Cell Transport Mechanisms
1/115
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
116 Terms
Membrane
- Membrane controls what gets in/out of the cell
- Some things pass through easier than others
Brownian motion
Innate random movement of molecules
Natural movement
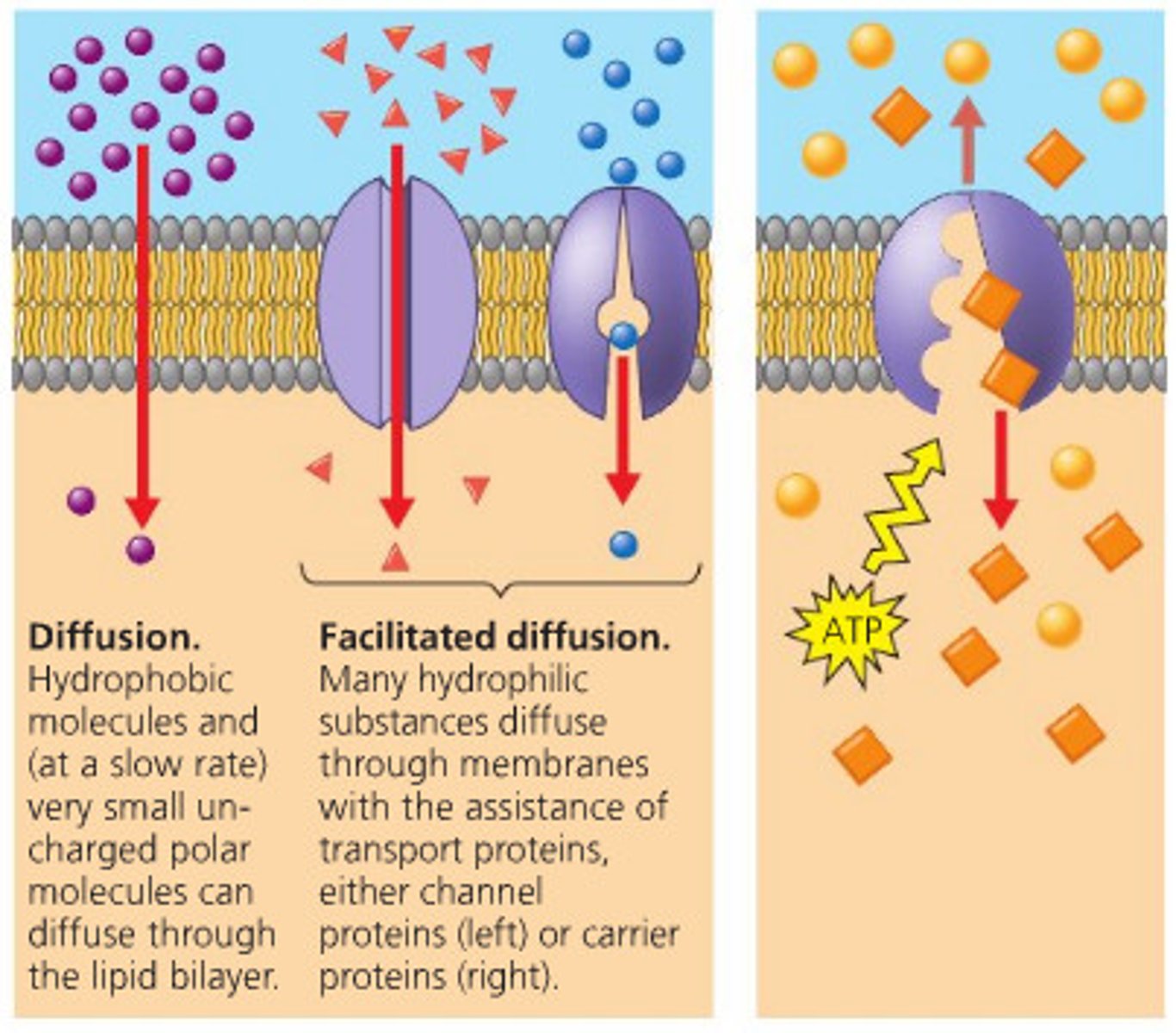
Transport: Passive
- No energy required for these transport materials
- The Moving through materials WITH concentration gradient (HIGH TO LOW)
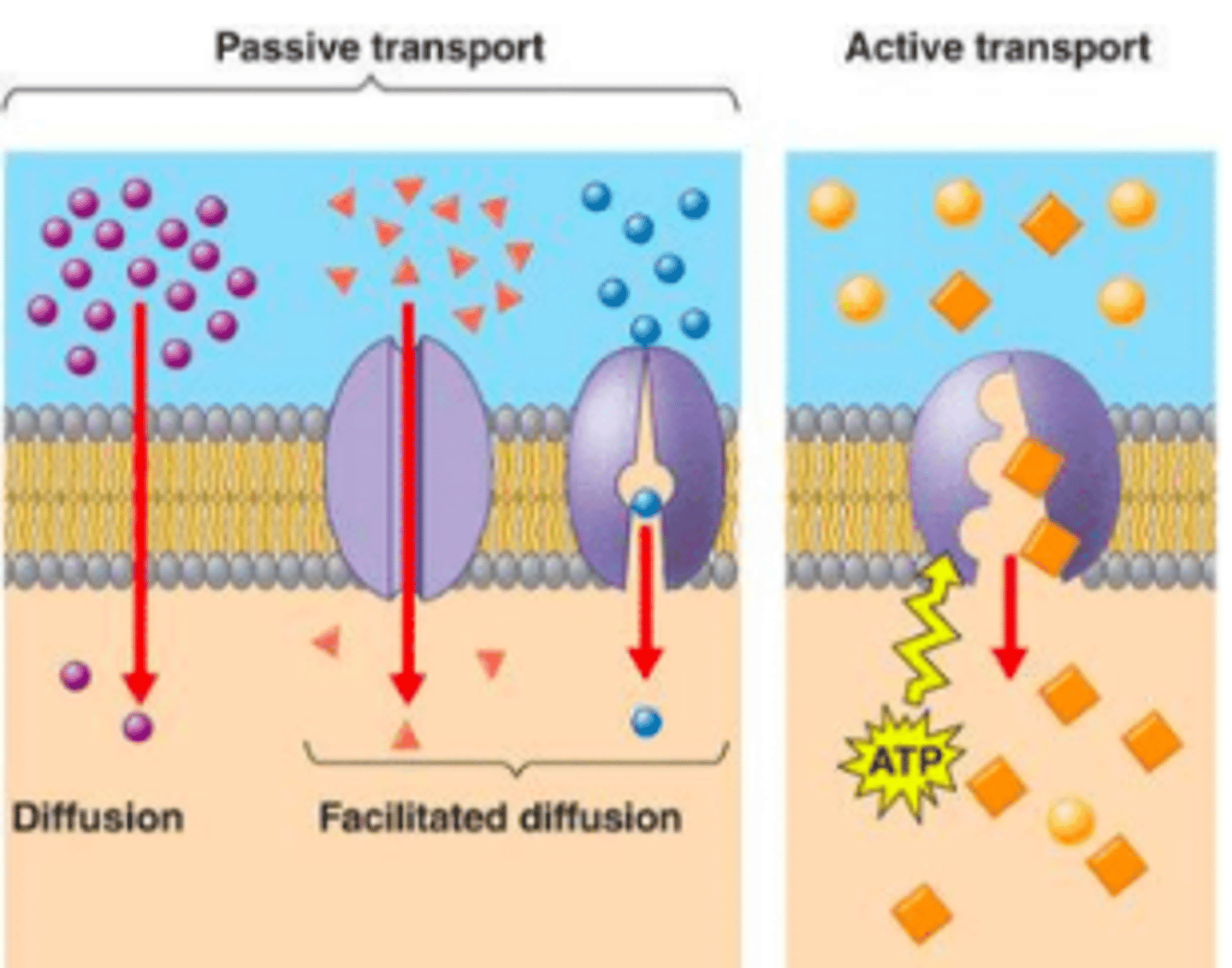
Transport: Active
- Requires use of energy to transport
- Moving materials AGAINST concentration gradient (LOW TO HIGH)
Passive Transport: Diffusion (Simple)
- Movemen of parcels down a concentration gradient (HIGH TO LOW)
- Particles naturally spread out
- Diffusion continues until dynamic equilibrium is reached
Passive Transport: Facilitated Diffusion
Diffusion through protein channels
Passive Transport - Osmosis (Water)
- Diffusion of water across a membrane.
- Is influenced by solutes (dissolved particles) in the water.
- (HIGH TO LOW concentration of water)
Hypotonic
- solution with less solute (more water) compared to another solution
Isotonic
- equal solute (equal water) compared to another solution
Membranes are/are NOT selectively permeable?
ARE
Hypertonic
- solution with more solute compared to another solution
HYPERtonic
more
HYPOtonic
less
ISOtonic
equal
Hypotonic Environment
Creates the problem of water moving into the cell
Hypotonic Environment: No cell wall
Animal cells will swell and possibly lyse(pop)
Hypotonic Environment: Has cell wall
- Some protists have contractile vacuoles
- Plant cells become turgid(swollen)
Hypertonic Environment
Creates the problem of water loss
Hypertonic Environment: No cell wall
Animal cells shrivel = crenate (shriveling up) = could die
Hypertonic Environment: Has cell wall
- Plant cells will plasmolyze
- More likely to recover
Isotonic Environment
No difference in concentration of water between cell & environment
Isotonic Environment: No cell wall
Animal cells - no problem: cell is stable
Isotonic Environment: Has cell wall
Plant cells - cells are flaccid - lower pressure inside
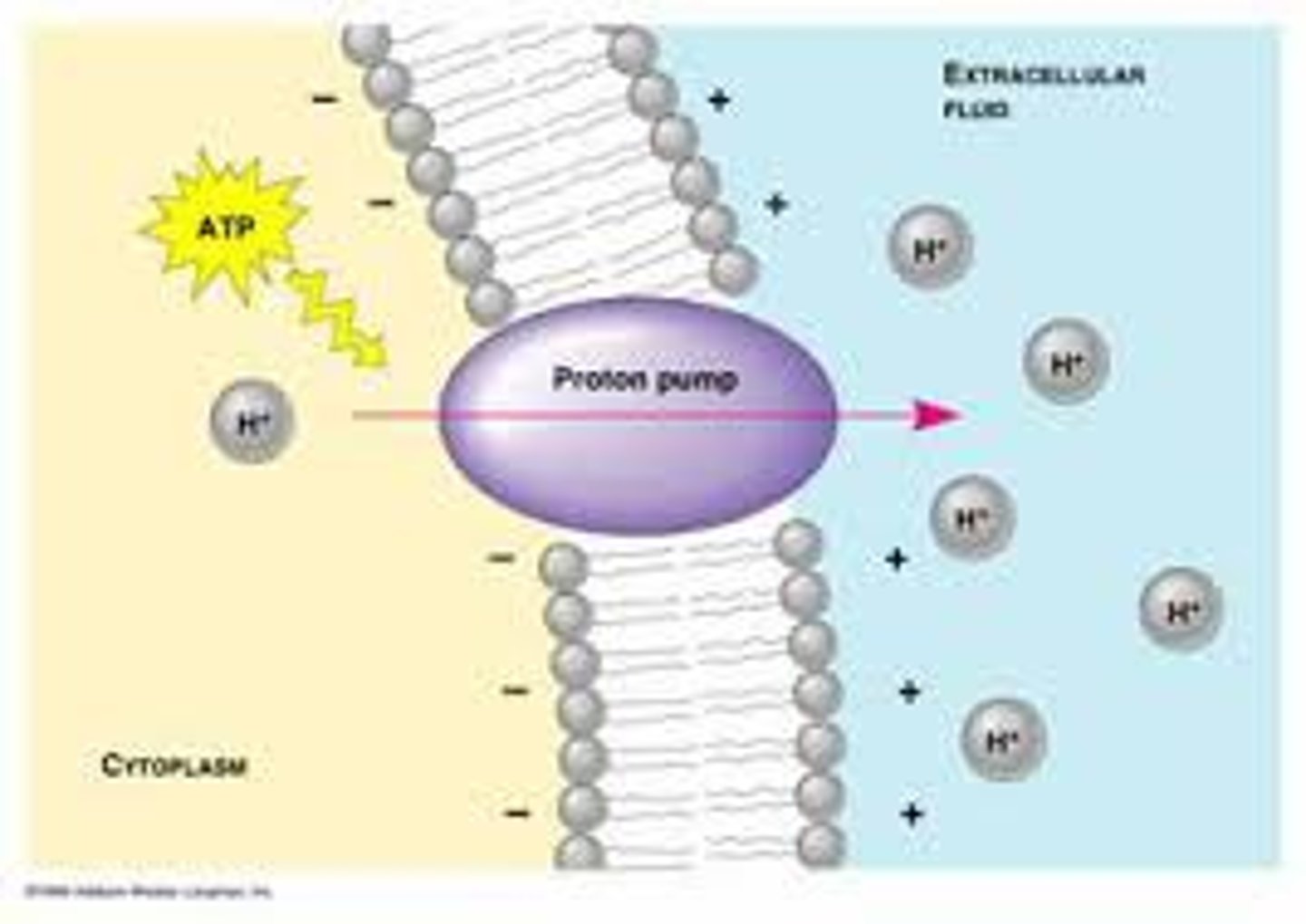
Active Transport: Protein Pumps
- Cells may need to move molecules AGAINST the concentration gradient
- "Costs" energy = ATP
- shape change transports solute from one side of the membrane to the other
- Moves sodium and potassium ions in/out of the cell
Active Transport: Protein Pumps - How many sodium ions and potassium ions gets moved in and out of the cell?
3 sodium ions OUT of the cell and 2 potassium ions INTO the cell
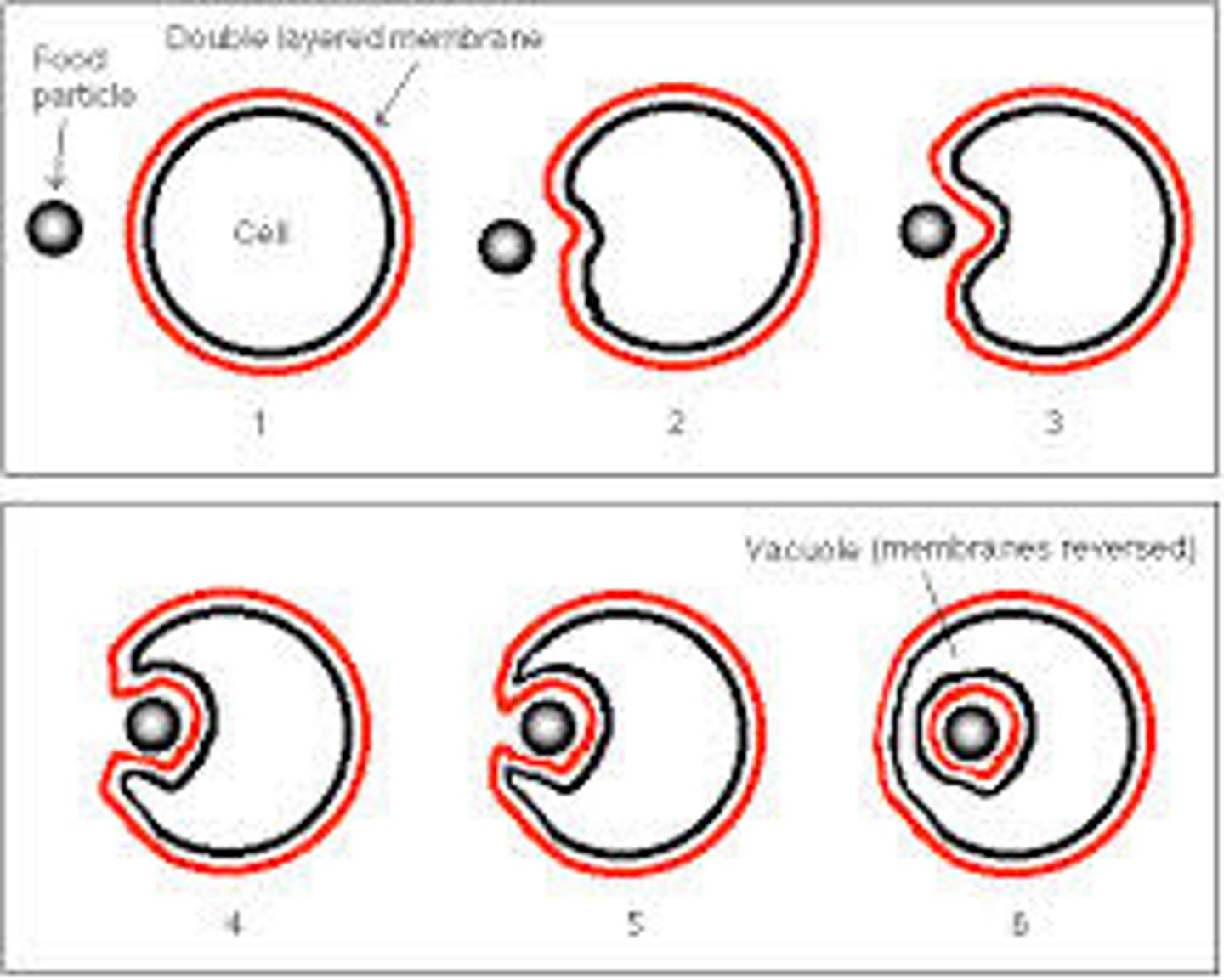
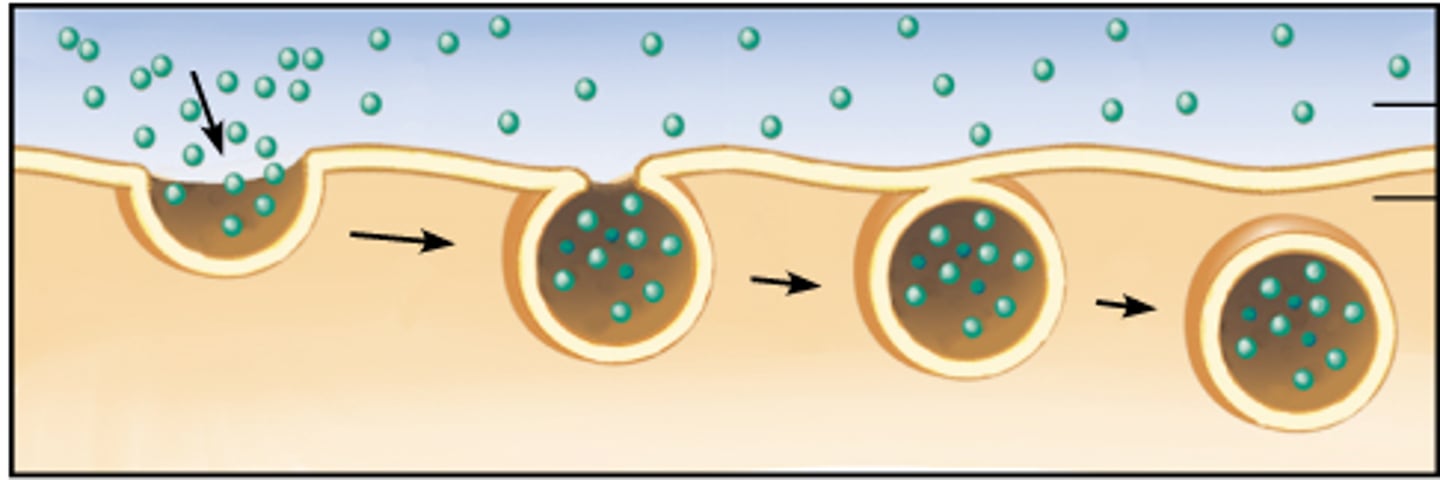
Endocytosis
is how the cell brings in large particles
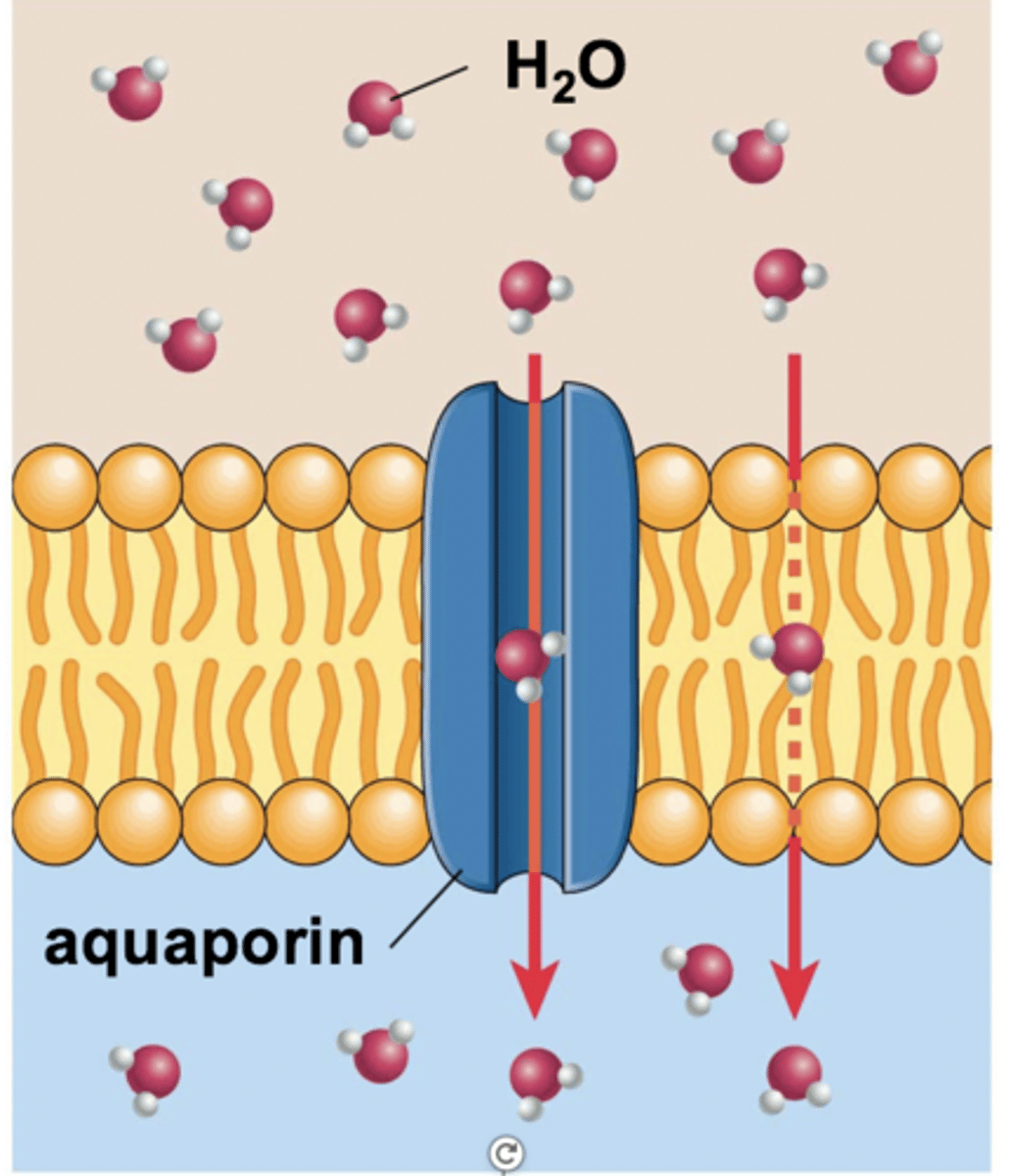
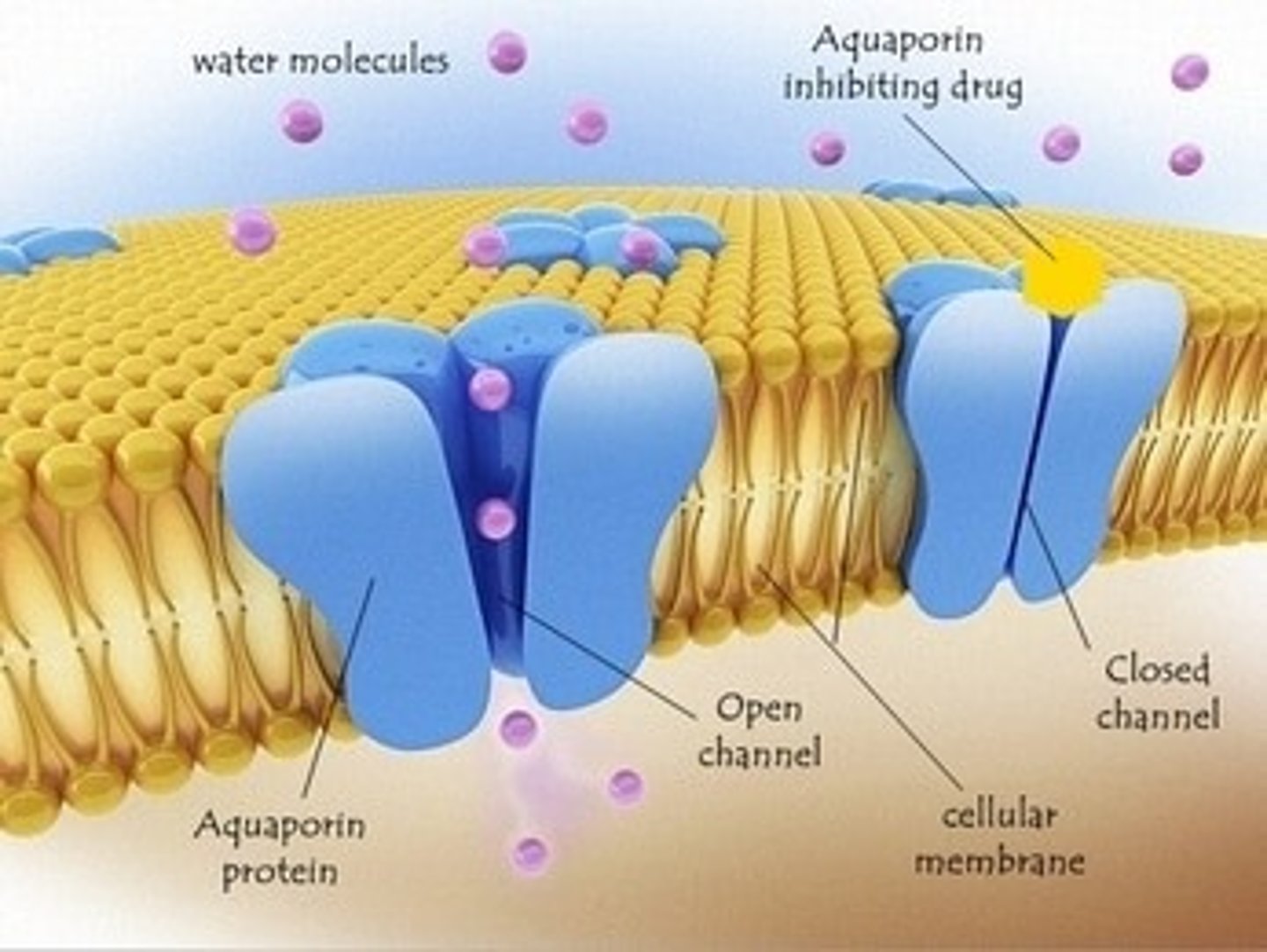
Aquaporins
protein channels found in cell membranes that allow water molecules to pass through
Active Transport: Endocytosis: Phagocytosis
Brings in large solid particles
Phagocytosis means
cell eating
Pinocytosis means
cell drinking
Active Transport: Endocytosis: Pinocytosis
Brings in liquids
Active Transport: Endocytosis:
Receptor-mediated endocytosis
- They bond to specific particles on the outside of the membrane
- triggering the cell membrane to fold inward and engulf these bound molecules into a new vesicle, thereby bringing them into the cell
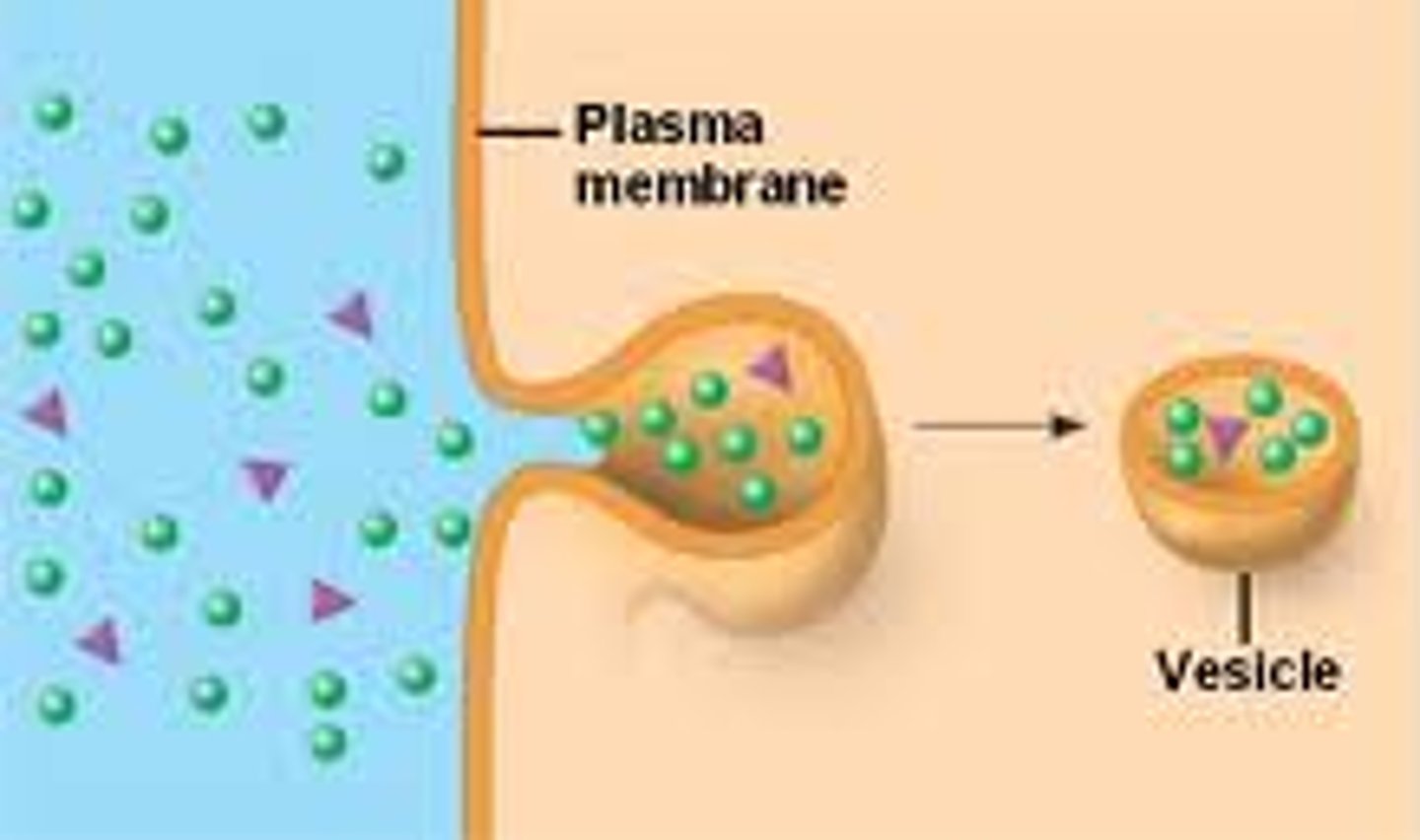
Active Transport: Exocytosis
- Gets rid of large particles or large amounts of particles in the cell
- Could be waste, something that the cell makes intentionally (hormones, proteins)
Receptor-mediated endocytosis means
bonding specfic
Definition of metabolism
- sum or all cheminal reactions in a cell/organizam
- involves energy transformations and transformations of matter
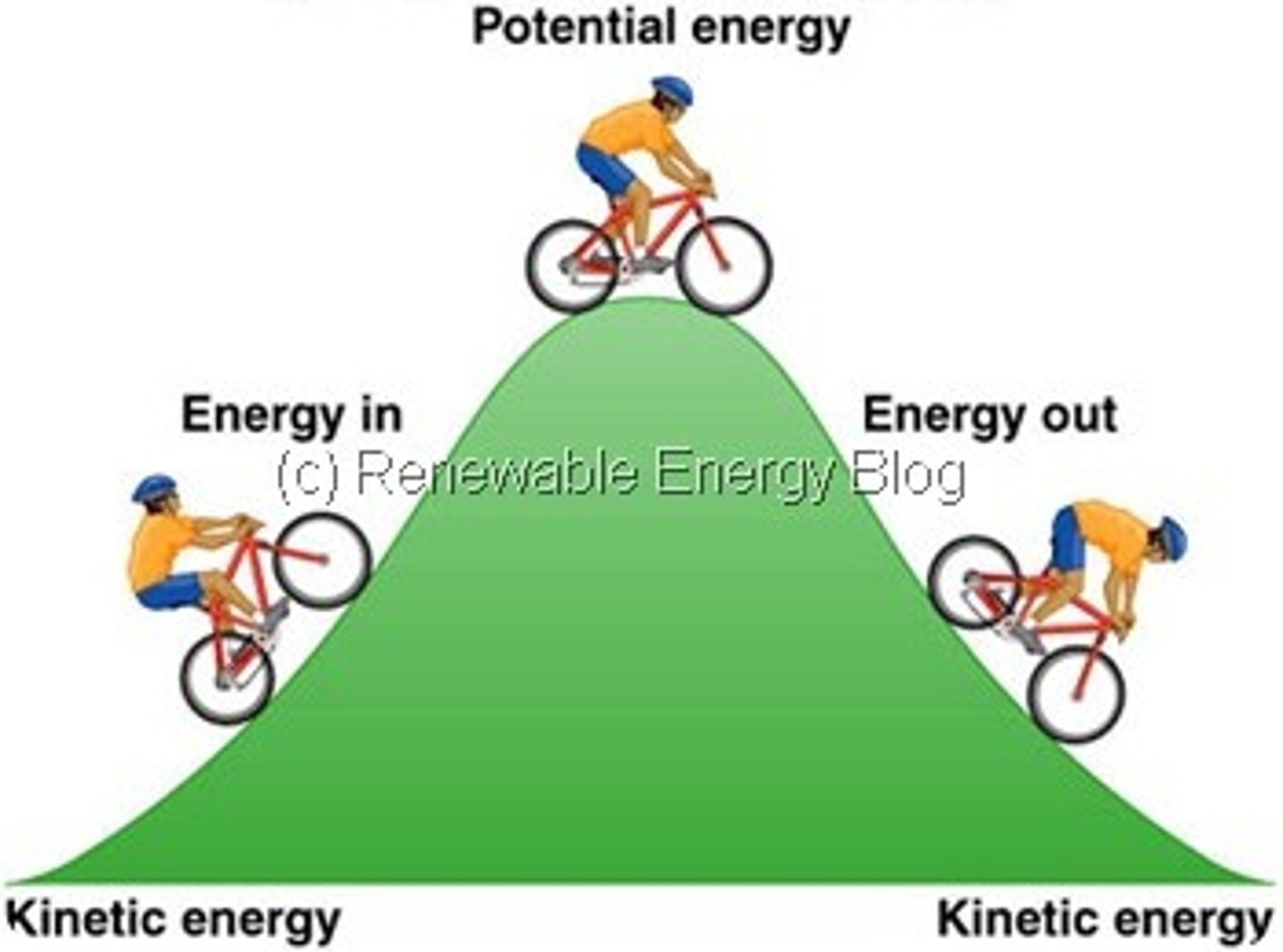
Potential Energy means
stored energy or location of material
Potential Energy examples
- Chemical
- Nuclear
- Gravitational
- Elastic
Kinetic Energy means
energy of motion
Kinetic Energy examples
- Mechanical
- Thermal (heat)
- Sound
- Electrical
- Radiant (light)
Anabolic Pathways consist of
- Build complicated molecules from simpler ones
- Endergonic Reaction: Consume energy
- Also called up-hill and non-spontaneous reactions
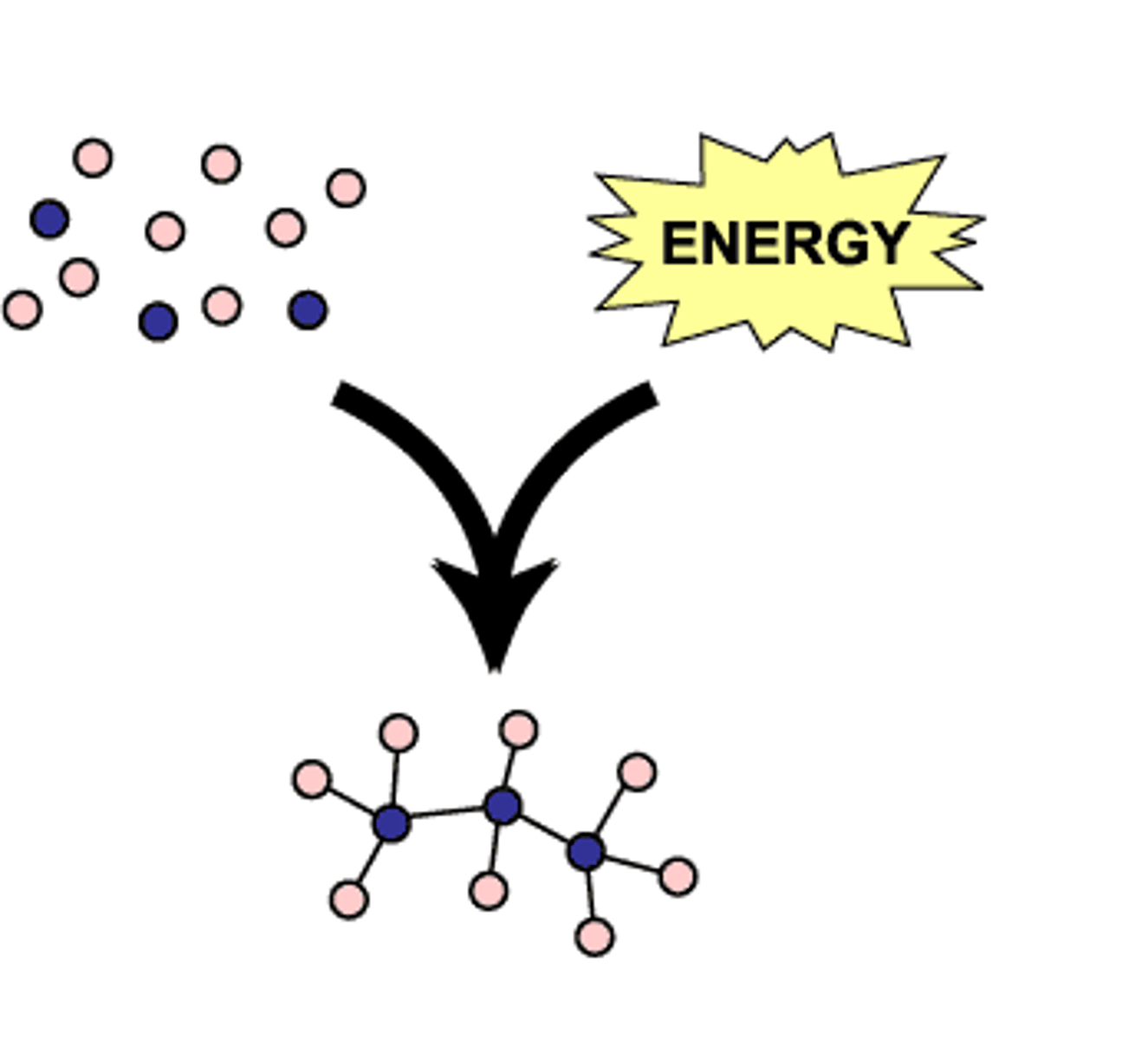
Anabolic Pathways defintion
use energy to build complex molecules from simpler precursors
Catabolic Pathways consist of
- Break down complex molecules into simpler compounds
- Exergonic Reactions: Release energy
- Also called down-hill and spontaneous reactions
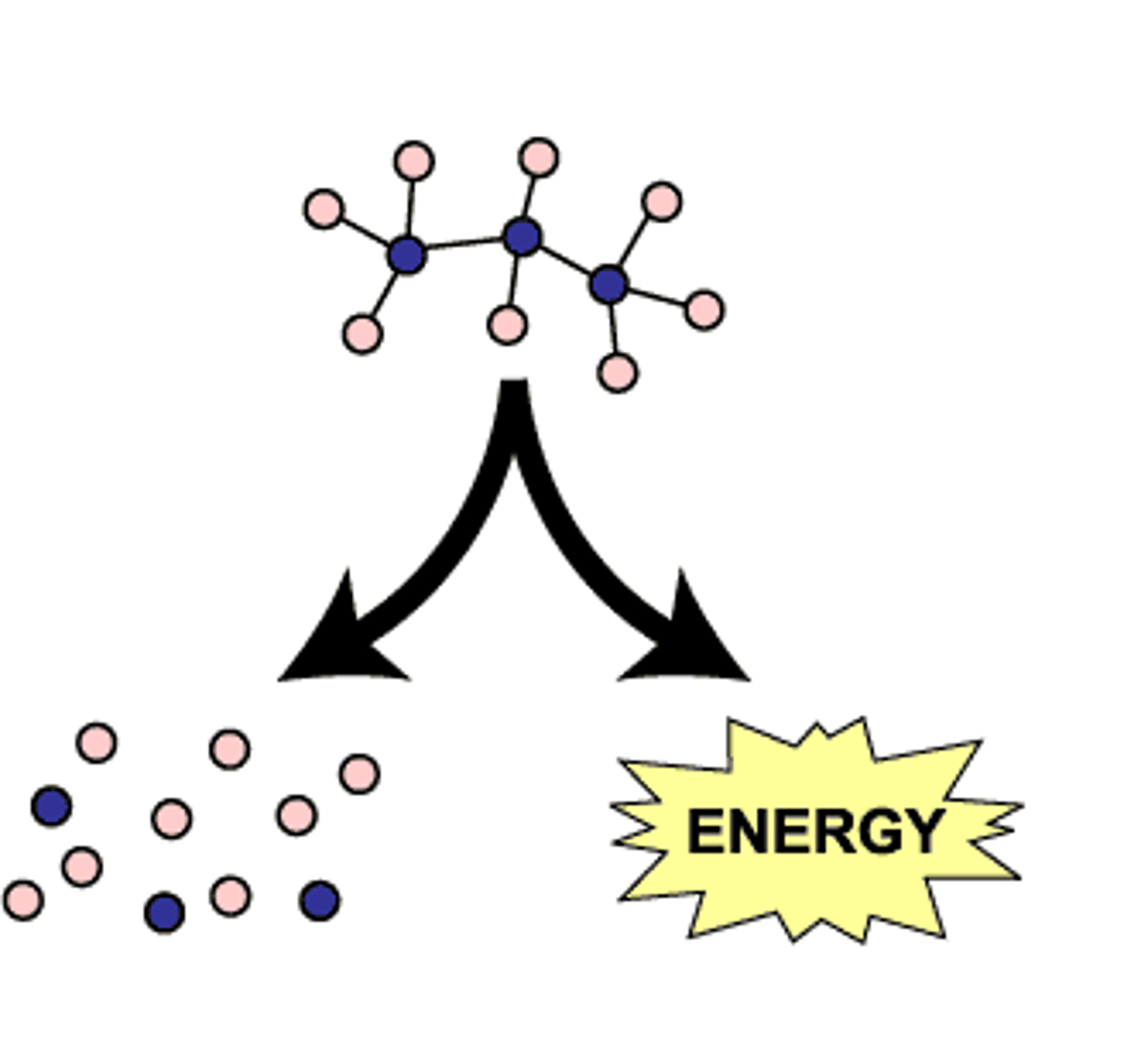
Catabolic Pathways definition
break down complex molecules into simpler ones, releasing energy
What does not affect membrane permeability?
The polarity of membrane phospholipids
How can a lipid be distinguished from a sugar?
Lipids are mostly nonpolar.
True or false? Osmosis is a type of diffusion.
True
What property of dishwashing liquid (detergent) makes it useful to wash grease from pans?
Amphipathic nature
Which of the following particles could diffuse easily through a cell membrane?
Oxygen
True or false? The water-soluble portion of a phospholipid is the polar head, which generally consists of a glycerol molecule linked to a phosphate group.
True
If a red blood cell is placed in a salt solution and bursts, what is the tonicity of the solution relative to the interior of the cell?
Hypotonic
What name is given to the process by which water crosses a selectively permeable membrane?
osmosis
If a solution surrounding a cell is hypertonic relative to the inside of the cell, how will water move?
It will move out of the cell via osmosis.
Energy coupling uses
energy released from exergonic reactions to drive essential endergonic reactions (usually the energy in ATP reactions), includes redox reactions
Exergonic
releases energy
Endergonic
absorbs energy
What does Redox Reactions stand for?
reduction-oxidation reactions
What are redox reactions
Chemical reactions that involve the transfer of electrons between atoms/molecules
Reduction meaning in Redox Reactions
Gain of electrons (reduction in valence)
Oxidation meaning in Redox Reactions
Loss of electrons
LEO the lion goes GER stands for
- Lose electrons oxidation
- Gain electron reduction
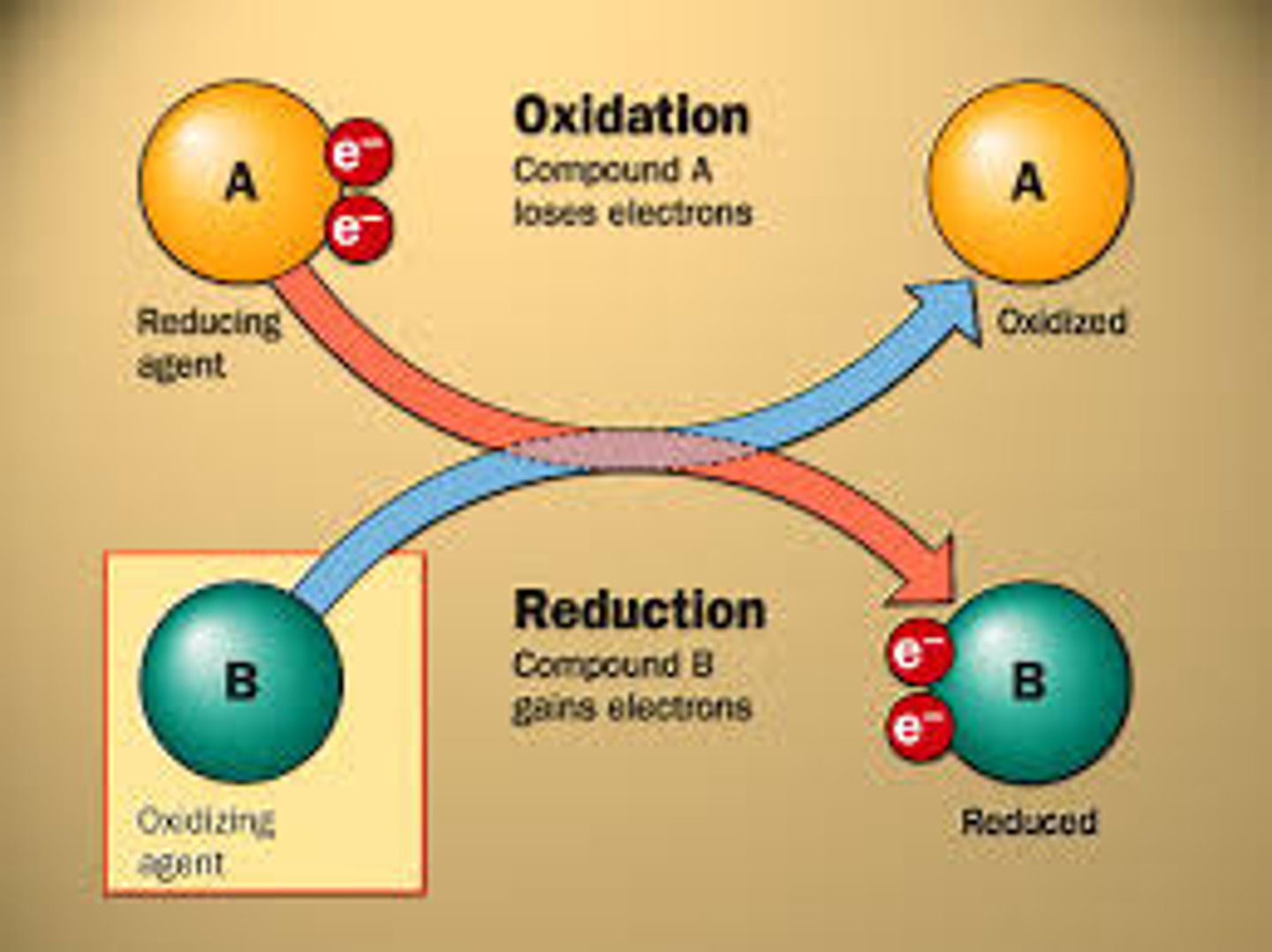
OIL RIG stands for
Oxidation is LOSS
Reduction is GAIN
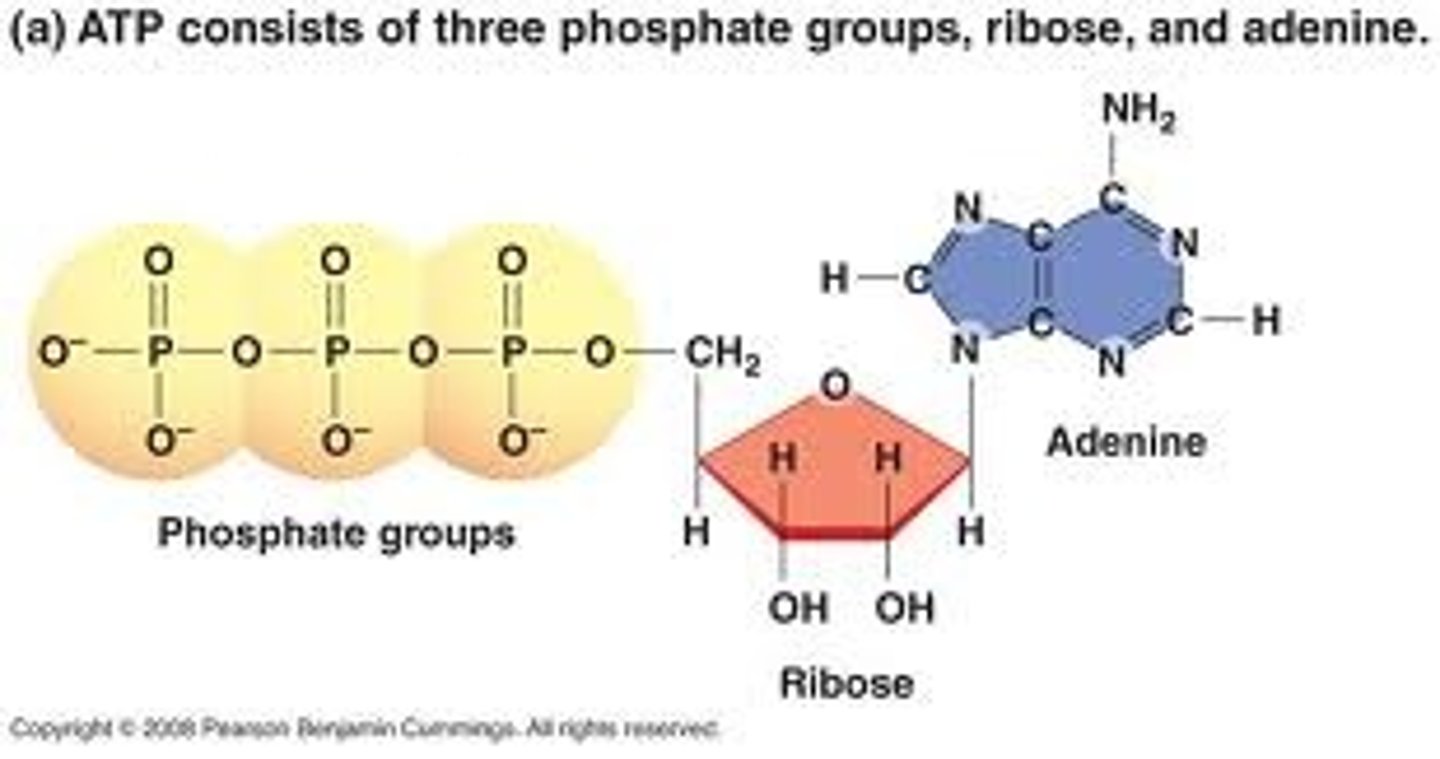
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP)
compound used by cells to store and release energy
Phosphorylation
The transfer of a phosphate group, usually from ATP, to a molecule. Nearly all cellular work depends on ATP energizing other molecules by phosphorylation.
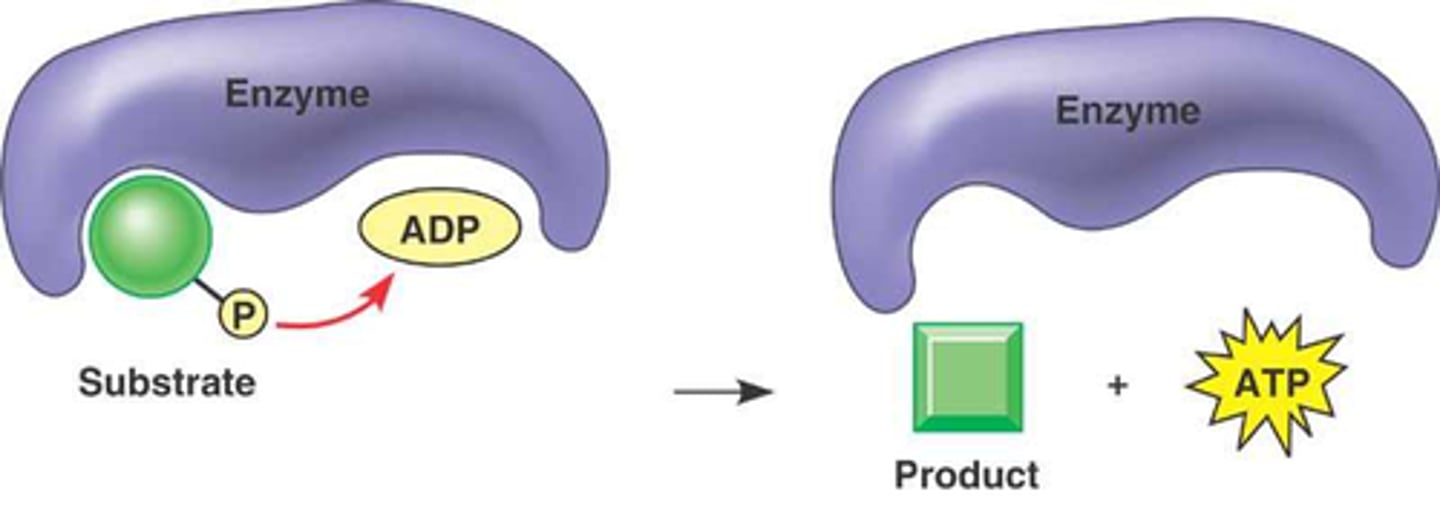
How does ATP work?
Phosphorylation
What is the summary equation for photosynthesis?
6 CO_2 + 6 H_2O + Light energy → C_6H_12O_6 + 6 O_2
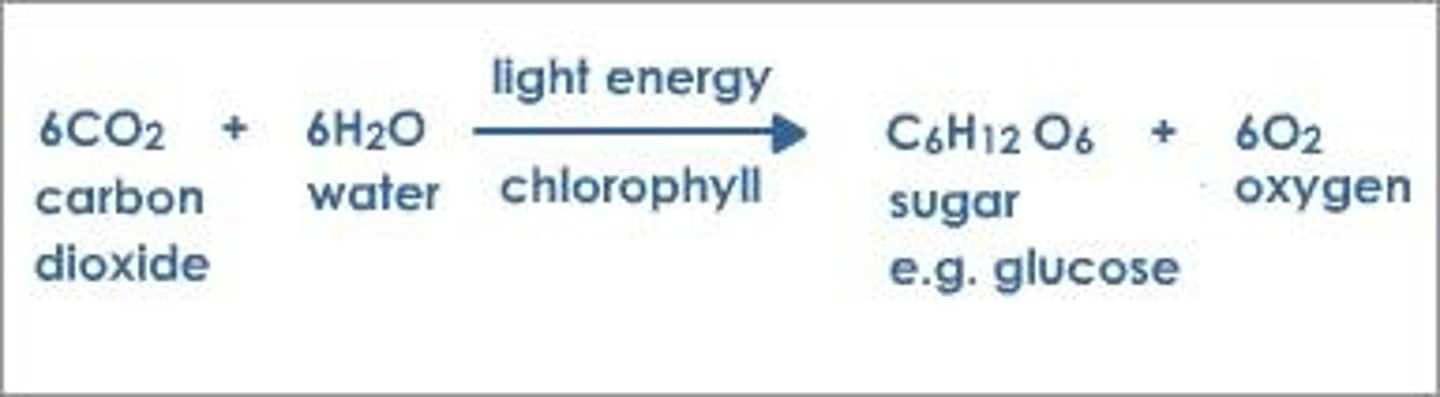
What metabolic/energetic categories apply?
- Anabolic
- Endergonic
- Non-spontaneous
- Uphill
What types of organisms conduct photosynthesis?
- Plants
- Algae
- Certain types of protists
- Some prokaryotes
Why is photosynthesis an important process?
- Make own food
- Base of food webs
- Provide glucose + oxygen for respiration
- Key role in carbon cycle
- Remove & store carbon
Organ = Roots
Anchors the plant in the soil, absorbs water and dissolved nutrients/minerals
Organ = Stem
Holds up leaves and transports materials through the plant body
Organ = Leaves
Site of photosynthesis
Structure = Cuticle
- Waxy covering secreted by epidermal cells
- Barrier against pathogens and excess water loss/uptake
Structure = Stoma (or stomata)
- Openings in epidermis surrounded by two guard cells
- Open/close to regulate gas exchange and prevent transpiration (water evaporation)
Tissue = Mesophyll
Cells that perform photosynthesis and store products
Tissue = Vein
(also called Vascular bundle), transports materials
Tissue = Xylem (inside vein)
transports water and dissolved solutes (minerals and salts)
Tissue = Phloem (inside vein)
transports photosynthetic products
Light Definition
a form of electromagnetic energy, which travels in waves and particles called photons
Wavelength Definition
Is the distance between the crests of waves
- Determines the type of electromagnetic energy
The visible light spectrum definition
includes the colors of light we can see
The relationship between wavelength and light energy: Shorter wavelength = __________ energy? (Higher or Lower)
Higher
The relationship between wavelength and light energy: Longer wavelength = __________ energy? (Higher or Lower)
Lower
Pigments Definition
- are molecules that absorb light
- some light is reflected, which are the colors we see
Photosystem
- a group of pigments
- consists of the reaction center and accessory pigments
Reaction Center
Chlorophyll A - main photosynthetic pigment
Has electrons that become excited(gains so much energy) and leave the molecule
What happens when a pigment absorbs light
It goes from a ground state to an excited state, which is unstable
Accessory Pigments
Absorbs different wavelengths of light and pass the energy to the reaction center chlorophyll
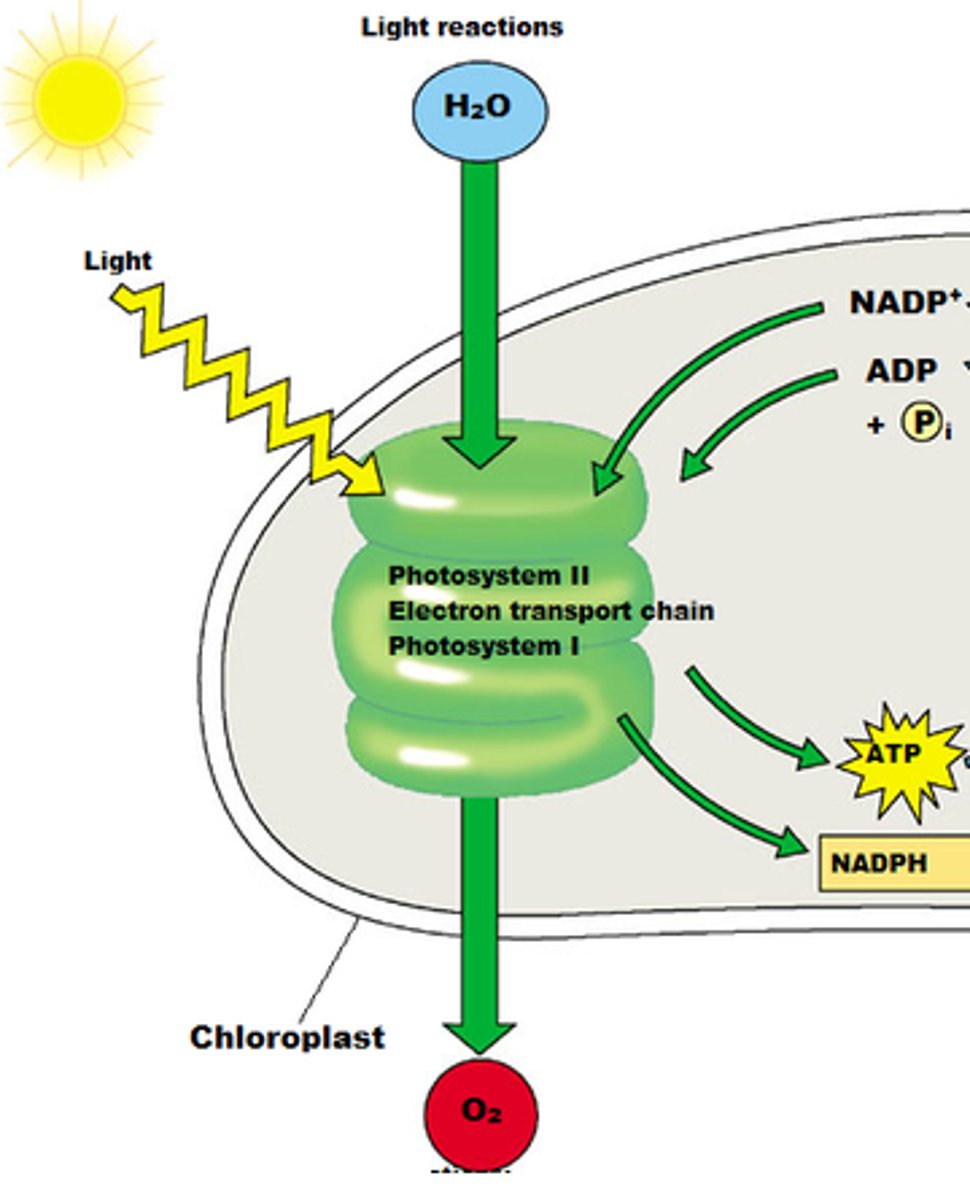
Light Reactions
- Occurs in the thylakoid membranes
- Convert solar energy into chemical energy
- Split water, release oxygen, produce ATP, and form NADPH
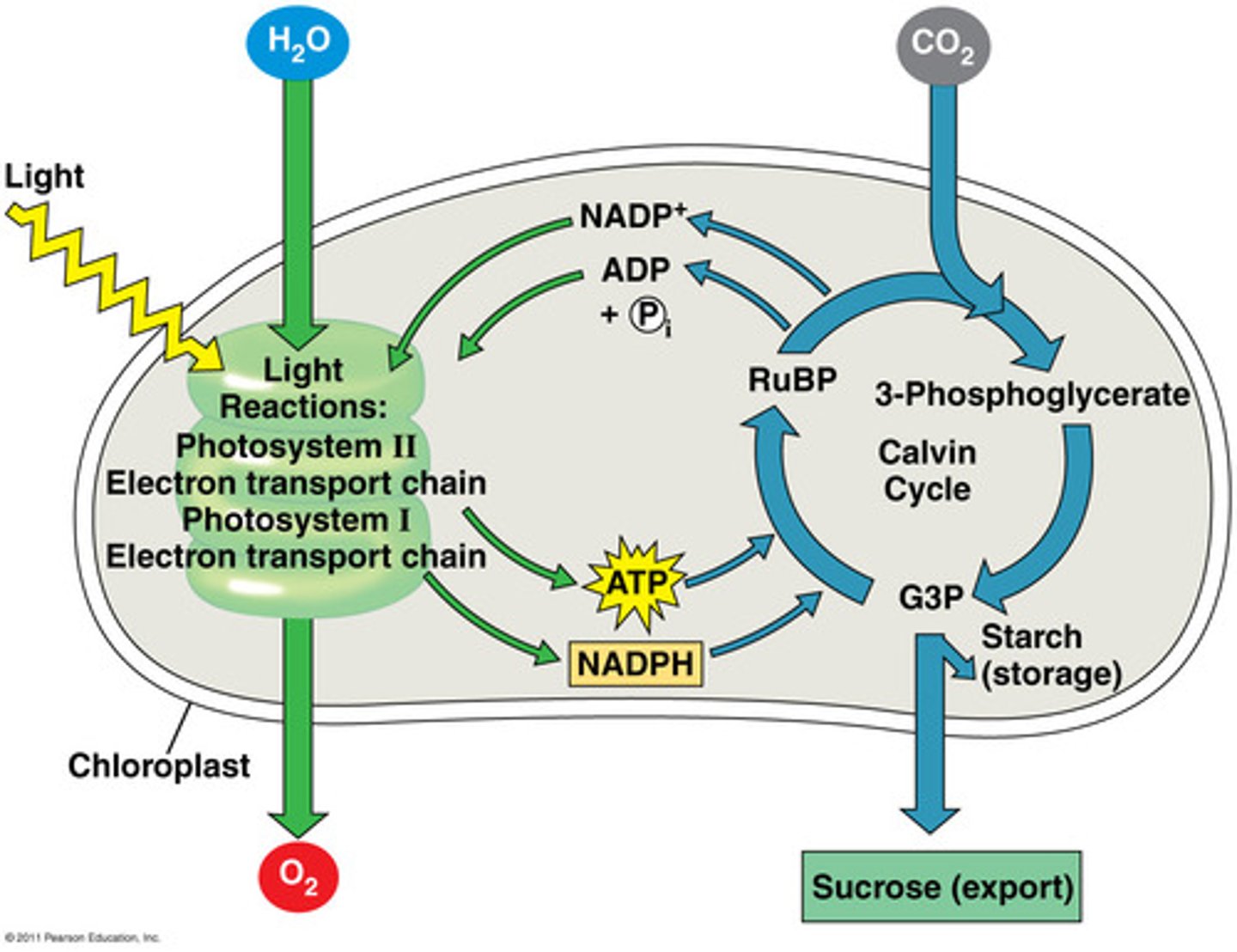
Calvin Cycle
- Occurs in the stroma
- Forms sugar from carbon dioxide using ATP for energy and NADPH for reducing power
Molecules of _______ _______ (originally found in the air or water) diffuse into the _________ of the chloroplast
carbon dioxide, stroma
The molecule carbon dioxide combines with a molecule of ________ __________
RuBP
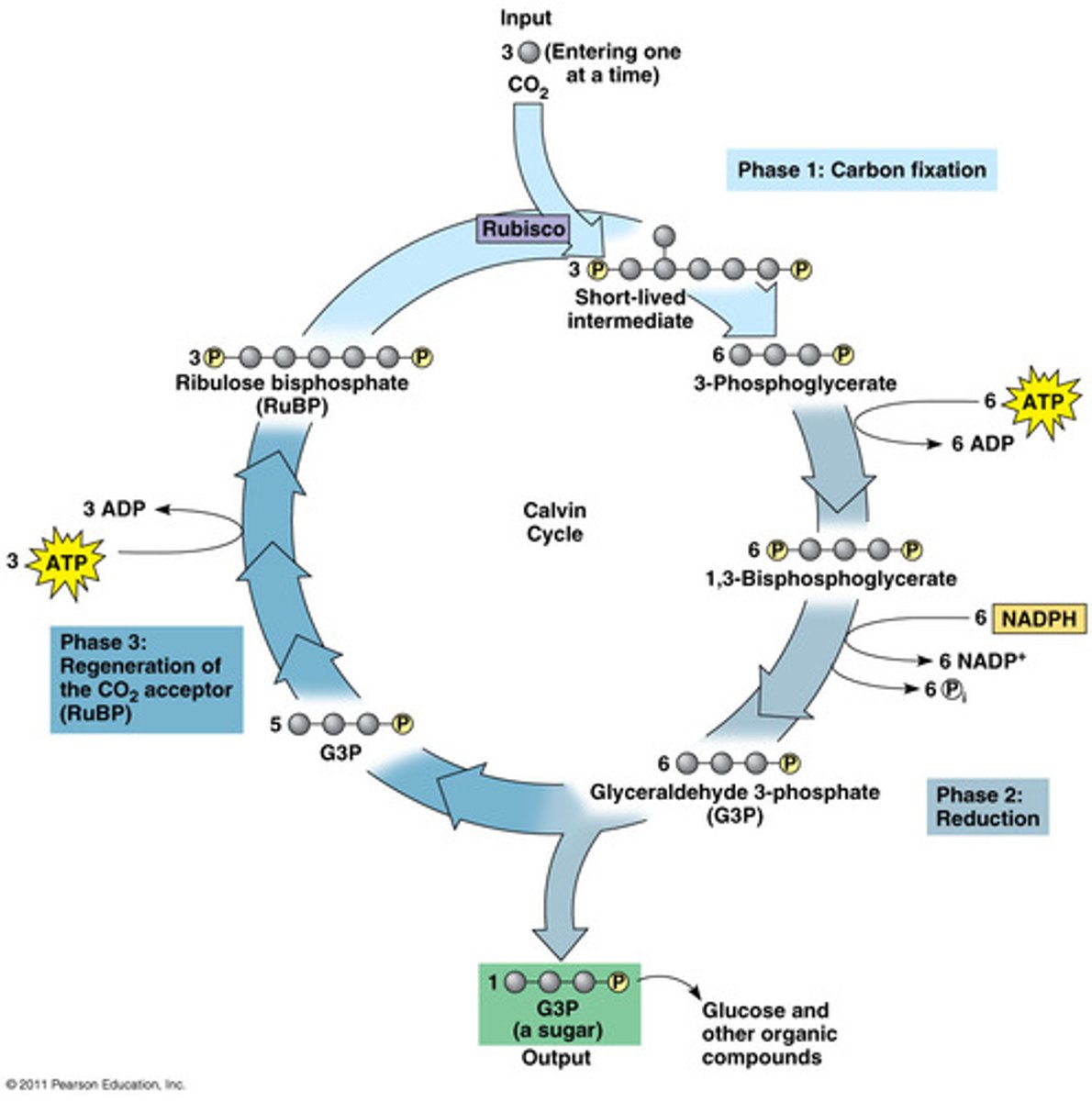
This anabolic and endergonic reaction is catalyzed by the enzyme __________.
rubisco
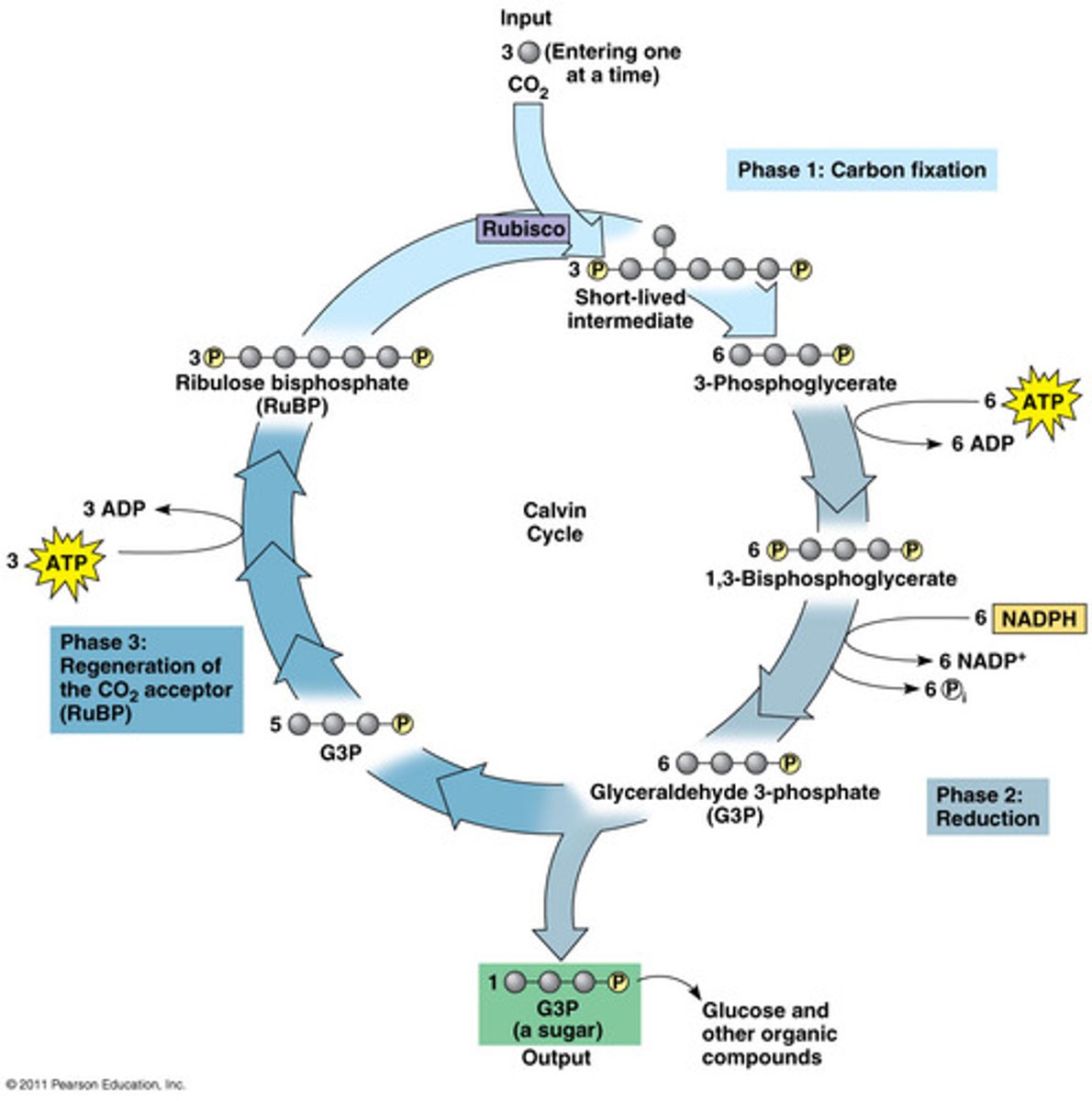
Since the molecule from #3 is an enzyme, CO_2 and RuBP are its:
substrates
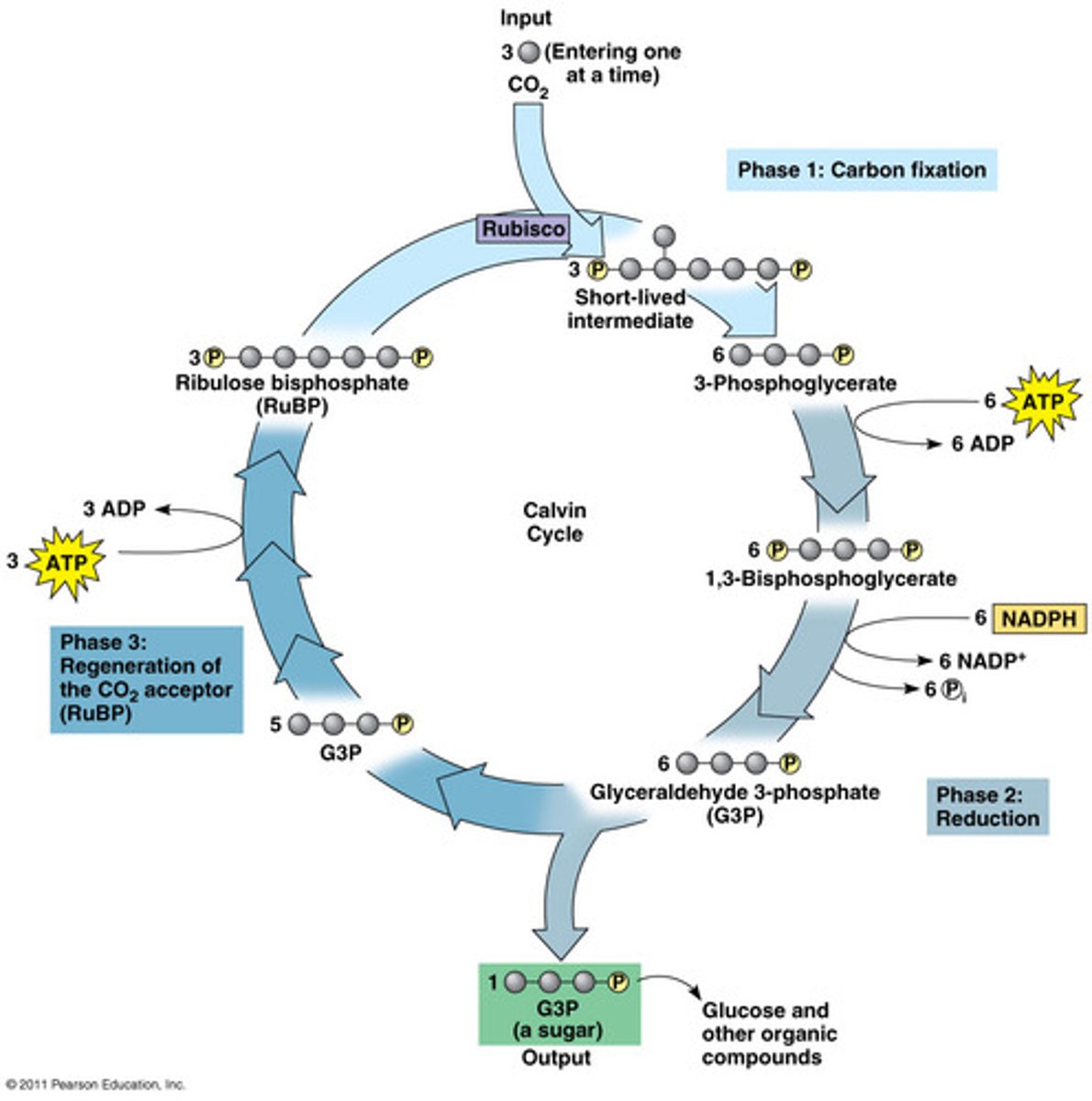
The unstable molecule that forms from CO2 coming with RuBP immediately breaks apart into two molecules of __________.
PGA
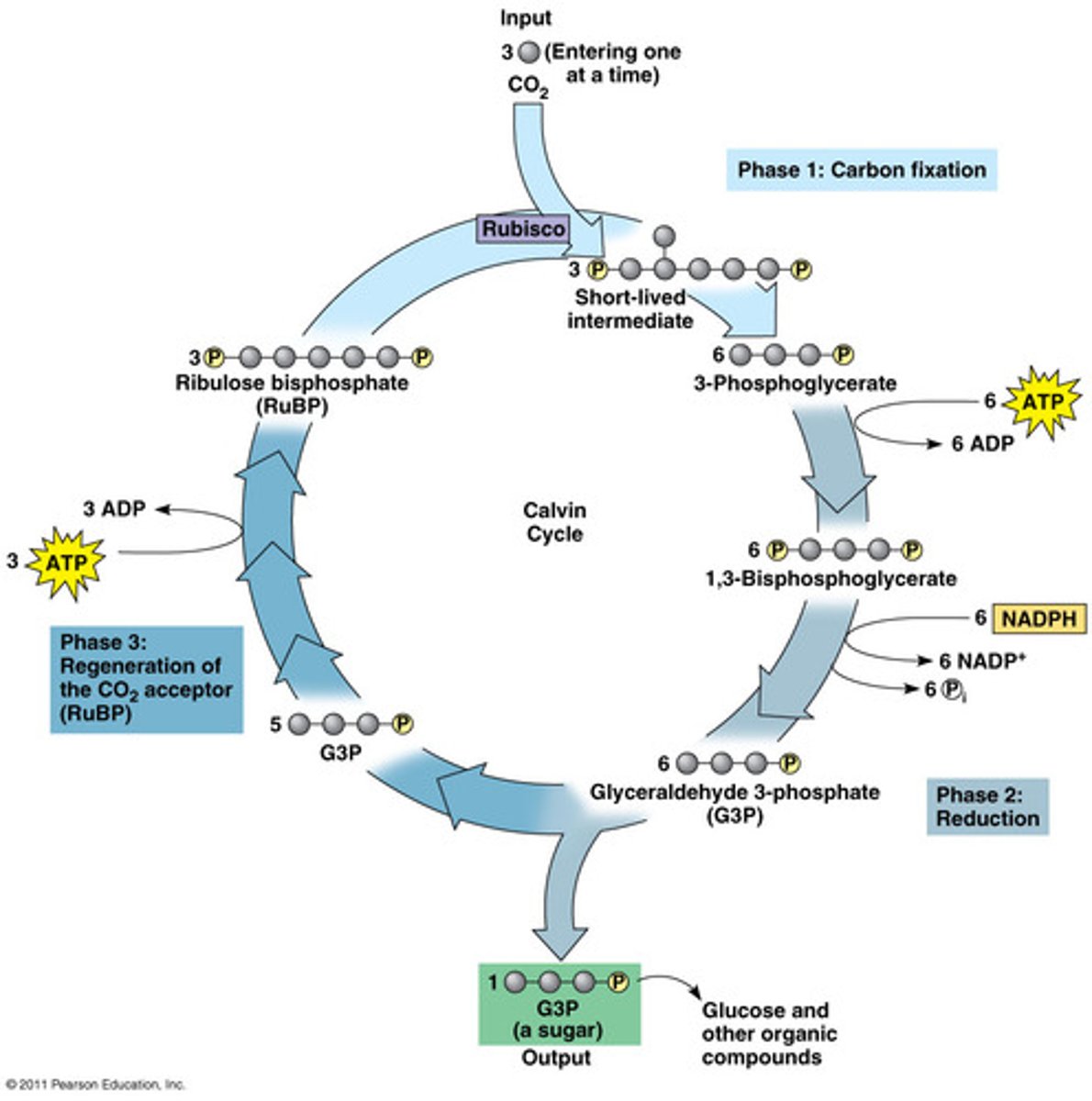
ATP from the light reactions phosphorylate both of these molecules turning them into _______.
bi-PGA
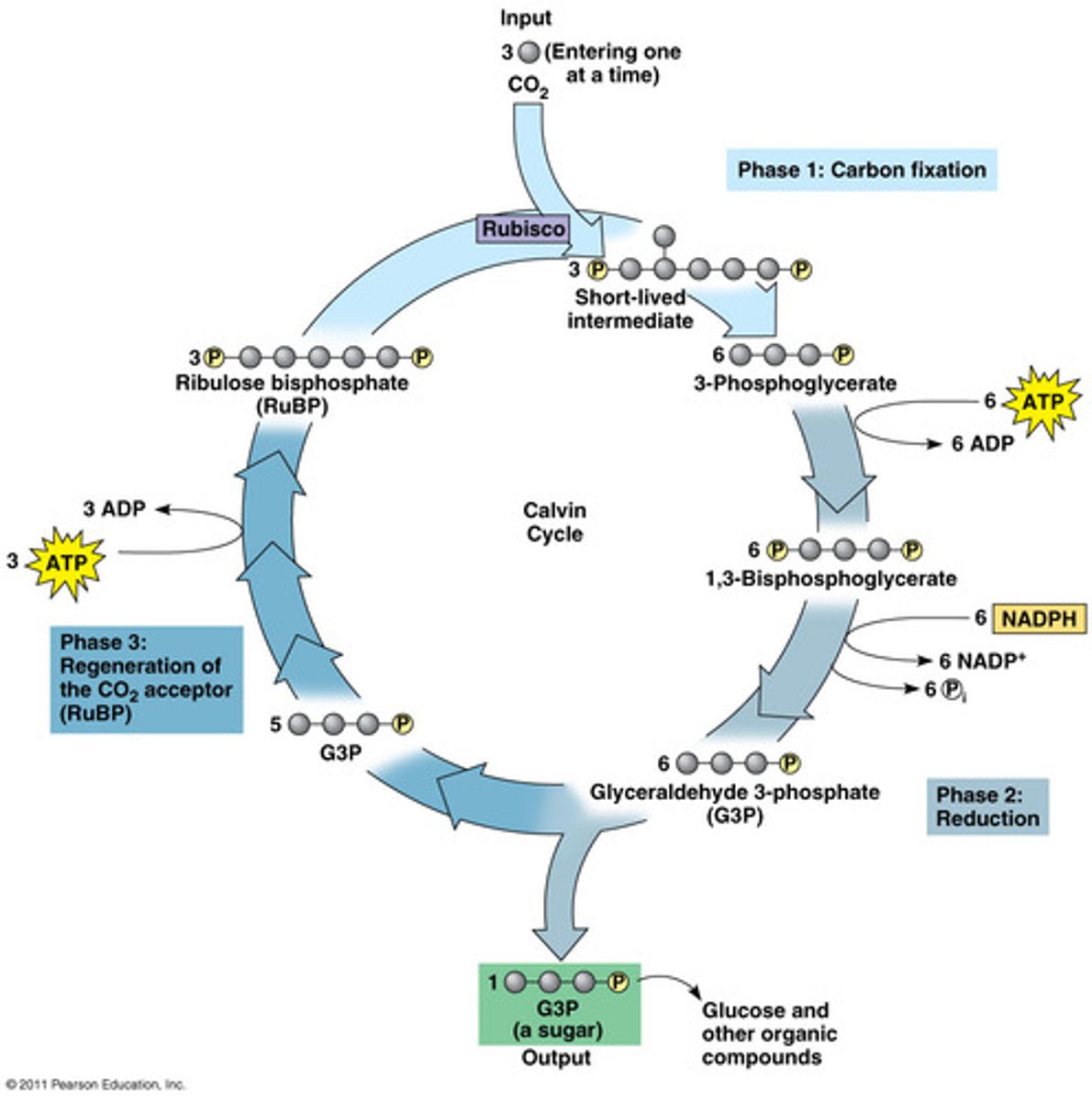
NADPH from the light reactions provides electrons to reduce these molecules to form two molecules of ______.
G3P
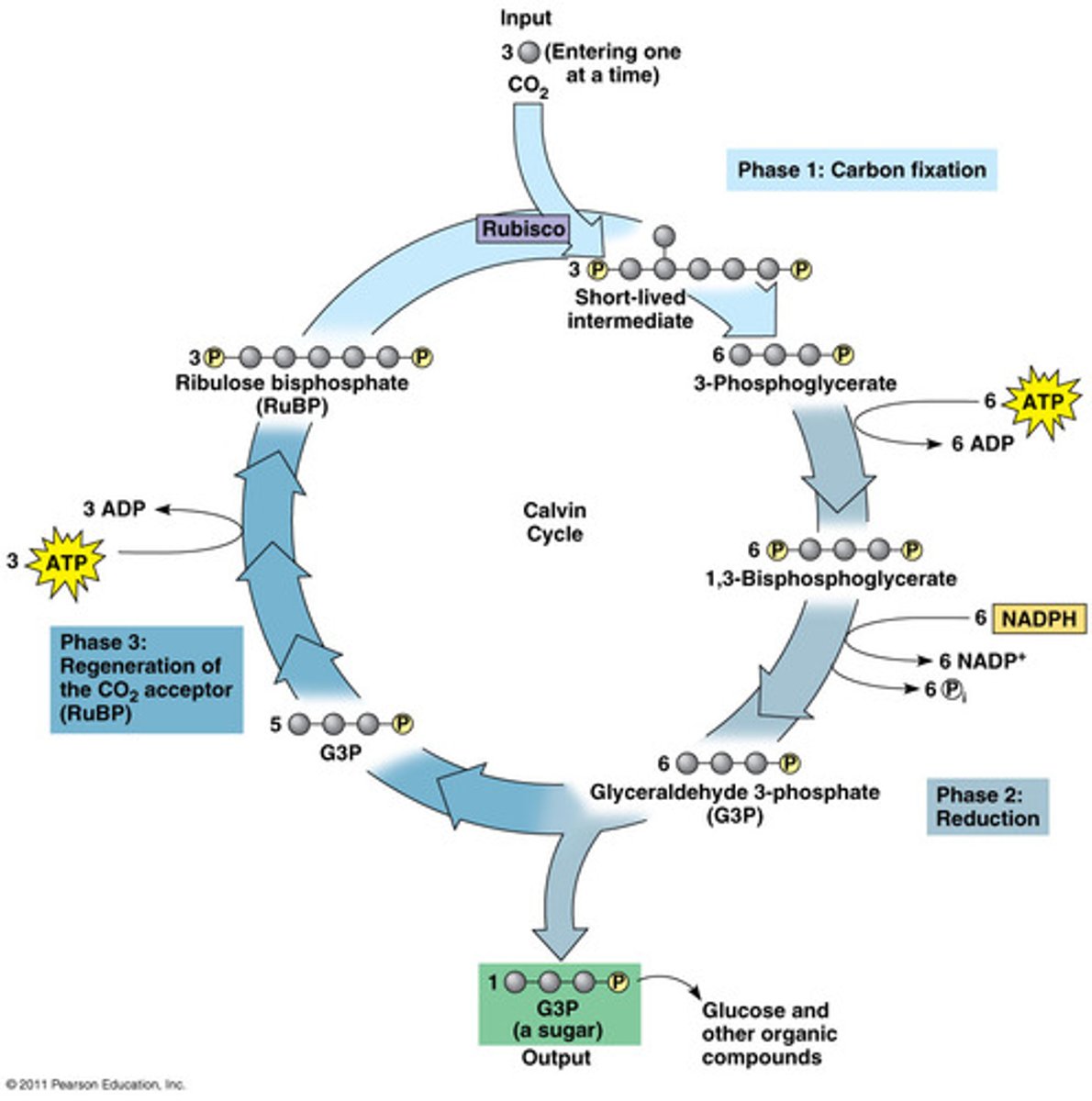
In total, after 6 carbon dioxide molecules go through the Calvin Cycle, how many molecules of G3P are formed?
12
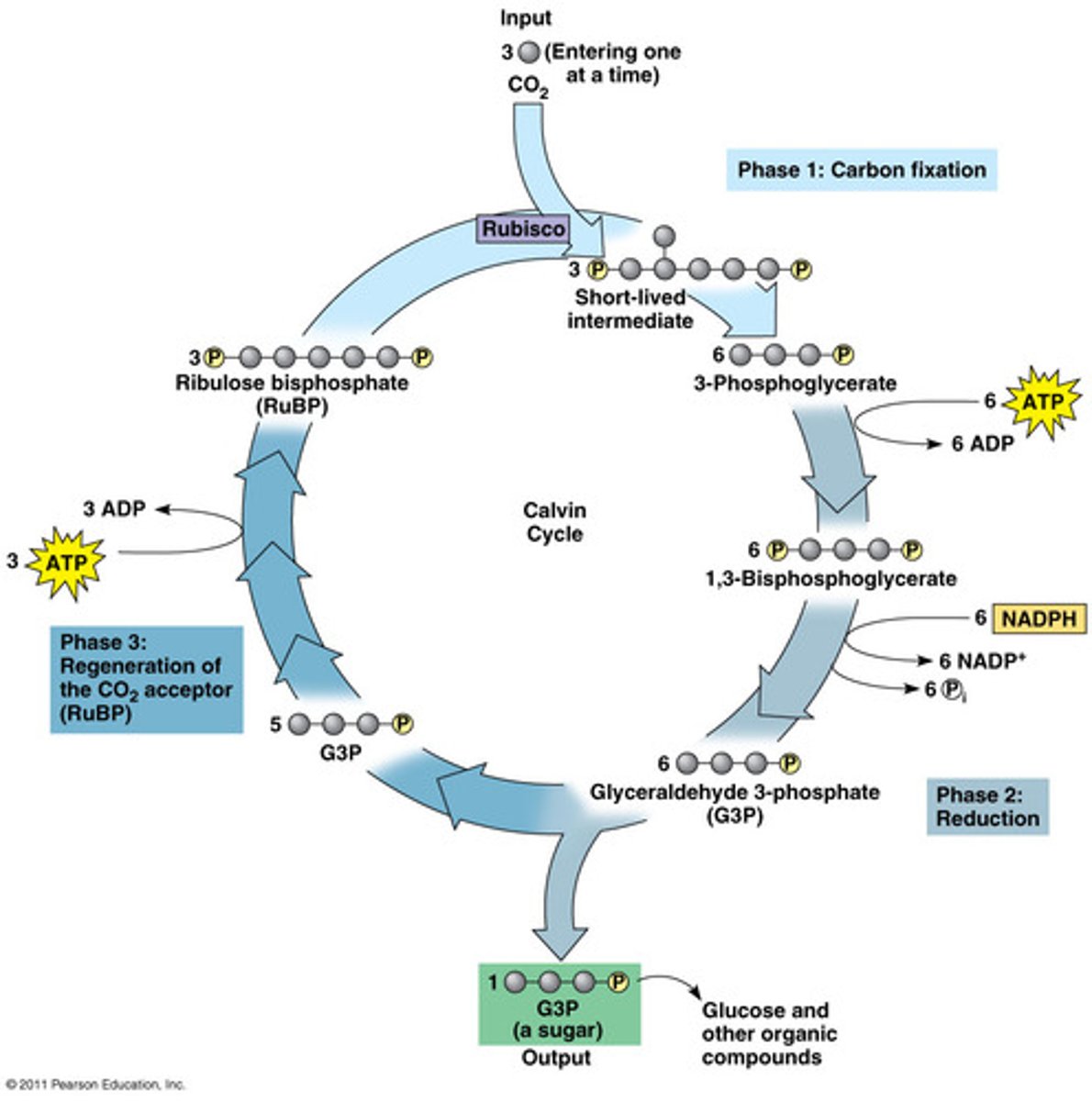
Two molecules of G3P are removed to produce ________.
glucose
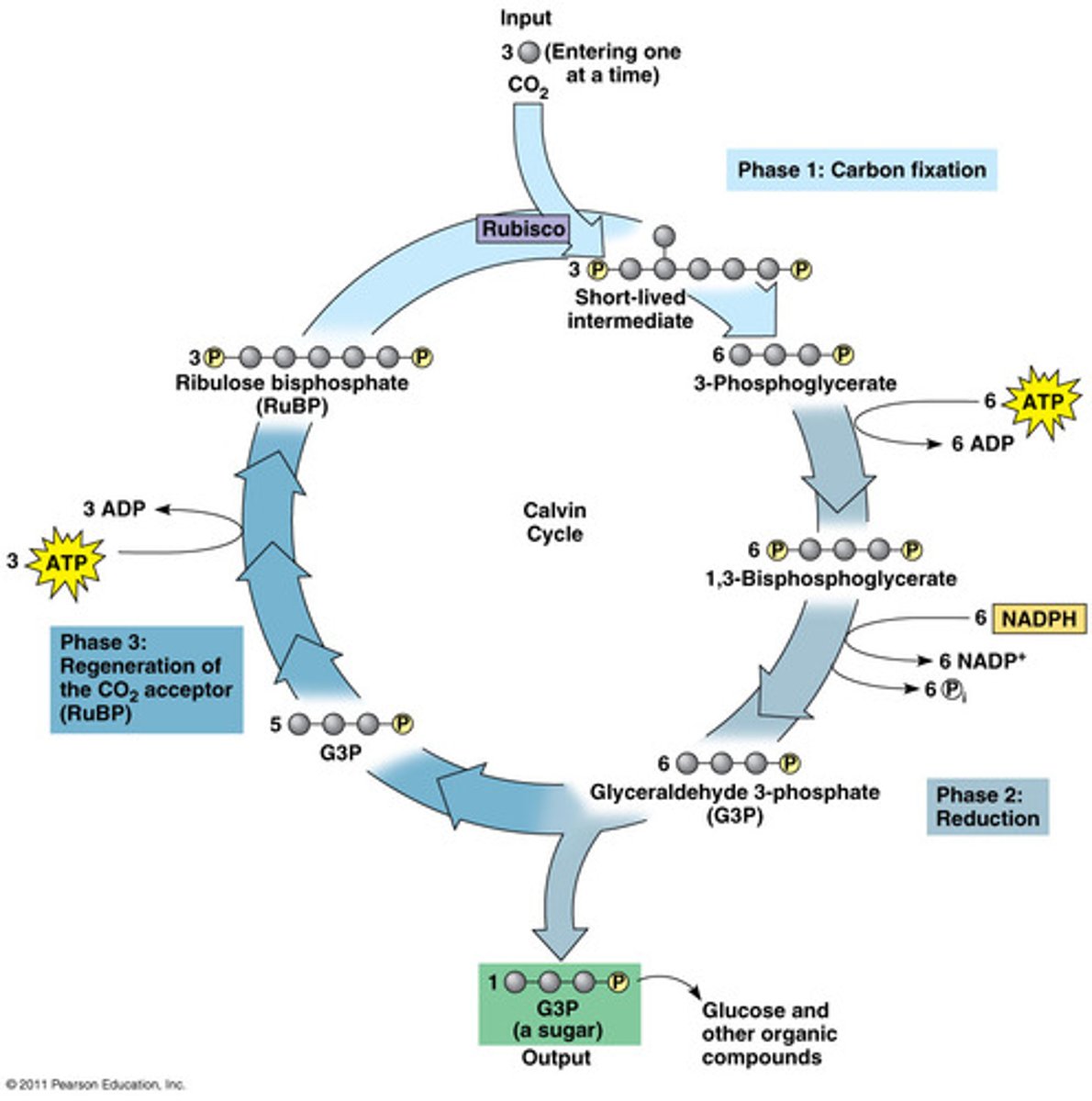
The remaining 10 molecules of G3P are phosphorylated by ATP and their atoms rearranged to re-make _______.
RuBP
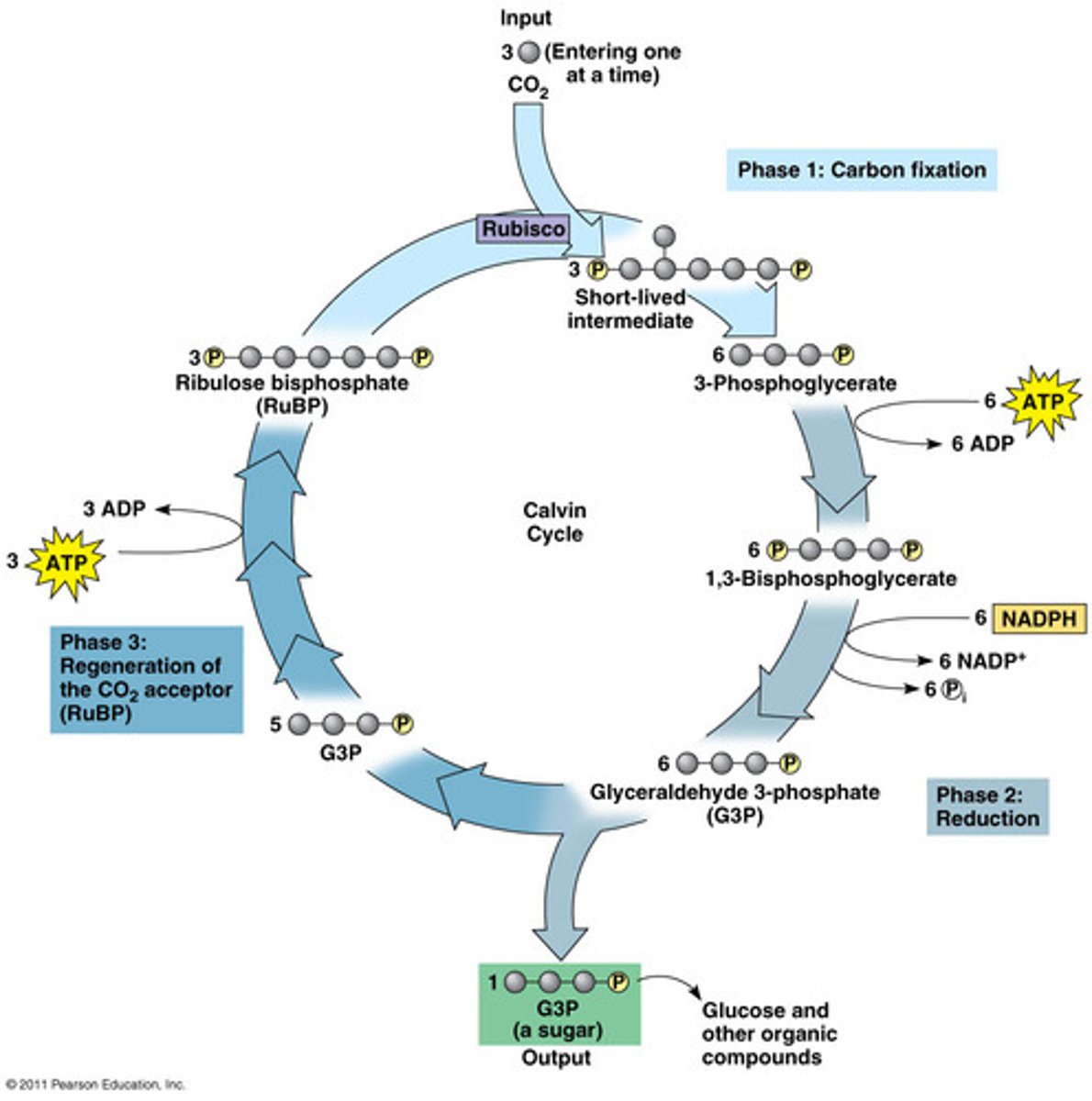
The 3 stages of the Calvin Cycle are ________ ________, ________, and _________.
carbon fixation, reduction, regeneration