Bones of the Skull
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
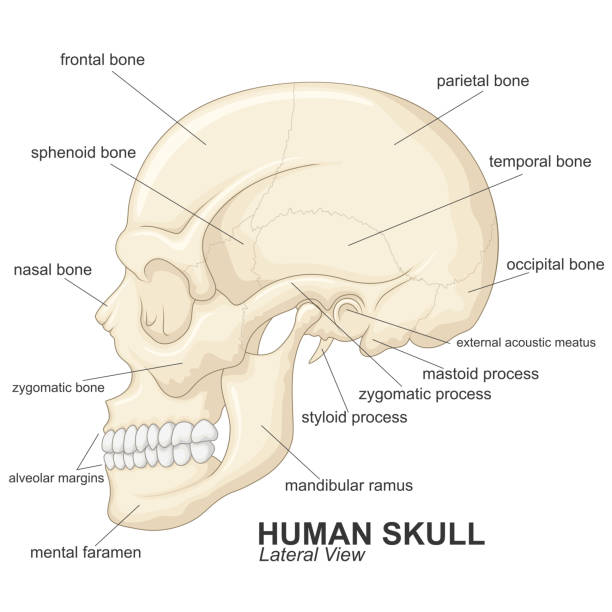
The human cranium
22 bones interconnected through immobile sutures
Divided into:
Neurocranium
The calvaria (The dome), which is the superior portion of the cranium
The base (The floor of the skull)
Viscerocranium
Cranial cavity
Continuous with the vertebral canal through a large opening in the base, called the foramen magnum
The upper (domed) part
The base of the skull
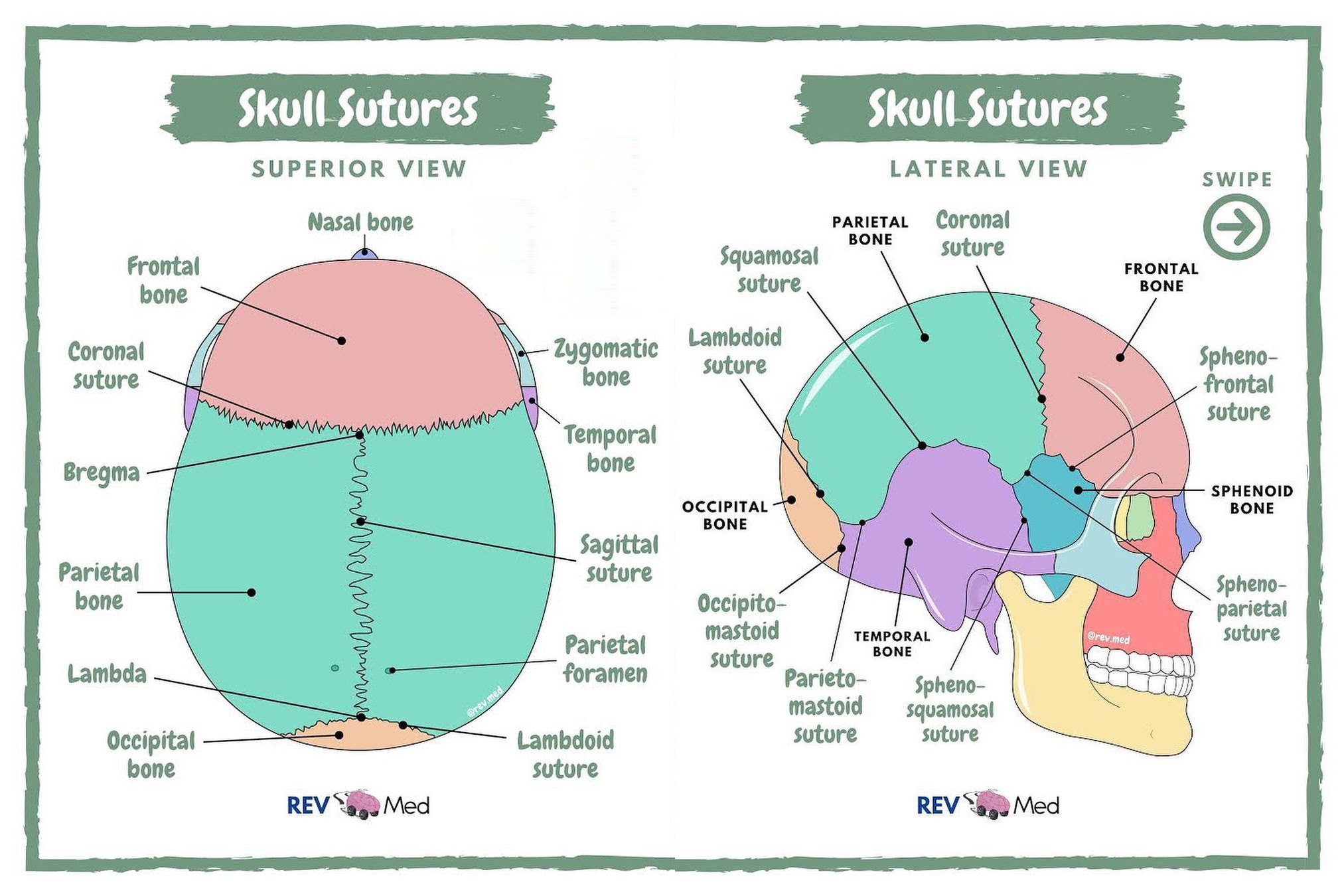
Cranial sutures
Synarthroses (fibrous, strong, immobile bands between the bones of a fully grown adult)
Developed after birth over the course of 2 years
Flexible in infancy and early childhood
Most important:
Coronal suture (between the two parietal bones and the posterior margin of the frontal bone)
Sagittal suture (median sagittal plane between the two parietal bones)
Lambdoid suture (between the superior margin of the occipital bone and the two parietal bones)
Squamous suture (lies between each temporal bone and the superior parietal bone)
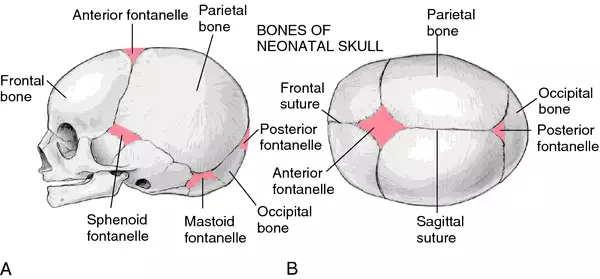
Fontanelles
Soft membranous gaps between cranial bones of the calvaria —→ present until age 2
Function: To allow the rapidly growing brain to expand
6 fontanelles at the cranial joints
Posterior fontanel
At the lambdoid suture
Anterior fontanel
At the coronal suture
Posterolateral fontanel (mastoid)
Anterolateral fontanel (sphenoid)
Craniosynostosis is a pathological process leading to complete ossification prematurely
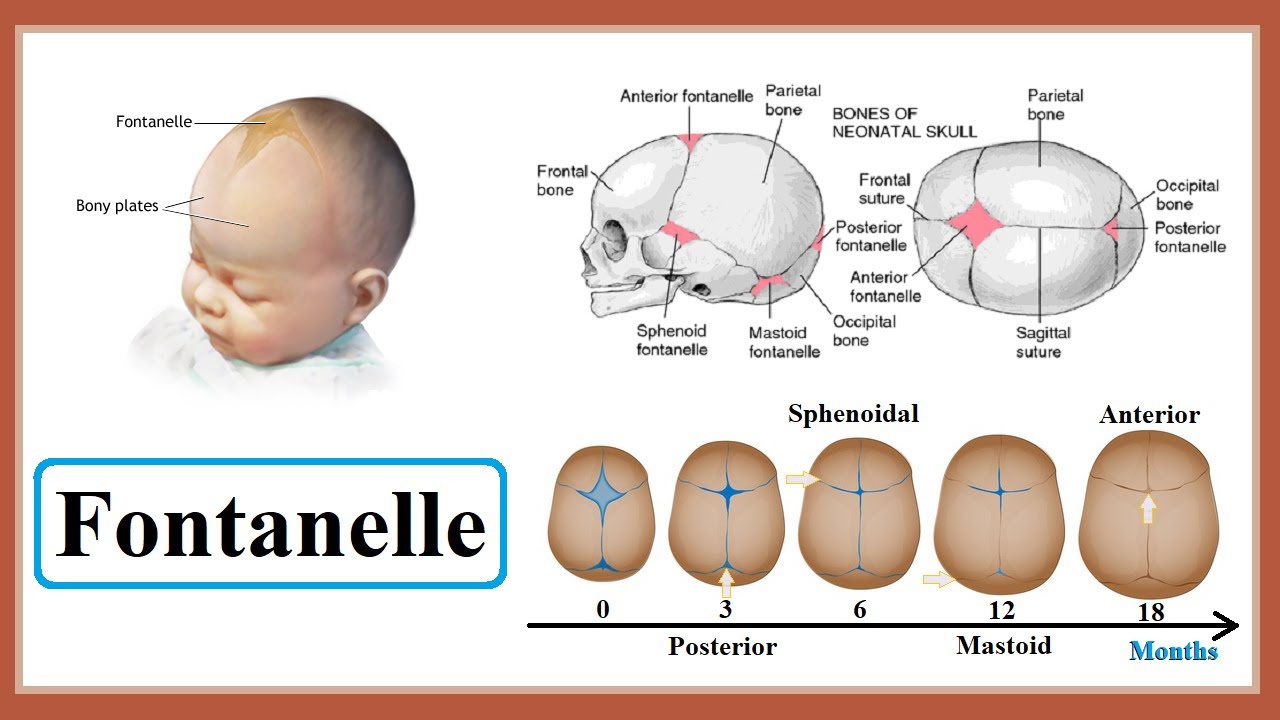
Fontanelle closure
Fontanelles also allow the bone plates to flex and thus the child’s head is able to pass through the birth canal
The posterior fontanelle is the first to close
Happens around 2 to 3 months postpartum
The sphenoid fontanelle is the second to close
Happens around 6 months after birth
The mastoid fontanelle is the third to close
6 to 18 months after birth
The anterior fontanelle is the last to close
12 to 18 months after birth
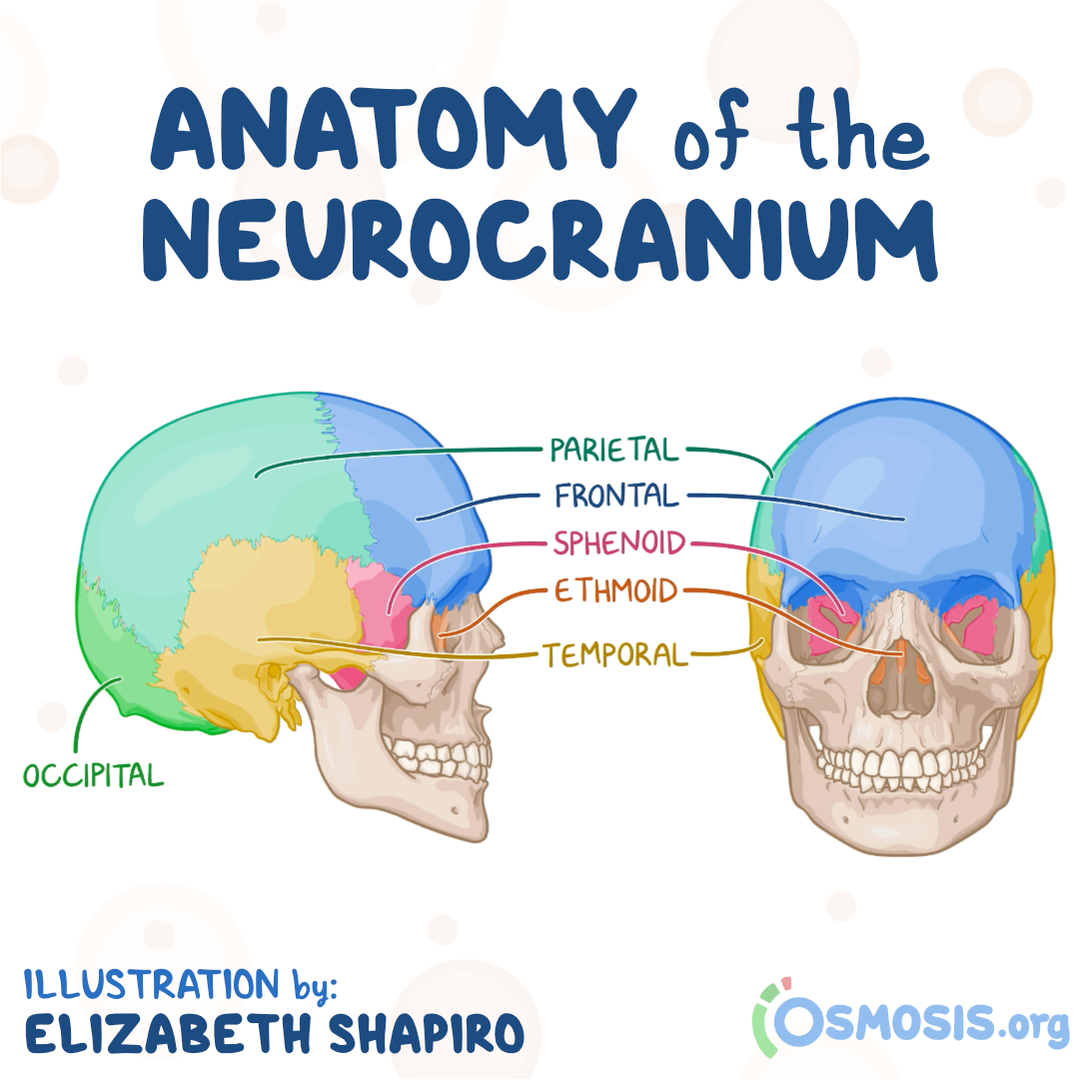
Neurocranium
Composed of:
Calvaria, which is the membranous part of the roof of the skull formed by flat bones and slightly curved bones
Cranial base, the cartilaginous part
Deliminated the cranial cavity
The cranial cavity houses the cerebral hemispheres, cerebellum, and brain stem
The cranial cavity communicates below with the vertebral canal through foramen magnum
Calvaria
Upper part of the neurocranium
Composed of flat bones
Frontal bone (unpaired)
Occipital bone (unpaired)
Paired parietal bones
Paired temporal bones
Smooth outer convex surface
Inner concave surface
Calvaria bone structure
Composed of flat bones
Two layers of compact bone tissue
The inner layer is thinner than the outer.
The diploe separates the two compact layers (some areas lack diploe)
Diploe is a cancellous (spongy) bine tissue containing bone marrow and diploic veins
Frontal bone
The forehead and superior rim of the orbit
Pneumatized bone
Inside the bone there are two cavities filled with air, called the frontal sinuses
Superior to each orbital rim
Supraciliary arch (more evident in men)
Supraorbital notch
The eponymous nerve and vessels pass through
Glabella: A small depression between the two arches
Partially forms the medial rim of the orbit
Laterally, the frontal bone extends with the frontal process
Forms a joint with the zygomatic bone
Frontal bone articulation
With the parietal bones, through the coronal suture
With the greater wing of the sphenoid
With the frontal process of the zygomatic bone, through the zygomatic process
With the nasal and lacrimal bones
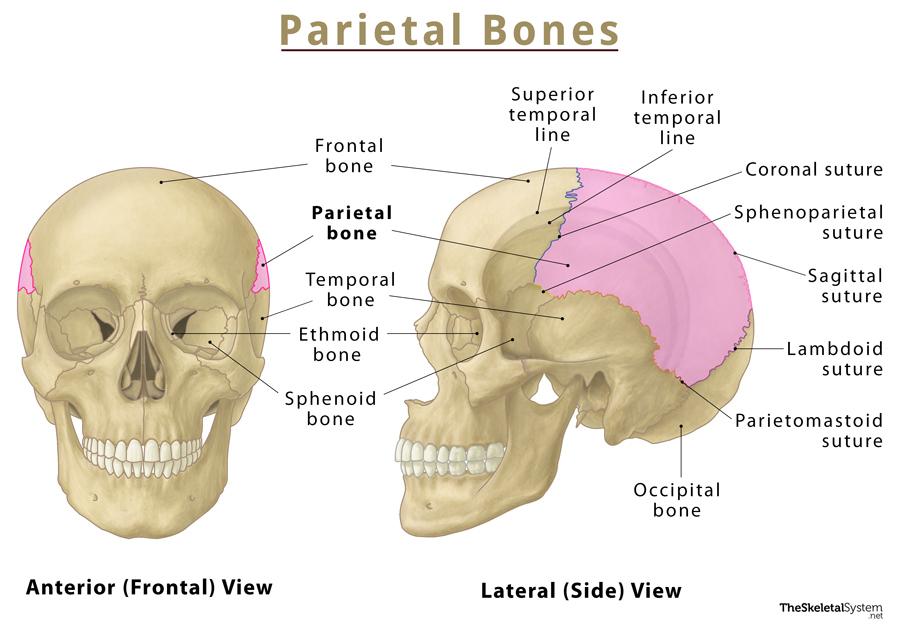
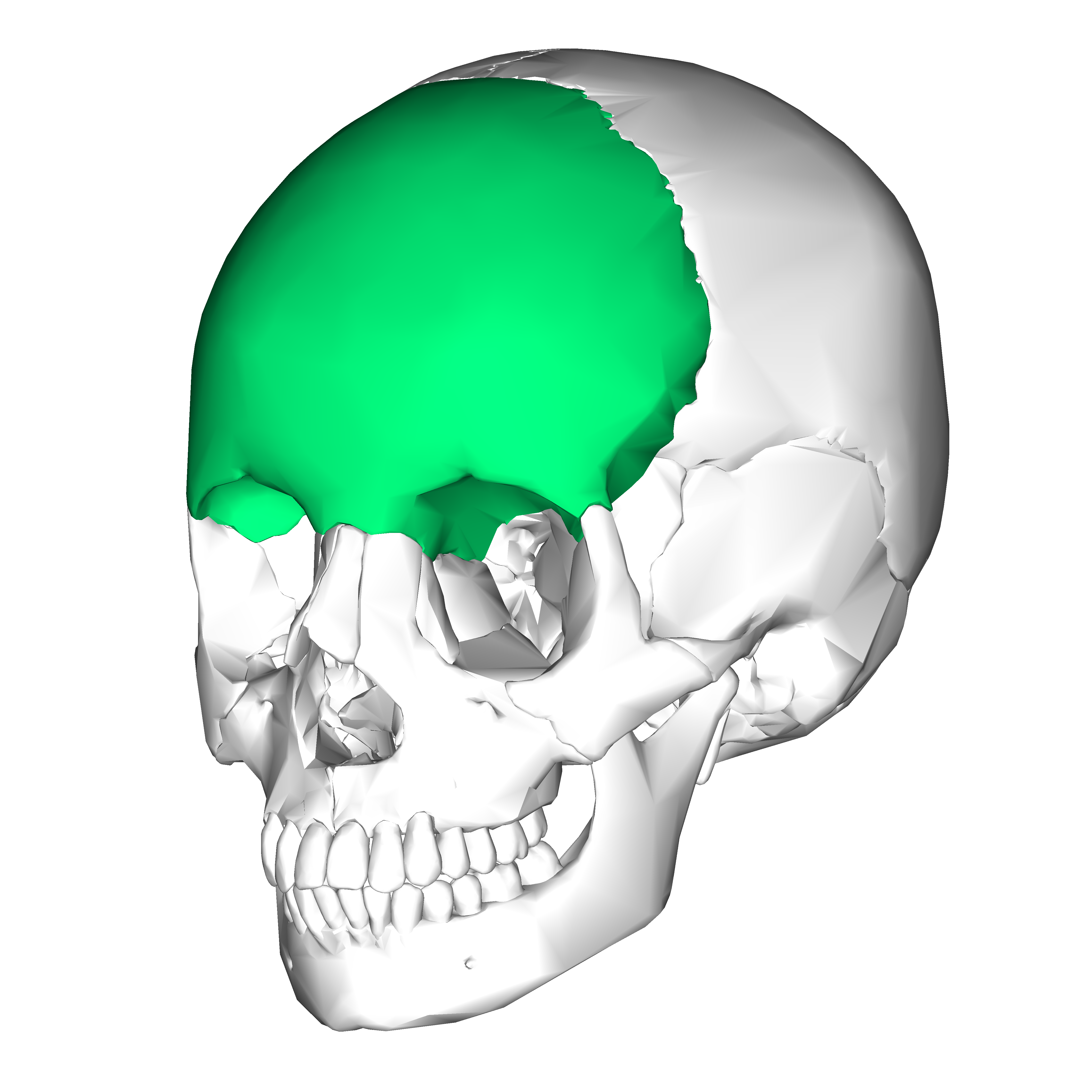
Parietal bone
Paired quadrilateral bone
Forms the roof and sides of the cranium
Composed of:
2 surfaces (Inner and outer)
4 angles
4 margin
Margins
Frontal, with the coral suture
Occipital, with the lambdoid suture
Sagittal, with the eponymous suture
Squamous, with the identical suture
Angles
Frontal
Sphenoid
Mastoid
Occipital
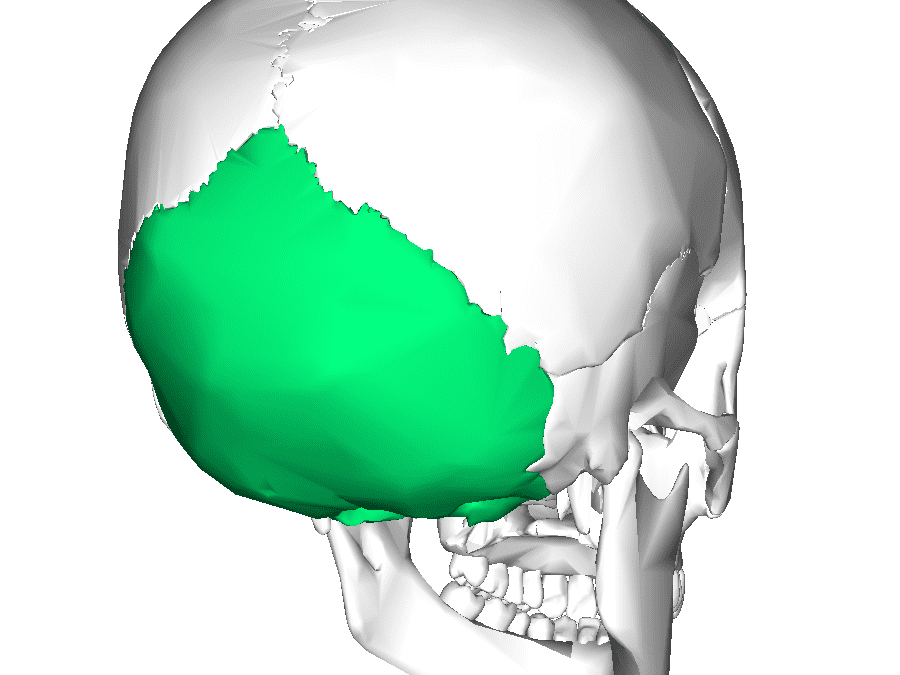
Occipital bone
Trapezoidal curved bone
Main bone of the occiput
Overlies the occipital lobes
4 parts
Squamous
Smooth portion located centrally
Basilar
Participates in the formation of the cranial floor
Two lateral parts
Contains a large opening through which the spinal cord passes: Foramen magnum
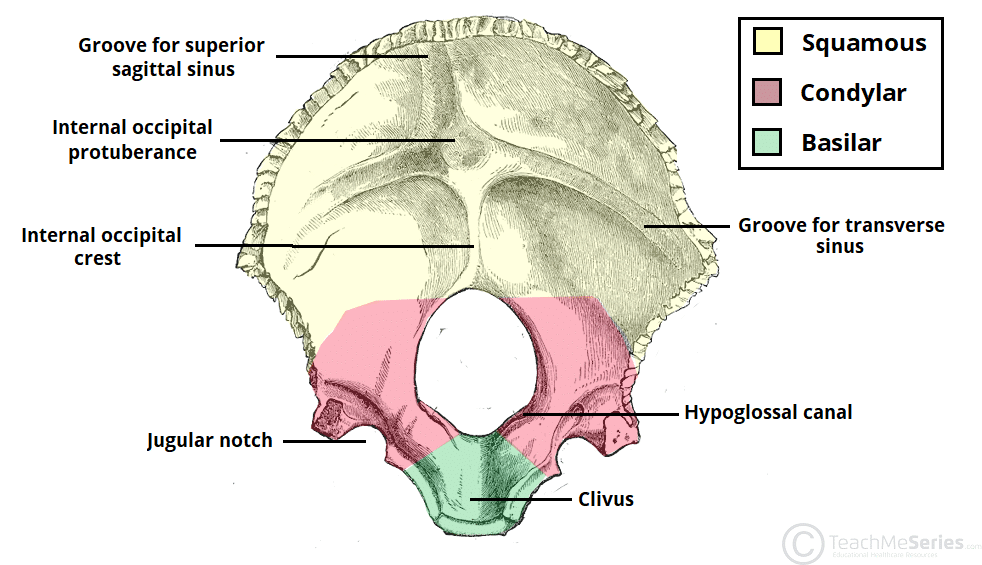
Inner occipital surface
Base of the posterior cranial fossa
Exposes the basilar portion of the bone
Foramen magnum is bound
Anteriorly by the clivus
Posteriorly by the internal occipital crest
Laterally by the jugular tubercles and hypoglossal canals
A transverse ridge and the occipital crest divide the surface into 4 depressions.
At their intersection: internal occipital protuberance
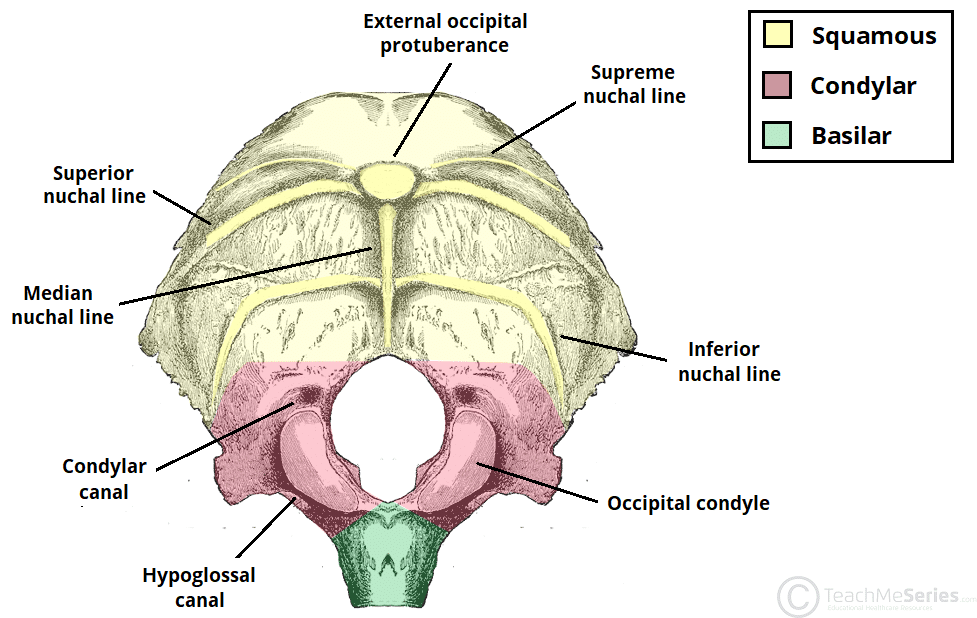
External occipital view
Each internal element has a correspondent on the the outer surface
External occipital crest
External occipital protuberance
Hypoglossal canal
Three transverse nuchal lines
Highest
Superior
Inferior
Two occipital condyles on each side of the foramen magnum —→ articulates with the atlas
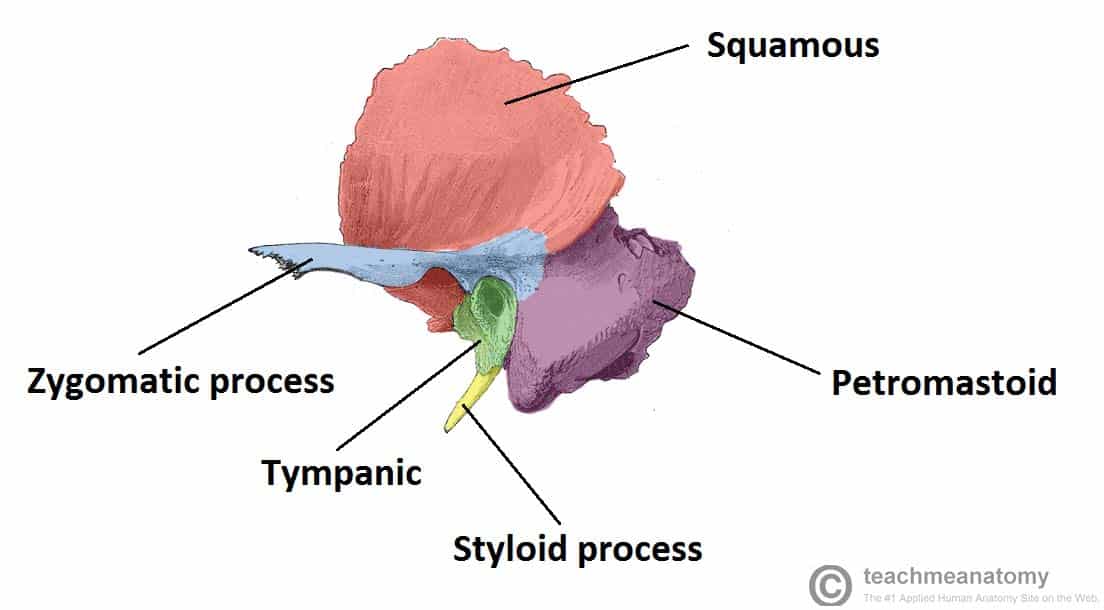
Temporal bone
Paired flat bones located on the sides of the cranium
Houses structures of the ear
Pneumatized bone
Composed of 4 parts
Squamous
Zygomatic process
Tympanic and styloid
Petromastoid: with two further subdivisions, petrous and mastoid
Temporal bone components
Squamous
Flat plate —→ anterior and superior parts
Articulates with the greater wing of the sphenoid and the parietal bone
Zygomatic
Anterior projection, curves anteriorly
Forms the zygomatic arch with the temporal process of the zygomatic bone
Tympanic
Below the zygomatic process and the squamous bone
External acoustic opening with the external acoustic meatus
Petromastoid
Mastoid—→ posterior part
Mastoid and styloid process
petrous—→ the base
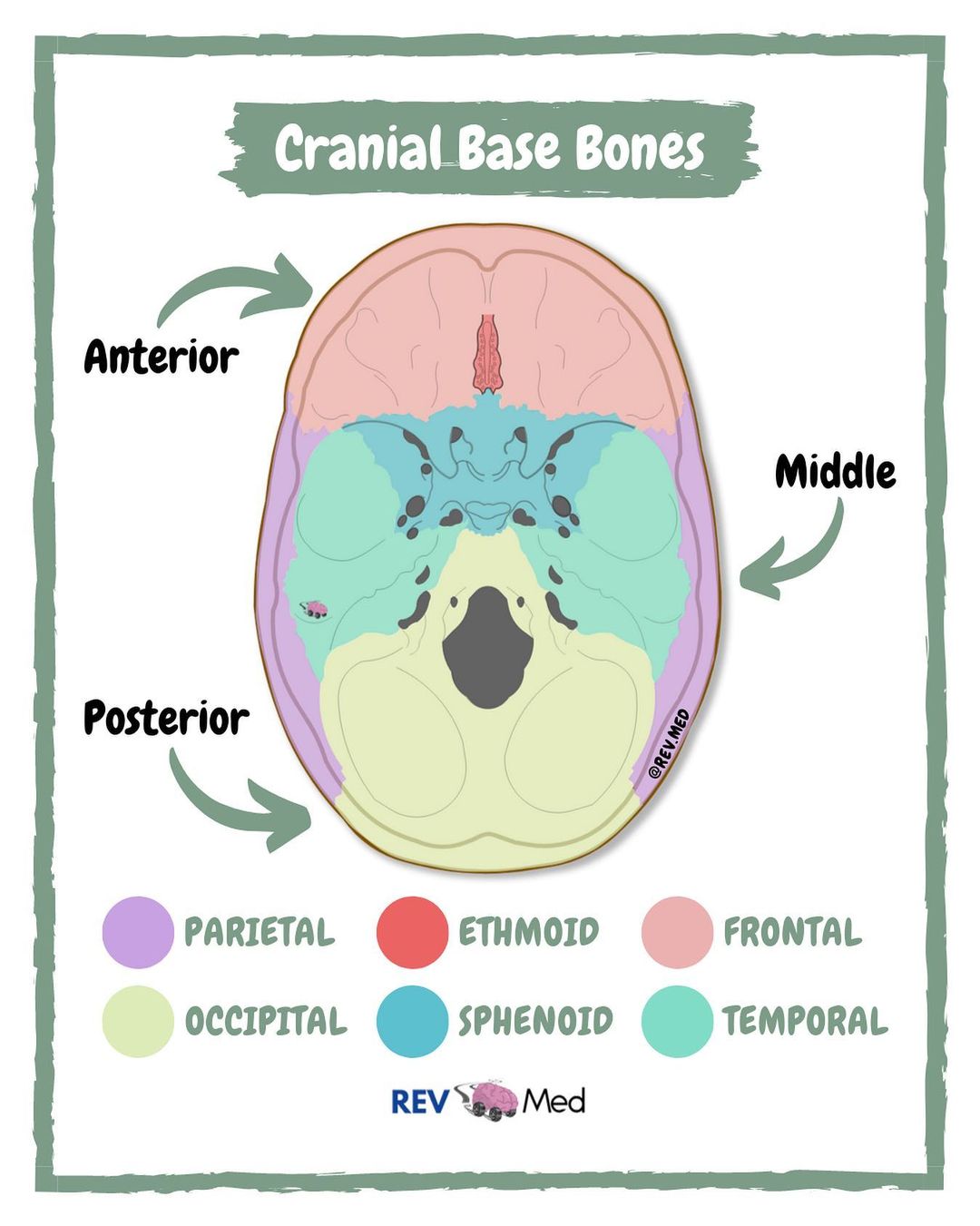
Cranial base
The floor of the cranial cavity
Two surfaces
Endocranium (Inner surface of the cranial cavity)
External cranial base
Some bones of the calvaria
Components:
Sphenoid bone
Ethmoid bone
Occipital bone
Frontal bone
Temporal bone
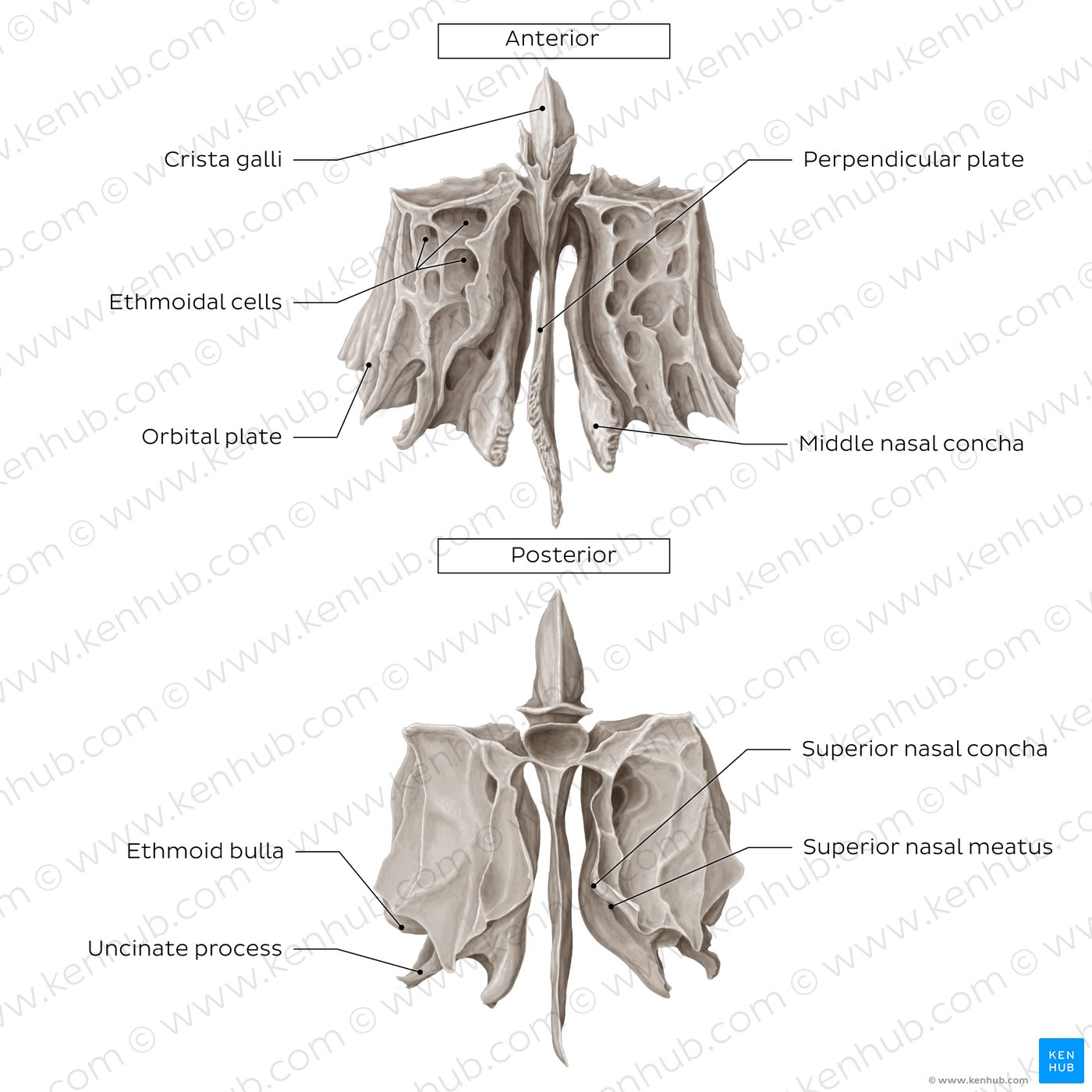
Ethmoid Bone
Small, unpaired bone, irregular shape
Separates the nasal from the cranial cavity
Pneumatized bone
Superior projection—→ crista galli
Sieve-like structure on each side of the ridge allows passage of small olfactory fibers to the olfactory bulb → cribriform plate
Forms a small portion of the orbit
Articulates with the frontal and with sphenoid bones
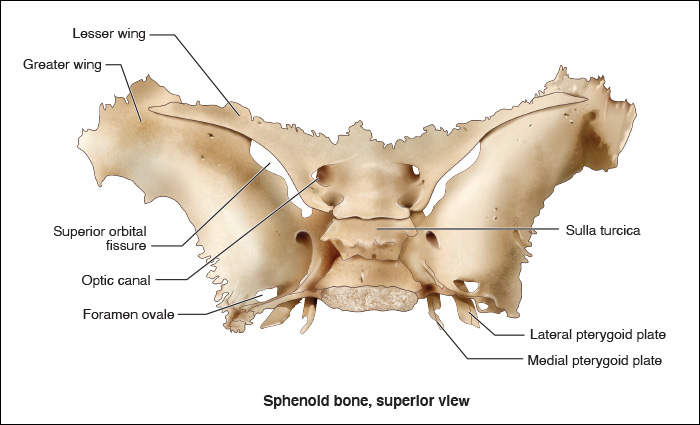
Sphenoid Bone
Butterfly-shaped, unpaired bone
Location:
Anterior to the basilar portion of the occipital bone
Middle part of the neurocranium
Pneumatized bone: sphenoidal sinuses
Composed of:
Body
Greater wing
Lesser wing
Two pterygoid process
Sphenoid bone
One of the most complex bones of the neurocranium —> numerous bone articulations
Participates in formation of:
Nasal cavity
Orbits
Middle portion of the endocranium
The body contains a depression
Sella turcica —> home of the pituitary gland
The saddle
Optic nerves pass through the optic canal
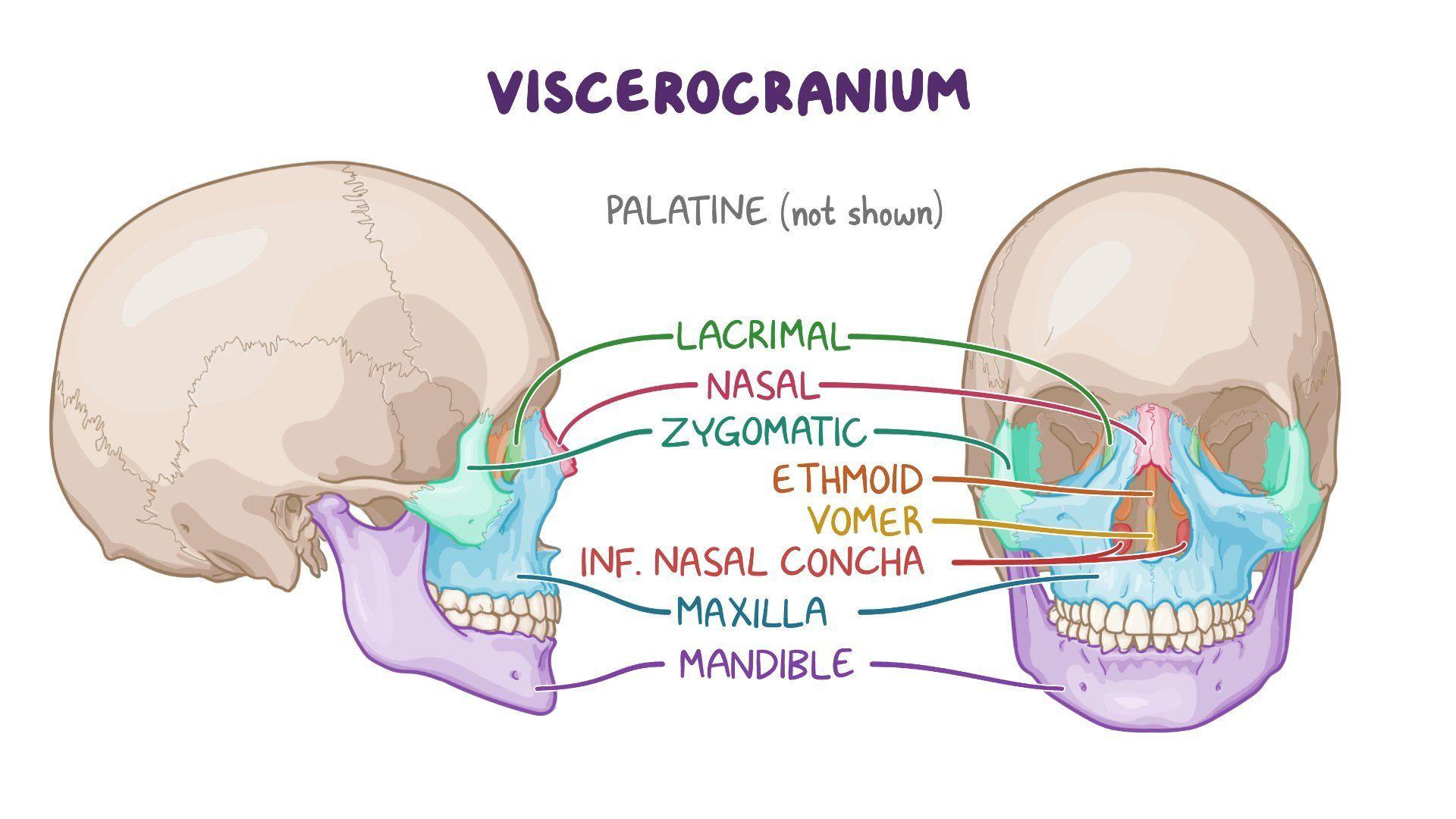
Viscerocranium
The facial skeleton, located anterior to the neurocranium
Supports the facial features
Nose bridge
Cheeks
Jawline
Comprised of 14 bones
All bones are joined together through synarthroses, except the mandible.
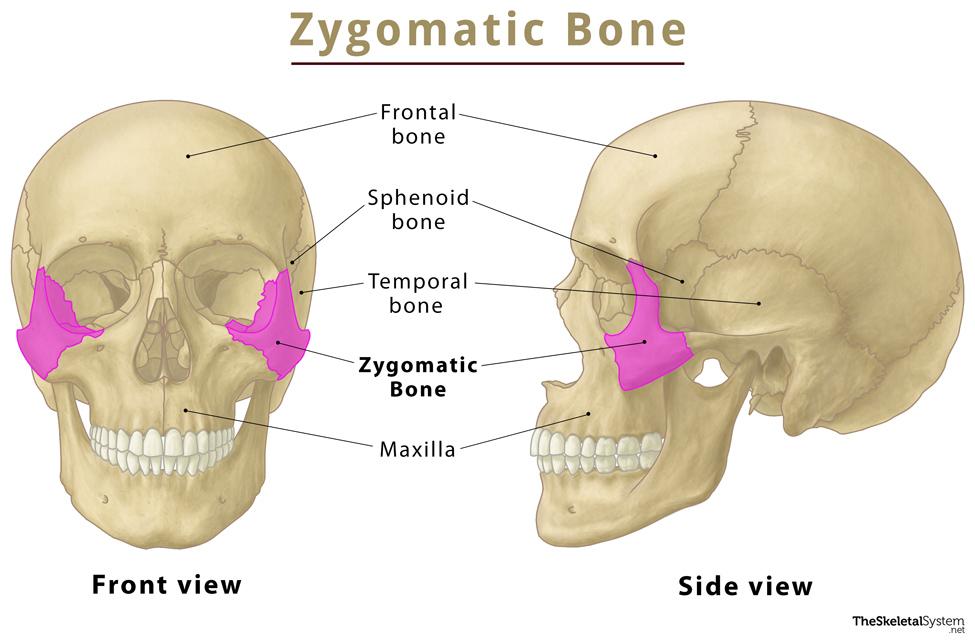
Zygomatic bone
Irregular paired bone
Forms the face’s lateral prominences
Part of the orbit inferior and lateral rims
Composed of:
4 processes
3 surfaces
4 borders
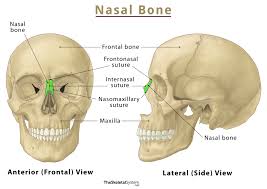
Nasal bone
Small, obling, paired bones
Forms the bridge of the nose
Articulates medially through the internasal suture (synarthrosis)
Each side has two surfaces: Inner and outer.
Articulates
Superiorly with the frontal bone
Inferiorly with the maxillae
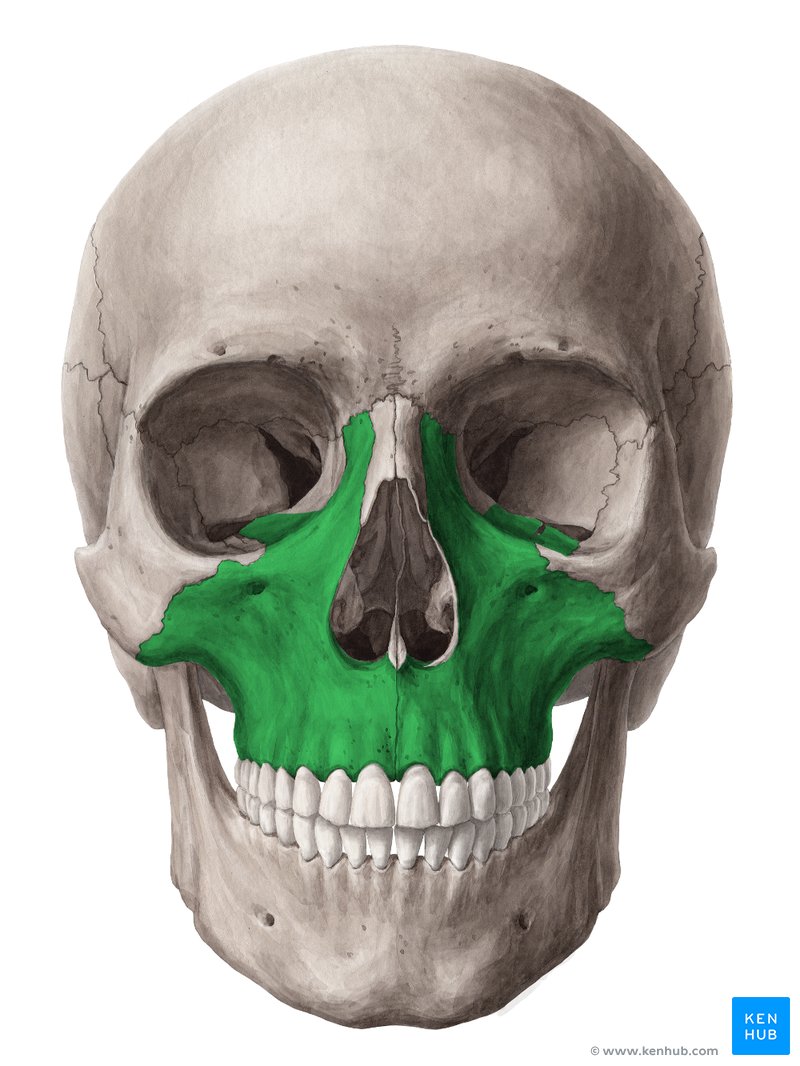
Maxillae
Large paired bones: the upper jaw
Pneumatized bones —→ maxillary sinuses
Hold the upper teeth
Involved in formation of:
Orbit
Nasal cavity
Palate
Composed of:
Body
Four processes: zygomatic, frontal, alveolar, and palatine
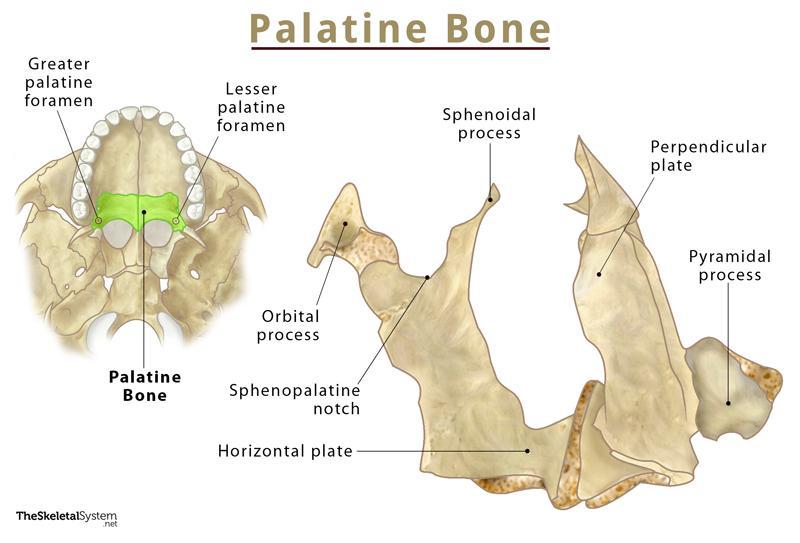
Palatine Bone
Irregular paired bones
Alongside the maxillae, forms the hard palate
Location: between maxilla and the pterygoid process of the sphenoid
Fuse together on the midline
Composed of two perpendicular plates
Horizontal plate: the hard palate
Vertical plate: nasal cavity lateral wall
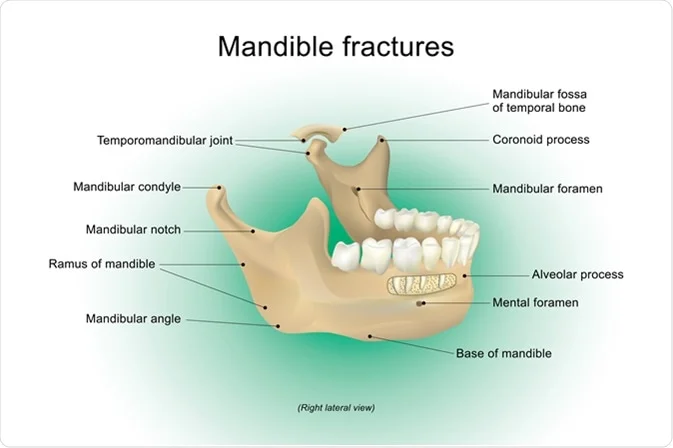
Mandible
Large bone forming the chin and jawline
Unpaired
Not an actual part of the skull
Articulates with the temporal bone through the temporo-mandibular joint
Hold the lower teeth
Composed of:
Ramus (coronoid and condylar processes)
Quadrilateral body
Alveolar process