𝘢𝘨𝘳𝘪𝘤𝘶𝘭𝘵𝘶𝘳𝘦 𝘶𝘯𝘪𝘵
1/114
Earn XP
Description and Tags
joey the cow only wanted to frolic in the fields...
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
115 Terms
this rev. was because of the advances of the Industrial Revolution
2nd ag. rev.
cause of the 2nd ag. rev. and explain
the enclosure acts: laws from British gov. that enabled landowners to purchase land; introduced private property.
polar climate zone
cold, arid (dry), semi arid climates
warm mid-latitude
warm and humid summers and mild winters
tropical
hot & humid, with substantial precipitation
shift cultivation traits
subsistence
extensive
tropical
rice, corn, etc.
pastoral nomadism traits
subsistence | extensive | drylands | cattle, reindeer, goats, yaks, sheep, horses, camels etc. |
plantation farming traits
commercial | intensive | tropical | coffee, rubber, tea, sugarcane, bananas, tobacco, etc. (sold to richer countries) |
mixed crop/livestock traits
commercial | intensive | cold/warm mid-latitude | corn, soybeans, grain (to feed animals) |
grain farming traits
commercial | extensive | cold mid-latitude | wheat, corn, barley, etc. |
market gardening traits
commercial | intensive | warm mid-latitude | fruits and vegetables |
dairy farming traits
commercial | intensive | warm and cold mid-latitude | milk |
mediterranean agriculture traits
commercial | intensive | warm mid-latitude | figs, olives, grapes, etc. |
livestock ranching traits
commercial | extensive | drylands | cows, sheep, goats, bison, alpaca, emus, etc. |

clustered settlement

linear settlement

dispersed settlment

metes & bounds

township & range

long lot
long lot explanation
by the French, taxes based on width of land so it became long and thin
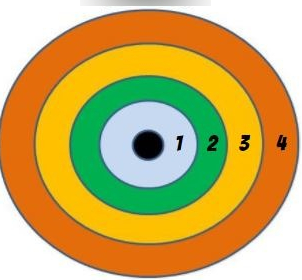
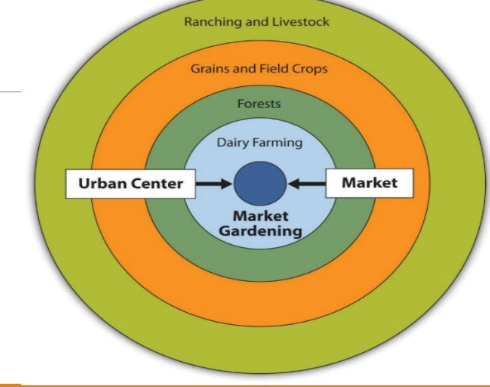
what does von thunens model of agriculture use show? (2)
closest to farthest from Market
transportation costs were proportional to the distance from the market
assumptions of von thunen model
a city is an isolated region which all agricultural products are sold at a central market
markets are in the middle of plains that are flat and featureless and within which all land has similar characteristics
farmers are rational economic producers (want to make much money as possible)
dairy and market farming in von thunens model is…
horticulture. perishable
explain all rings of von thunen model
dairy & market farming are horticulture
perishable items; therefore near market
forests bec. of wood.
close to market bec. they’re difficult to transport
grain & field crops don’t spoil, so they’re further away.
lots of landdairy
ranching & livestock furthest bec. they could walk there. requires lots of land
sustainable agriculture
urban farming
better access to education and employment
incrased foreign aid
increased access to credit
population control
female empowerment
solutions for food insecurity
↑ women working outside =
↓ female involvement in food prep
female owned farms tend to…
be more smaller, more diversified, less mechanized. agriculture has gender inequality, less women are in agriculture, which correlates to world hunger
fallow
natural vegetation and nutrients returning after shift-burning.