West Coast University Dr. Kolb Midterm
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Structures that cannot be seen without magnification
cytology- Study of cells (Lysosomes, ribosomes, Golgi, etc
Histology- Study of tissues (Epithelial, connective,muscle, Nervous)
Surface Anatomy
superficial markings
Regional Anatomy
Specific area of body (Head neck or trunk) whether they are superficial or deep
systemic anatomy
organ systems (Digestive system,cardiovascular system, etc)
Levels of organization
chemical/molecular, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, organism
Cell
smallest unit of life (Organelles)
Tissue
Cells and surrounding material such as: Epithelial. muscular,neural and connective tissue
Organ
a combination of tissues. For example: the heart consists of all tissues (Epithelial, muscular, neural, and connective tissue
organ system
composed of several organs working together
For Example: the stomach,small intestine,large intestine, liver, gallbladder, and pancreas make up the digestive system.
The heart and blood vessels make up the cardiovascular system,
Humans are composed of 11 organ systems.
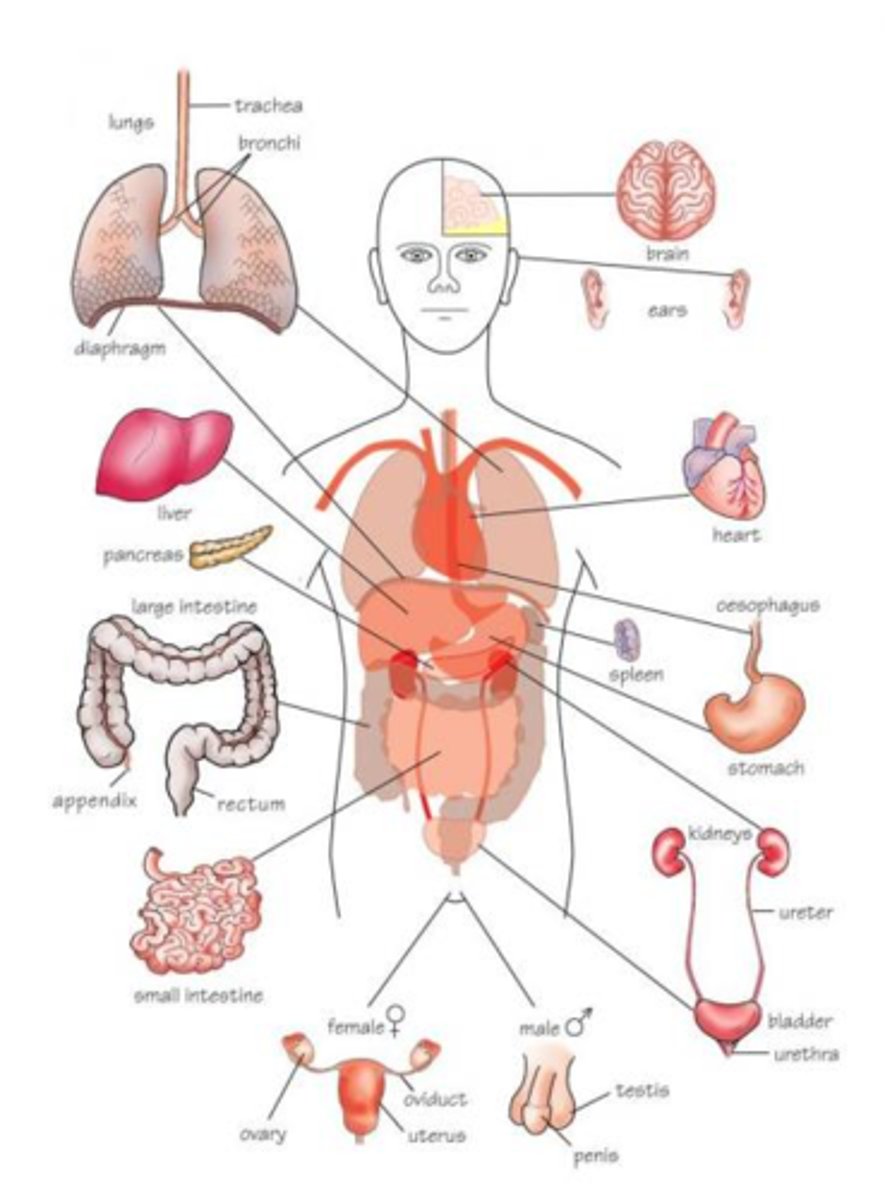
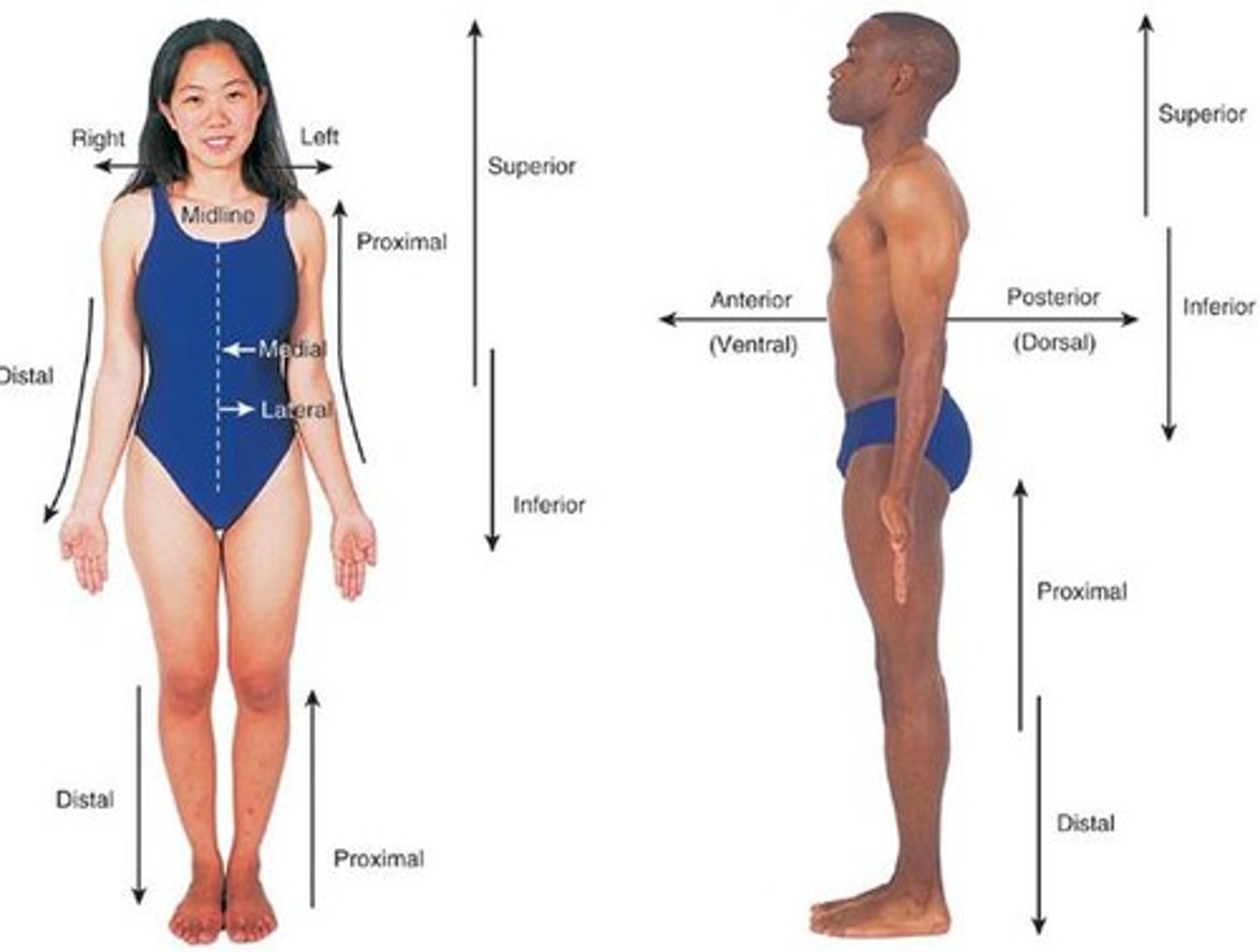
anatomical position
To stand erect with arms at the sides and palms of the hands turned forward
Supine: lying down (face up) in the anatomical position
prone:lying down(face down) in the anatomical position
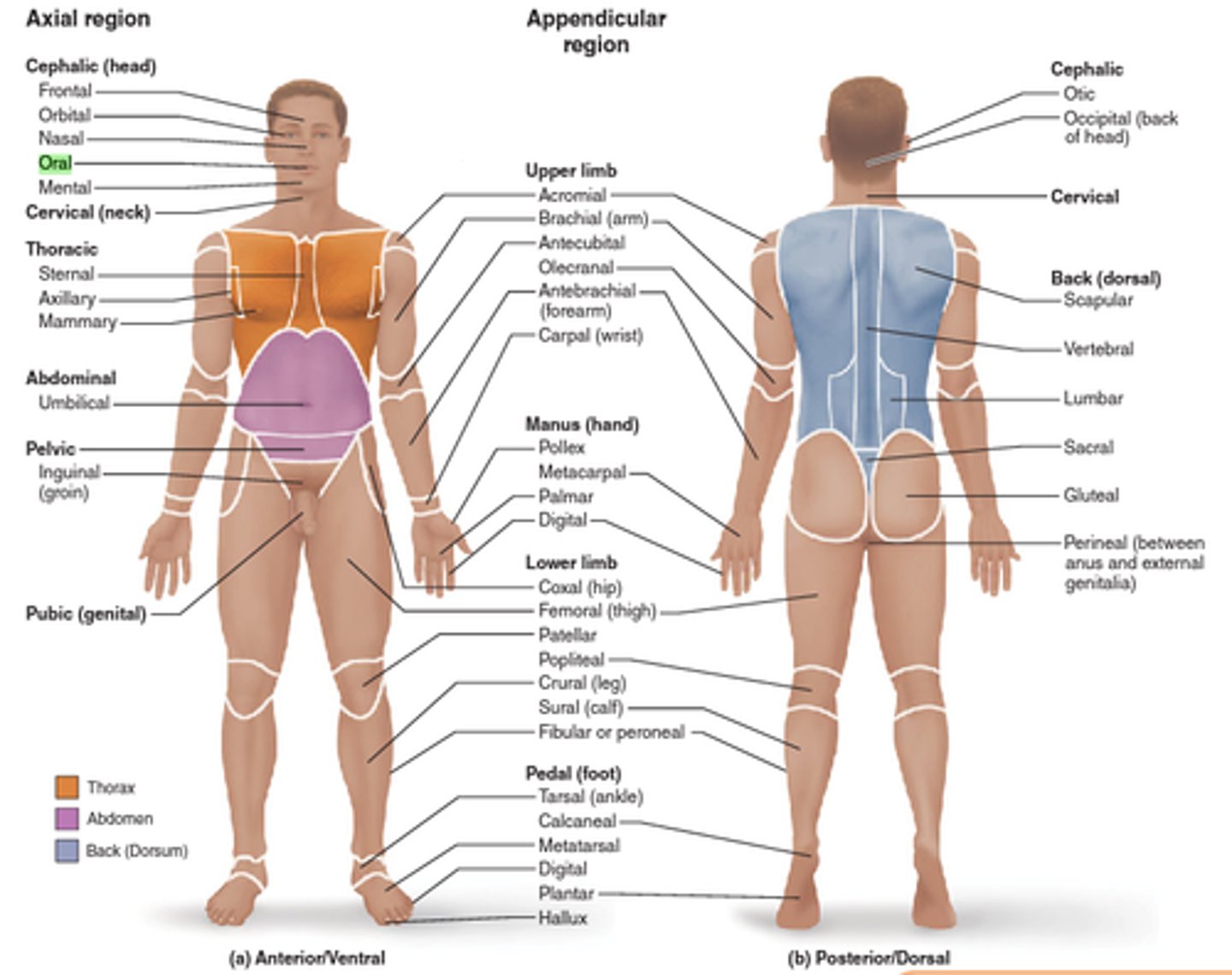
Anatomical areas (regions)
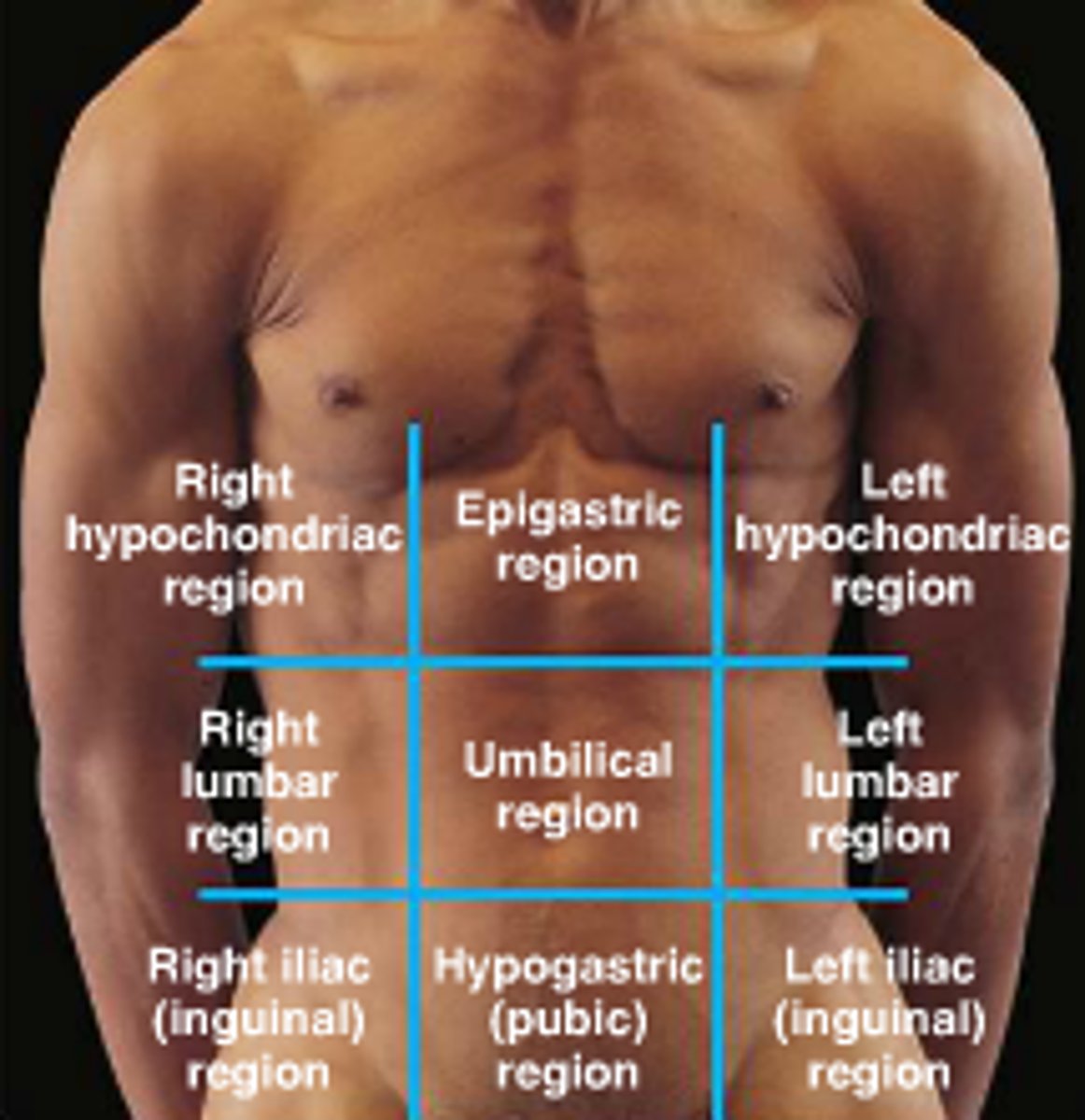
Abdominopelvic regions
nine specific anatomic areas of the abdominopelvic cavity
Directional regions
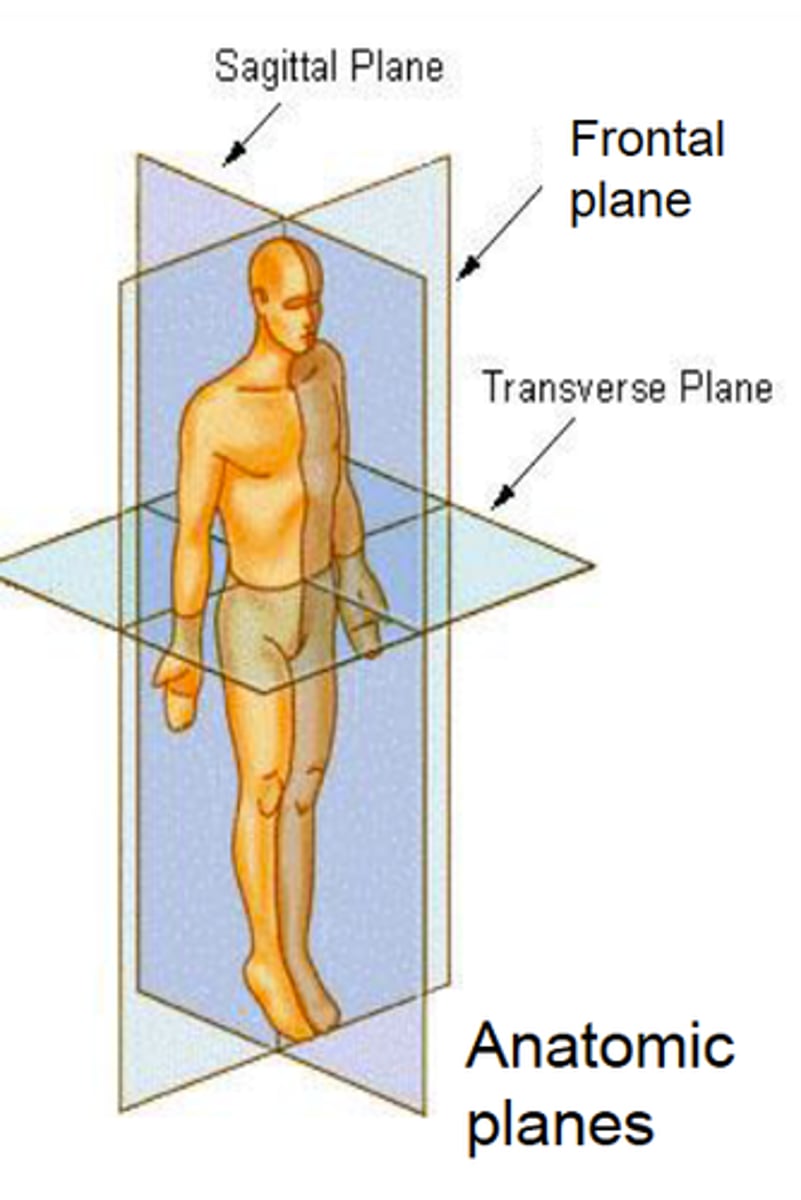
Planes and sectional regions
•Sagittal cut: separating left and right
•Midsagittal: separating left and right equally
•Parasagittal: separating left and right unequally
•Transverse cut: separating superior and inferior
•Frontal cut: separating anterior and posterior
•Oblique cut: separating the tissue at an angle
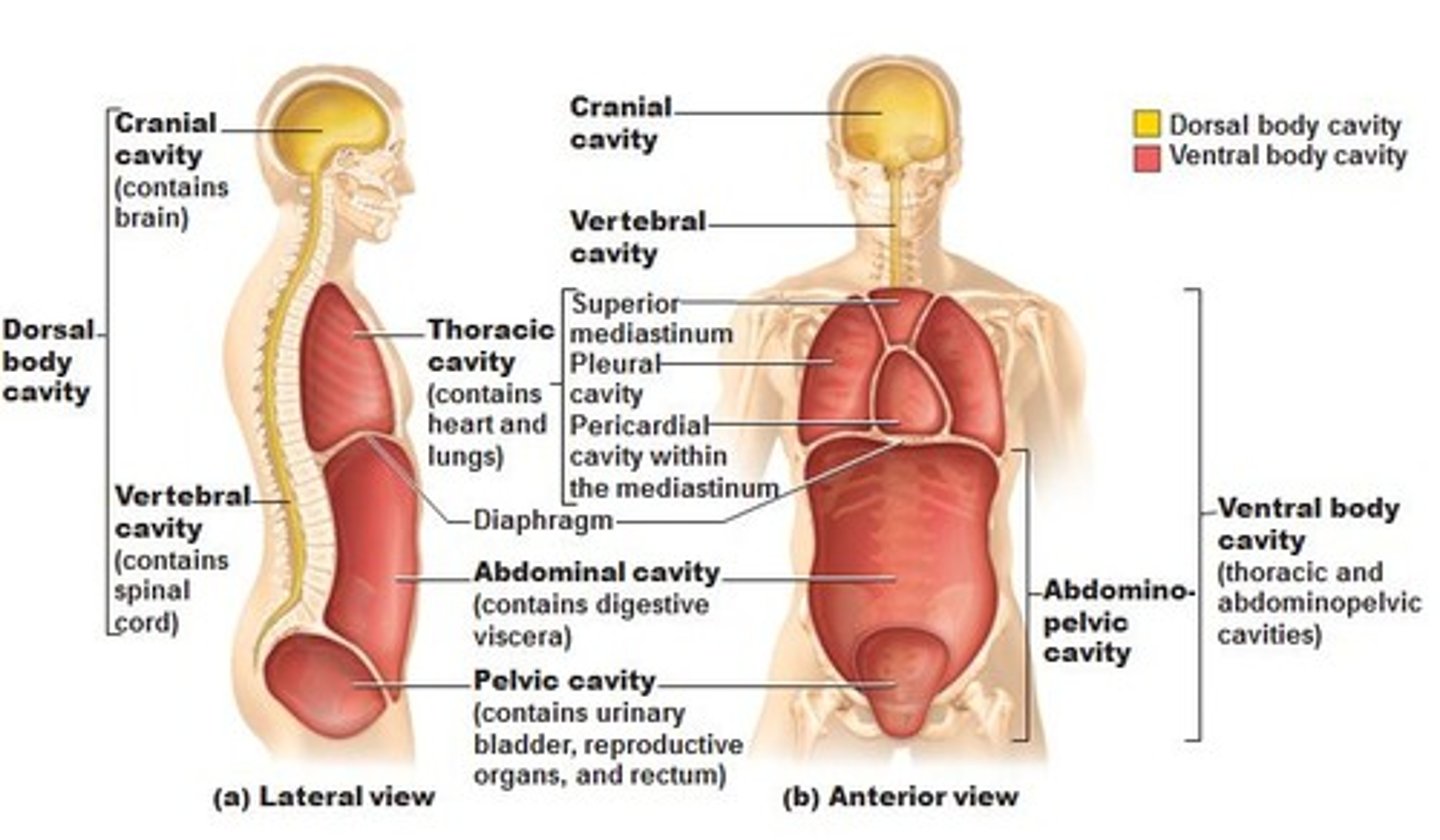
body cavity regions
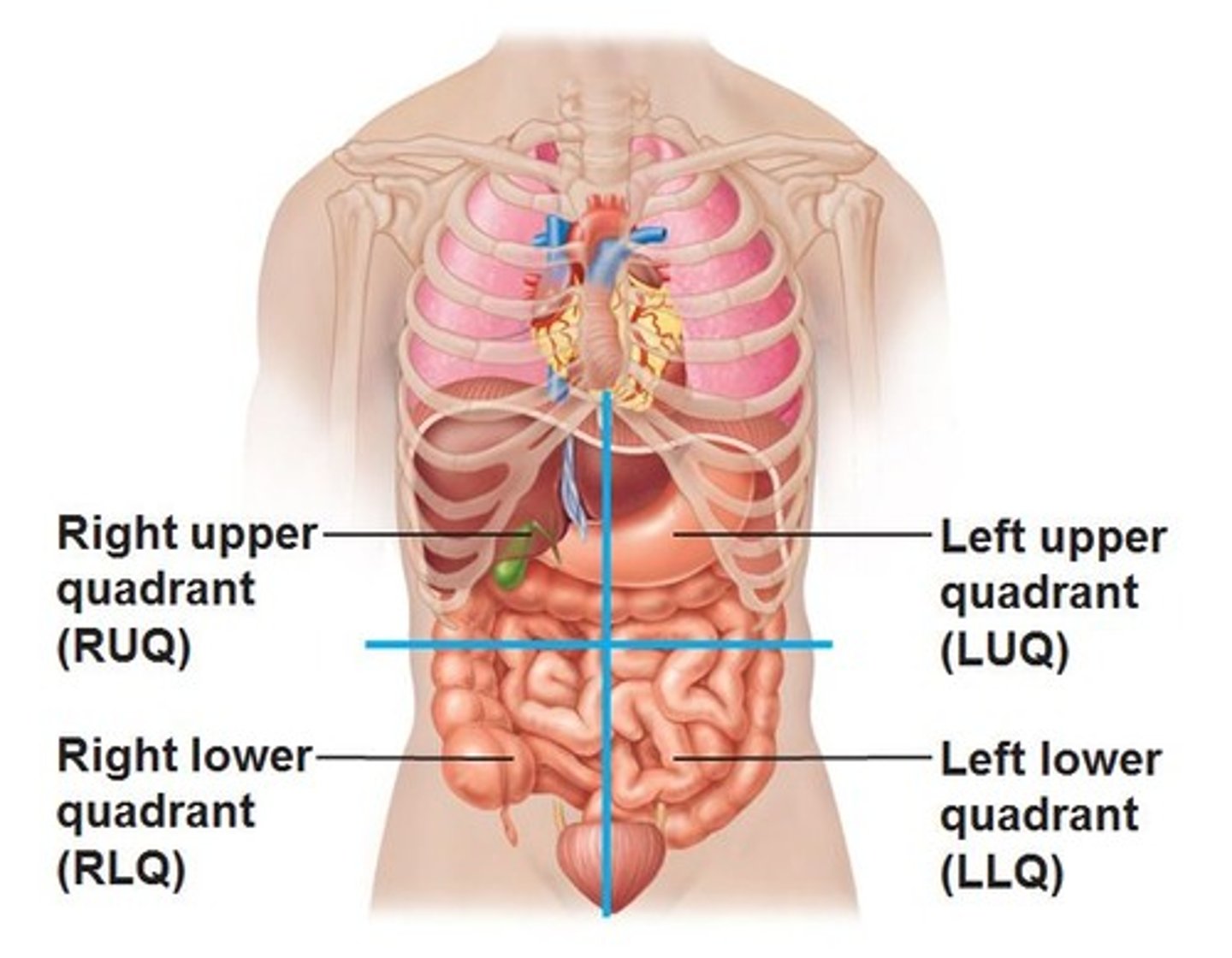
Abdominopelvic Quadrants
right upper RUQ (most of liver & gallbladder), left upper LUQ (Stomach and spleen), right lower RLQ (cecum, appendix,right ureter, right ovary,right spermatic cord), left lower LLQ (intestines, left ureter, left ovary, left spermatic cord)
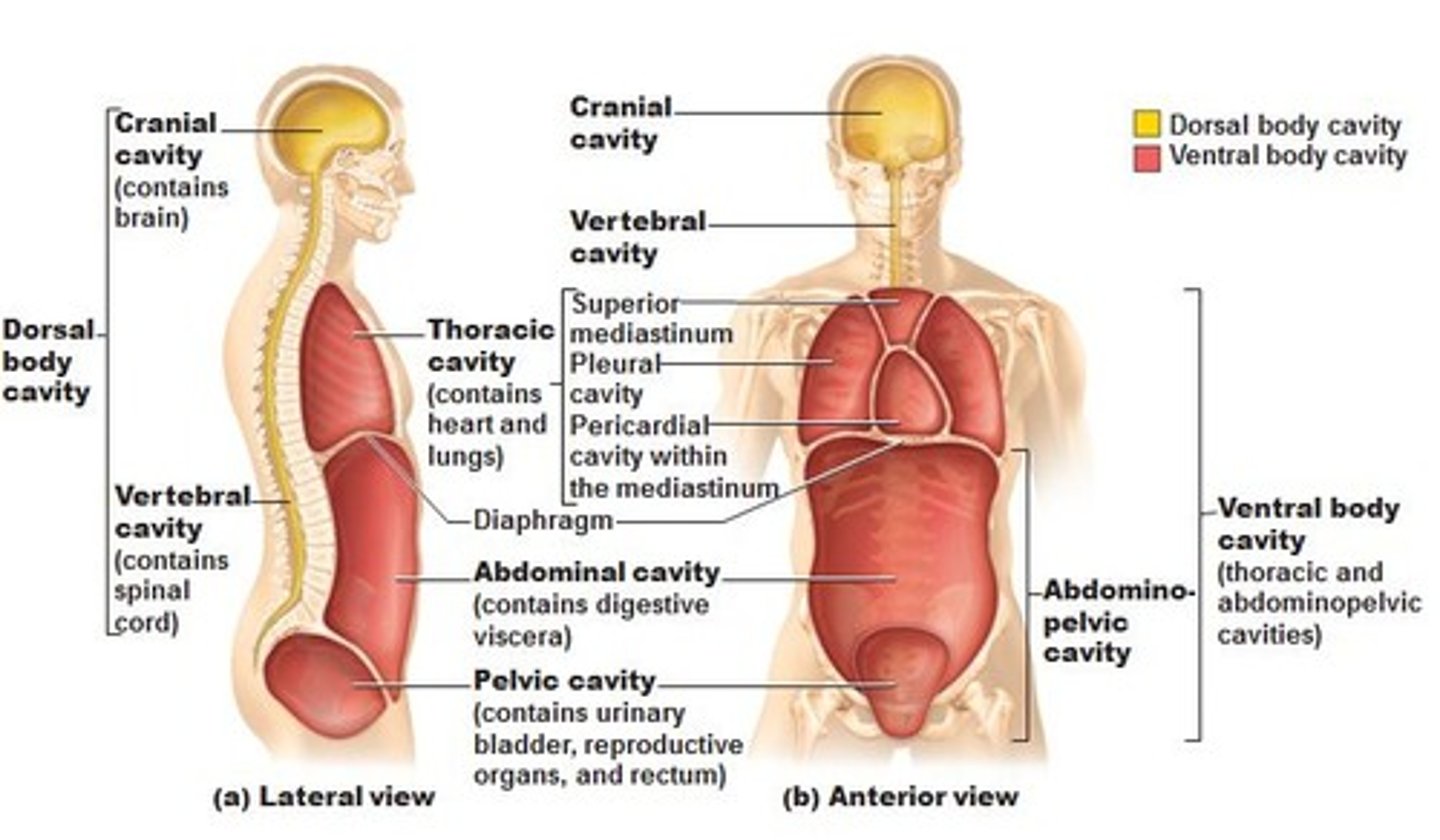
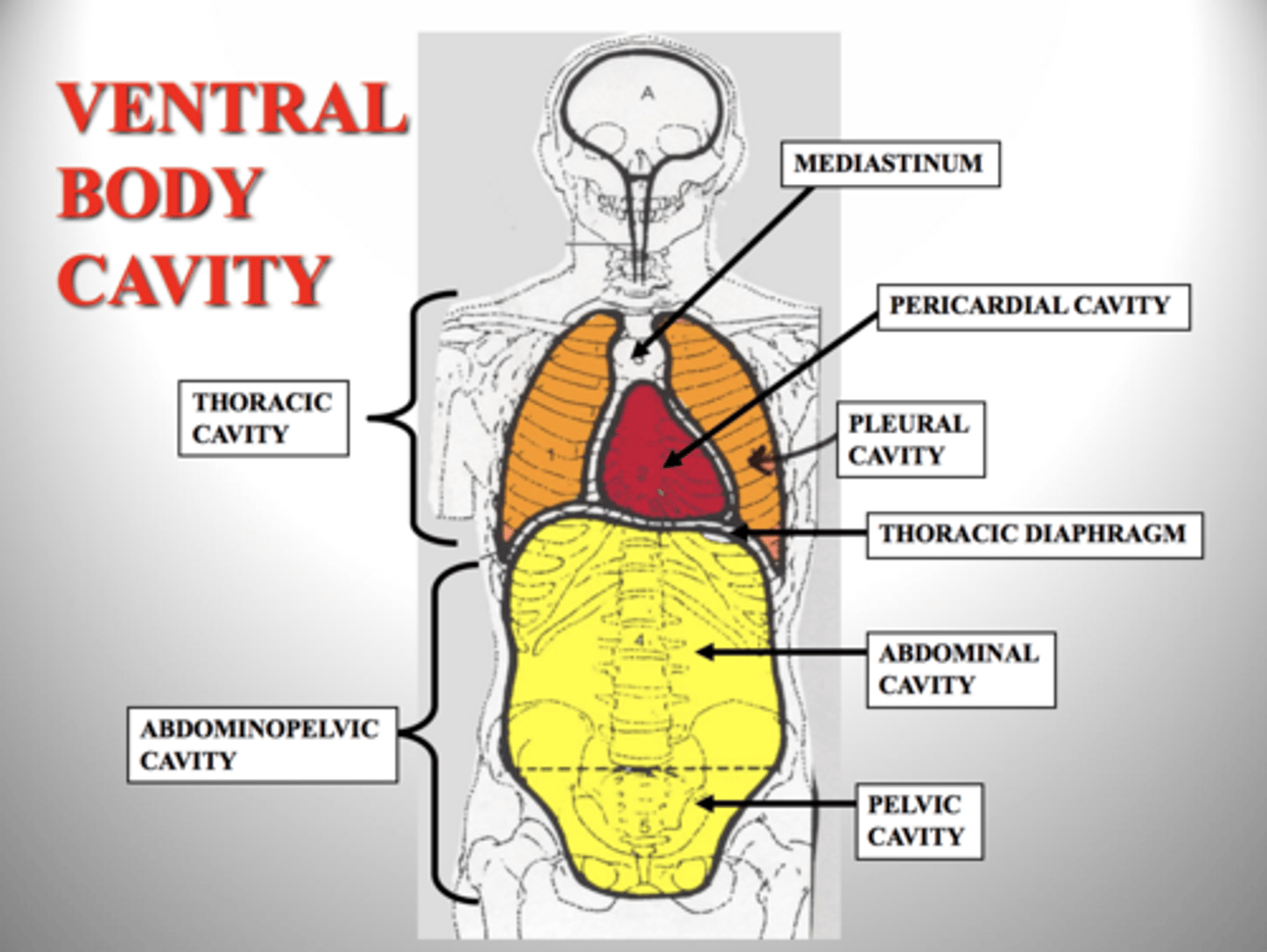
body cavities
Posterior cavity
Cranial cavity:consist of brain
spinal cavity: spinal cord
Anterior cavity
Thoracic cavity
abdominal cavity
pelvic cavity
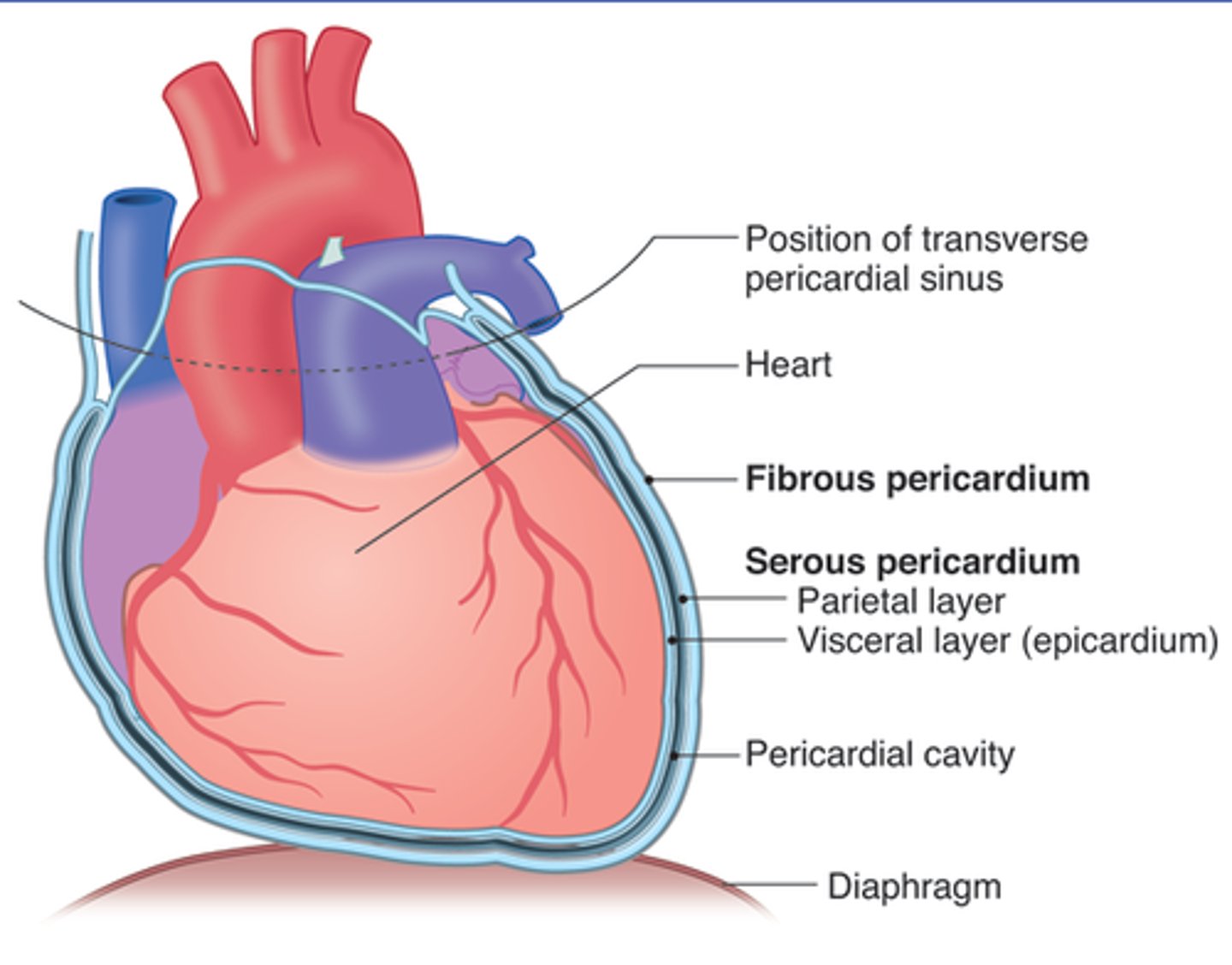
parietal membrane
lining of body cavity (e.g. parietal pleural membrane lines the pleural cavity )
visceral membrane
The membrane farthest from the wall of the body (nearest the organs)
thoracic cavity contains
Pleural cavity: Lungs
Pericardial cavity: heart
mediastinal cavity: space between apex of lungs
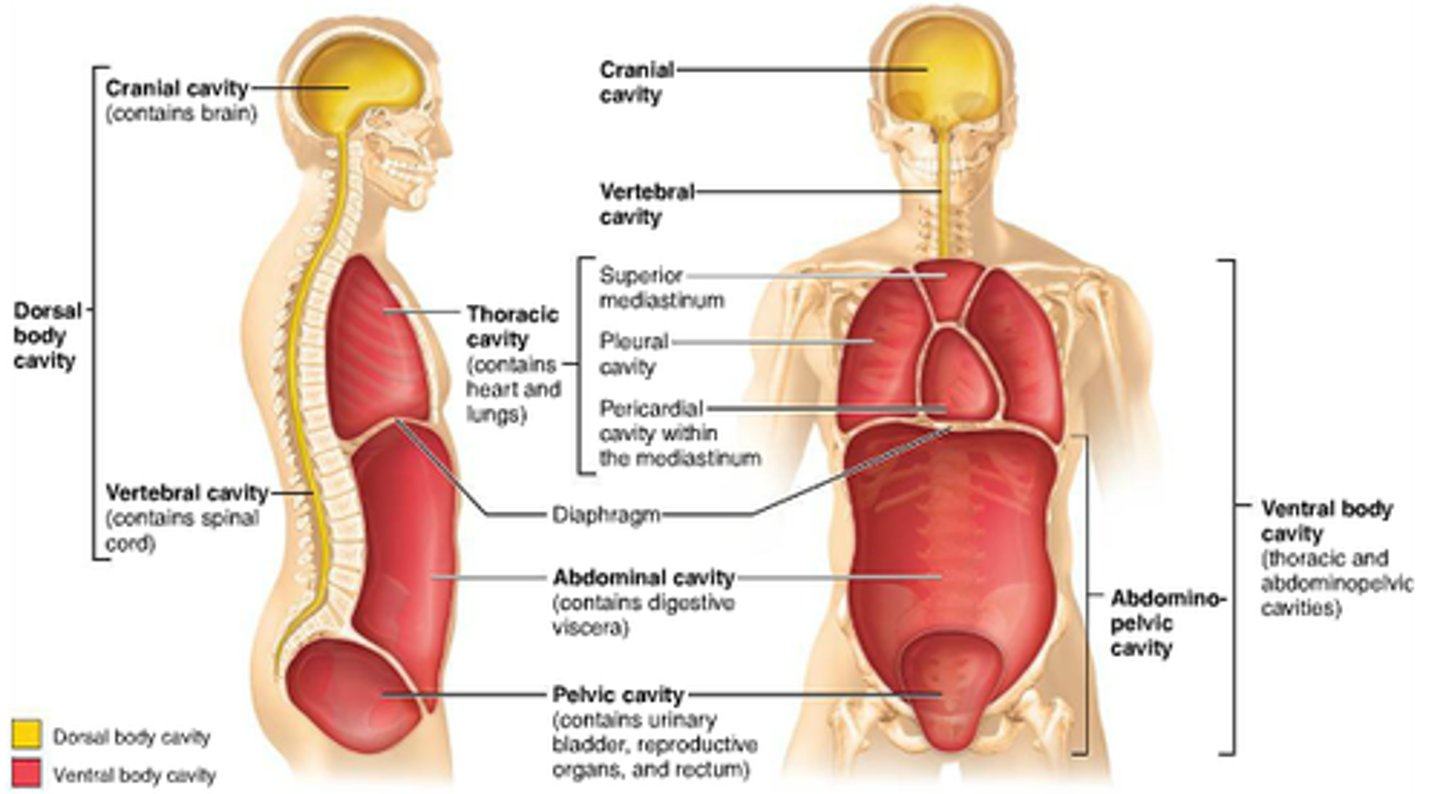
Abdominopelvic cavity consist of
Peritoneal cavity:Stomach,intestines, spleen, liver etc.
pelvic cavity: urinary bladder
nonmembranous organelles
cytoskeleton, microvilli, cilia, flagella, ribosomes
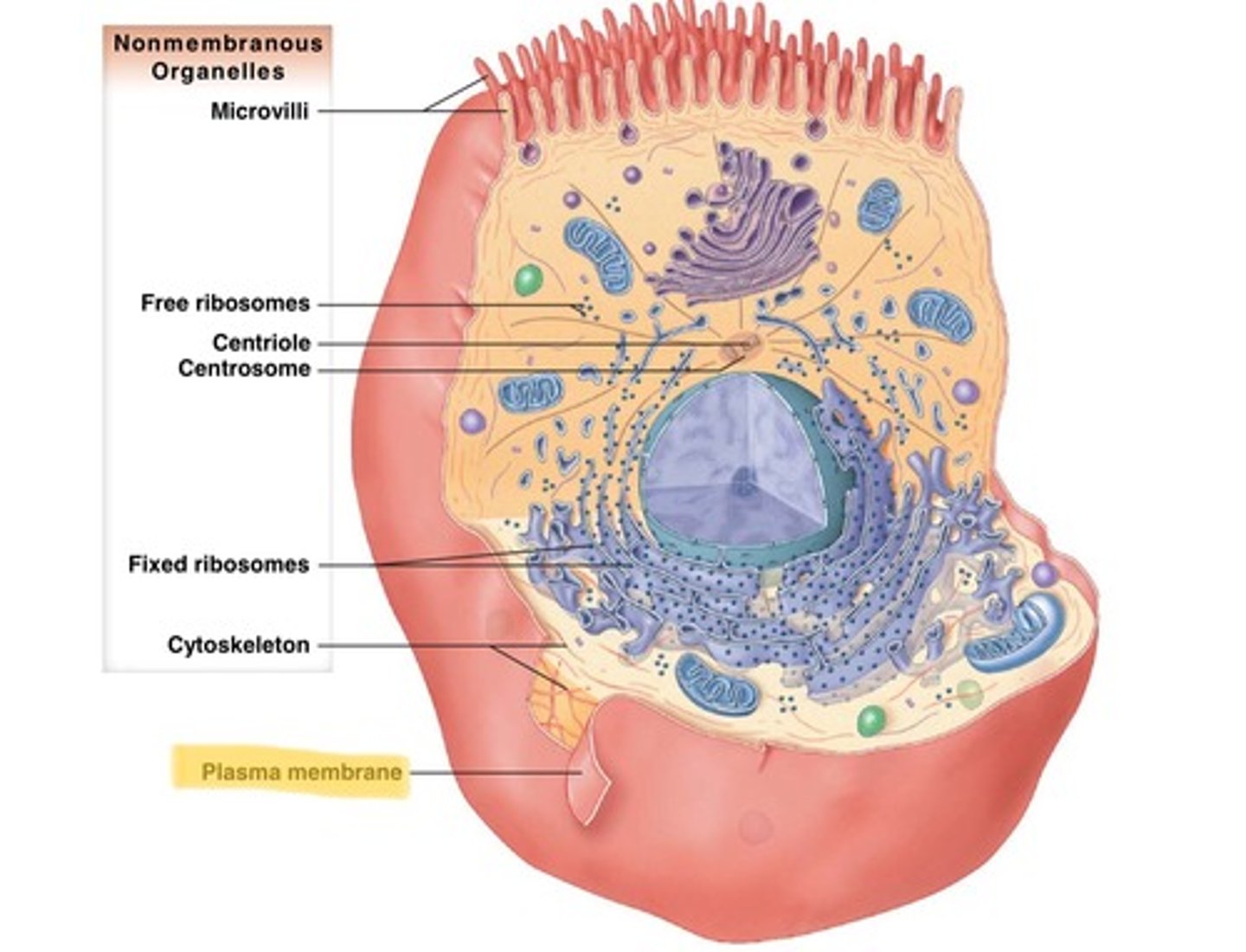
membranous organelles
mitochondria, nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, golgi apparatus, lysosomes, peroxisomes

function of plasma membrane
Controls what enters and leaves the cell
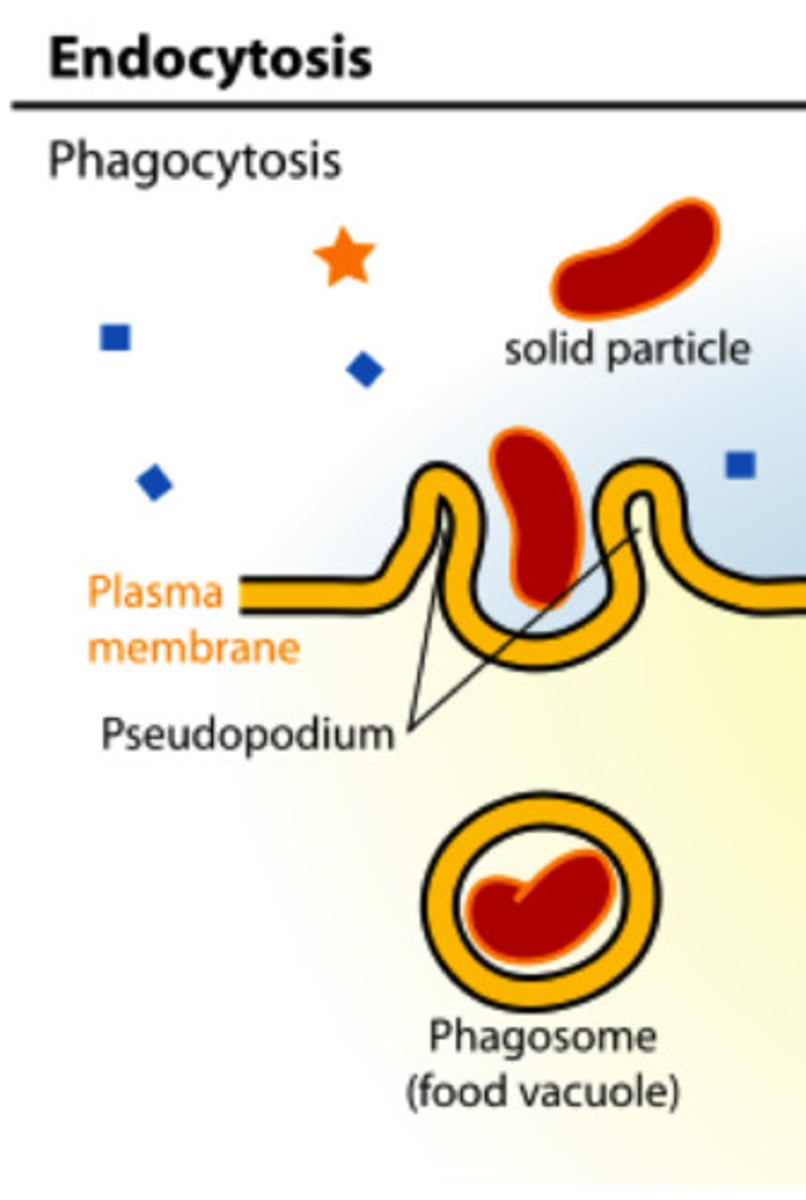
Phagocytosis
"Cell eating"; an endocytic pathway by which a cell engulfs particles such as microbes or cellular debris.
Bacteria, viruses, foreign matter, and cell debris can be engulfed (ie., phagocytized)
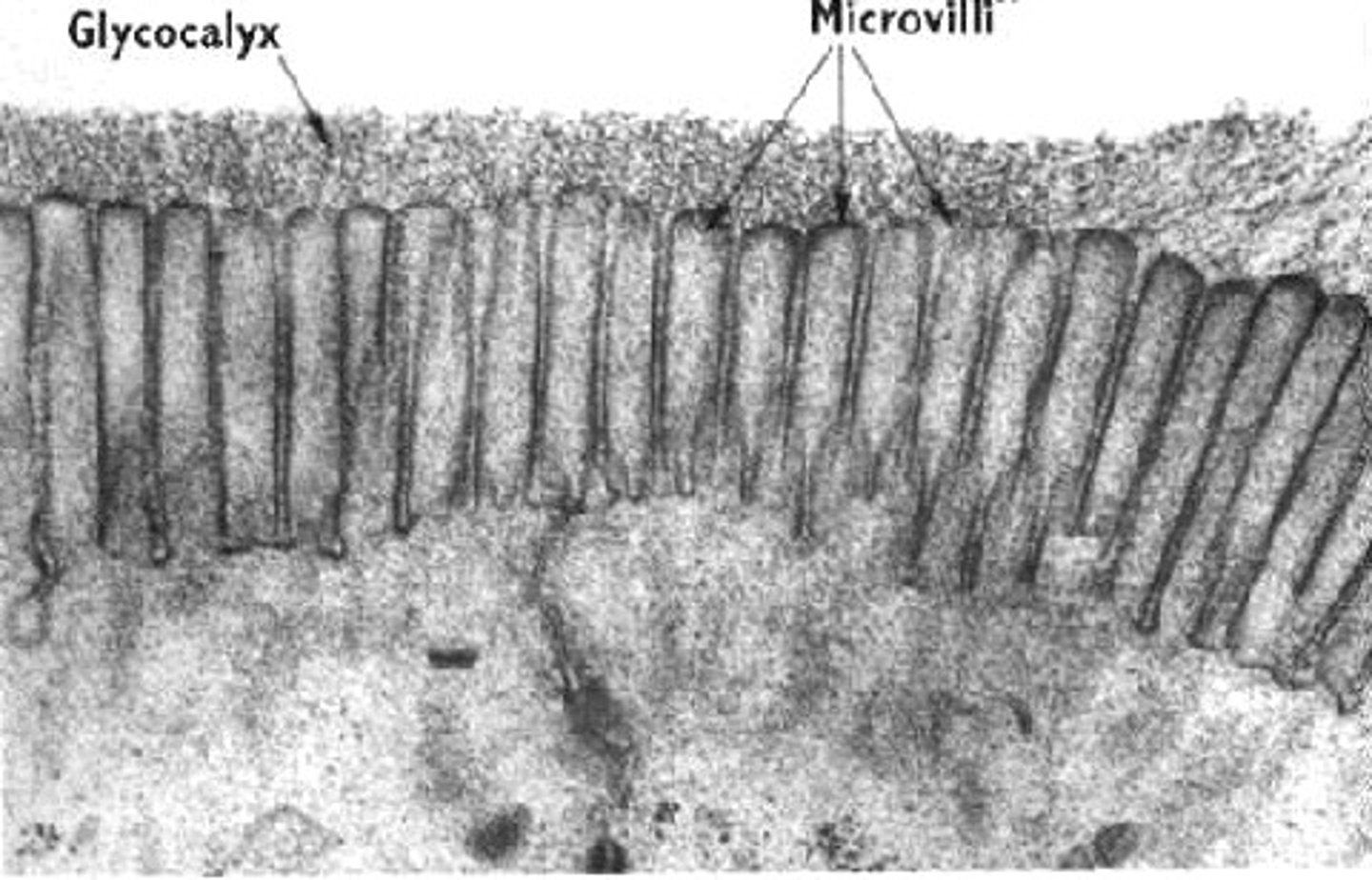
microvilli
Fingerlike extensions of plasma membrane of apical epithelial cells, increase surface area, aid in absorbtion, exist on every moist epithelia, but most dense in small intestine and kidney
Cytoskeleton
A network of fibers that holds the cell together, helps the cell to keep its shape, and aids in movement "skeleton" of the cell or "building frame"
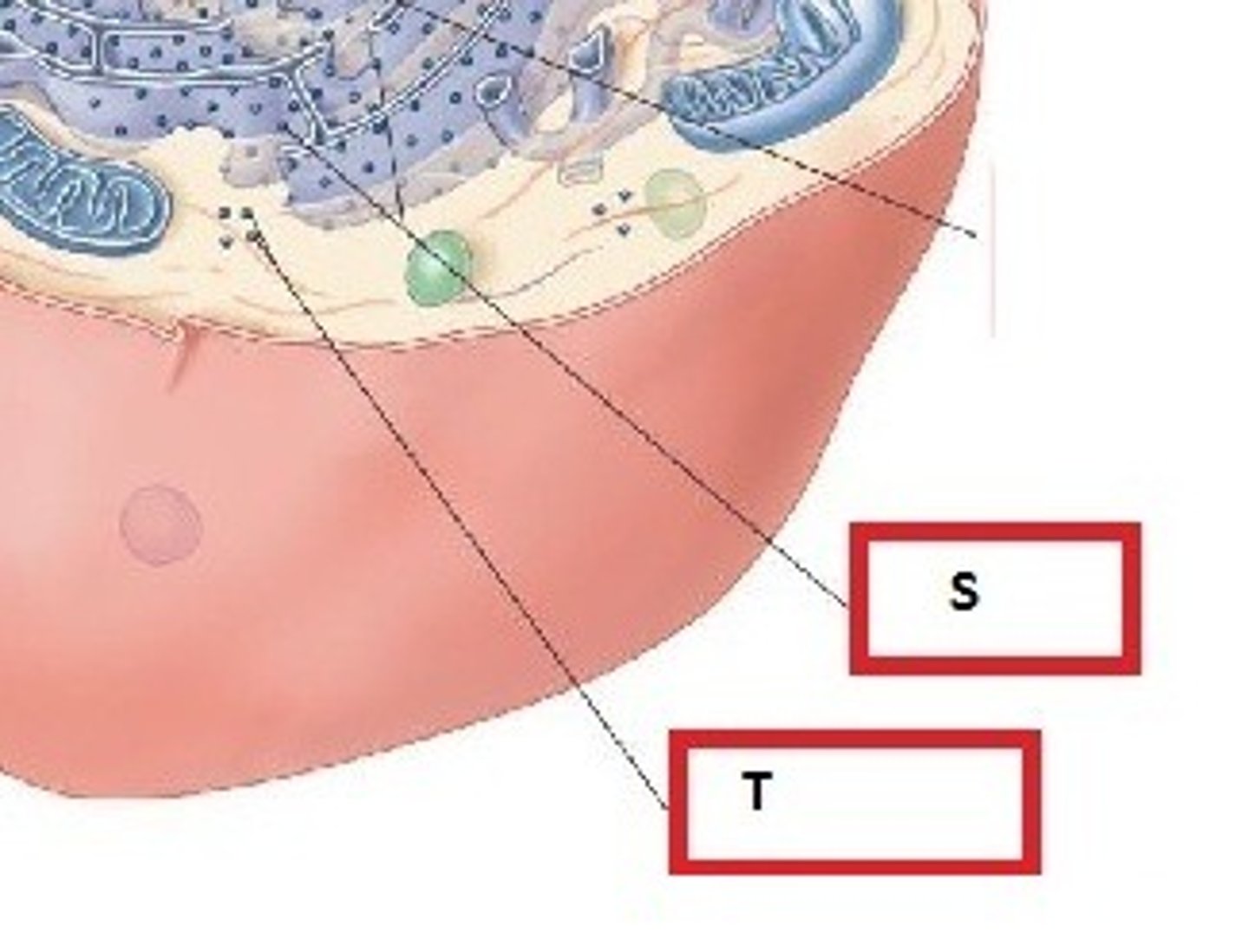
Ribosomes
(T) Free ribosomes: Float in the cytoplasm
(S) Fixed ribosomes: attached to the endoplasmic recticulum
(Both produce protein)
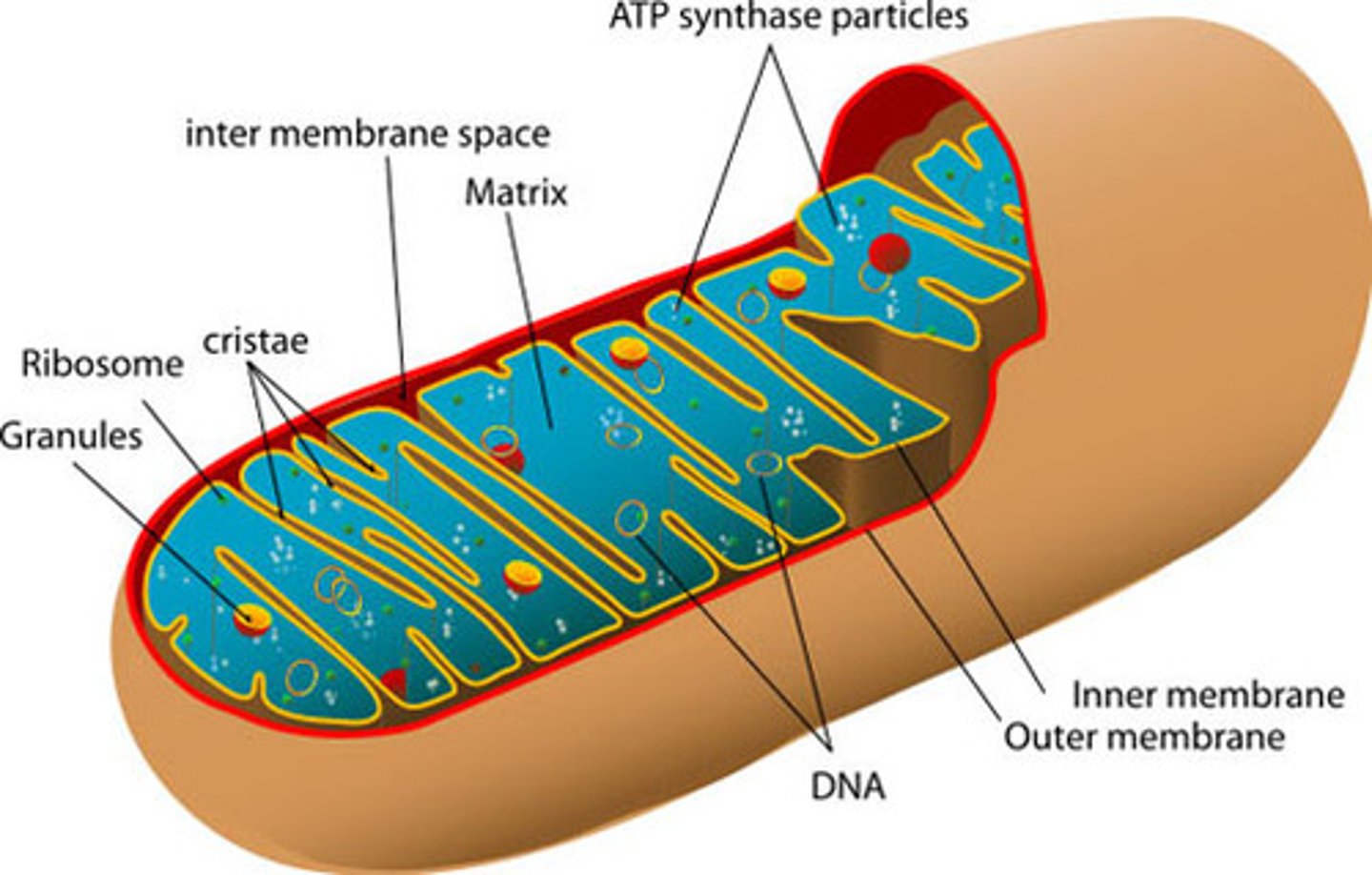
Mitochondria
powerhouse of the cell, produces ATP
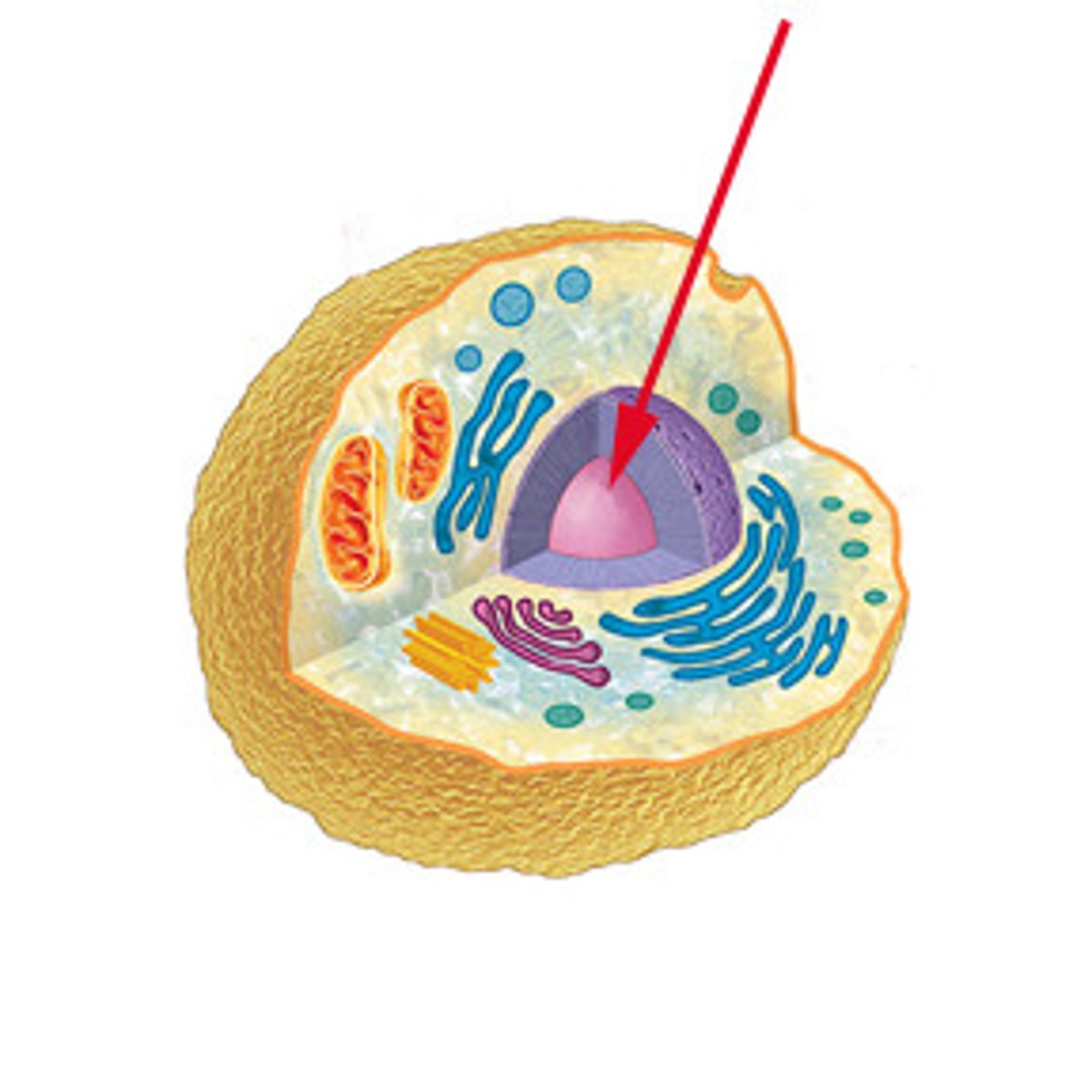
Nucleus
Control center of the cell. Contains chromosomes.
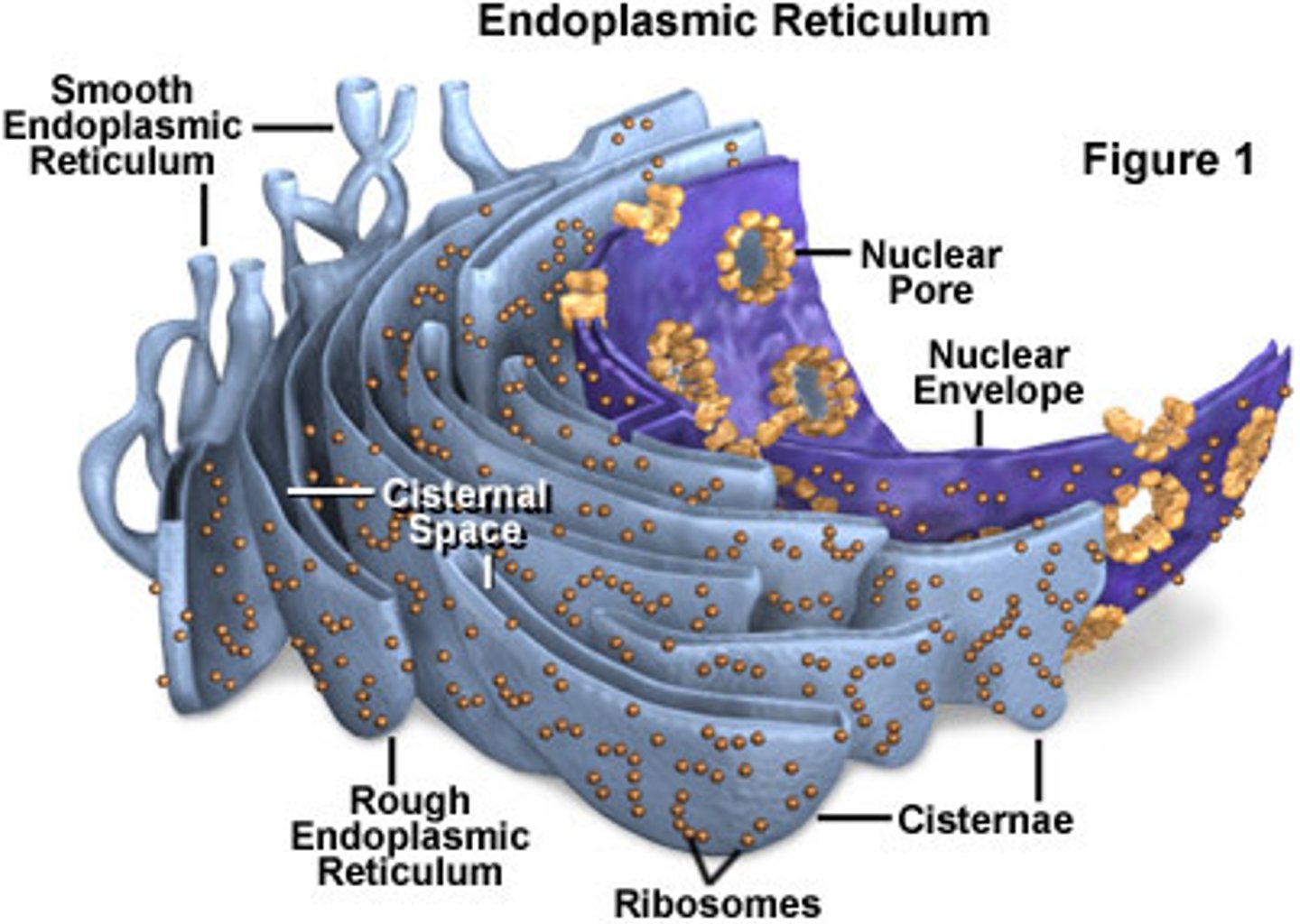
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Rough ER and Smooth ER
Rough ER
-with ribosomes
-synthesizes proteins
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
-w/out ribosomes
-synthesizes non-proteins: lipids, steroids, and carbohydrates
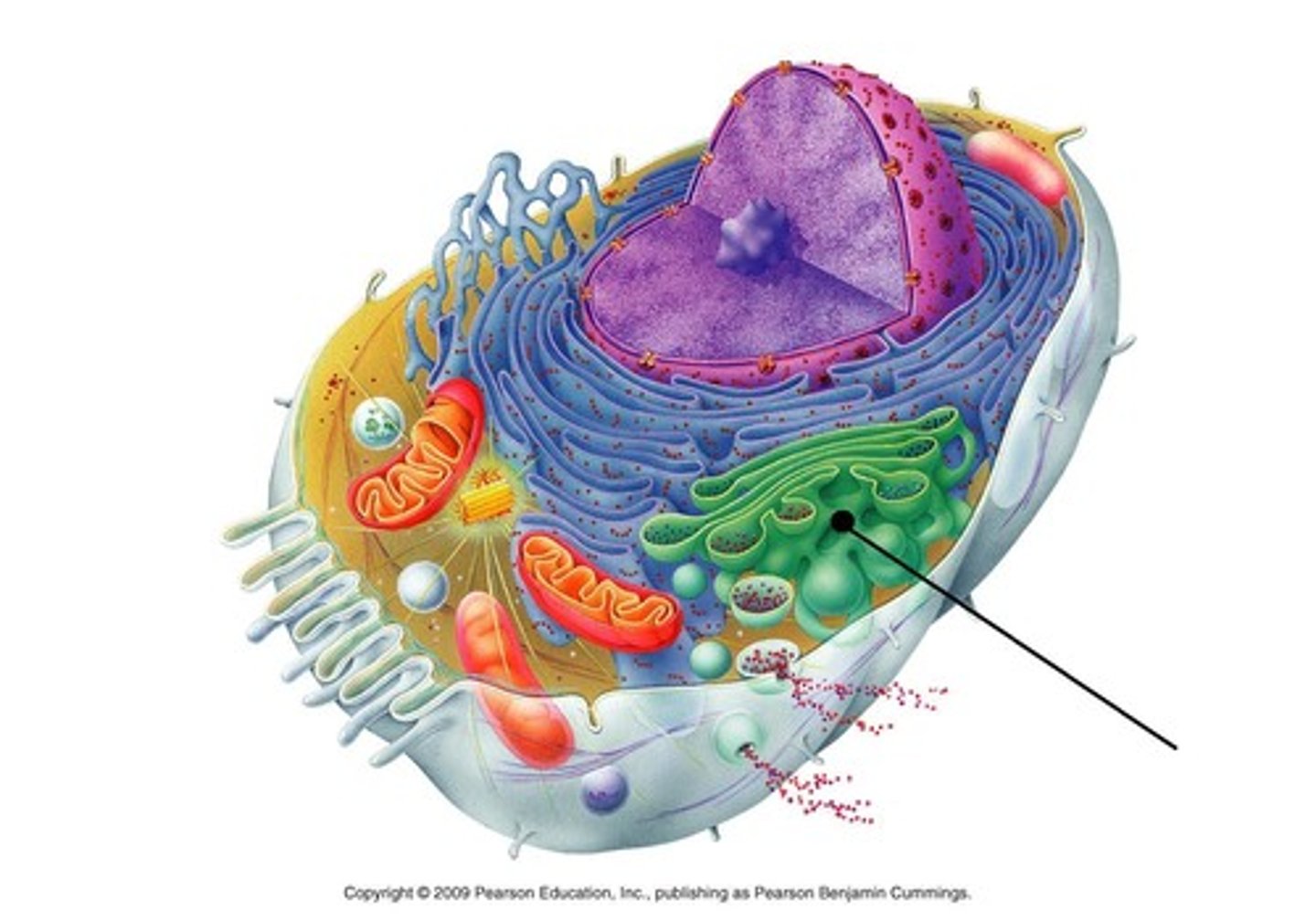
Golgi apparatus
s•Synthesis and packaging of secretions
•Packaging of enzymes (modifies protein)
•Renewal and modification of the plasmalemma
"packaging and shipping"
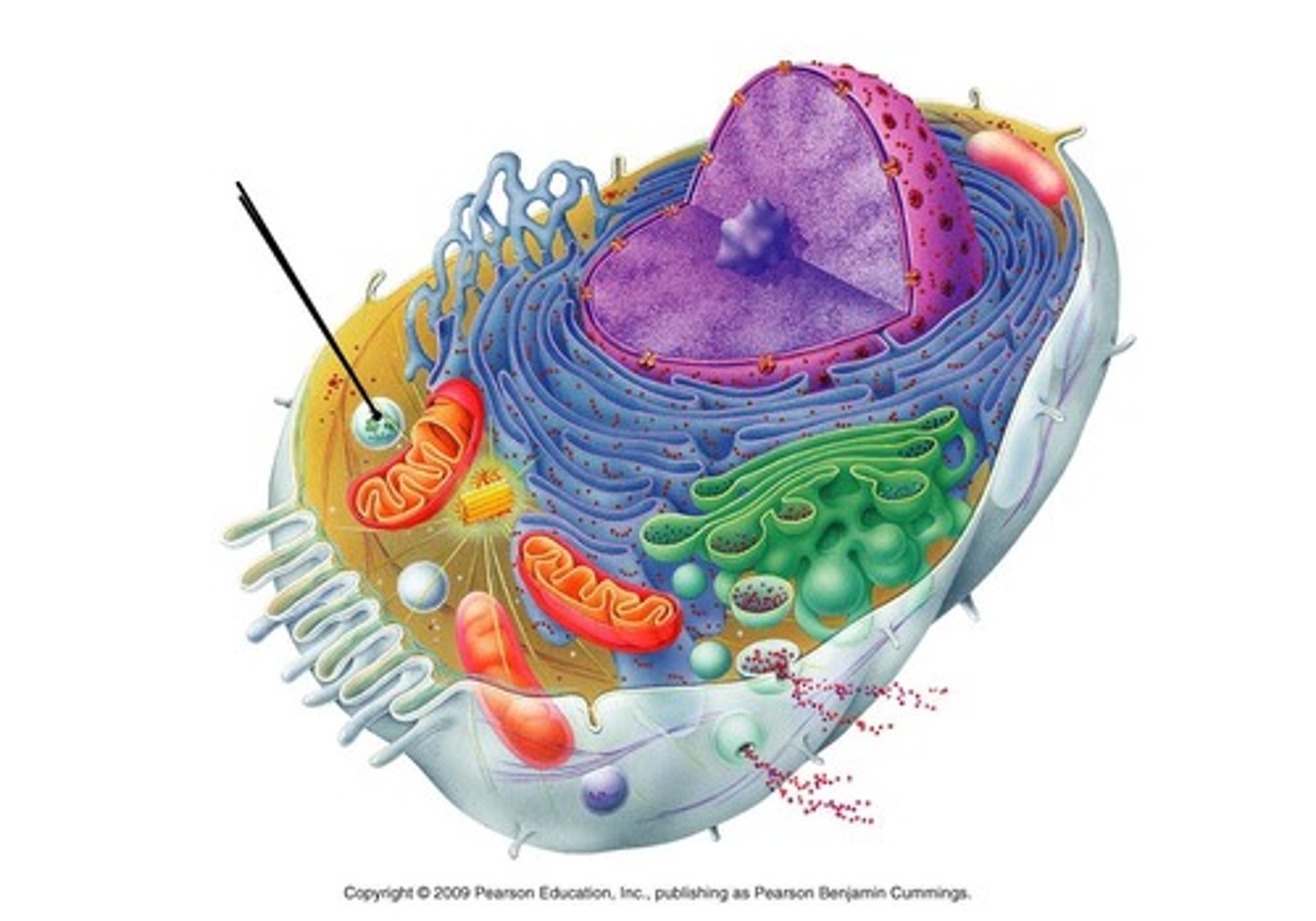
Lysosomes
-destroy ingested particles
-recycle damaged organelles
-rupture,killing cell (called autolysis)
"wrecking crew" of cell
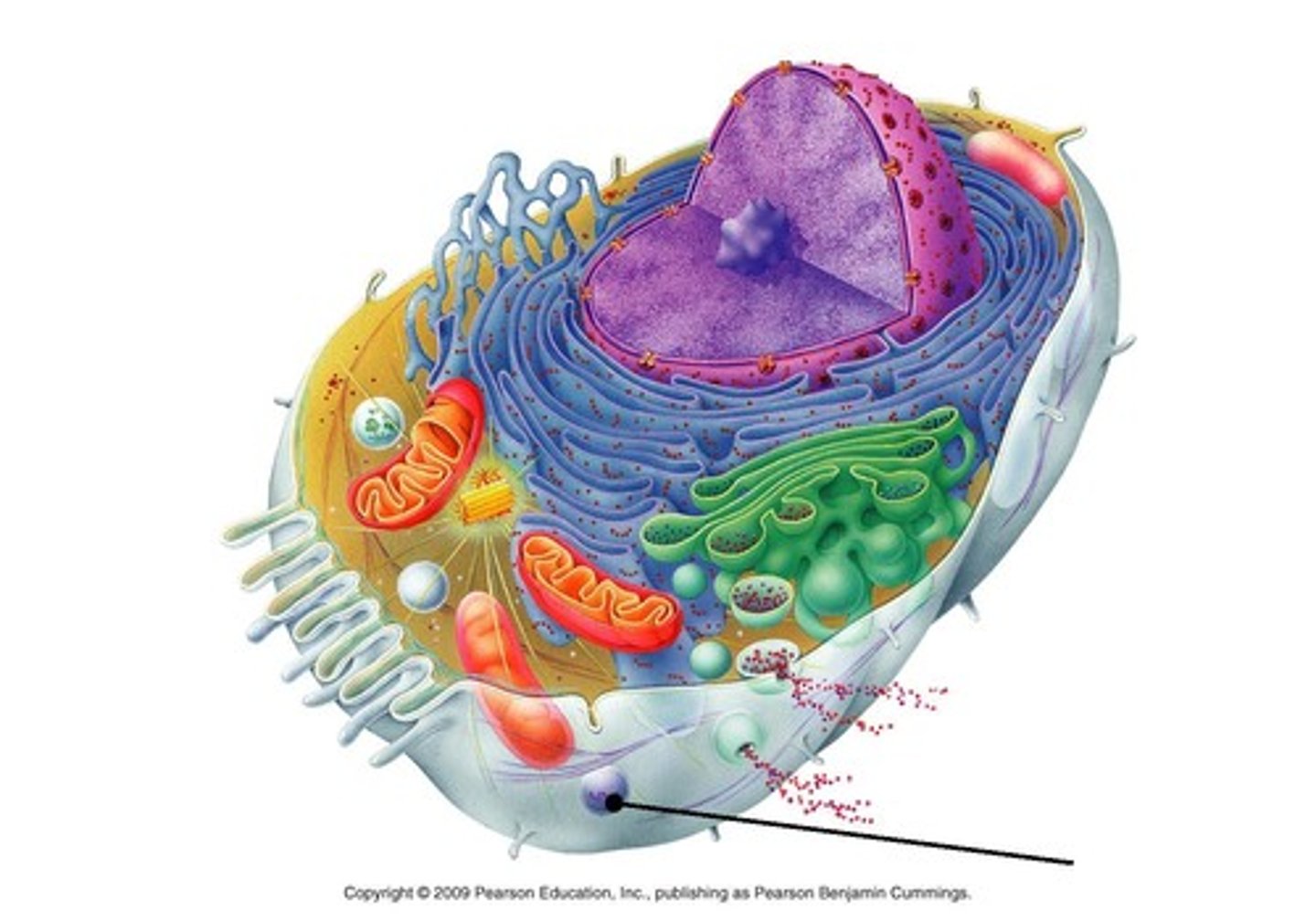
Peroxisomes
consist of catalase
abundant in liver cells
convert hydrogen peroxide to water and oxidants
Toxic waste removal, or HAZMAT team of the cell
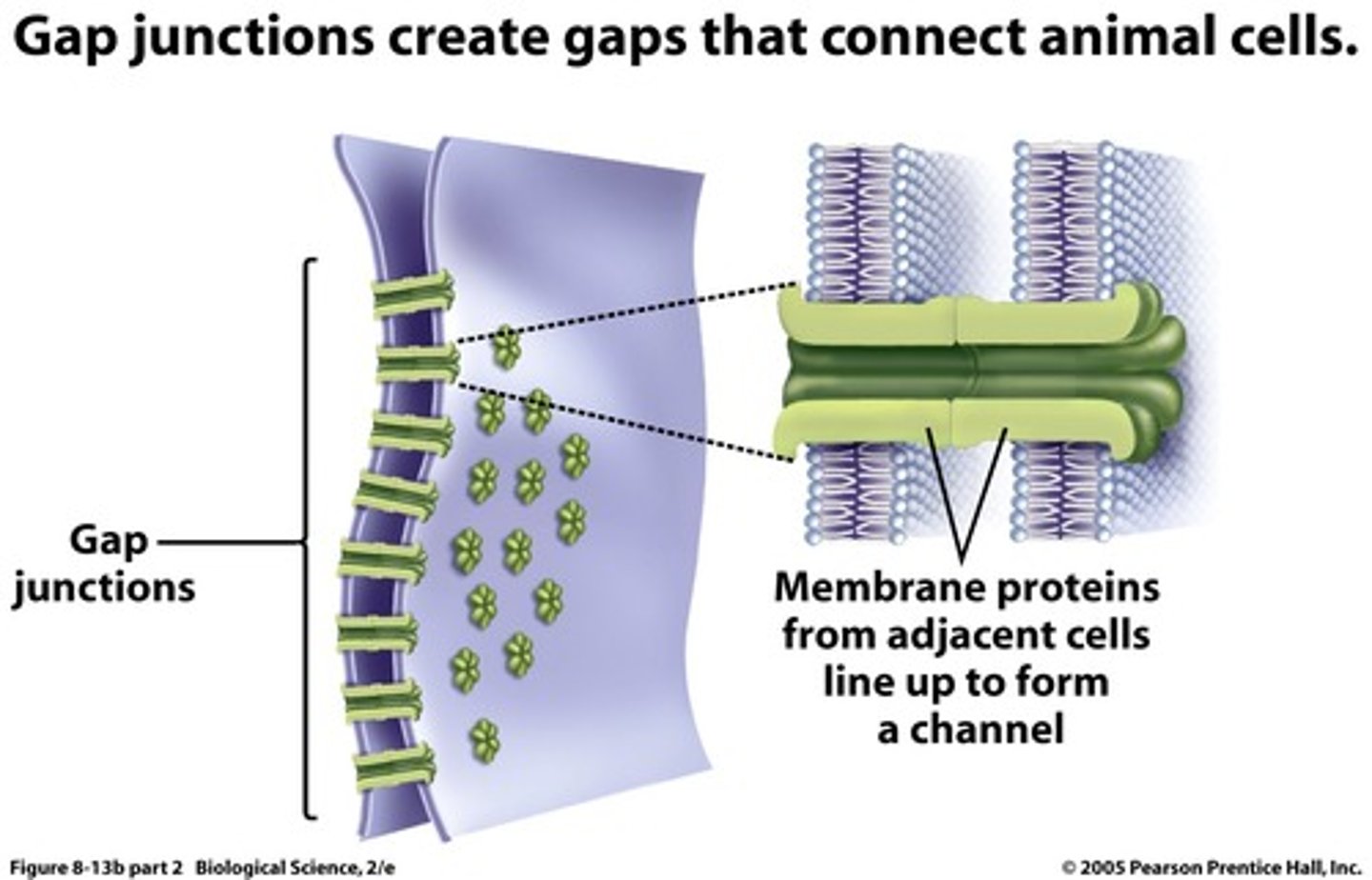
Gap junctions (communicating junctions)
provide cytoplasmic channels between adjacent cells
tight junctions
•Prevent the movement of water and other molecules from passing between the cells
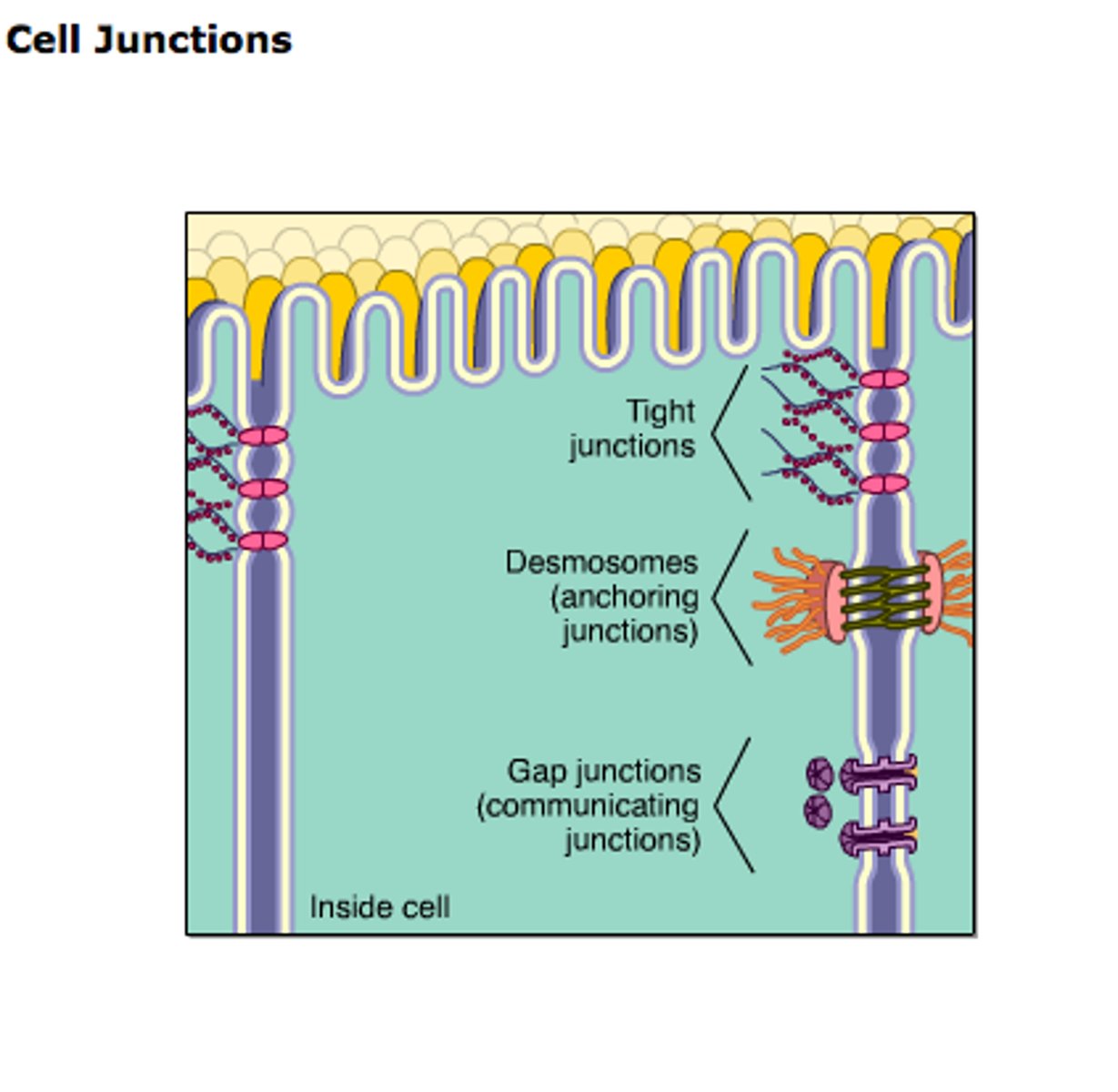
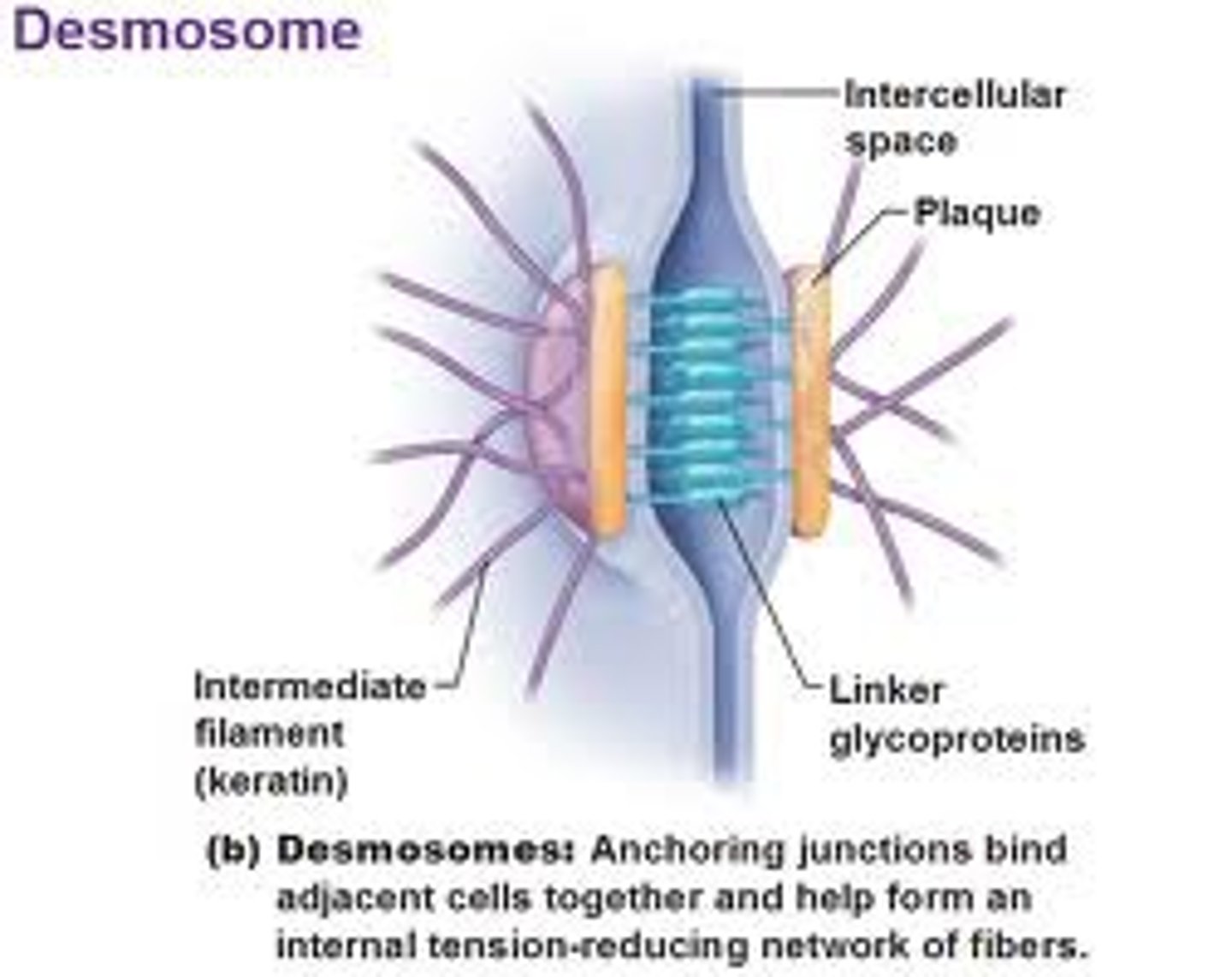
anchoring junctions (desmosomes)
•small, localized anchoring junctions
•Most abundant in superficial layers of the skin
integumentary system
skin, hair, nails, sweat/oil glands, mammary glands
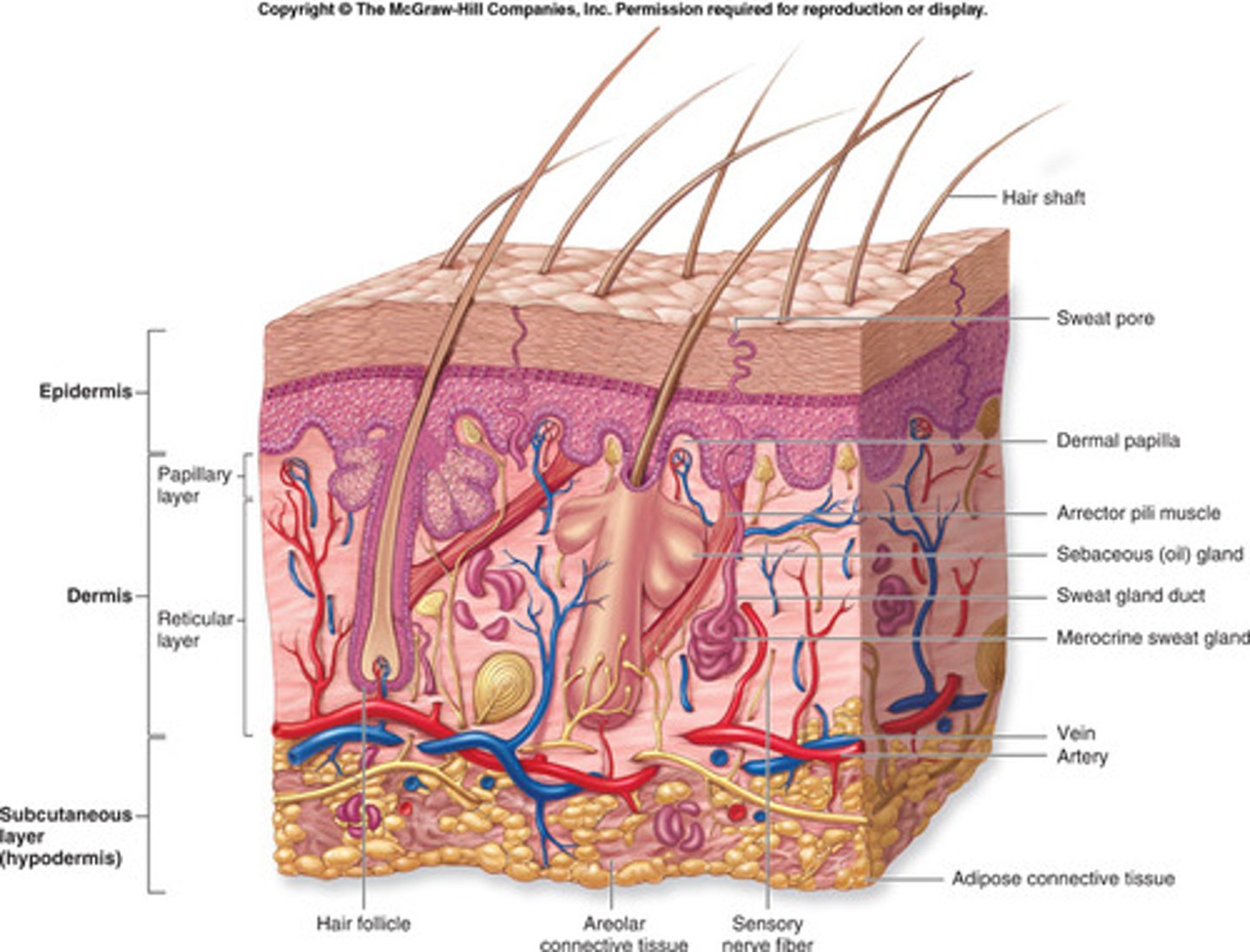
cutaneous membrane
epidermis and dermis
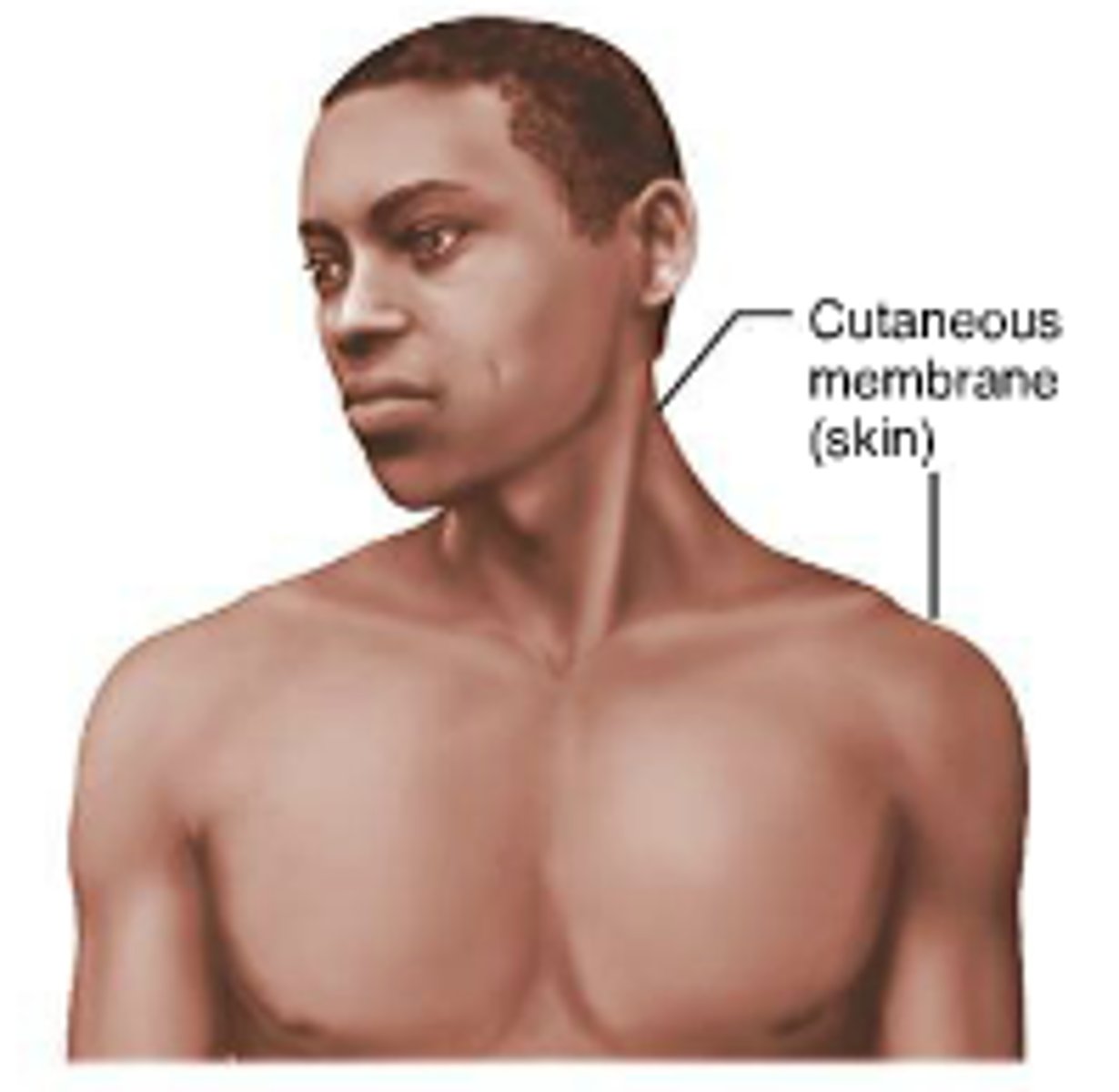
accessory structures
hair, nails, exocrine glands
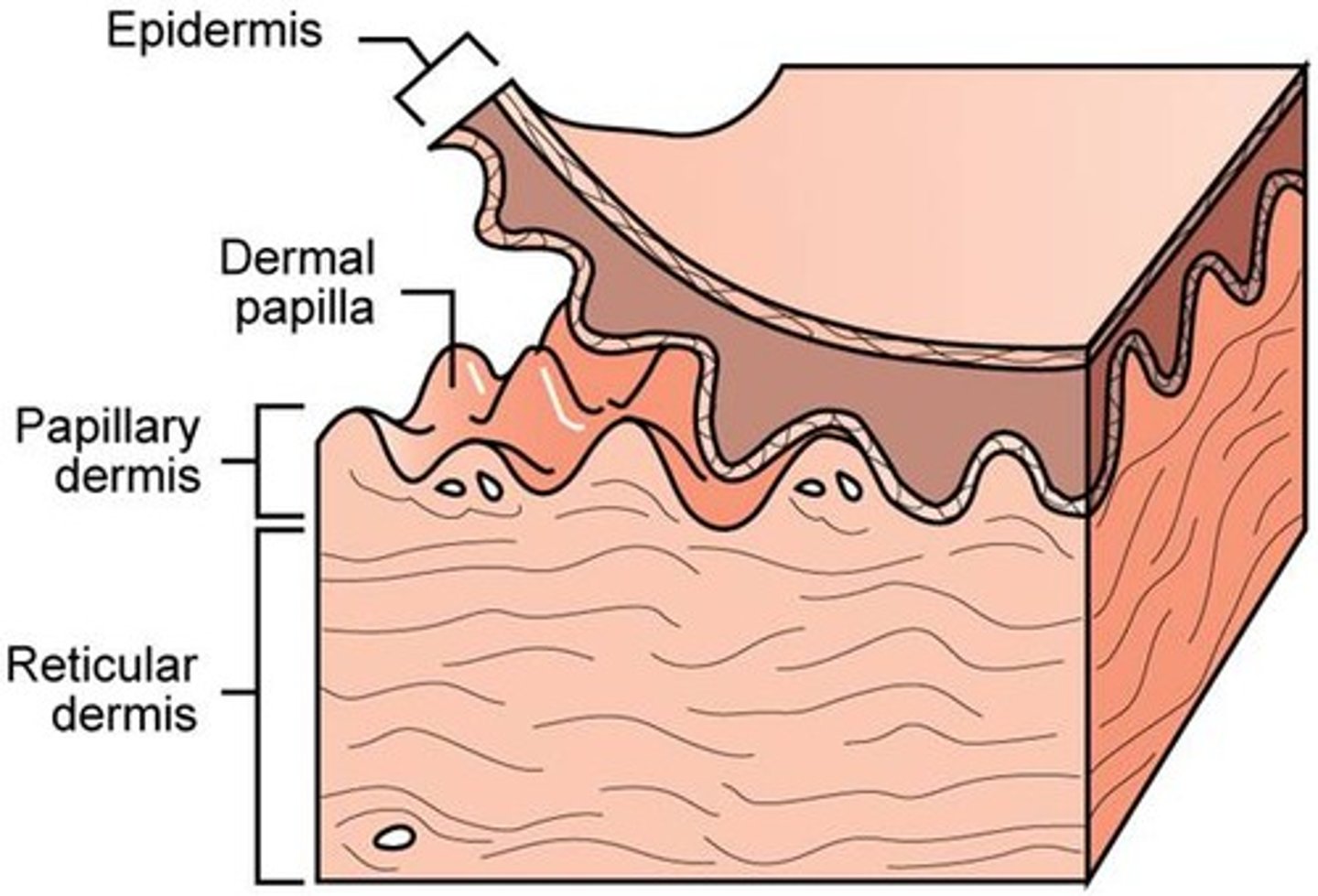
Epidermis
Superficial epithilium
Outer layer of skin
Dermis
•Underlying connective tissue
•Deep to the dermis is the hypodermis
•Also known as the subcutaneous layer or superficial fascia
•This is not normally considered to be a part of the integument
"under layer of skin"
Integumentary structure and functions
•Physical protection
•Regulation of body temperature
•Excretion of products
•Synthesis of products
•Sensation
•Immune defense
Thick skin
Covers the palms of the hands and soles of the feet
Has five layers of keratinocytes
Thin skin
Covers most of the body
Has four layers of keratinocytes