13 bandaging and bandaging techniques for small animal
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
1. protects wounds/provides wound cleanliness
2. speeds wound healing
3. controls wound environment
4. eliminates dead space
5. immobilizes injured tissue
6. minimizes scar tissue
7. makes patient more comfortable
8. reduces edema and hemorrhage
Name the advantages of bandages
1. may result in limb amputation
2. can kill your patient
(pet owners may want to blame you so you must educate owner)
3. patient discomfort if done incorrectly
4. bacterial colonization of wound
5. ischemic injury because of too much compression
6. damage to healing tissue
7. become GI foreign body obstruction if patient eats bandage
8. patient mutilation of bandage and wound
Name the disadvantages of bandages
Below elbow and stifle, but above and below the affected joint to stabilize them
At what areas will you typically use bandages?
Modified Robert Jones aka Soft Padded
What is the "work horse" of bandages in small animal medicine?
1. Primary contact layer
2. Secondary intermediate layer
3. Tertiary outer layer
Name the 3 basic layers of a Modified Robert Jones Bandage:
1. debrides tissue
2. delivers medication
3. transfers wound exudate
4. forms an occlusive seal
5. minimizes pain
6. prevents excessive loss of body fluids
List the basic functions performed by the primary layer of the Modified Robert Jones bandage:
Tefla or some fenestrated thin plastic for absorbing exudate, breathable
What type of material typically makes up the primary layer of bandages like Modified Robert Jones?
1. absorbs and stores deleterious/toxic agents (like cytokines or bacteria from wound)
2. retards bacterial growth
3. pads wound from trauma
4. splints wound to prevent movement
5. holds primary bandage layer in place
List the basic functions performed by the secondary layer of the Modified Robert Jones bandage:
Secondary layer (this is roll gauze, put on second to roll cotton)
Material like this often makes up what layer of the Modified Robert Jones and other bandages?
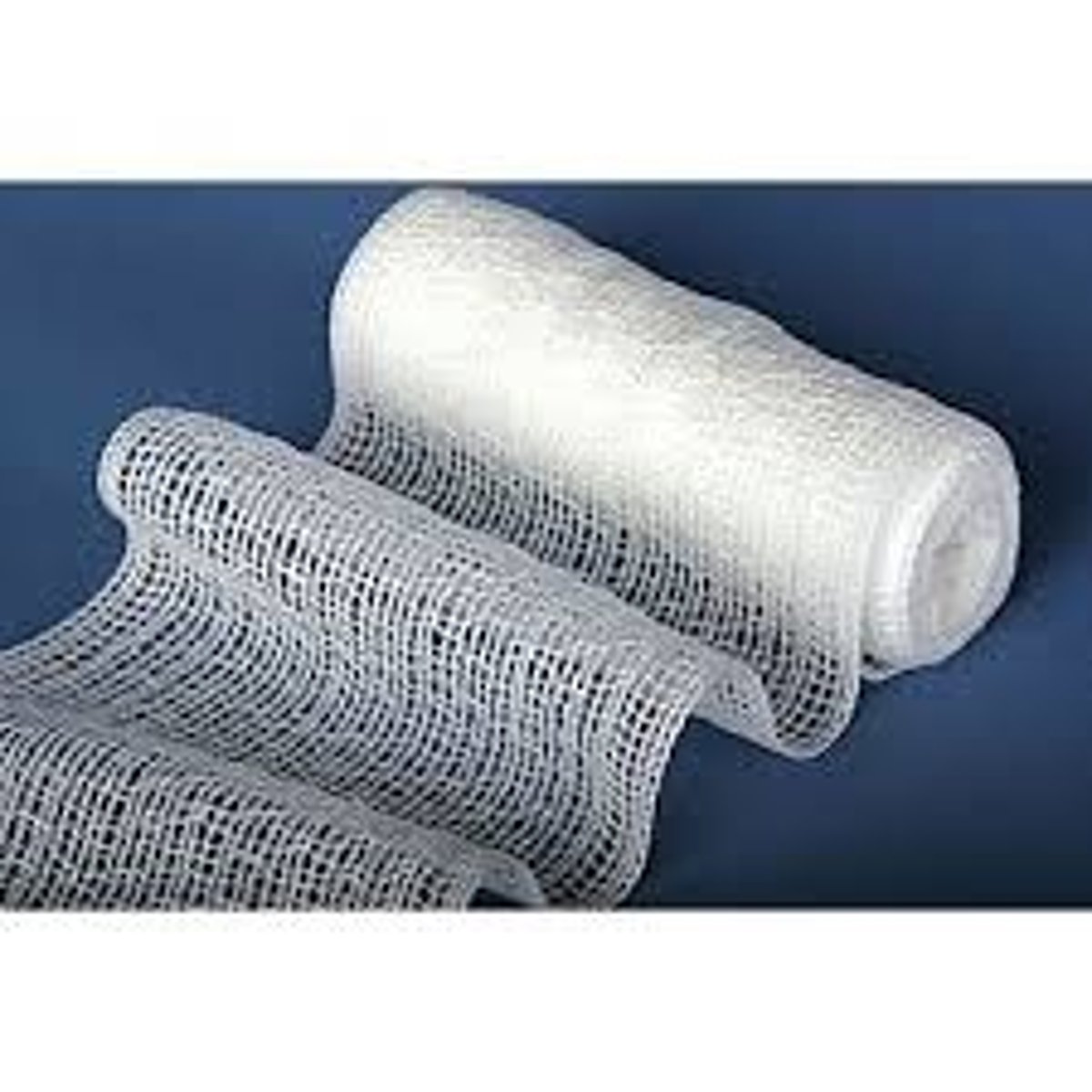

Secondary layer (this is roll cotton, which goes on first followed by roll gauze)
Material like this often makes up what layer of the modified Robert jones and other bandages?
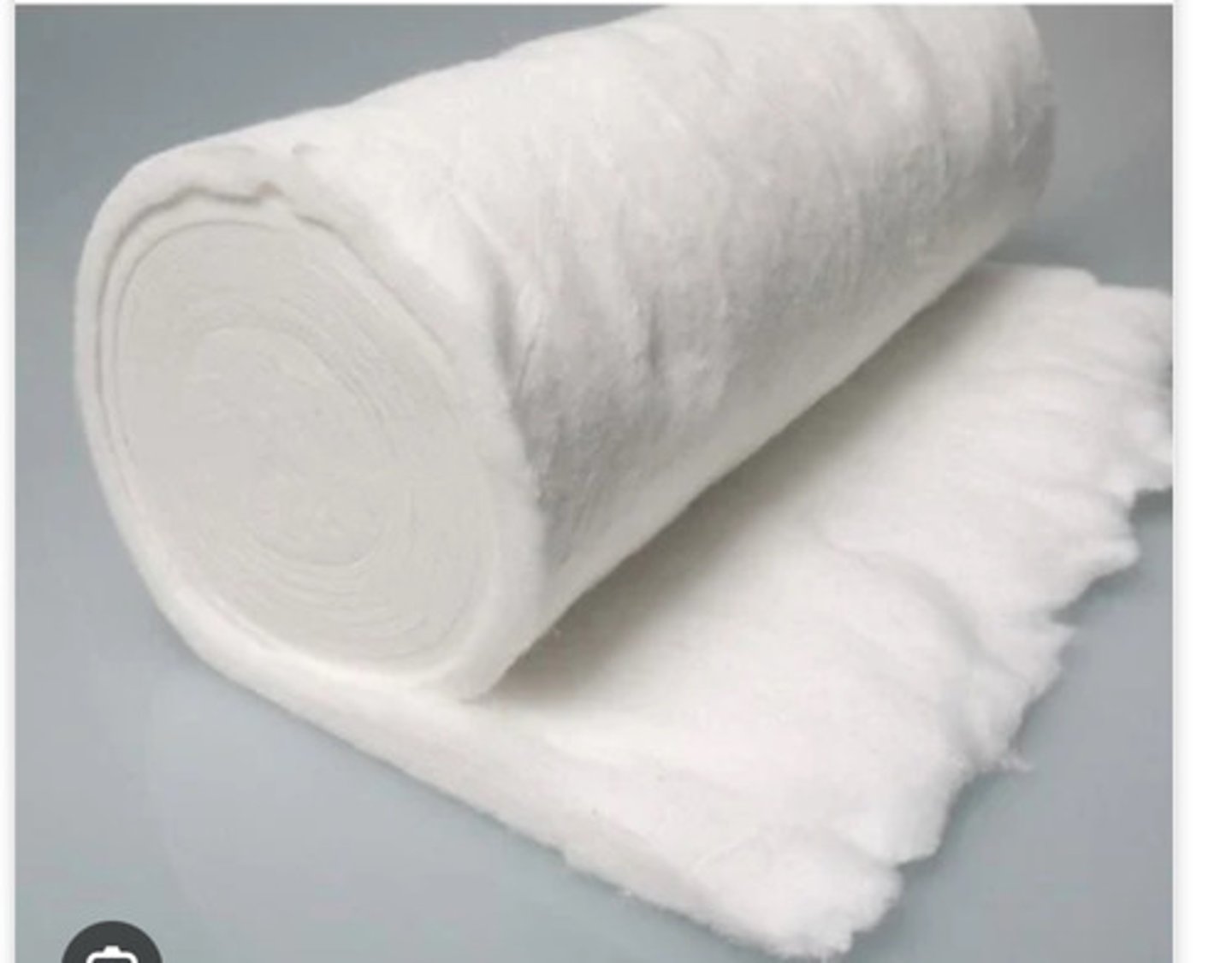

Telfa pad or covering wound
Name the materials which make up the primary layer.
Plain roll gauze (nonstretch and very "holey") OR roll gauze (more elastic and looks more compact) AND roll cotton
Name the materials which make up the secondary layer
1. holds other bandage layers in place
2. protects against external bacterial colonization
3. cosmesis
Name the functions of the tertiary Modified Robert Jones bandage
Vet wrap
What is a common material that makes up the tertiary layer of Modified Robert Jones bandages?

1. adherent
2. nonadherent
3. occlusive
4. semi-occlusive
What are the different types of primary layers?
Adherent
This type of primary layer may be used wet or dry, when wound debridement is required
Nonadherent
This type of primary layer may be used during the repair phase of healing or if there is no necrotic debris, retaining moisture which promotes epithelialization/prevents dehydration, while also draining excess fluids/preventing maceration (further damage to tissue)
Occlusive
This type of primary layer may be used on nonexudative wounds to keep them moist as it is impermeable to air, speeding rate/quality of healing in partial thickness wounds without necrosis or infection
Semi-occlusive
This type of primary layer allows air to penetrate and exudate to escape, which is the MOST COMMONLY USED
Wet-to-wet
When using adherent primary layer bandages, which is the only type recommended in small animal?
1. tape stirrups on distal 1/3 of limb
2. primary layer
3. secondary layer
3. tertiary layer
4. walking pad
5. labels (date, initials, reminders, warnings)
Broadly name the steps for applying a soft padded bandage:
They have sweat glands there = decreases moisture build up
Why is cotton often placed between dog toes in a Modified Robert Jones bandage?
TRUE
TRUE OR FALSE: The primary layer on a Modified Robert Jones bandage is often sterile and wicking.
Start down at the toes and move up
Where on the dogs leg should you start applying the Modified Robert Jones bandage?
Secondary Layer
When casting with a Modified Robert Jones bandage, in what layer should you separate the tape stirrups and rotate them proximally while twisting 180 degrees in order to prevent distal slipping
Tertiary layer
Which layer of the Modified Robert Jones Bandage is the one the client sees?
Wounds in areas inaccessible to standard bandaging techniques
Where should you use Tie-Over bandages?
FALSE: ALL 3 layers are present in tie-over bandages.
TRUE OR FALSE: Only the primary contact layer and secondary absorbent layer are present in Tie-Over bandages due to the difficulty of holding the bandage in place.
Hip, shoulder, axilla, perineum
Name a few areas tie over bandages would be appropriate
Pressure Relief Bandages
This bandage type is typically over bony prominences to prevent pressure sores
Pressure bandages
This bandage type facilitates control of minor hemorrhages, edema, and excessive granulation tissue.
FALSE: The more convex the surface, the MORE pressure exerted by the dressing on the tissue
TRUE OR FALSE: The more convex the surface, the less pressure exerted by the dressing on the tissue.
Dry adherent
Which type of bandage should you use when the wound has a large quantity of low-viscosity exudate that does not aggregate? Wet or Dry adherent bandages?
The fracture must be BELOW elbow or stifle in order to use
What is important to note about where you place Robert Jones and Modified Robert Jones bandages?
Robert Jones is for short term/temporary, emergency stabilization for transport going to another place.
Modified Robert Jones is more long term (several weeks) and adds splint material.
Though the purpose of both is to immobilize, decrease soft tissue swelling, and absorb wound exudate.
What is the difference between Robert Jones and Modified Robert Jones bandages?
To prevent swelling of the distal limb
If you have proximal extremity lesions, why should you continue to bandage up and down the leg?
Digits are covered unlike in leg bandages
What is special about paw bandages?
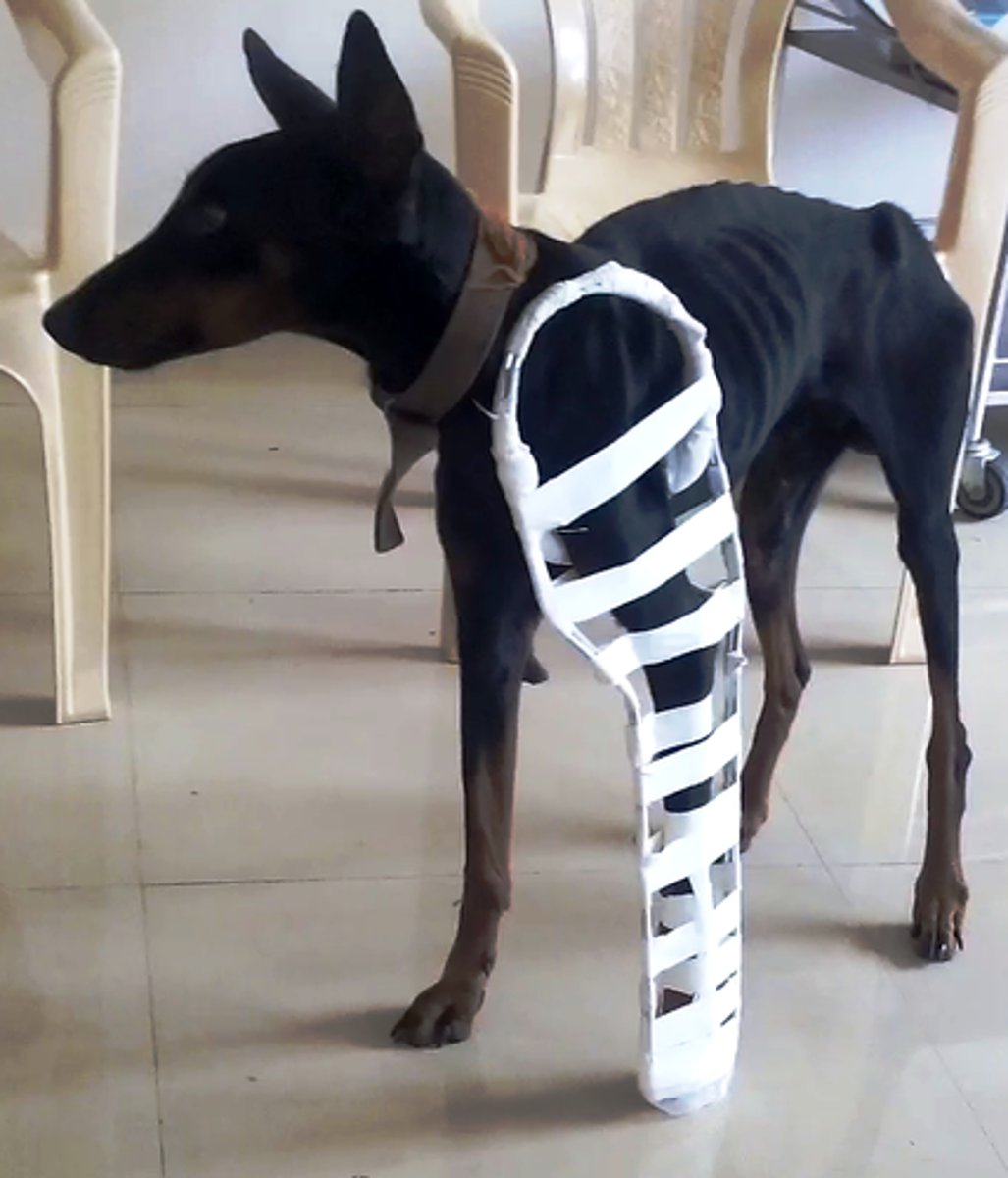
Schroeder Thomas Splint
What is the name of this split which basically only has historical significance?

Spica Splint
What is the name of the splint used to immobilize the shoulder, often to fix lateral shoulder luxation. Problem is patient should be anesthetized as it is very labor intensive
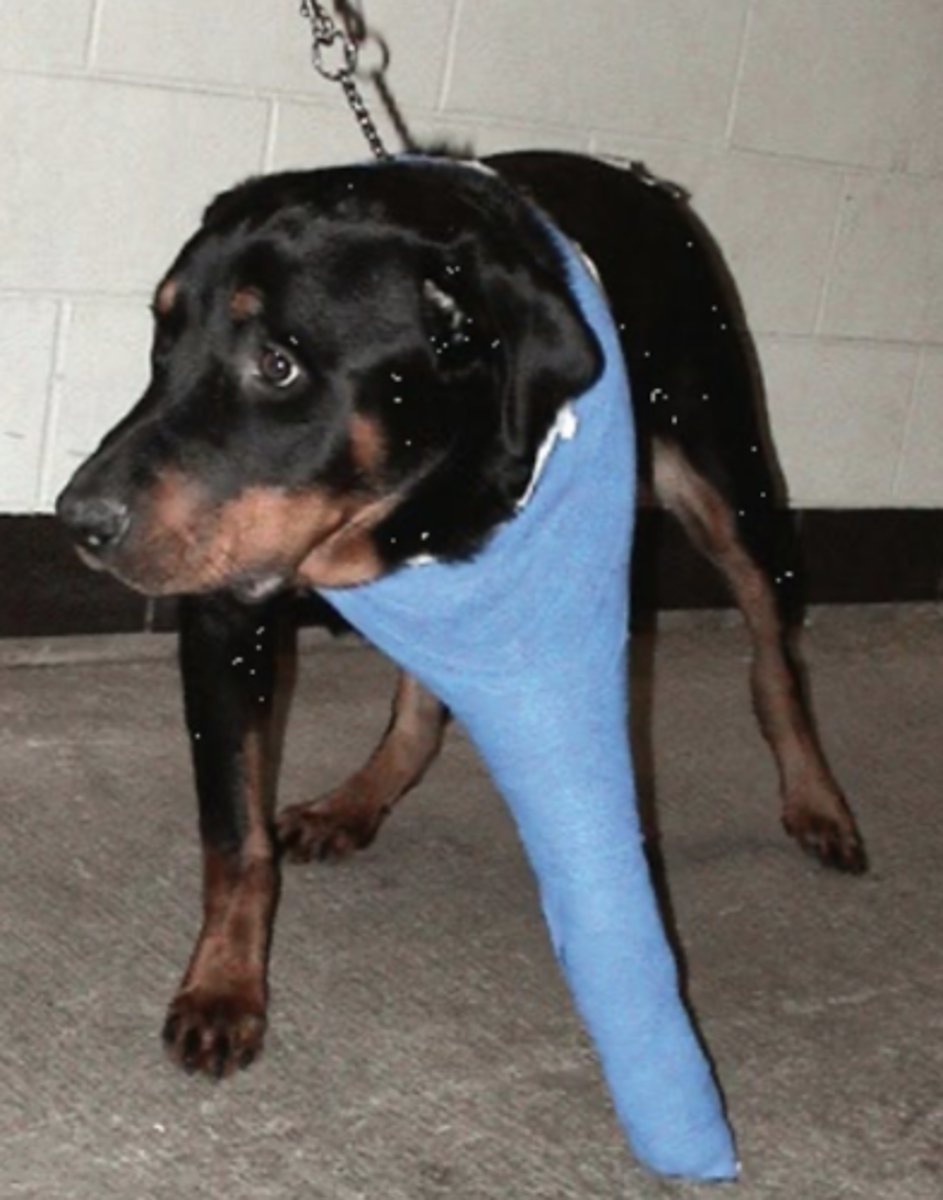
Ehmer Sling ("ehmer femur")
What is the name of the sling used to prevent the pelvic limb from weight bearing, often used post hip reduction or acetabular fractures
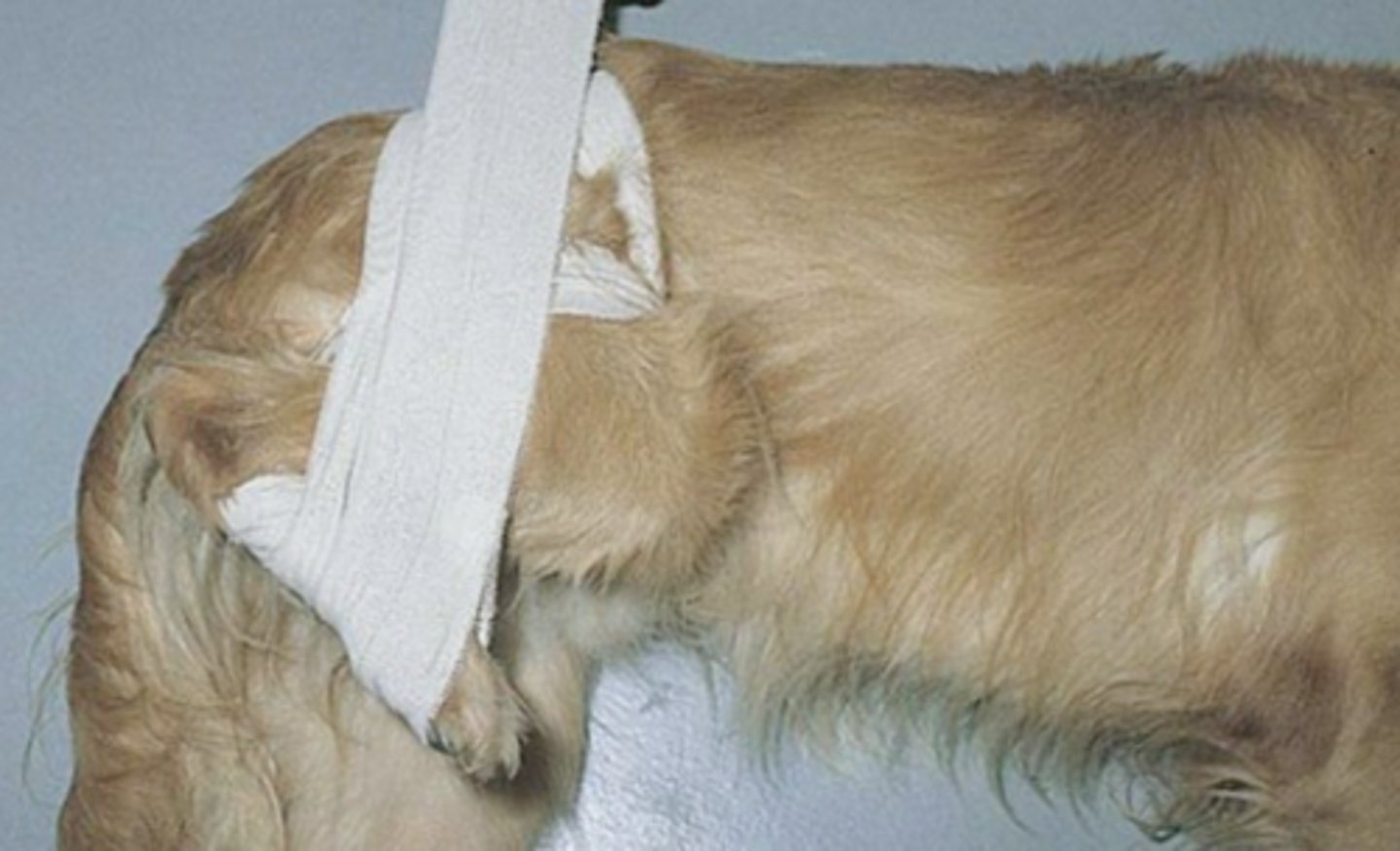
Velpeau Sling ("velpeau elbow")
What is the name of the sling used to prevent forelimb weight bearing after shoulder/forelimb procedures, often medial shoulder luxation?
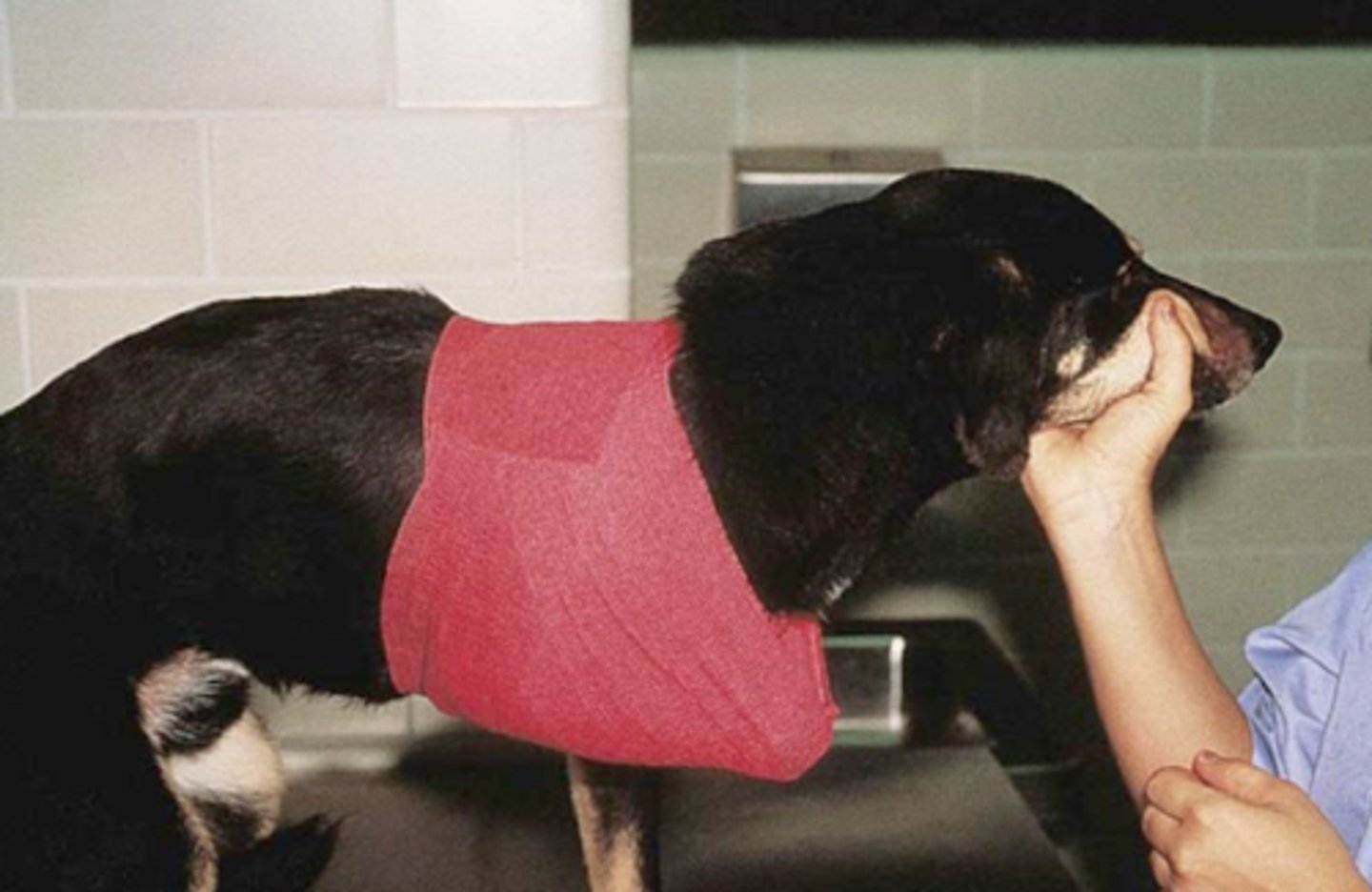
Open fractures
What type of fractures should you NOT CAST?
Distal to elbow/stifle
Only injuries located WHERE can be casted for fracture repair?
Young, rapidly healing animals
In which age of animal do you typically only cast for fractures?
For stable minimally displaced fractures
What types of fractures should you cast?
TRUE
TRUE OR FALSE: You should ALWAYS radiograph after casting in at least 2 views.
Over 50% overlap
To determine successful casting, how much overlap should there be of fracture ends on a radiograph
It encourages use when walking, limits muscle atrophy/stiffness, and shortens recovery
Why should you place a limb cast for fractures in a standing position? (like make the cast to simulate the animal is standing up and not bent or in a laying down position)
At least every 2 weeks
How often should you check on fracture casts?
1. slipping
2. water/urine soaked
3. joint stiffness and muscle atrophy
4. pressure sores
Name some common complications of casting fractures:
More padding = less mobilized
How is padding related to mobilization when casting fractures?
It required a HIGH DEGREE of client compliance, so there should be verbal, written AND visual instructions requiring frequent checking
What is important to note about bandaging in terms of the owner?
1. age
2. activity
3. cleanliness
4. associated wounds
5. swelling
Name the factors that determine how often fracture bandages should be checked and changed?
There is odor and swelling, assess toe temperature and nail bed cyanosis
How do you know when to remove a bandage?
Sometimes get bandage paralysis
What is a special consideration for cats when bandaging?
To avoid swelling
Why do you start bandaging at the toes then go up the limb?
Functional anatomic position AKA PHYSIOLOGIC positions which is typically standing... do NOT apply with limb in full extension or straight
What position should you keep an animals leg in when casting?
1. sedation may be required
2. leave middle 2 toes exposed when possible
3. bandages start at toes then go up to avoid swelling
4. keep limb in physiologic position
5. overlap 1/3 to 1/2 the width of your wrap
6. apply firm even pressure during application (proportional to amount of padding and size of patient)
7. owner compliance is key
8. identify underlying structures (like ear) to prevent iatrogenic injury
9. no single dressing produces optimum microenvironment for all wounds or all stages of wound healing
Name a few rules to remember when bandaging a small animal patient:
FALSE: NO SINGLE DRESSING produces optimum microenvironment for all wounds or all stages of wound healing
TRUE OR FALSE: vet wrap almost always produces the optimum microenvironment for all wounds in all stages of healing
Owner compliance
What is the KEY TO SUCCESS for bandaging?
Prevents iatrogenic injury
Why should you identify and mark underlying structures like the ear when bandaging small animal patients?
Elasticon or coozies
What typically makes up walking pads in a bandage?
Carpal contraction
What is a potential complication that can come from leaving a velpeau sling on for too long?
Femur fractures = DO SURGERY
What should you NOT use ehmer slings for?
Robert Jones (much bulkier and temporary)
What bandage is this?
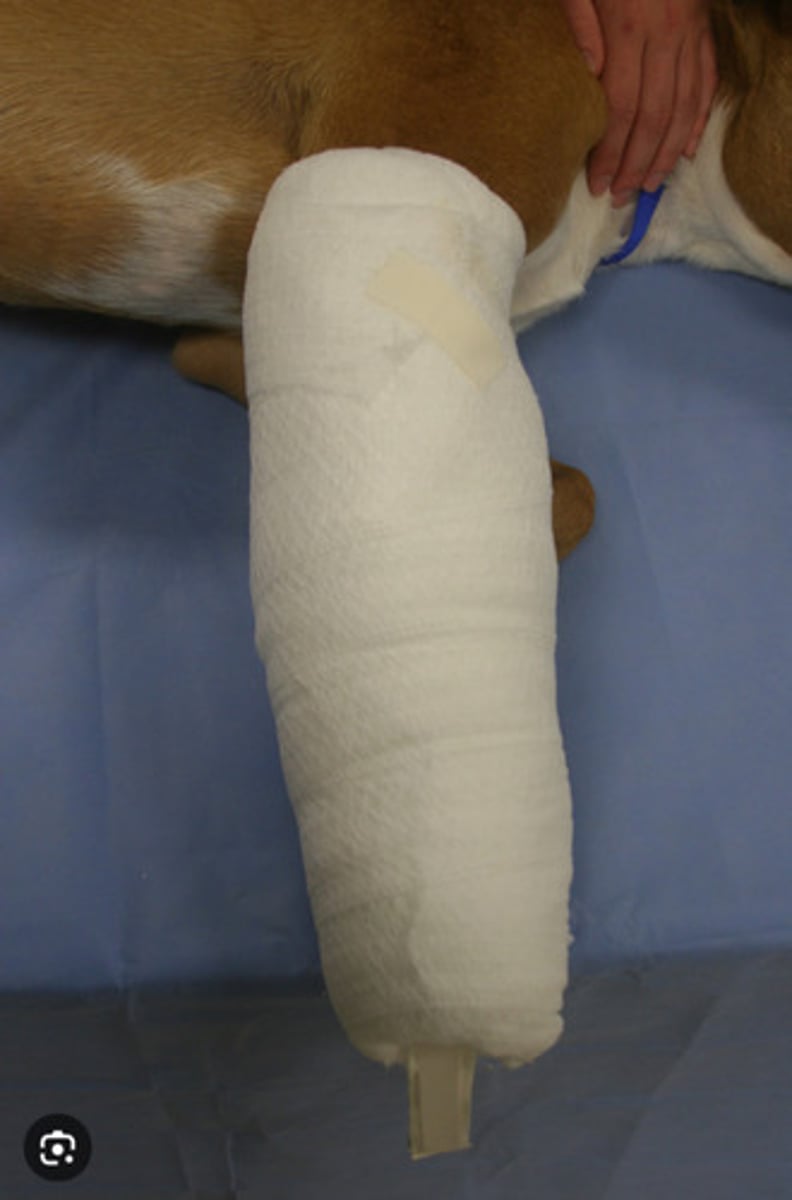
Modified Robert Jones (thinner cotton layer and more permenant)
What bandage is this?
Prevent the bandage from slipping distally, sitting under primary and over secondary layer
What is the purpose of tape stirrups?