SLC Anatomy Wk 2: everything except circulatory system anatomy
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
Agglutination
clumping of cells and particles in blood
Anemia
condition in which RBC do not transport enough oxygen to the tissues
Anisocytosis
condition with abnormal variation in the size of RBC
Anticoagulants
agent that prevents the formation of blood clots
Blood types or Groups
classification of blood according to its antigen and antibody qualities
Coagulation
changing of a liquid (blood) into a semi-sold
Dyscrasia
any disease with abnormal particles in the blood
Erythropenia
disorder with abnormally low RBC count
Globin
protein molecules in the blood, part of hemoglobin
Hemochromatosis
hereditary condition with excessive iron buildup in the blood
Hematocrit
measure of the % of RBC in a blood sample
Heme
pigment containing iron in hemoglobin
Hemoglobin
protein in RBC essential to the transport of oxygen
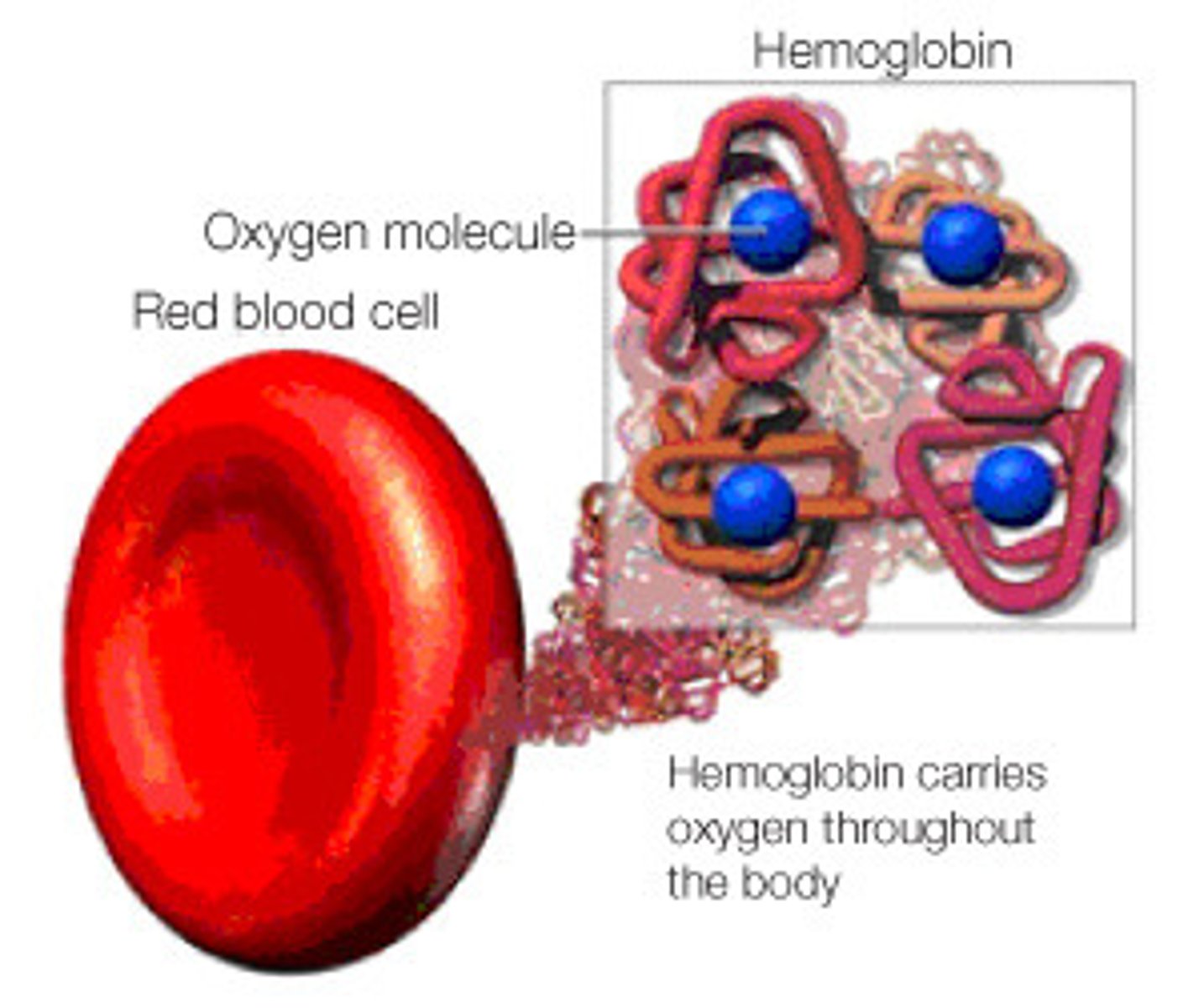
Hemolysis
disorder with breakdown of RBC membranes
Hemophilia
hereditary disorder with lack of clotting factor proteins in the blood
Hemostatics
agent that stops bleeding
Macrocytosis
disorder with abnormally large RBC
Microcytosis
disorder with abnormally small RBC
Pancytopenia
Condition with low number of blood components
Phlebotomy
insertion of a needle into a vein to extract a blood sample
Plasma
liquid portion of unclotted blood
Platelets (Thrombocytes)
part of a megakaryocyte that initiates clotting
Poikilocytosis
disorder with irregularly shaped RBC
Polycythemia
Disorder with abnormal increase in RBC and hemoglobin
Purpura
condition with multiple tiny hemorrhages under the skin
Red Blood Cell Count
measurement of RBC in a cubic milimeter of blood
Red blood cells (Erythrocytes)
one of the solid parts of blood formed from stem cells and having hemoglobin within
Reticulocytosis
disorder with an abnormal number of immature RBC
Rh Factor
type of antigen in blood that can cause a transfusion reaction
Serum
the liquid left after blood has clotted
Thrombocytopenia
bleeding condition with insufficient production of platelets
Thrombolytics
agent that dissolves blood clots
Transfusion
injection of donor blood into a person needing blood
White blood cells (Leukocytes)
one of the solid parts of blood from stem cells that plays a role in defense against a disease
Arrhythmias
irregularity in the rhythm of the heartbeat
Bradycardia
heart rate <60 bpm
Diastole
relaxation phase of a heartbeat
Dysrhythmia
abnormal heart rhythm
Hypertensive
high blood pressure
Hypotensive
low blood pressure
Systole
contraction phase of the heart beat
Tachycardia
heart beat >100 bpm
blood
fluid (containing plasma, RBC, WBC, and platelets) circulated throughout the arteries, veins, capillaries, and heart