3.01. Border Gateway Protocol 101
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
What is BGP?
BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) is a routing protocol used to exchange routing and reachability information between Autonomous Systems (AS).
Why is BGP important in AWS?
It is used in services like AWS Direct Connect and dynamic VPNs to manage routing between on-premises networks and AWS.
What is an Autonomous System (AS)?
A self-managed network or group of routers controlled by a single organization, treated as a "black box" from BGP’s perspective.
What is an ASN?
An Autonomous System Number, a unique identifier for each AS used in BGP routing.
What is the bit size and range of ASNs?
ASNs are 16-bit numbers ranging from 0 to 65,535.
What ASN range is reserved for private use?
64,512 to 65,534.
How does BGP identify different networks?
Using their ASN (Autonomous System Number).
Which transport protocol and port does BGP use?
TCP, port 179.
Is BGP automatic or manual?
Manual – BGP peering relationships must be manually configured.
What is a BGP peering relationship?
A manually created connection between two ASes to exchange routing information.
What is exchanged between BGP peers?
The best known paths to destination networks.
What is ASPATH in BGP?
The list of ASNs that a route advertisement has passed through.
What type of routing protocol is BGP?
A path-vector protocol.
What does BGP prioritize when selecting routes?
Shortest ASPATH – not speed, latency, or bandwidth.
What is the difference between eBGP and iBGP?
eBGP routes between ASes (used in AWS); iBGP routes within the same AS.
What is a common use case for BGP in AWS?
Integrating hybrid architectures using Direct Connect or VPN between AWS and on-premises networks.
What happens when an AS learns new routes via BGP?
It advertises the best (shortest) path to its peers.
What does the "I" symbol represent in the ASPATH?
The origin of the advertised route – it's the AS where the network originated.
How does BGP build a global routing topology?
Through a mesh of ASes exchanging best paths with their peers.
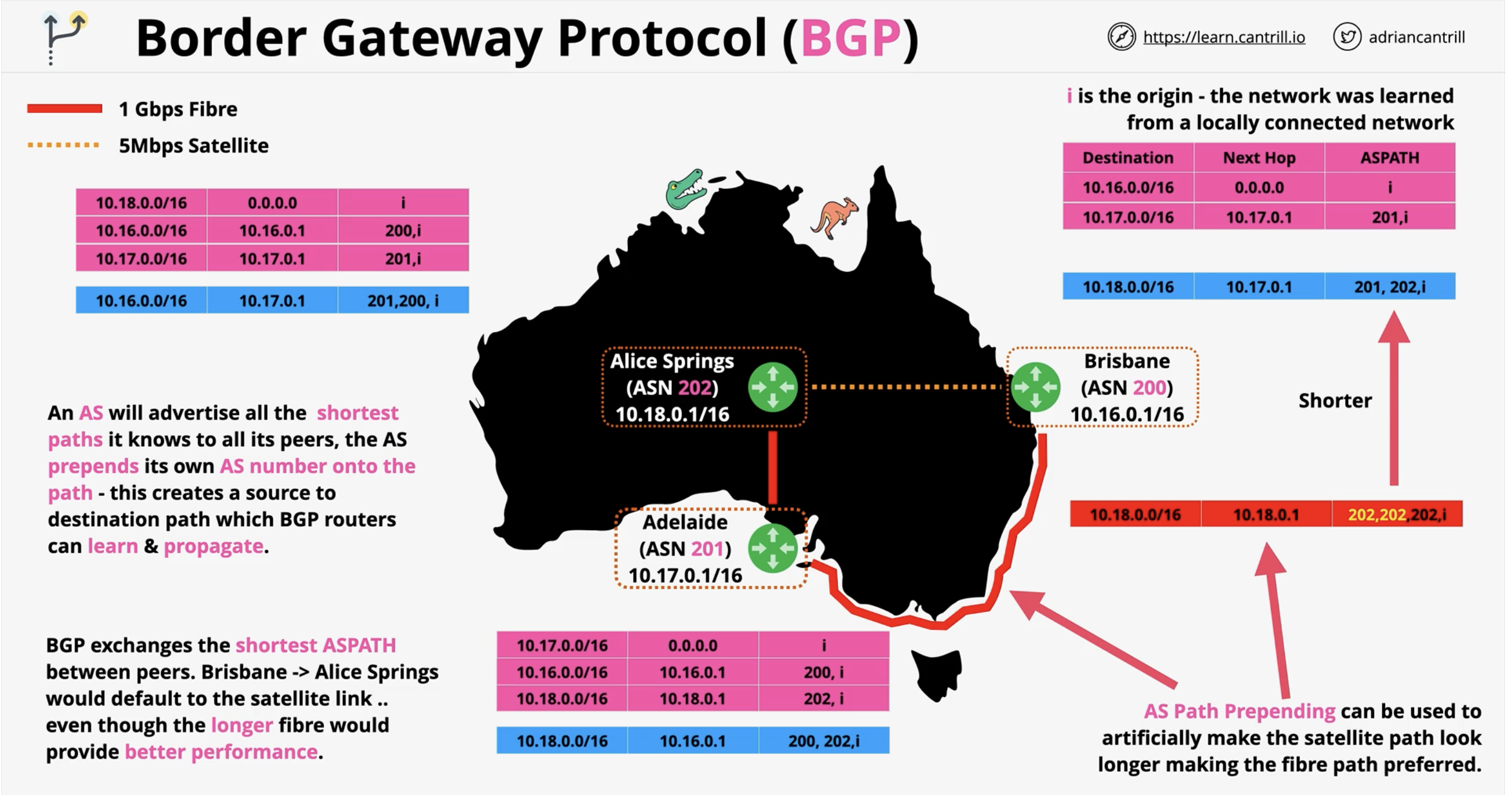
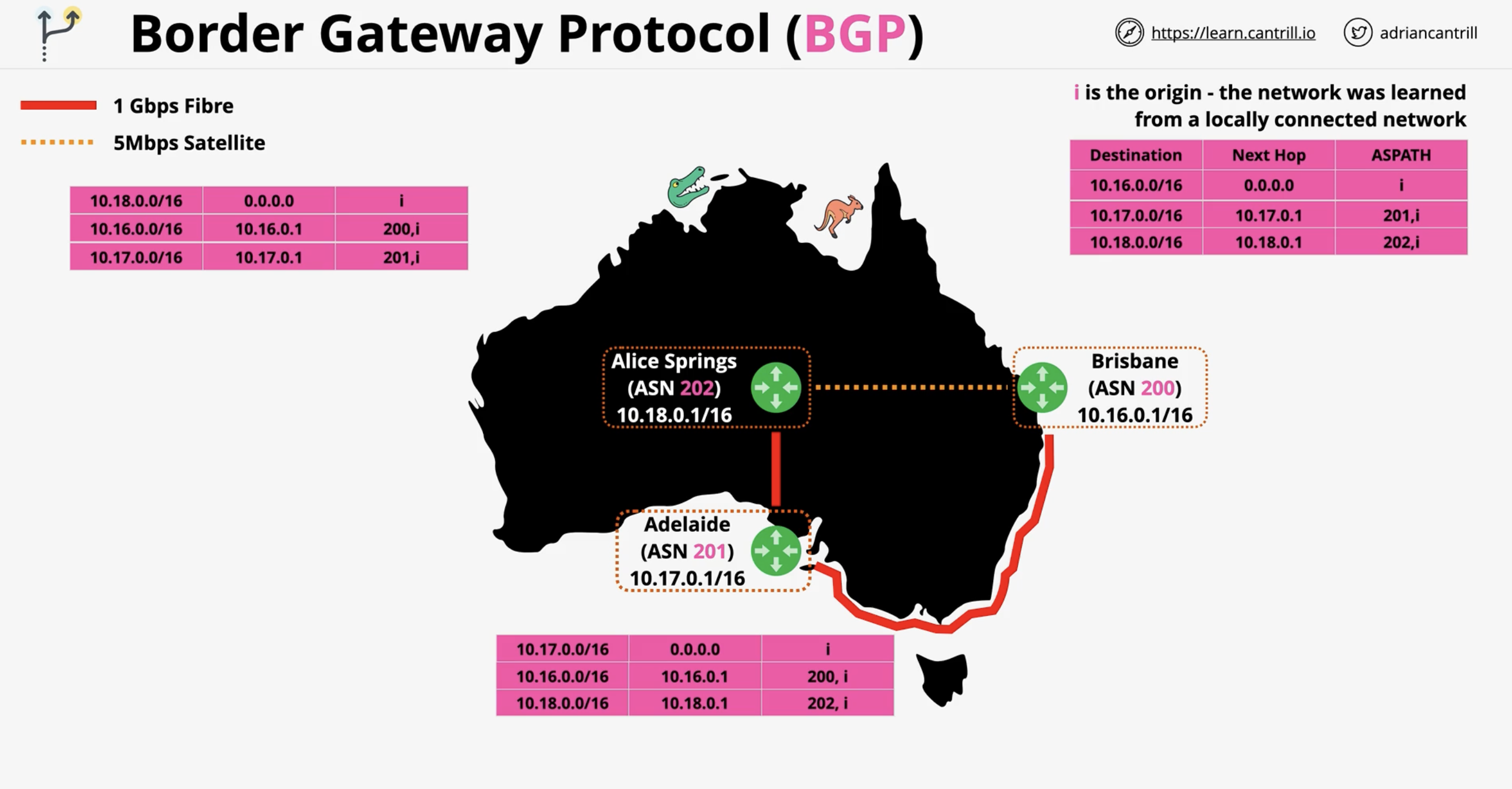
In the example with Brisbane, Adelaide, and Alice Springs, what does each AS represent?
Brisbane: ASN 200, Adelaide: ASN 201, Alice Springs: ASN 202.
What kind of links existed between the cities in the example?
Fiber (1 Gbps) and satellite (5 Mbps).
Which path does BGP prefer by default?
The one with the shortest ASPATH.
What is ASPATH Prepending?
A method to artificially lengthen a path by adding extra ASNs to the ASPATH to make a route less preferred.
Why would you use ASPATH Prepending?
To influence BGP to prefer a higher bandwidth or lower latency path over a shorter, but less optimal one.
Can BGP consider latency, bandwidth, or link condition when choosing routes?
No, BGP uses only ASPATH length.
What happens when a link between two ASes fails in a BGP network?
BGP automatically reroutes traffic via alternate known paths.
Does BGP advertise all known paths to a destination?
No, only the best (shortest) one.
What AWS services rely on BGP for dynamic routing?
AWS Direct Connect and Site-to-Site VPN with dynamic routing.
What does BGP enable in a hybrid AWS environment?
Dynamic route propagation between on-premises networks and VPCs.
What does a route table entry in BGP contain?
Destination network, next-hop IP, and ASPATH.
In the example, why did Brisbane choose the fiber path via Adelaide over the direct satellite?
ASPATH Prepending made the satellite path artificially longer, so the fiber route via Adelaide appeared shorter.
What is the practical takeaway of BGP for AWS Solutions Architects?
Understand its use in hybrid connectivity and how to influence routing decisions using techniques like ASPATH Prepending.
What is BGP?

In the start when BGP peering relationships are set up in the ASNs, what does the initial route tables of each look like?
All routes are registered for other nodes in all route tables in ring network.
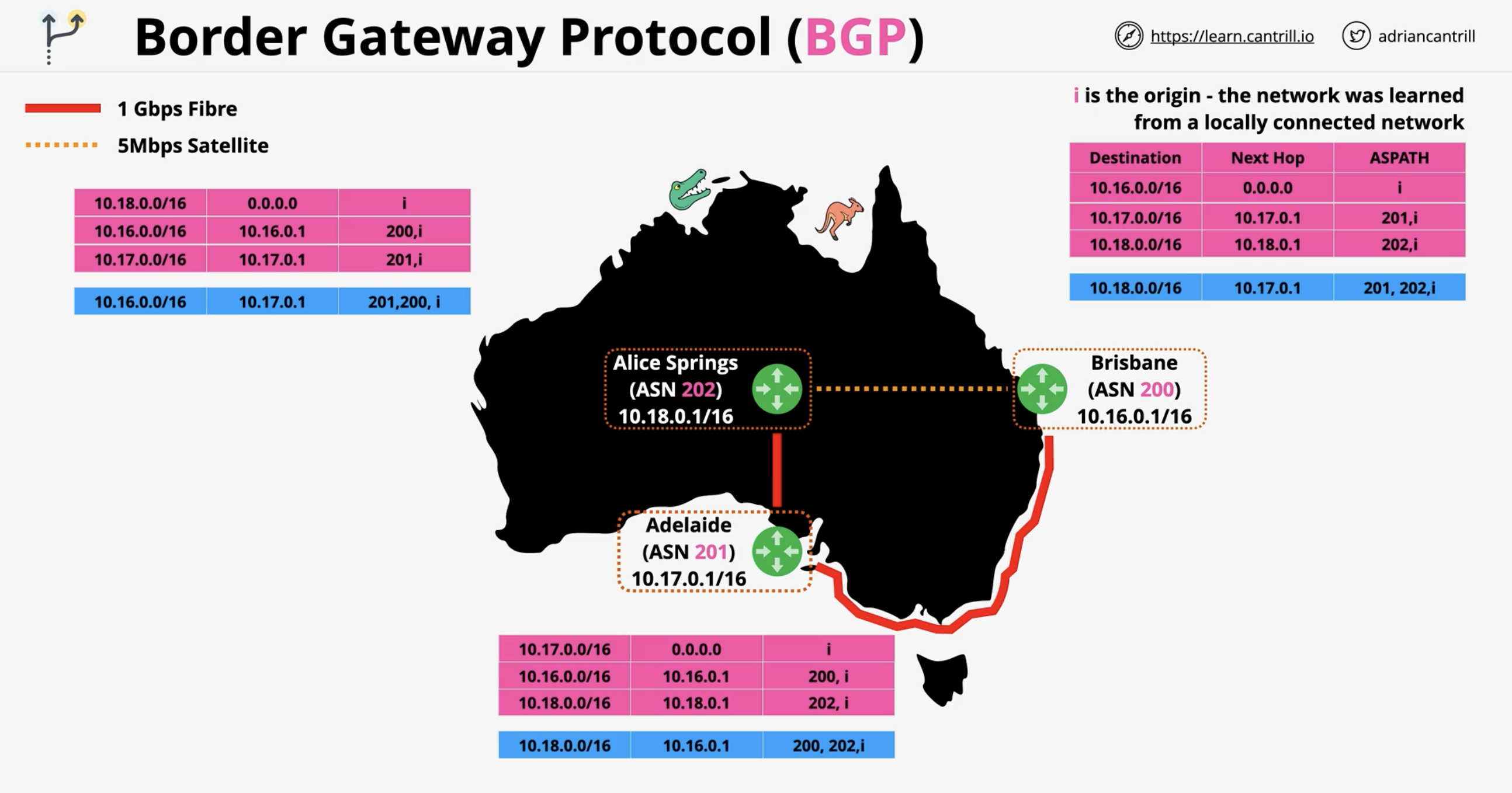
Apart from one-hop paths, more paths are added.
Longer doesn’t necessarily mean slower though. See the blue paths. Remember in this example red is 1 Gbps, orange is 5 Mbps. (Fiber vs. satellite)
BGP doesn’t take into consideration performance.
What is AS path prepending?
Adding additional autonomous system numbers to the path to make it longer than it physically is. Path length based!