FBLA Business Management
1/203
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
204 Terms
business communication
process of sharing info btwn ppl within the workplace and outside a company
communication skills help leaders:
-define goals clearly
-foster open rapport
-increases productivity and efficiency
examples of communication skills
active listening, constructive feedback, nonverbal, written, oral, voice modulation, negotiation, storytelling
3 c's of good communication
courteous, concise, correct
effective verbal communication needs
tactful forming of phrases and tone, concise, informative, clear, relevant
effective nonverbal communication needs
eye contact, body language, tone of voice, posture, facial expressions
effective technological communication needs
accuracy, clearness, conciseness, coherency, appropriateness
effective listening skills needs
-eye contact
-no interruption
-don't plan what to say next
-don't judge or jump to conclusions
-ask questions
-paraphrase and summarize what they told u
5 types of communication barriers
physical (too far to hear; mitigated by technology), physiological (impaired hearing), language (speak dif lang; gen z using slang to talk to a boomer), attitudinal (lack of motivation, personality conflicts)
how to overcome comm barriers
-use clear lang and neutral tone
-comm w/ need of receiver in mind
-keep message consistent
-follow up communication
-ask for feedback/make sure message conveyed successfully
purpose of internal and external analytical reports
examine problem and recommend an action
structure of internal analytical report
1. title page
2. table of contents
3. intro
4. methodology
5. body section
6. conclusions
7. recommendations
8. bibliography
internal analysis is about the ________ whereas external is about ________ ___________
organization; business environment
SWOT analysis
strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, threats
PESTLE analysis
external political, economic, social, technological, legal and environmental factors affecting a business
challenges of international business
-lang barrier
-cultural differences
-managing global teams (lang, culture, time zones, tech access)
-currency exchange and inflation
-foreign politics and relations
common workplace conflicts and solutions
-reports of discrimination and sexual harassment (hear reporter w/ open mind. investigate their story and take it seriously. look into professional discrimination training)
-employee accused of harassment or discrimination (take action immediately. record all relevant facts. make it clear any act of retaliation is not tolerated. bring in harassment awareness training)
-poor comm leads to mistake (address situation openly w/out blame. lead by example. corporate leadership training)
-clashing personalities (find source of tension/difference. pay them for executive coaching!)
-tension btwn departments (reward collaboration, communicate transparently, encourage company networking, estb central goals for everyone)
silo effect
workers complete their tasks in their functional silos without regard to the consequences for the other components of the process (poor communication)
__% of US employees have experienced or witnessed workplace discrimination
61
c suite
high ranking officers w/ "chief" in their titles
how to plan effective agenda (and thus, meeting)
1. define results to achieve by end of meeting (purpose). make sure to end w/ an action plan
2. identify timeframe
3. list topics and match time accordingly
4. plan participation strategies. give everyone a role
5. "sanity check." are the planned stuff doable?
4 p's of effective meetings
purpose, people, planning, (facilitate) process
purpose of liaisons in business environment
often on PR team. builds mutually beneficial relationships, facilitates communication, coordinates activities
written evaluation of job performance include
-quality (accuracy, thoroughness, competence)
-quantity (mtng deadlines, productivity)
-knowledge
-working relationships
-achievements
advantages of word processing in business
-accurate info (spell check)
-can save and share files
-extra features like text layout, borders, etc.
human relations skills needed by managers
-communication
-conflict resolution
-multitasking
-negotiation
-organization
staffing plan
strategic planning process to determine the personnel needs of the organization (number and type of employees)
how to minimize costs with staffing plan
-only keep core staff and hire temporary personnel as needed
-eliminate overtime
-limit benefits
-reduce training costs and mistake hires
impact of outsourcing on business
-helps lower cost of production and maximize profits
-lowers barrier to entry and increases competition
-erodes company loyalty
-affects insourced countries (ex: china, india), whose workers might start demanding higher wages
12 recruitment strategies
1. direct advertising (use company's careers site, job boards, social media, etc)
2. talent pool (past applicants who weren't hired, but saved)
3. employee referrals
4. boomerang employees (rehire past employees)
5. promotions and transfers (use internal employees)
6. employment exchanges (government given details about suitable candidates)
7. recruitment agencies
8. professional organizations
9. internships and apprenticeships
10. recruitment events
11. word of mouth
full cycle recruiting
when entire recruitment cycle handled by a single recruiter, from initiation to job offer and onboarding
5 stages of recruitment process
1. qualifying vacancies
2. sourcing
3. interviews
4. job offers
5. onboarding
__% of new hires start looking for a new job within 6 months
33
employee performance evaluation procedures
1. review their job description
2. highlight areas of improvement
3. compare strengths and weaknesses
4. recommend actionable goals
5. provide constructive feedback
6. invite employee input
grievance process
means of internal dispute resolution that starts with employee meeting the supervisor. if unresolved by company, eventually passed onto the CA department of human resources
termination process
1. identify and document issues
2. coach employees to see if problem can be solved
3. create performance improvement plan
4. terminate if still no change. best to sit face to face
5. HR conduct exit interview
affirmative action in the work place
ensures equal employment opportunities for all. workforce should reflect demographics of all qualified applicants. put in place by title vii of the civil rights act.
federal contractors are required by department of labor to have affirmative action
Title VII of the Civil Rights Act
prohibits discrimination in employment and created the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission
3 part test for companies to enact affirmative action plan?
1. show past discrimination (usually w/ stats)
2. cannot "unnecessarily trammel" rights of current employees (can't fire white employees to hire poc)
3. most be temporary (only until past discrimination corrected)
privacy act of 1974
a law that gives citizens access to the government's files on them. name, social security number, other identifying number are protected. can request change to records if any inaccurate info.
americans with disabilities act (1990) in the workplace
-can't discriminate based on disabilities, but candidate must be able to perform essential functions
-employers must make reasonable accommodations (accessible parking, service animals, alternative formats of work, etc)
EEOC
equal employment opportunity commission
employee compensation package
direct and indirect compensation. includes pay rate, bonuses, savings plan, insurance, scheduling (ex: paid time off), support services (ex: discounted access to stuff, childcare, meal plans, telecommuting options)
5 traits of successful employee onboarding
1. indoctrination into the culture
2. formal learning
3. social learning
4. set clear expectations
5. have strong communication
labor union
group of two or more employees who joined together to advance common interests like wages, benefits, schedules, etc.
collective bargaining
negotiation of wages and other conditions of employment by employees
3 stages of collective bargaining
1. prepare by selecting team and reaching out to community partners to draft proposal
2. conduct negotiations
3. ratify contract (can be changed if both parties agree during duration of contract)
ways of resolving contract dispute
-mediation
-arbitration
-strike/lockout
advantages and disadvantages of unions
adv:
-increased wages
-increased negotiating power
-legal protection from wrongful termination
-better healthcare, pensions, retirement funds
dis:
-union fees
-negotiations may not reflect ur opinion
-increased competition for jobs
-hierarchical structure
motivation theory: job rotation
employees who rotate roles (transitioning employees btwn dif jobs so they gain exposure to all aspects of company) are more motivated. breaks up monotony and encourage flexibility
motivation theory: job enlargement
adds additional activities w/in same level to existing role. broadens job to make more motivating. reduces monotony, but also less efficient
job creep
the slow and subtle expansion of employee job duties that is not officially recognized by the organization, until they burn out
motivation theory: job enrichment
gives increased responsibility and variety (more control overall). creates meaningful roles (growth mindset) and work culture based on psychological safety
tenets of employee wellness programs
-flexible working hours
-remote working arrangements
-give employees autonomy
-require work life balance
-onsite fitness accommodations
-financial education
ways to raise capital?
1. equity financing (raises money by selling shares of company stock)
2. debt financing (borrows money to pay back later)
3. retained earnings (money left over after financing other obligations)
common vs preferred stock
common: highest return and risk. have voting rights.
preferred: are paid dividends before common shareholders, but no voting rights
bond
a loan from an investor to a company/government
financial instrument
real/virtual documents representing legal agreement involving monetary value. can be divided into cash and derivative instruments
cash vs derivative instruments
cash: directly influenced by the market and easily transferrable
derivative: based on underlying components, like assets, interest rates, etc.
instrument (economics)
the means by which something of value is transferred, held, or accomplished
derivative (economics)
security with a price dependent upon one or more underlying assets
mutual funds institutions
investments made by multiple parties that are managed by a professional
cpa firms
certified public accountant (helps w accounting, management and financial advisory)
5 types of financial service institutions
1. banking
2. advisory
3. wealth management
4. mutual funds
5. insurance
money market account
low transaction checking accounts with high interest rate in exchange for high minimum balance requirement
examples of common financial data
-assets
-liabilities
-equity
-income
-expenses
-cash flow
cash flow statement
financial statement that summarizes the movement of cash and cash equivalents
income statement
revenue, expenses, gains, losses of company during particular period
aka profit and loss statement
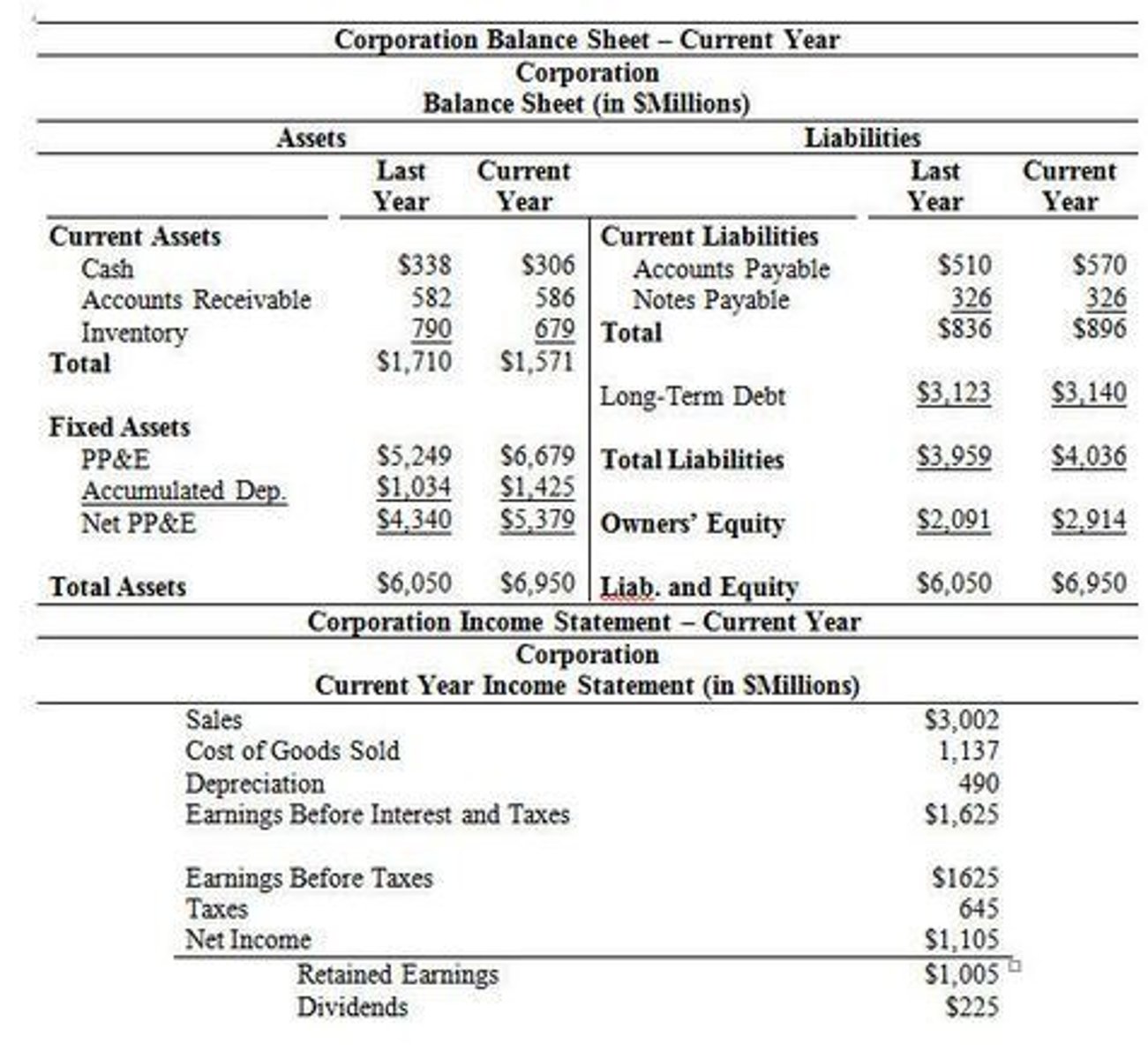
balance sheet
reports assets, liabilities, shareholder equity at specific point in time. provides basis for computing rates of return for investors and evaluating company's capital structure
3 most important financial statements
1. income statement
2. cash flow
3. balance sheet
5 approaches to managing risk
1. avoiding risk (pre-emptive)
2. transferring risk (buy insurance or other third party company to deal with risk)
3. preventing loss (unavoidable risk, but tries to reduce impact of risk)
4. retaining risk (handle risk internally)
5. spreading risk (mainly for insurance companies who share large clients with other insurance companies)
how long does short term budget usually cover
1 month to 1 year
how long does long term budget usually cover
3 years to 10 years
3 types of accounting controls
1. detective (inventory checks, audits, cash counts)
2. preventative (segregation of duties, expense verification, limiting physical access to assets)
3. corrective (audits, adjustments, ledger verification)
credit rating
evaluation of the credit risk of a prospective debtor
in united states, scale goes from 300-850 (below 629 is bad. 630-689 is fair. 690-719 is good. 720 and higher is excellent)
credit agencies
for profit data collection agency that gathers account info from creditors and sends it to a consumer reporting agency in the US
debt collection process
1. 30 days past due
2. 60 days past due
3. charge off status (collection agency contacted)
4. court (judge can record lien against your home, force sale of expensive asset, etc.)
lien
a right to keep possession of property belonging to another person until a debt owed by that person is discharged
3 types of taxes
1. sales tax (state and local revenue. funds education, transportation, healthcare, etc)
2. income tax (big source of revenue for federal, state government)
3. property tax (local revenue, from parks to public safety)
americans spent _____ percent of income in taxes each each
29.2
federal tax rates range from
10-37%
types of tax on goods and services
-sales tax
-excise taxes (quantity of item, not value)
-user fees (variety of services, from airline tickets to rental cars to hotel rooms)
-sin taxes (cigarettes, alcohol)
types of taxes on income
-payroll tax (employers must subtract payroll tax each pay period, then match the sums deducted)
-capital gains taxes (paid on profits made from the sale of an asset)
-estate/gift/inheritance tax (for the richest 0.1%)
components of a financial plan
1. set financial goals
2. net worth statement (serve as baseline)
3. budget and cash flow planning
4. debt management plan
5. retirement plan
6. emergency funds
7. insurance coverage
8. estate plan
most necessary insurance for business owners
1. general liability (protect from claims of bodily, personal injury and property damage)
2. commercial property insurance (building and equipment)
3. business income insurance (replace lost income for ongoing expenses)
4. professional liability insurance (in case u make mistakes)
5. worker's compensation insurance (in case workers get hurt)
6. data breach insurance (in case data is stolen)
what type of coverage is included in a business owner's policy (BOP)
general liability, property damage, business interruption, workers' comp
quality control processes should
1. minimize errors
2. maximize operational effectiveness
3. expedite workflow
3 most important factors when selecting suppliers
1. quality
2. price
3. reliable delivery
inventory control
ensuring the right amount of supply is available within a business
physical design to maximize productivity at the office
1. instead of open spaces, have spaces with variety/specialized for different activities
2. improve lighting
3. raise the ceilings
4. paint walls (NOT WHITE)
5. control noise level
data mining
using sophisticated statistical analysis to "discover" unhypothesized relationships in large sets of data, turning findings into business insights and predictions
4 functions of management
1. planning (set long-range vision and goals, workload management)
2. organizing (distribute resources, delegate tasks, structure departments, etc)
3. leading (provide direction and inspiration)
4. controlling (managing schedule, train employees, evaluate performances, adjustment to staffing schedules)
5 steps of the control function of management
1. set standards
2. measure performance
3. compare performance to standards
4. identify reasons for deviations from performance to standards
5. take corrective action if needed
3 types of control systems
1. output control (focus on measurable results)
2. behavioral control (focus on actions, which should lead to results)
3. clan control (informal. relies on shared traditions, expectations, values and norms to guide ppl to work towards the good of their organization)
9 types of management styles
1. authoritative (expect staff to obey without questioning u)
2. democratic (encourages team to give feedback. collaborative)
3. consultative (hear everyone's opinions before decision. best for teams where everyone has specialized knowledge)
4. laissez-faire (members make own decisions, but leader will always back them up, offer guidance)
5. collaborative (work together, decisions based on majority vote)
6. transformation (innovation, employee development)
7. coaching (like in sports, u as the coach take a backseat. prioritize long term growth over mistakes)
8. delegative (main role to assign tasks, then give feedback)
9. visionary (motivate team members but give them complete freedom to work)
joint venture
business entity created by two or more parties, characterized by shared ownership, shared returns and risks, shared governance
employee right to know
employees must be informed of likely hazards in the workplace and be provided info, training, ppe necessary
3 ways in which businesses demonstrate social responsibility
1. providing jobs
2. paying taxes
3. contributing to community projects
4 p's of marketing (ie marketing mix)
product, price, place, promotion
5 common pricing strategies
1. cost plus pricing (calc costs + mark up)
2. competitive pricing (set price based on what competition charges)
3. price skimming (set high price, then lower it as market evolves)
4. penetration pricing (set low price, then increase it as market evolves)
5. value-based pricing (base it on what the customer believe it's worth)