Chemistry - Chapter 21 - Nucleic Acids
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
OBJ: Course Objective Chapter 21
INFO: Nucleic Acid rundown
INFO: Nucleic Acid rundown 2

Put the following terms in the correct order of information transfer according to the central dogma of molecular biology.
RNA
PROTEIN
DNA
DNA → RNA → PROTEIN
Which of the following are components of a nucleotide within a DNA molecule?
A nucleotide consists of a sugar, a phosphate, and a nitrogenous base.
Which base is found in DNA but not in RNA?
thymine
Which of the following best describes tRNA?
tRNA binds specific amino acids and carries them to the ribosomes during protein synthesis.
Which of the following bases are found in DNA?
Which of the following bases are found in RNA?
a) Adenine, guanine, thymine, and cytosine are found in DNA.
b) Adenine, guanine, uracil, and cytosine are found in RNA.
In what way might two DNA molecules that contain the same number of nucleotides differ?
Two DNA molecules that contain the same number of nucleotides may differ in the order as well as relative numbers of the bases and the order of nucleotides.
Select all of the following which are steps involved in DNA replication.
These are the steps involved in DNA replication:
The double helix unwinds.
The new DNA segments are synthesized.
The "nicks" in the new strand are closed.
How does the sugar–phosphate backbone of RNA differ from the backbone of DNA?
The sugar in the RNA backbone is ribose, and that in the DNA backbone is deoxyribose.
Identify whether each of the following describes mRNA, rRNA, or tRNA.
associated with a series of proteins in a complex structure
contains genetic information needed for protein synthesis
smallest of the RNA molecules
(a)
rRNA
(b)
mRNA
(c)
tRNA
Which interactions hold double-stranded DNA together?
Strands of DNA are held together by hydrogen bonds between complementary bases.
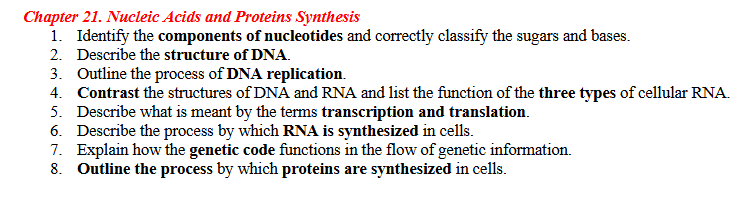
1: Identify the components of nucleotides and correctly classify the sugars and bases
A nucleotide has THREE parts:
Phosphate group
Pentose sugar
DNA: deoxyribose
RNA: ribose
Nitrogenous base
Purines: Adenine (A), Guanine (G)
Pyrimidines: Cytosine (C), Thymine (T), Uracil (U)
Purine = 2 rings
Pyrimidine = 1 ring
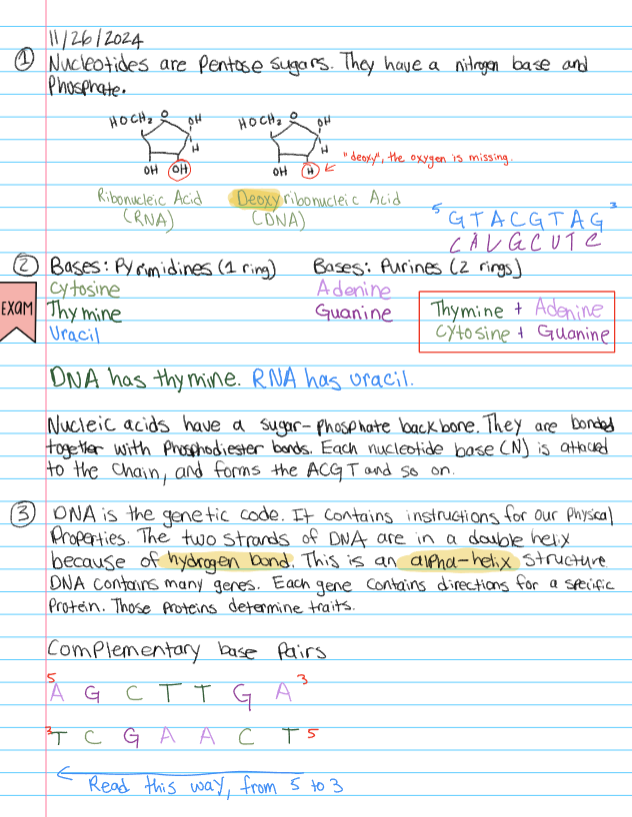
2: Describe the structure of DNA
DNA is a double helix with:
Sugar–phosphate backbone on the outside
Hydrogen-bonded base pairs on the inside
Antiparallel strands (5’→3’ and 3’→5’)
Base pairing:
A = T
G ≡ C
(2 H-bonds) (3 H-bonds)
More G–C = higher melting/boiling temp.
3: Outline the process of DNA replication
Each strand serves as a template.
Steps (condensed):
Helicase unwinds helix
DNA polymerase adds complementary nucleotides
Each new DNA molecule =
one old strand + one new strand
This is called semi-conservative replication.
4: Contrast the structures of DNA and RNA and list the function of the three types of cellular RNA
Feature | DNA | RNA |
|---|---|---|
Sugar | deoxyribose | ribose |
Bases | A, T, C, G | A, U, C, G |
Strands | double | single |
Location | nucleus | nucleus + cytoplasm |
Function | stores genetic info | protein synthesis |
Three types of RNA:
mRNA – messenger, carries code
tRNA – transfers amino acids
rRNA – part of ribosomes
5: Describe what is meant by the terms transcription and translation
Transcription (DNA → RNA)
Occurs in the nucleus.
Steps:
DNA unwinds
RNA polymerase builds mRNA using base pairing
A → U
T → A
C → G
G → C
mRNA leaves nucleus → ribosome
Translation (mRNA → Protein)
Occurs in the ribosome.
Steps:
mRNA binds ribosome
tRNA brings amino acids
Anticodon on tRNA pairs with codon on mRNA
Peptide bonds form
Continues until STOP codon
Protein released
tRNA has:
amino acid attachment site
anticodon (3 bases)
6: Describe the process by which RNA is synthesized in cells
RNA is synthesized during transcription in three short steps:
1. Initiation
• RNA polymerase binds to the promoter region of DNA
• DNA unwinds
2. Elongation
• RNA polymerase builds an RNA strand using complementary base pairing
A → U
T → A
C → G
G → C
3. Termination
• Polymerase reaches a stop signal
• RNA detaches
• The new RNA molecule (mRNA, tRNA, or rRNA) is released
Summary: RNA polymerase reads DNA → builds RNA.
7: Explain how the genetic code functions in the flow of genetic information
Genetic Code
Written in codons (3-base sequences on mRNA)
Each codon = 1 amino acid
Start codon: AUG (methionine)
Stop codons: UAA, UAG, UGA (no amino acid)
Redundancy: multiple codons code for same amino acid.
How proteins are synthesized in cells
A. Transcription (in nucleus)
Occurs in nucleus
Uses RNA polymerase
Produces mRNA, tRNA, or rRNA
Base pairing: A↔U, C↔G
B. Translation (in ribosome) 1. Initiation
• mRNA binds to ribosome
• Start codon (AUG) is recognized
• First tRNA (carrying methionine) attaches
2. Elongation
• tRNAs bring amino acids to ribosome
• Each codon on mRNA pairs with a tRNA anticodon
• Peptide bonds form
• The chain grows
3. Termination
• Stop codon reached
• Protein is released and folded
Summary:
mRNA carries the recipe → tRNA delivers amino acids → ribosome builds the protein.