MOD 4 - Leg and Foot Fractures
1/70
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards about leg and foot fractures for exam review.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
Why are leg fractures significant in terms of mobility?
Because leg bones are weight-bearing, fractures severely impair mobility.
What are common leg fracture types?
Femoral condyle, tibial plateau, patella, tibial tuberosity, tibia and fibula, stress fractures of the tibia.
What are femoral condyle fracture types?
Intracondylar and supracondylar.
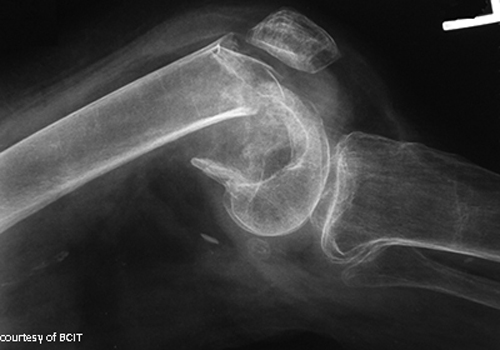
What causes femoral condyle fractures?
Direct trauma such as being struck by a car.
What muscle displaces femoral condyle fragments?
Gastrocnemius muscle.
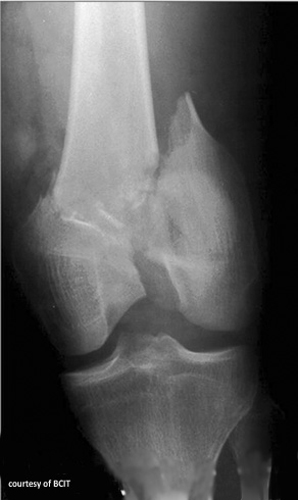
What complications are linked with femoral condyle fractures?
Sciatic nerve or popliteal vessel damage, arthritis, altered mobility.
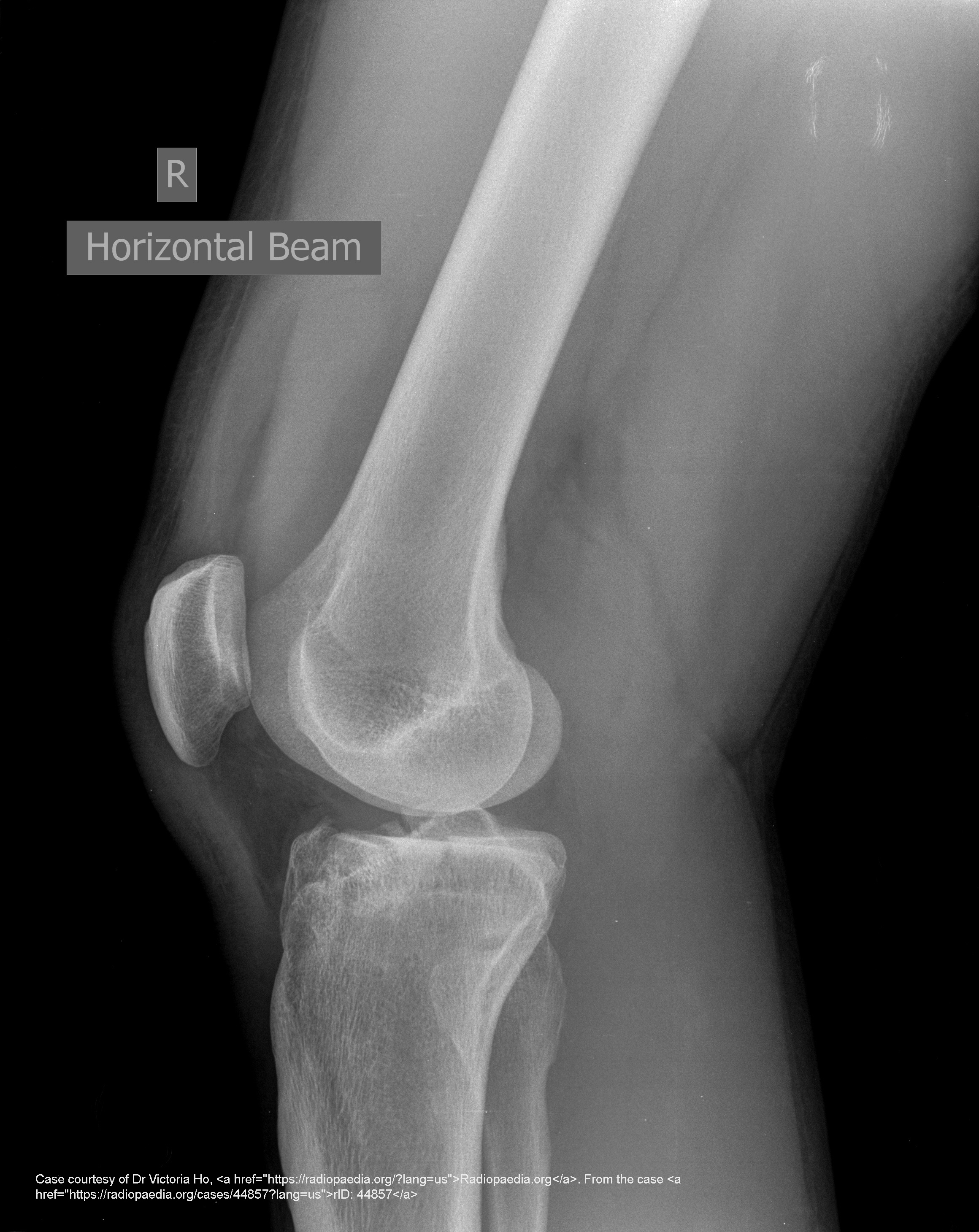
What signs suggest a tibial plateau fracture?
Joint pain and knee effusion.
What injuries often accompany tibial plateau fractures?
Ligament, meniscus, or alignment issues.
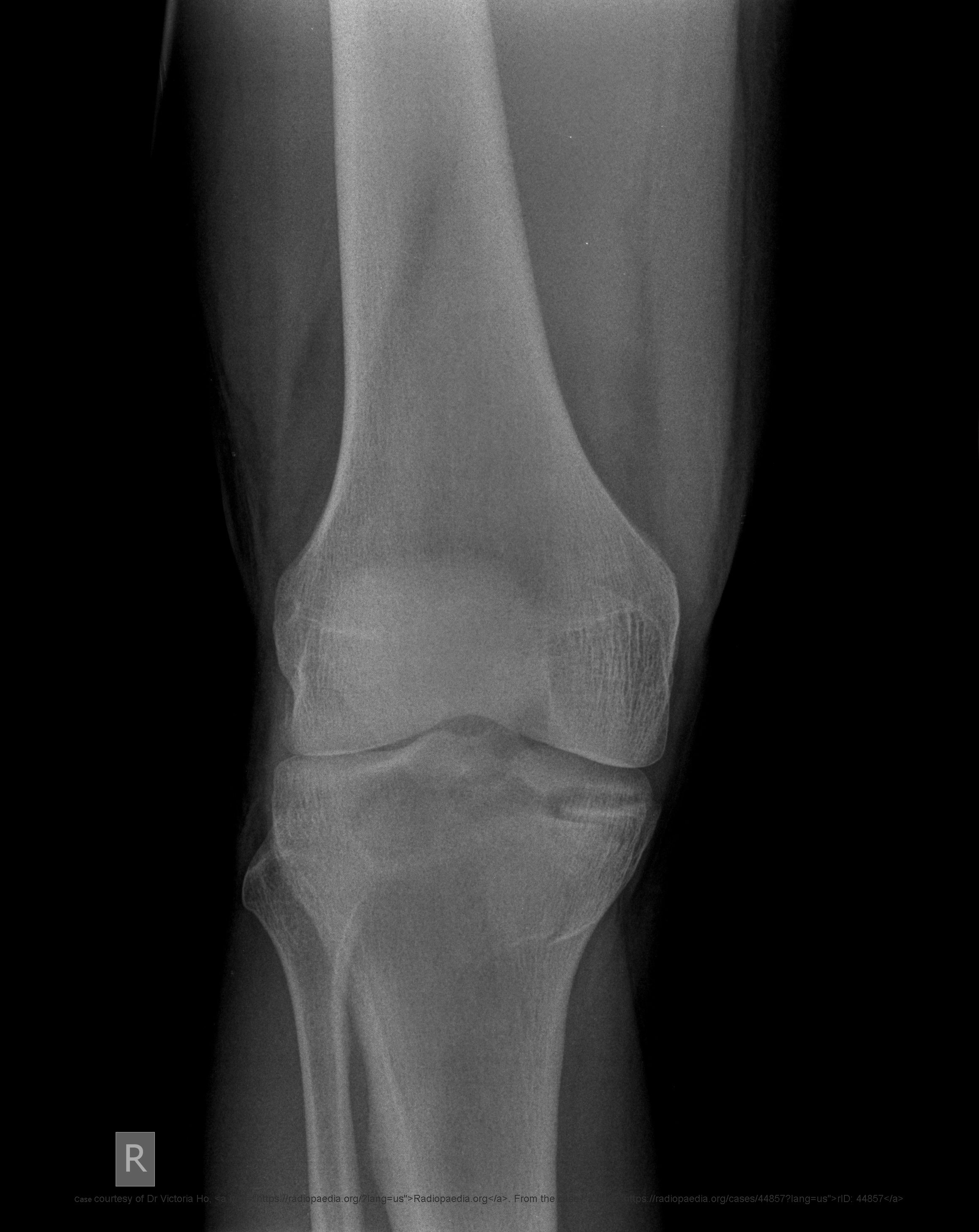
What commonly causes tibial plateau fractures?
Lateral force, compression, twisting, or MVA.
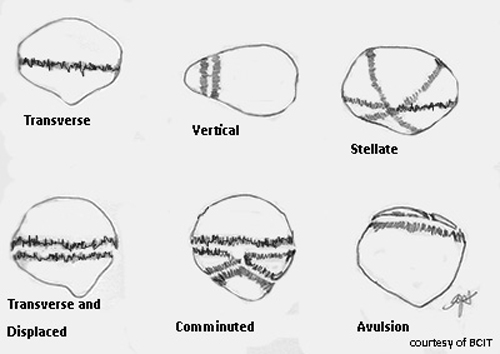
What are patella fracture types?
Transverse, stellate, linear.
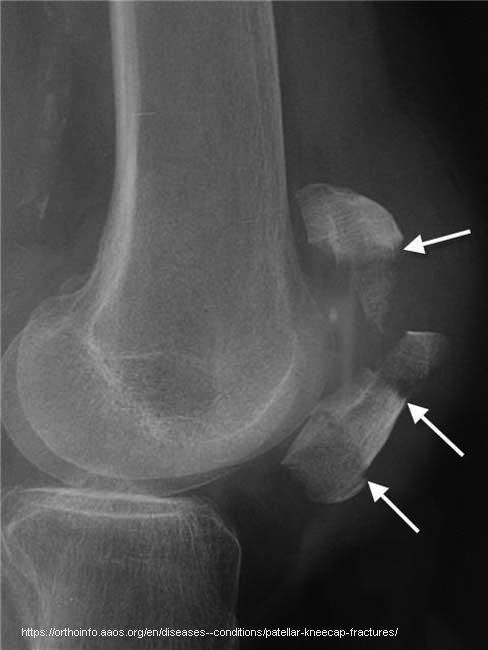
What causes avulsion fractures of the patella?
Superior pole: quadriceps; Inferior pole: infrapatellar tendon.
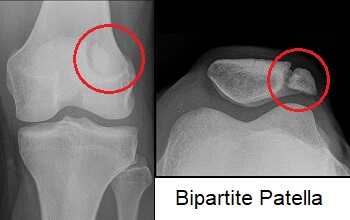
How do you distinguish a bipartite patella from a fracture?
Smooth edges and location at the upper lateral patella.
What complications may result from patella fractures?
Avascular necrosis, neurovascular injury.
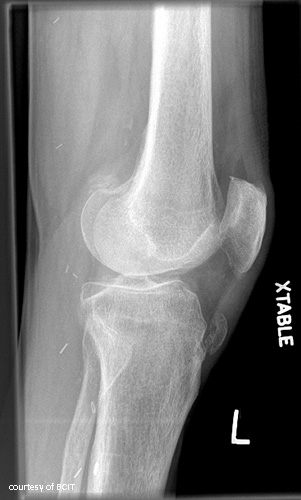
What causes tibial tuberosity avulsion fractures?
Sudden strong quadriceps contraction.
Who is most affected by tibial tuberosity fractures?
Active teenagers in sports.
What differentiates Osgood-Schlatter from a fracture?
Osgood-Schlatter involves inflammation, not a break.
What are complications of tibial tuberosity fractures?
Pain, deformity.
What are “boot top” fractures?
Spiral fractures of the distal tibia/fibula.
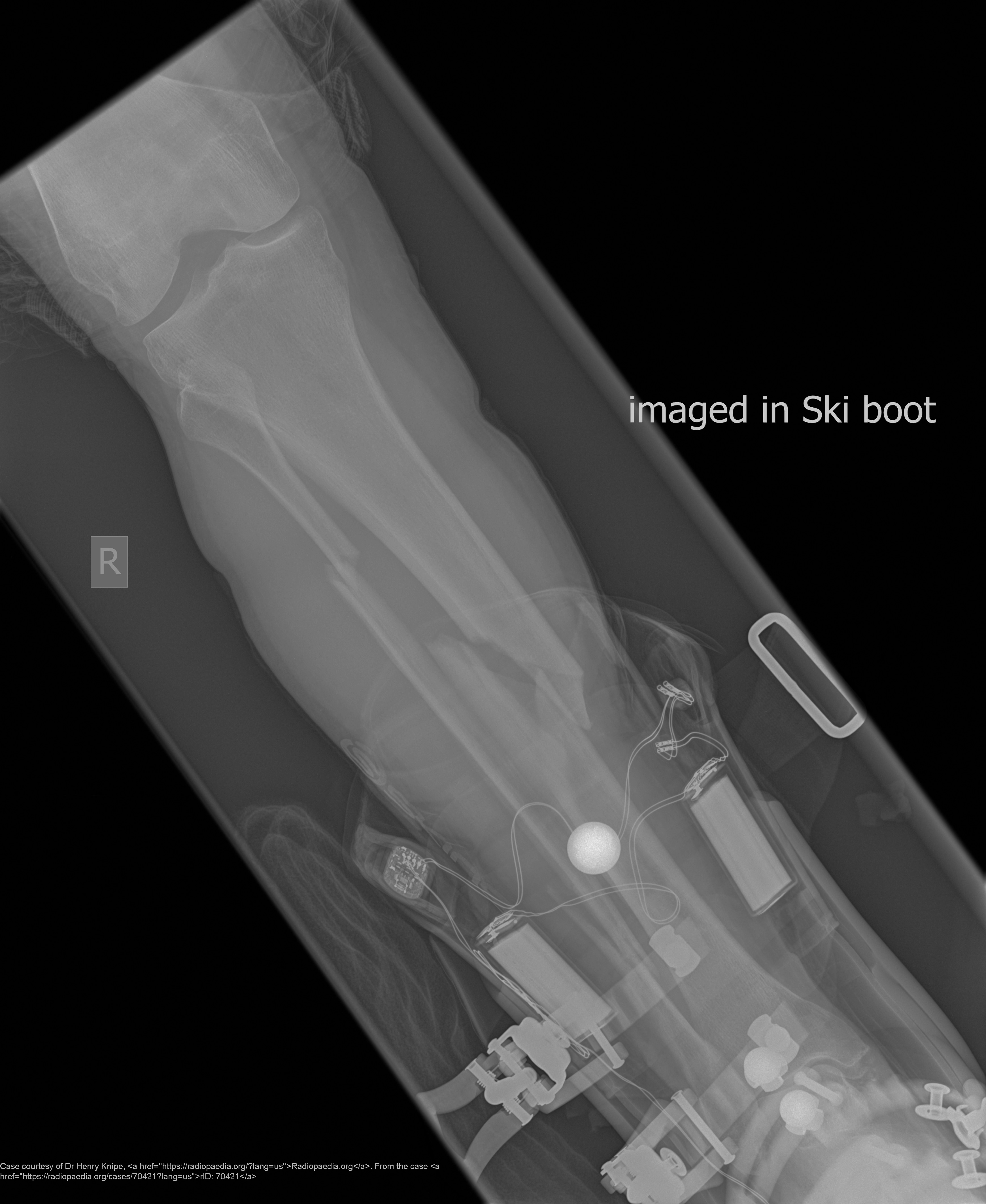
What activities cause boot top fractures?
Skiing or direct leg trauma.
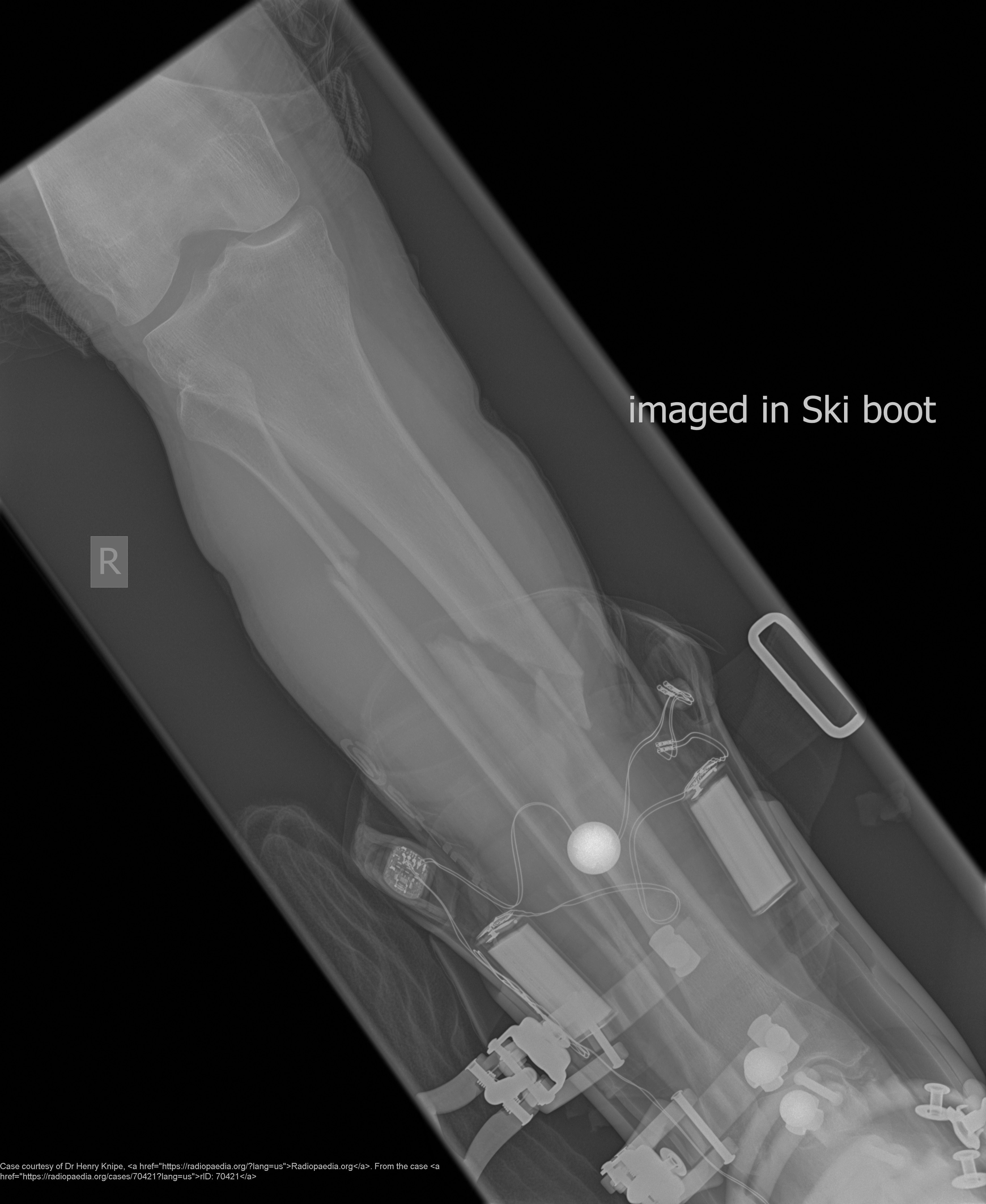
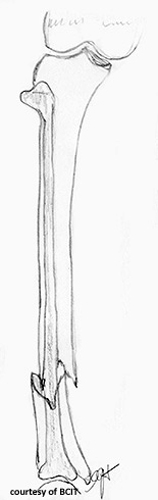
What is a major concern with tibia/fibula fractures?
Malunion, deformity, poor weight-bearing.
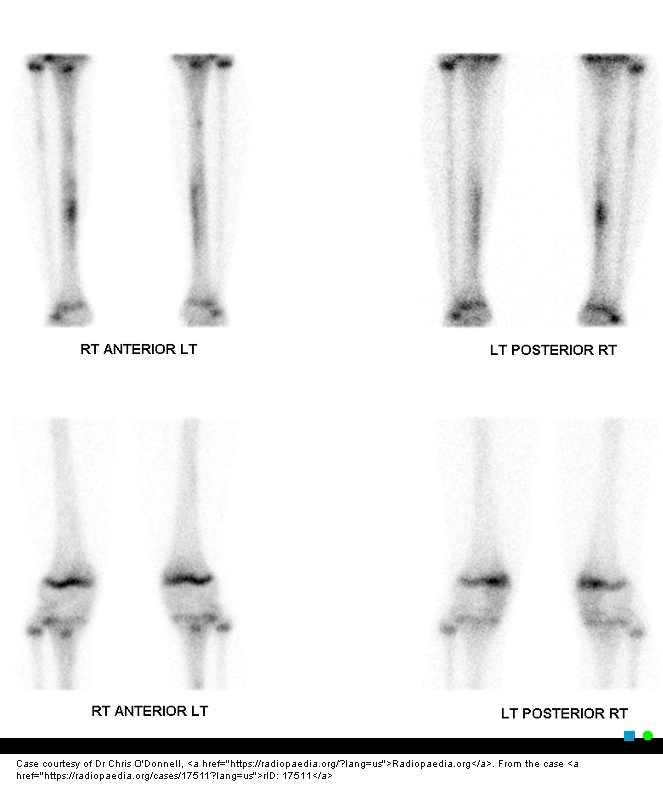
What causes tibial stress fractures?
Repetitive exercise overuse.
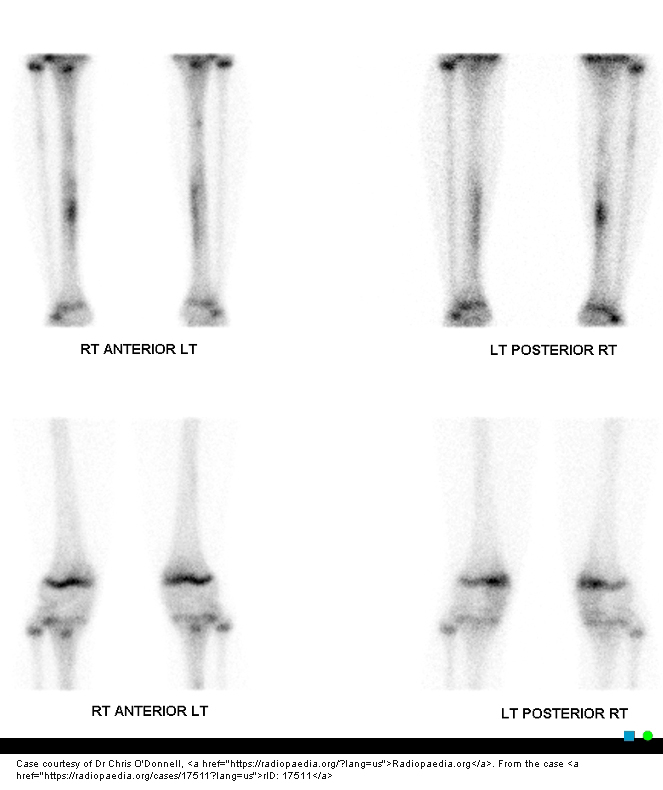
Another name for tibial stress fracture?
Shin splints or medial tibial stress syndrome.
What happens if stress fractures go untreated?
They can become complete fractures.
Why are ankle fractures complex?
Because of ligament involvement and joint mechanics.
What injuries can occur with ankle fractures?
5th metatarsal avulsion, proximal fibula fracture.
What is a stable ankle fracture?
Undisplaced with intact ligaments.
What makes an ankle fracture unstable?
Involvement of medial/posterior malleoli or tibiofibular widening.
What causes medial malleolus fractures?
Inversion with axial loading.
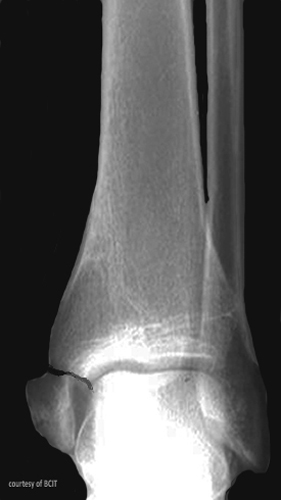
What tendon can avulse (pull or tear) the 5th metatarsal?
Peroneus brevis.
Complications of medial malleolus fractures?
Impaired motion, abnormal gait.
Most common ankle fracture type?
Lateral malleolus fracture.
What causes lateral malleolus fractures?
Eversion injury.
What complications follow lateral malleolus fractures?
Pain, joint instability.
Posterior malleolus fracture mechanism?
Axial loading with plantar flexion.
Complications of posterior malleolus fractures?
Arthritis, limited ankle mobility.
What is a bimalleolar fracture?
Fracture of both medial and lateral malleoli.
What ligaments are often torn in bimalleolar fractures?
Deltoid and peroneus.
What causes trimalleolar fractures?
Combined inversion, eversion, plantar flexion, rotation.
What structures are fractured in a trimalleolar injury?
Medial, lateral, and posterior malleoli.
What imaging is needed to confirm trimalleolar fractures?
AP and lateral X-ray views.
What foot fractures are common?
Bedroom fracture, Jones fracture, 5th metatarsal avulsion, calcaneal fracture.
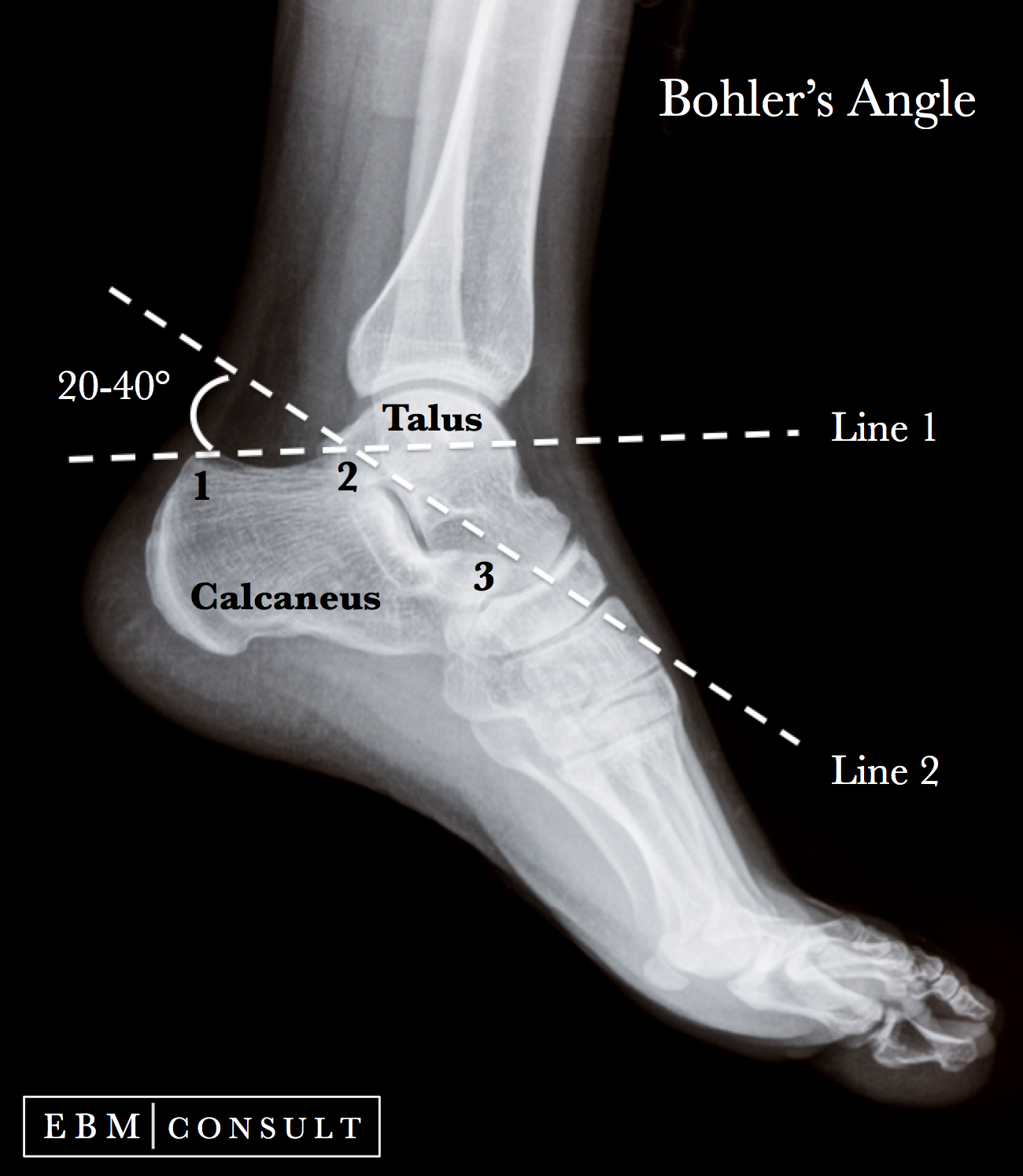
What is Boehler’s angle?
25°–45° on lateral view; used to assess calcaneal compression.
What causes calcaneal avulsion fractures?
Achilles tendon pull.
What causes compressive calcaneal fractures?
Fall from height.
Complications of calcaneal fractures?
Spinal injury, compartment syndrome.
What is a Lisfranc injury?
Tarsometatarsal joint dislocation.
Who commonly suffers Lisfranc injuries?
Athletes, gymnasts.
What causes Lisfranc injury?
Axial load on plantar-flexed foot or direct trauma.
Complications of Lisfranc fractures?
Arthritis, chronic pain, gait issues.
What are March fractures?
Stress fractures of metatarsals 2 and 3 from marching.
What causes metatarsal impact fractures?
Heavy object falling on foot.
Treatment difference: stress vs. impact metatarsal fractures?
Stress = rest; Impact = surgery.
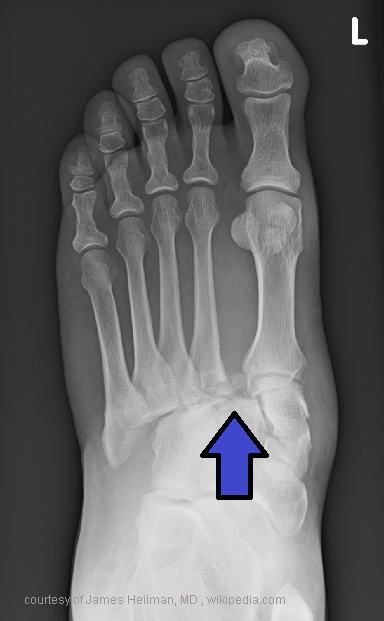
What is a Jones fracture?
Transverse fracture 2 cm from base of 5th metatarsal.
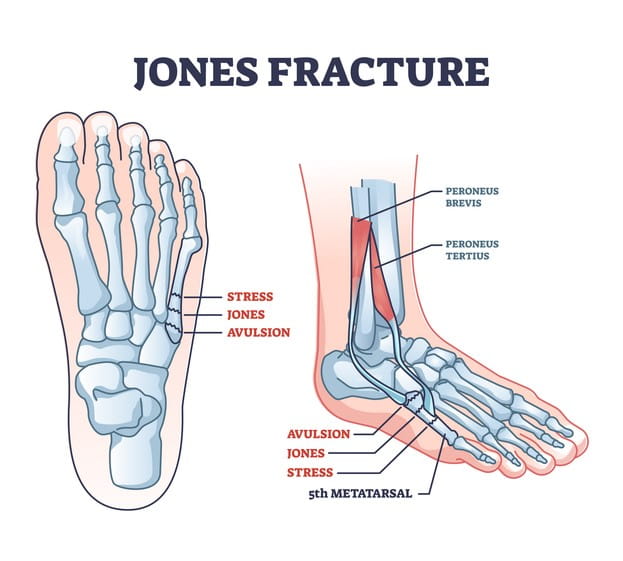
What complicates healing of a Jones fracture?
Poor blood supply.
How is a Jones fracture treated?
Non-weight bearing cast, often surgery.
What causes avulsion fracture of 5th metatarsal?
Peroneus brevis pulling during inversion.
Common cause of avulsion fracture of 5th metatarsal?
Dance injury or awkward step.
Treatment for avulsion of 5th metatarsal?
4–6 week cast, usually heals well.
What is a bedroom fracture?
Fracture of the 5th toe from direct trauma.
How is a bedroom fracture treated?
Reduction, immobilization.
Complications of bedroom fractures?
Non-union, arthritis
What is the primary treatment goal for lower limb fractures?
To restore anatomical alignment, preserve function, and prevent complications.
Why is early mobilization important after leg or foot fracture treatment?
It reduces the risk of joint stiffness, muscle wasting, and thromboembolic events.
Which imaging view is essential for assessing tibial plateau fractures?
AP and lateral knee views; CT may be used for complex fractures.
How do you differentiate a stress fracture from a full fracture on imaging?
Stress fractures show cortical thickening or a faint line; full fractures have a clear fracture line.
What soft tissue complication may accompany tibial shaft fractures?
Compartment syndrome due to swelling within fascia-enclosed muscle groups.
What is a common long-term complication of intra-articular ankle fractures?
Post-traumatic osteoarthritis.
Why is the base of the 5th metatarsal prone to avulsion fractures?
Because of strong pull from the peroneus brevis tendon during forced inversion.
Why might a Lisfranc fracture be missed on initial X-rays?
Because subtle displacements may only appear under weight-bearing conditions.
Which foot fracture is most likely to require surgical fixation due to poor blood supply?
Jones fracture.
What sign on X-ray indicates possible Lisfranc injury?
Misalignment between the 1st and 2nd metatarsal bases and cuneiforms.