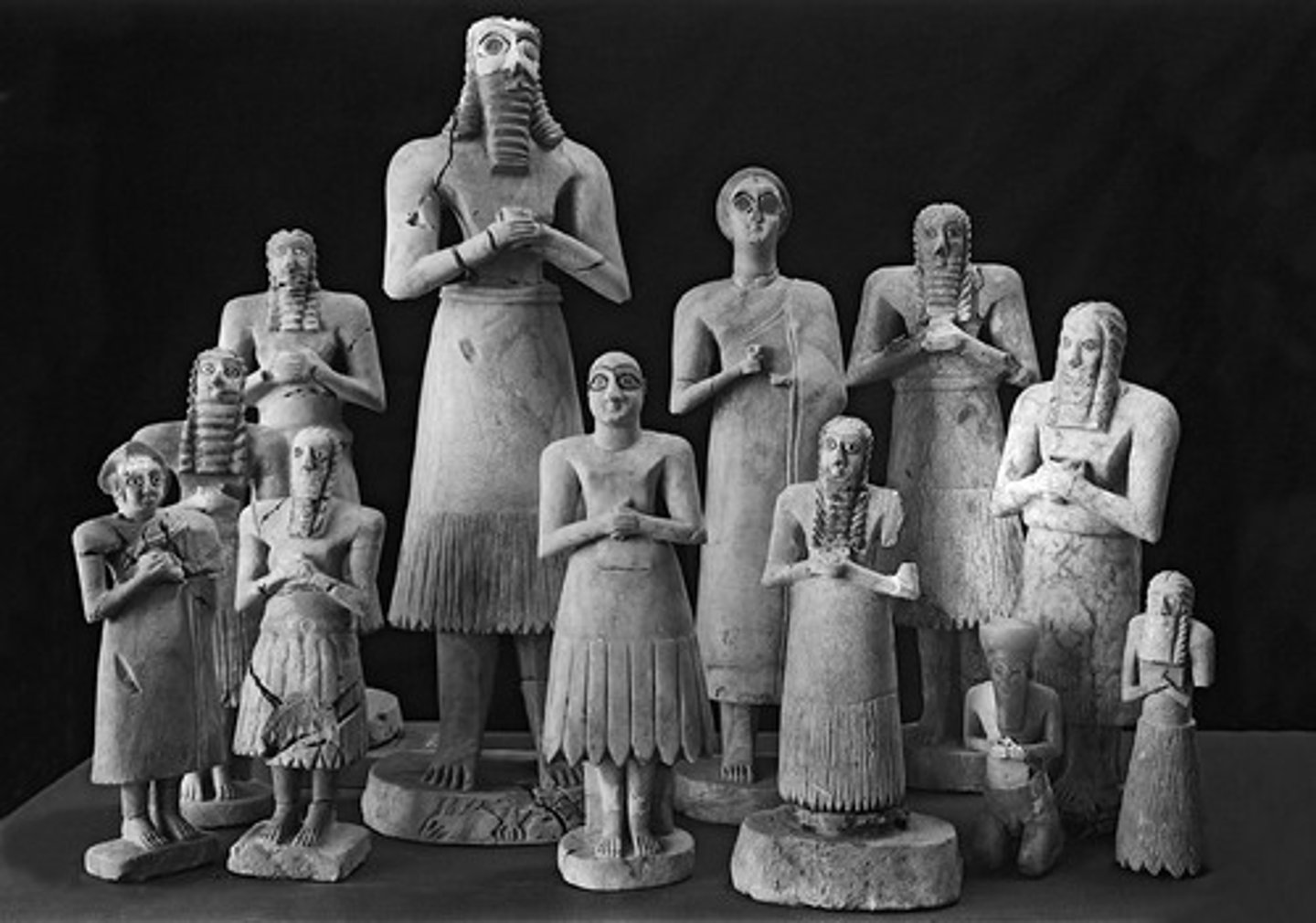
Votive Statues from the Abu Temple, Sumerian, ***c. 3,300 BCE

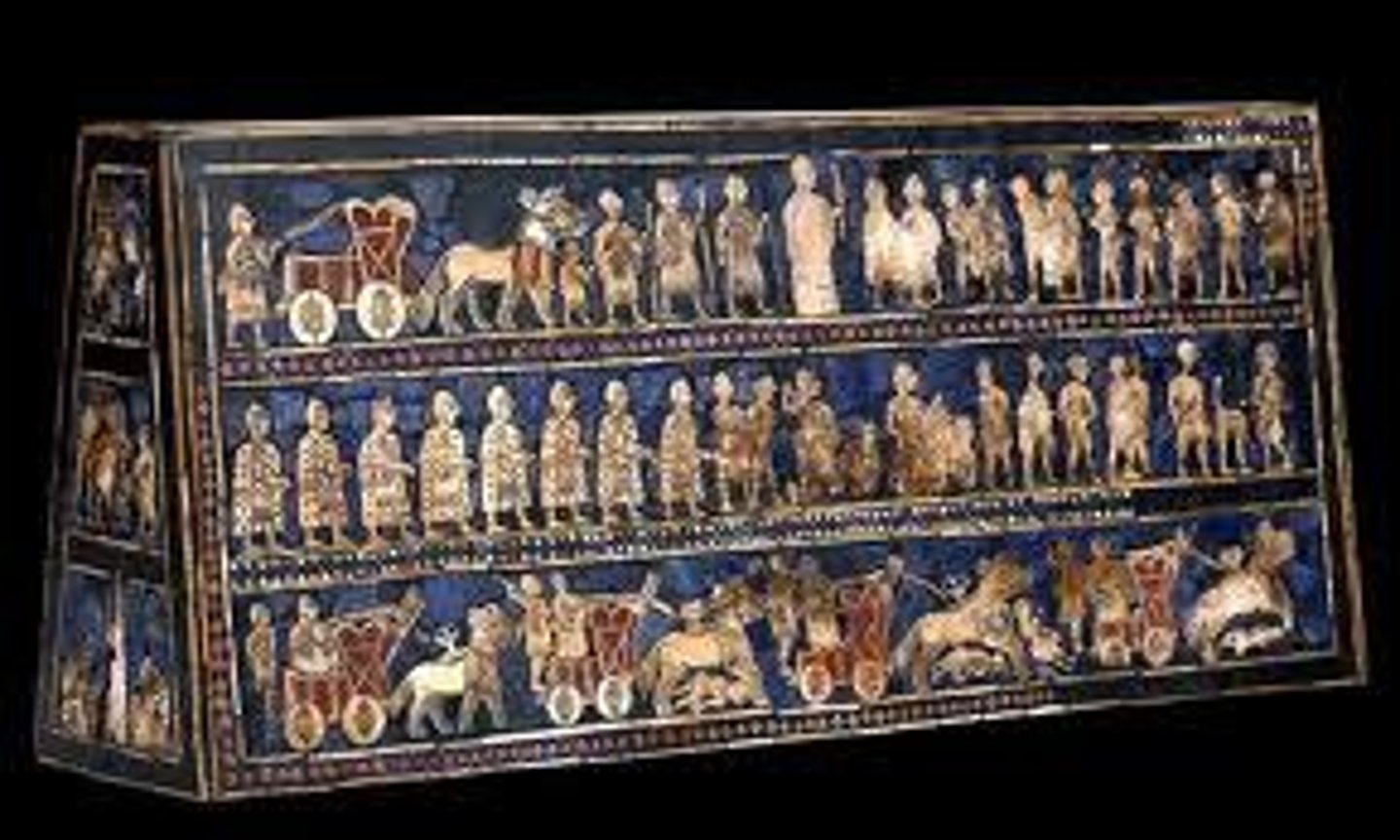
Standard of Ur, Sumerian, ***c. 3,300 BCE

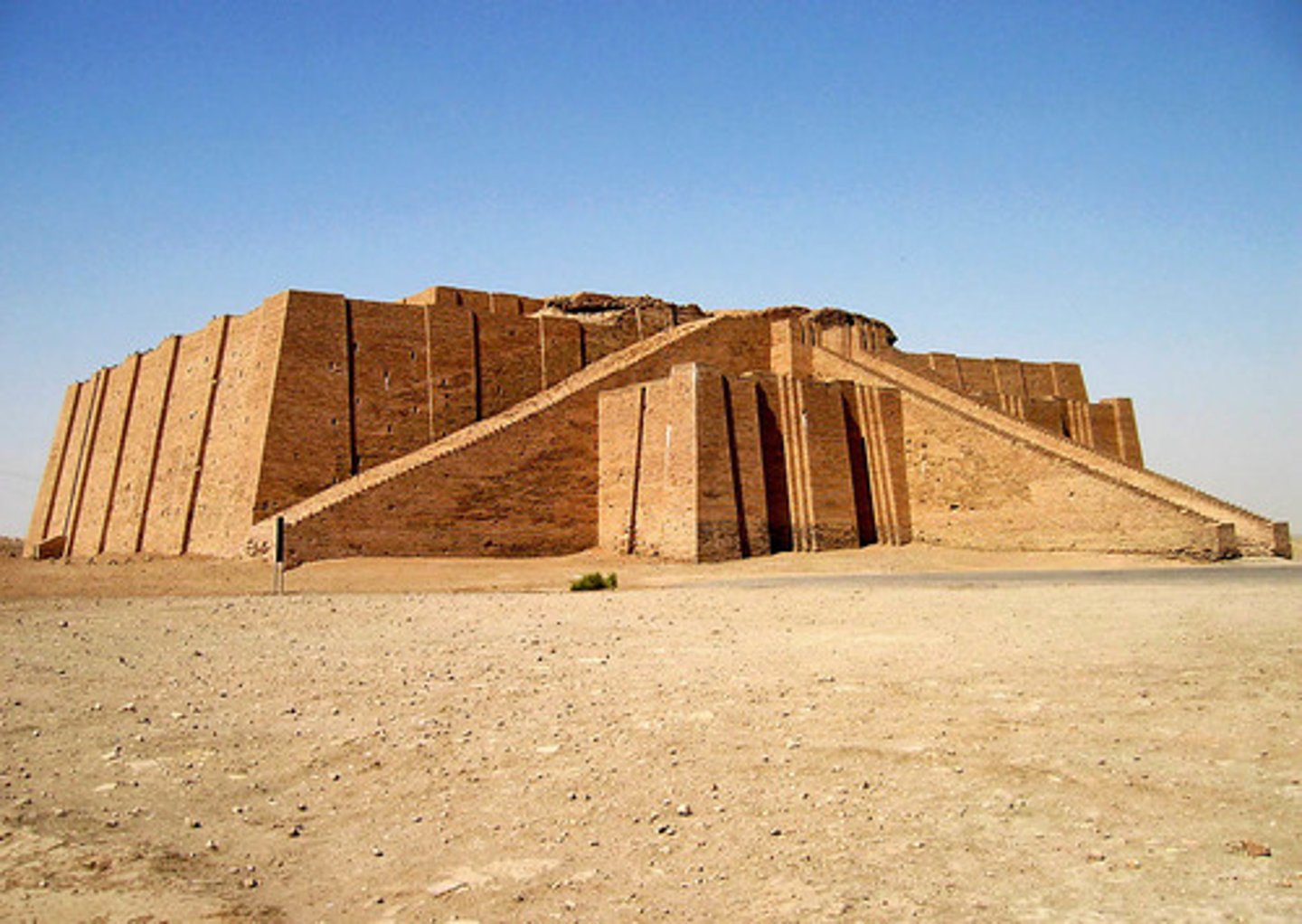
Ziggurat at Ur, Neo Sumerian, ***c. 2,100 BCE

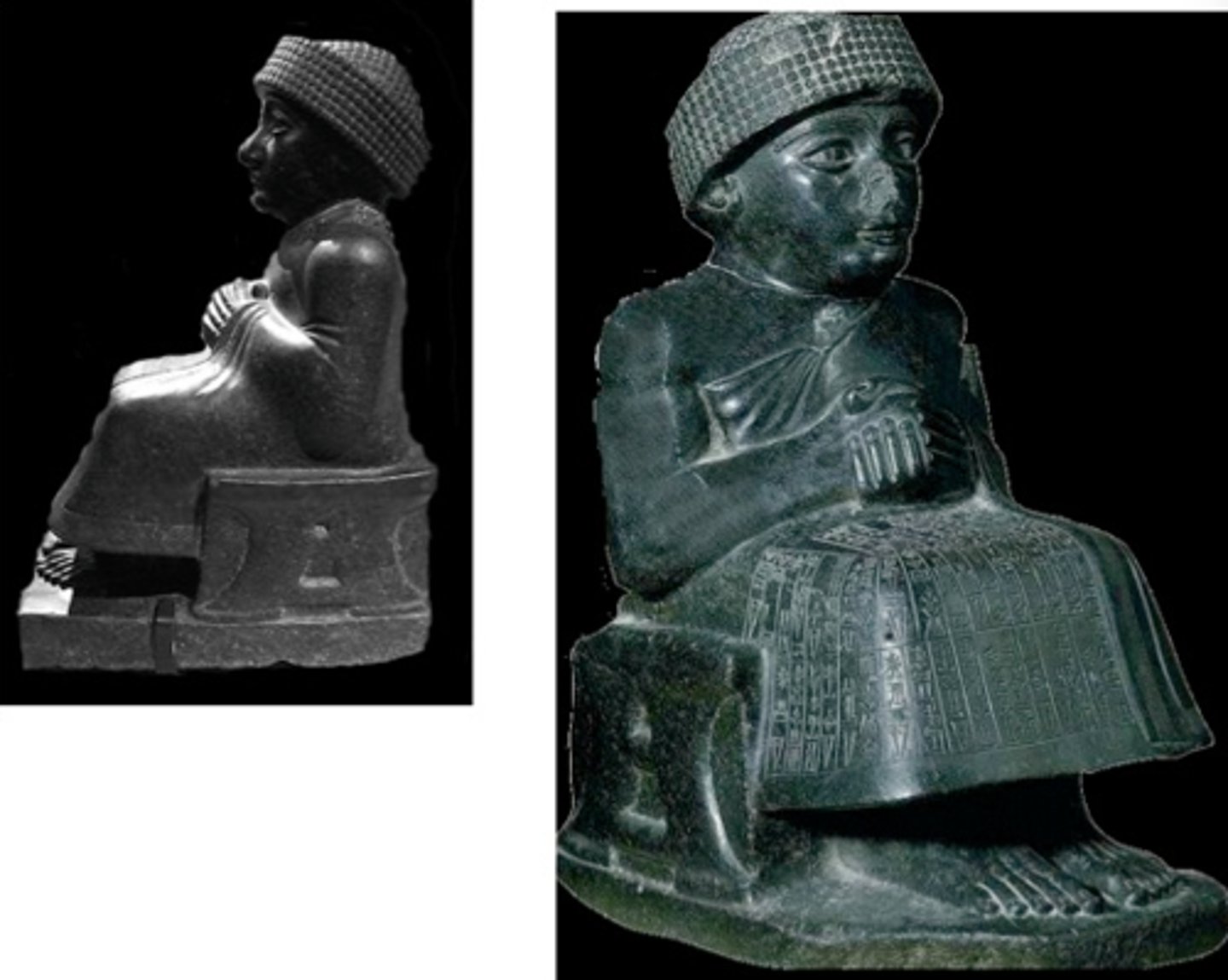
Seated Statue of Gudea, Neo Sumerian, ***c. 2,100 BCE

Stele of King Naram-Sin, Akkadian, ***c. 2,250 BCE
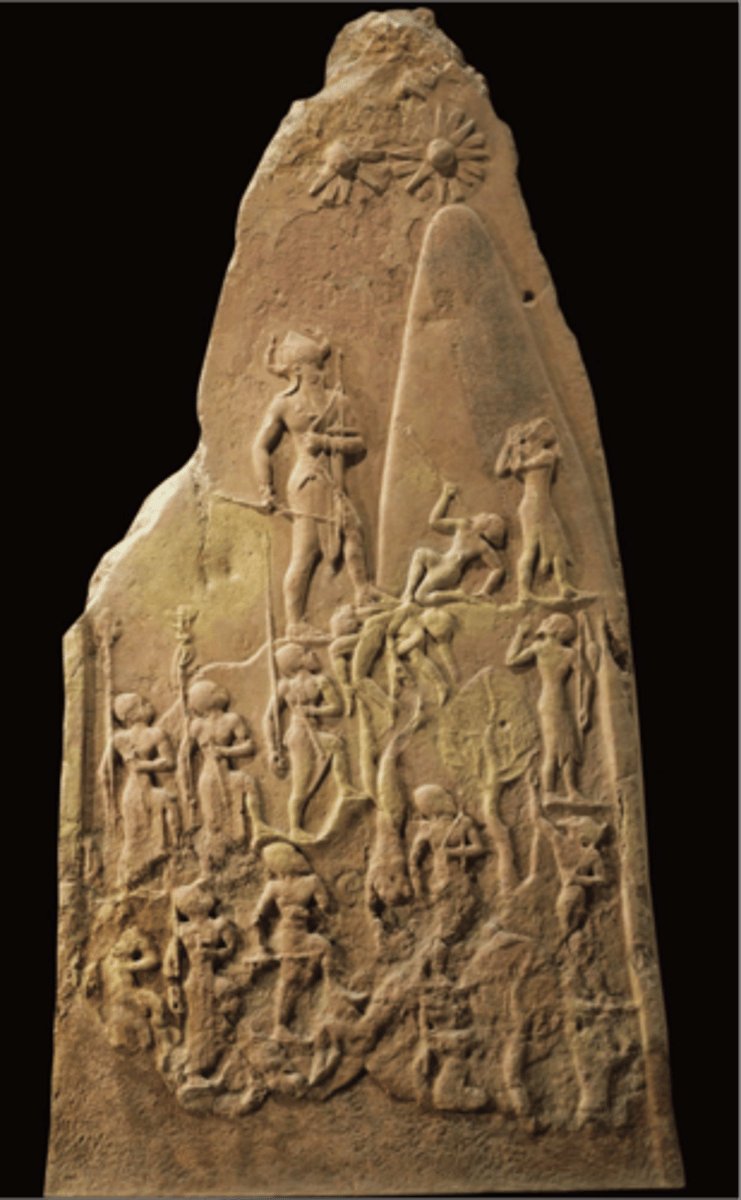

Head of an Akkadian Ruler, Akkadian, ***c. 2,250 BCE
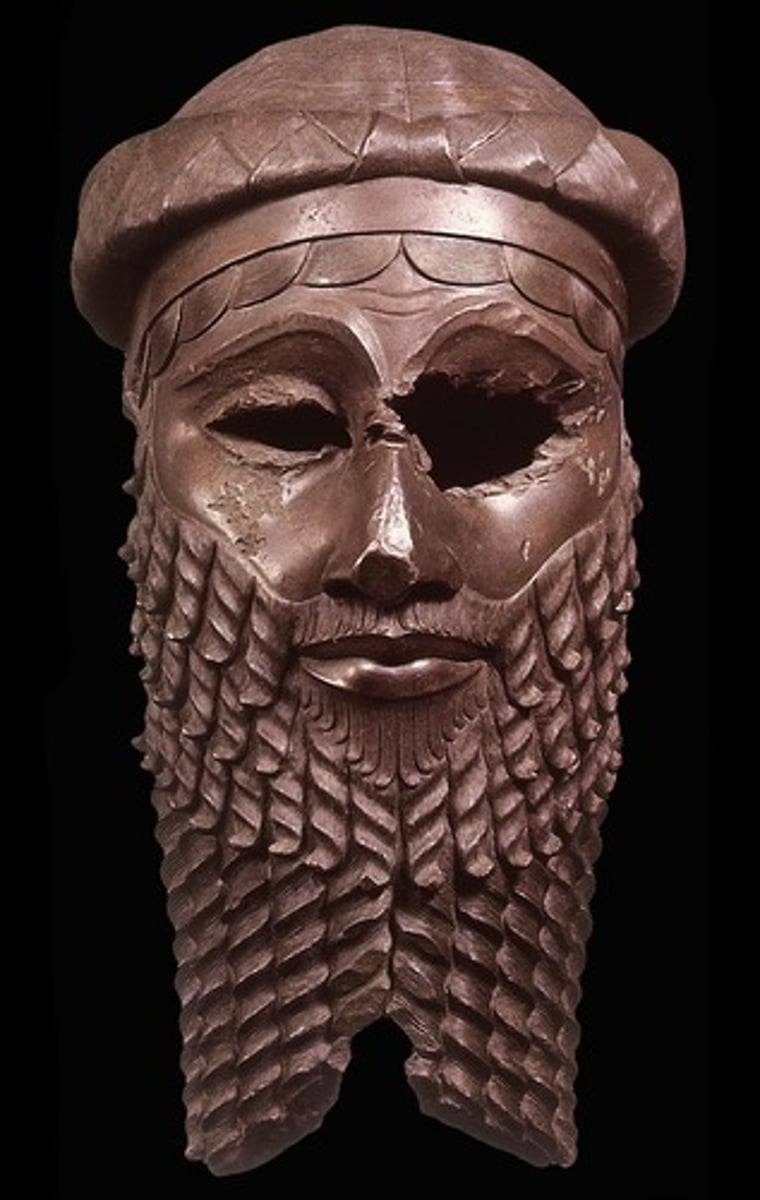

Stele with the Law Code of Hammurabi, Babylonian, ***c. 1,750 BCE

Ishtar Gate, Neo-Babylonian, ***c. 600 BCE

Lamassu from the Palace of King Sargon II, Assyrian, ***c. 850 BCE
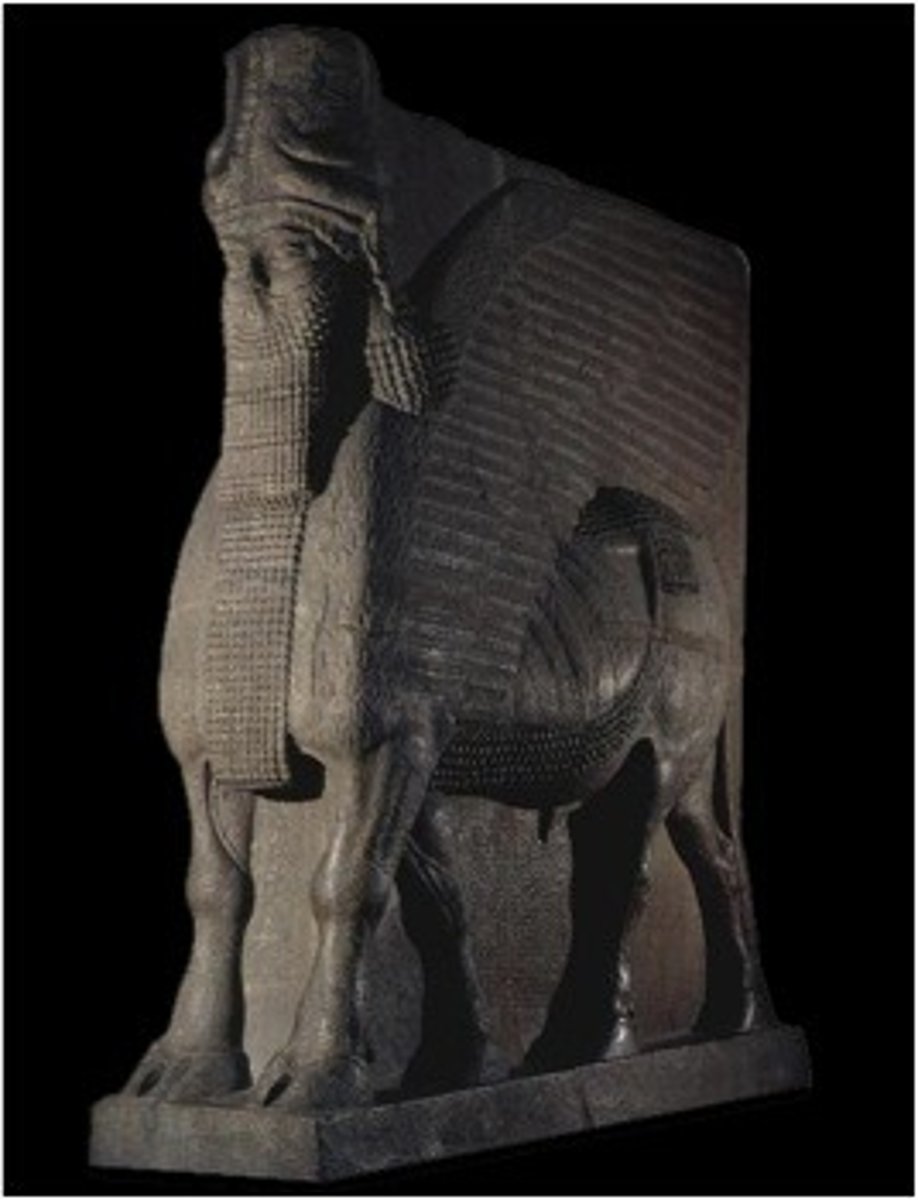

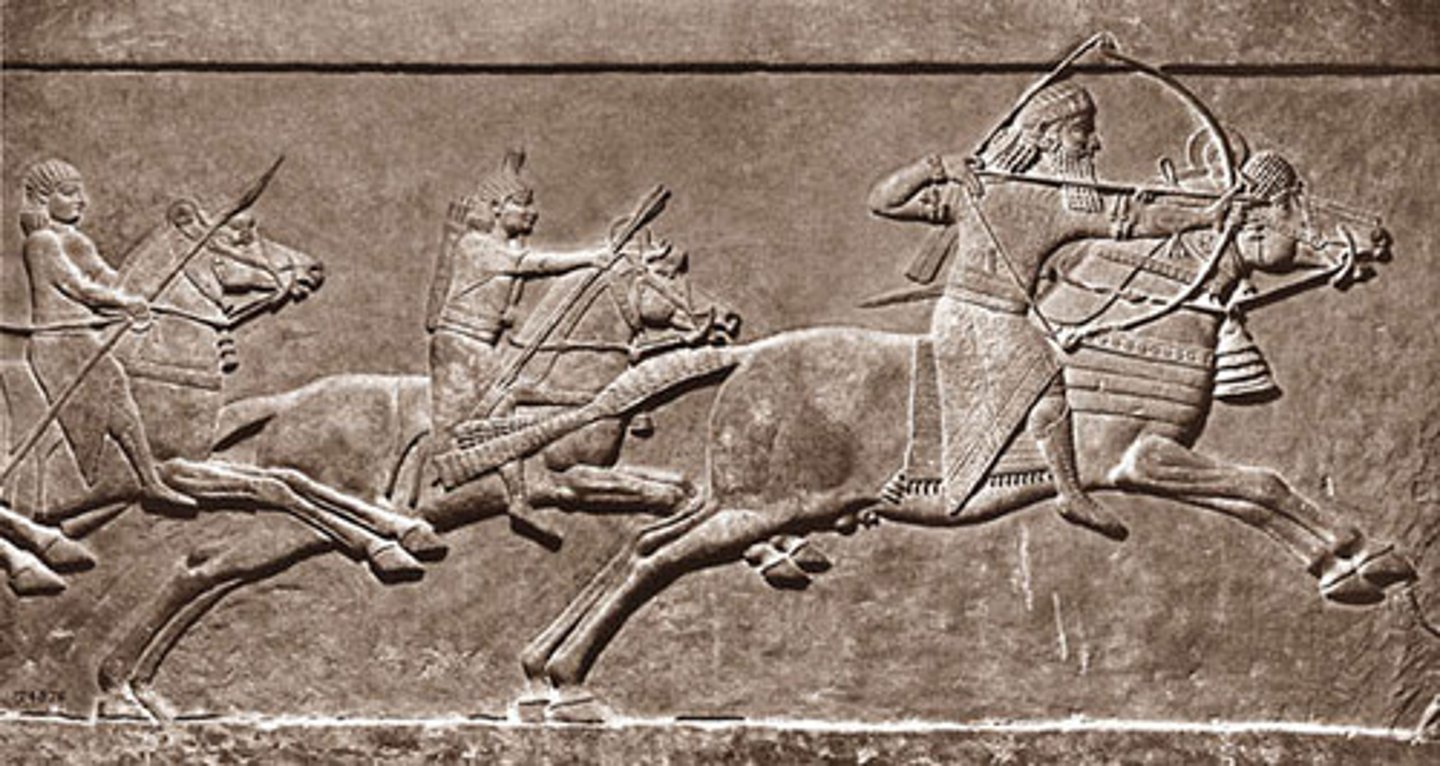
King Ashurnasirpal II Hunting Lions, Assyrian, ***c. 850 BCE

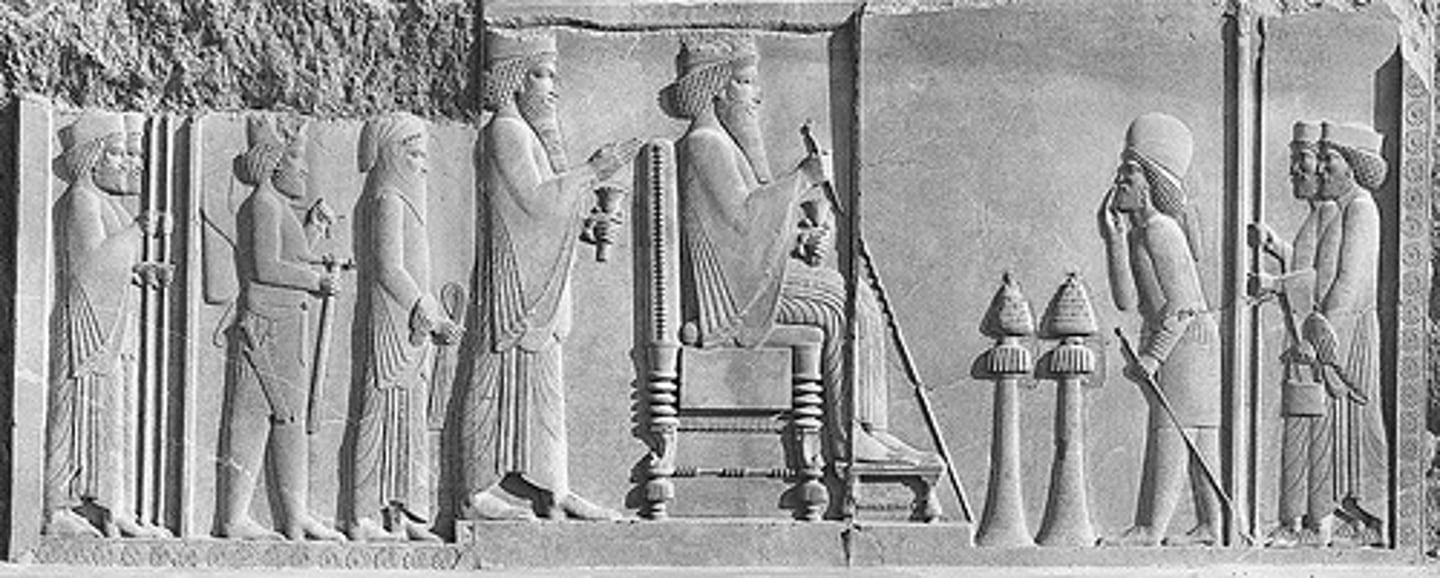
Darius I and Xerxes Receiving Tribute, Persian, ***c. 500 BCE

The Aegean
a center for civilizations which flourished in the 2nd and 3rd millenniums BC
Cycladic
c. 2,500 BCE
Minoan
c. 1,800 BCE
Mycenean
c. 1,500 BCE
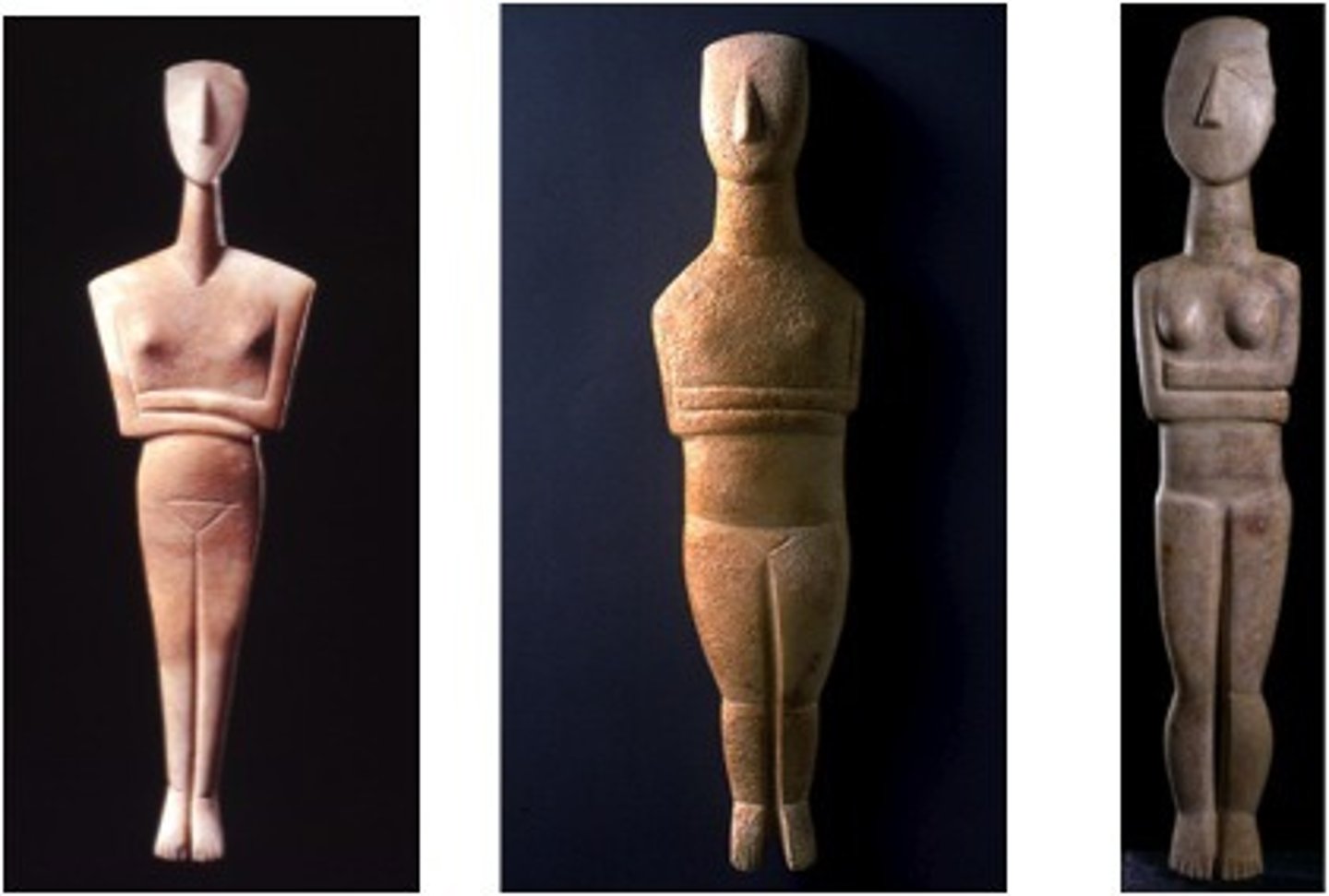
Cycladic Figures, Cycladic, ***2,500 BCE

The Palace Complex at Knossos, Minoan, ***1,800 BCE

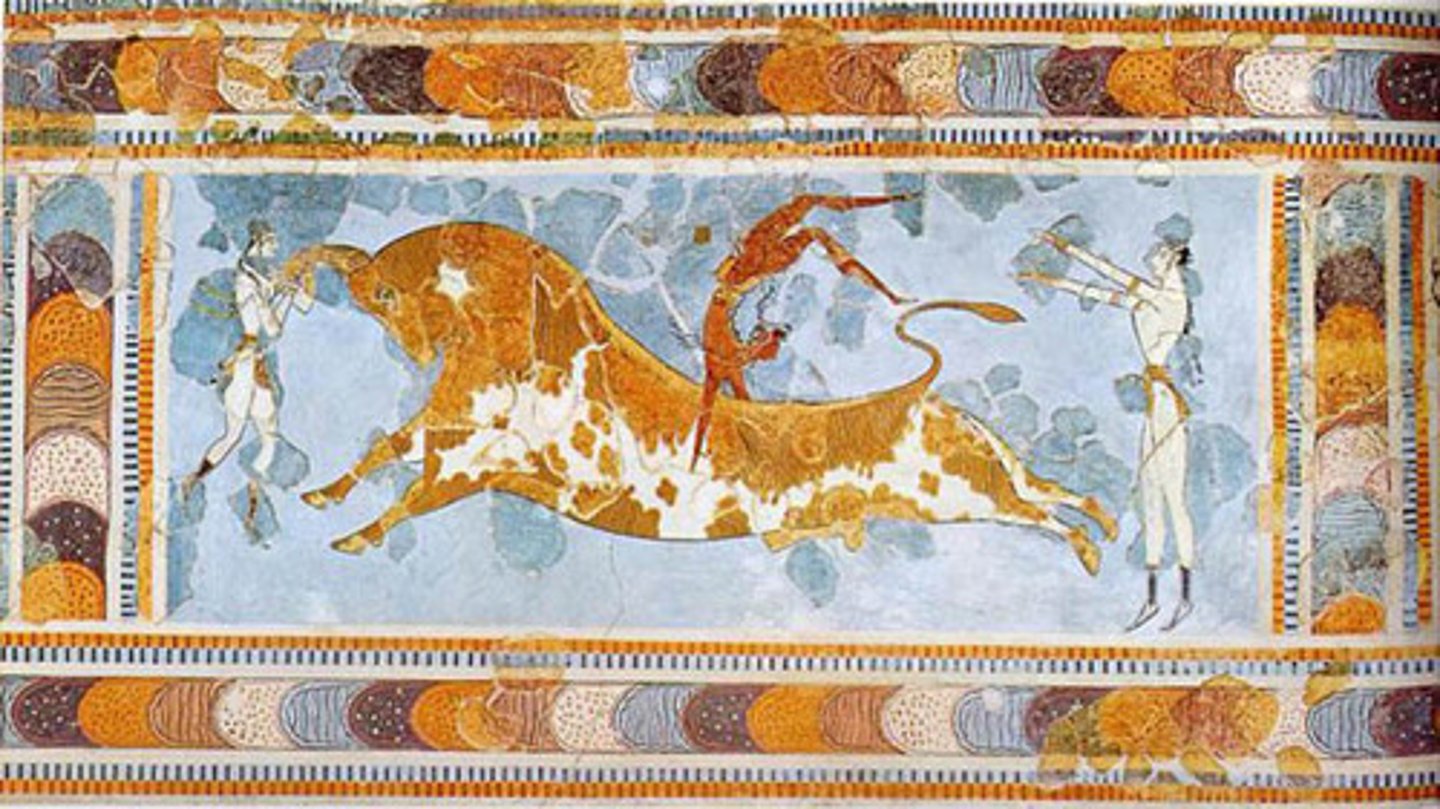
The Toreador Fresco, Minoan, ***c. 1,800 BCE

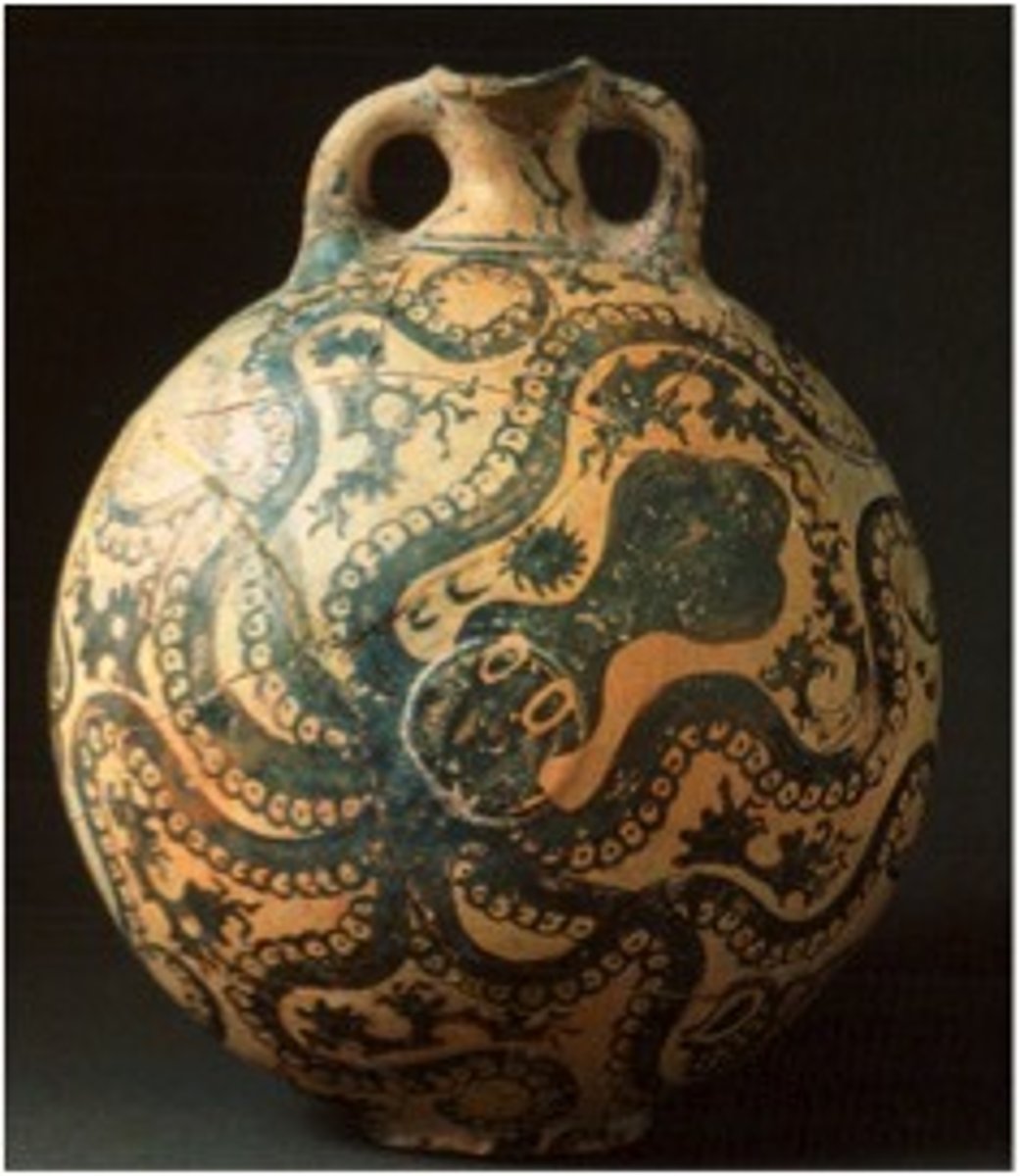
Octopus Vase, Minoan, ***1,800 BCE

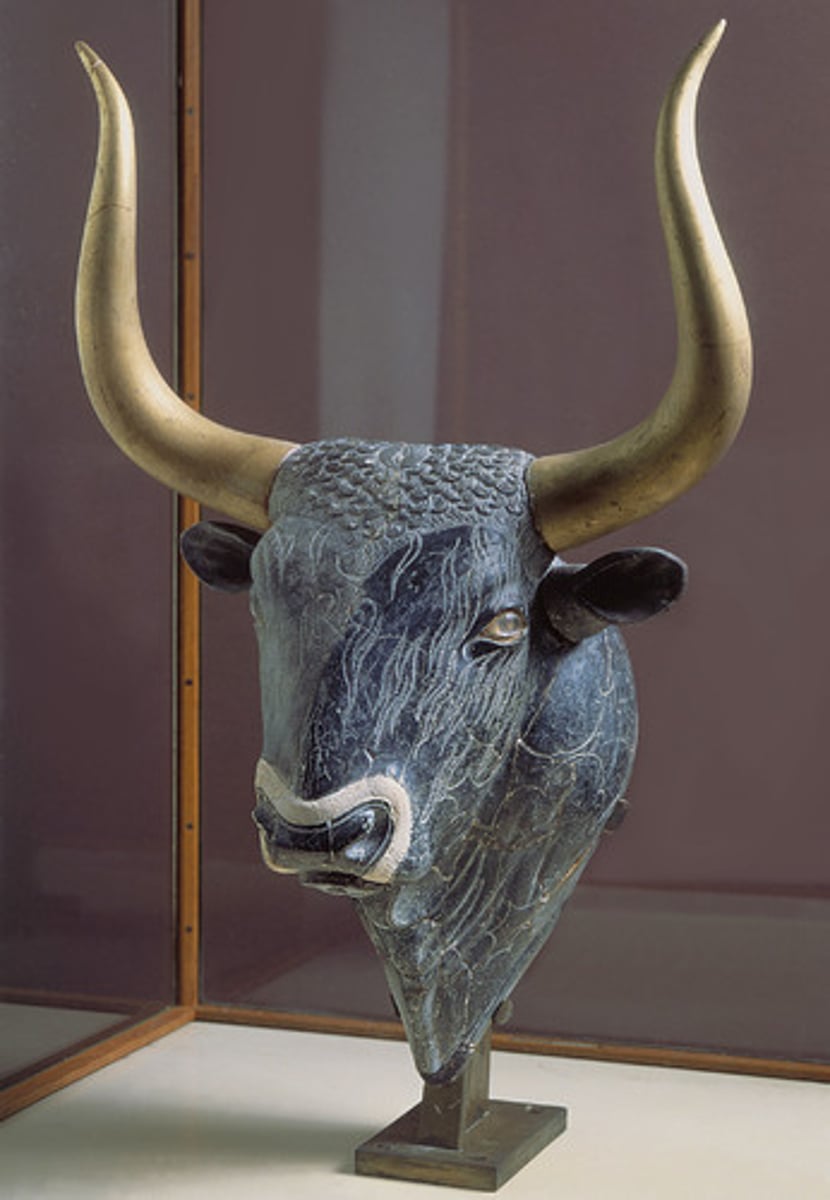
Bull's Head Rhyton, Minoan, ***1,800 BCE

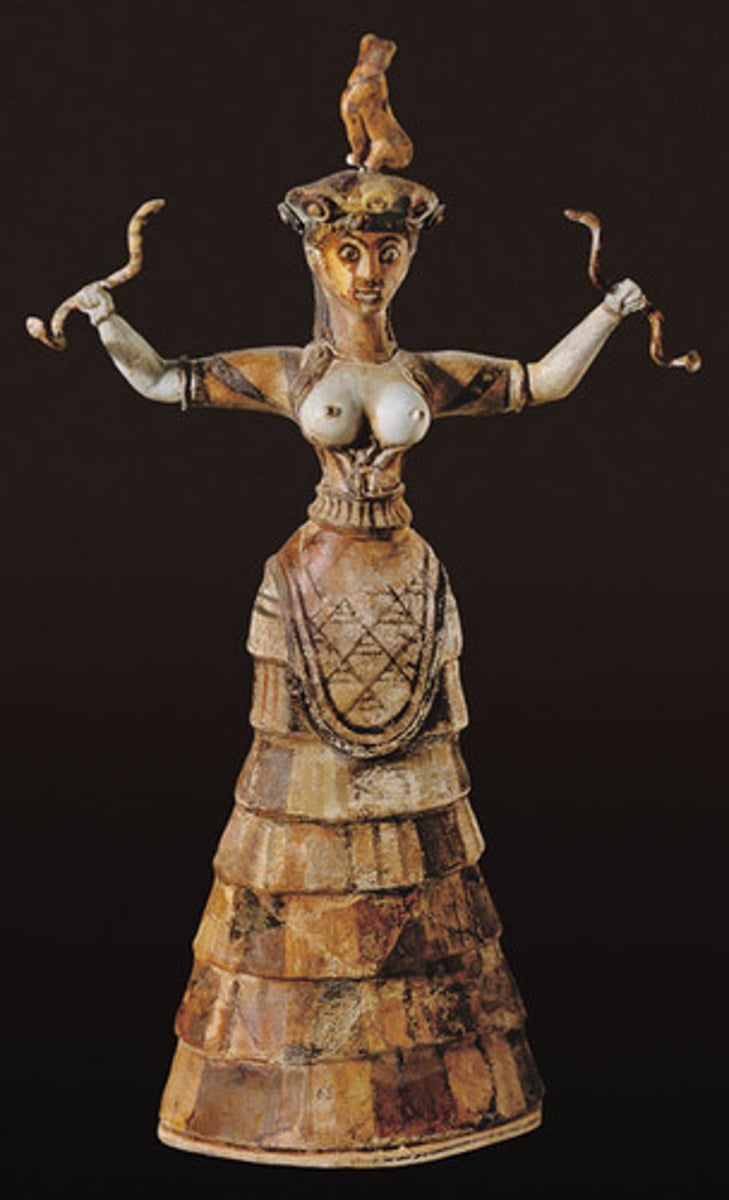
Woman with Snakes, Minoan, ***1,800 BCE

Citadel at Mycenae, Mycenean, ***1,500 BCE
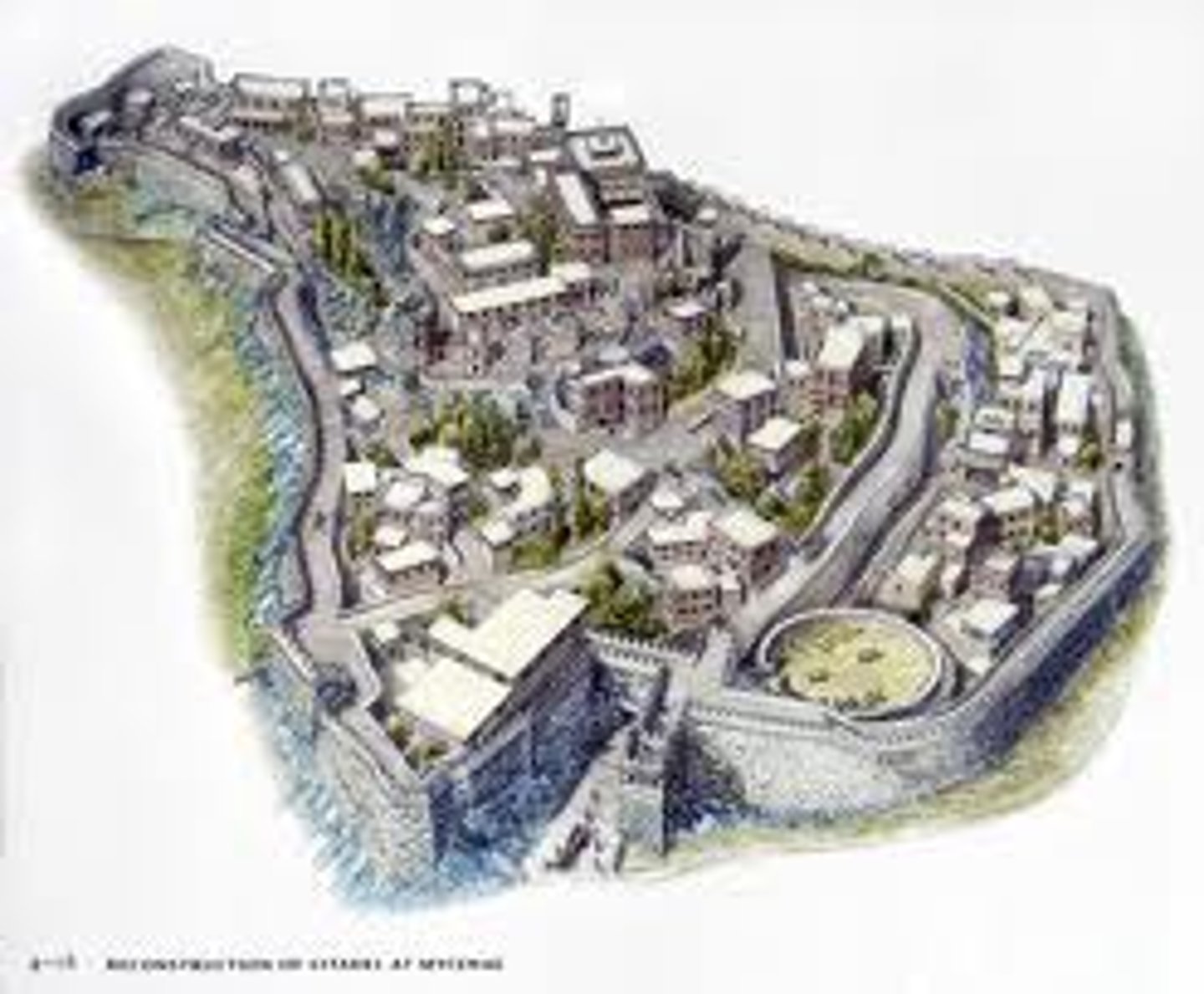
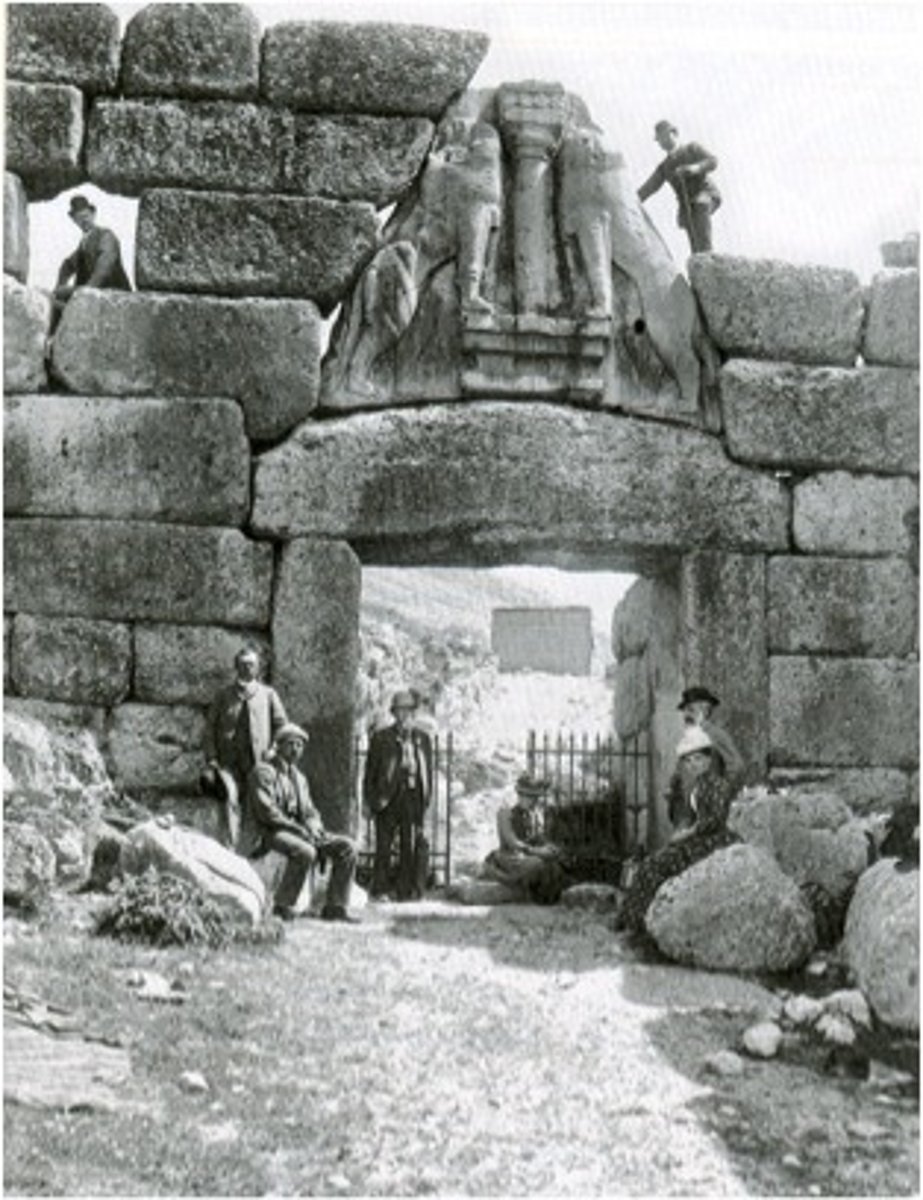
Lion Gate, Mycenean, ***1,500 BCE

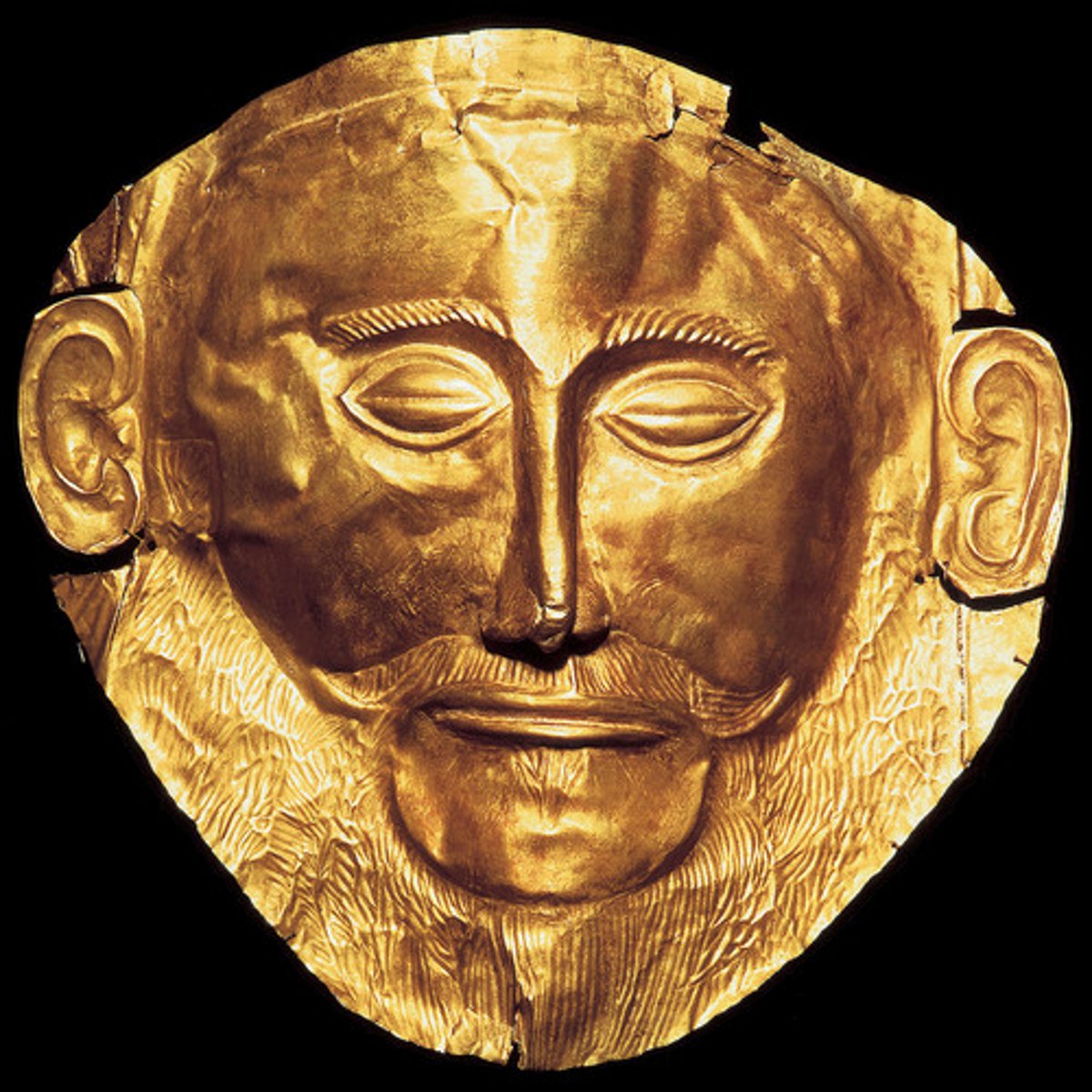
Mask of Agamemnon, Mycenean, ***1,500 BCE

T/F King Akhenaten changed his name (to Akhenaten) in honor of what he believed to be the one true god.
T: King Akhenaten, the heretic king, changed his name (to Akhenaten) in honor of what he believed to be the one true god, a disk-like sun god named Aten. His son (or possibly son-in-law), King Tutankhamen, also changed his name later in life -- he was originally called Tutankhaten. "King Tut" is best known today for the beautiful objects found in his tomb when the British archaeologist Howard Carter discovered it in 1922.
For whom was the first step-pyramid created?
Djoser - Imhotep was the architect - the first architecht whose name is known to history.
For whom was the smallest of the three great pyramids in Giza created?
Mycerinus - The smallest of the three great pyramids was built for Mycerinus, whose pair statue--with his wife/sister--we looked at in class.
This two-foot tall palette illustrates, on two sides, the victory of King Narmer (also known as Menes) over upper and lower Egypt, and thus the first king to unify upper and lower Egypt into one kingdom. Which of the terms below refers to the fact that the bigger the figure, the more important he/she/it was?
hierarchal scale

Who was the heretic king? Under his rule, there was only one god, the Aten, and art became more naturalistic. This greater naturalism is known as the Amarna style, named after the city this king had built during his reign.
Akhenaten - He changed his name from Akhen-amun to Akhen-aten to reflect his worship of the sun disk Aten.
The Mesopotamian Cultures in order -
Sumerian, Akkadian, Babylonian, Assyrian, Persian
Which Mesopotamian culture invented writing?
Sumerian
T/F In comparison to Egypt, where sculptures were based on a cube or grid shape, the Mesopotamians leaned towards more round and cylinder shapes.
T
What are some characteristics of the cave paintings in the Paleolithic era?
- Animals painted largely (most important creatures on Earth at the time )
- painted high up on walls
- naturalistic looking
- earth tones
- painted by memory
- Animals in side profile
- overlapping (no sign of organization because humans had no control over them)
- there was no apparent story
- no sign of vegetation or humans in paintings
What was the main goal of cave paintings?
To capture the spirit of the animal in hopes that some would either emerge from the cage or in hopes to capture the spirit to make it easier for hunting.
What kind of human living society occurred during the Paleolithic era?
Hunter Gatherers
Besides cave paintings, what other kind of art was created in the Paleolithic era?
small statues - made easy for transportation for ever-moving communities (had to move with the food source)
There was a shift in how people ____ during the Neolithic era.
lived - there was architecture created as well as settlement due to the control of food sources (animal domestication)
Pottery was created during the ___ era.
Neolithic
What methods were used to create pottery in the Neolithic era?
Coil and Pinch (used for cooking and storage)
megalithic architecture
Structures which comprised of massive stones during the Neolithic period. Tombs and other important ceremonial structures were built with this style, which required a massive amount of strategic planning and strength.
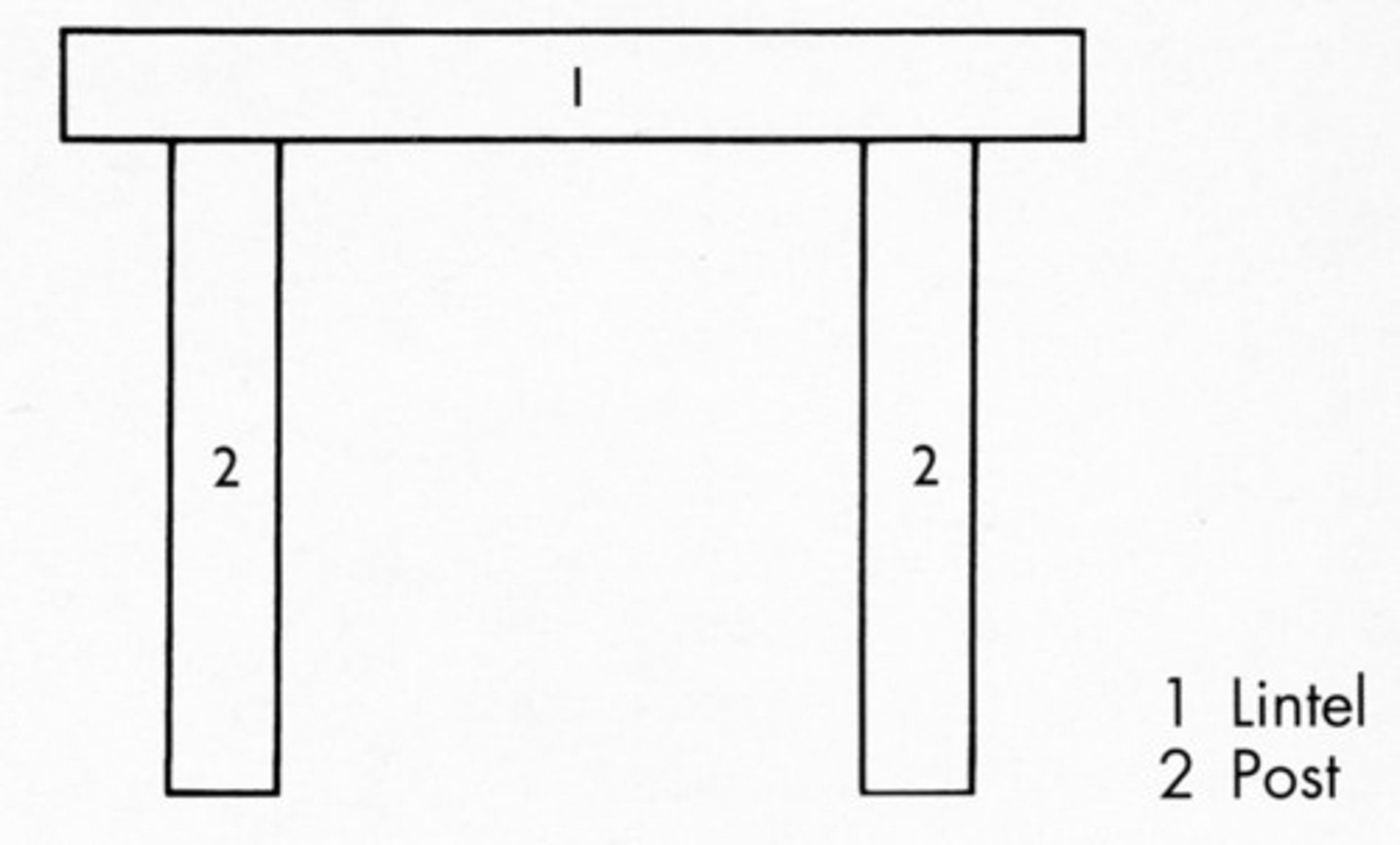
post and lintel construction
Wall construction utilizing a framework of vertical posts and horizontal beams to carry floor and roof loads. (example- Stonehenge)
What does the word henge mean in megalithic architecture?
large circle earthwork - usually dug down
Old Stone Age
Paleolithic Age
New Stone Age
Neolithic Age
Naturalistic
realistic
register
a section or part of the artwork, sometimes found on vases or slabs to tell a story
Substrate
the material onto which the print ink is ultimately applied, such as paper, canvas or cloth
pigment
are used for coloring paint, ink, etc -- animal fat was used to create pigment in the prehistoric times
What was found in 1879?
The first cave painting
corbel construction
A space-spanning technique in which each layer of stone increasingly tapers inward to form an arch or vault.
Altamira, Spain
First cave-paintings discovered here, 1879.
Lascaux, France
In 1940 cave paintings were discovered they showed the lives of early humans
Stonehenge Cursus
a large Neolithic cursus monument on Salisbury plain, near to Stonehenge in Wiltshire, England. It is roughly 3 kilometres long and between 100 metres and 150 metres wide.
Woodhenge
A circular feature demarcated by large upright timbers, probably used by prehistoric groups as astronomical observatories.
Bluehenge
Bluestonehenge or Bluehenge is a prehistoric henge and stone circle monument that was discovered by the Stonehenge Riverside Project about 1 mile south-east of Stonehenge in Wiltshire, England.
Mastaba
an ancient Egyptian mudbrick tomb with a rectangular base and sloping sides and flat roof
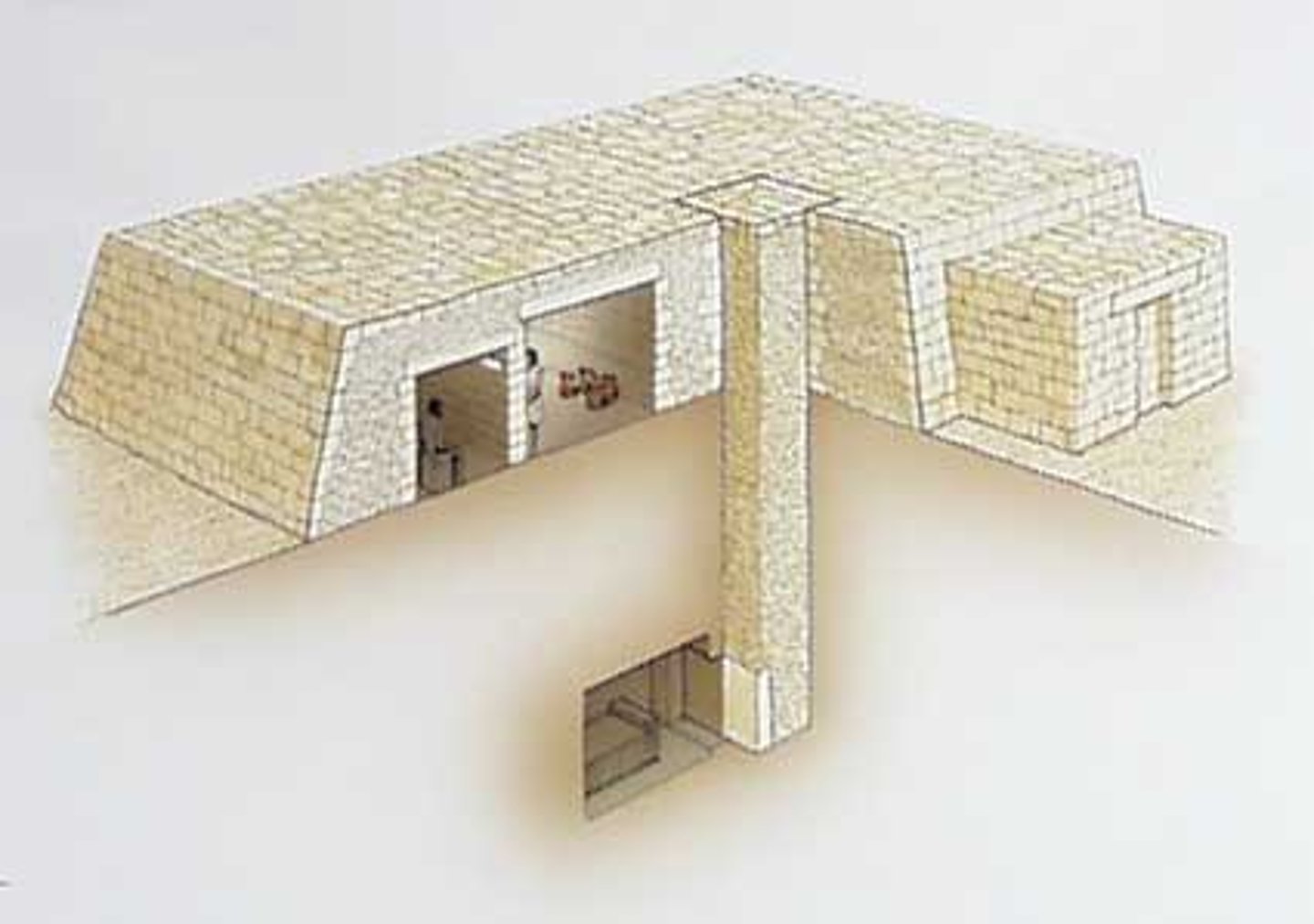

necropolis
a cemetery, especially a large one belonging to an ancient city.
Rosetta Stone, 196 BCE
allows us to translate hieroglyphics to greek and other languages

relief sculpture
sculpture that projects from a flat background
bas-relief
low-relief sculpture
high relief
a carved panel where the figures project with a great deal of depth from the background
sunken relief
a carving in which the outlines of figures are deeply carved into a surface so that the figures seem to project forward, more than 50% of the sculpture is carved out
Stele
A carved stone slab used to mark graves or to commemorate historical events.
Ka
In ancient Egypt, the immortal human life force (soul/spirit)