BIO112 Intro to the Oceans
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
How do oceans influence the planet
70% Earth's surface covered in water
Extensive biomass of photosynthetic organisms
Regulates climate/atmosphere (heat/carbon store)
What is the importance of the oceans to humanity
- fisheries
- aquaculture
- global trade
- energy potential
Examples of biological advances from the marine realm
- developmental biology = molluscs
- immune system = sea anemones
- fertilisation = sea urchin eggs
- neuroscience
Is there only one ocean?
it's all connected but not homogenous
What is the geological distinction between ocean and continents?
continental crust
- granite
- lower density
- thicker
- can be geologically old
- light colour
- felsic (Na, K, Ca, Al)
oceanic crust
- basalt
- higher density
- thinner
- geologically young
- dark colour
- mafic (Fe, Mg)
Crust
oceanic and continental
Lithosphere
crust and uppermost mantle
tectonic plates
Athenosphere
upper mantle below the lithosphere
weak, allows plates to move
Who proposed uniformitarianism?
Charles Lyell
What is uniformitarianism?
Belief that Earth's geology shaped by gradual processes operating at the same intensity for millions of years
What did Alfred Wagner propose?
theory of continental drift
Pangea!
Continental drift
a series of large tectonic plates moving - involves the entire surface of the earth
What was proposed about tectonic plate theory in 1965
Sea-floor spreading
How can the reversals of the Earth's magnetic field be observed in the sea floor?
magnetic polarity at the time of cooling can be observed in magma in the sea floor
Sea floor spreading
a geologic process in which tectonic plates—large slabs of
Earth's lithosphere—split apart from each other
Where does seafloor spreading occur
at divergent plate boundaries
divergent plate boundary
Boundary between tectonic plates in which the two plates move away from each other, and new crust is created between them
What causes seafloor spreading?
mantle convection
mantle convection
the slow, churning motion of Earth's mantle
convection currents carry heat from the lower mantle and core to the lithosphere
tectonic plates
sections of the lithosphere that move
subduction zone
where 2 plates meet and 1 is subducted under the other
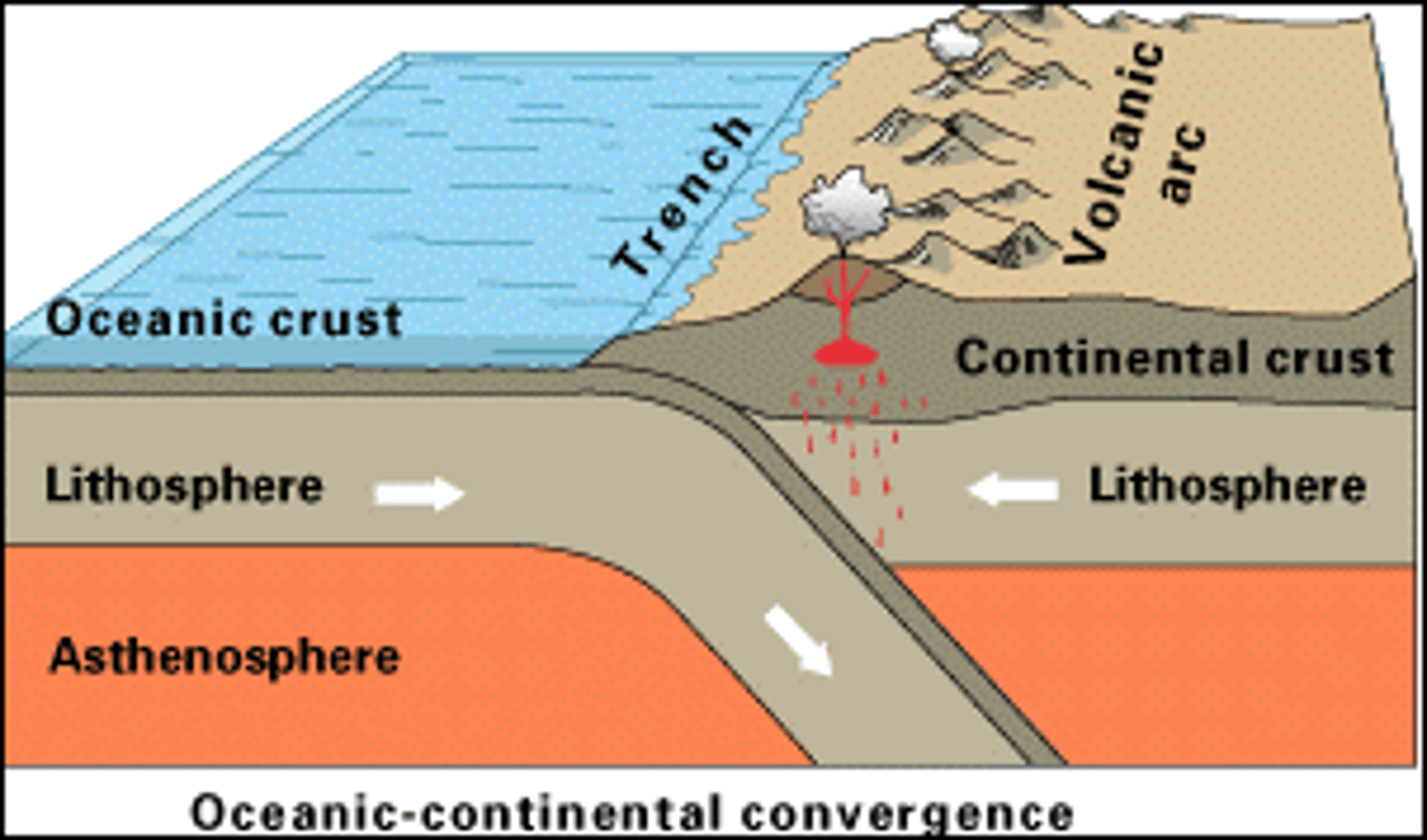
When an oceanic plate meets a continental plate, which will be subducted?
the oceanic plate always
shear boundary
two plates slide past each other creating extreme friction
what do shear boundaries cause
earthquakes
immense friction prevents them moving smoothly so they lock up until stress builds up and they break free
continental margin
a boundary between continental crust and oceanic crust
continental shelf definition
the shallowest part of the continental margin
very gently sloping continental crust
ends at the shelf break
continental shelf features
varying width
~8 % of ocean area
biologically richest part of the ocean
continental slope
the steep slope between the outer edge of the continental shelf and the deep ocean floor
submarine canyon
begin at continental shelf and cut across continental slope to its base
channel sediments to the deep sea
continental rise
thick layer of sediment piled up on the sea floor
from submarine canyons and currents
deep-sea fans
a deposit of sediment from submarine canyons
active margin
a continental margin that coincides with a plate boundary
steep continental slope and a trench
passive margin
a continental margin that is not a plate boundary
gentle continental slope and a continental rise
Abyssal plain definition
deep ocean floor
Abyssal plain features
supports a variety of life
relatively flat
BUT has:
- submarine channels
- low abyssal hills
- plateaus
- rises
- seamounts
- volcanic islands
How many ocean basins are there?
4
What are the ocean basins?
Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Arctic
What is the Southern ocean?
a continuous body of water that surrounds Antarctica