8.3 Effects of the Cold War
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Proxy War
A war in which the powers in conflict use third parties as substitutes instead of fighting each other directly.

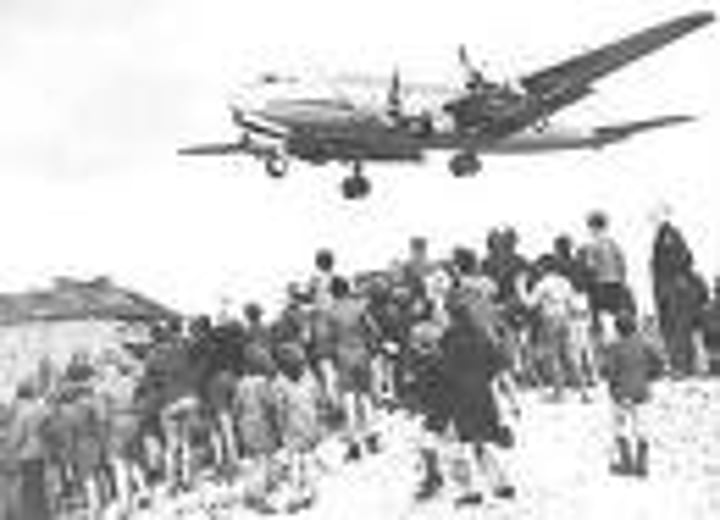
Berlin Airlift, 1948
In June 1948, the USSR-who wanted Berlin all for themselves-closed all highways, railroads and canals into Berlin from West Germany. This, they believed, would make it impossible for the people who lived there to get food or any other supplies and would eventually drive Britain, France and the US out of the city for good. However, the US and its allies decided to supply their sectors of the city from the air. The "Berlin Airlift," lasted for more than a year and carried more than 2.3 million tons of cargo in 277,000 flights into West Berlin. Year-long mission of flying food and supplies to blockaded West Berliners, whom the Soviet Union cut off from access to the West in the first major crisis of the Cold War.

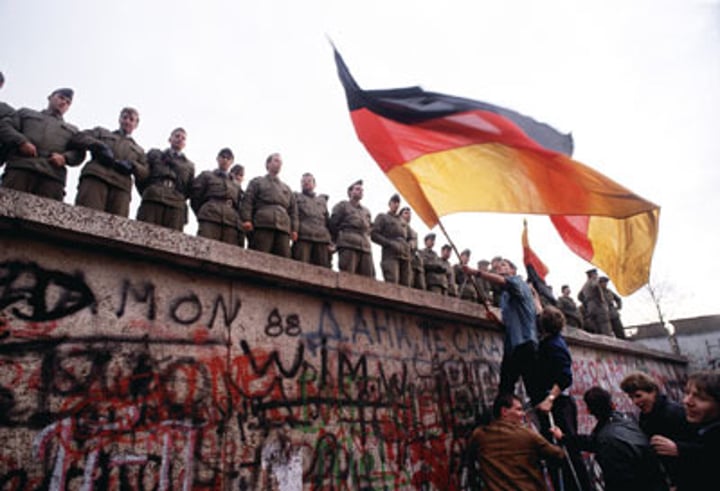
Berlin Wall (1961)
The Soviet Union, under Nikita Khrushchev, erected a wall between East and West Berlin to keep people from fleeing from the East, afterwards Kennedy asked for an increase in defense funds to counter Soviet aggression. Became a symbol of division between East and West.

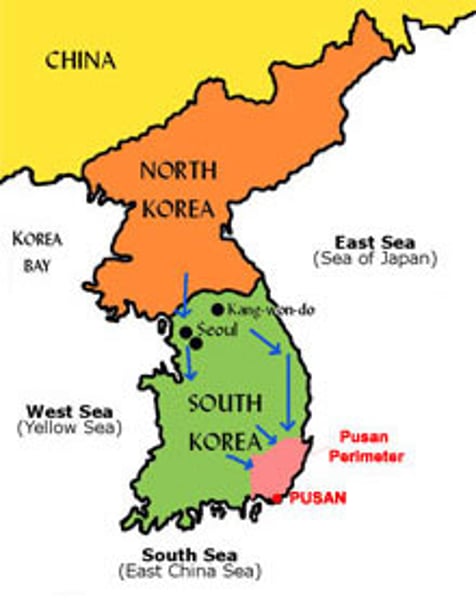
Korean War (1950-1953)
Began as a civil war between North and South Korea (which had been established by the USSR and US respectively), but the conflict soon became international when, under U.S. leadership, the United Nations joined to support South Korea and China entered to aid North Korea. The war left Korea divided along the 38th parallel. The Korean War was an example of the U.S. Cold War policies of containment and militarization, setting the stage for the further enlargement of the U.S. defense perimeter in Asia (Vietnam)
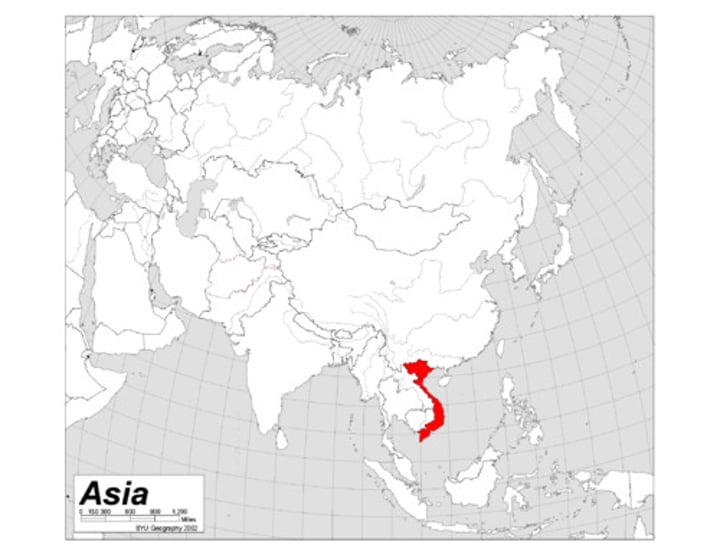
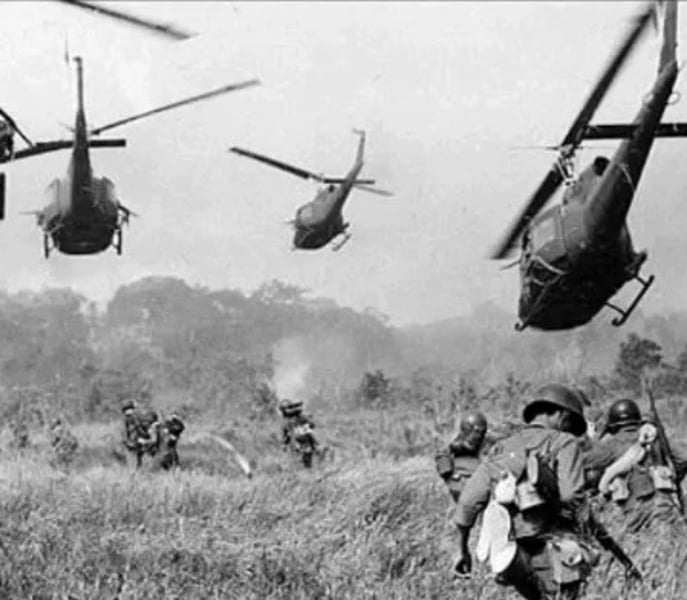
Vietnam War
A prolonged war (1954-1975) between the communist armies of North Vietnam who were supported by the Chinese and the non-communist armies of South Vietnam who were supported by the United States.
Domino Theory
A theory that if one nation comes under Communist control, then neighboring nations will also come under Communist control.

Bay of Pigs
In April 1961, a group of Cuban exiles organized and supported by the U.S. Central Intelligence Agency landed on the southern coast of Cuba in an effort to overthrow Fidel Castro. When the invasion ended in disaster, President Kennedy took full responsibility for the failure.

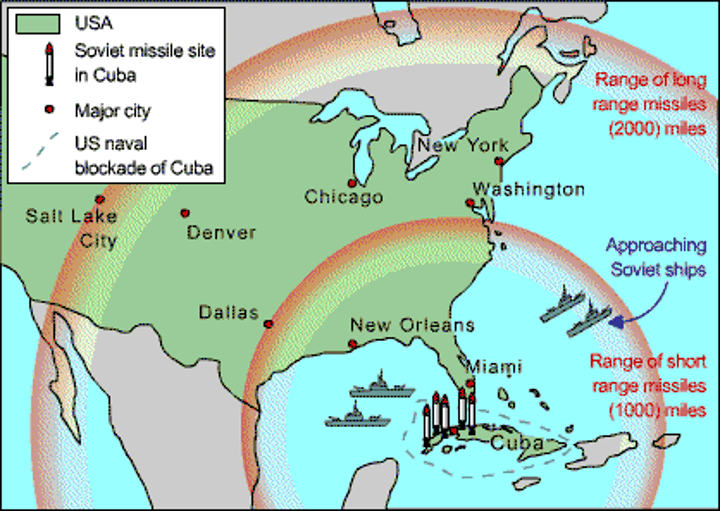
Cuban Missile Crisis (1962)
A n international crisis in October 1962, the closest approach to nuclear war at any time between the U.S. and the USSR. When the U.S. discovered Soviet nuclear missiles on Cuba, President John F. Kennedy demanded their removal and announced a naval blockade of the island; the Soviet leader Khrushchev acceded to the U.S. demands a week later. When the Soviet Union placed nuclear arms in Cuba the US was threatened. This initiated a stalemate between the Soviet Union and the US because each had the power to destroy each other.
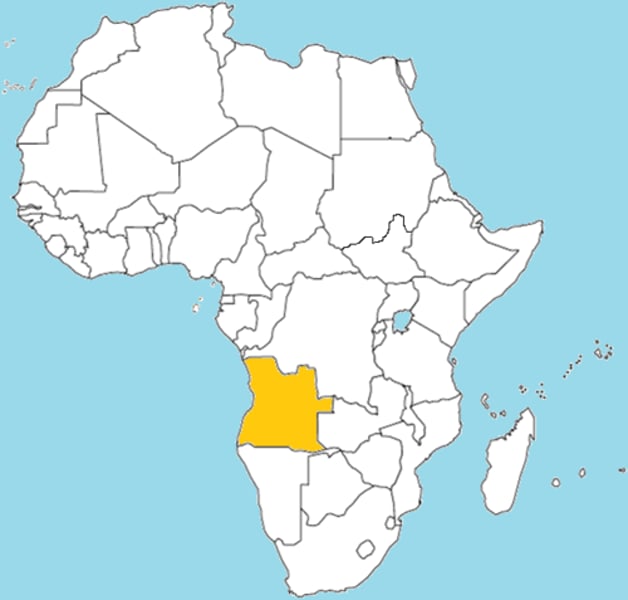
Angola Civil War
Angolan Civil War started when the nation gained independence from Portugal in 1975 Pro- and anti-communist forces in Angola set the stage for a proxy fight between the US/USSR.
Contra War
The contras is a label given to the various U.S.-backed and funded right-wing rebel groups that were active from 1979 to the early 1990s in opposition to the left-wing, socialist Sandinista Junta of National Reconstruction government in Nicaragua.
North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO)
A group of 28 countries that has agreed to protect each other in case of attack; founded in 1949

Warsaw Pact
Treaty signed in 1945 that formed an alliance of the Eastern European countries behind the Iron Curtain; USSR, Albania, Bulgaria, Czechoslovakia, East Germany, Hungary, Poland, and Romania. Response to NATO.
Communist Bloc
The group of Eastern European nations that fell under the control of the Soviet Union following World War II.
Southeast Asia Treaty Organization (SEATO)
1954-1977
*Created to oppose the spread of Communism in Southeast Asia after France's withdrawal from Indochina
*Original members included the US, Britain, France, Pakistan, Thailand, and the Philippines
*The organization was meant to justify an American presence in Vietnam, though some members did not support America in this effort
*Dismantled in 1977

Central Treaty Organization (CENTO) (1955)
Alliance formed under President Eisenhower to prevent Soviet expansion into the Middle East and Central
Asia; consisted of Britain, Iraq, Iran, Pakistan, Turkey, and the U.S.
Nuclear Test Ban Treaty of 1963
Reacting to Soviet nuclear tests, this treaty was signed on August 5, 1963 and prohibited nuclear testing undersea, in air and in space. Only underground testing was permitted. It was signed by all major powers except France and China.

Nuclear Nonproliferation Treaty (1968)
Goal of international efforts to prevent countries other than the five declared nuclear powers (United States, Russia, Britain, France, and China) from obtaining nuclear weapons. The first Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty was signed in 1968. Banned transfer of nuclear weapons' to countries that did not have them.

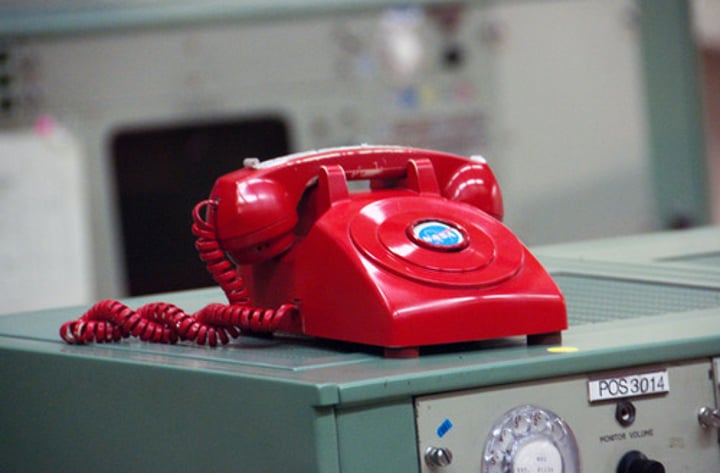
Hot Line
Direct telephone line between the White House and the Kremlin set up after the Cuban missile crisis. Linked Kennedy and Kruschev at the time. Used to connect leaders in times of need.

Antinuclear Weapons Movement
consists of more than 80 anti-nuclear groups that oppose nuclear power, nuclear weapons, and/or uranium mining. One of the first such movements developed in Japan in 1954 in opposition to U.S. testing of nuclear weapons in the Pacific Ocean.
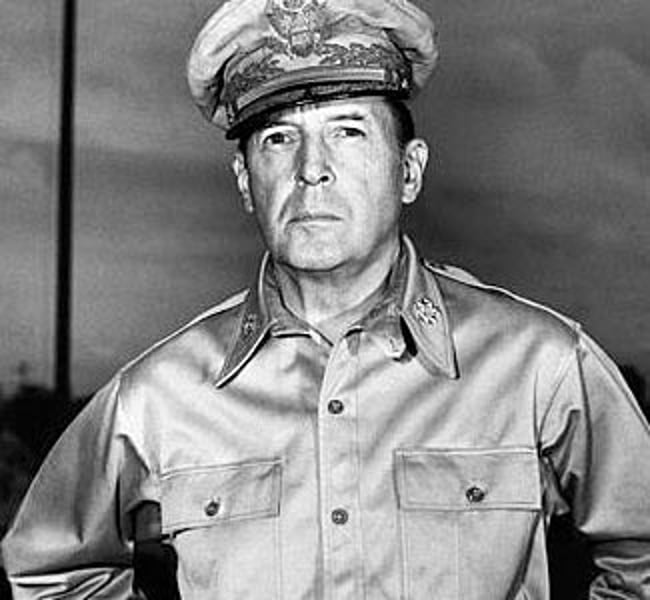
Douglas MacArthur
(1880-1964), U.S. general. Commander of U.S. (later Allied) forces in the southwestern Pacific during World War II, he accepted Japan's surrender in 1945 and administered the ensuing Allied occupation. He was in charge of UN forces in Korea 1950-51, before being forced to relinquish command by President Truman.

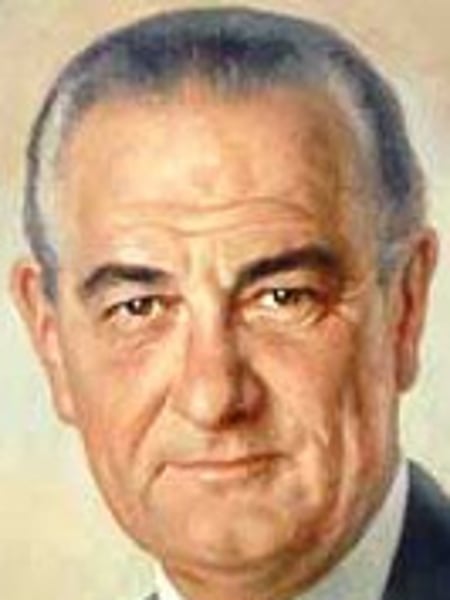
Lyndon B. Johnson
Signed the civil rights act of 1964 into law and the voting rights act of 1965. He had a war on poverty in his agenda. In an attempt to win, he set a few goals, including the great society, the economic opportunity act, and other programs that provided food stamps and welfare to needy families. He also created a department of housing and urban development. his most important legislation was probably Medicare and Medicaid.

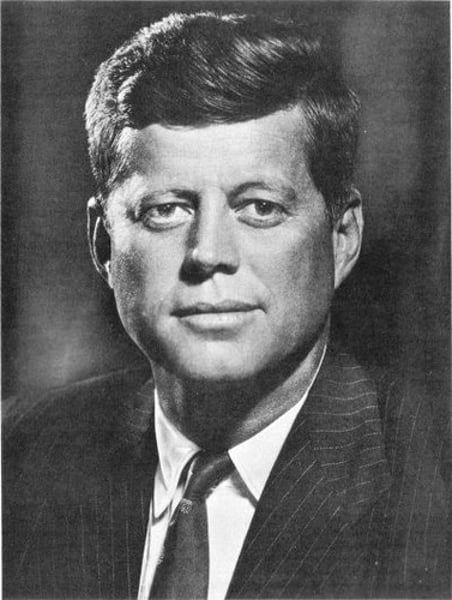
John F. Kennedy
President during part of the cold war and especially during the superpower rivalry and the Cuban missile crisis. He was the president who went on tv and told the public about the crisis and allowed the leader of the soviet union to withdraw their missiles. Other events, which were during his terms was the building of the berlin wall, the space race, and early events of the Vietnamese war.

Nikita Khrushchev
ruled the USSR from 1958-1964; lessened government control of soviet citizens; seeked peaceful coexistence with the West instead of confrontation. Soviet leader during Cuban Missile Crisis; denounced Stalin.
