D1- SPI, Basic Math and Sound wave
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
speed of sound in tissue
1540 m/sec OR 1.54 mm/microsec
~ 1 mile per sec
Distance Formula
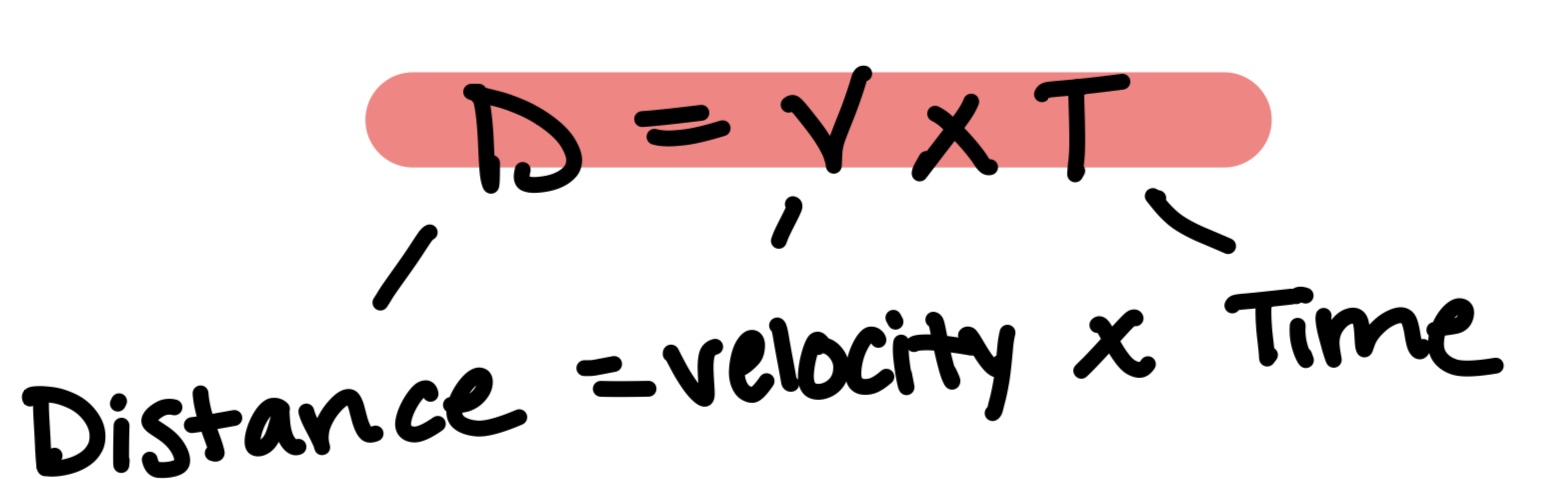
Sound
(1) is a mechanical wave (bc it has to travel through a medium)
(2) has to travel through a medium (tissue)
(3) travels in longitudinal waves/straight line
(4) is a pressure wave: when traveling through a medium, there are areas of compression and rarefaction
compression- ↑ pressure and density (SQUEEZED)
rarefactions- ↓ pressure and density (STRETCHED)
*can’t travel through a vacuum
Mechanical Waves
Longitudinal Wave- waves move ← to → and particles move PARALLEL to the direction of the wave
Transverse- waves move ← to → and particles move PERPENDICULAR to the direction of the wave (↑↓)
Sound Wave Interaction
In Phase Waves- peaks and troughs occur at the same time and location
Out of Phase Waves- peaks and troughs occur at different times and locations
Huygen’s Principle
states that when waves interact, secondary spherical wavelets are created having the same freq. as original wavelets. these wavelets interfere with each other, combining to create the hourglass shape of the beam
Soundwave Interference
Constructive- interference of in-phase waves creates a single wave that has an amplitude greater than its components
Destructive- interference of out-of-phase waves creates a single wave with an amplitude lesser than one of its components
Complete Destructive Interference- when 2 out-of-phase waves have equal amplitude
Acoustic Variables
changes that occur IN THE MEDIUM as a result of sound traveling through the medium
4 forms of acoustic variables
(1) Pressure
(2) Density
(3) Distance (particle motion)
(4) Temperature
(1) Pressure
concentration of force in an area
UNIT: Pascals (Pa)
Pressure = Force/Unit Area
varies cyclically as sound wave propagates through the medium
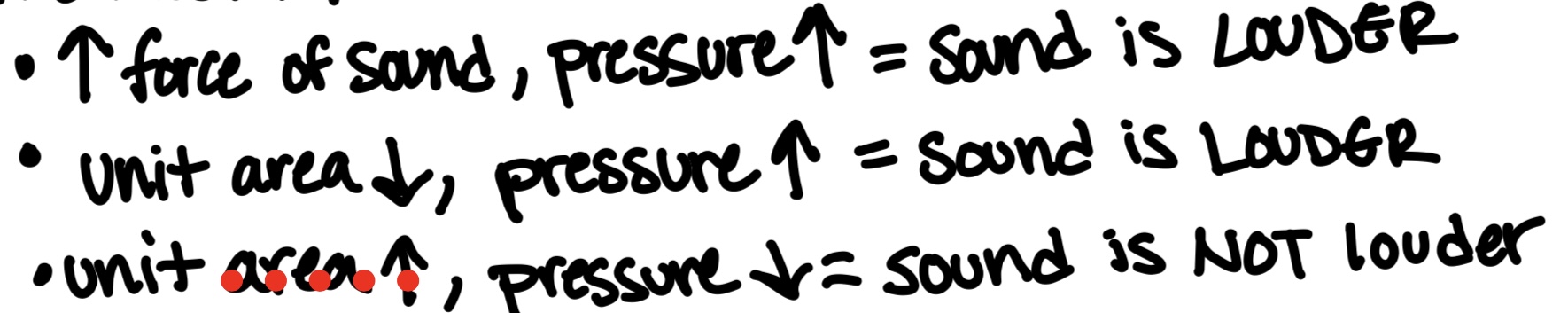
(2) Density
concentration of mass in volume
UNIT: kg/cm³
as mass ↑, density ↑
Compression Phase- higher particle concentration (↑ density)
Rarefaction Phase- lower particle concentration (↓ density)
(3) Distance (particle motion)
measure of particle motion
UNIT: cm, ft, mile
(4) Temperature
sound wave vibrates particles in medium —> friction generates heat
UNIT: degrees Celsius
Compression Phase- ↑ temp
Rarefaction Phase- ↓ density
Sound Wave Parameters
describes FEATURES of a sound wave
(1) Frequency
(2) Period
(3) Wavelength
(4) Propagation Velocity (speed of sound)
(5) Amplitude
Intensity
Power
(1) Frequency
(2) Period
(3) Wavelength
(4) Propagation Velocity (speed of sound)
(5) Amplitude