phy B3 gas laws
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
assumptions for ideal gas
a gas consists of a very large no. of molecules
gas molecules are in constant random motion and obey the laws of classical mechanics
gas molecules make perfectly elastic collisions with one another and walls of container
intermolecular forces are negligible except during time of collision, which is brief compared to time between collisions
total volume of molecules is negligible compared to volume of gas
pressure
P = F/A where force is exerted prependicular to the surface
P = 1/3 ρv²
= 1/3 ((n X Mr)/V) v² where v² is mean square speed NOT IN DATA BOOKLET
the change in momentum of particles due to collisions with surface gives rise to pressure in gases REMEMBER DEFINITION
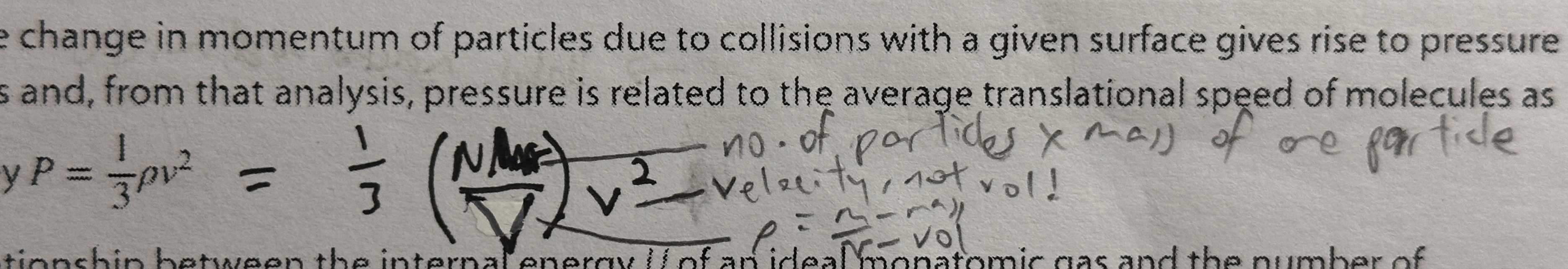
KE of 1 molecule
3/2 kT
derived from U / N
KE of system
= 3/2 NkT = 3/2 nRT = 3/2 pV
ideal gas equation
pV = nRT = NkT
note pressure is in kPa if dm3 and Pa if m3
approximate to ideal gas
low density + low pressure → so that intermolecular forces negligible
high temperature → so that KE>>PE
real gas vs ideal gas
real gas
intermolecular forces not negligible → actual pressure less than ideal
some volume is occupied by gas molecules → actual volume less than ideal
internal energy
KE + PE of molecules in a system
for ideal gas, assume PE = 0 since so far apart that negligible intermolecular forces
factors that affect potential energy
PE increases when distance increases
However, for ideal gas, molecules are so far apart that they don’t interact
Explain, with reference to the kinetic model of an ideal gas, how an increase in volume of the gas leads to a decrease in pressure
same no. of particles, collide with larger surface area → frequency of collision decreases
increased volume, constant velocity → frequency of collision decreases
why bubbles get larger when rise in water
Pressure of the water increases with depth of water. Thus the bubble experiences less pressure as it rises through the water.
Since pV= nRT, the number of moles of air trapped in the bubble and the temperature remains constant while the pressure decreases, the volume will increase
explain why volume increases when temperature increases (with constant pressure)
molecules overcome intermolecular forces (if boiled from liquid to gas)
gaseous molecules further apart
why is volume at very high pressure higher than the value calculated using PV=nRT?
volume of molecules not negligible, not behaving as ideal gas