HN204 Lecture 19 ILO's
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
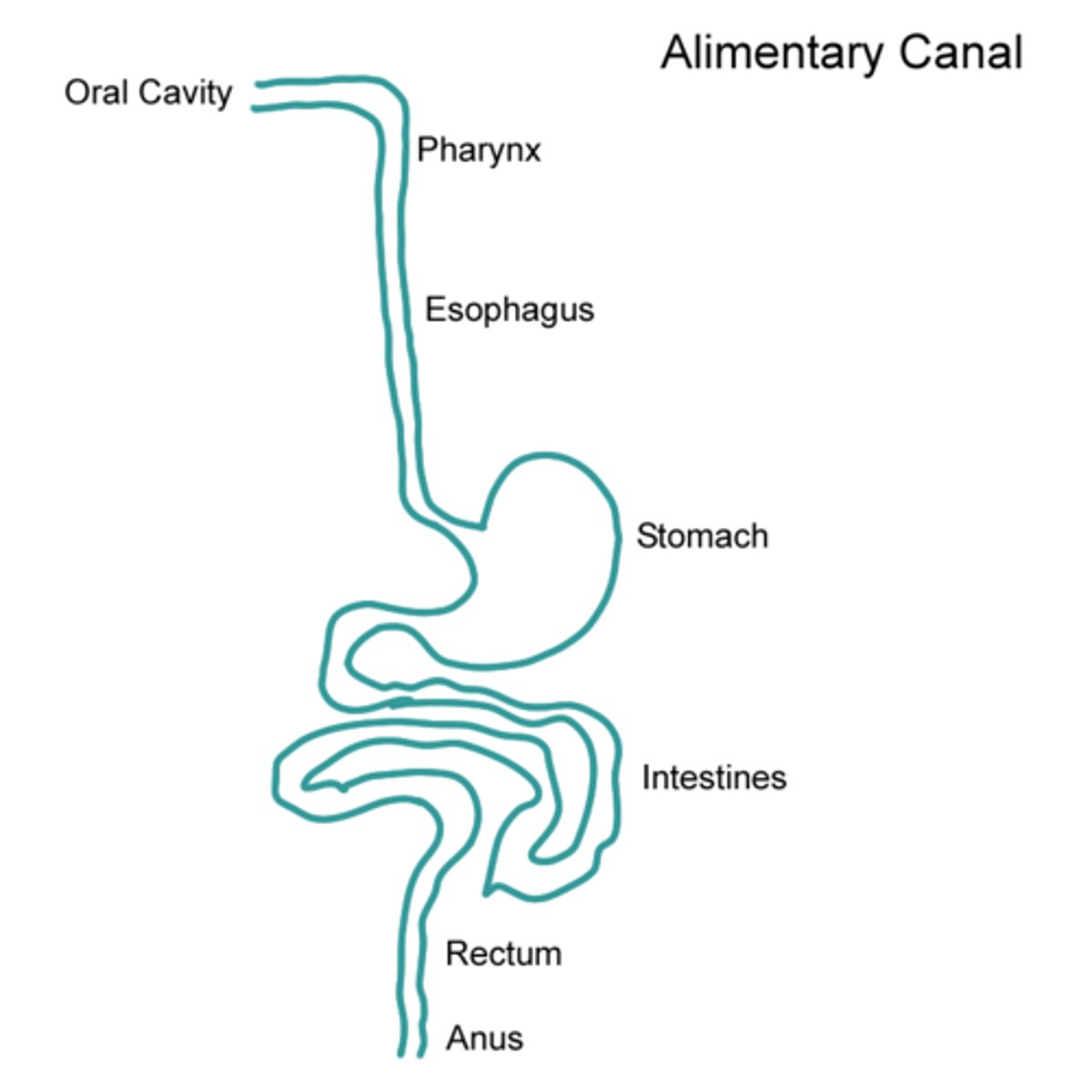
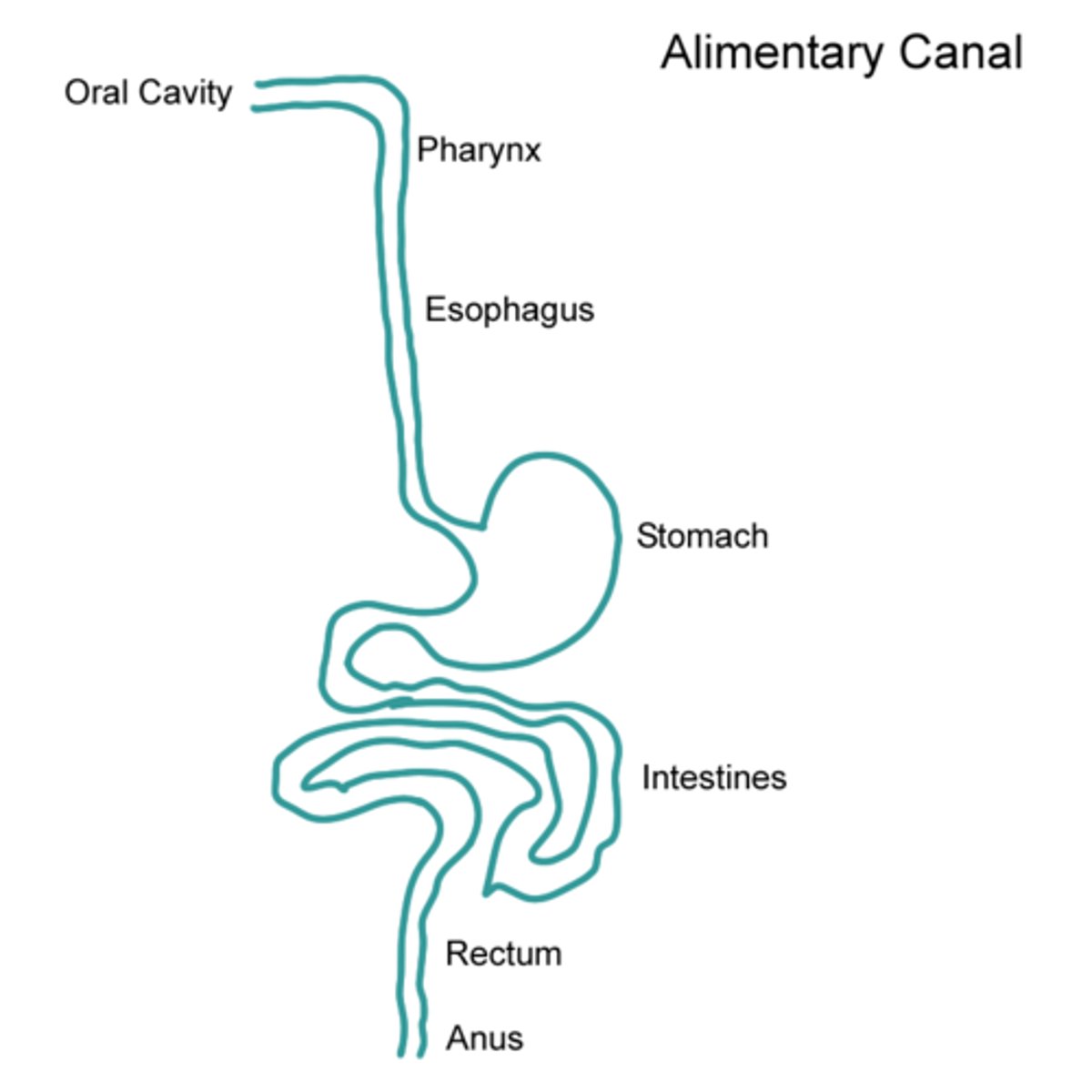
Alimentary canal
The continuous tube running from the mouth to the anus.
Gastrointestinal (GI) tract
The organ system responsible for digestion and absorption of food.
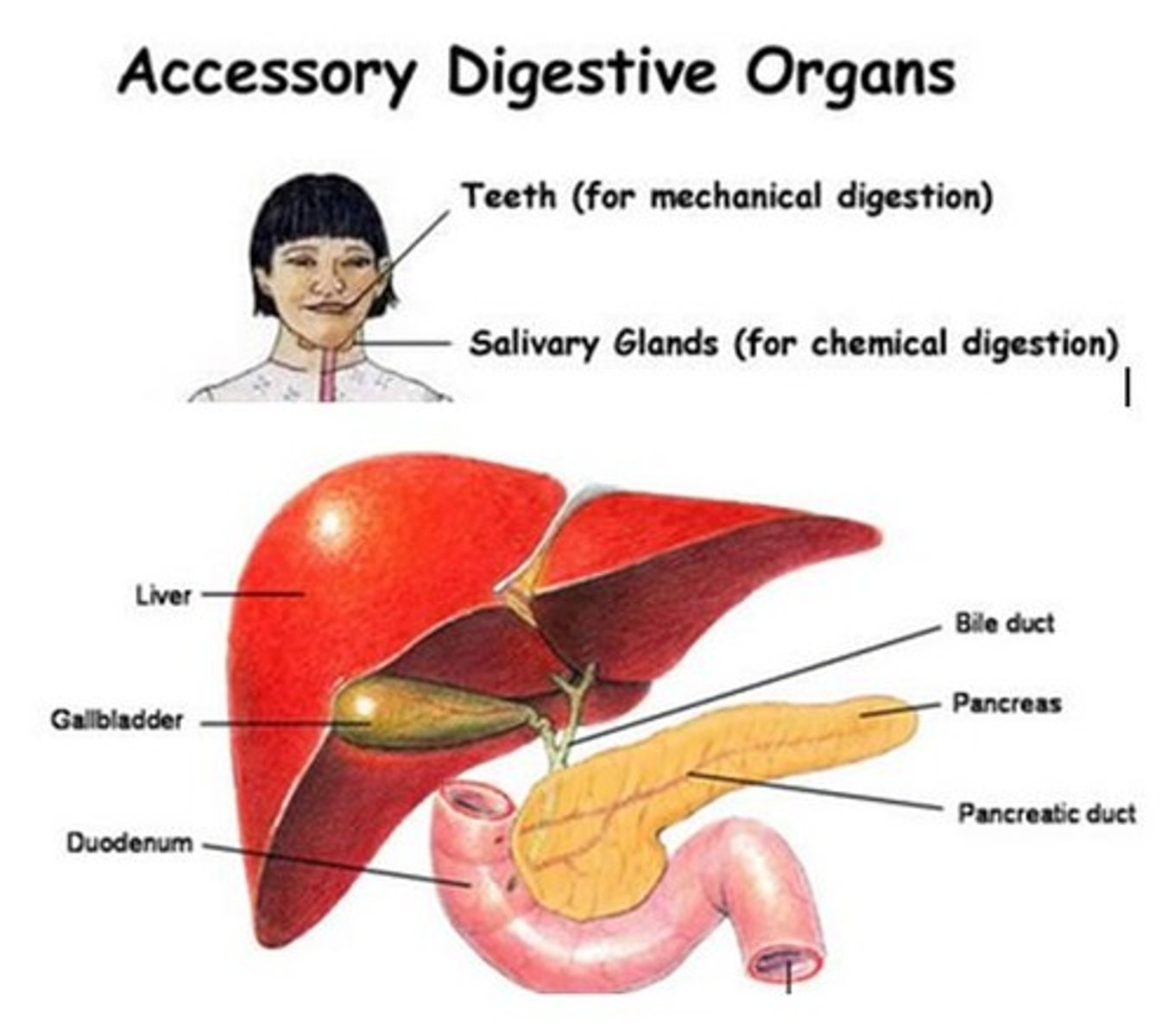
Accessory digestive organs
Organs that assist in digestion but are not part of the GI tract.
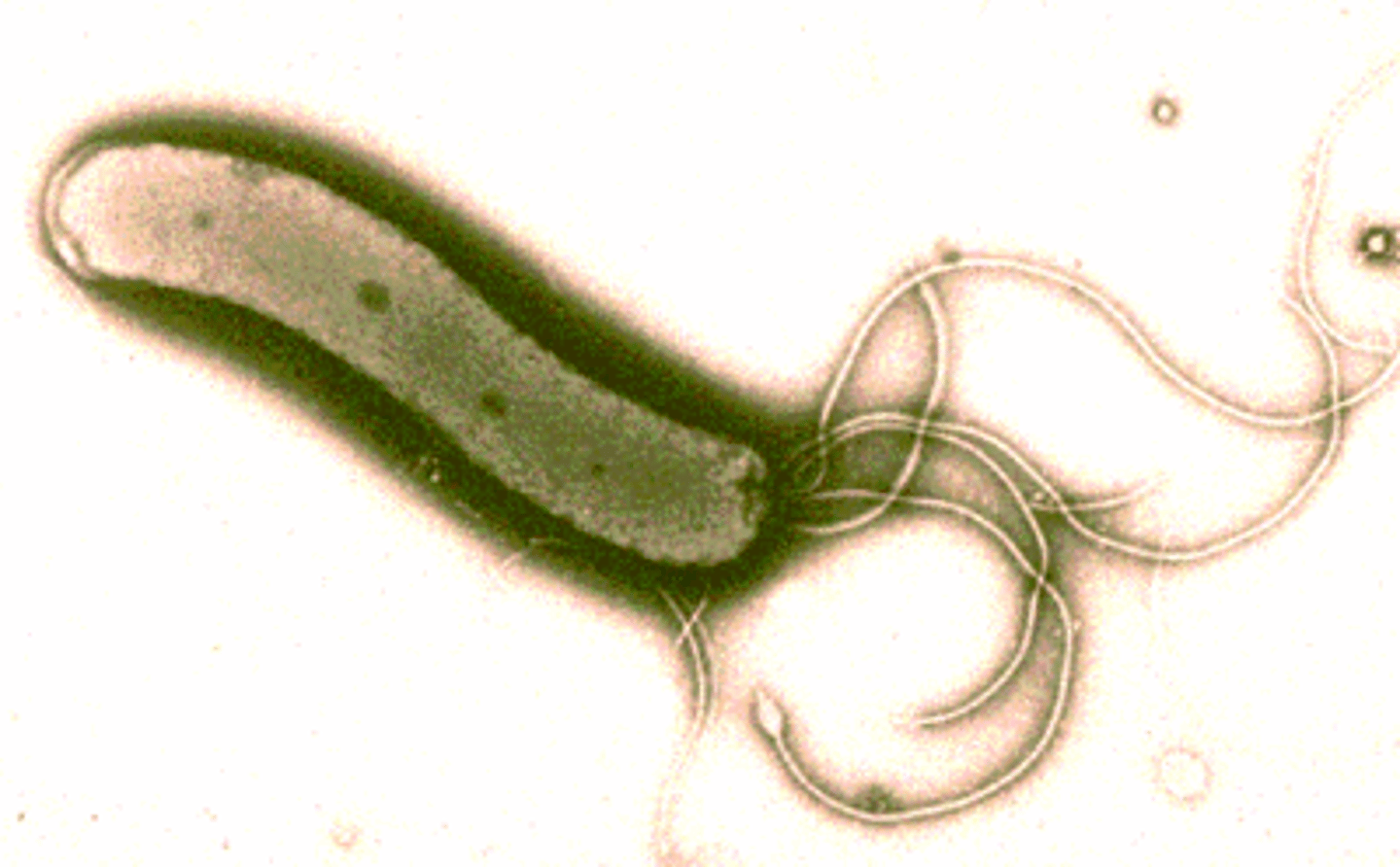
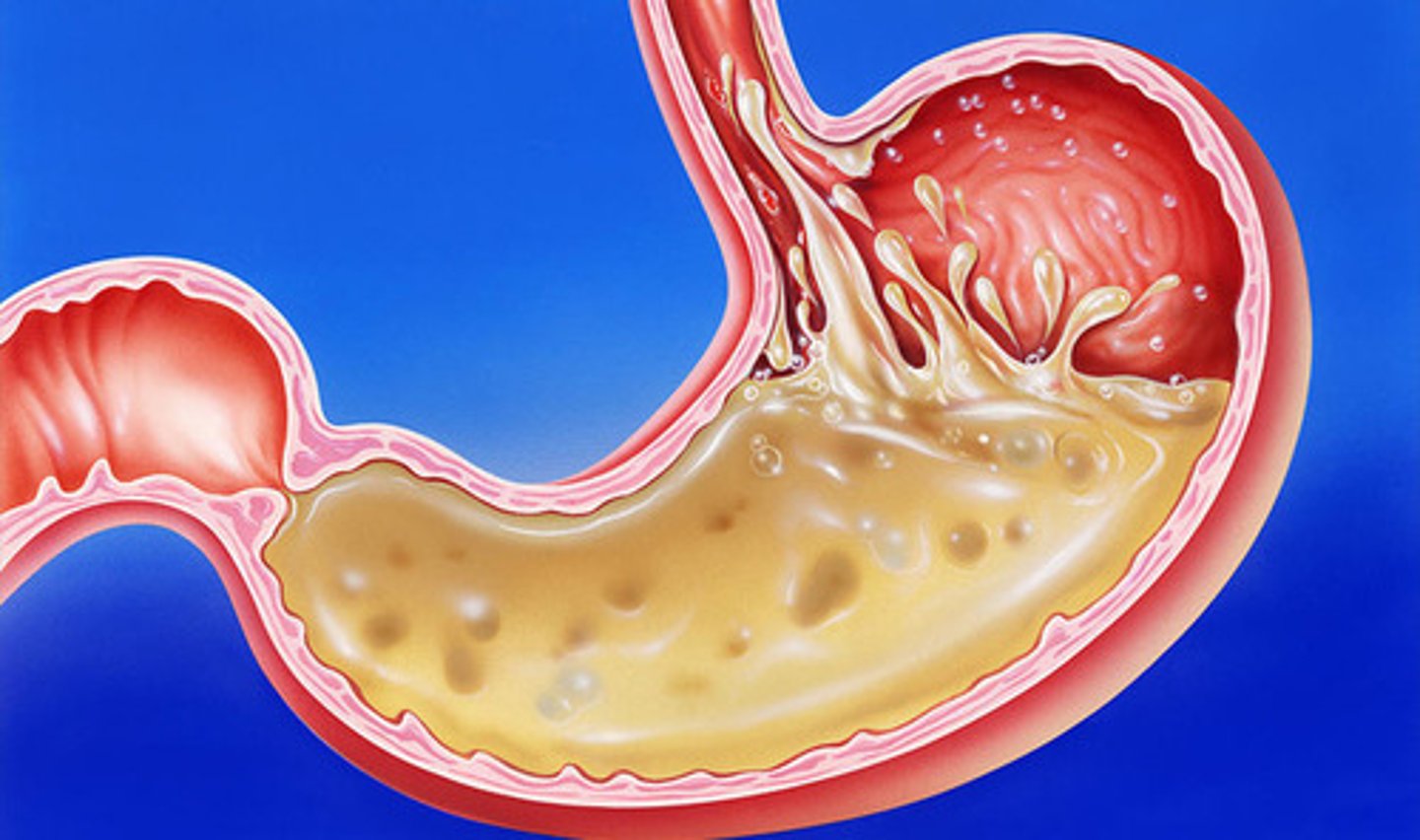
Helicobacter pylori
A type of bacteria that can cause stomach ulcers.
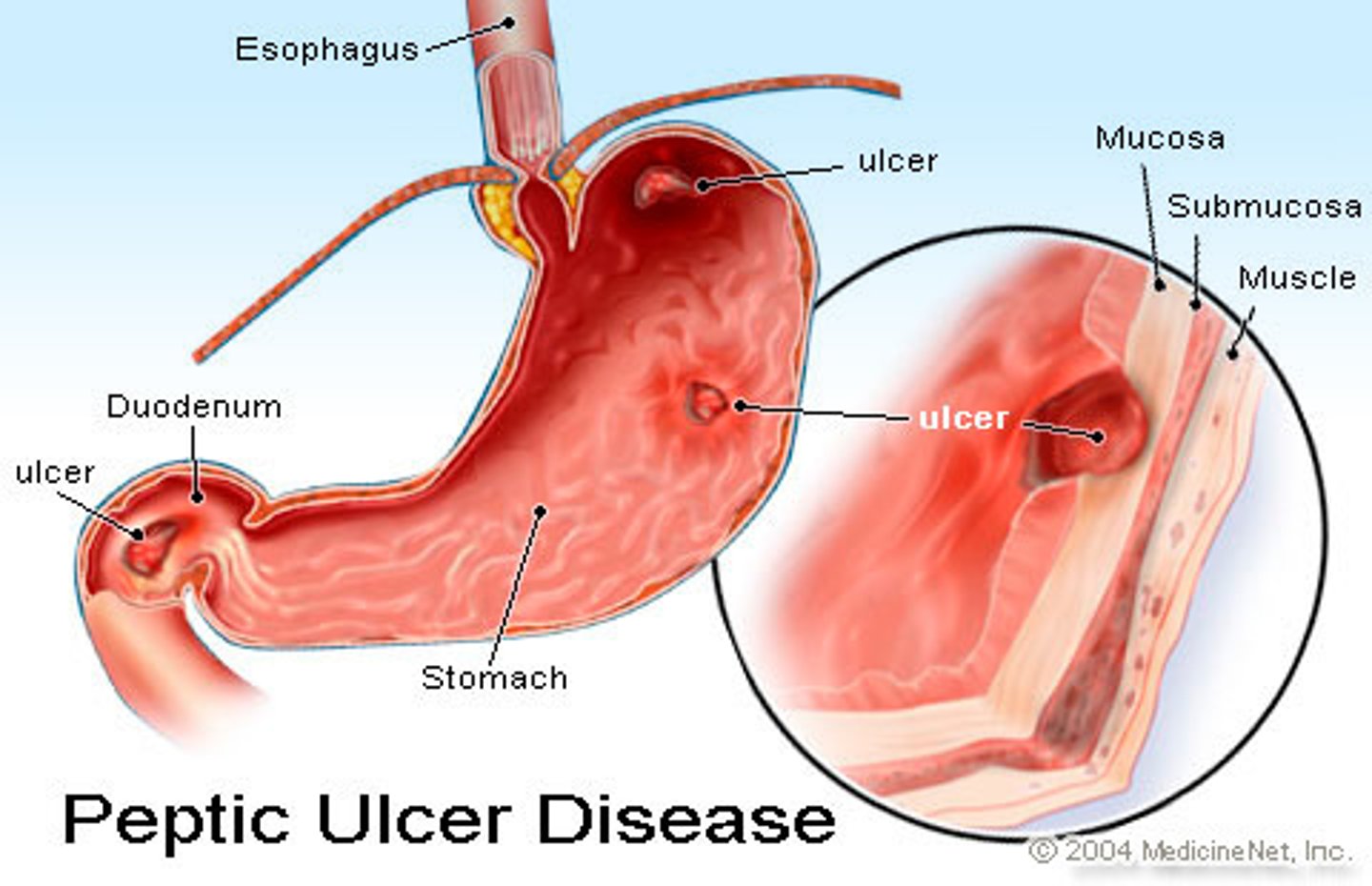
Peptic ulcer
A sore that develops on the lining of the stomach or the duodenum.
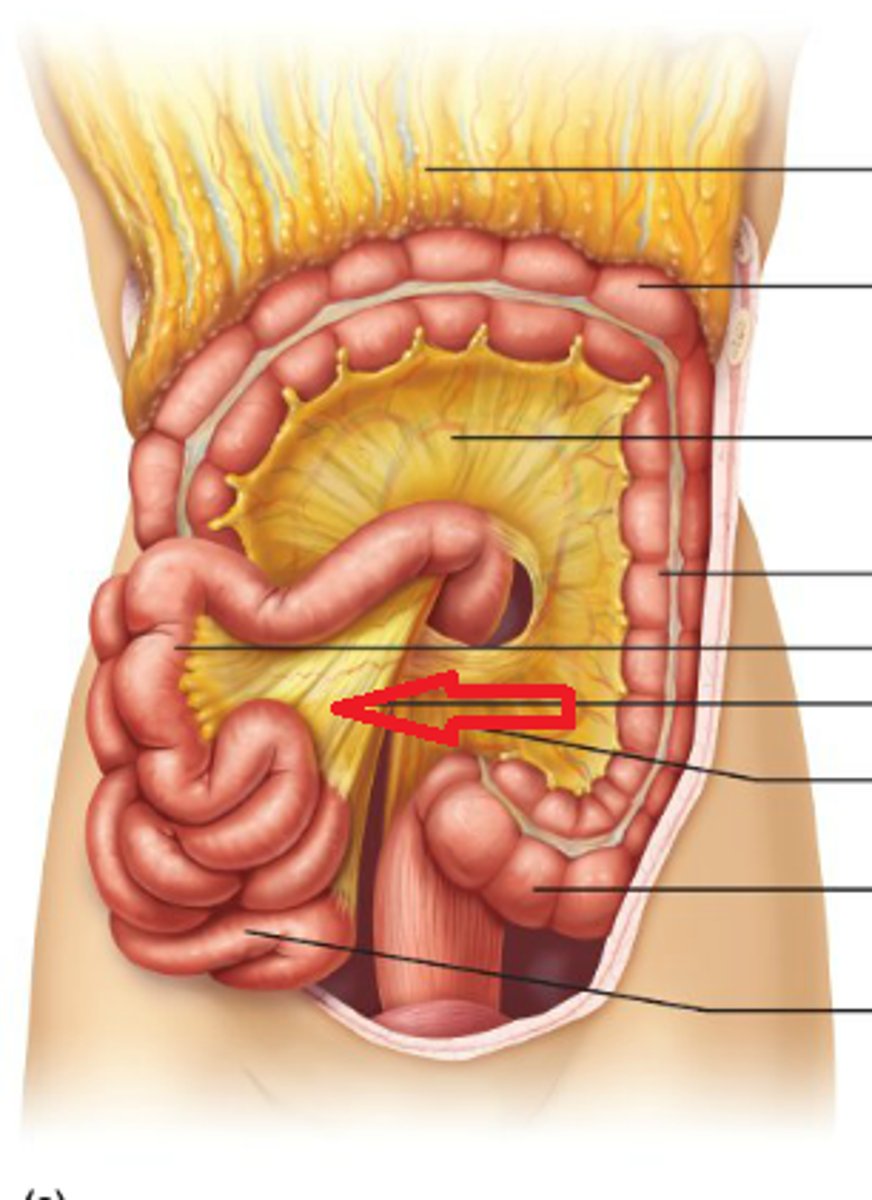
Mesentery
A fold of tissue that attaches the intestines to the abdominal wall.
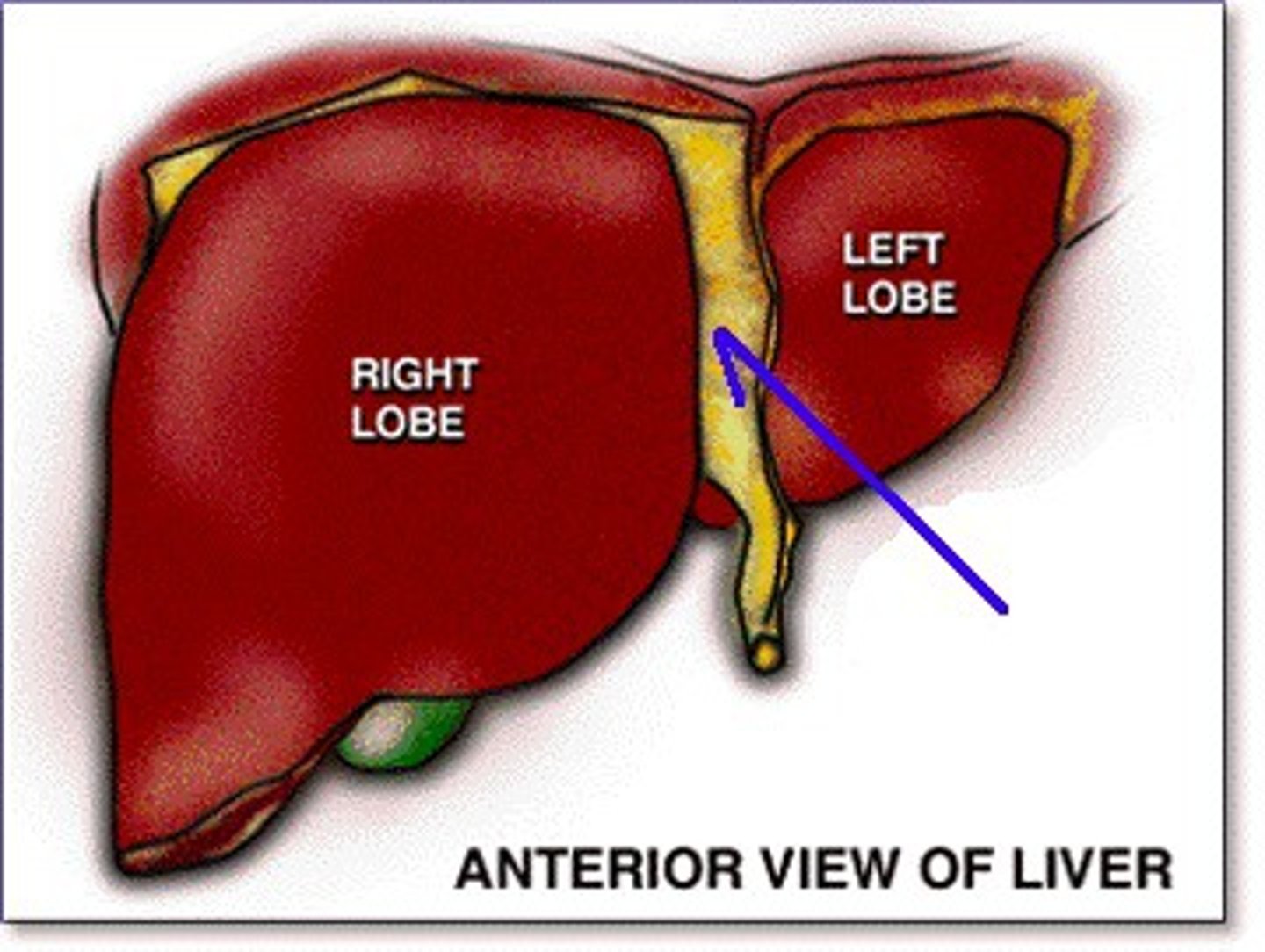
Falciform ligament
A ligament that attaches the liver to the anterior abdominal wall.
Lesser omentum
A fold of peritoneum that connects the stomach to the liver.
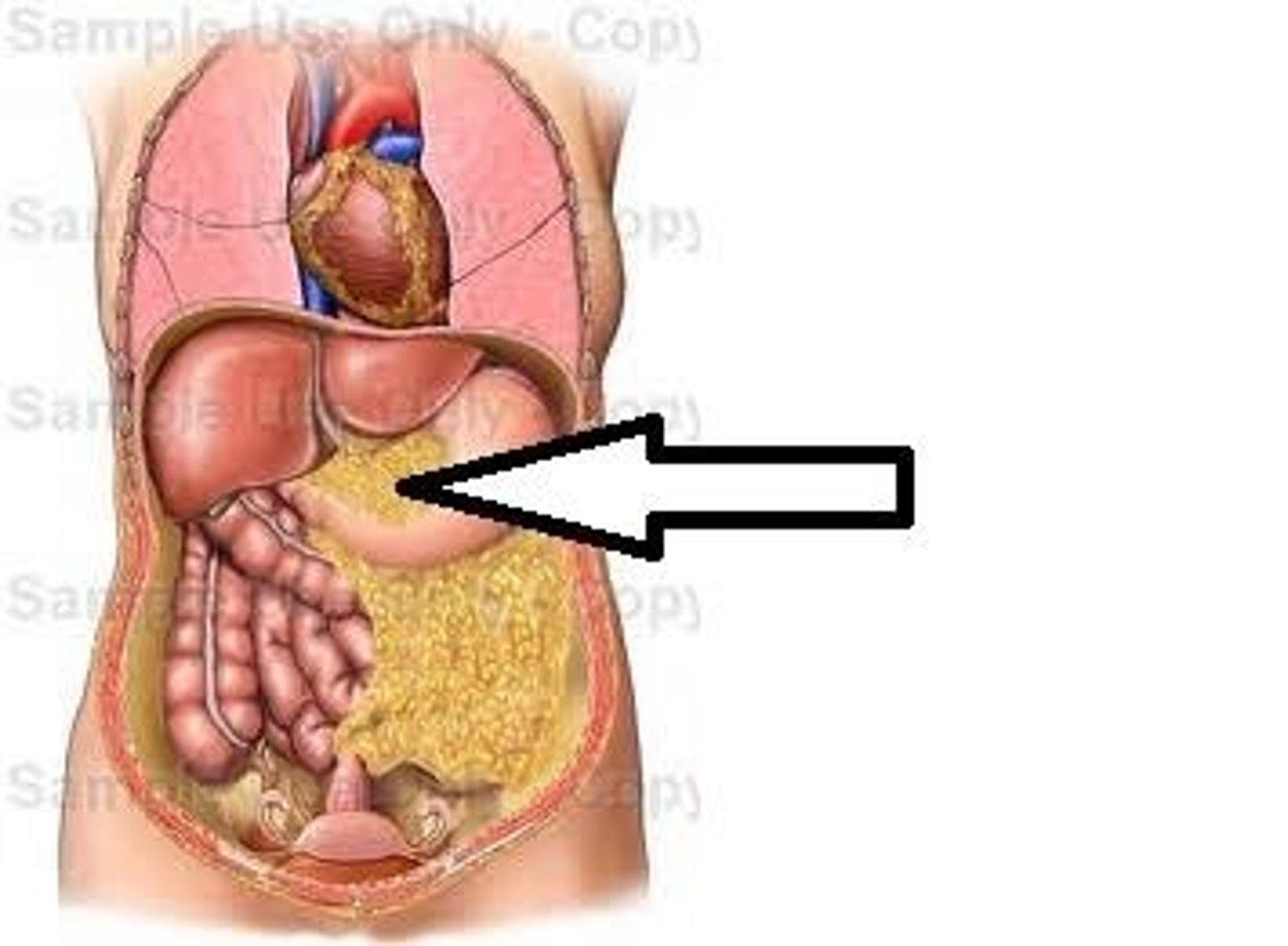
Greater omentum
A large fold of peritoneum that hangs down from the stomach.
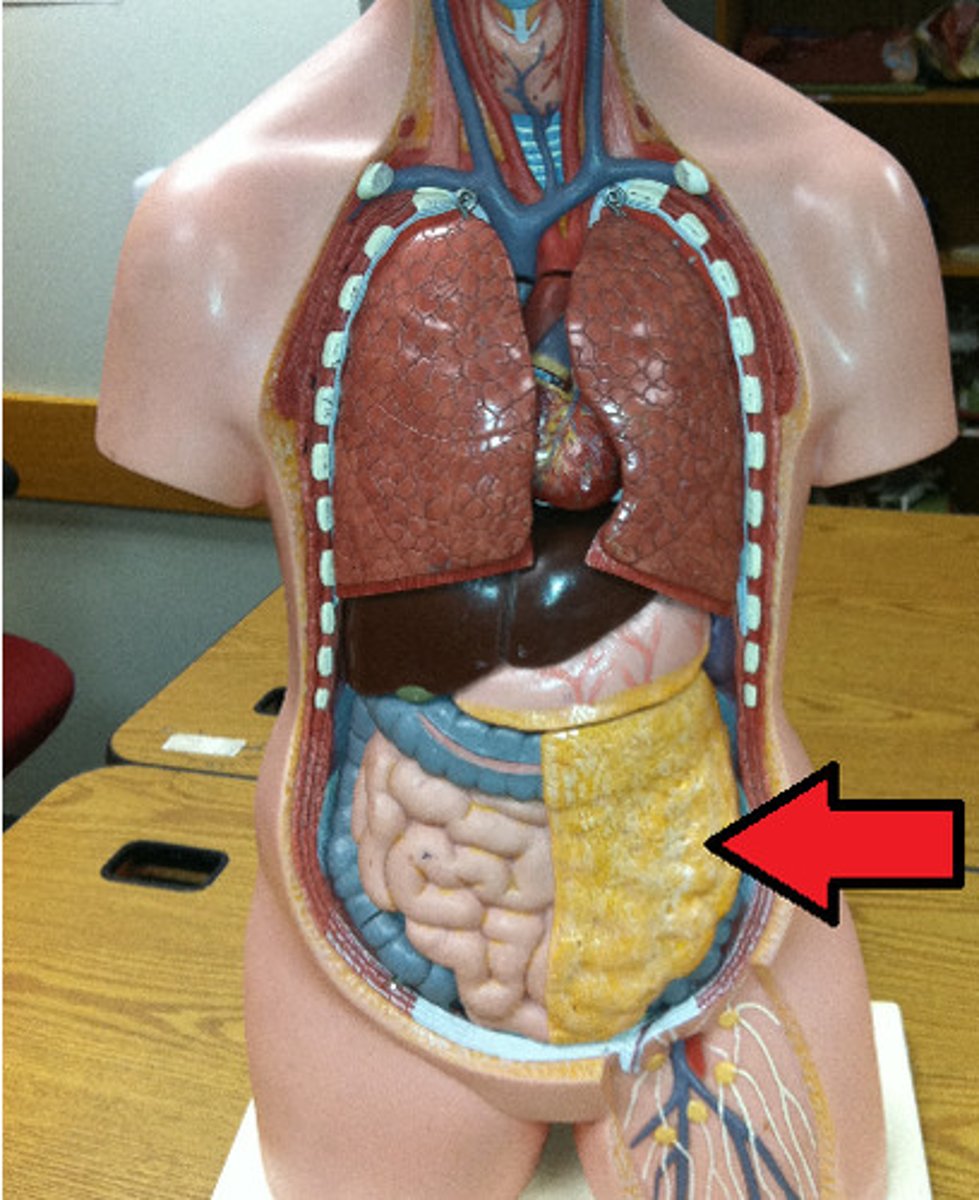
Transverse mesocolon
A peritoneal fold that connects the transverse colon to the posterior abdominal wall.
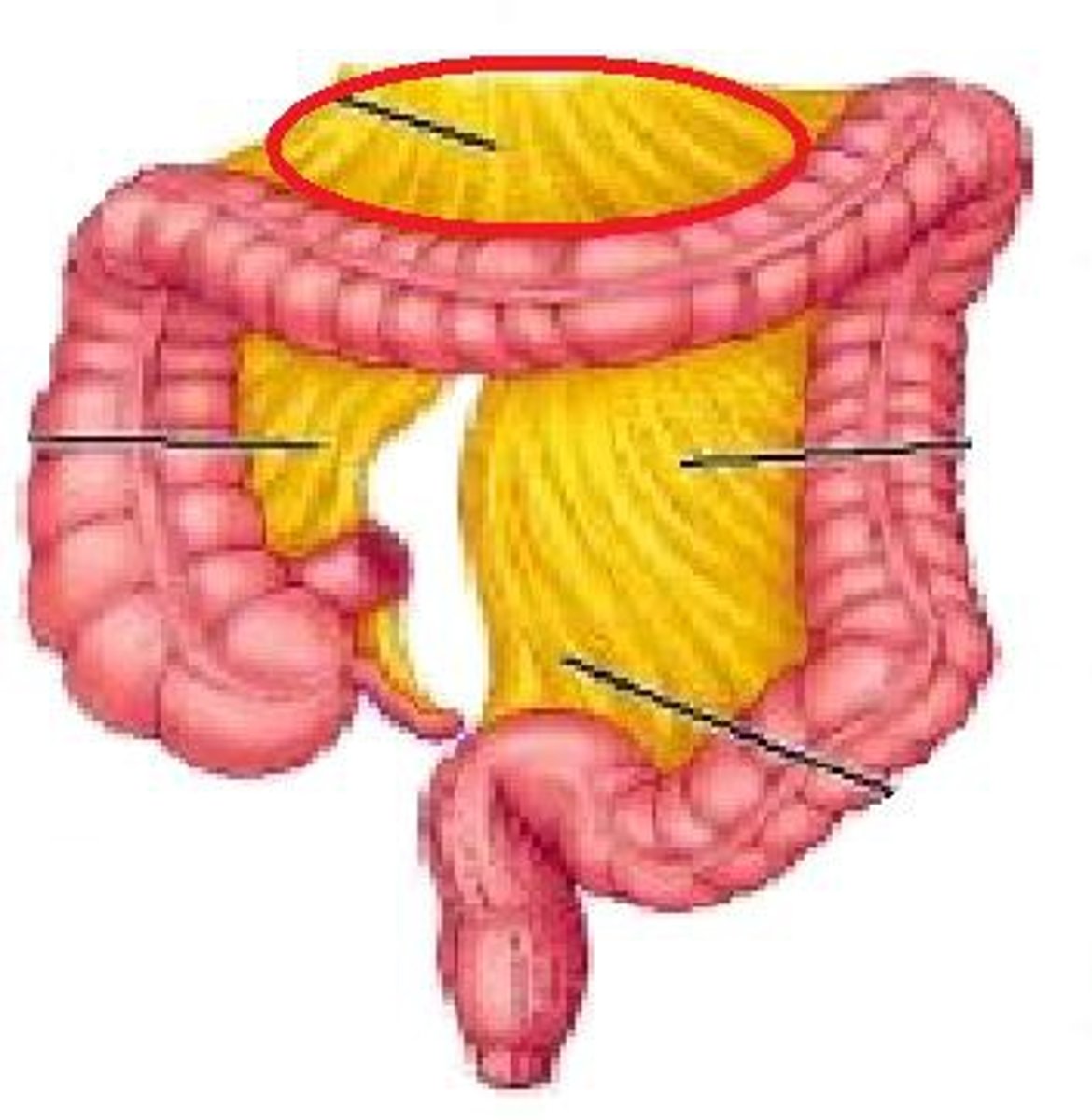
Visceral peritoneum
The layer of peritoneum that covers the abdominal organs.
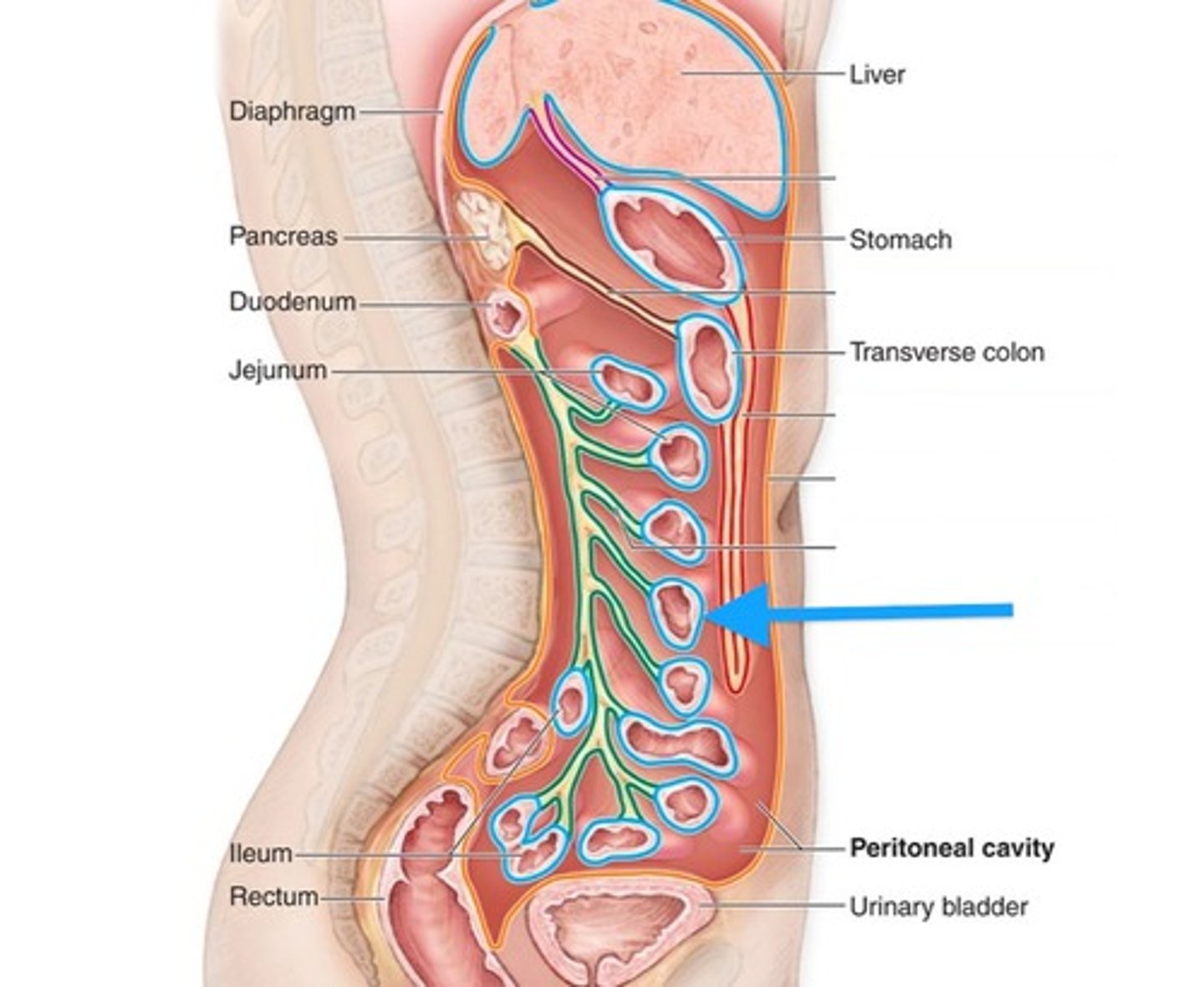
Parietal peritoneum
The layer of peritoneum that lines the abdominal cavity.
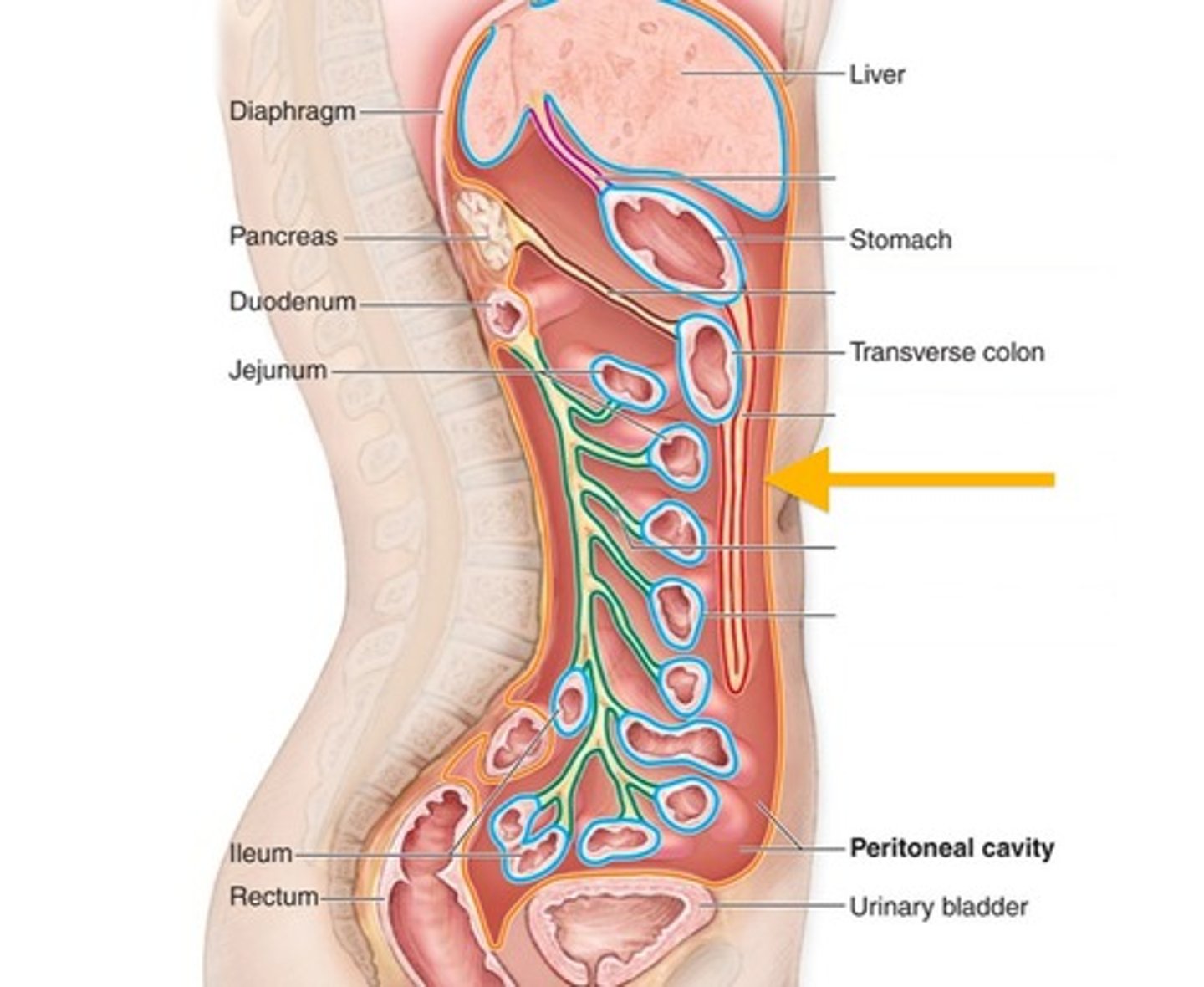
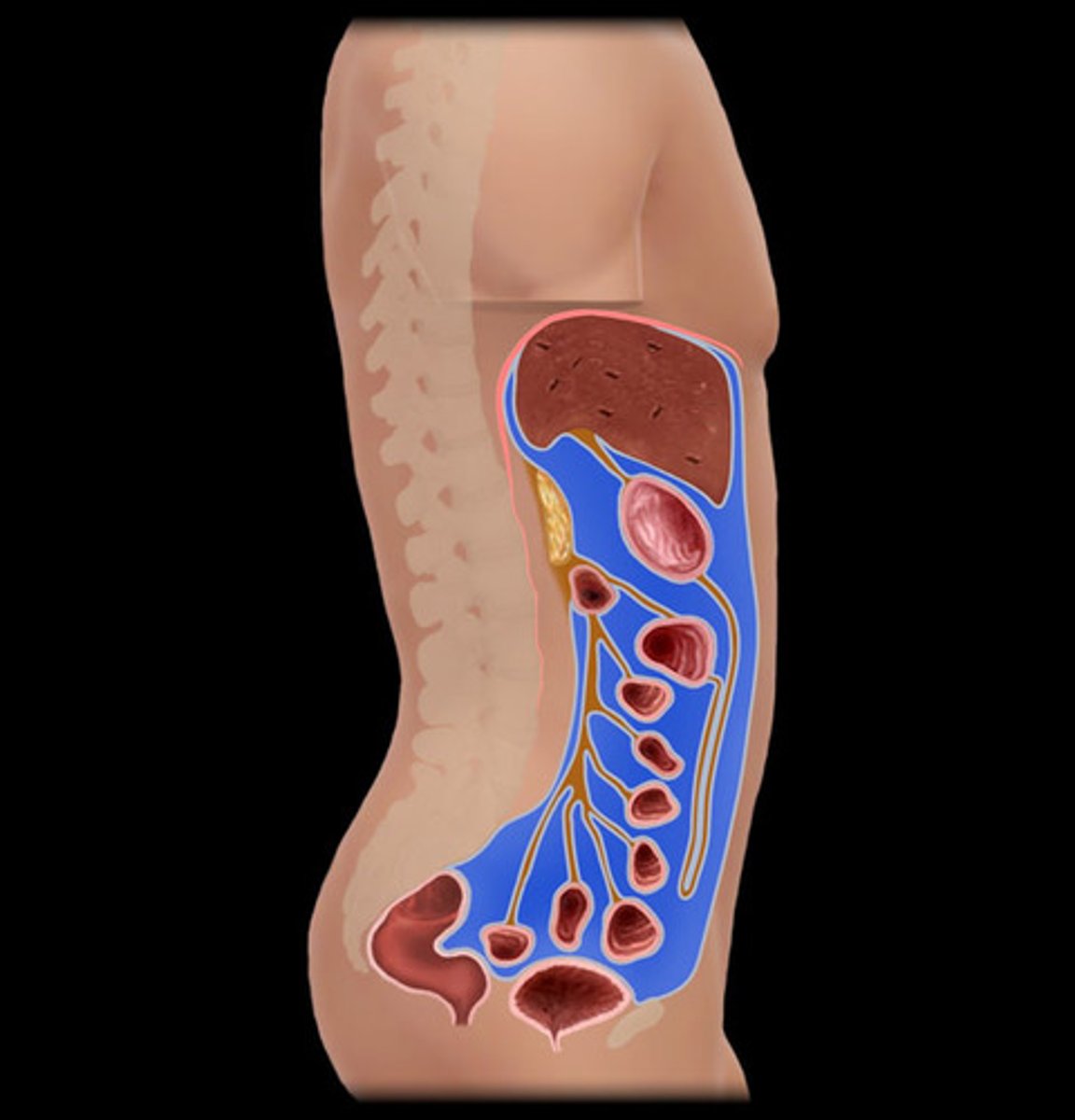
Peritoneal cavity
The space within the abdomen that contains the abdominal organs.
Ingestion
The process of taking food into the body.
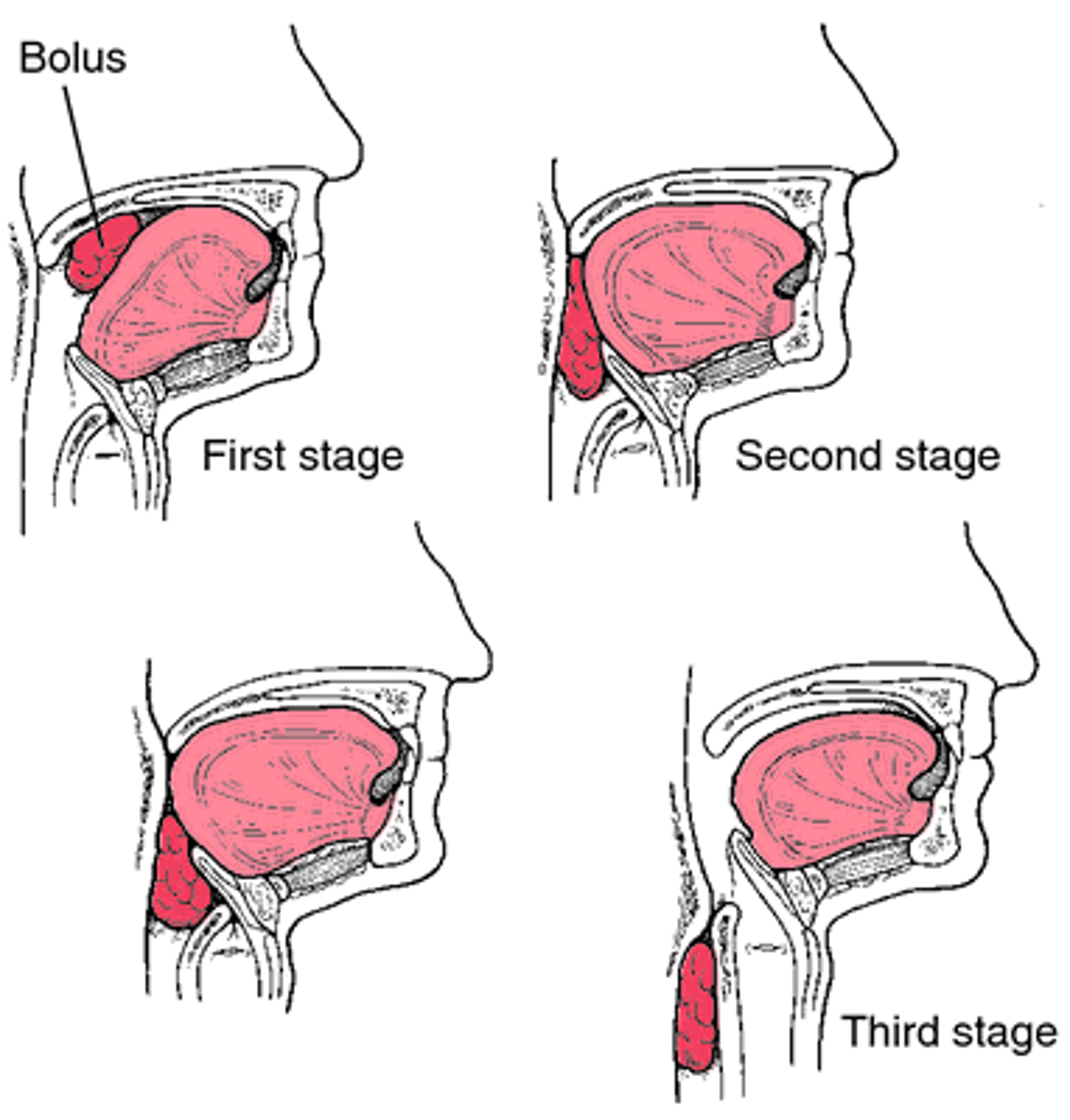
Deglutition
The act of swallowing.
Propulsion
The movement of food through the digestive tract.
Mechanical breakdown
The physical process of breaking down food into smaller pieces.
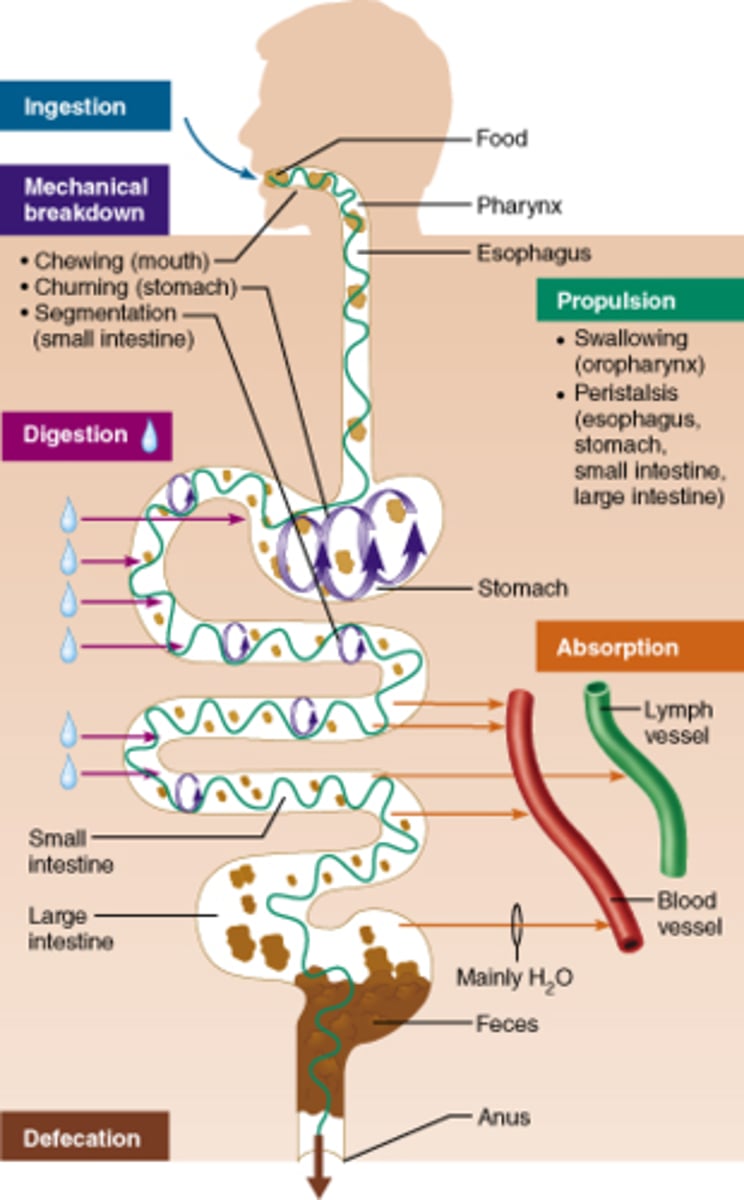
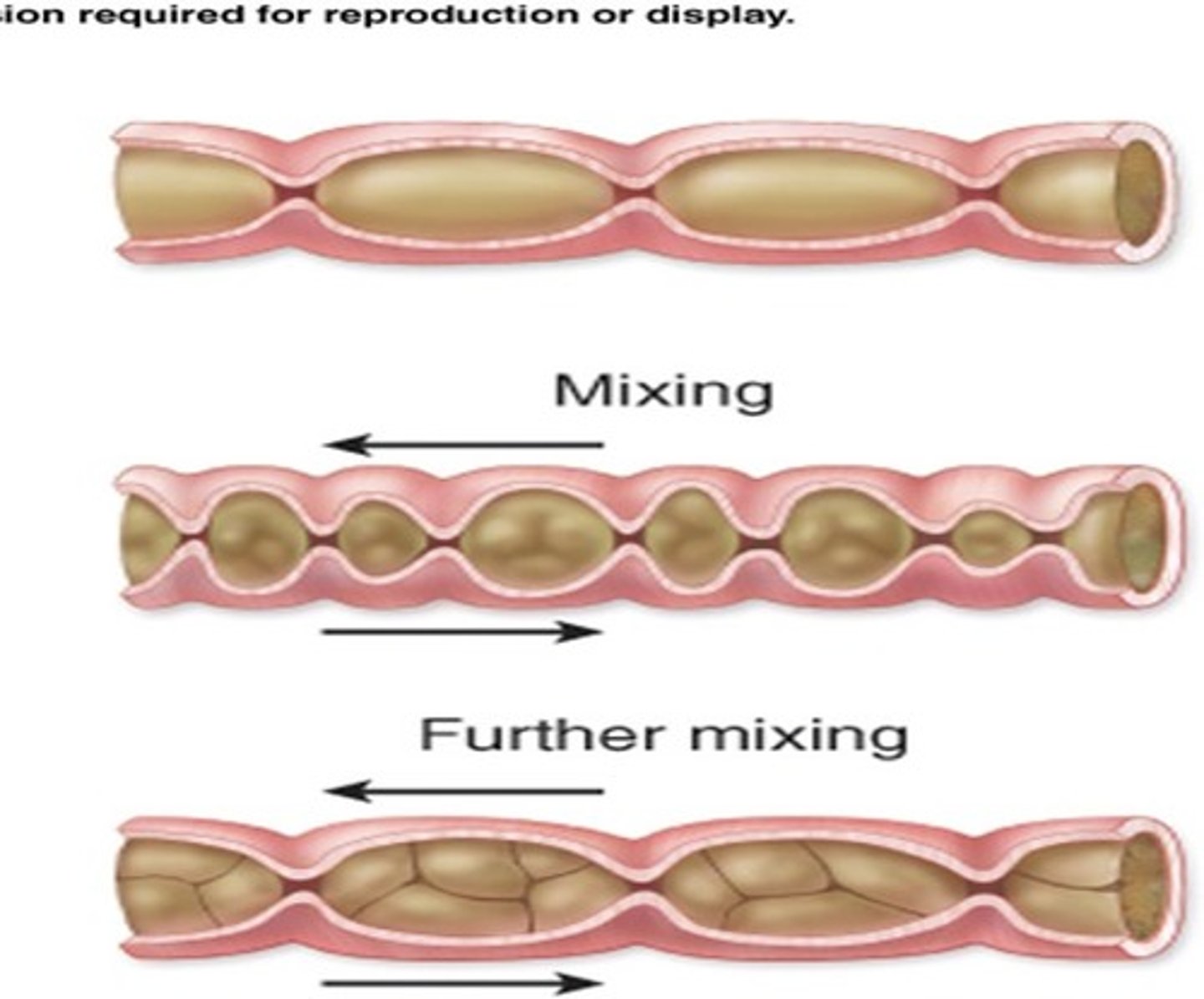
Segmentation
The process of mixing food in the intestines.
Digestion
The chemical breakdown of food into smaller molecules.
Absorption
The process of taking nutrients from the digestive tract into the bloodstream.
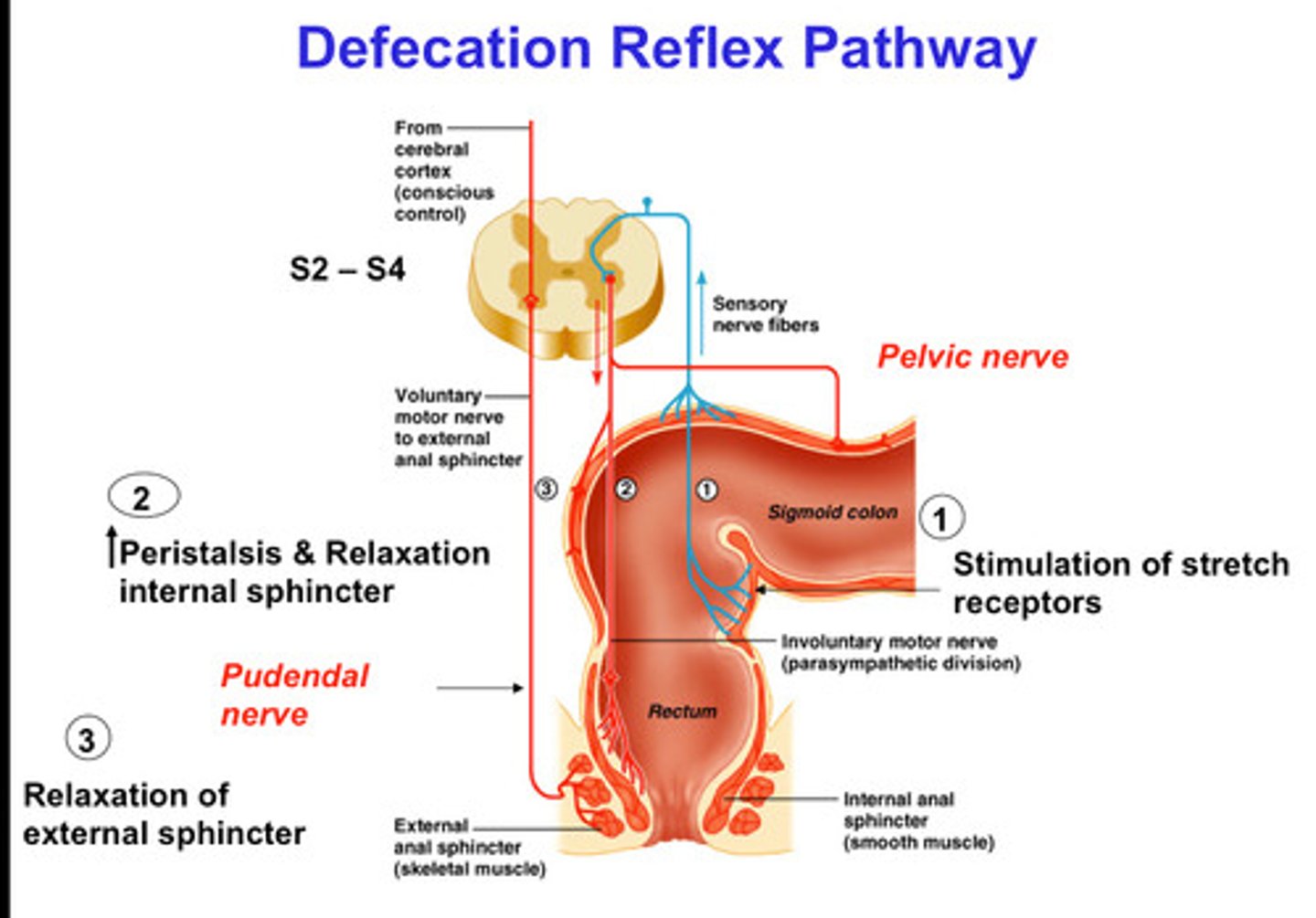
Defecation
The elimination of indigestible substances from the body.
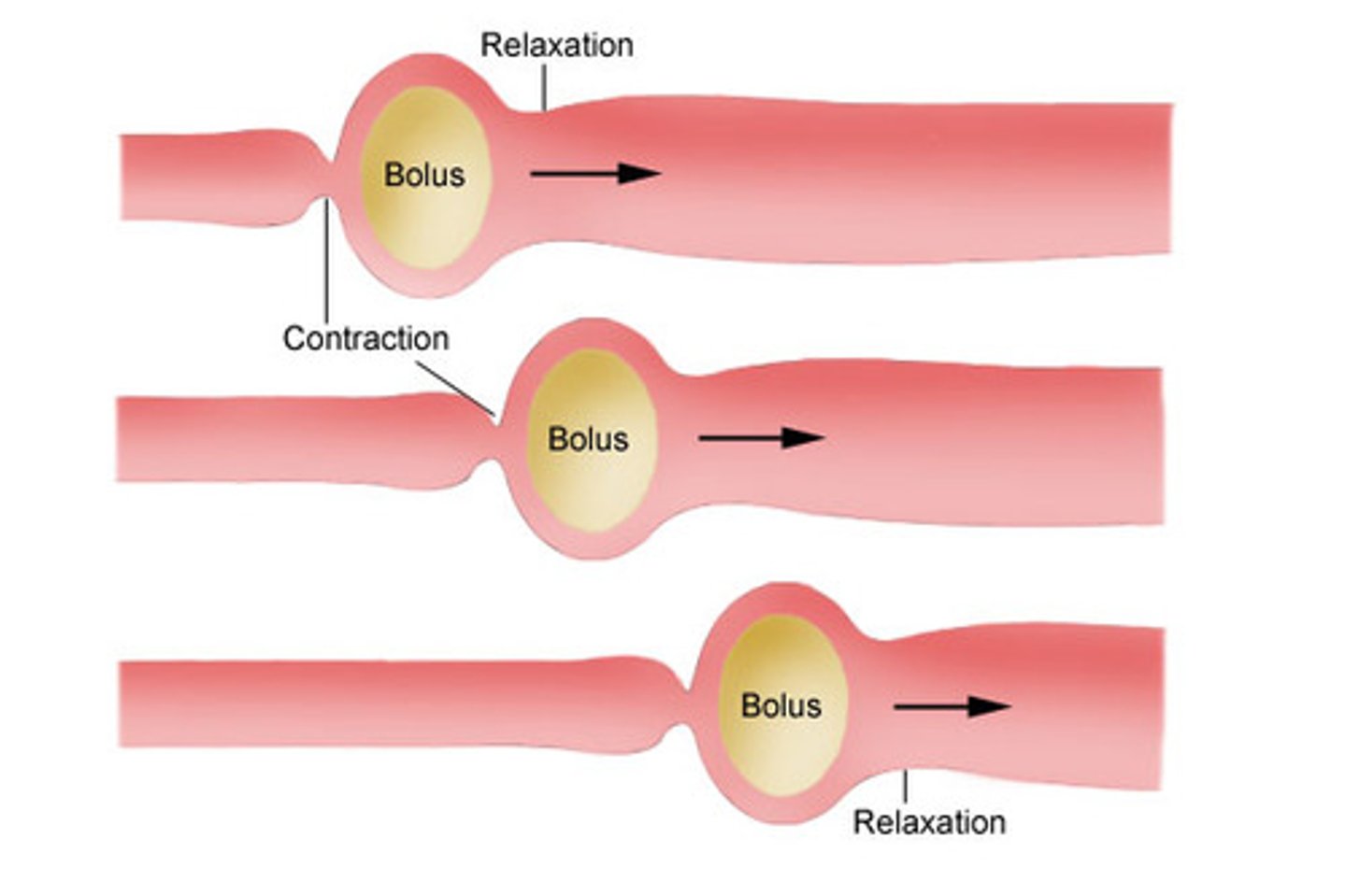
Peristalsis
The wave-like muscle contractions that move food through the digestive tract.
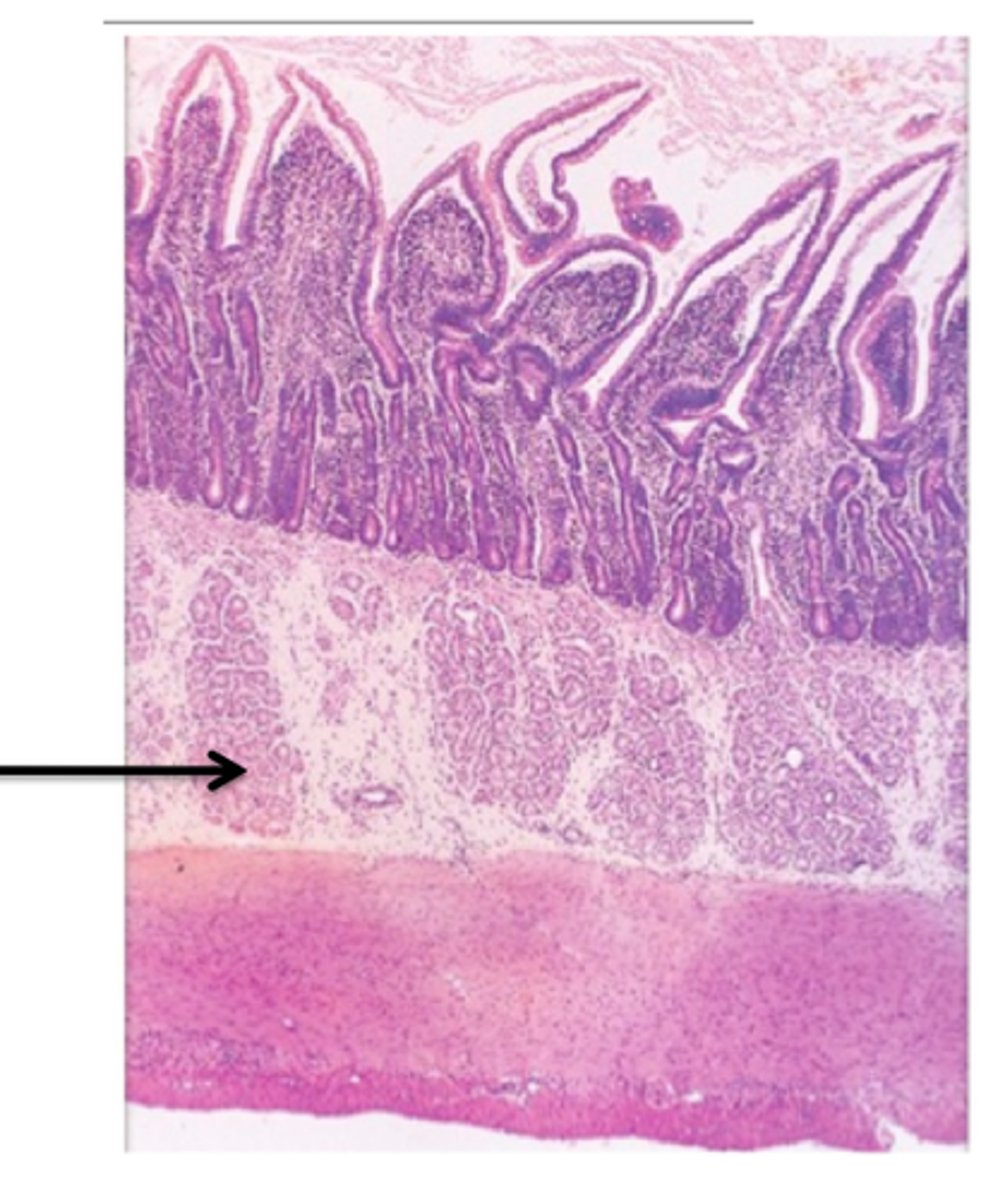
Mucosa
The innermost layer of the GI tract, consisting of epithelium, lamina propria, and muscularis mucosae.
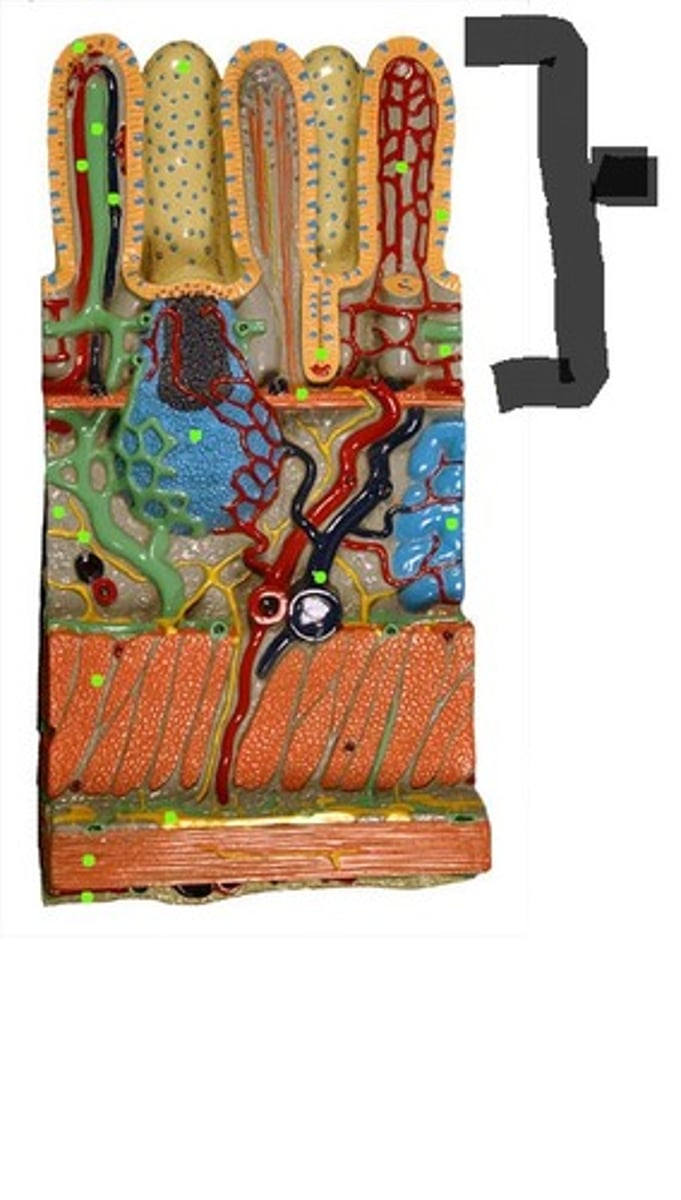

Submucosa
The layer of connective tissue beneath the mucosa.
Muscularis externa
The layer of muscle responsible for peristalsis, consisting of a circular layer and a longitudinal layer.
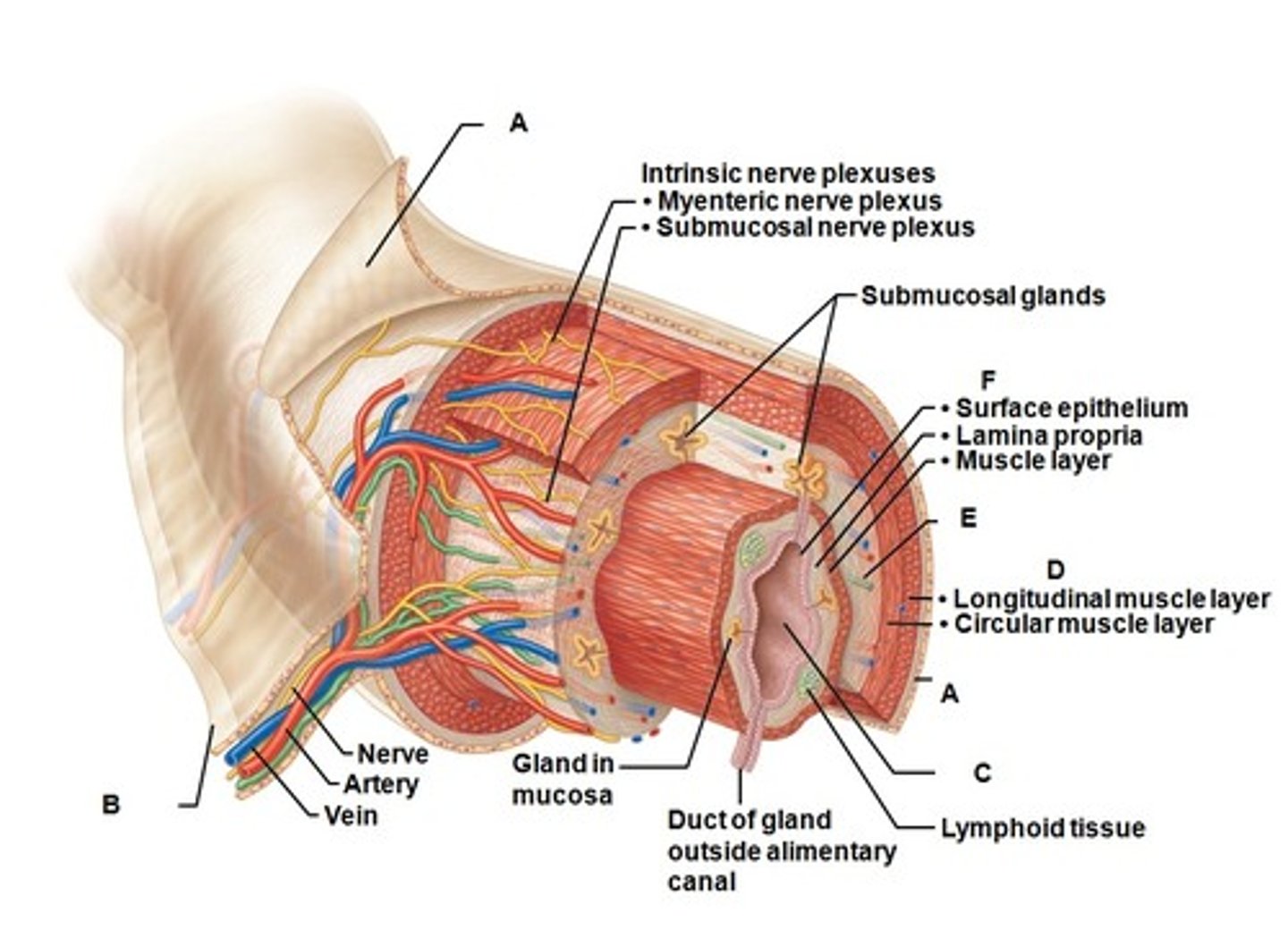
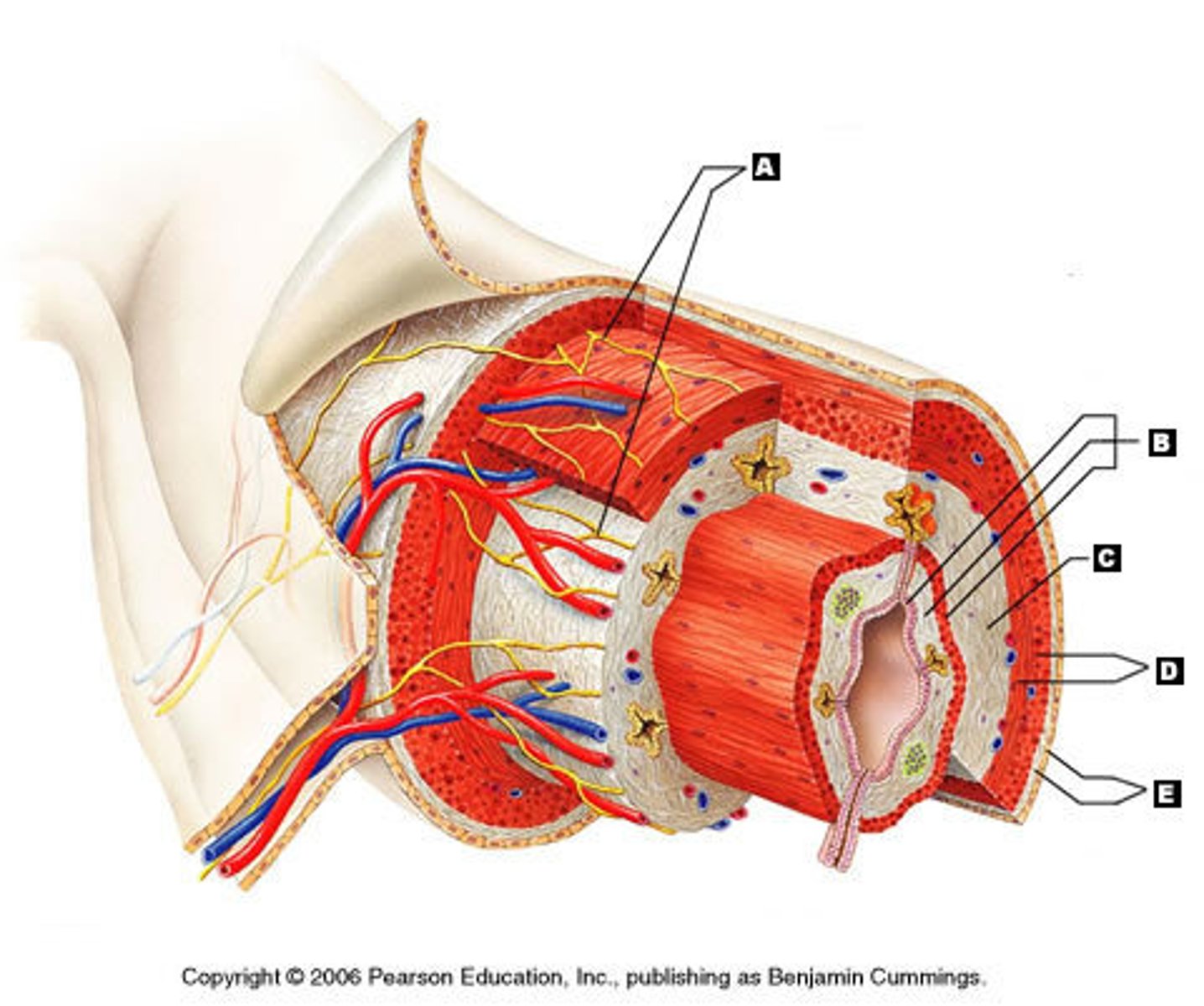
Enteric nervous system
A complex network of neurons that governs the function of the gastrointestinal system.
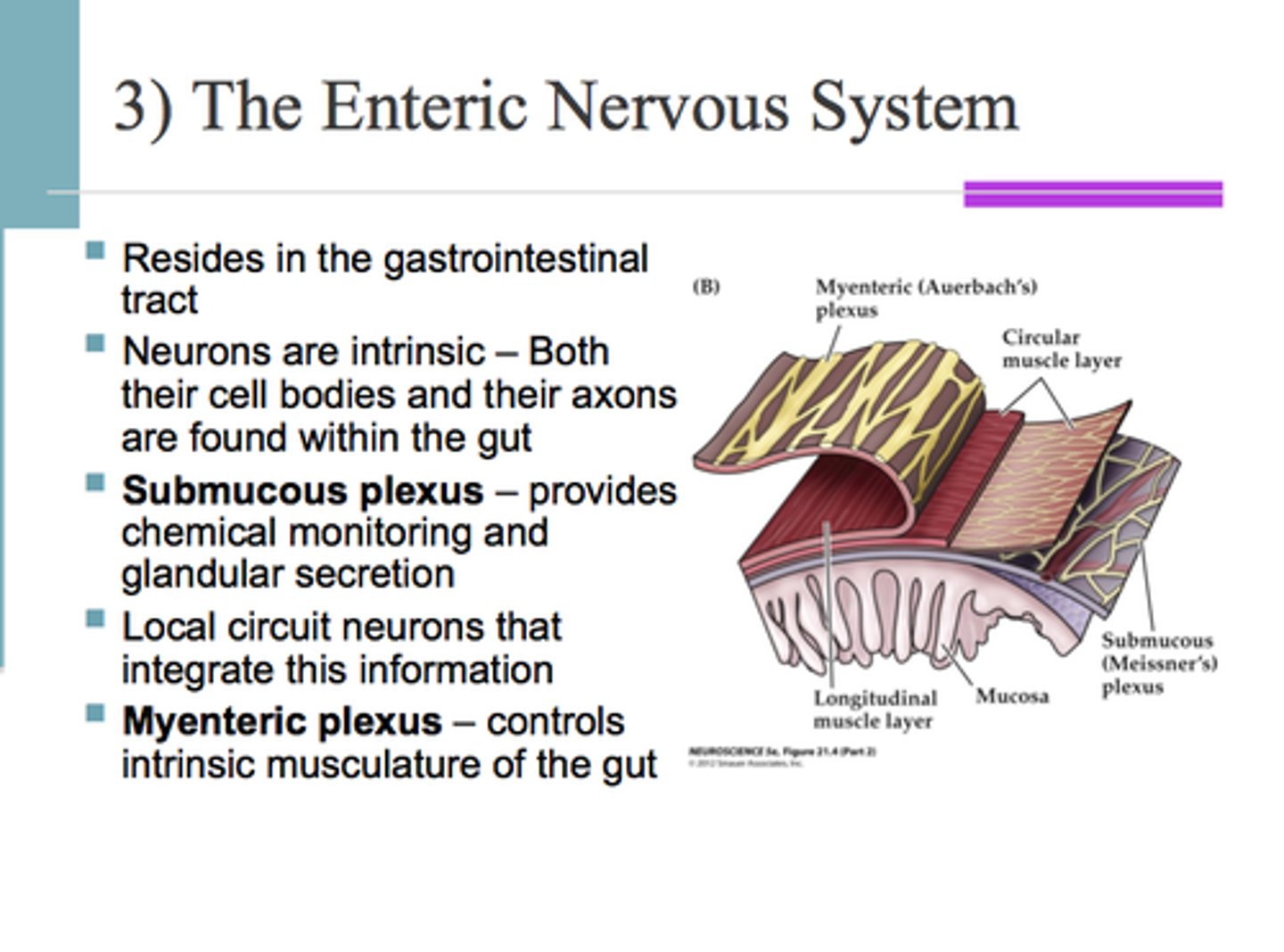
Myenteric nerve plexus
A nerve plexus located between the circular and longitudinal layers of the muscularis externa.
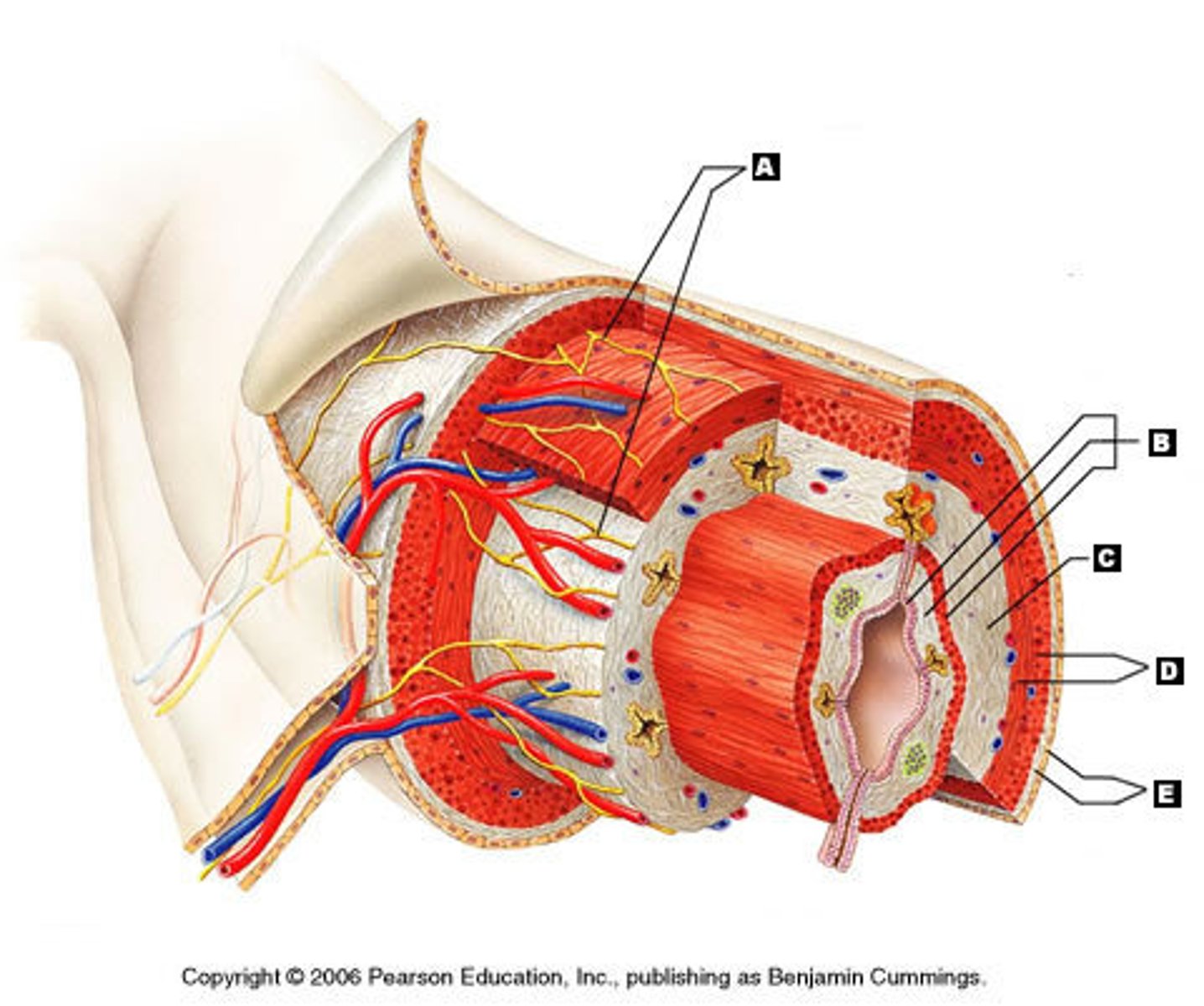
Submucosal nerve plexus
A nerve plexus located in the submucosa.
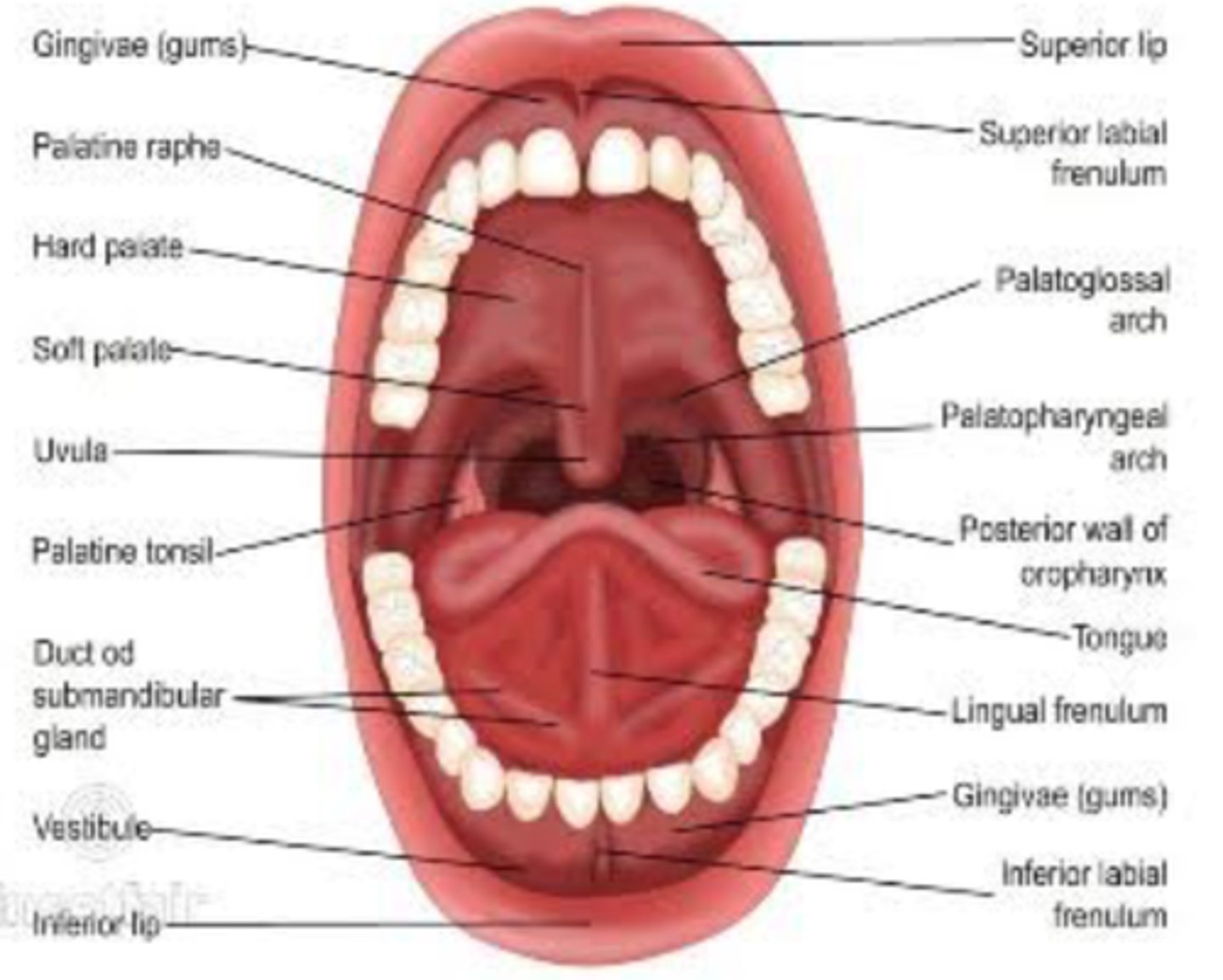
Mouth
The opening through which food enters the body.

Oral cavity proper
The space within the mouth behind the gums and teeth.
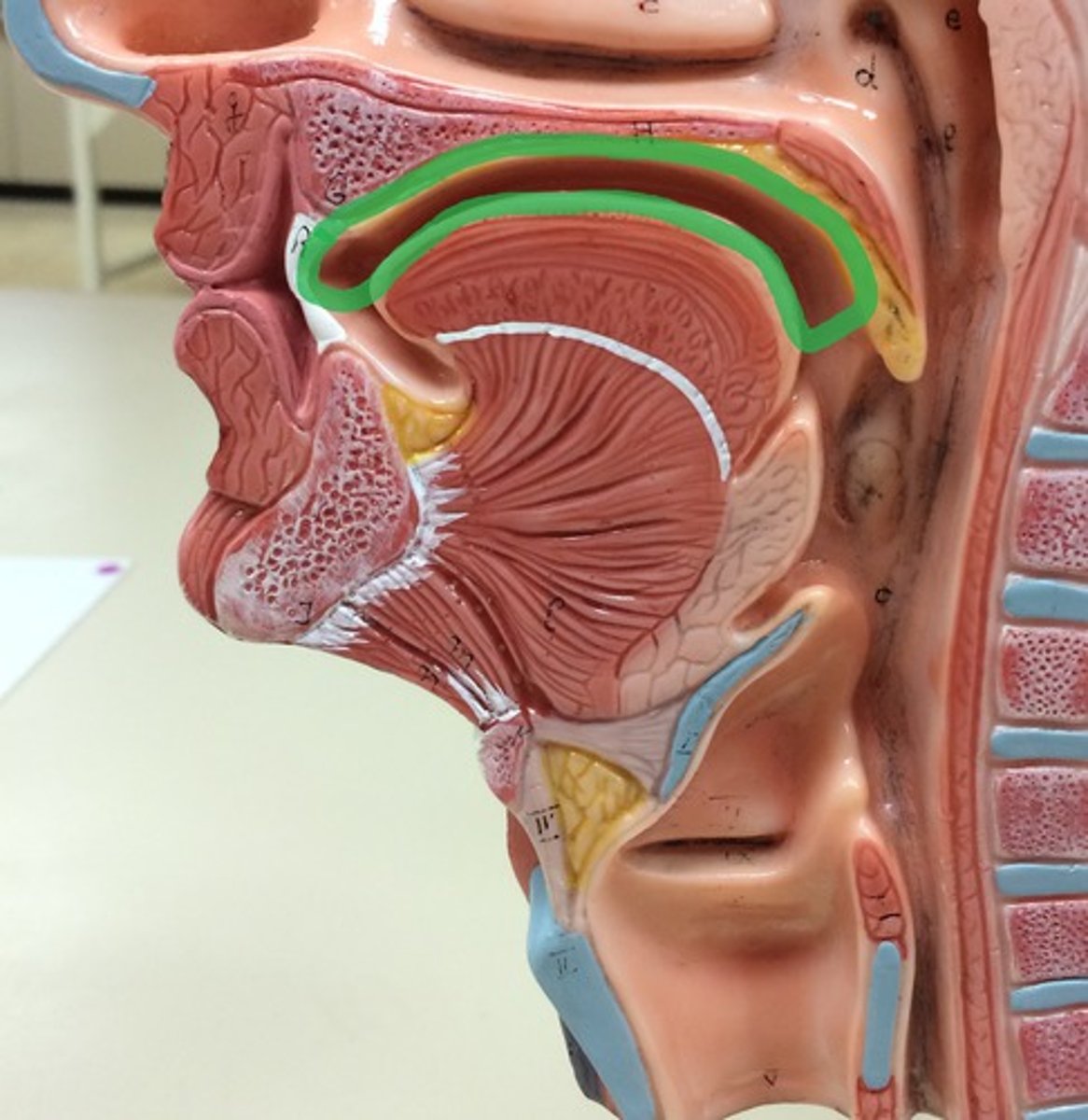
Oral vestibule
The space between the lips and the gums.
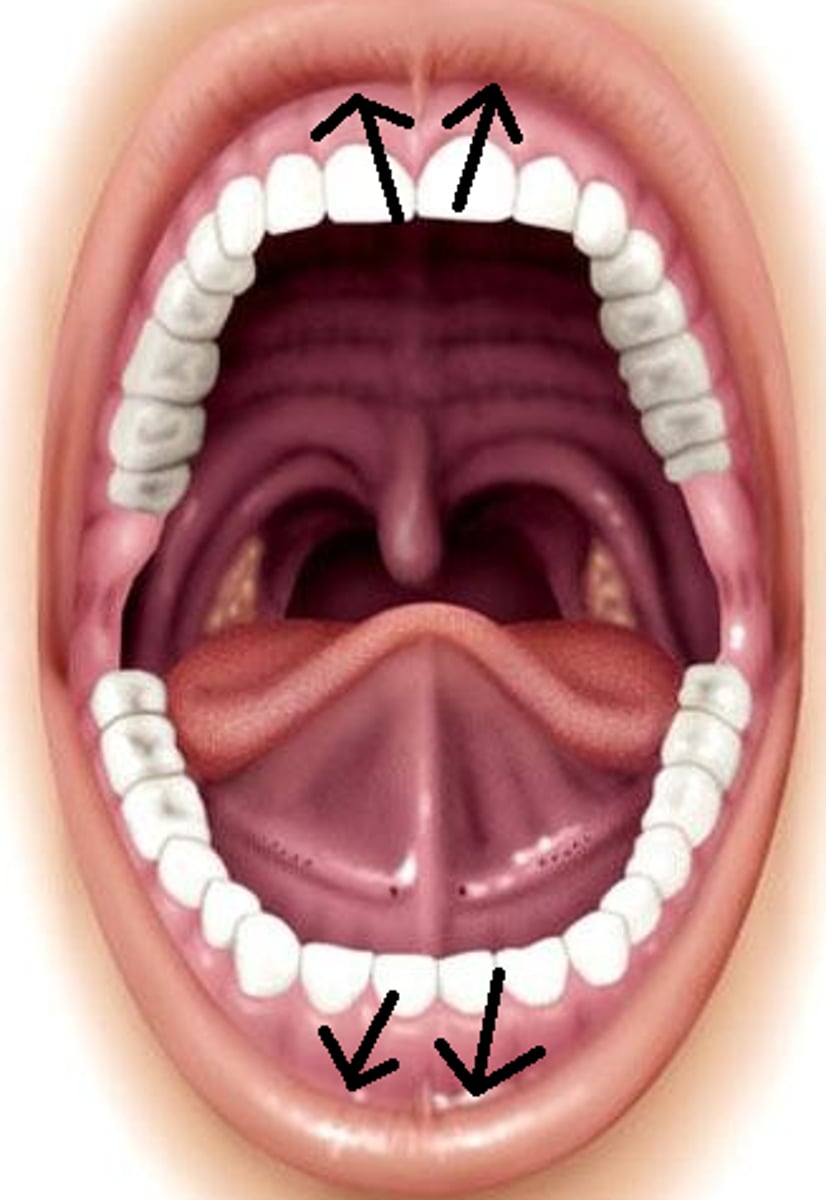
Tongue
A muscular organ in the mouth that aids in the manipulation of food.
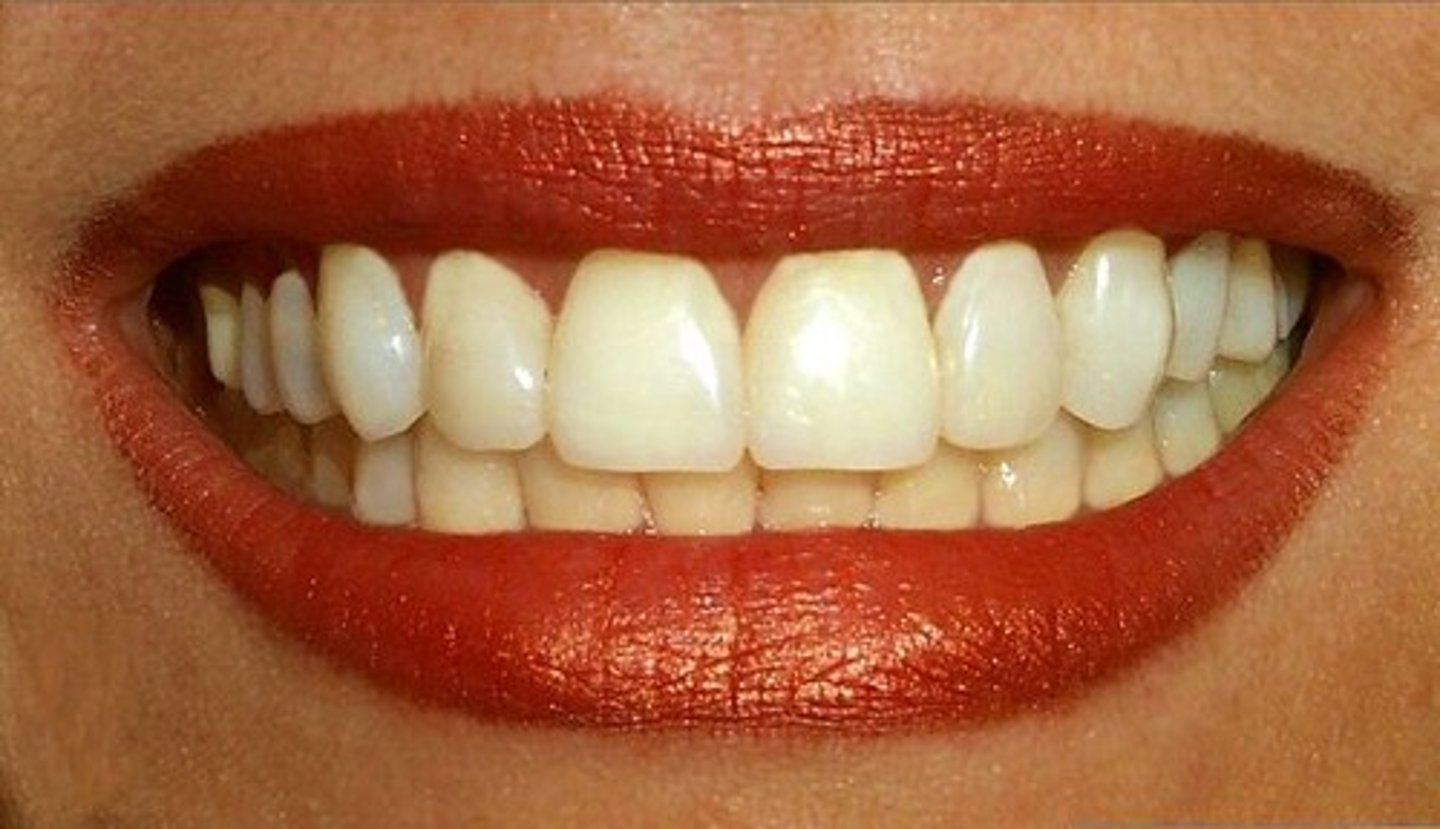
Teeth
Hard structures in the mouth used for biting and chewing food.
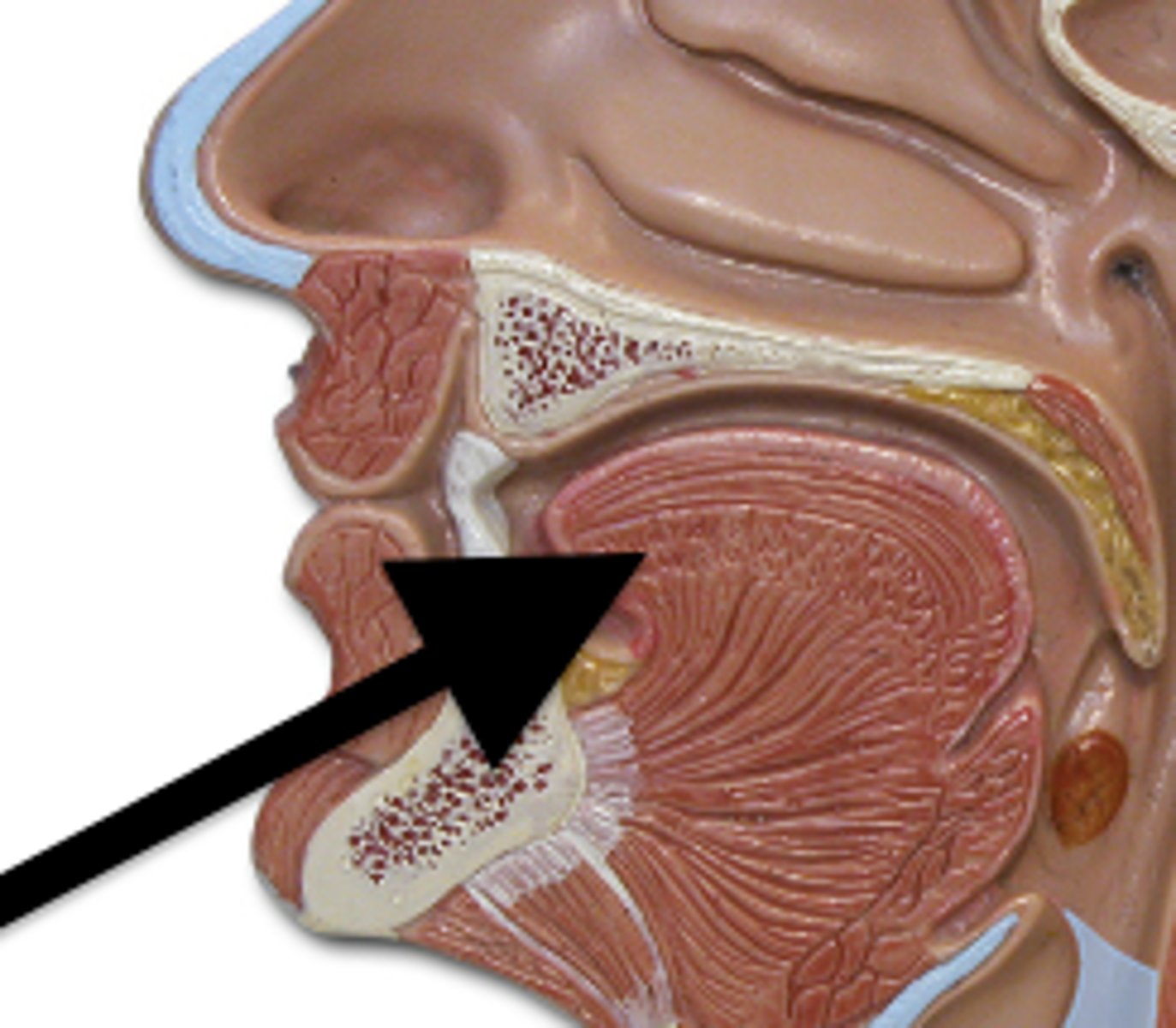
The different tonsils
Lymphoid tissues located in the throat that help fight infections.
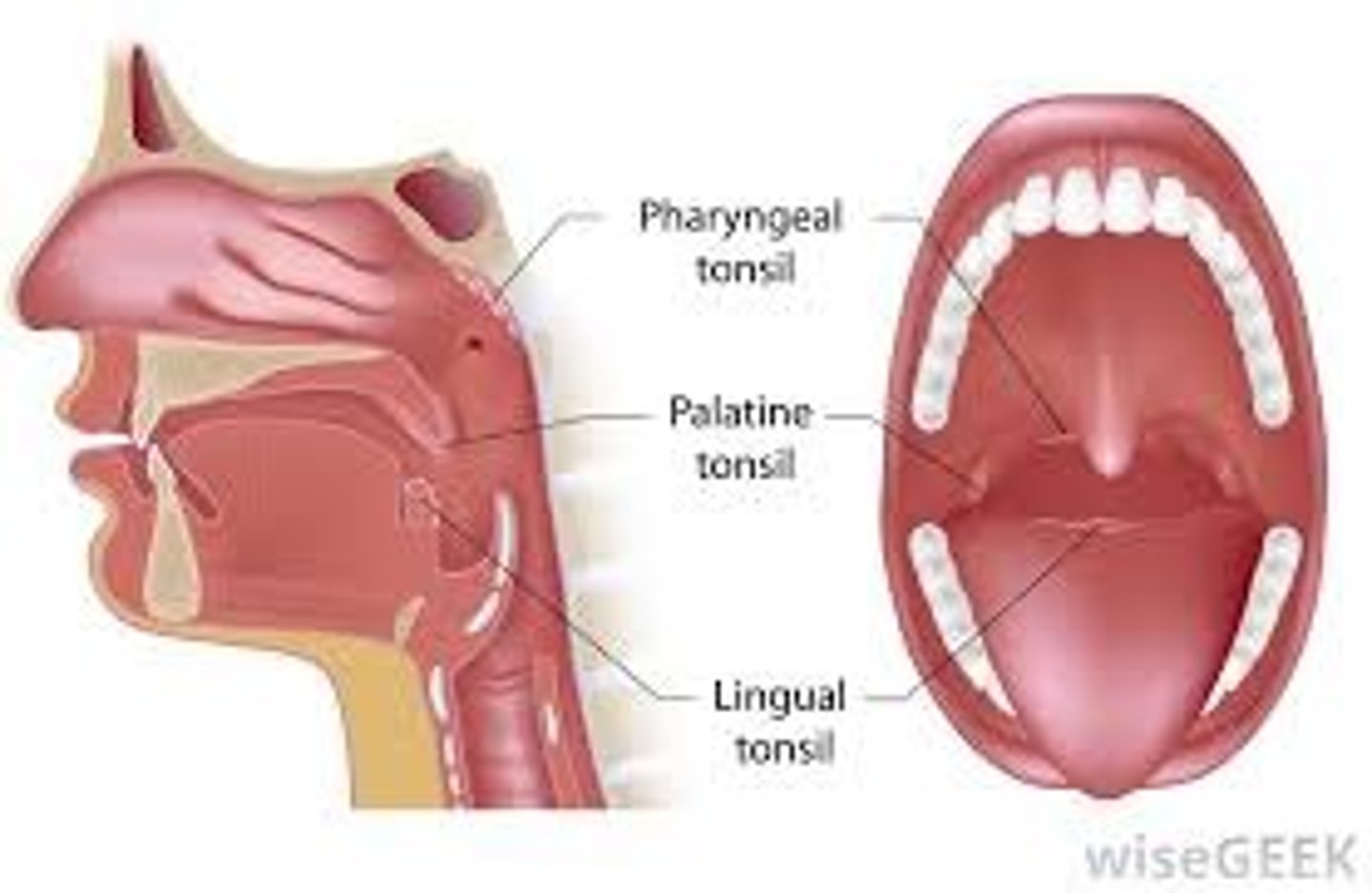
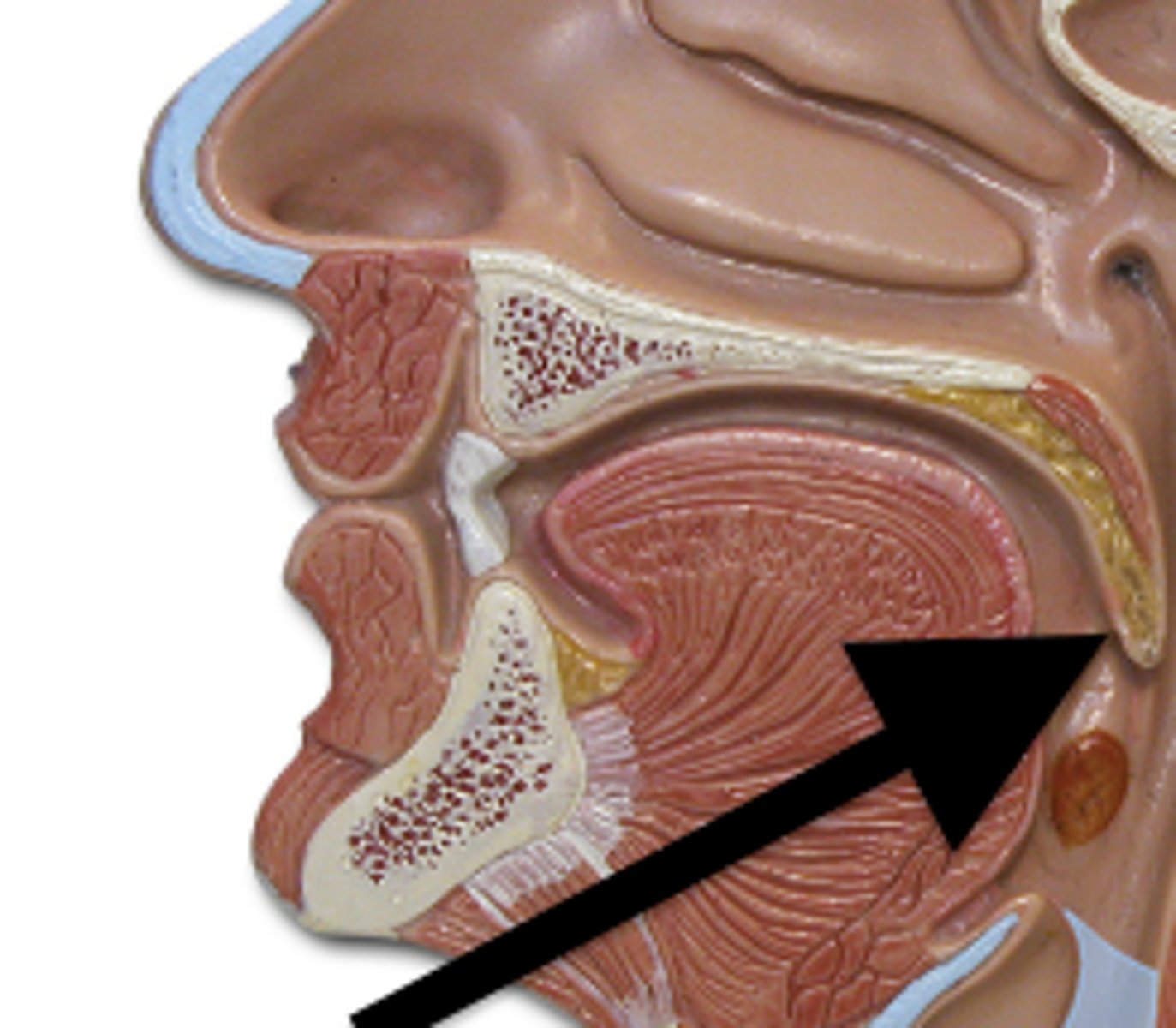
Uvula
The small fleshy extension at the back of the throat.
Labial and lingual frenula
Folds of tissue that attach the lips and tongue to the mouth.
Parotid gland
A major salivary gland located near the ear.
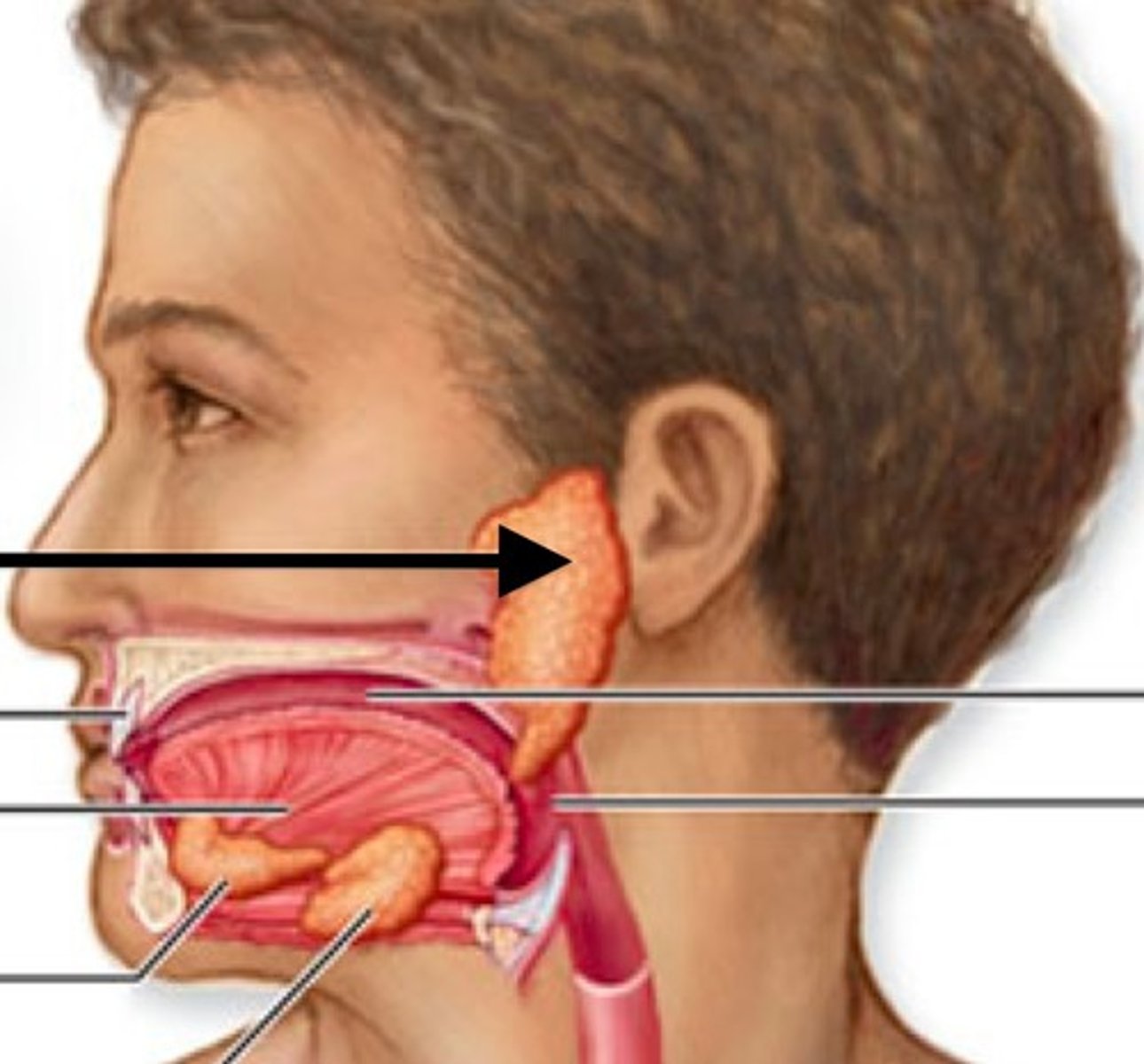
Sublingual gland
A salivary gland located under the tongue.
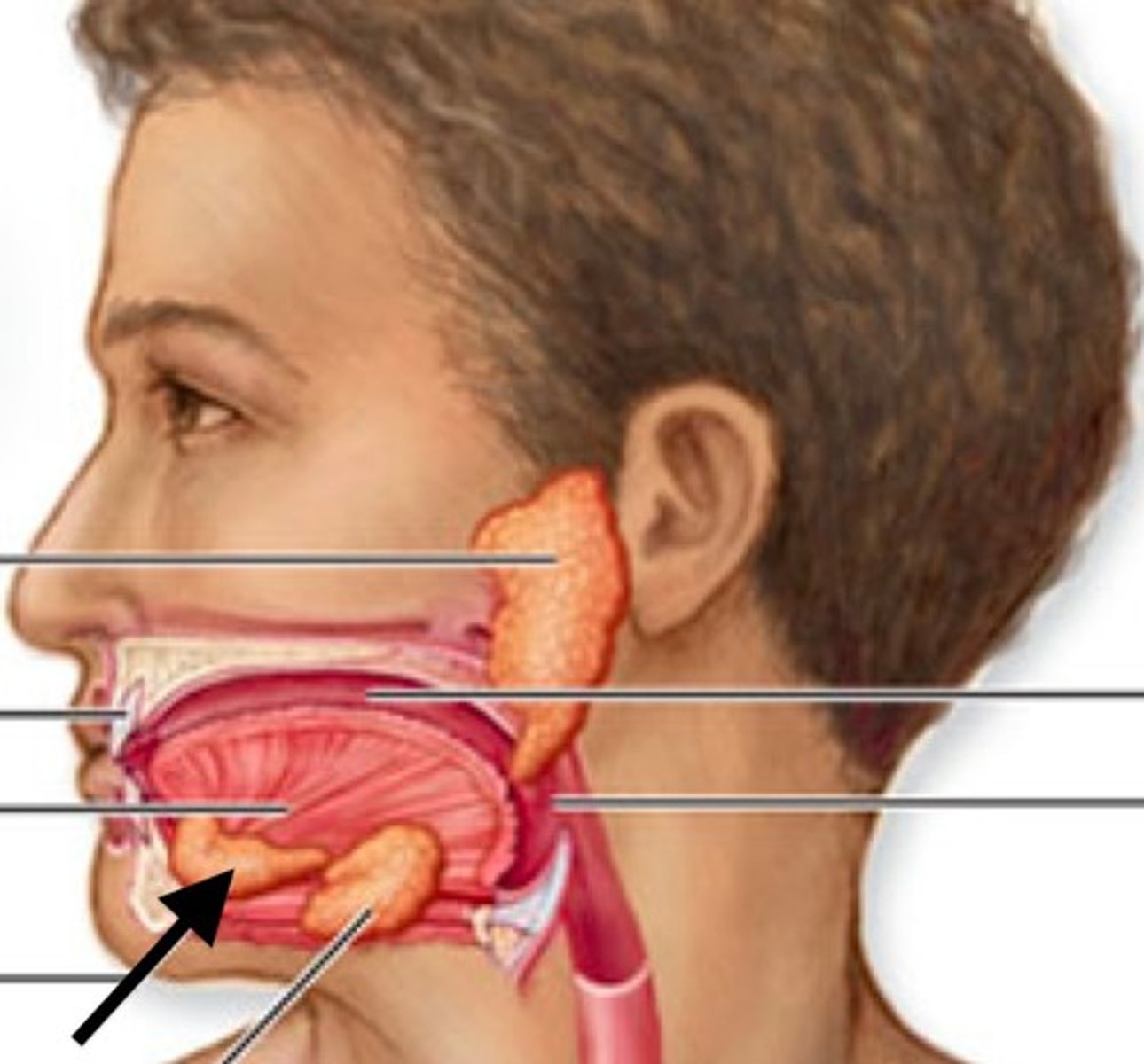
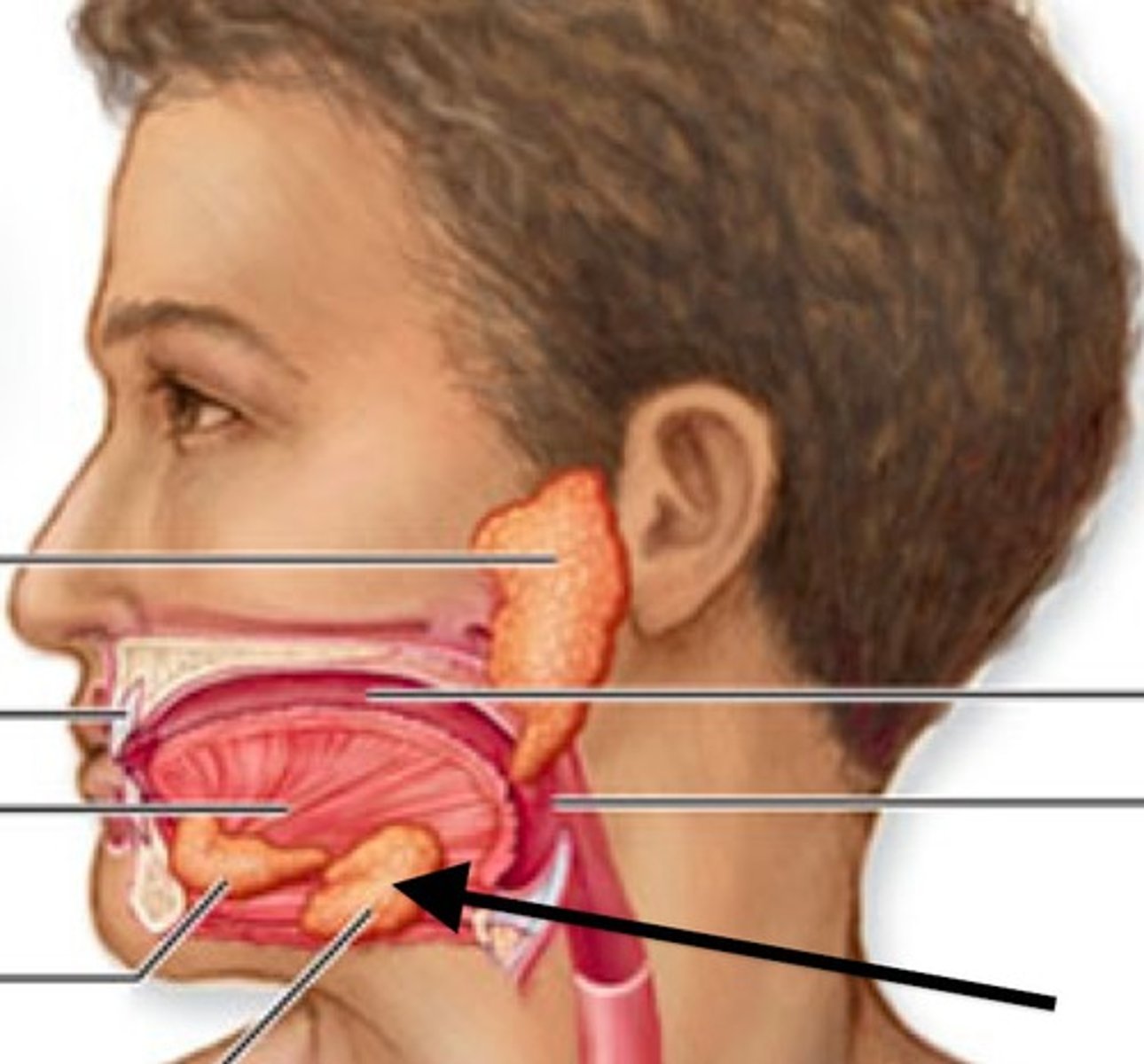
Submandibular gland
A salivary gland located beneath the jaw.
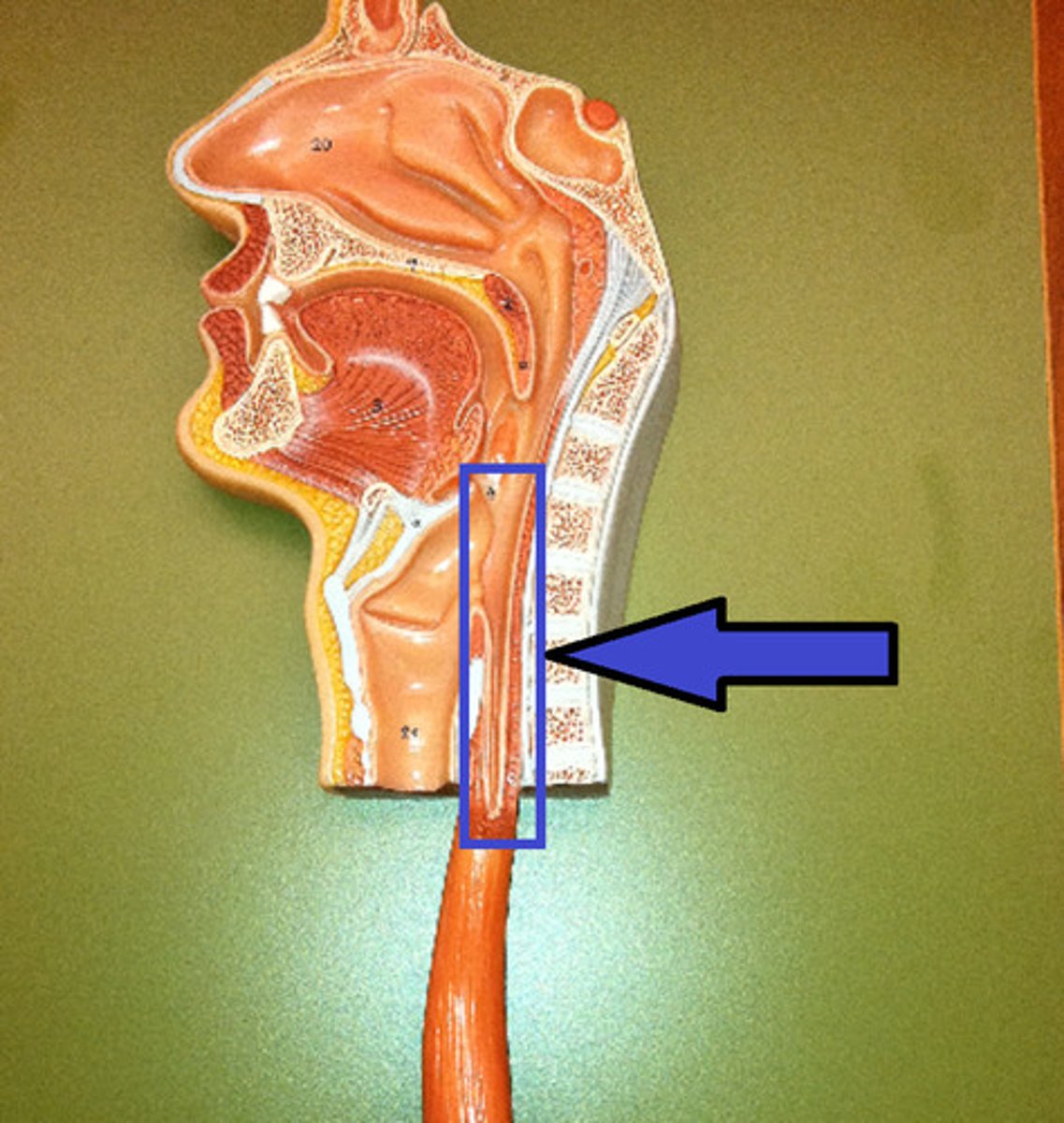
Pharynx
The part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity.
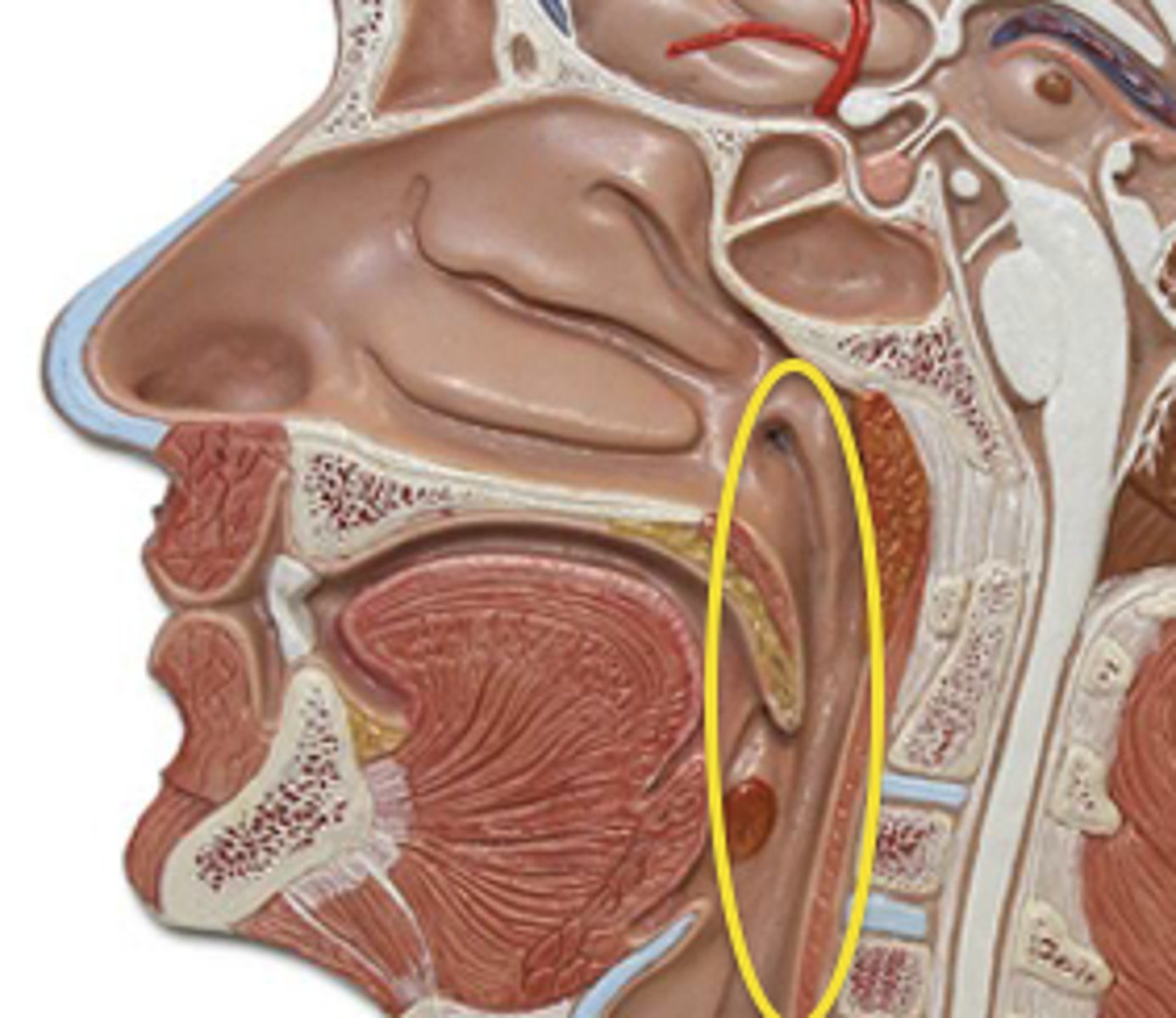
Esophagus
The tube that connects the throat to the stomach.
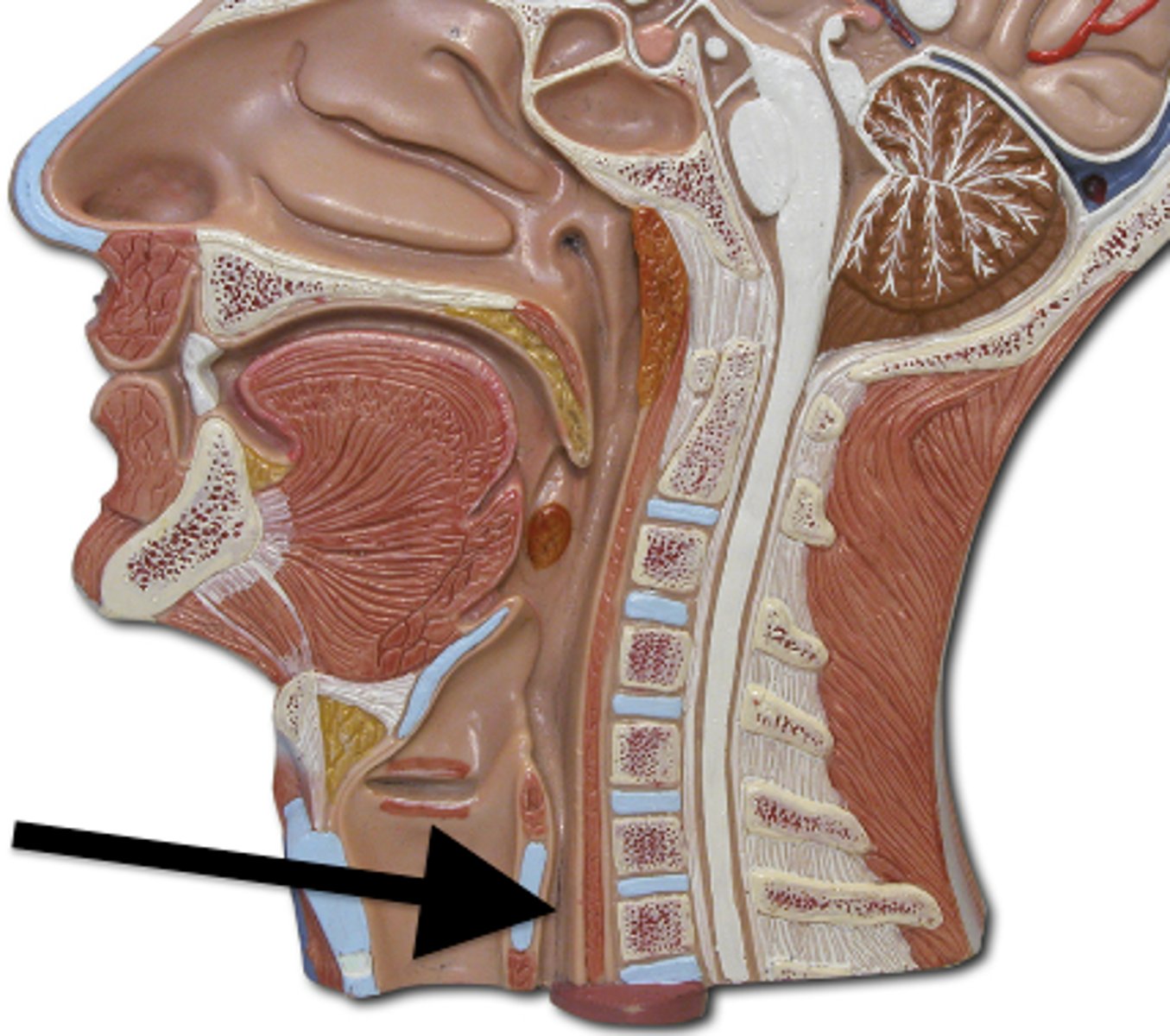
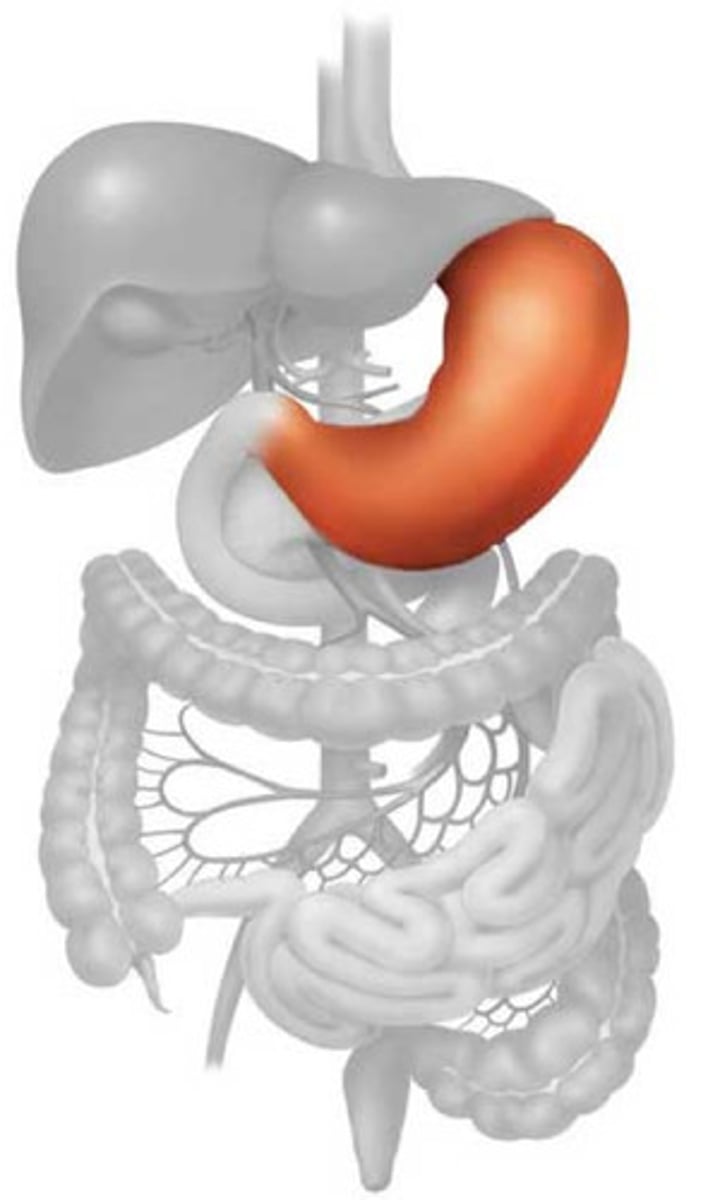
Stomach
The organ that holds food while it is being mixed with stomach enzymes.
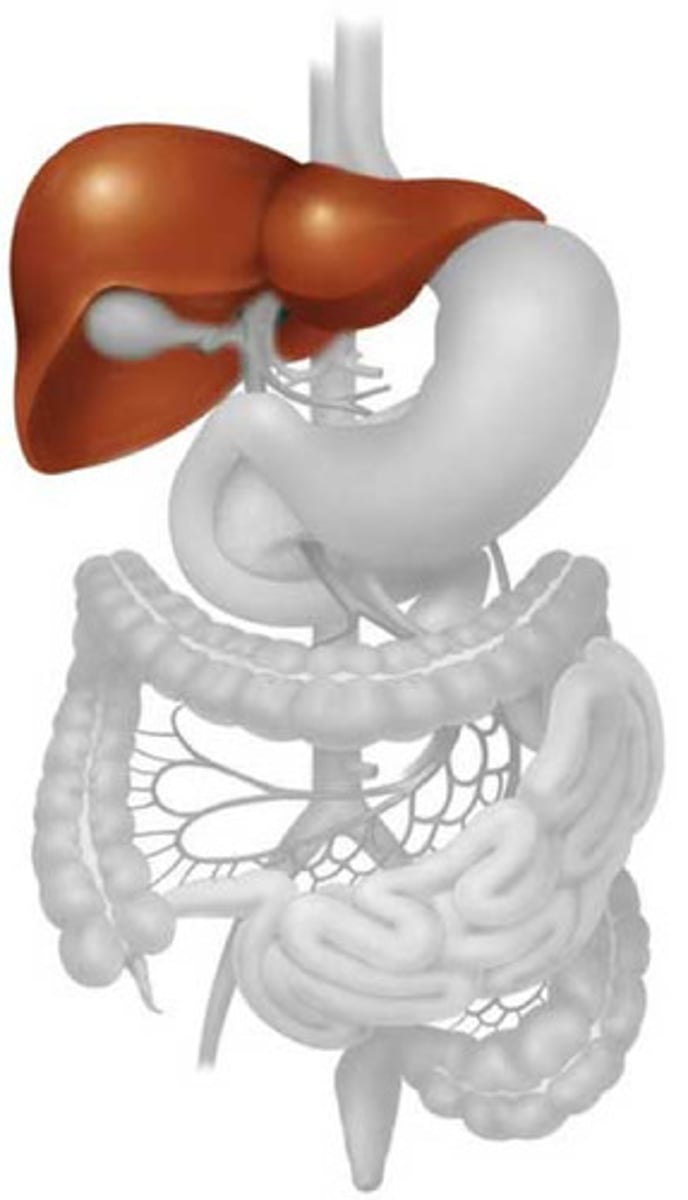
Liver
The organ that produces bile and processes nutrients from the digestive tract.
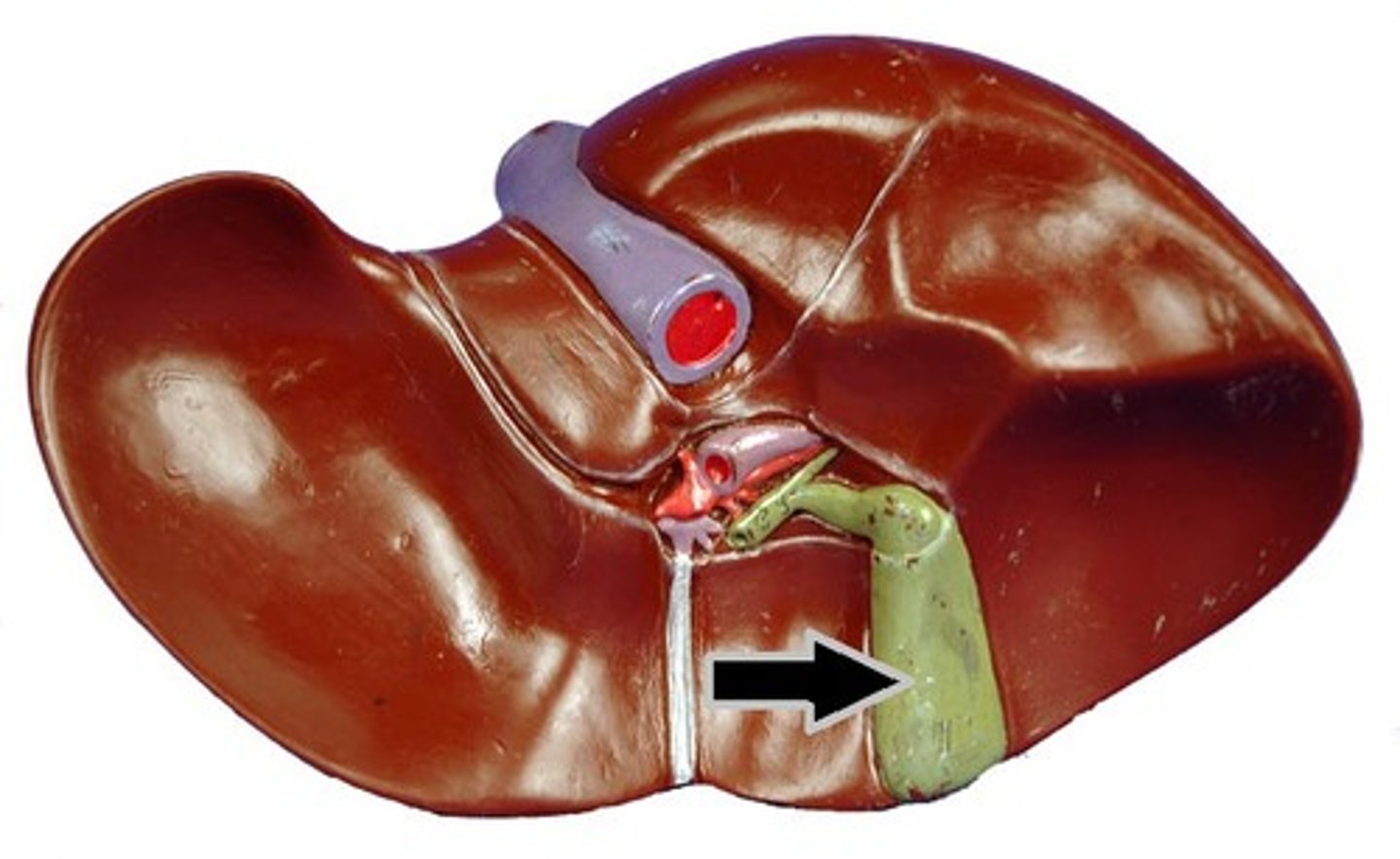
Gallbladder
The organ that stores bile produced by the liver.
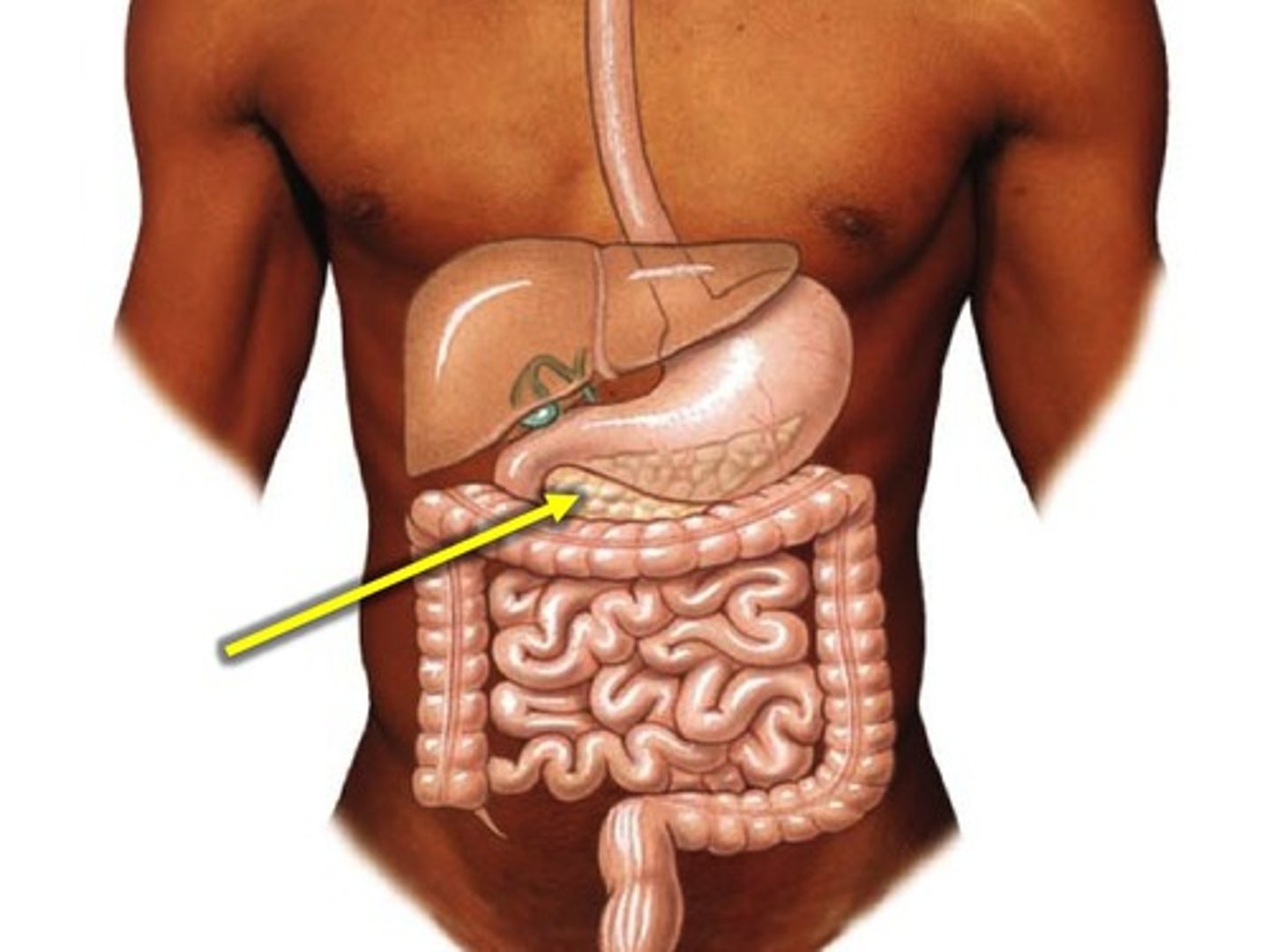
Pancreas
An organ that produces digestive enzymes and hormones.
Spleen
An organ involved in filtering blood and immune response.
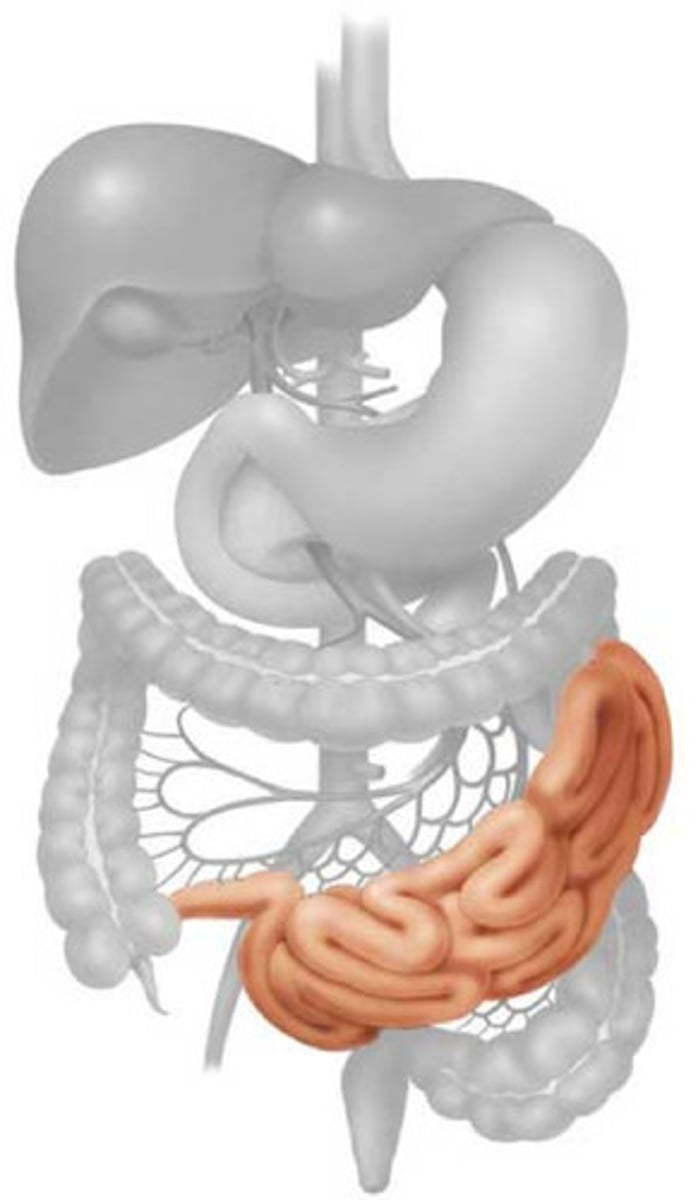
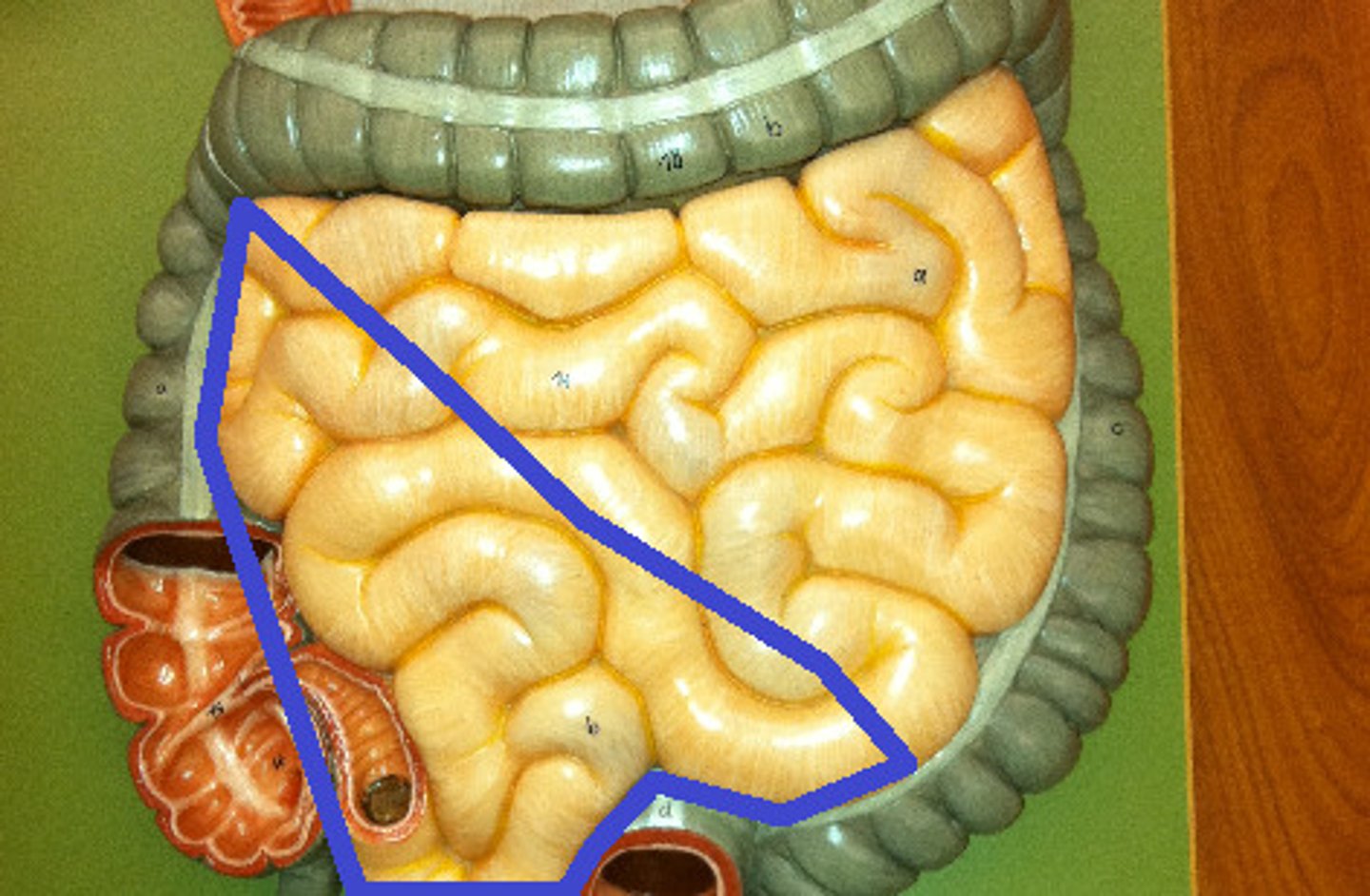
Small intestine
The part of the digestive system where most of the digestion and absorption occurs.
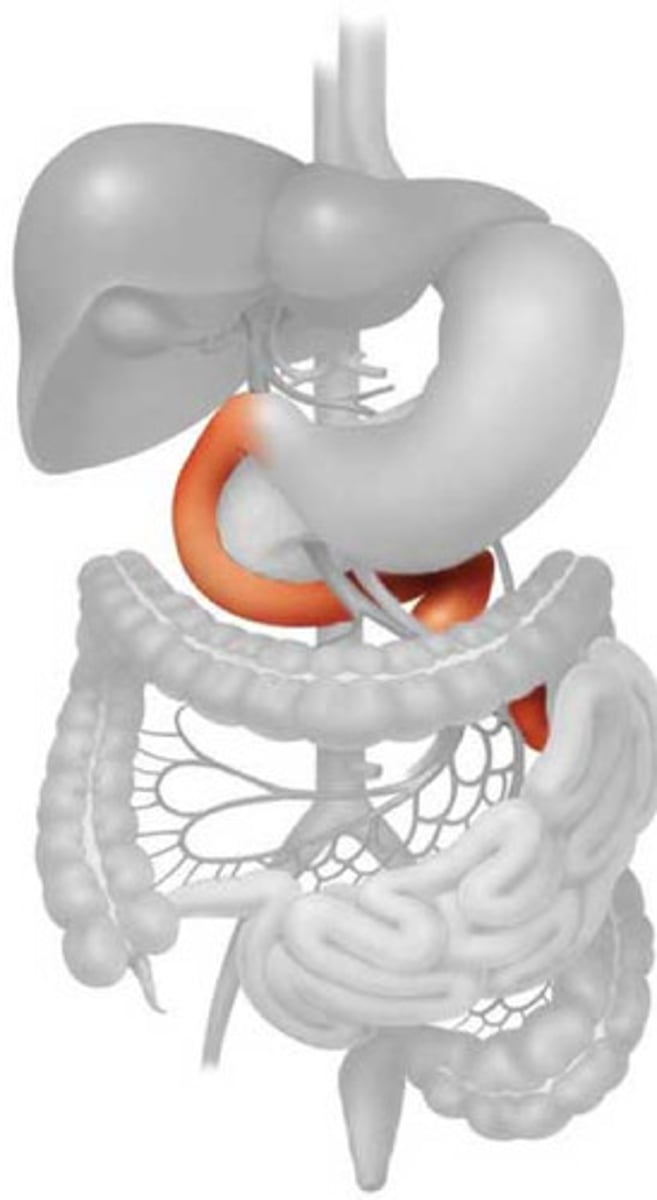
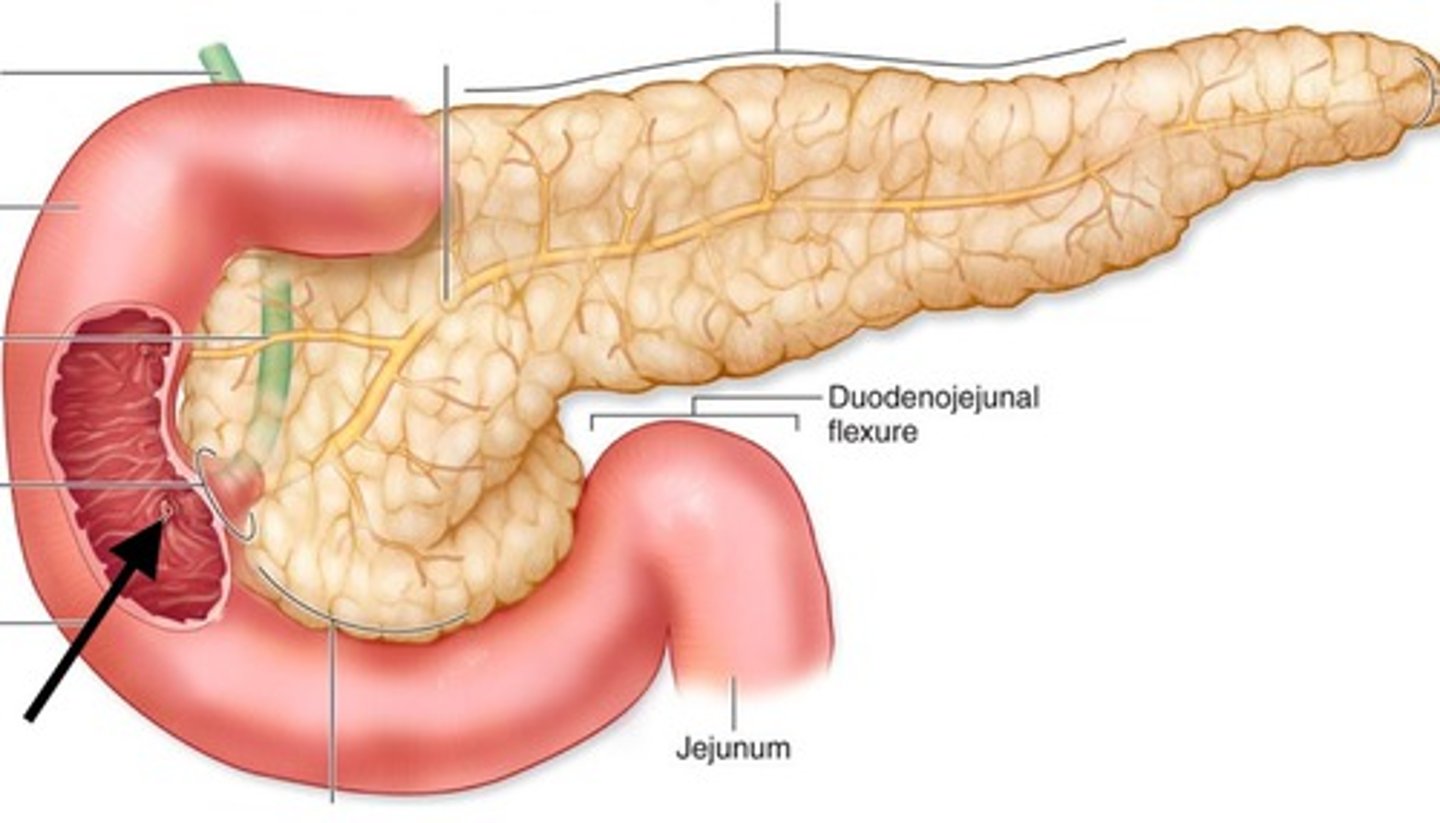
Duodenum
The first section of the small intestine.
Jejunum
The middle section of the small intestine.
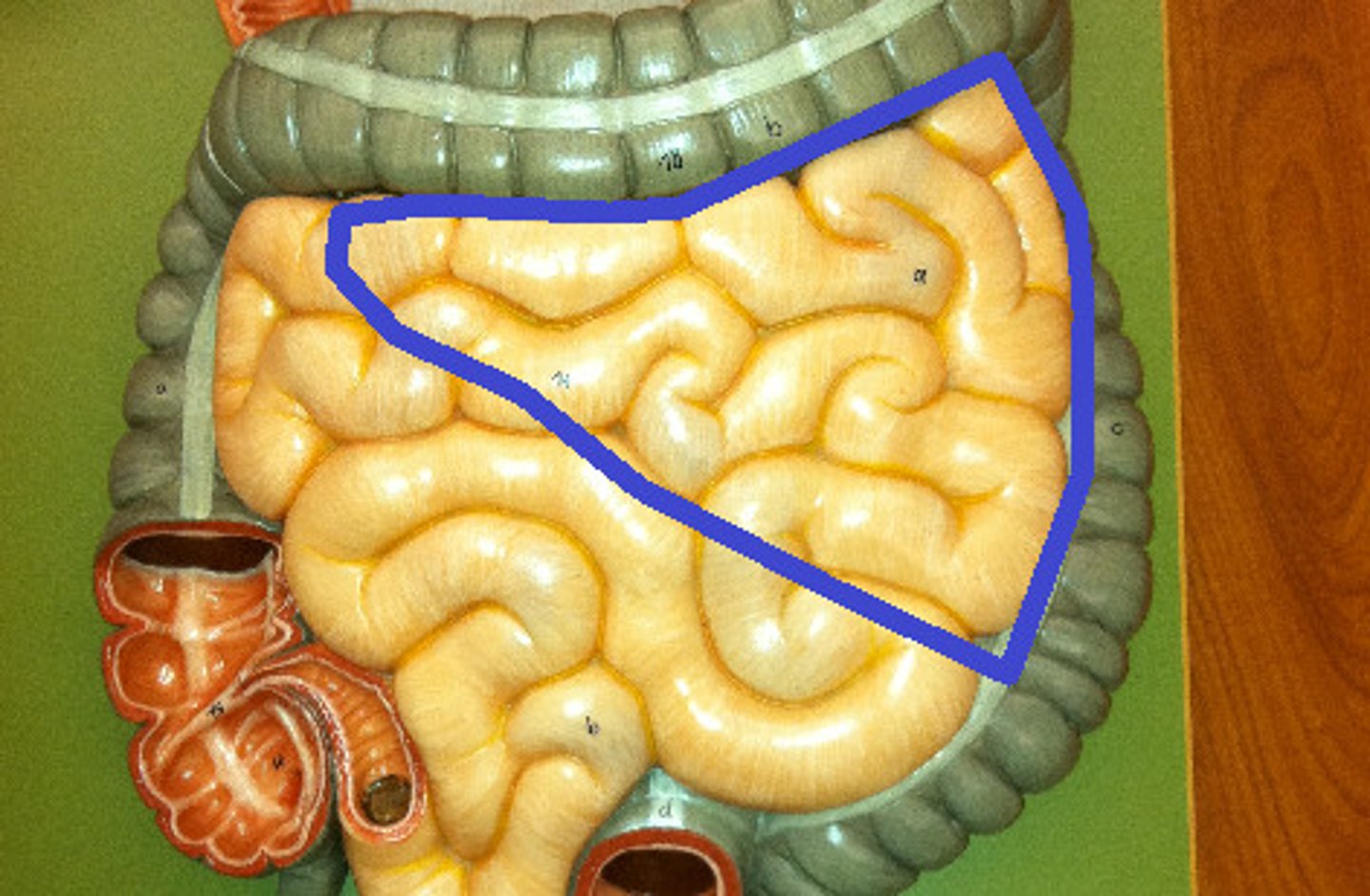
Ileum
The final section of the small intestine.
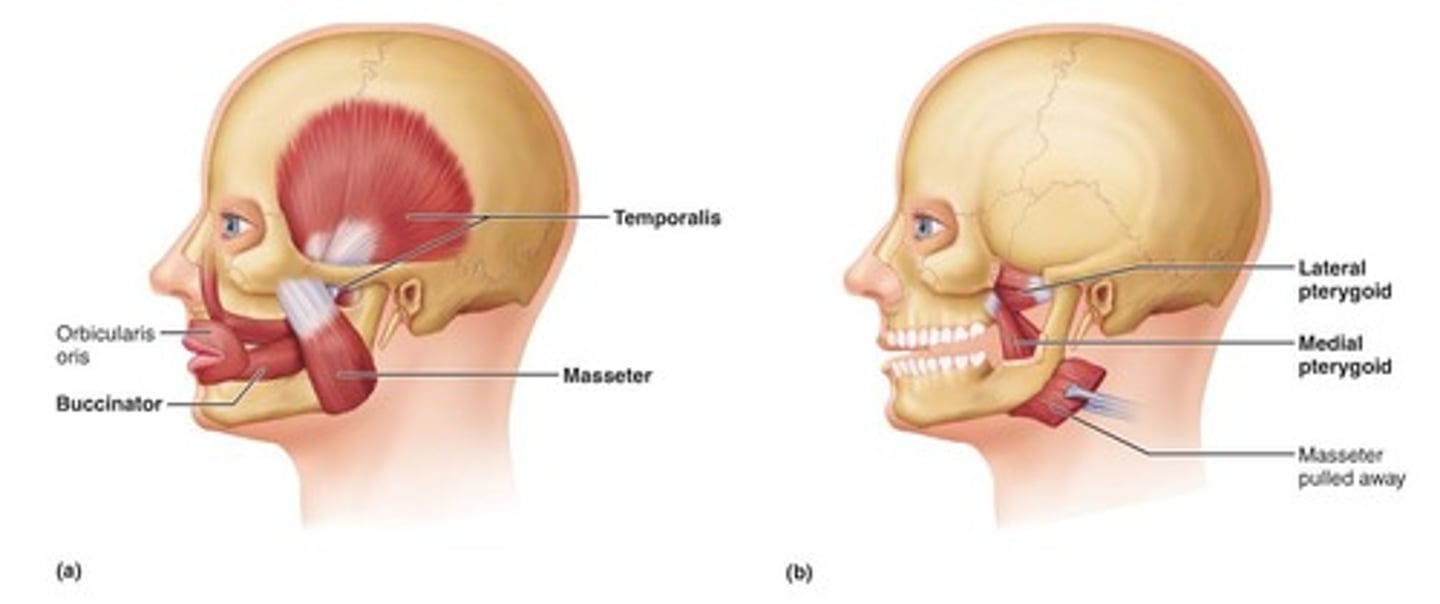
Mastication
The process of chewing food.
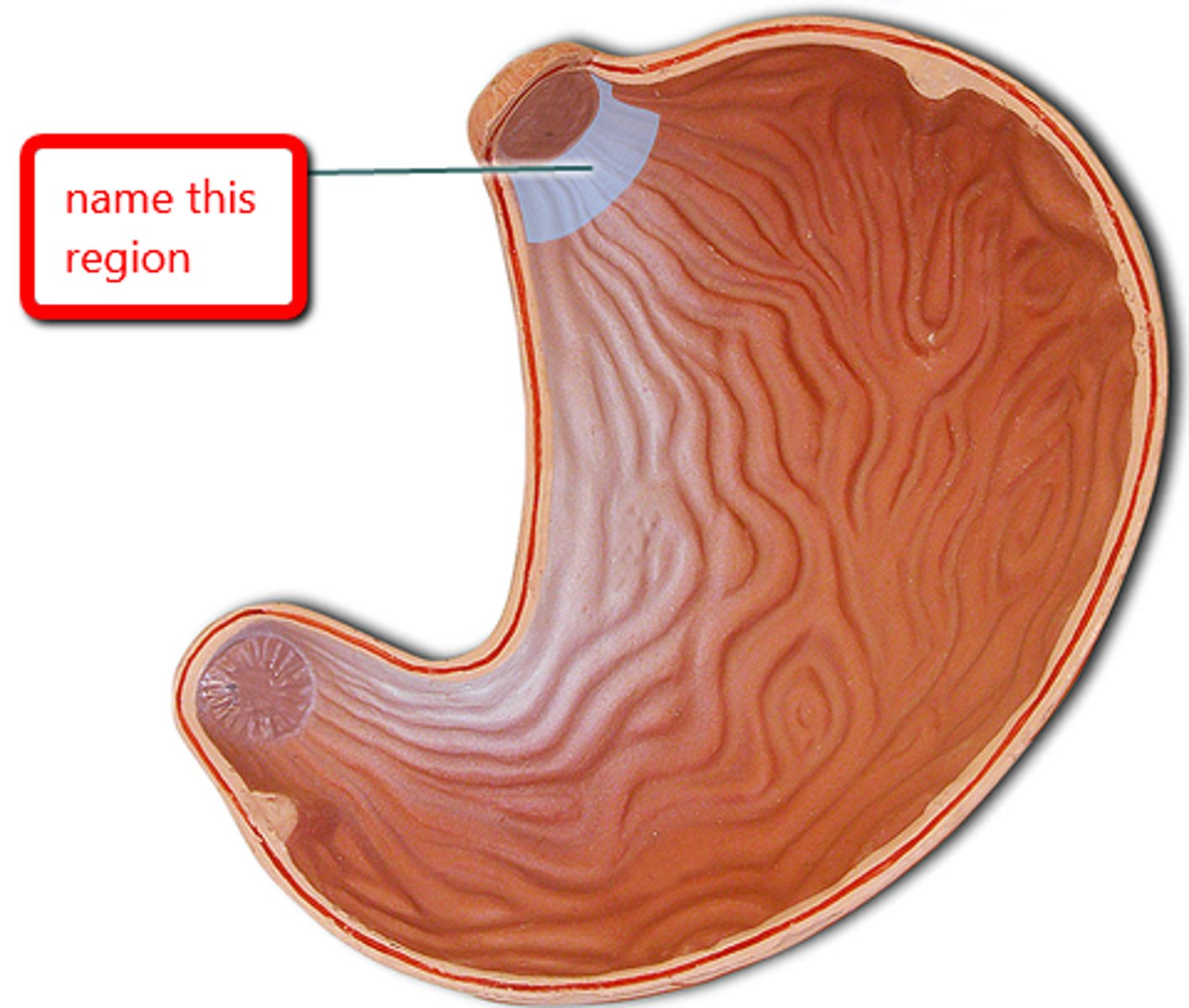
Cardia of the stomach
The area where the esophagus connects to the stomach.
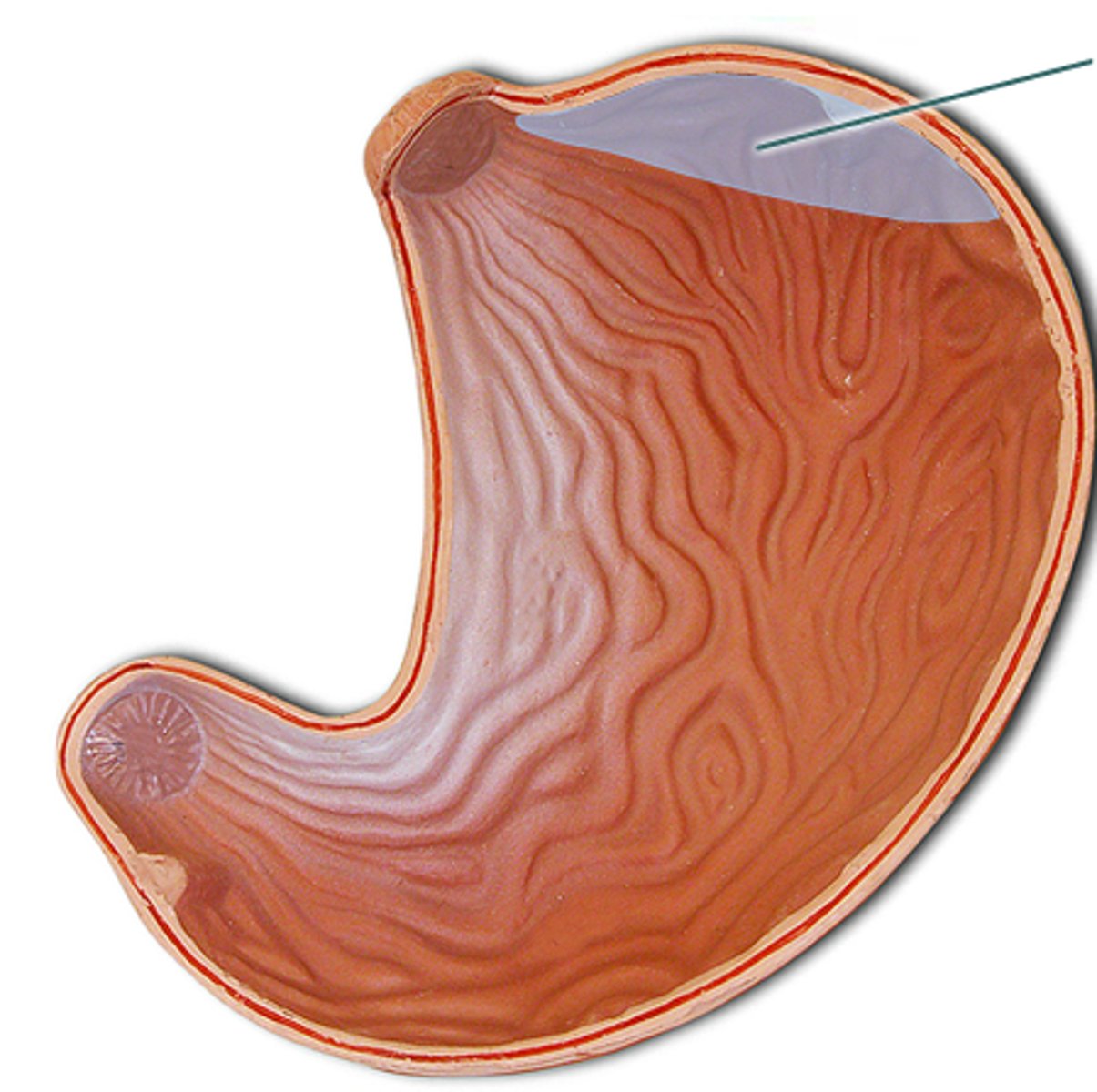
Fundus of the stomach
The upper part of the stomach.
Body of the stomach
The central region of the stomach.
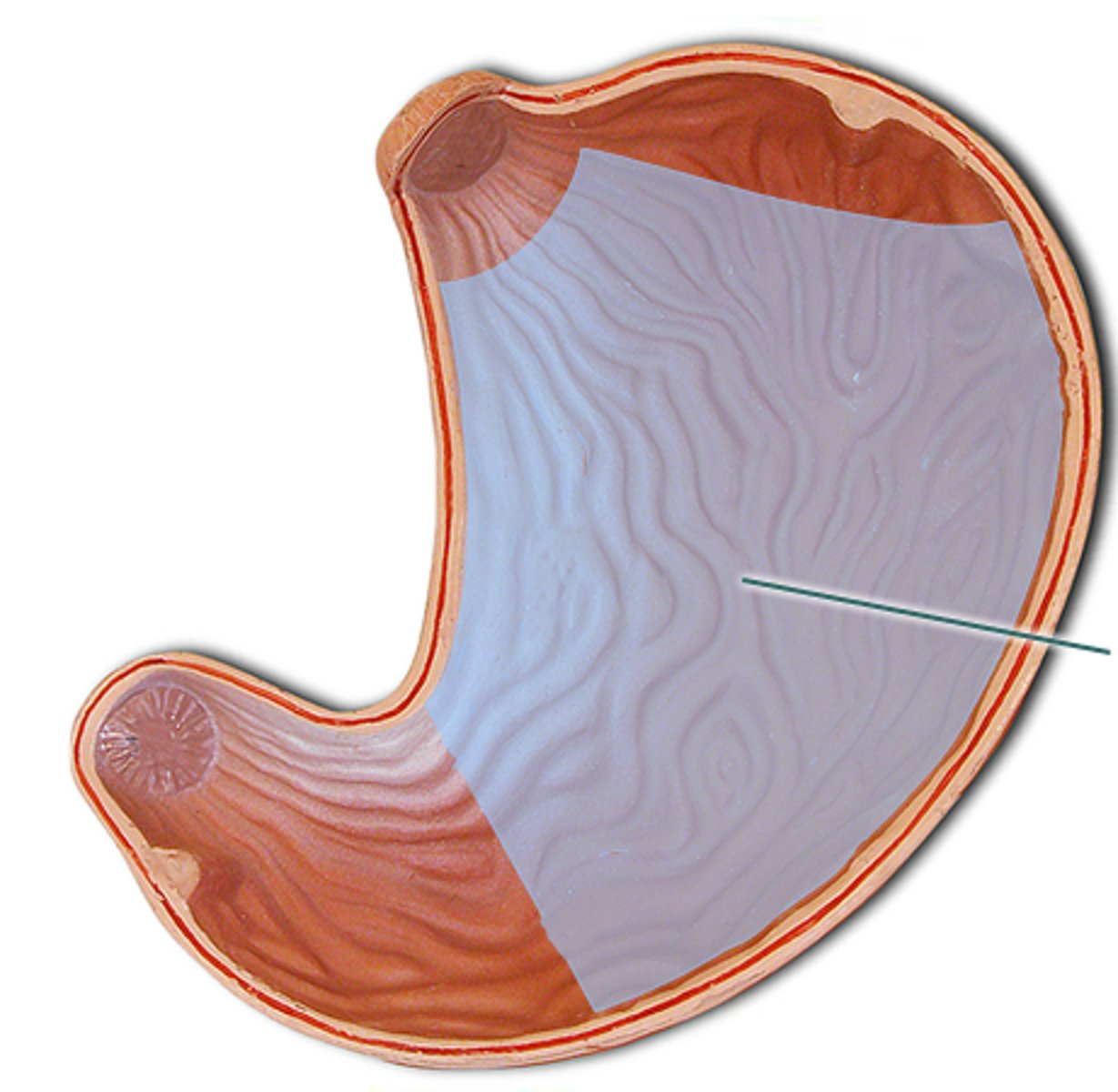
Greater curvature
The longer, convex border of the stomach.
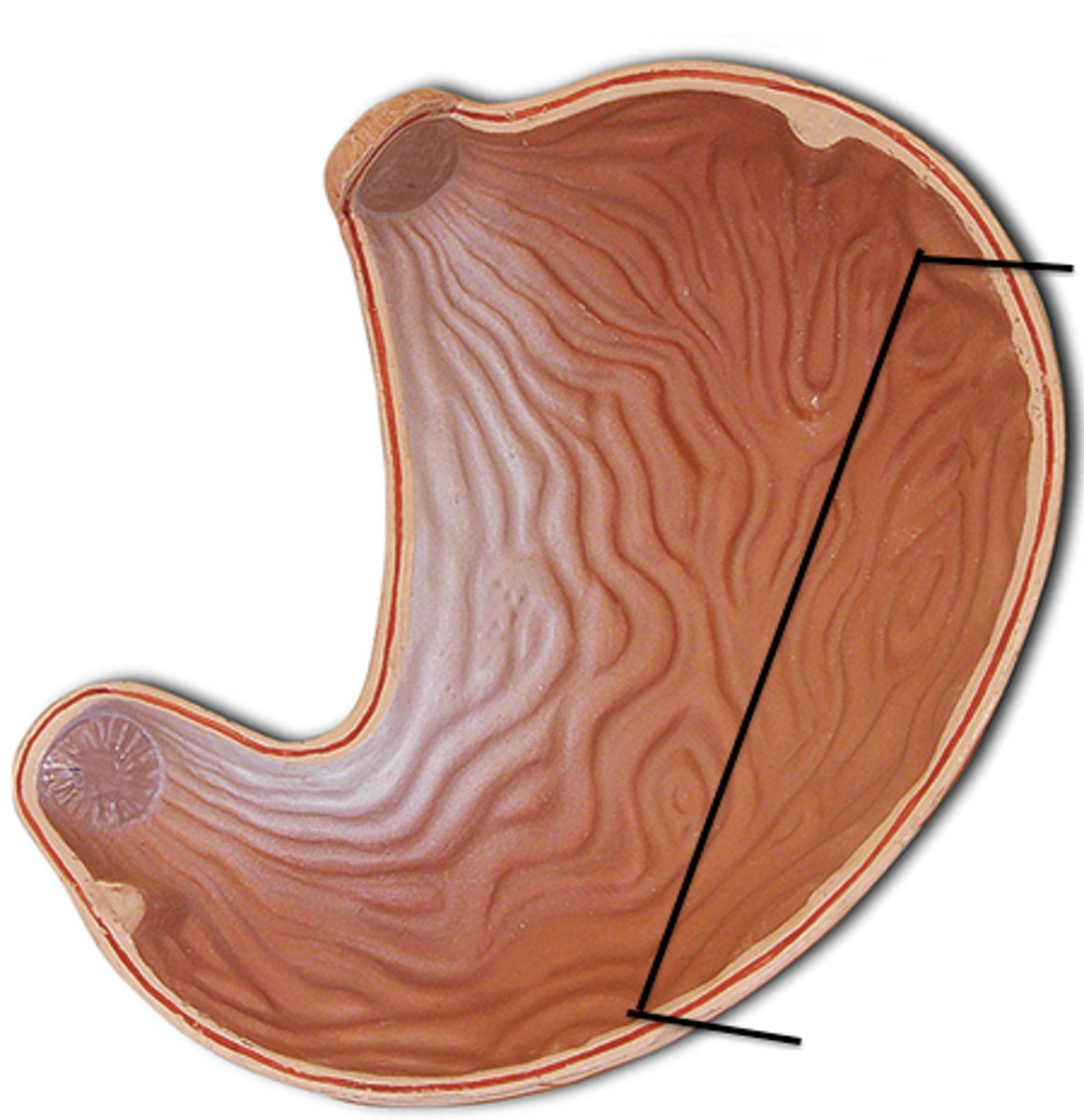
Lesser curvature
The shorter, concave border of the stomach.
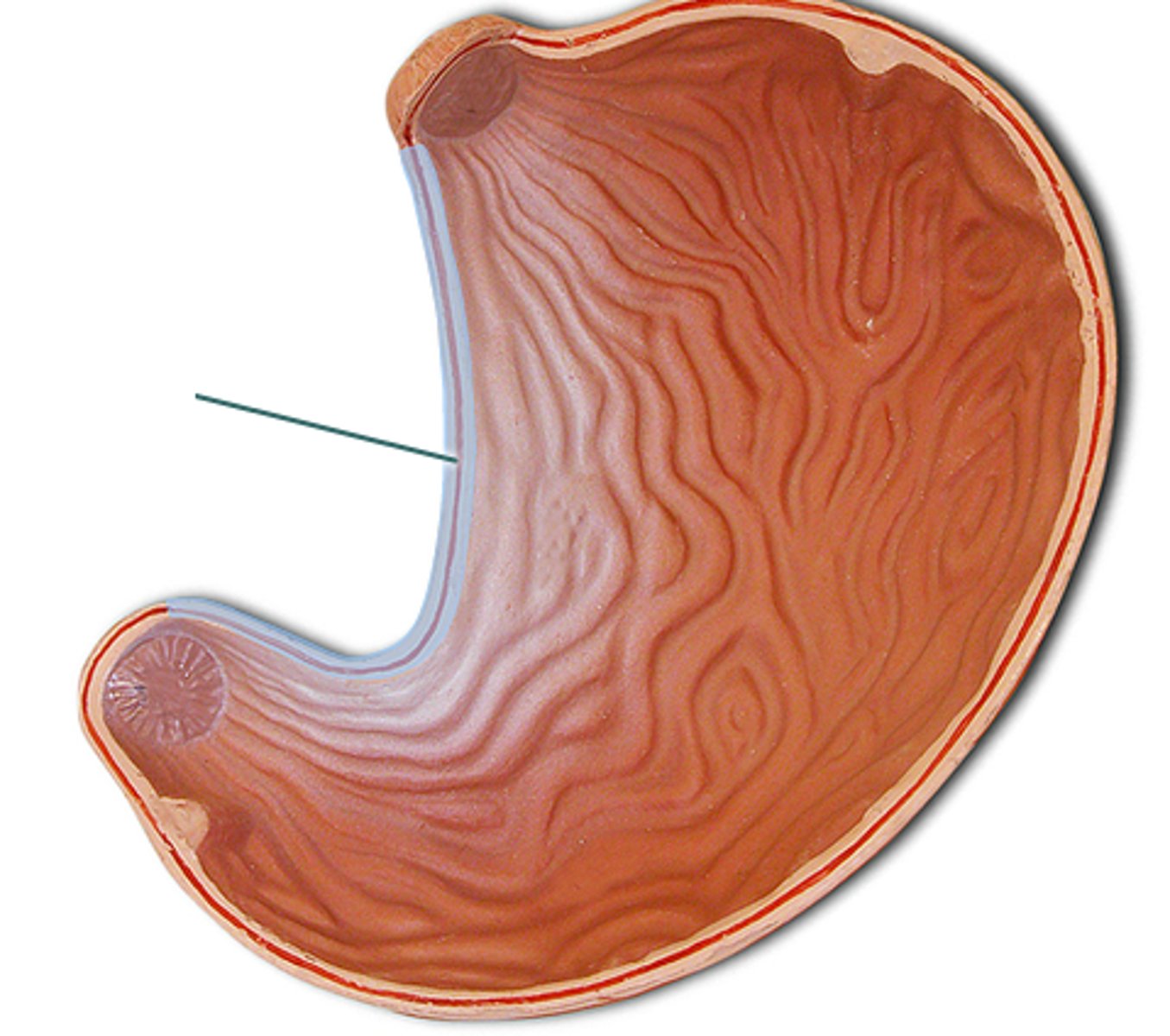
Pyloric antrum
The lower part of the stomach that connects to the pyloric canal.
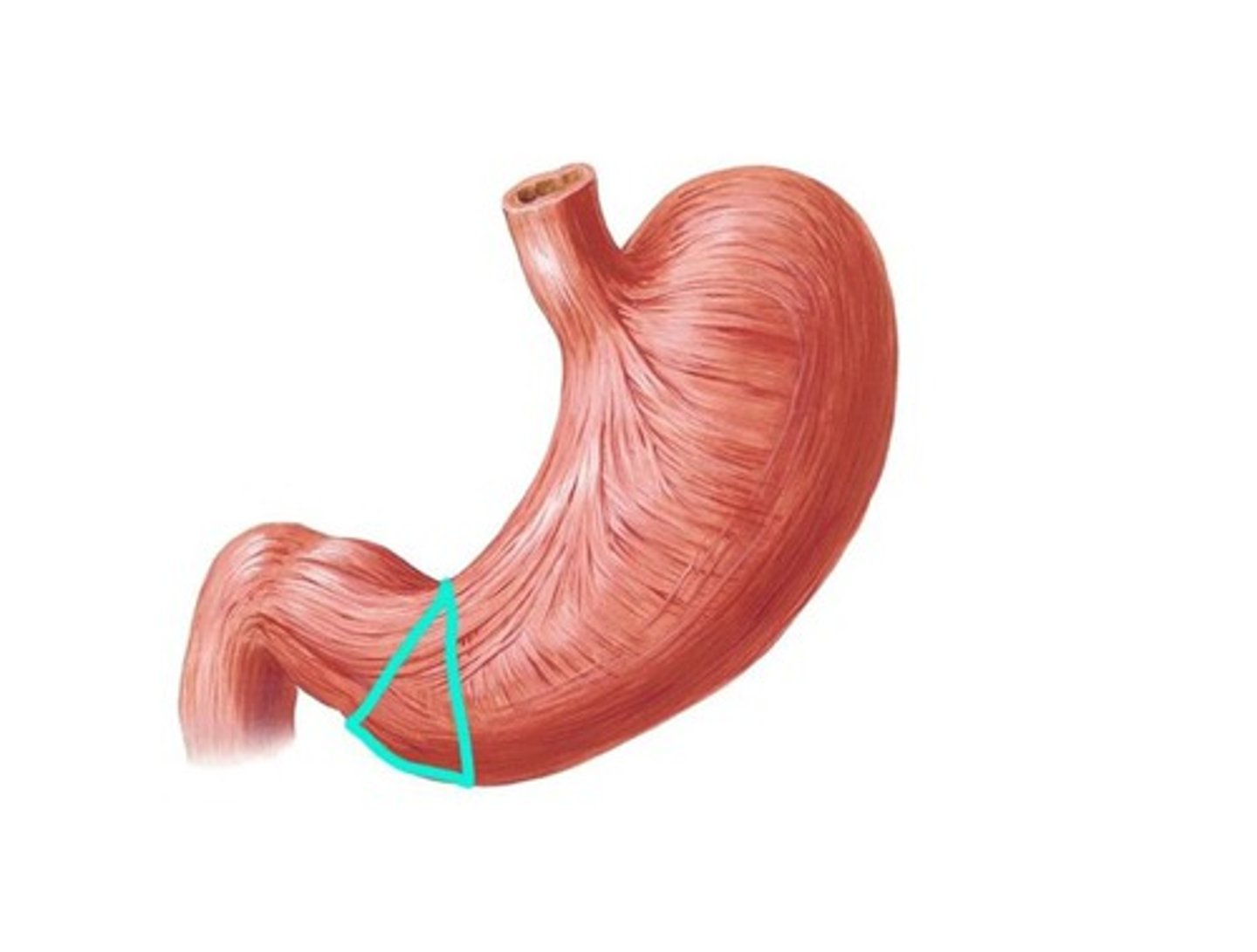
Pyloric canal
The passageway leading from the stomach to the duodenum.
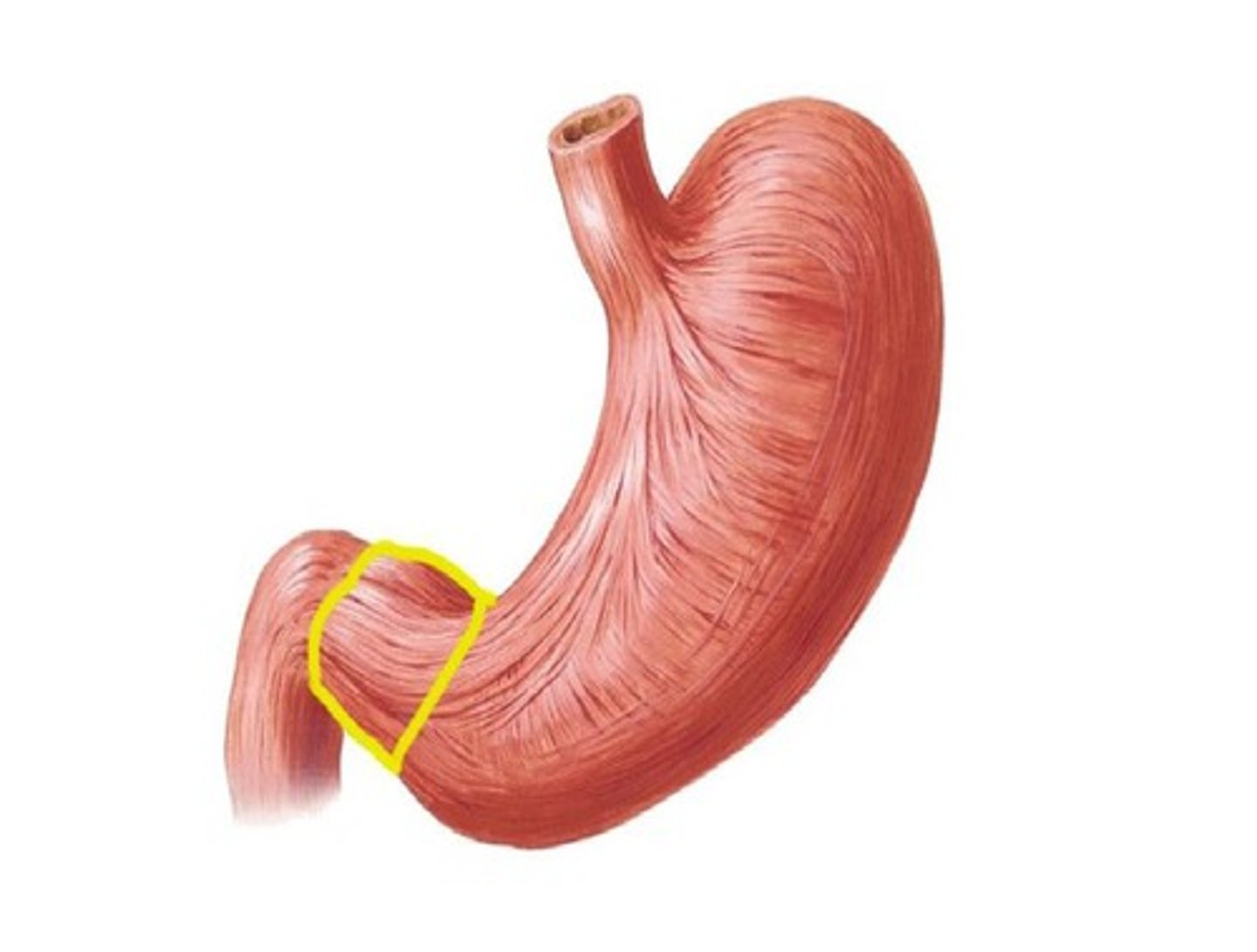
Pyloric sphincter
The muscle that controls the passage of food from the stomach to the duodenum.
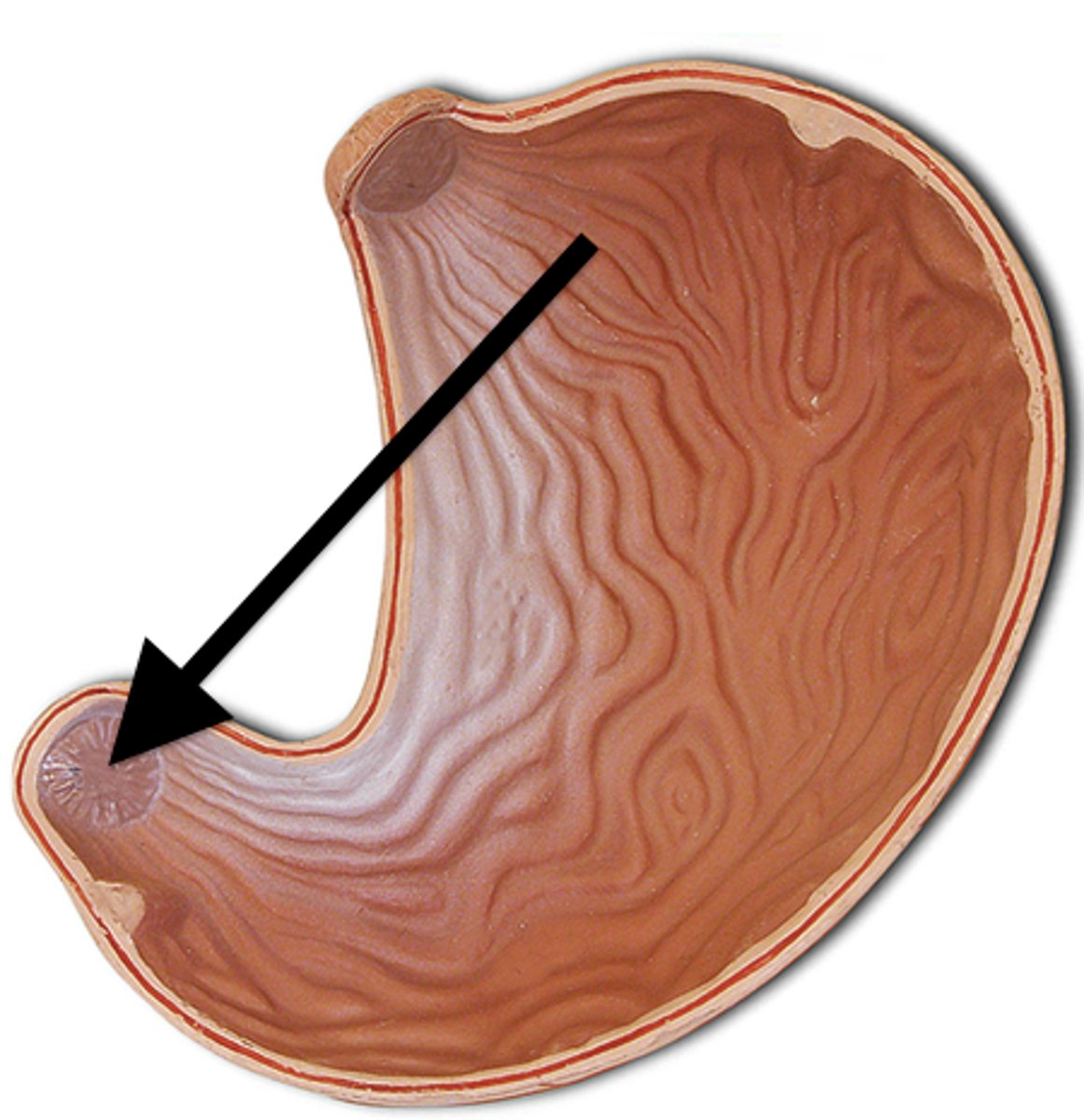
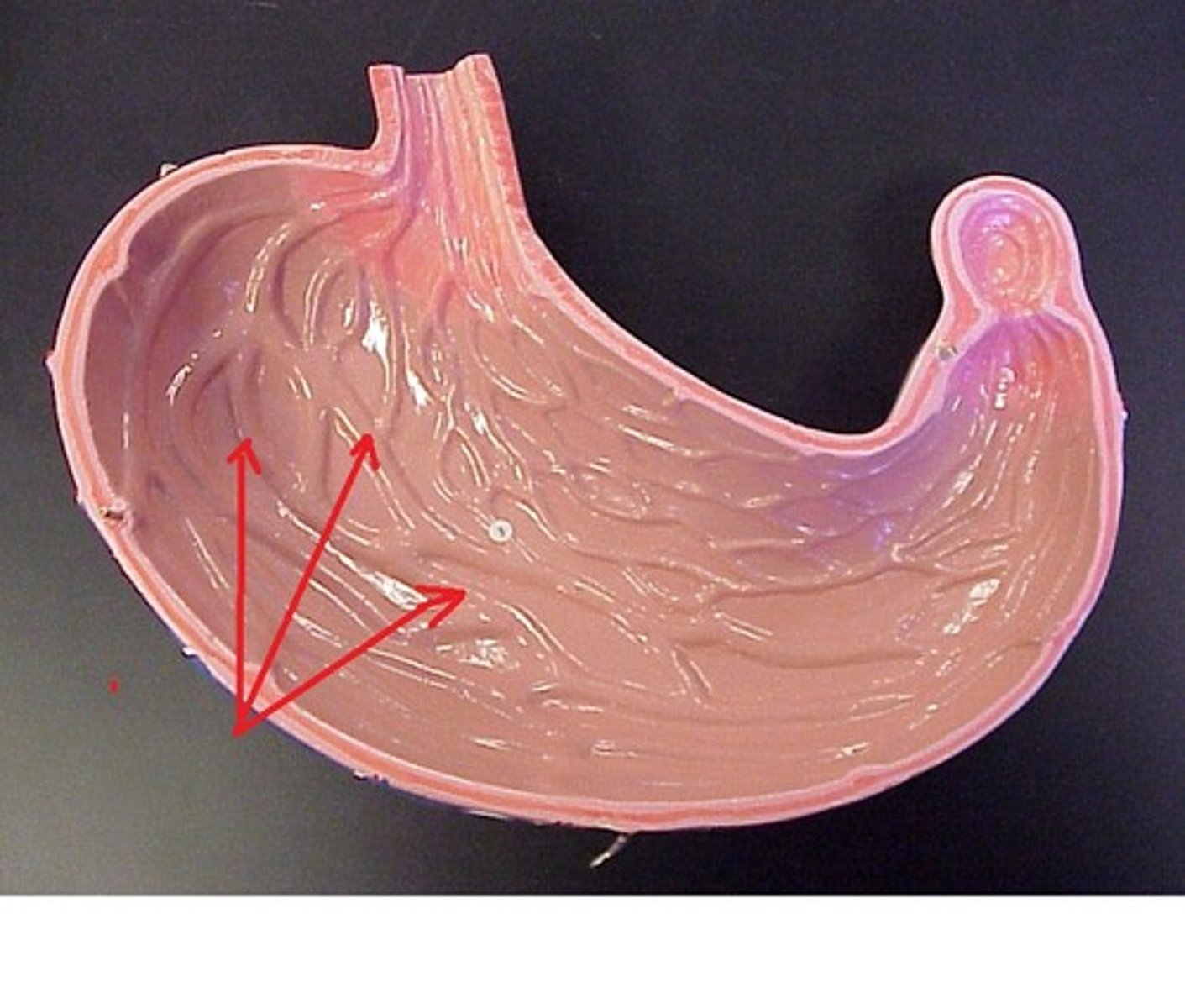
Rugae
The folds in the stomach lining that allow for expansion.
Gastric pits
Depressions in the stomach lining that contain gastric glands.
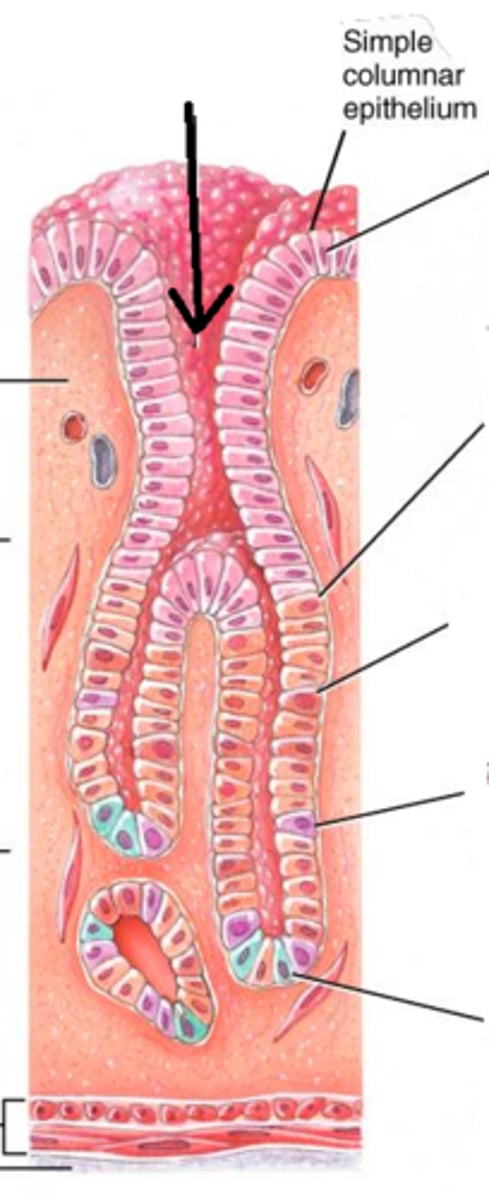
Gastric glands
Glands in the stomach that secrete digestive enzymes and acids.
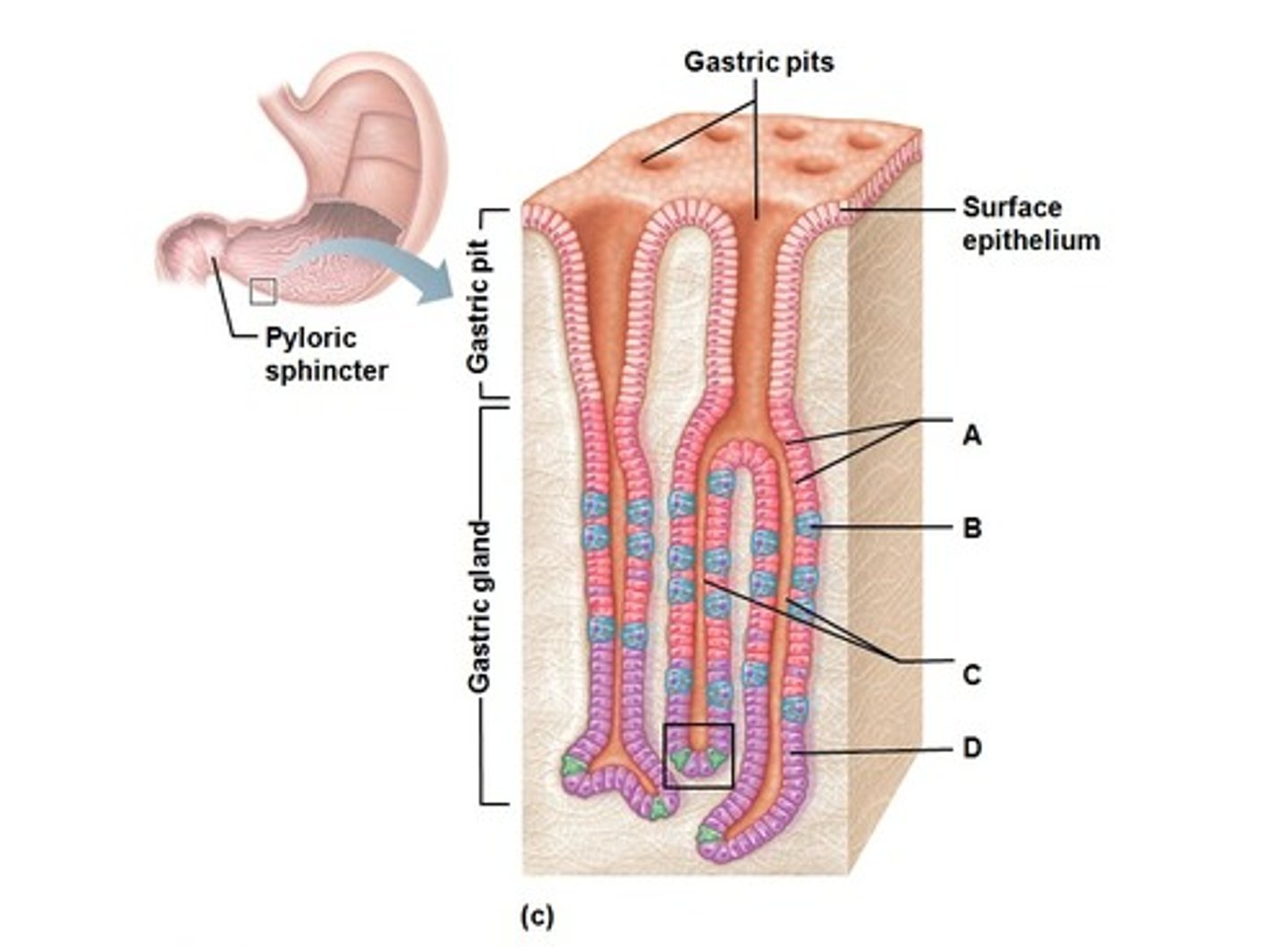
Neck cells
Cells in the gastric glands that secrete mucus.
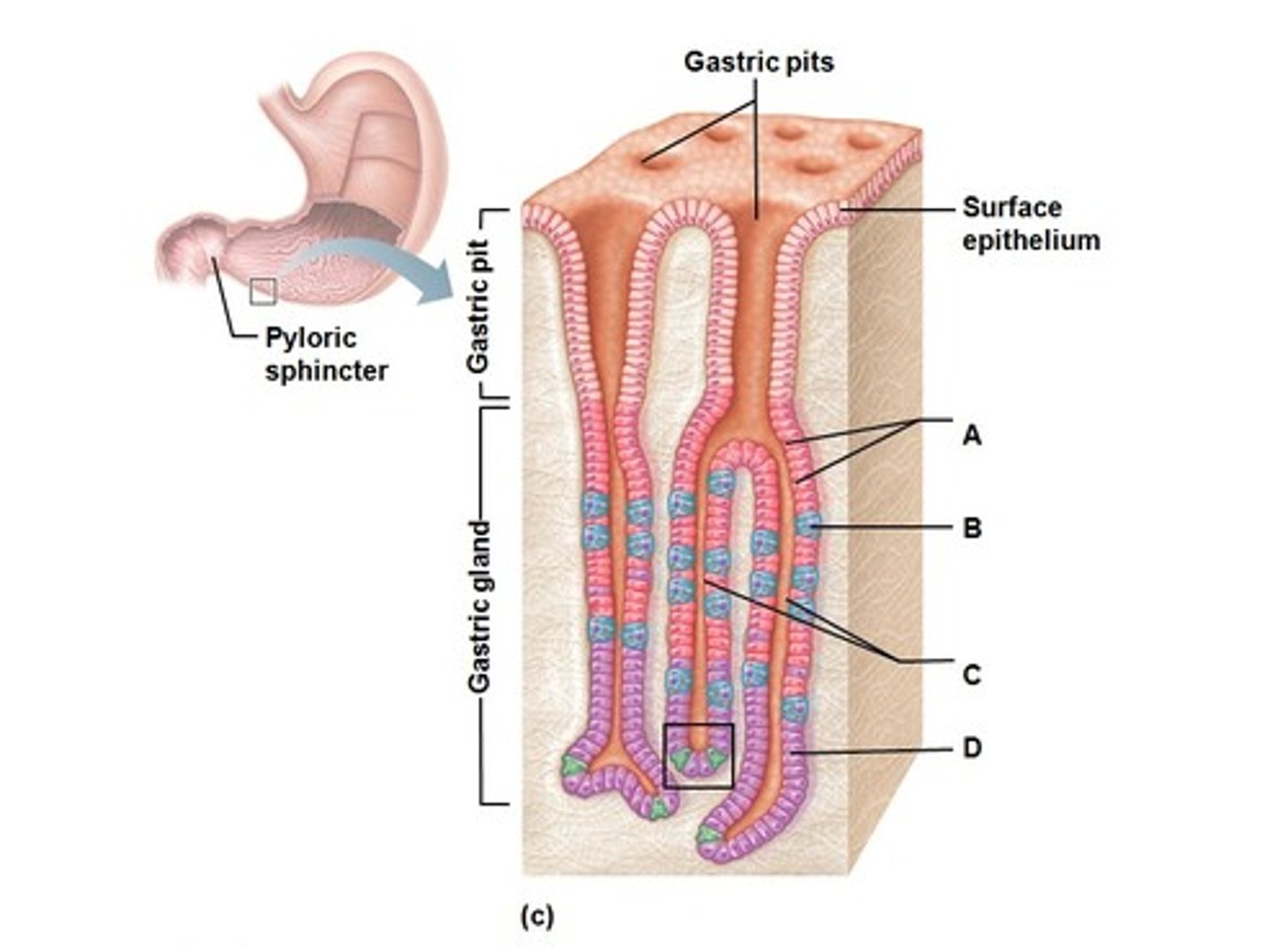
Parietal cells
Cells in the gastric glands that secrete hydrochloric acid.
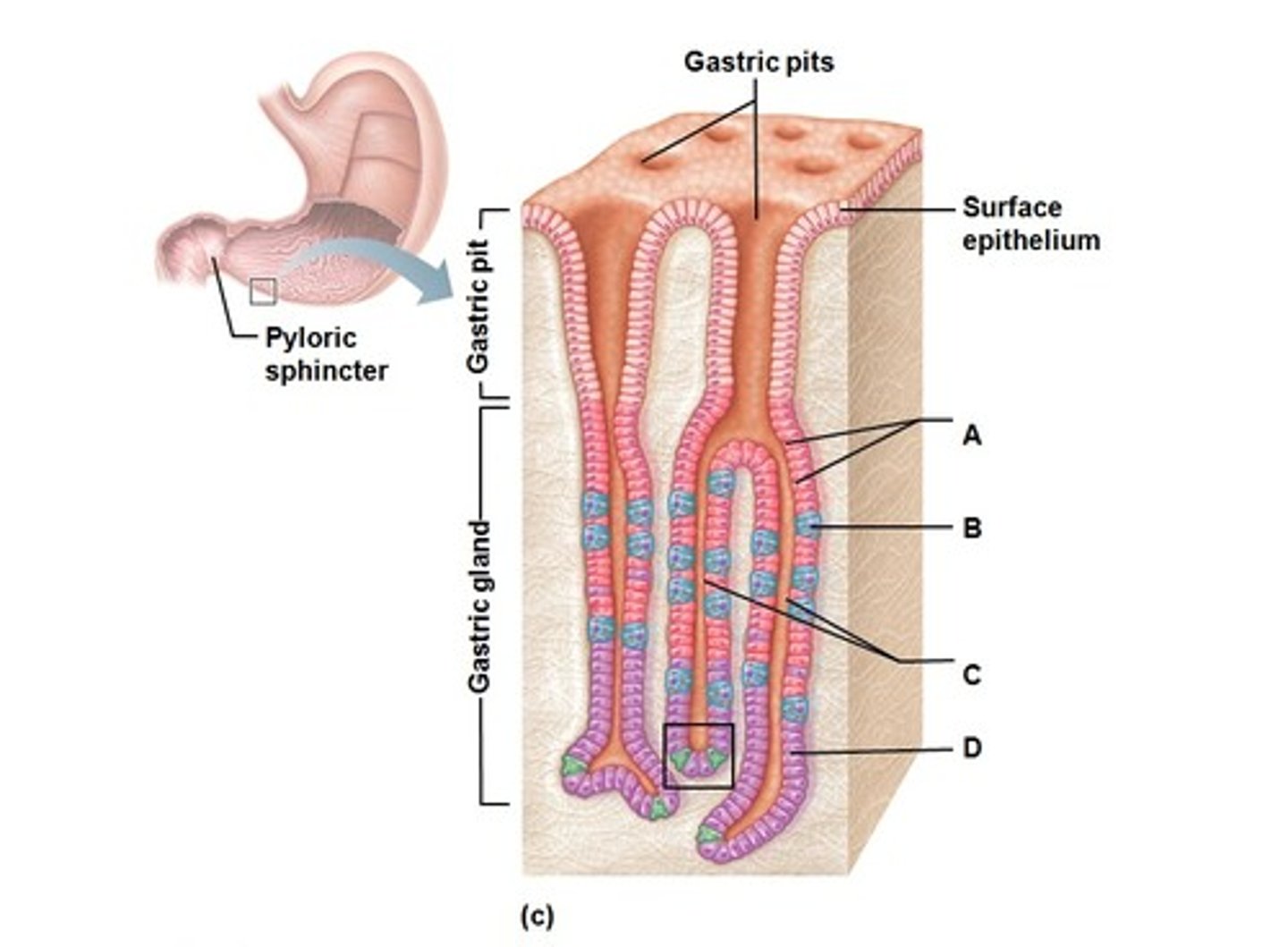
Chief cells
Cells in the gastric glands that secrete pepsinogen.
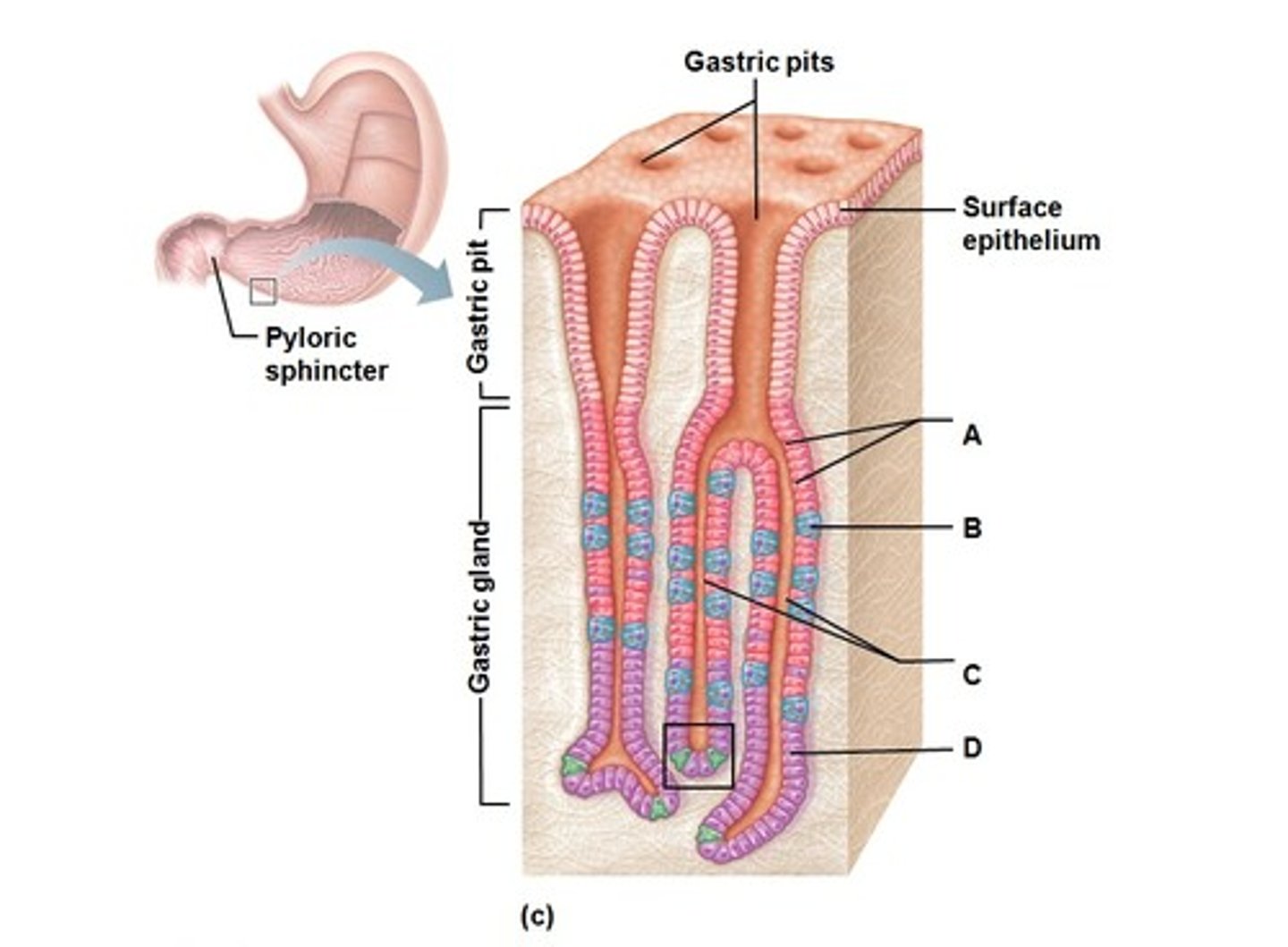
Enteroendocrine cells
Cells in the gastric glands that secrete hormones.
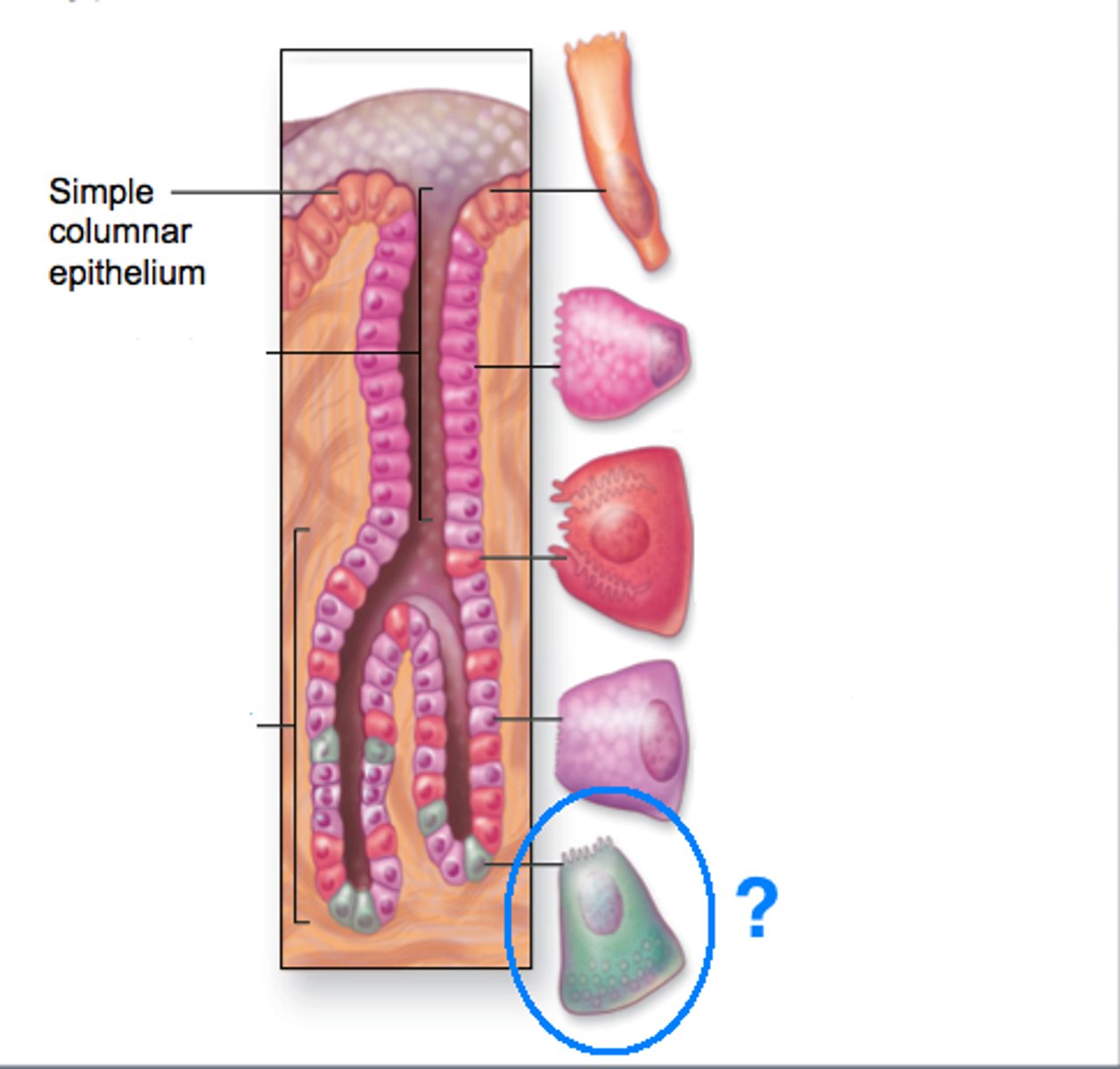
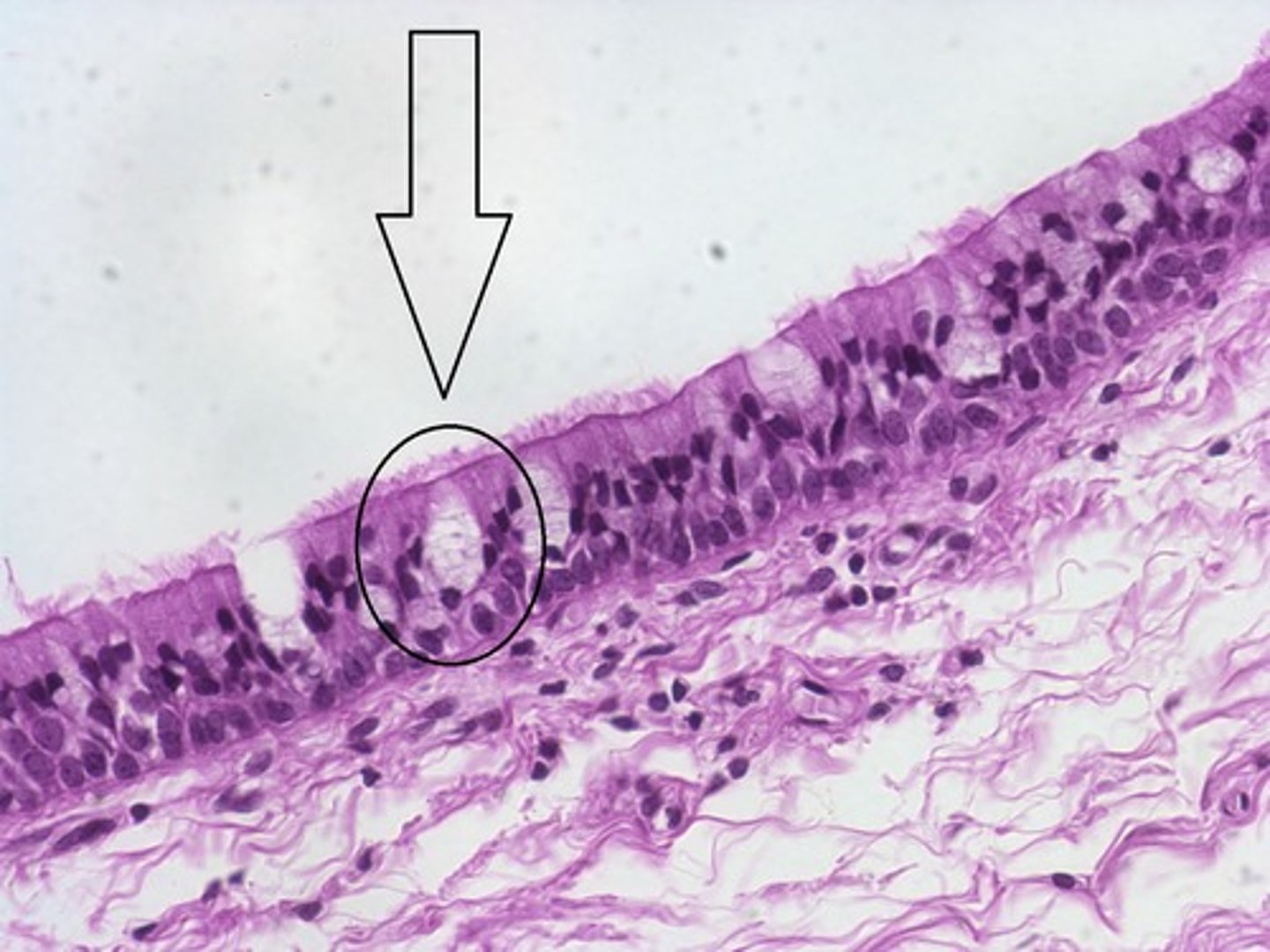
Goblet cells
Cells that secrete mucus in the intestinal lining.
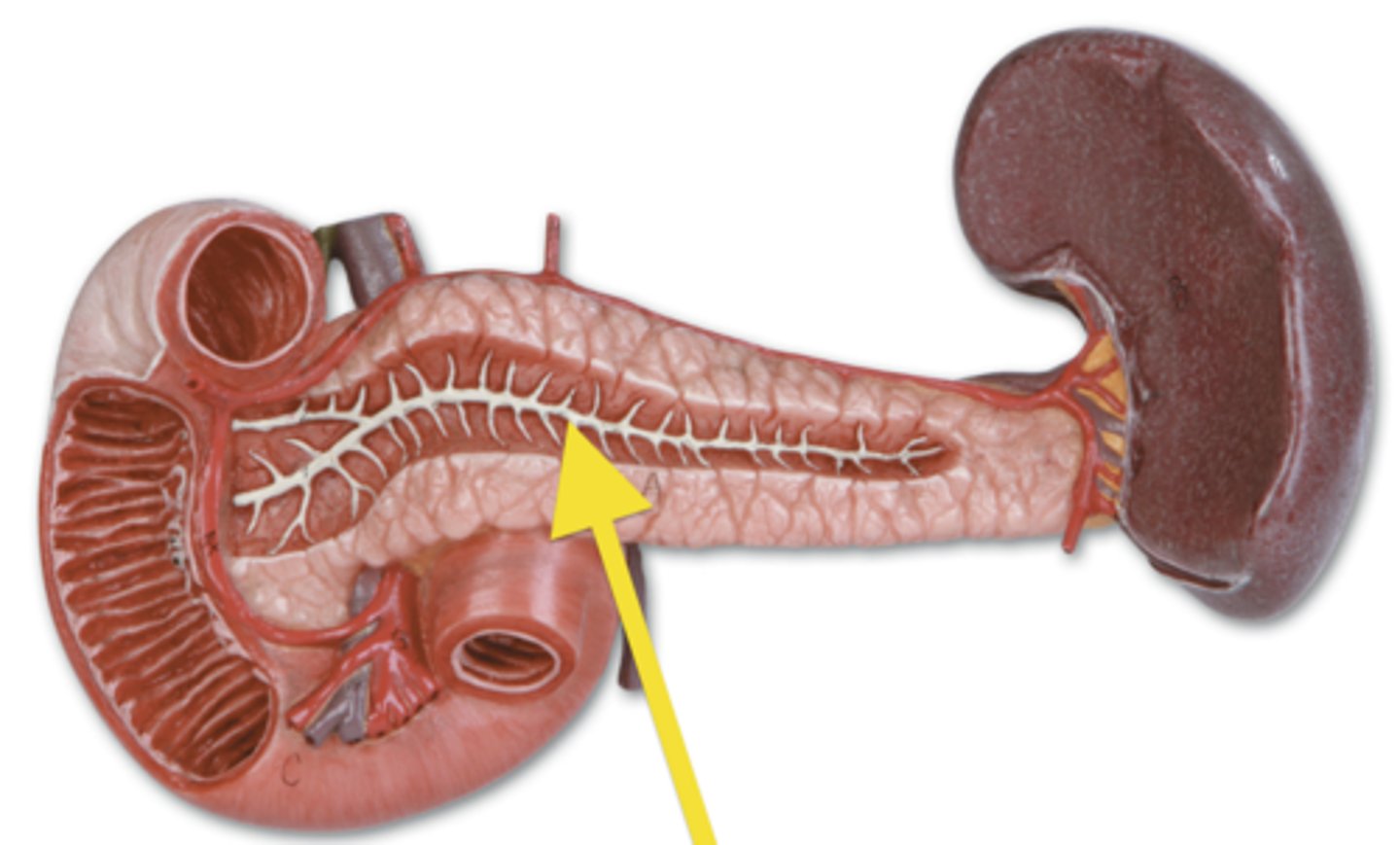
Pancreatic duct
The duct that carries digestive enzymes from the pancreas to the duodenum.
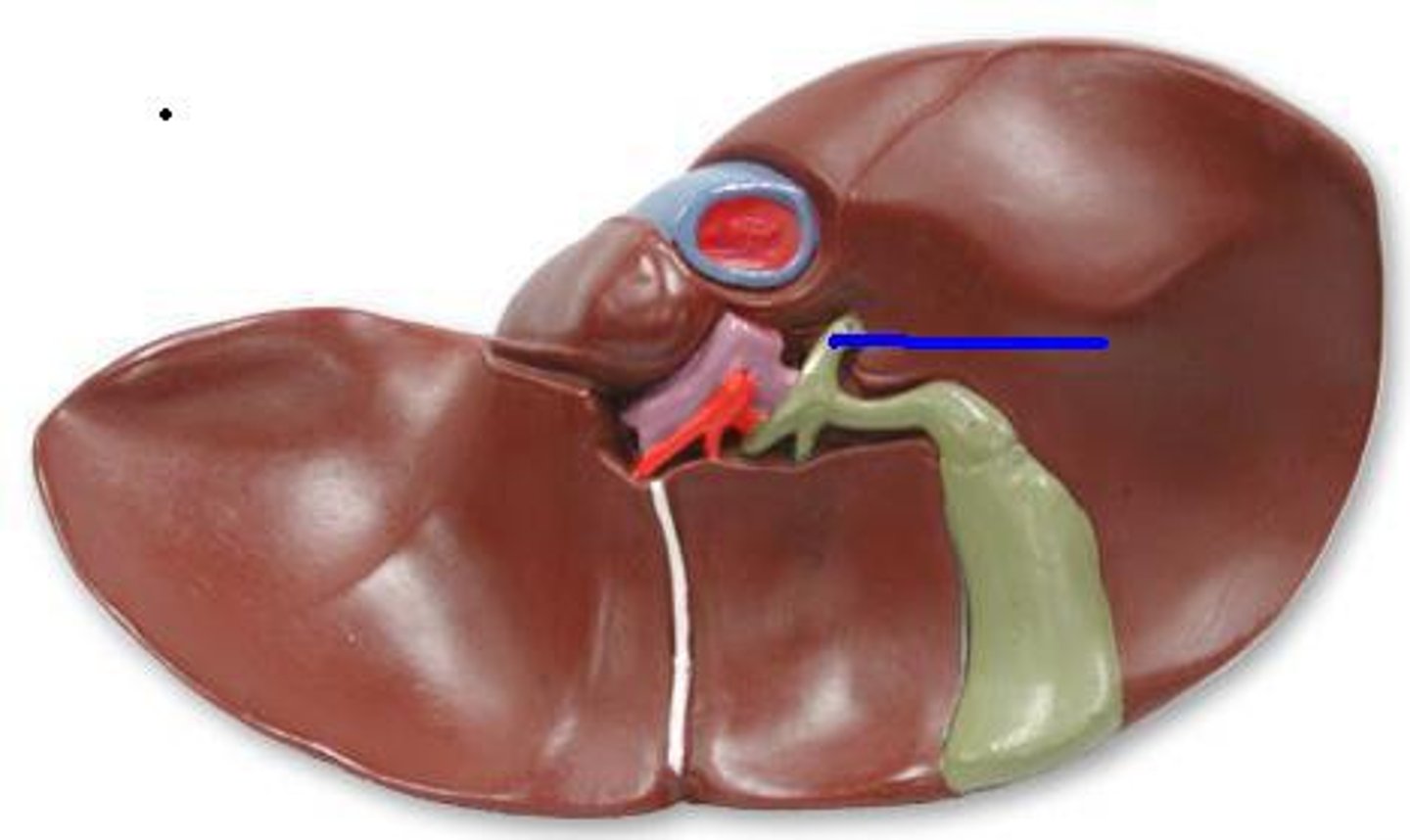
Bile duct
The duct that carries bile from the liver to the duodenum.
Hepatopancreatic ampulla
The junction where the bile duct and pancreatic duct meet.
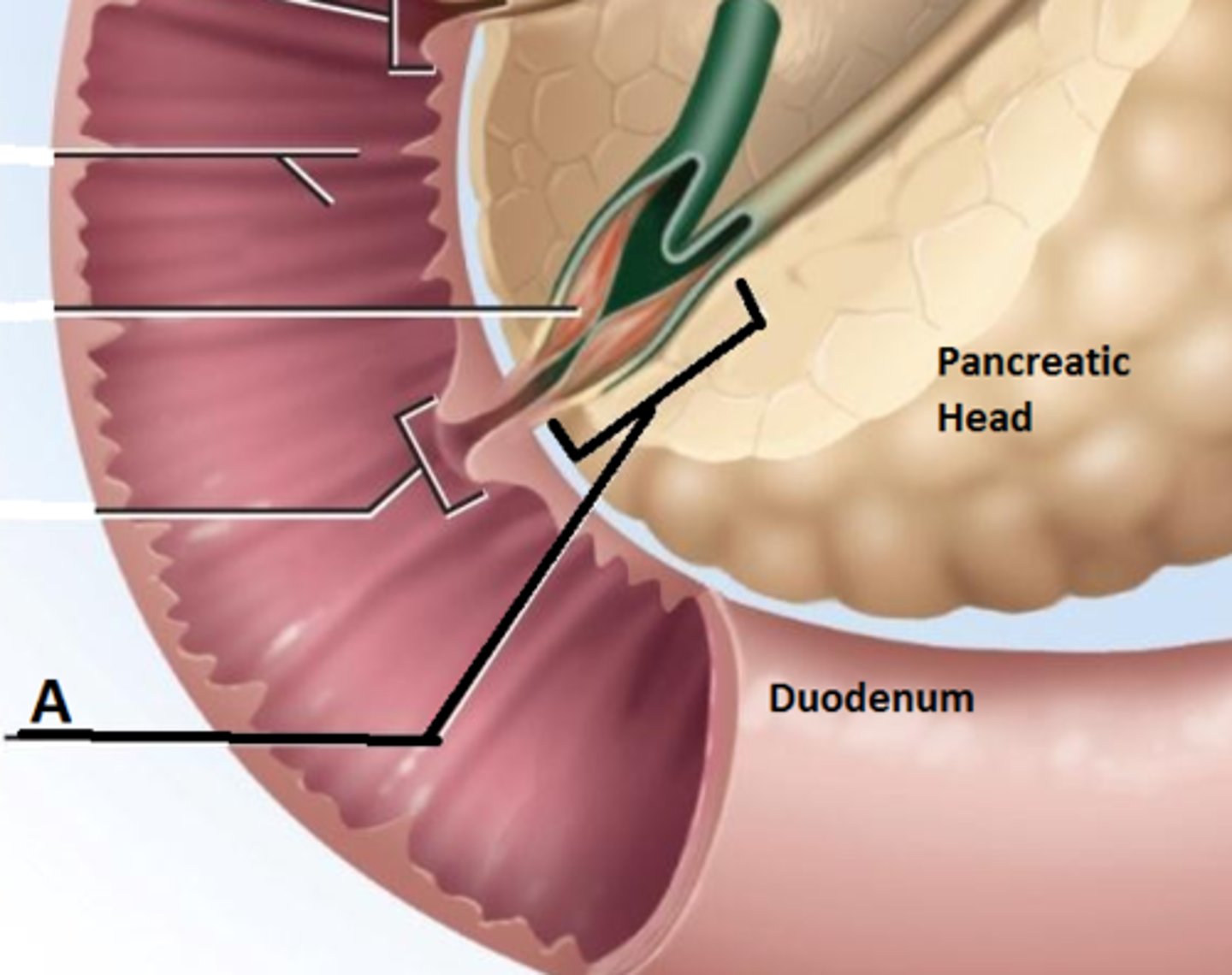
Major duodenal papilla
The opening in the duodenum where bile and pancreatic juices enter.
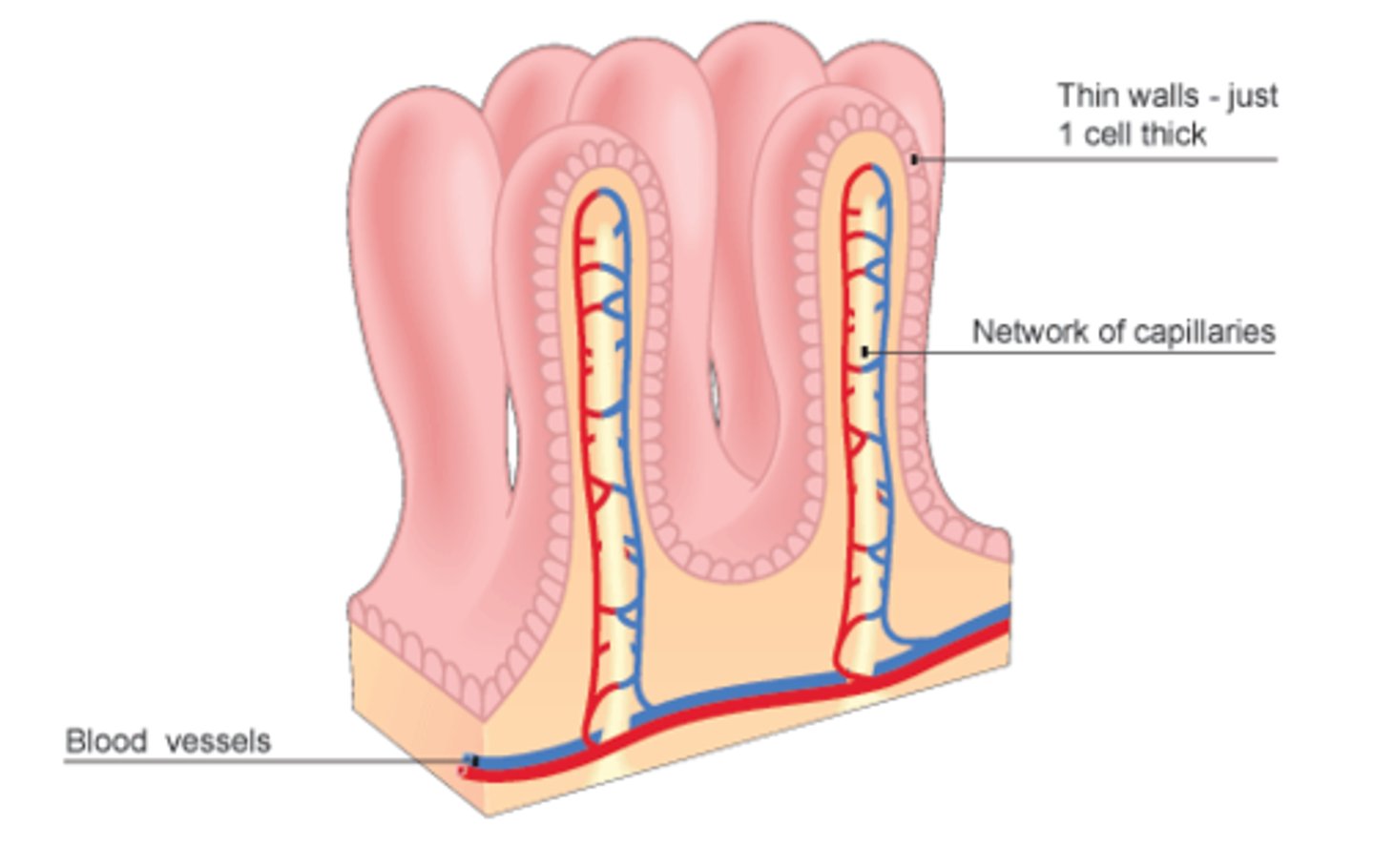
Villus
A small, finger-like projection in the small intestine that increases surface area for absorption.
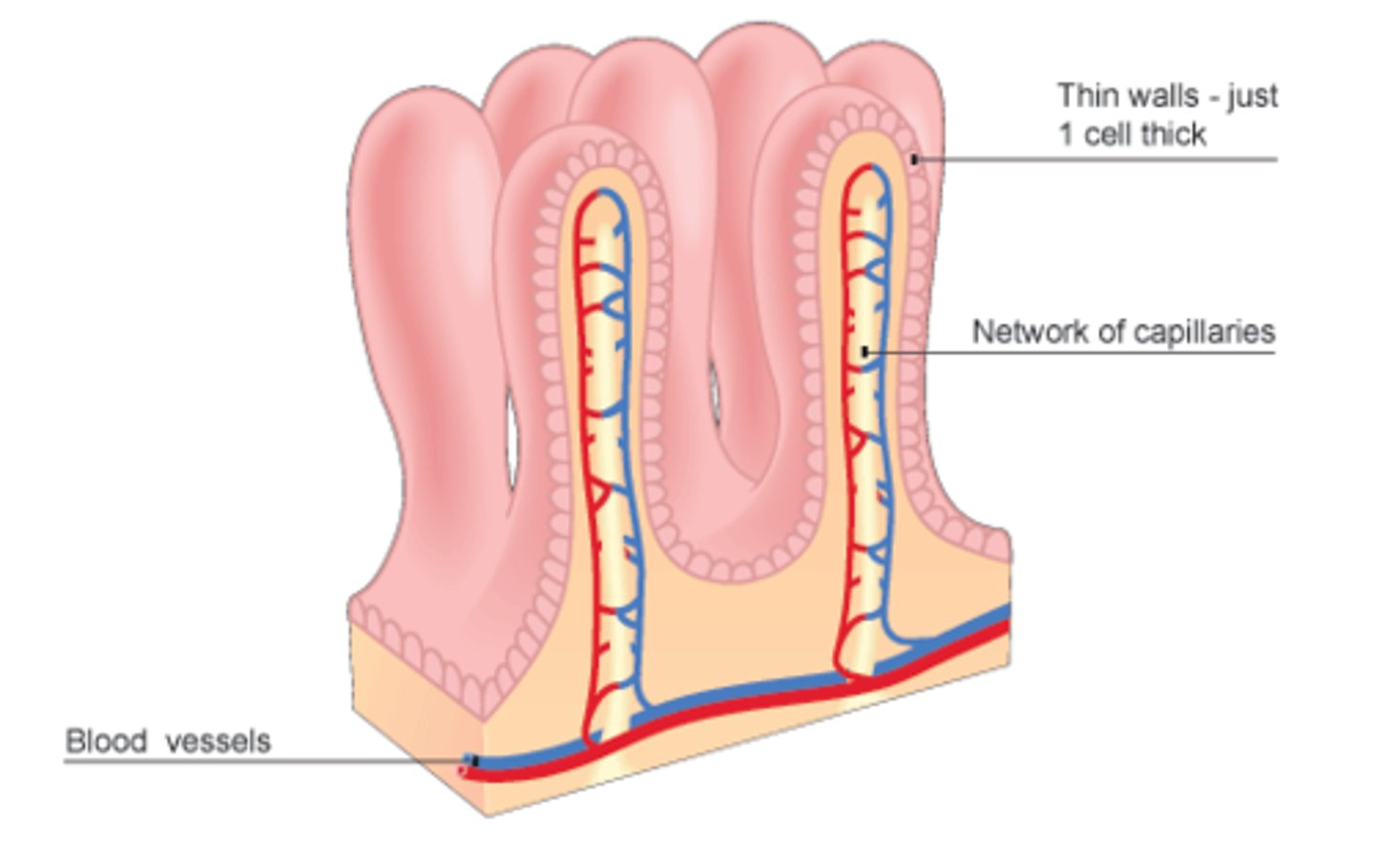
Villi
The plural form of villus.
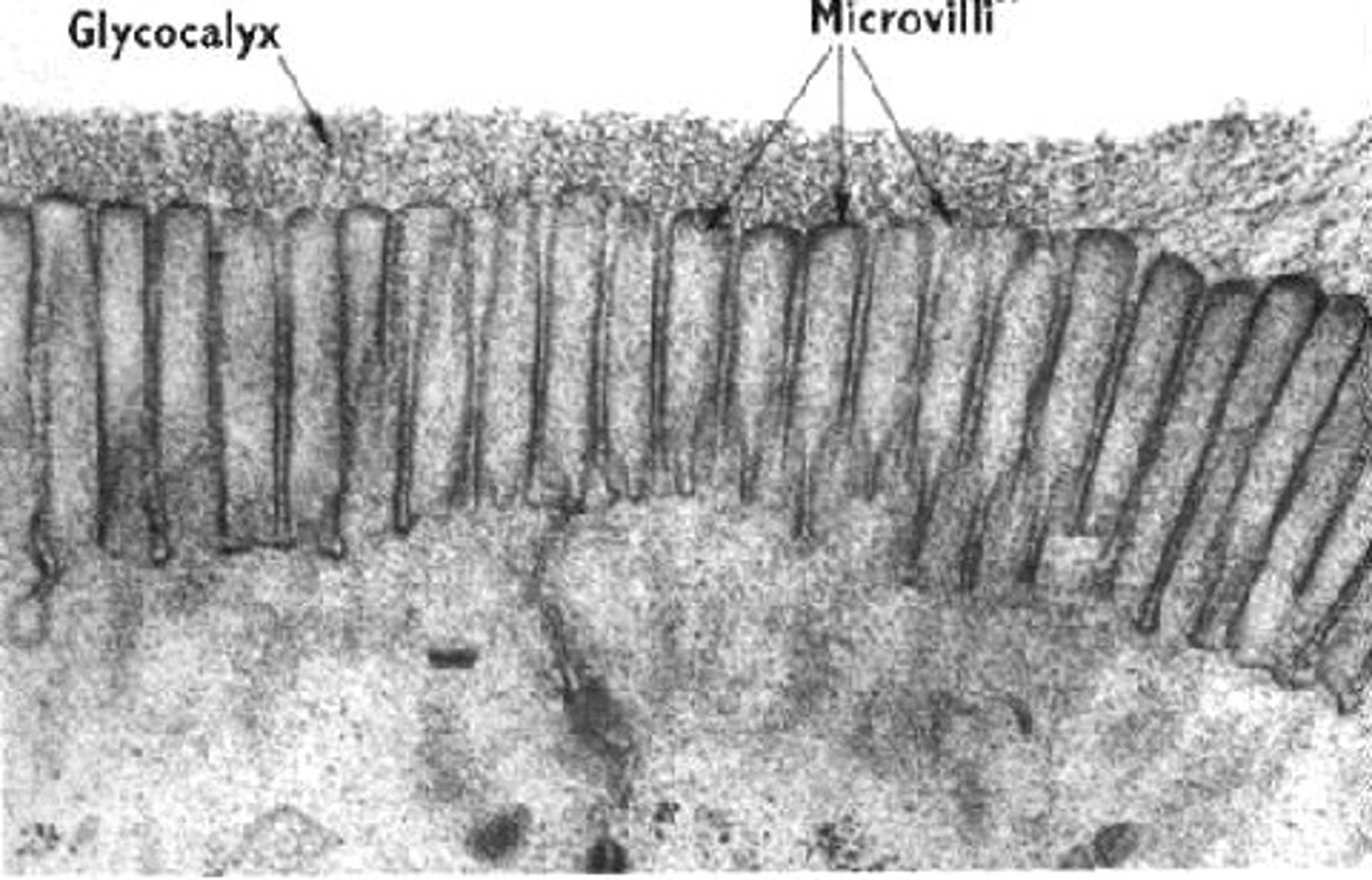
Microvilli
Tiny projections on the surface of intestinal cells that further increase surface area.
Intestinal flora
The community of microorganisms living in the intestines.