Eye, Cranial Nerves on the Brain, Cranial & random nerves dog, Cranial Nerves, CN & Foramen, Brain (Gross Anatomy Exam 3)
1/173
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
174 Terms
Trochela
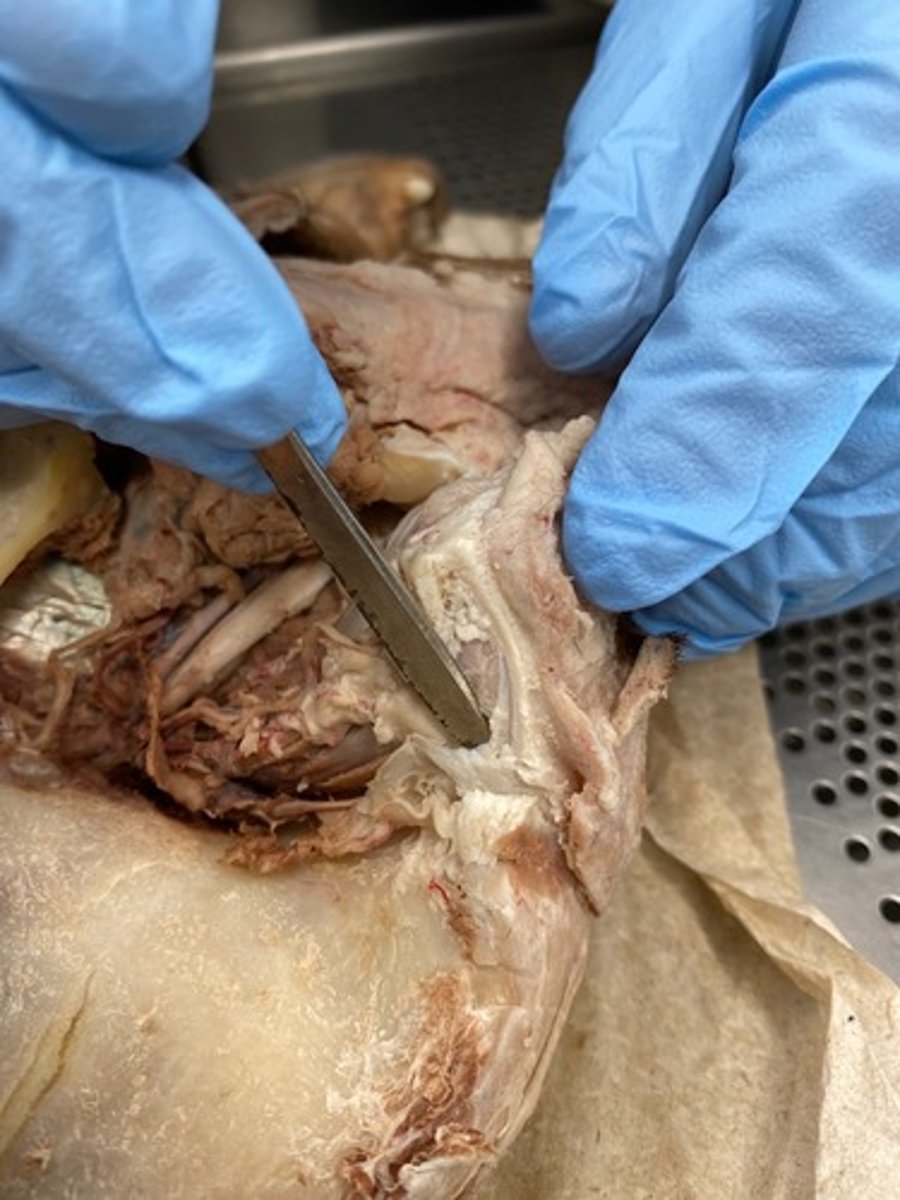
Dorsal rectus
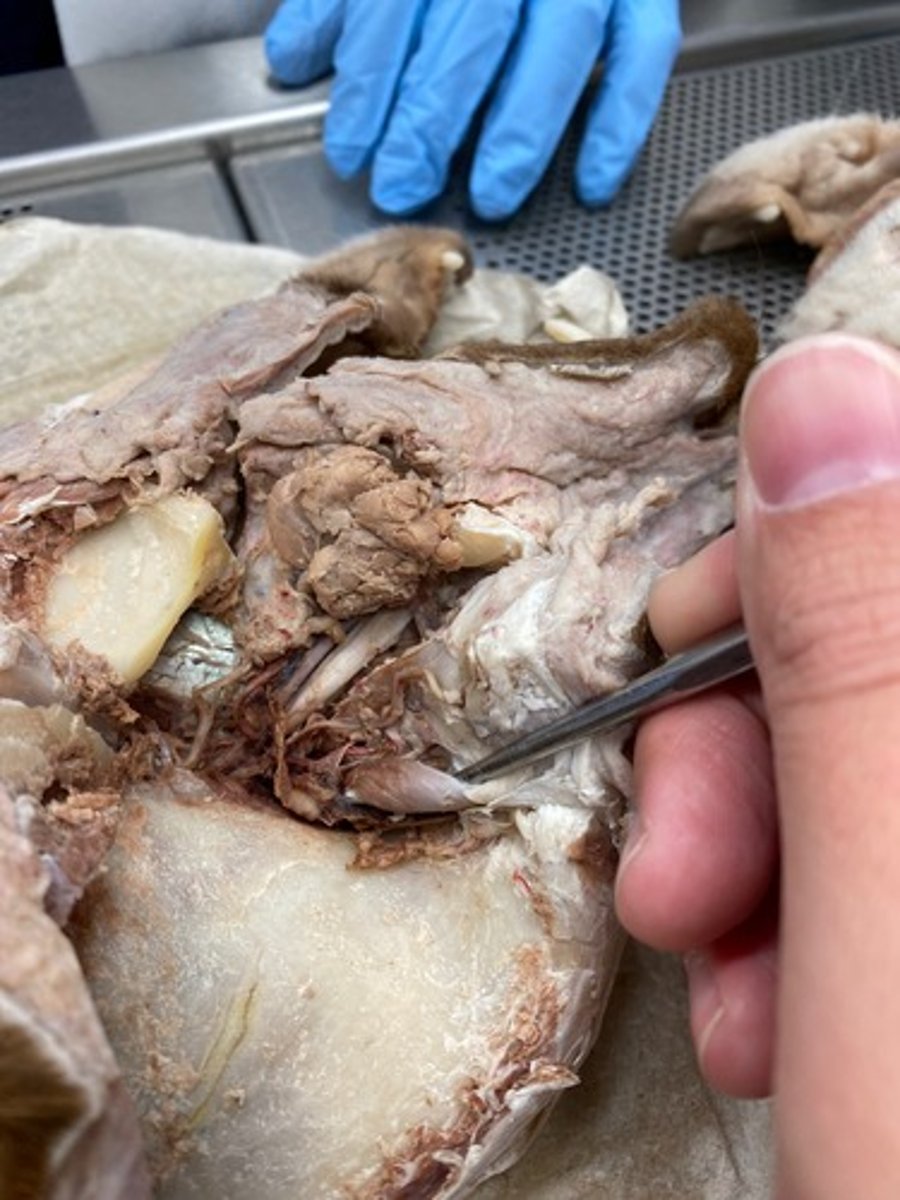
Lateral rectus
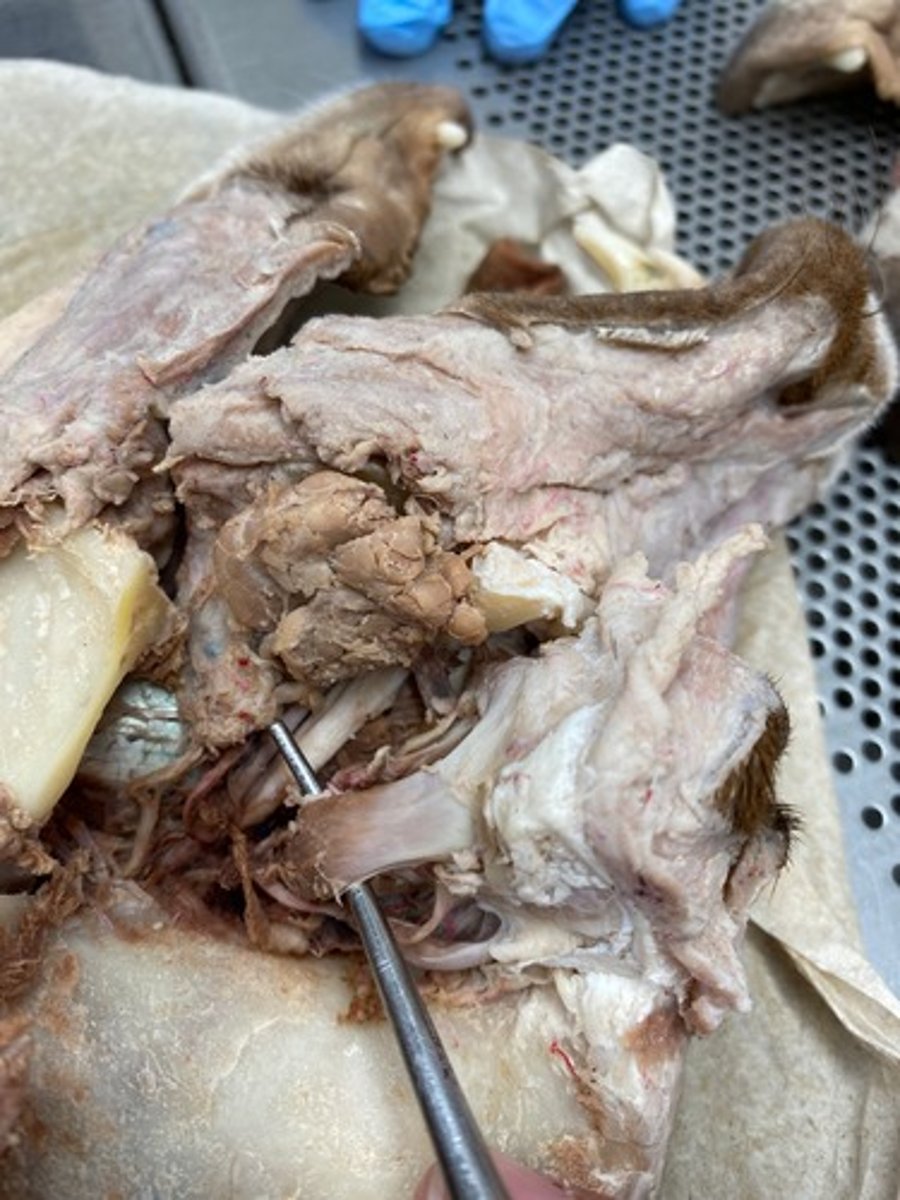
Ventral rectus
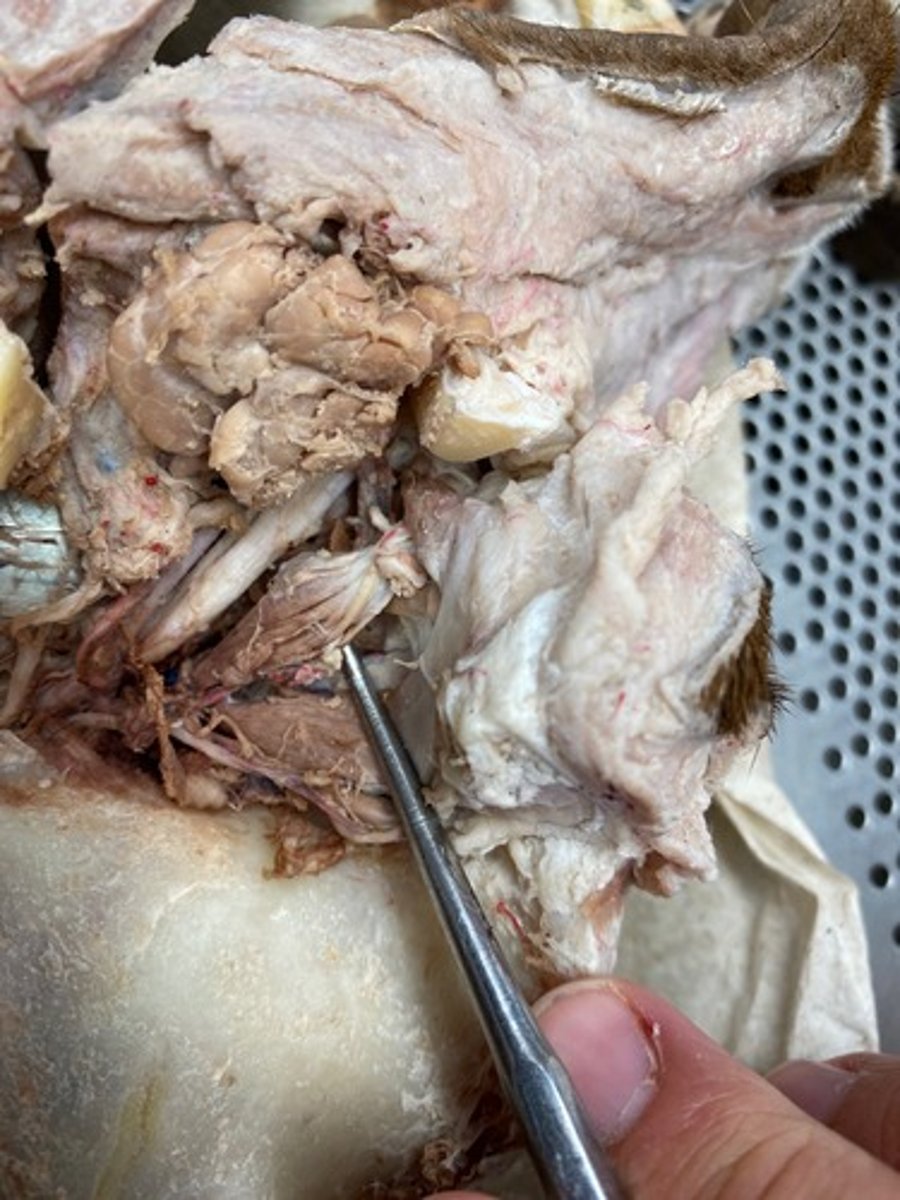
Ventral oblique
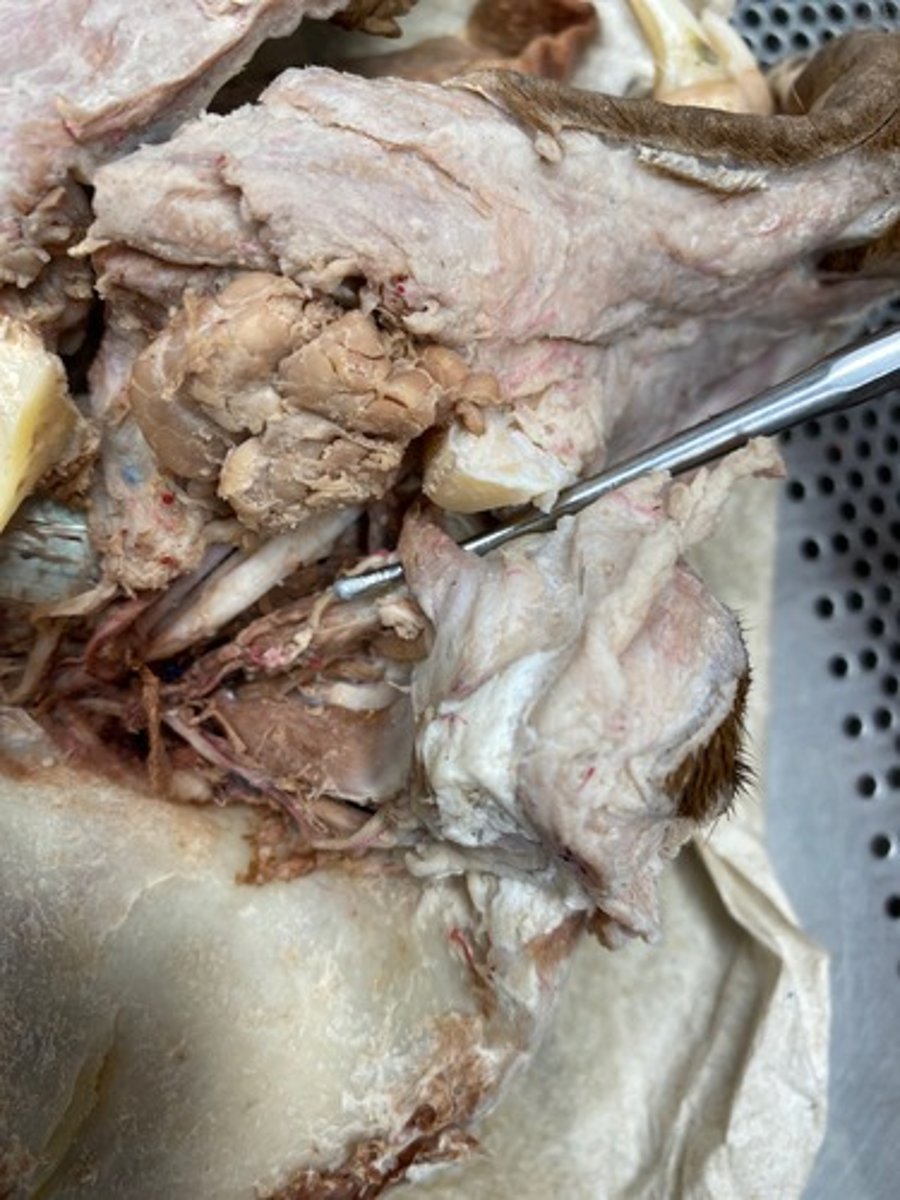
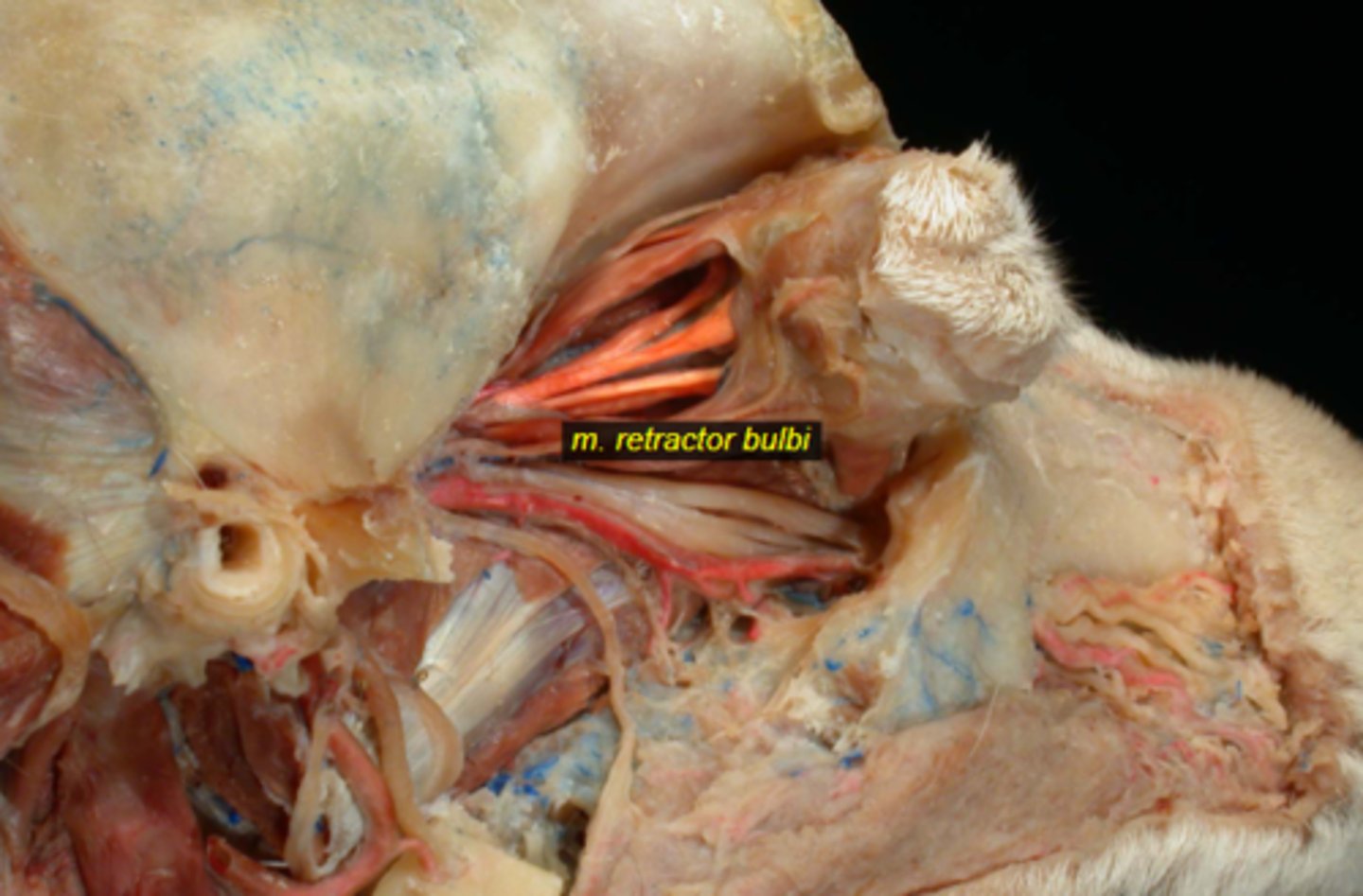
Retractor Bulbi
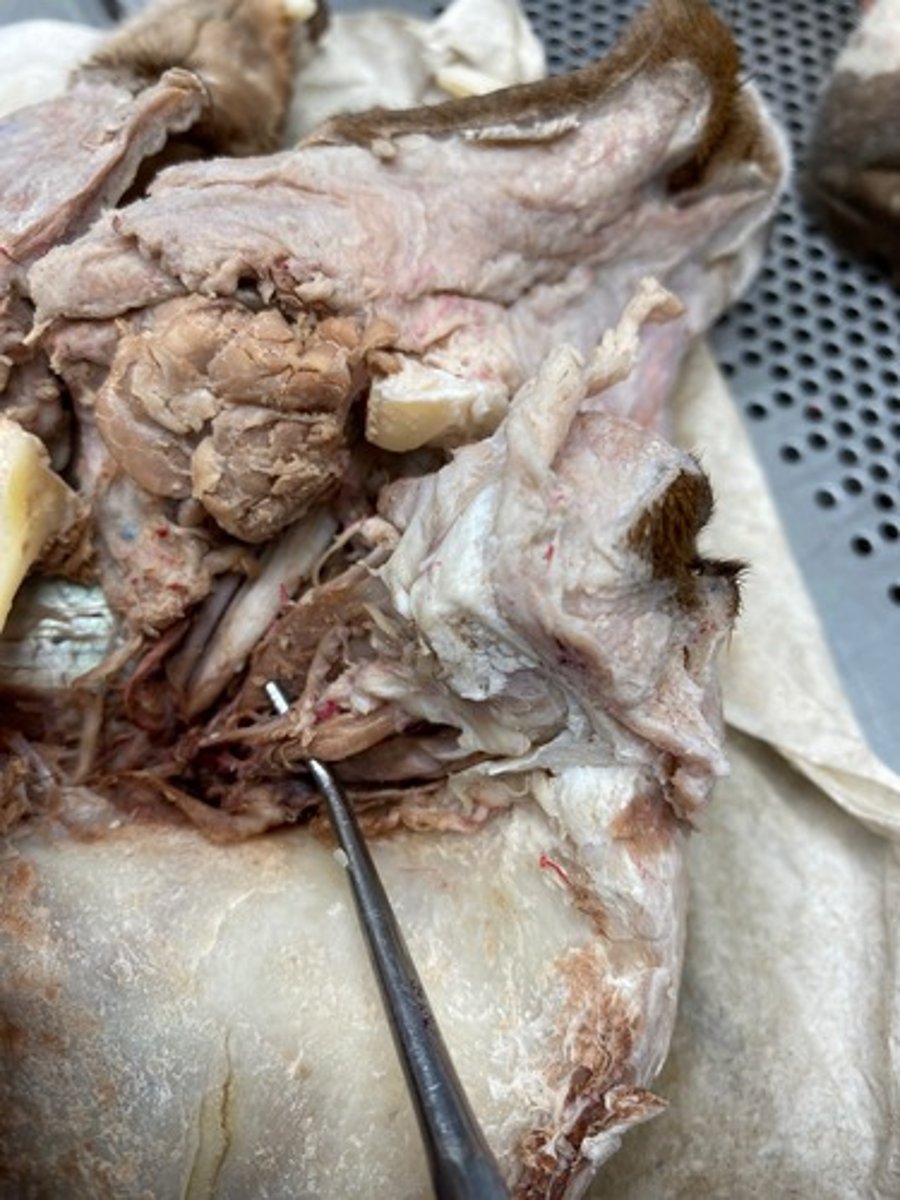
ventral oblique (CNIII)
ventral rectus (oculomotor n innervates)
lateral rectus (CNVI)
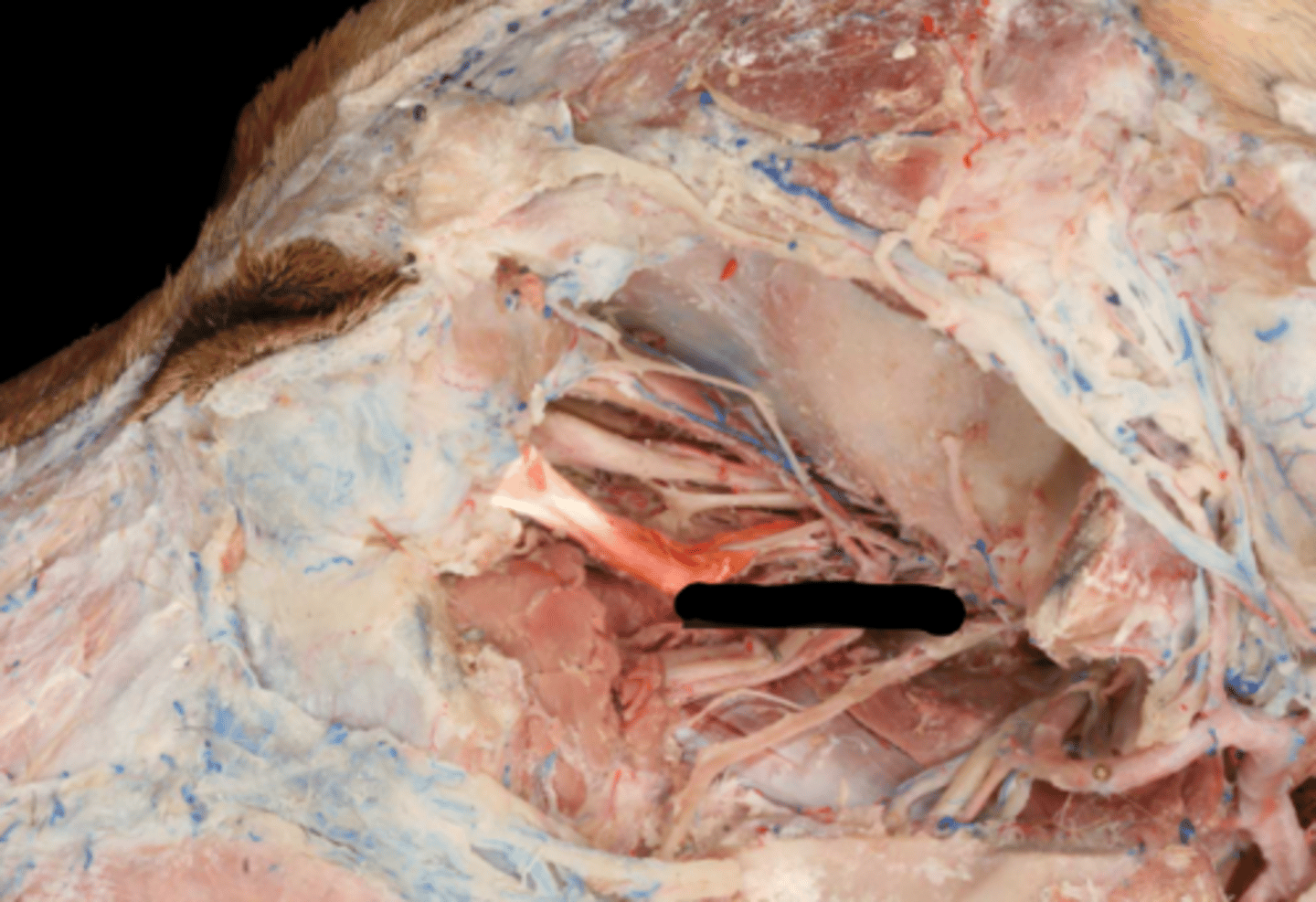
dorsal rectus (CN3)
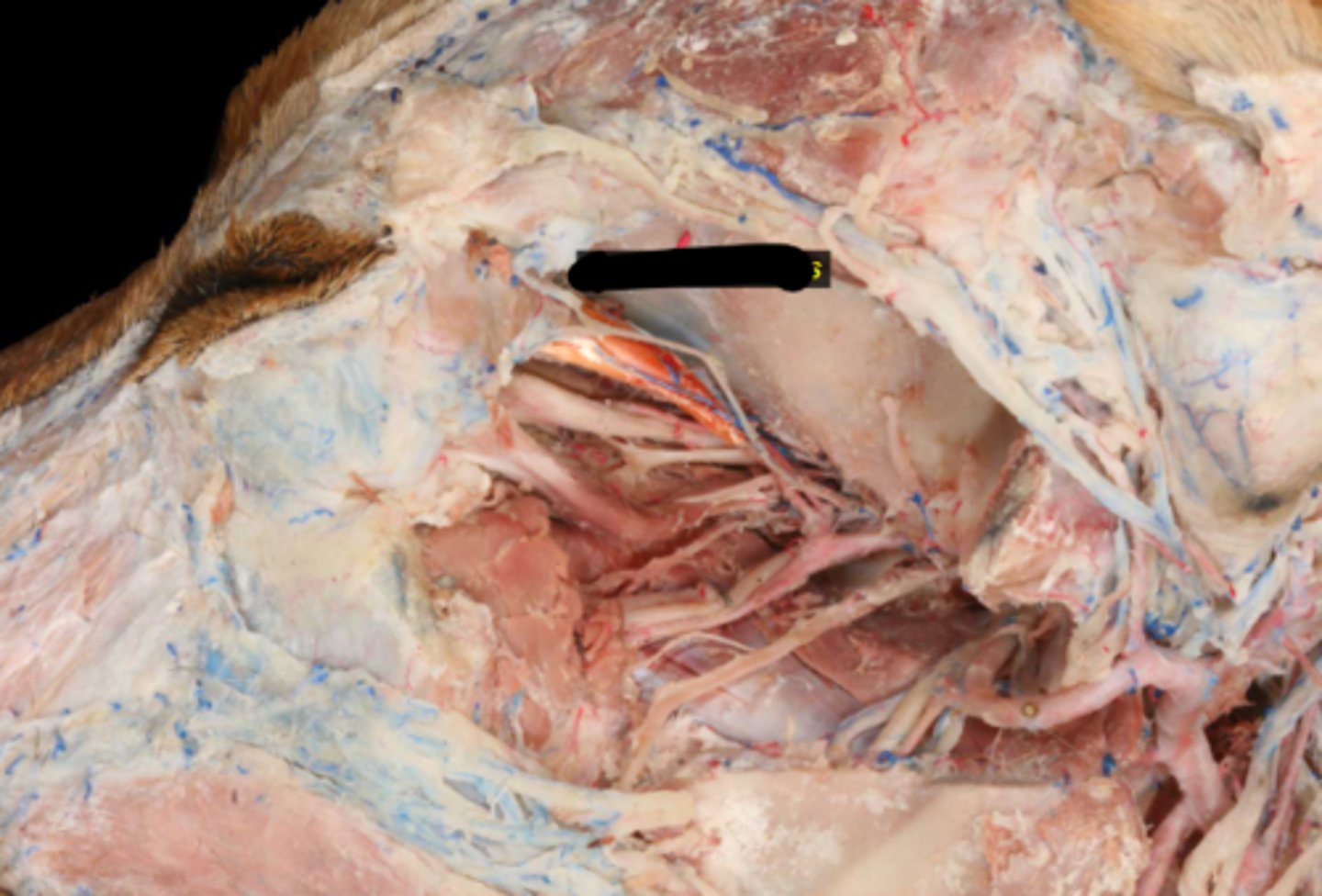
Dorsal oblique (CNIV)
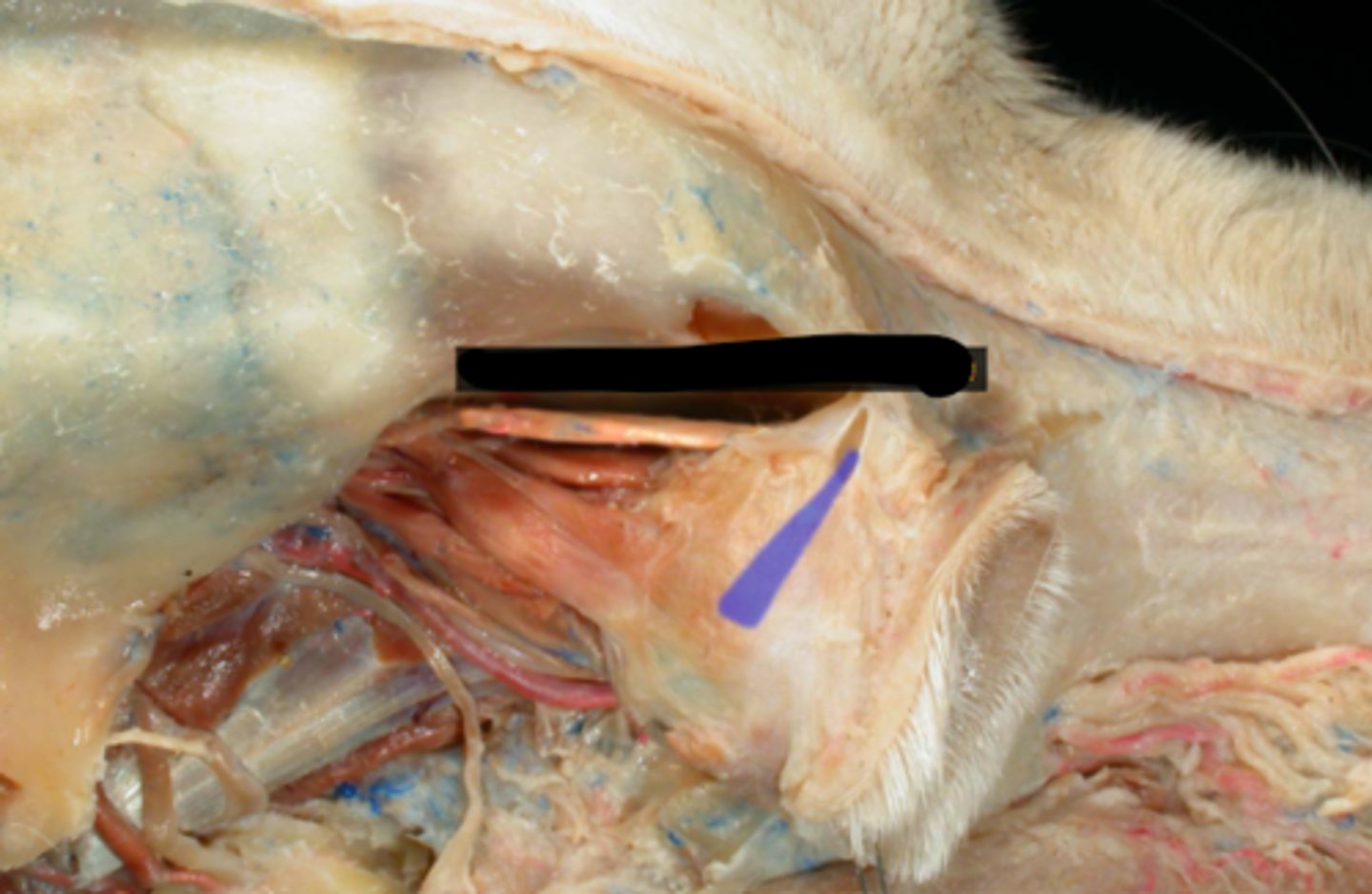
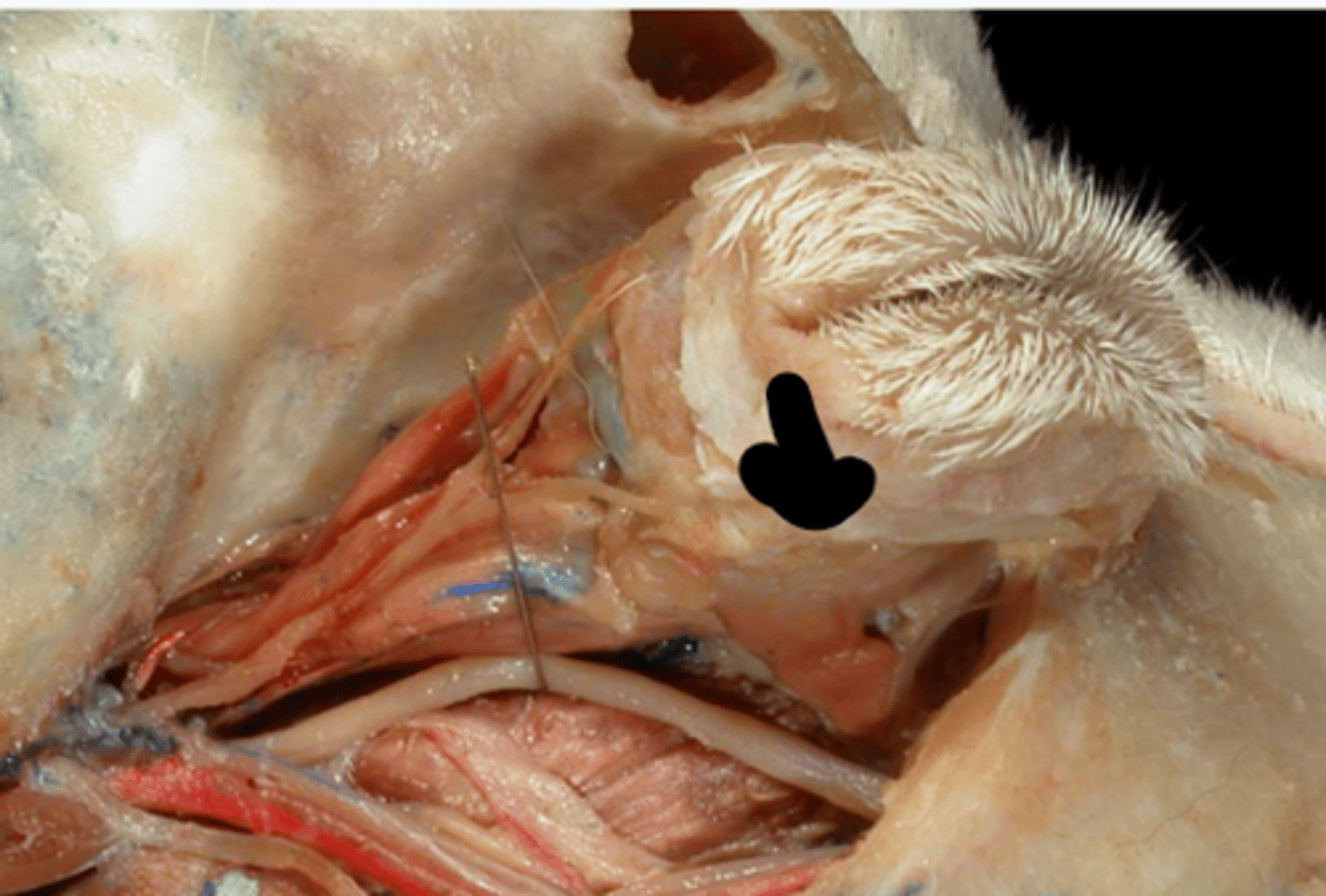
Retractor bulbi (CN VI)
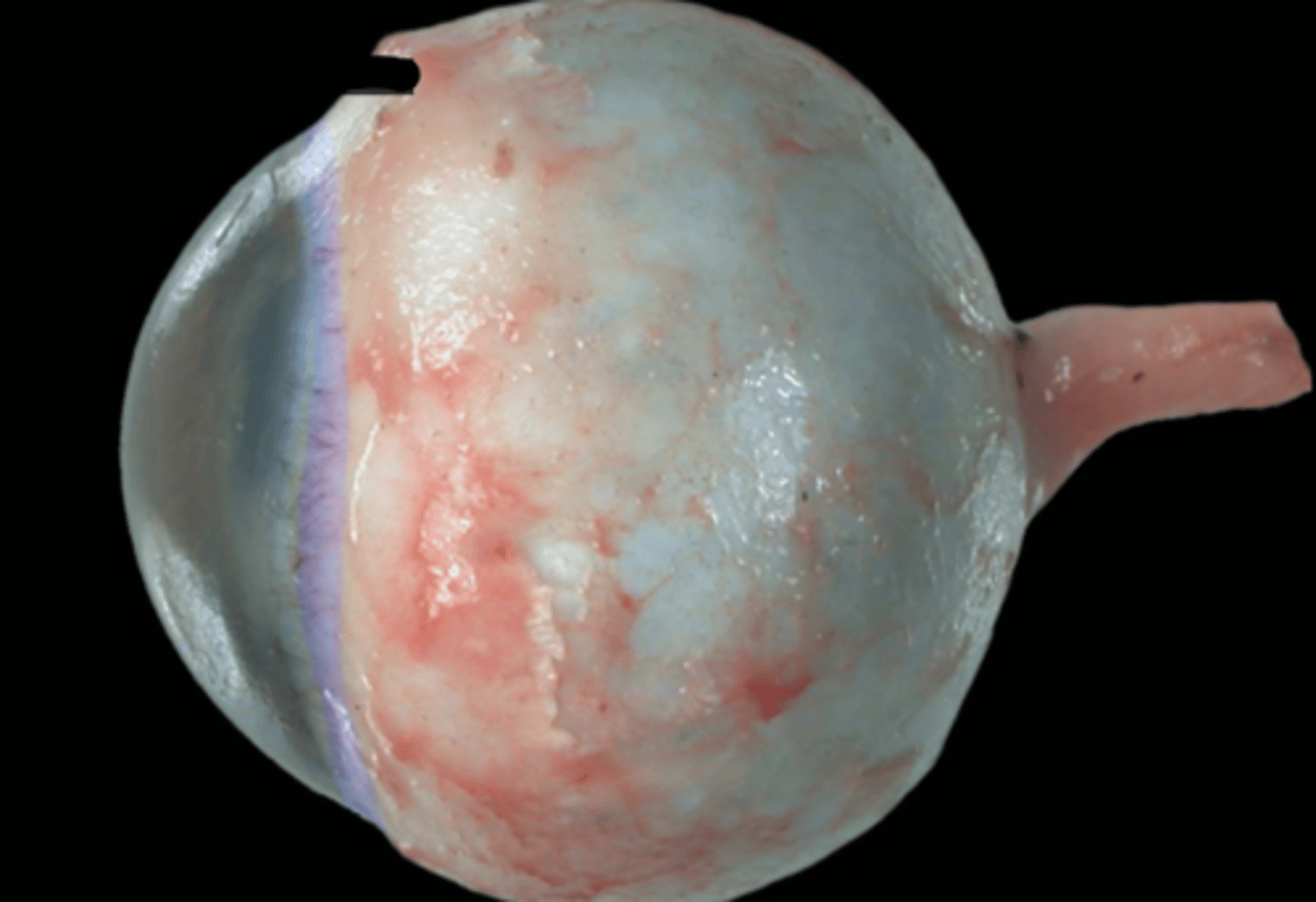
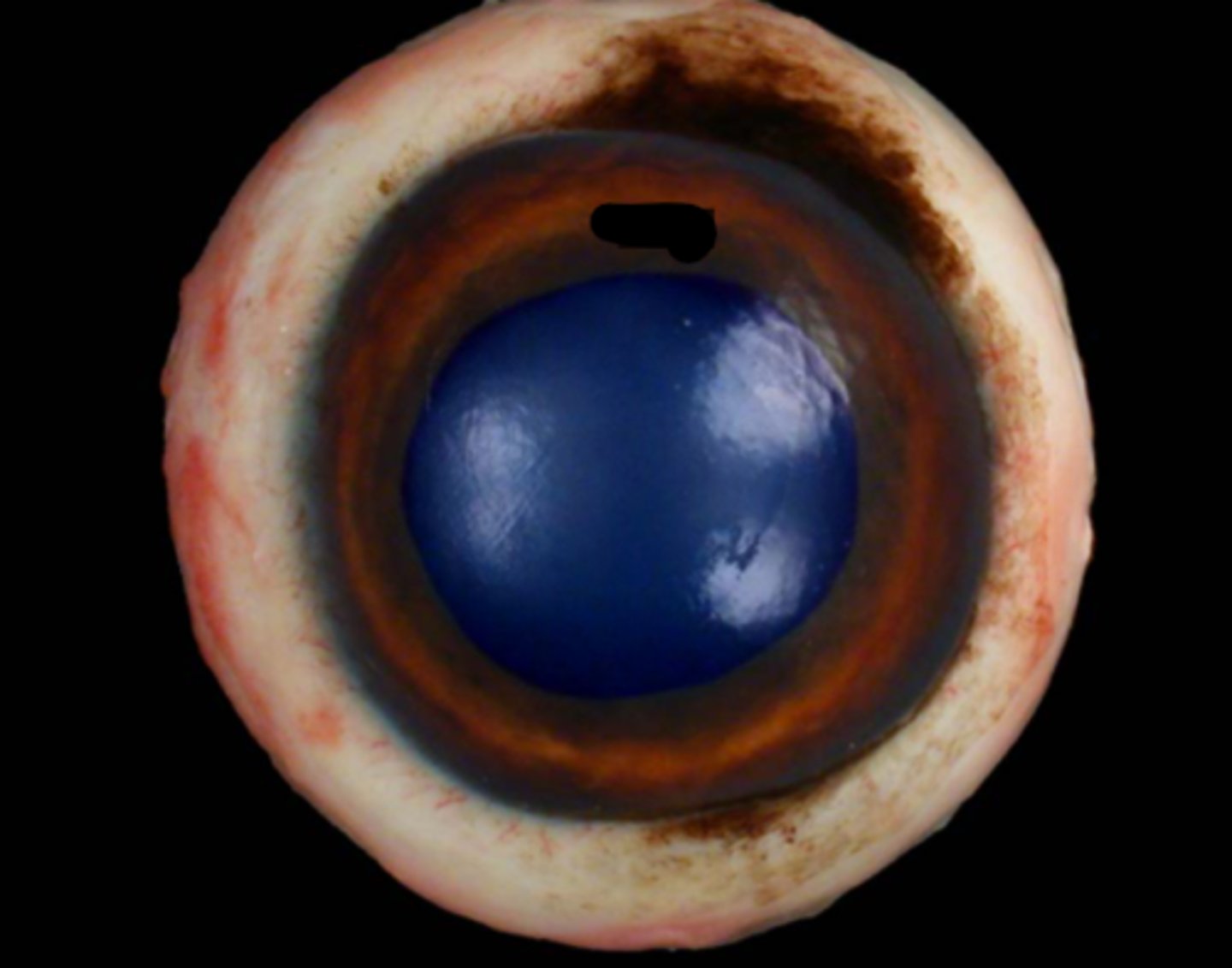
Cornea
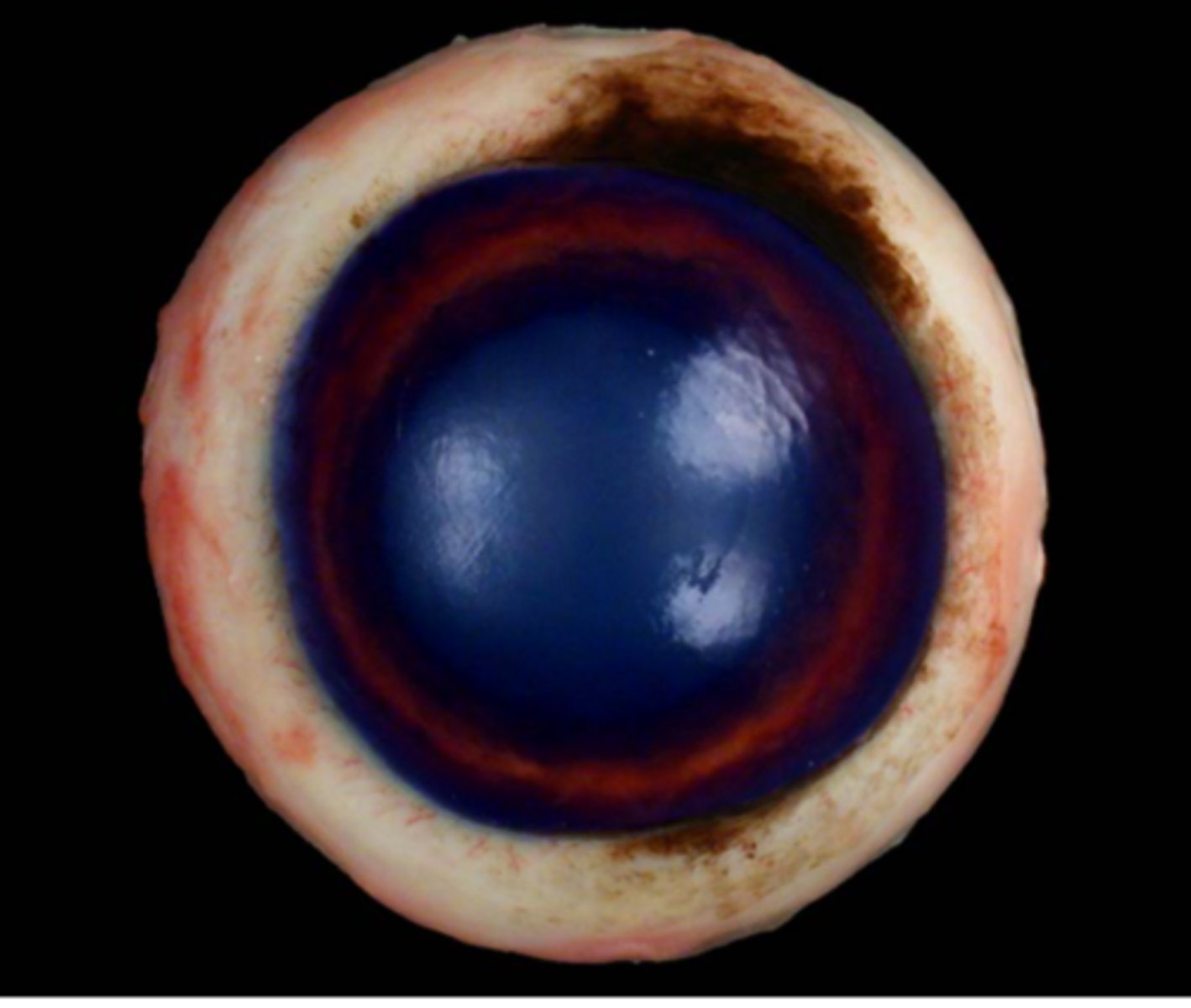
Sclera
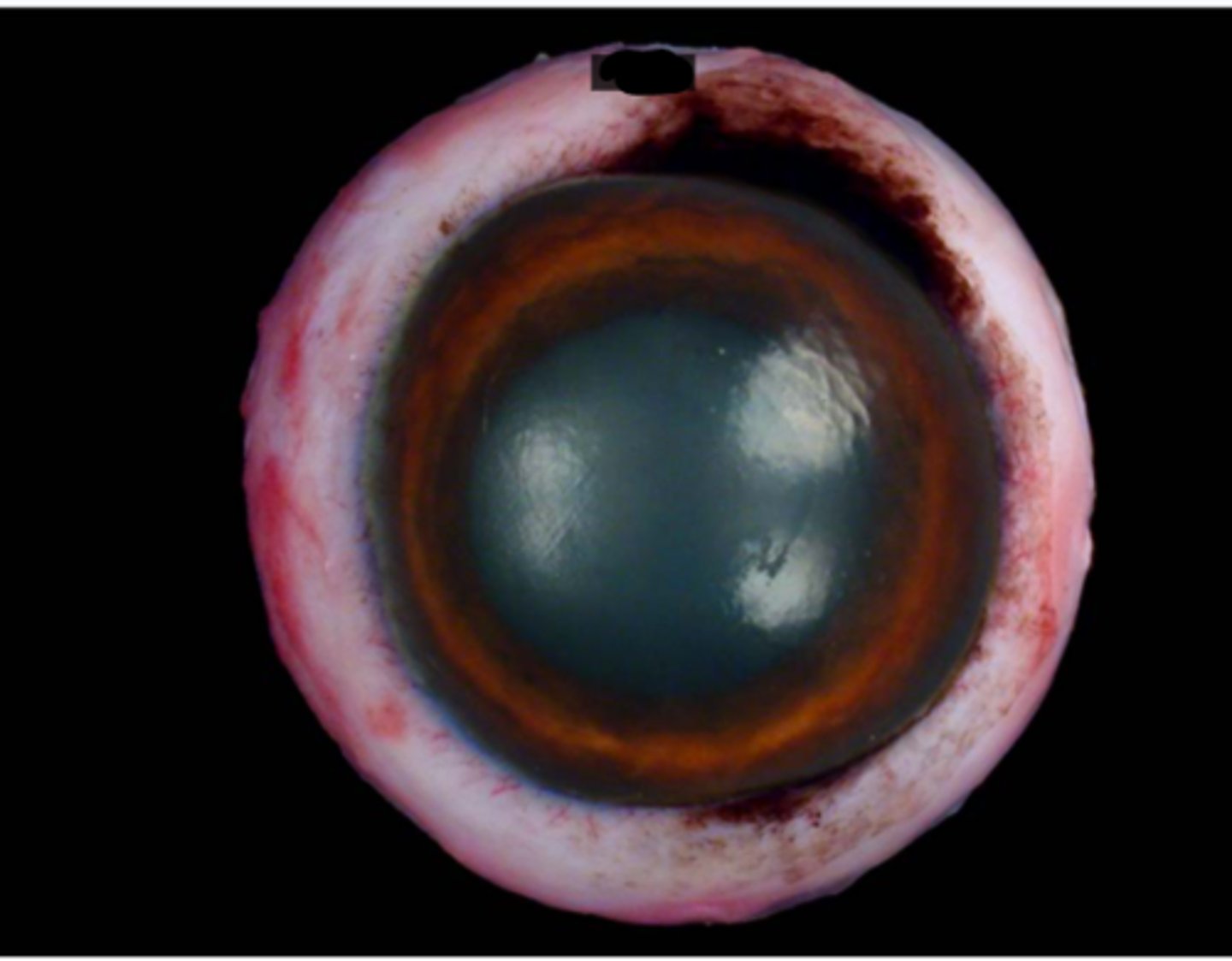
Limbus
Iris
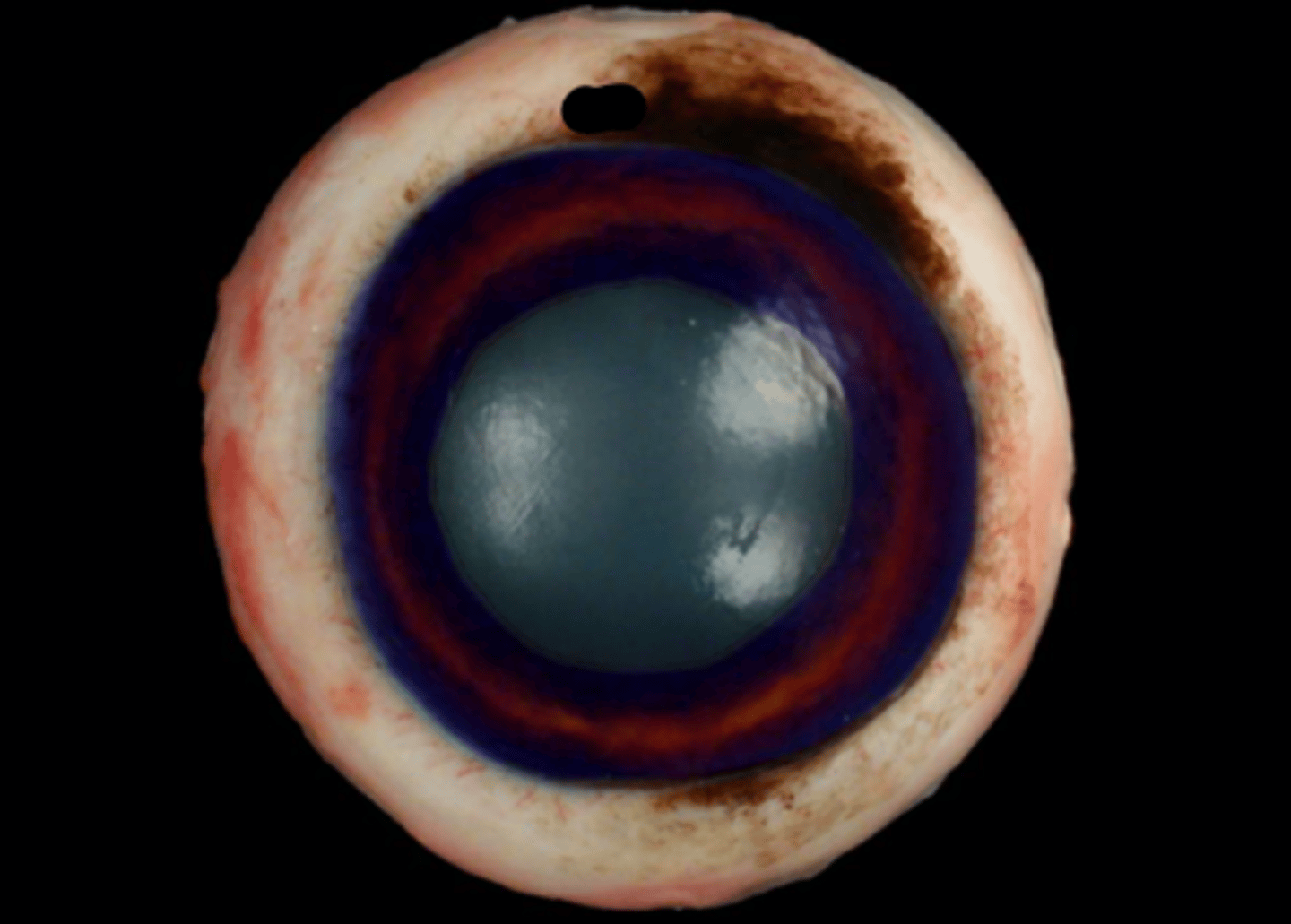
Pupil
Choroid
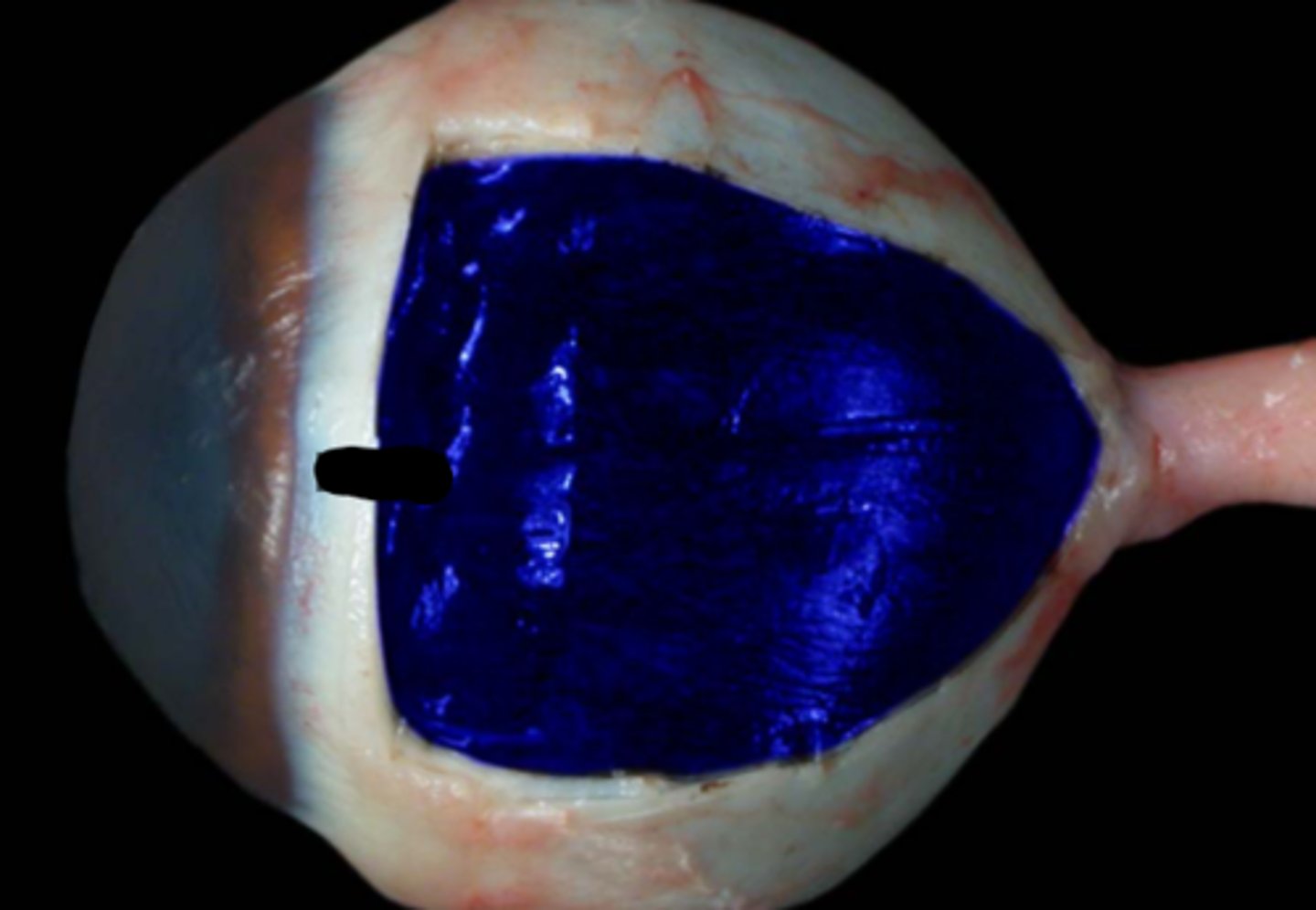
Tapetum lucidum
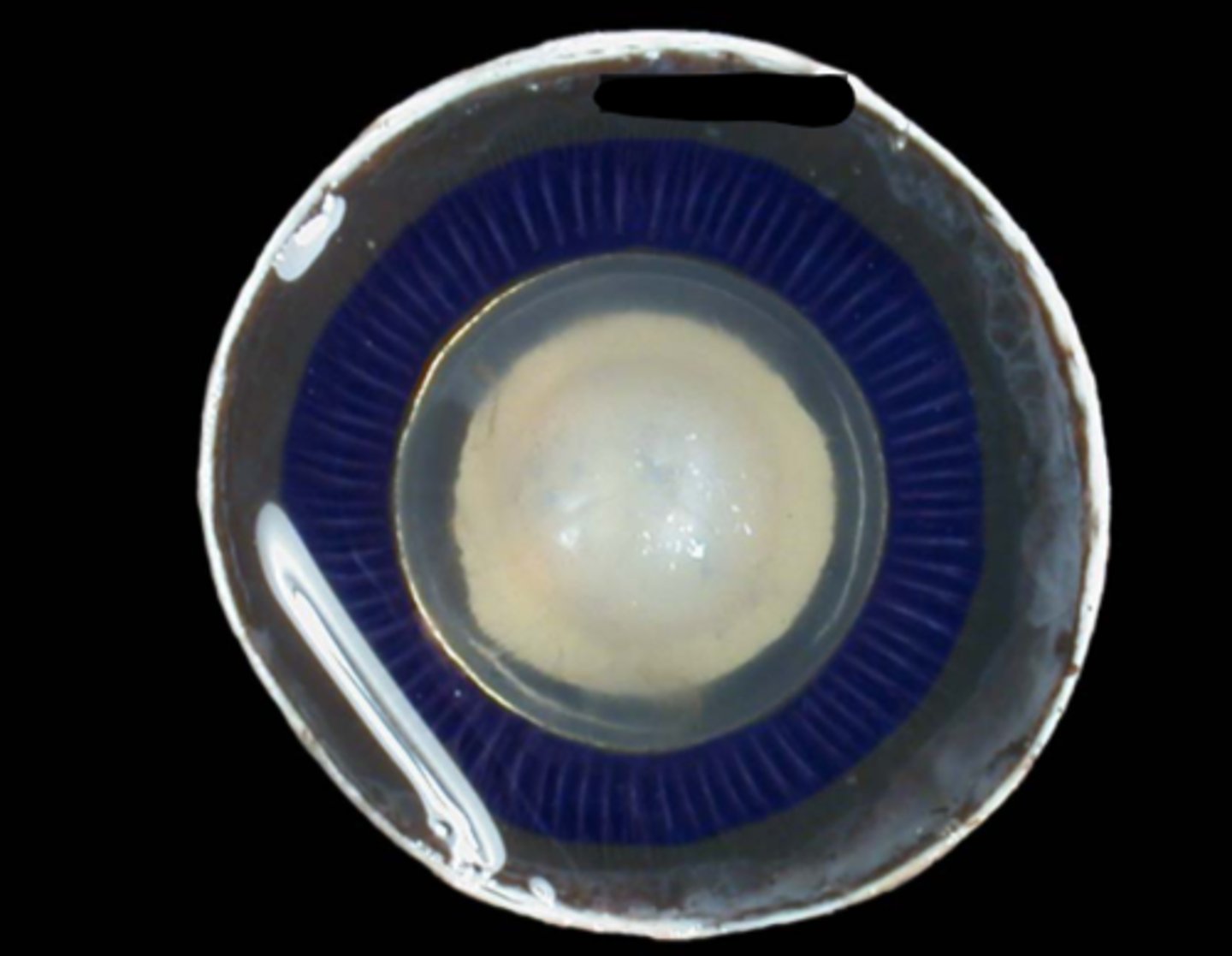
Ciliary body
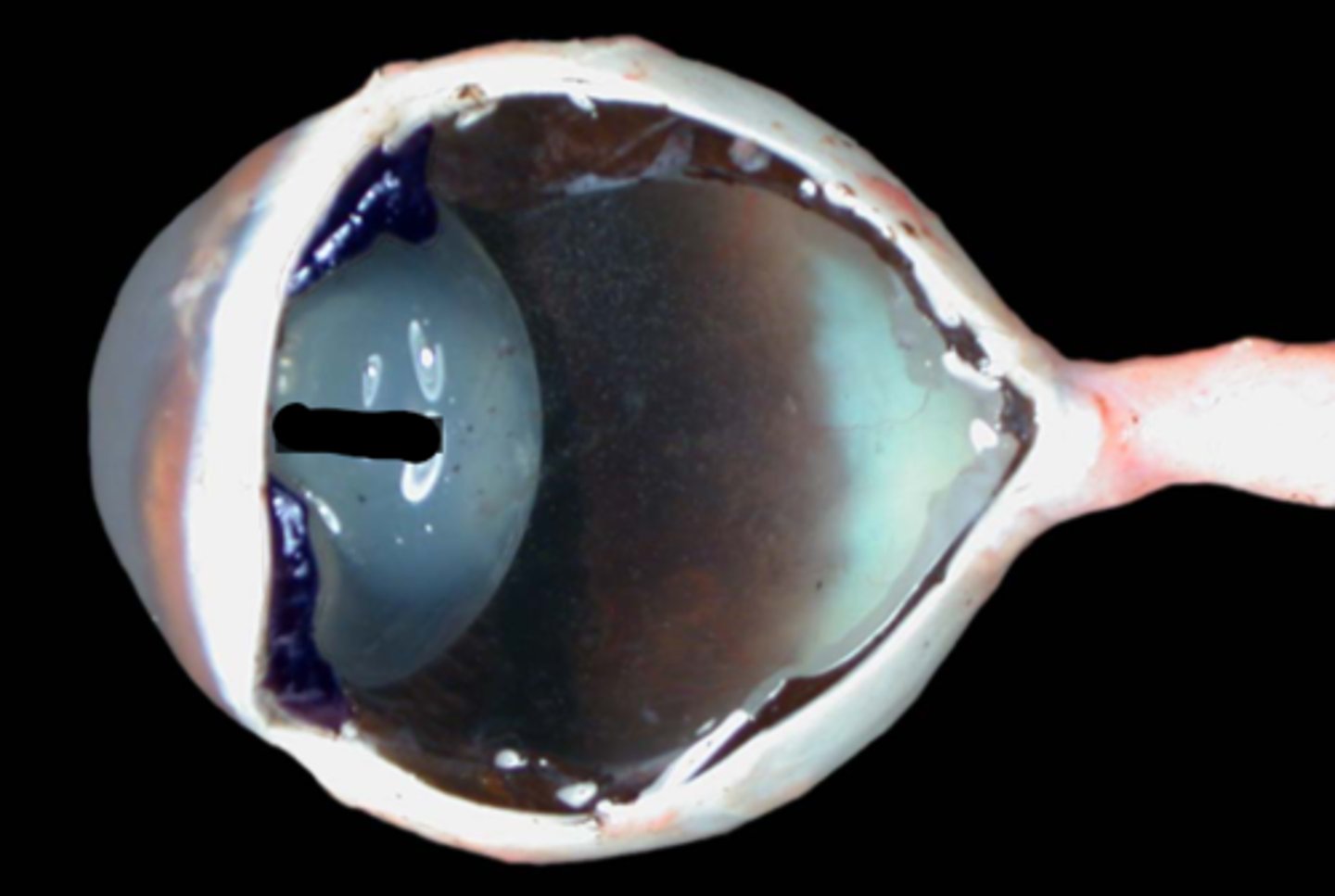
Ciliary processes

Retina
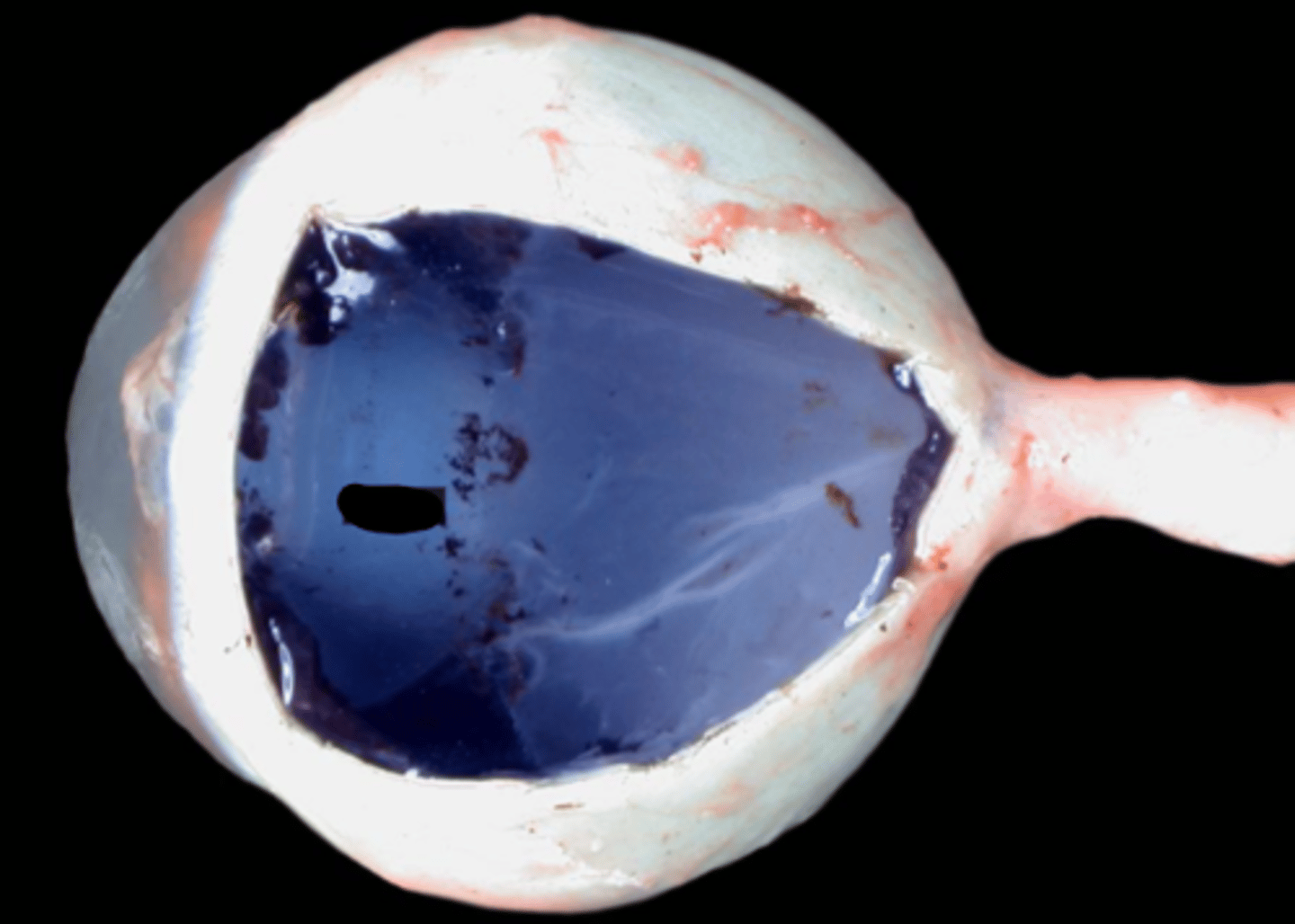
anterior chamber
posterior chamber
aqueous humor
The water that fills the space between the cornea and the lens is:
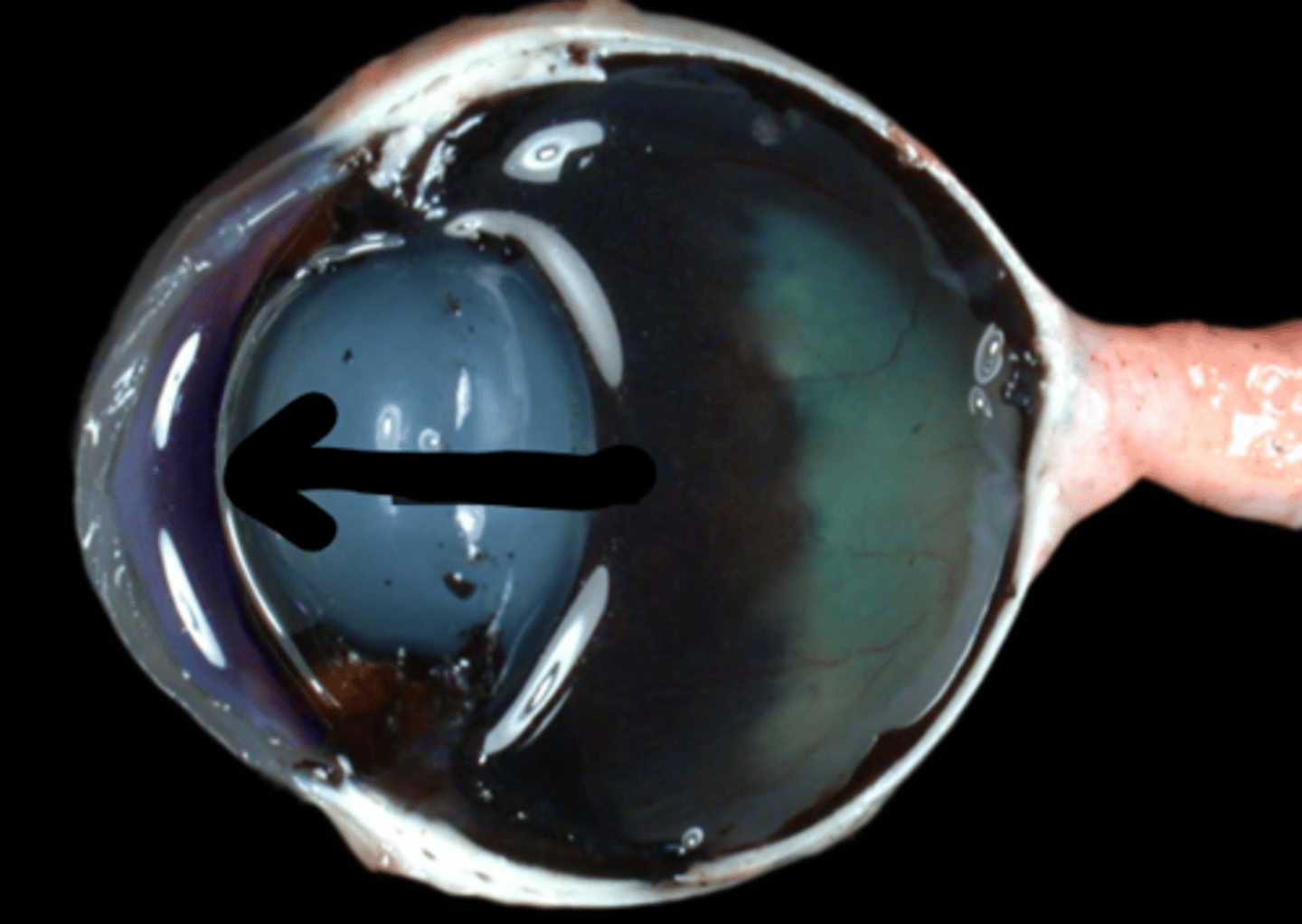
lens
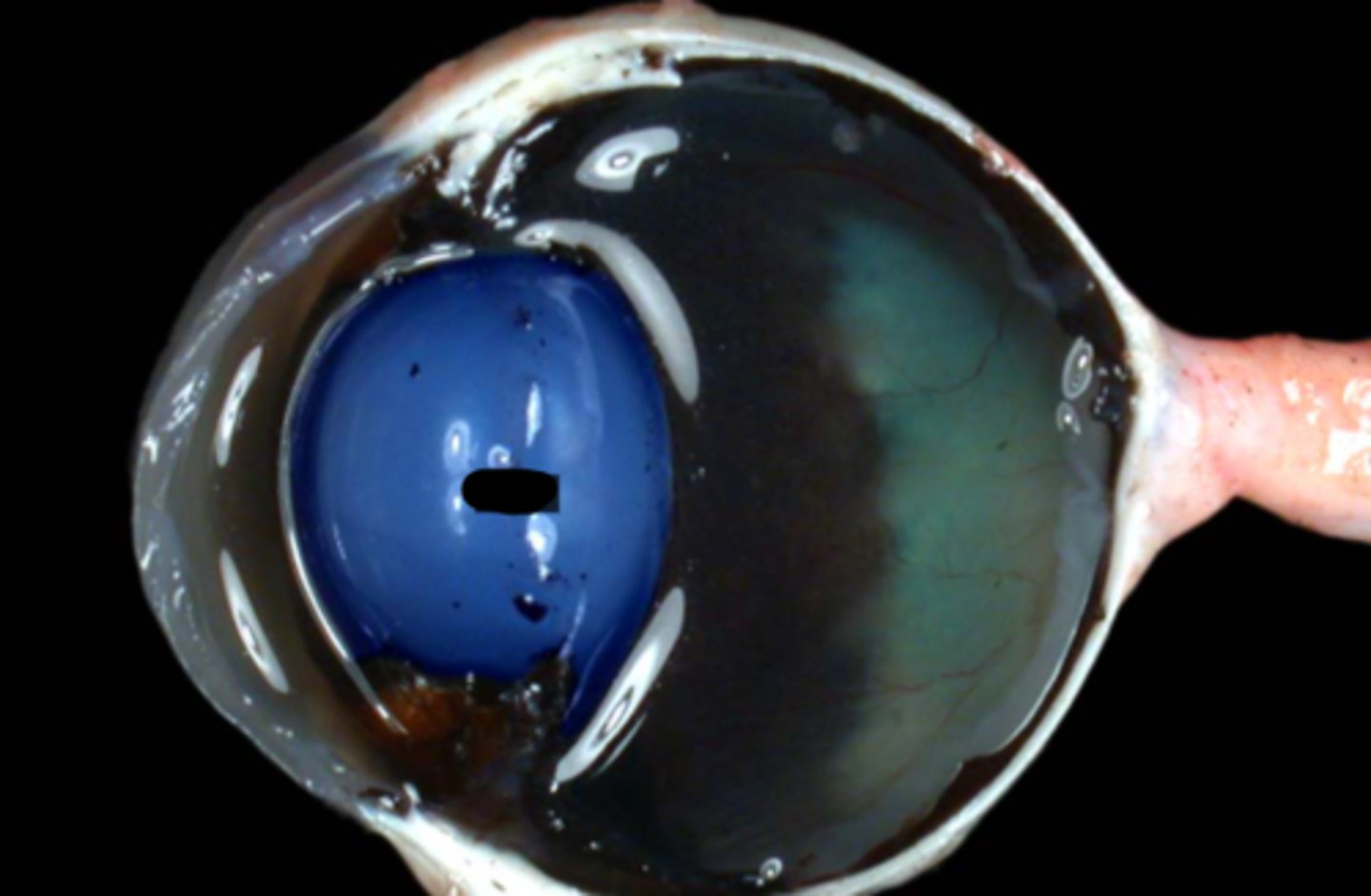
vitreous body
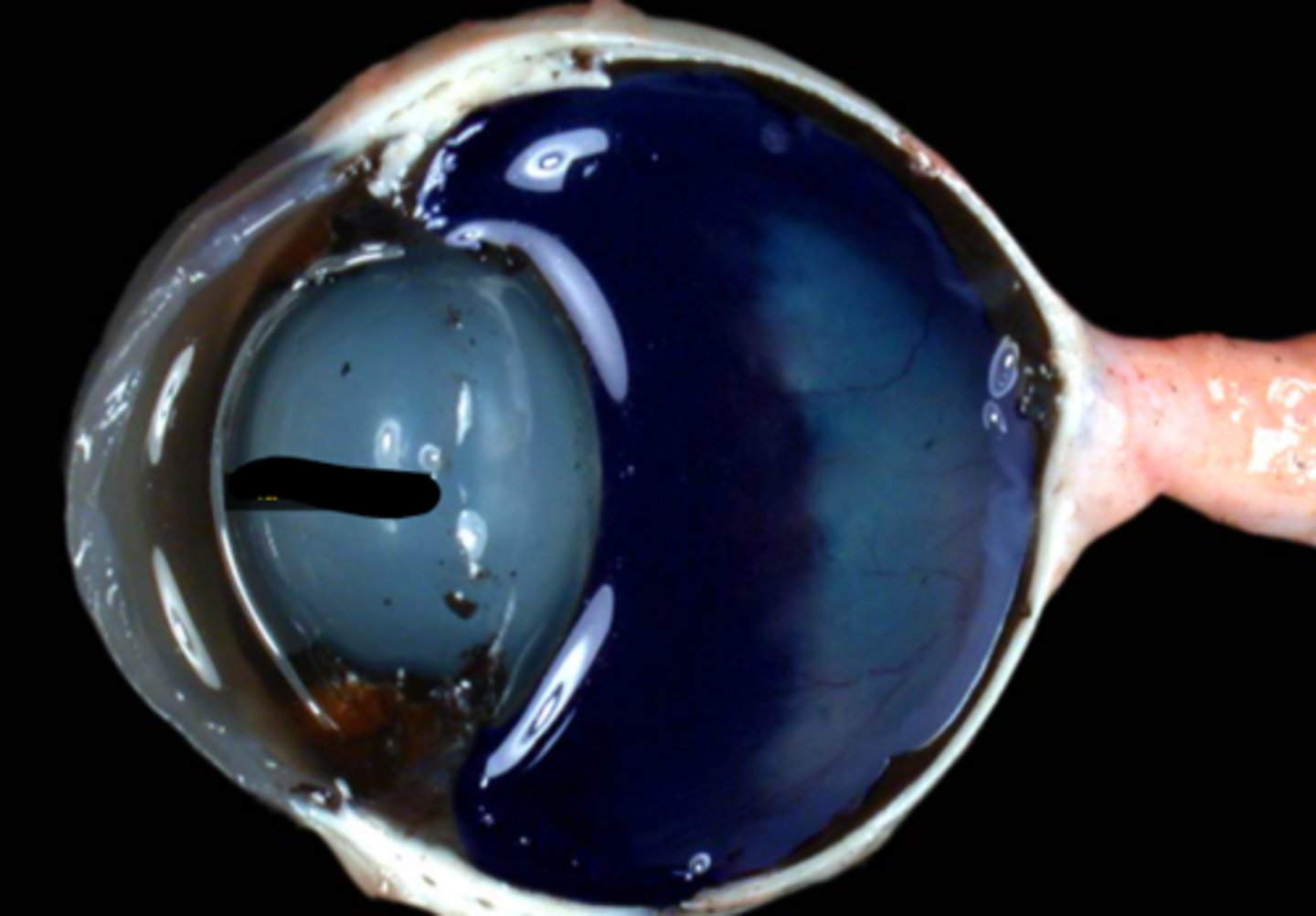
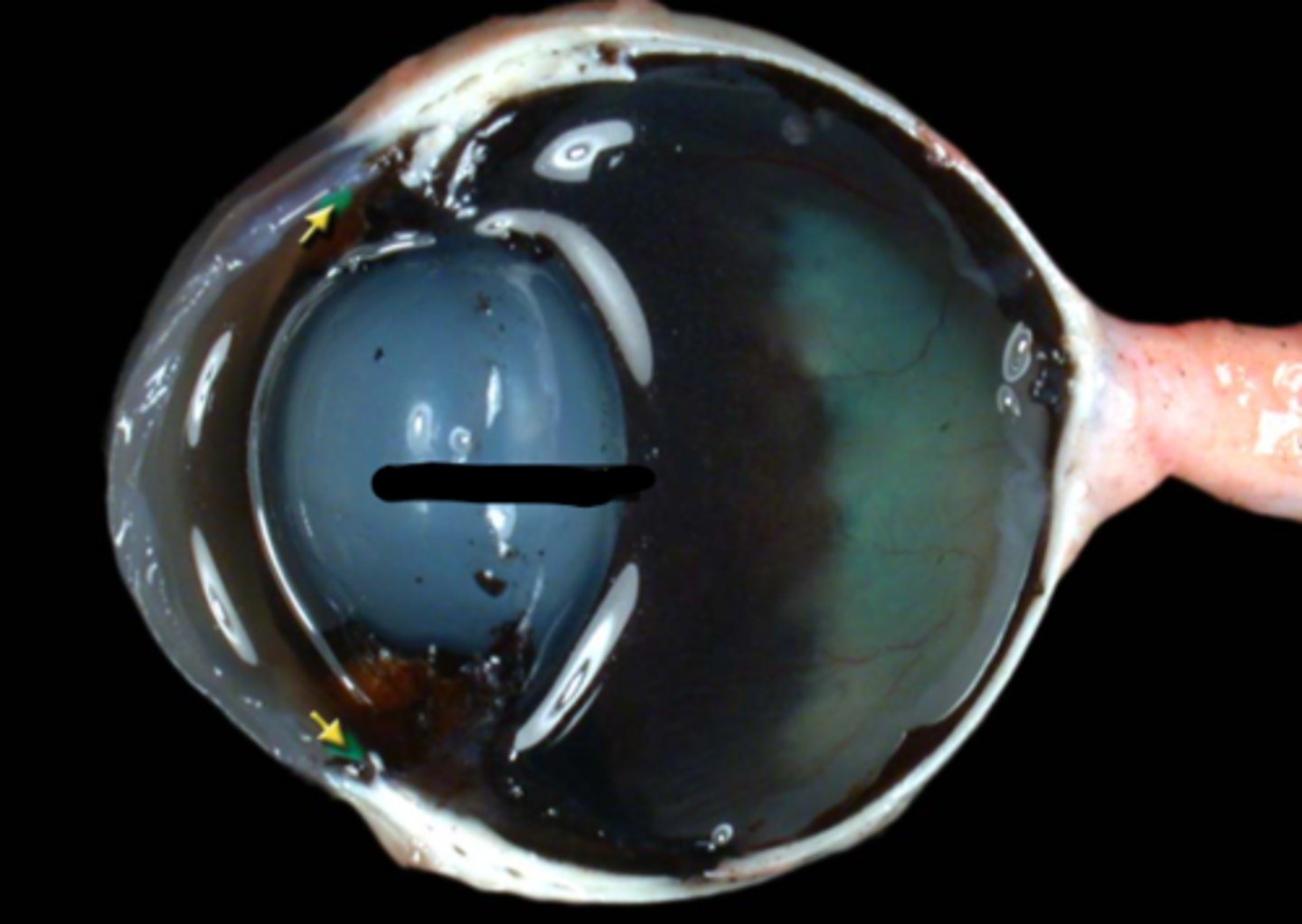
iridocorneal angle
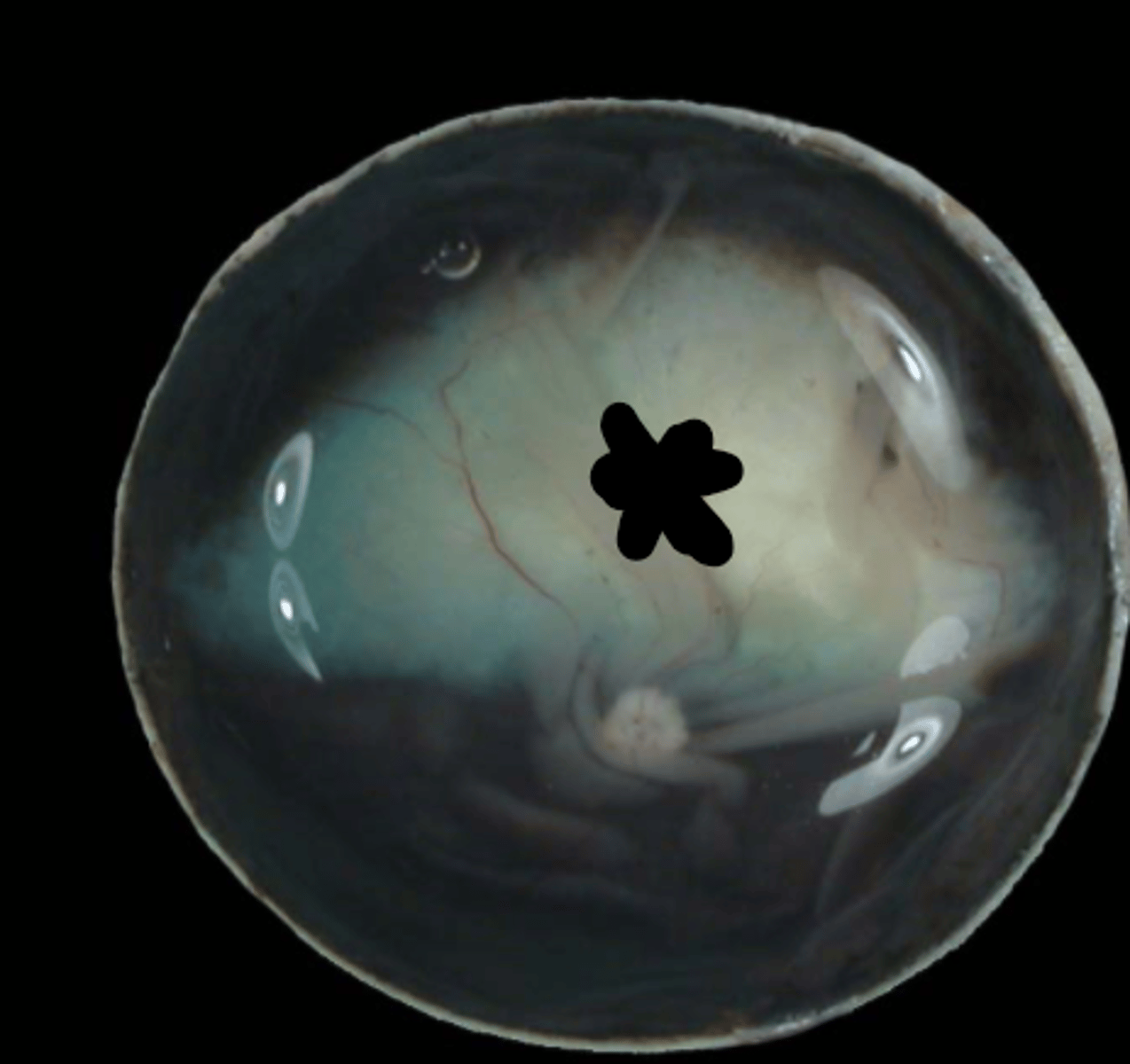
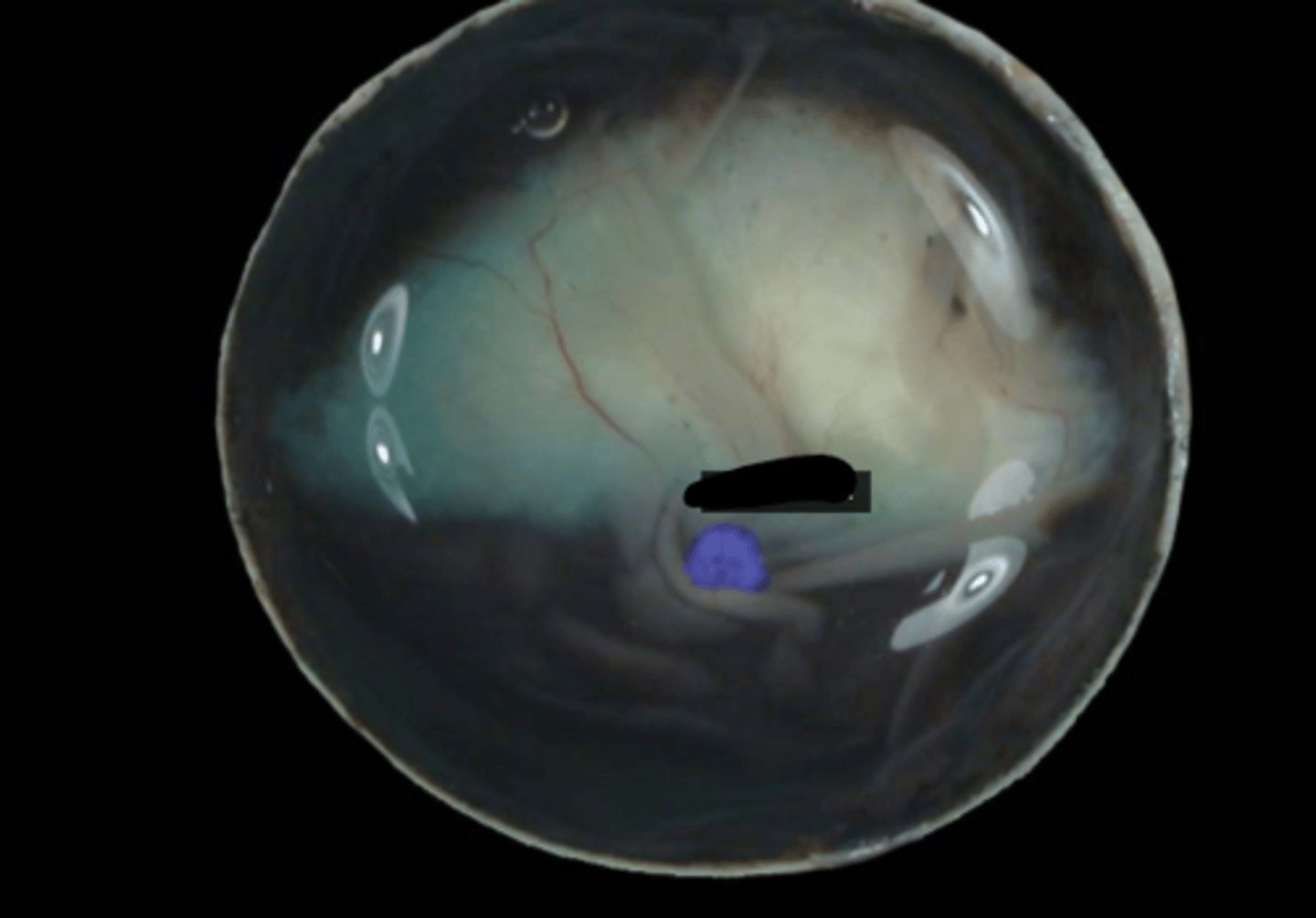
fundus
The posterior portion of the eyeball that includes the area of the optic disc and tapetum:
optic disk
palpebral fissure
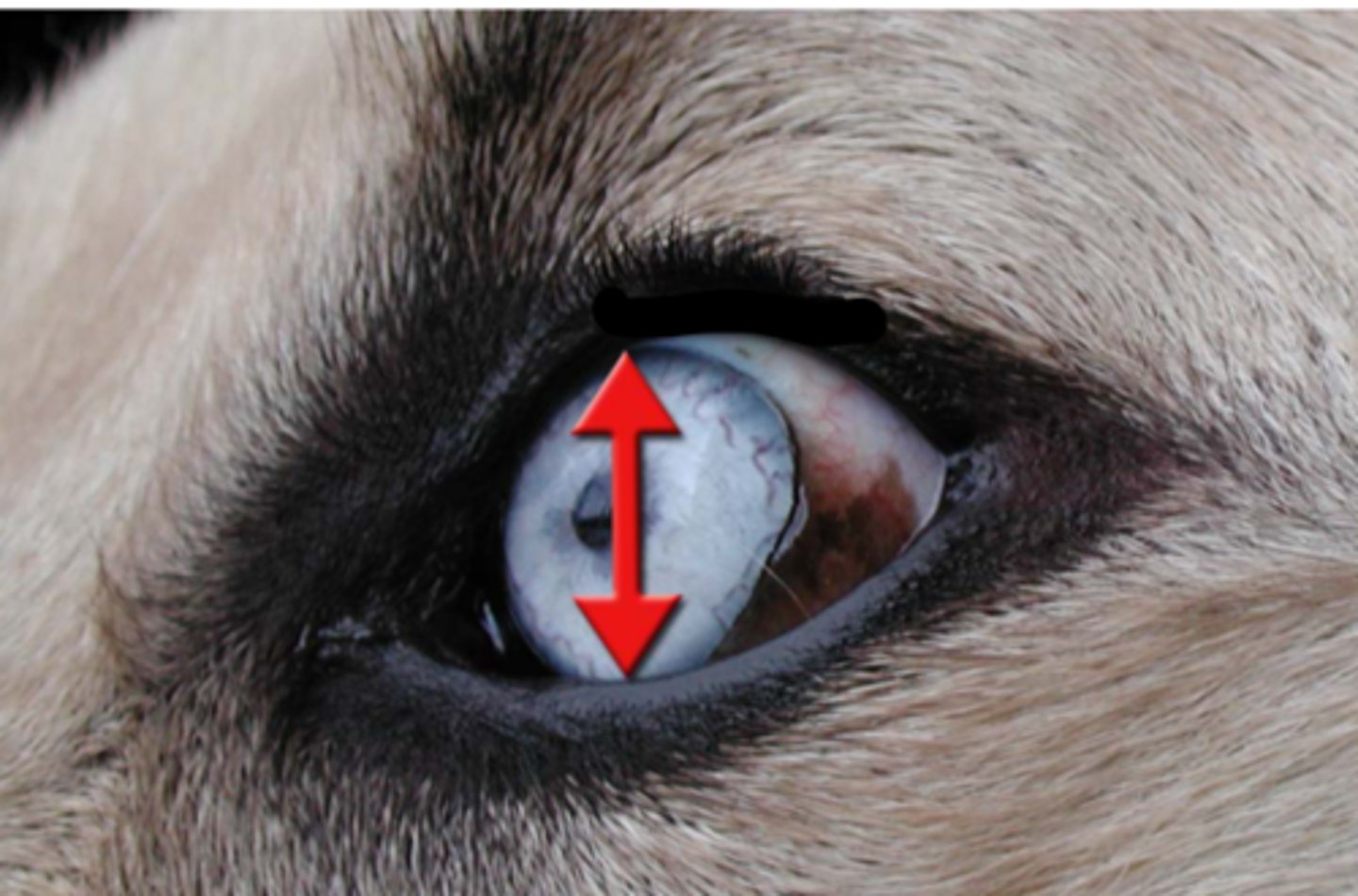
inferior palpebrae
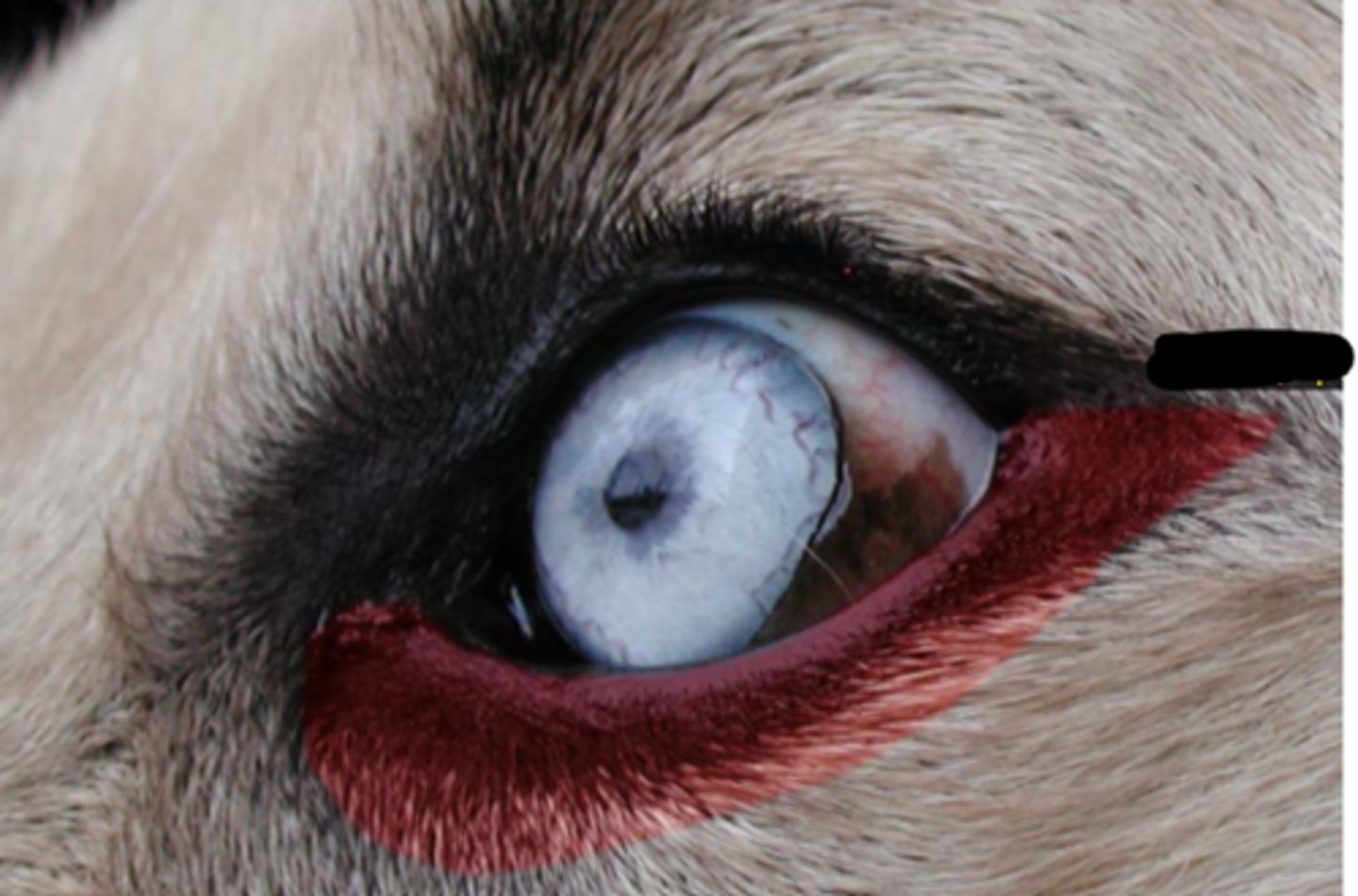

superior palpebra
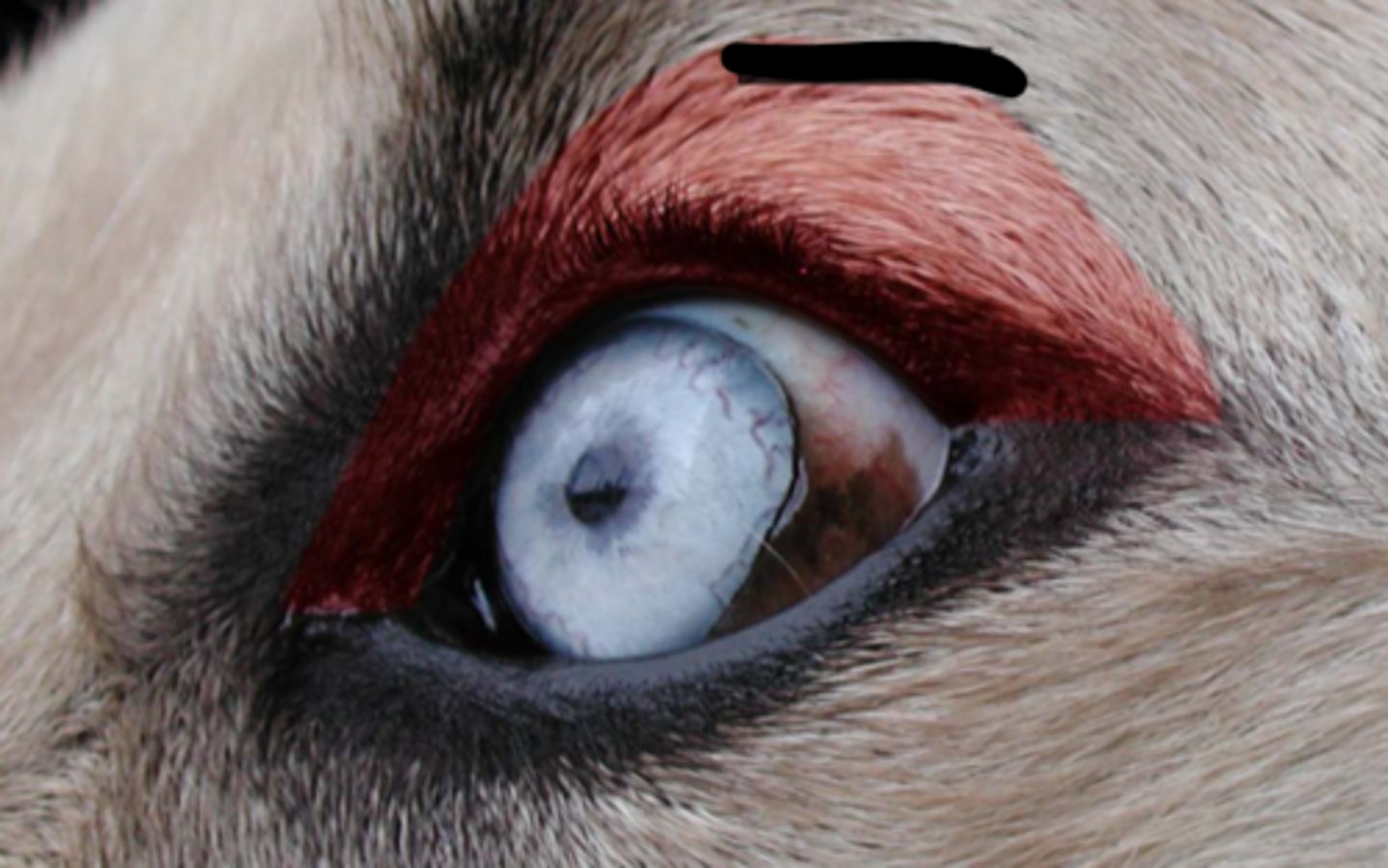
orbicularis oculi
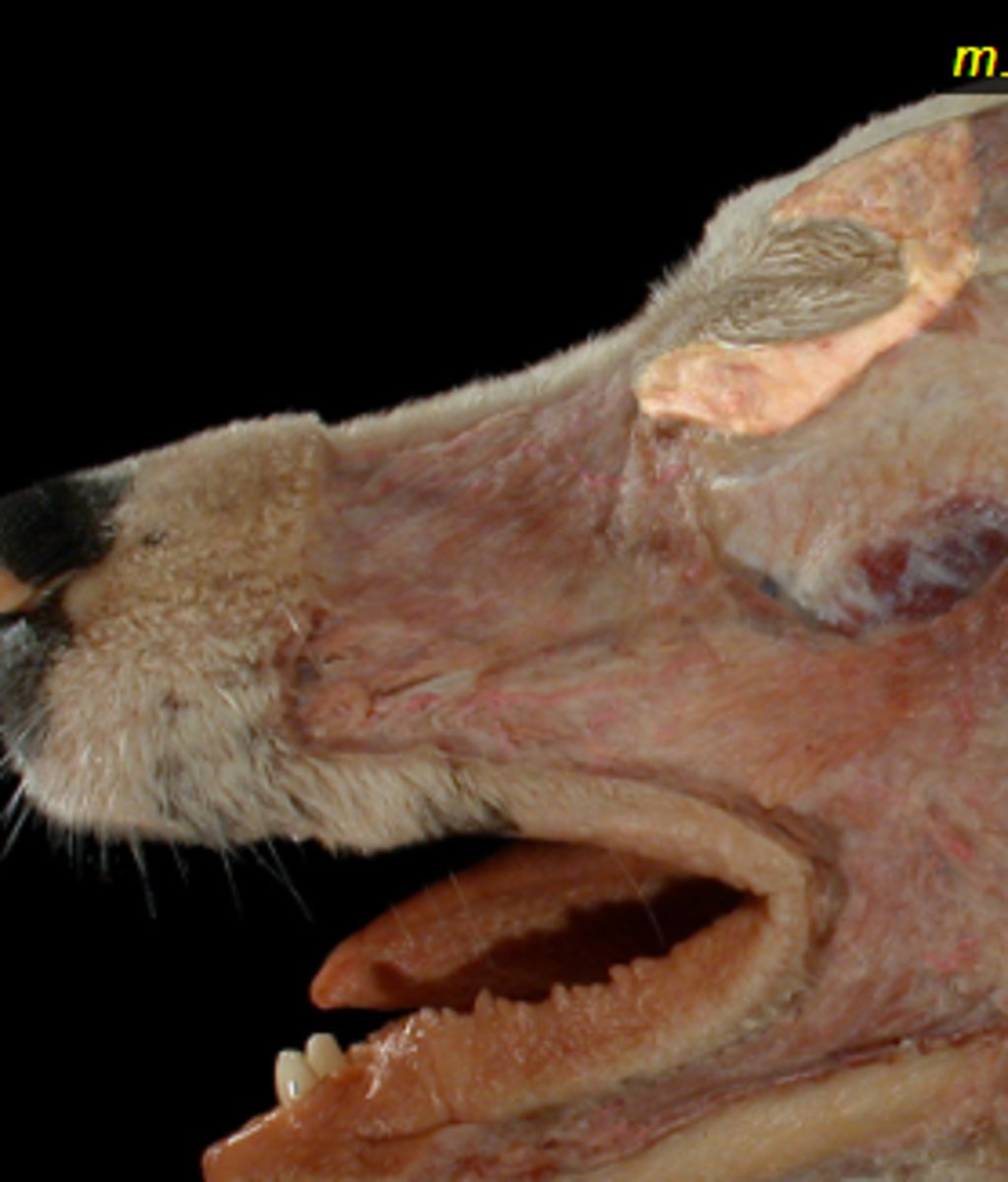
Olfactory
Optic
Oculomotor
Trochlear
Facial
Vestibulocochlear
optic nerve
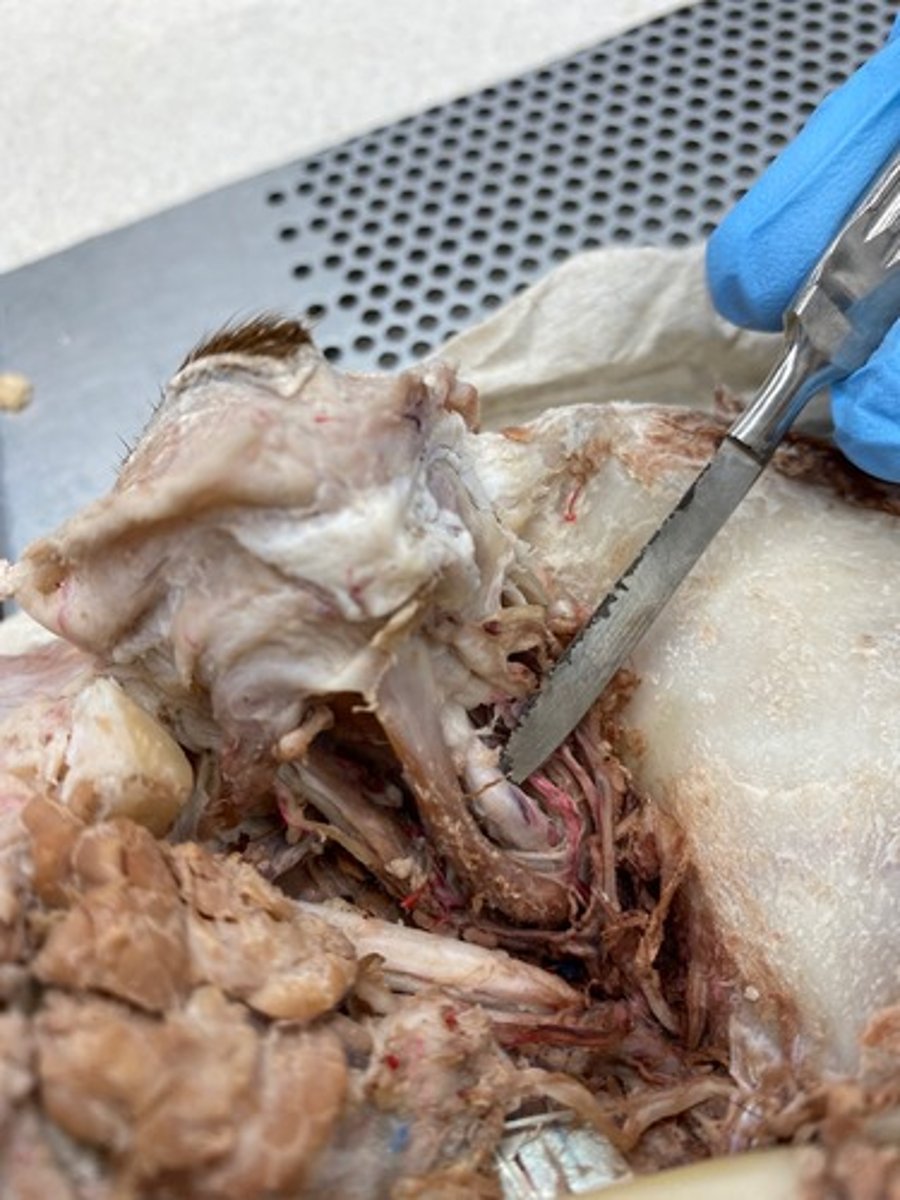
Oculomotor
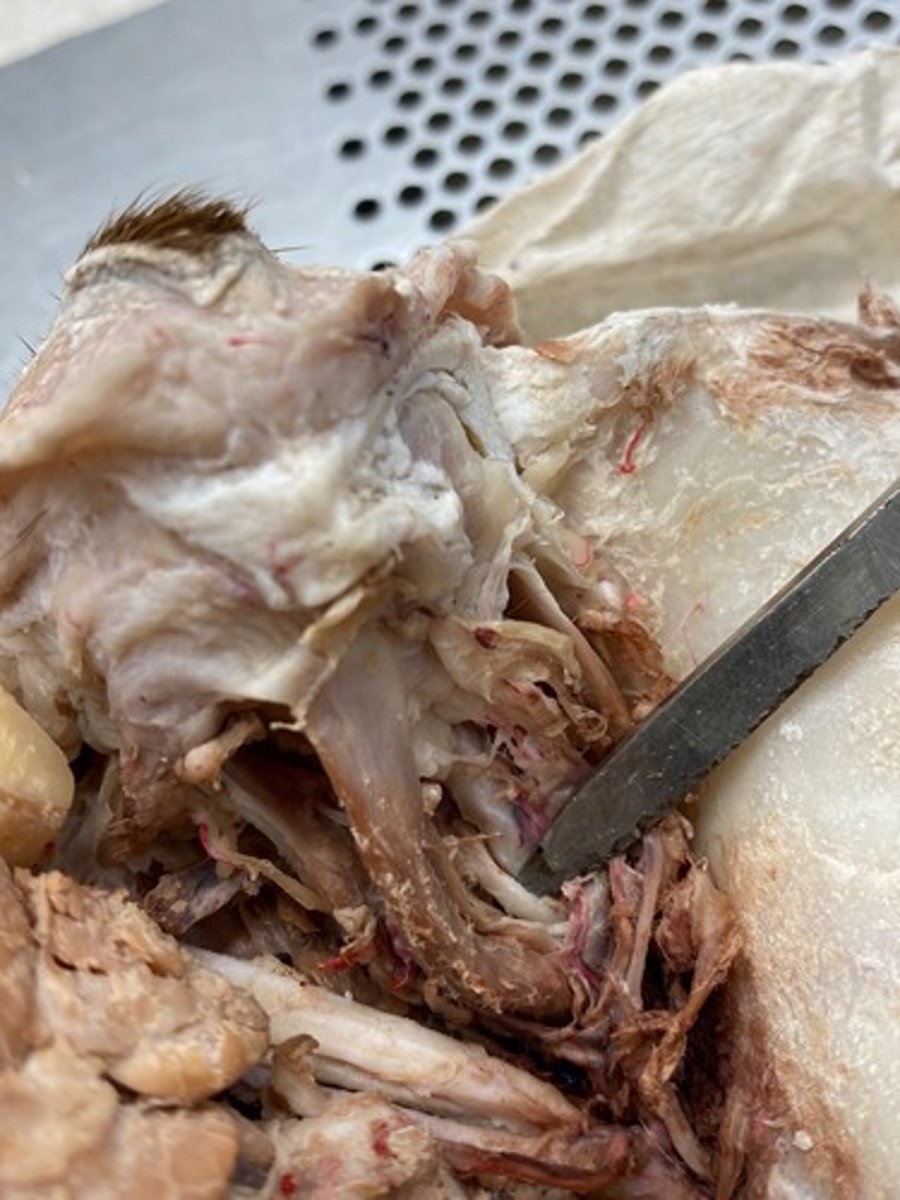
Abducent
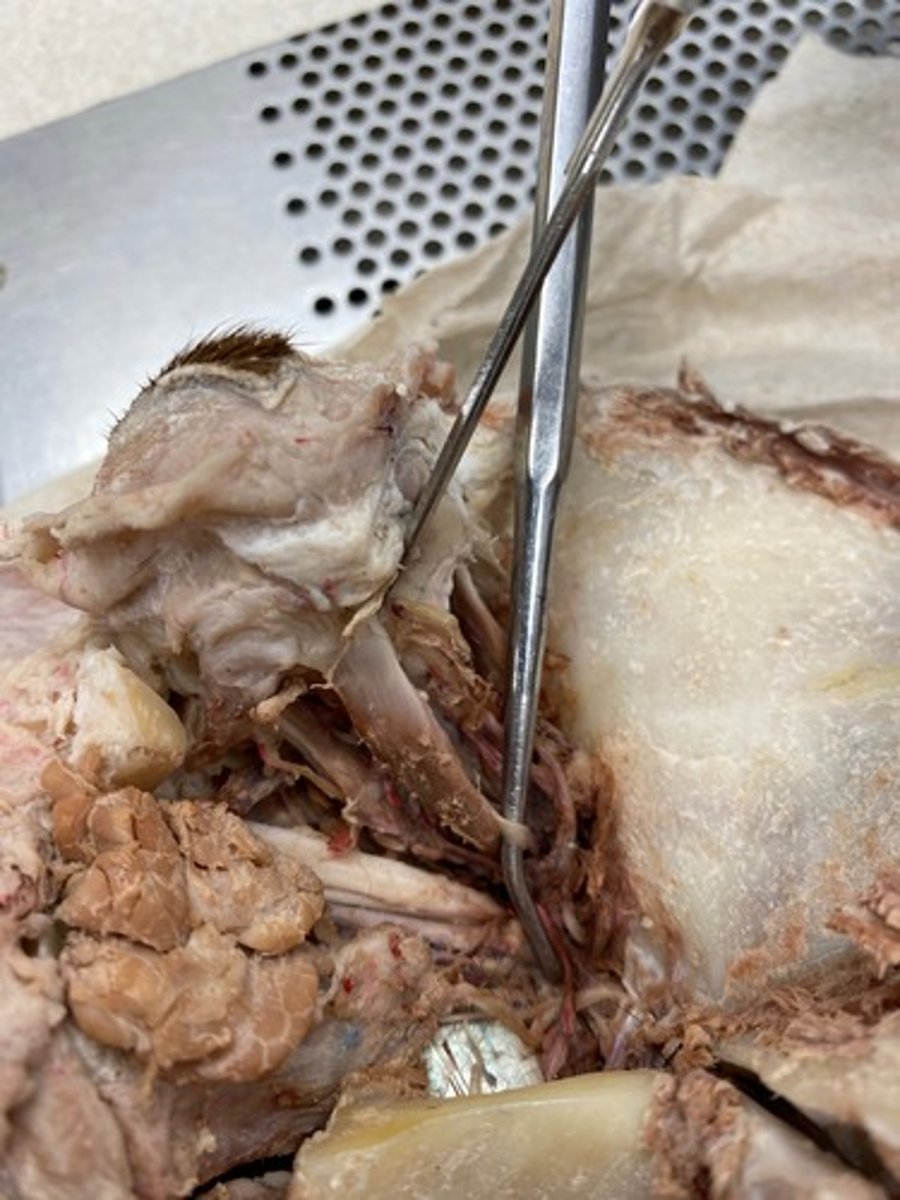
Maxillary nerve
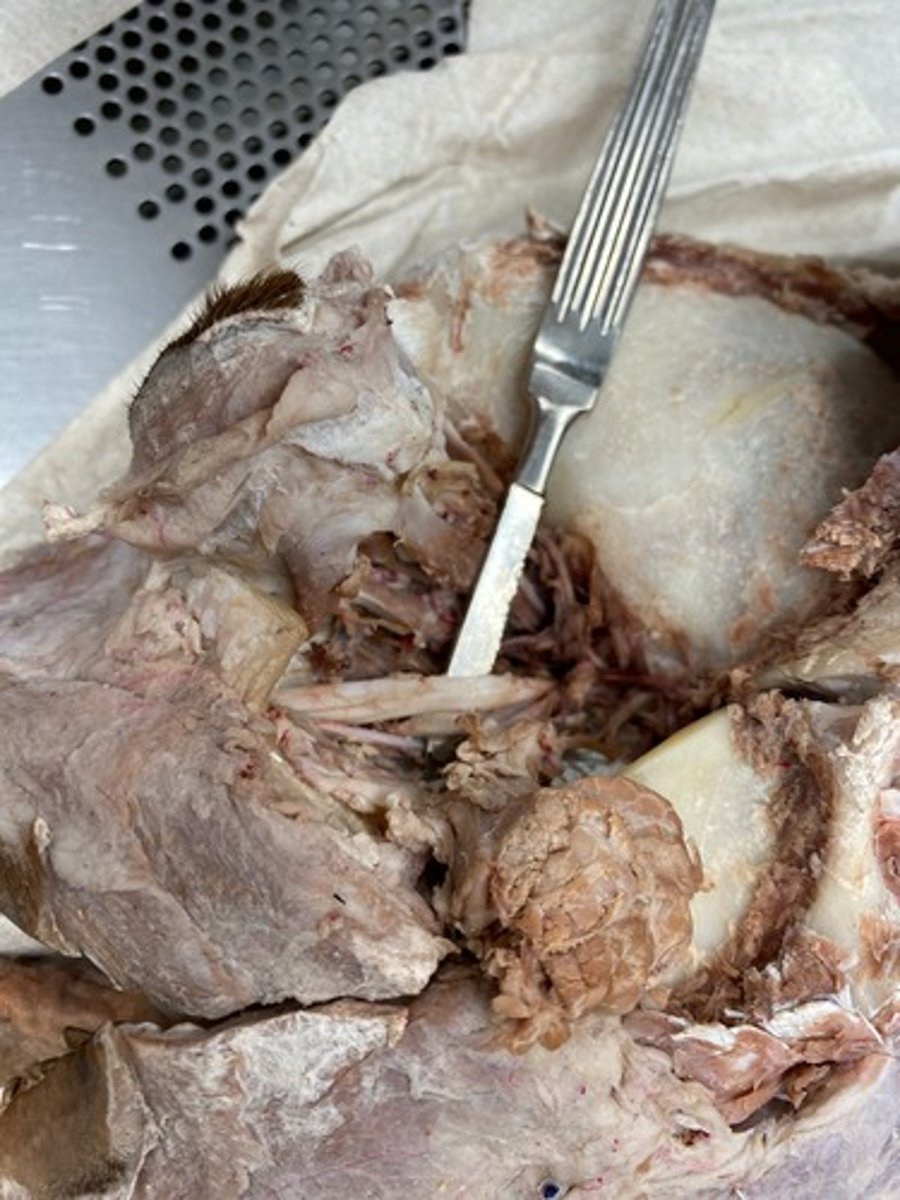
Inferior alveolar
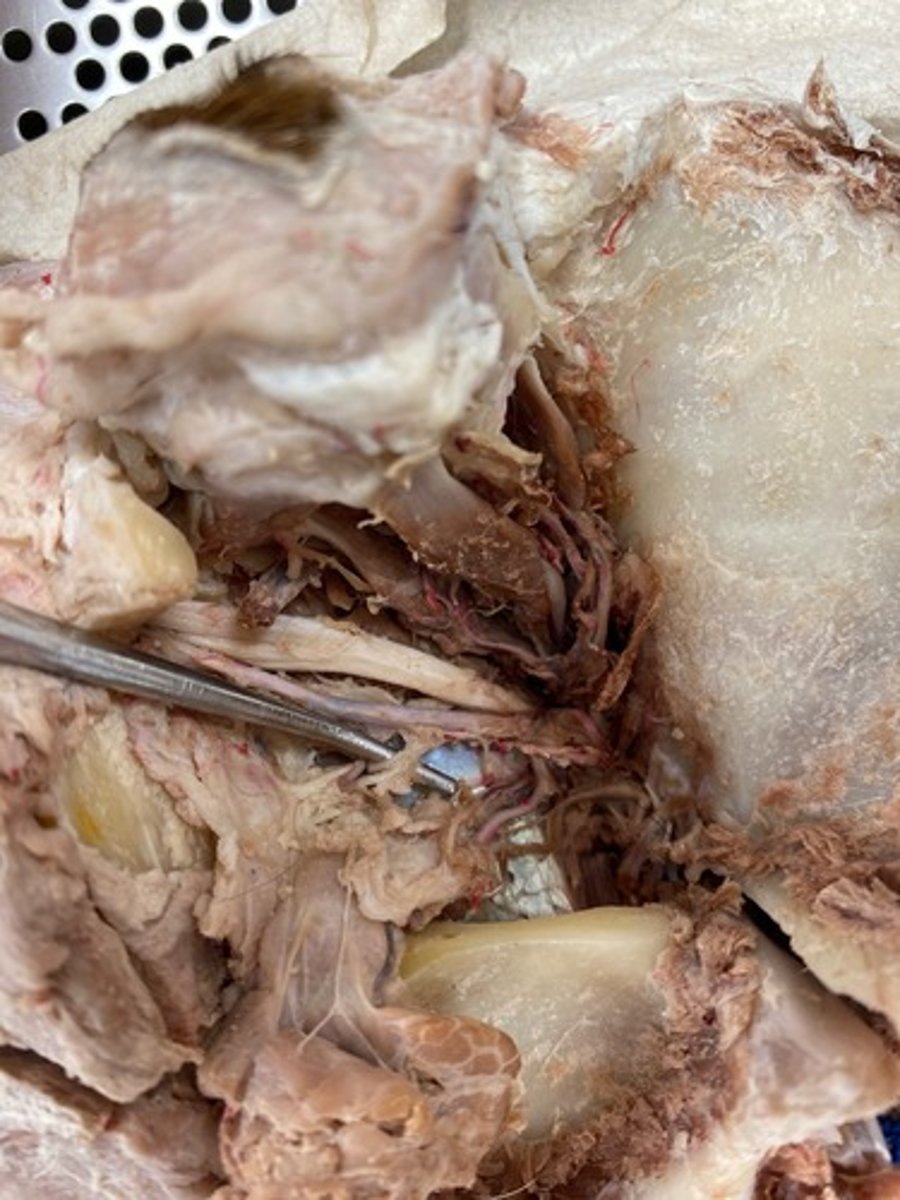
I. Olfactory
collective axons of these bipolar neurons pass through the foramina of the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone as the ______ nerves
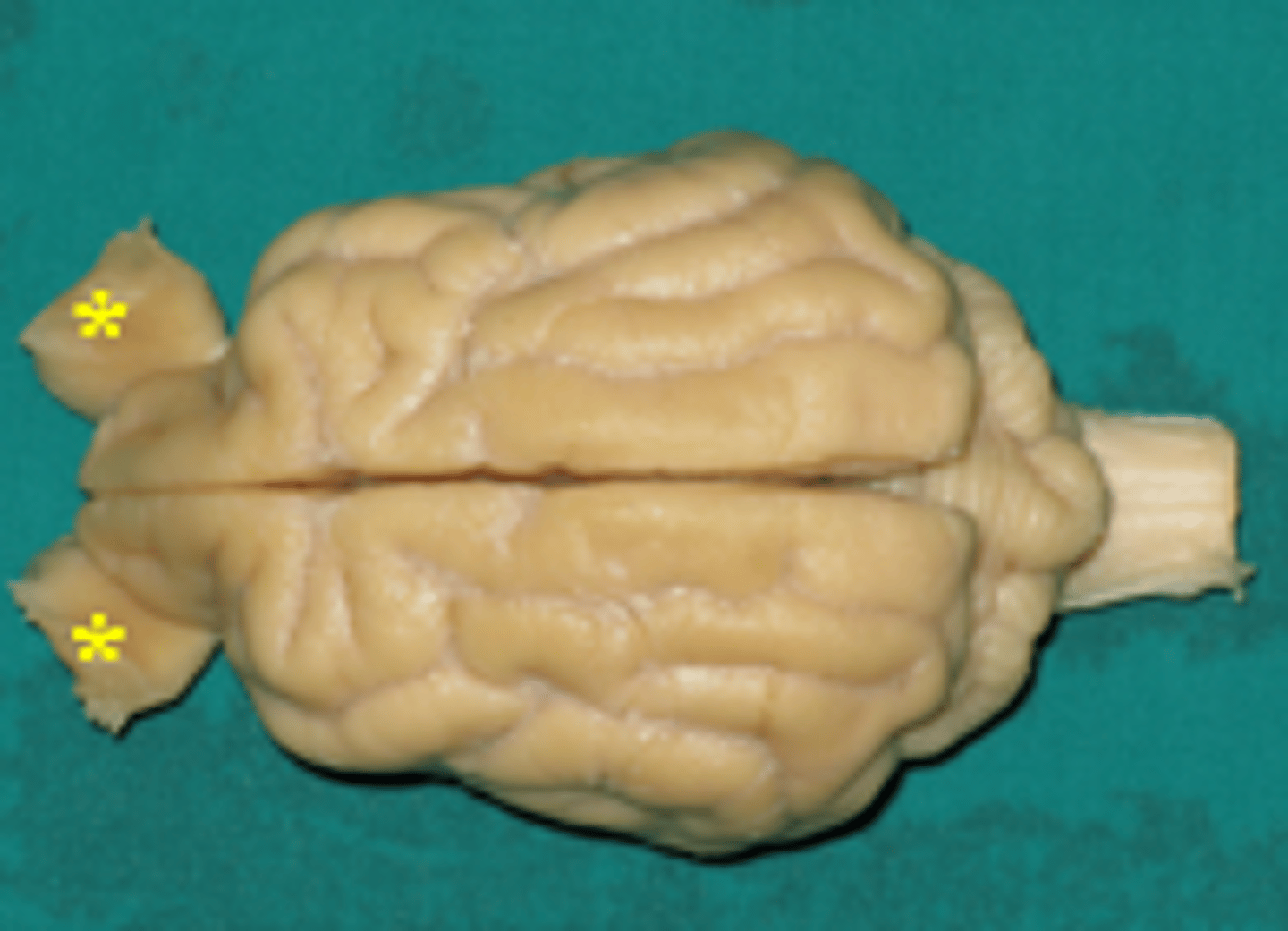
II. Optic
This nerve enters the optic foramen and passes through the optic canal
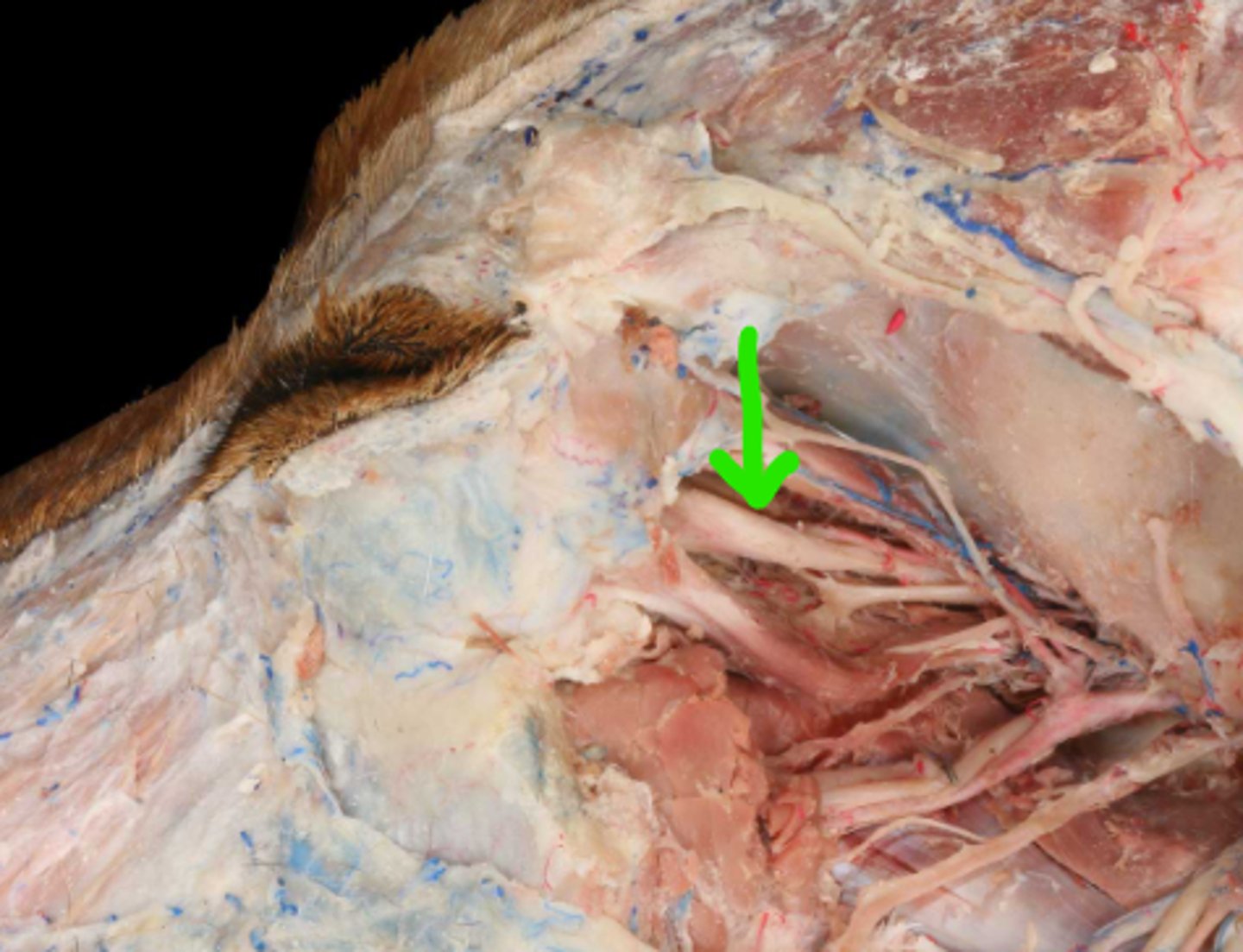
II. Optic
This nerve enters the optic foramen and passes through the optic canal
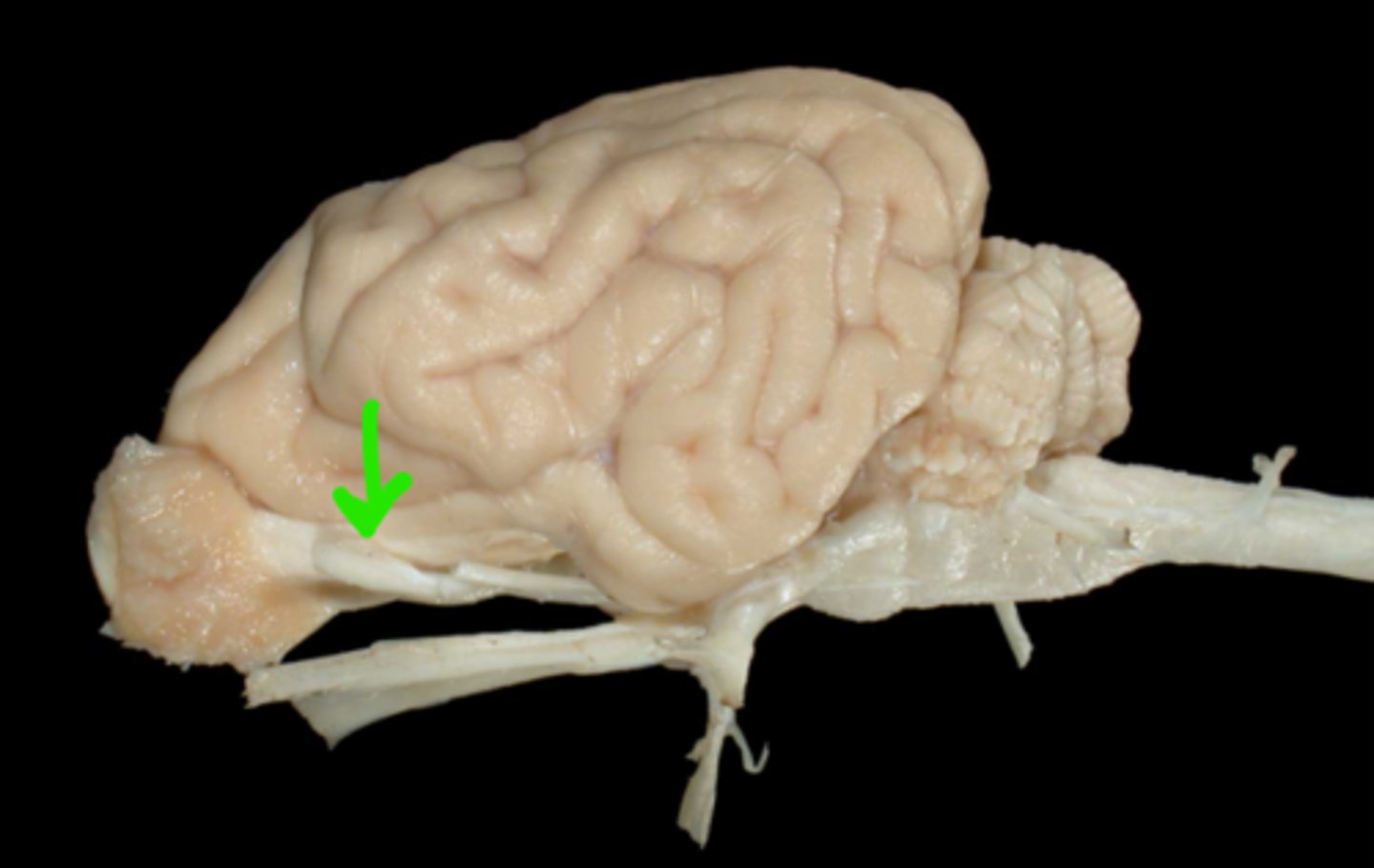
II. Optic
This nerve enters the optic foramen and passes through the optic canal
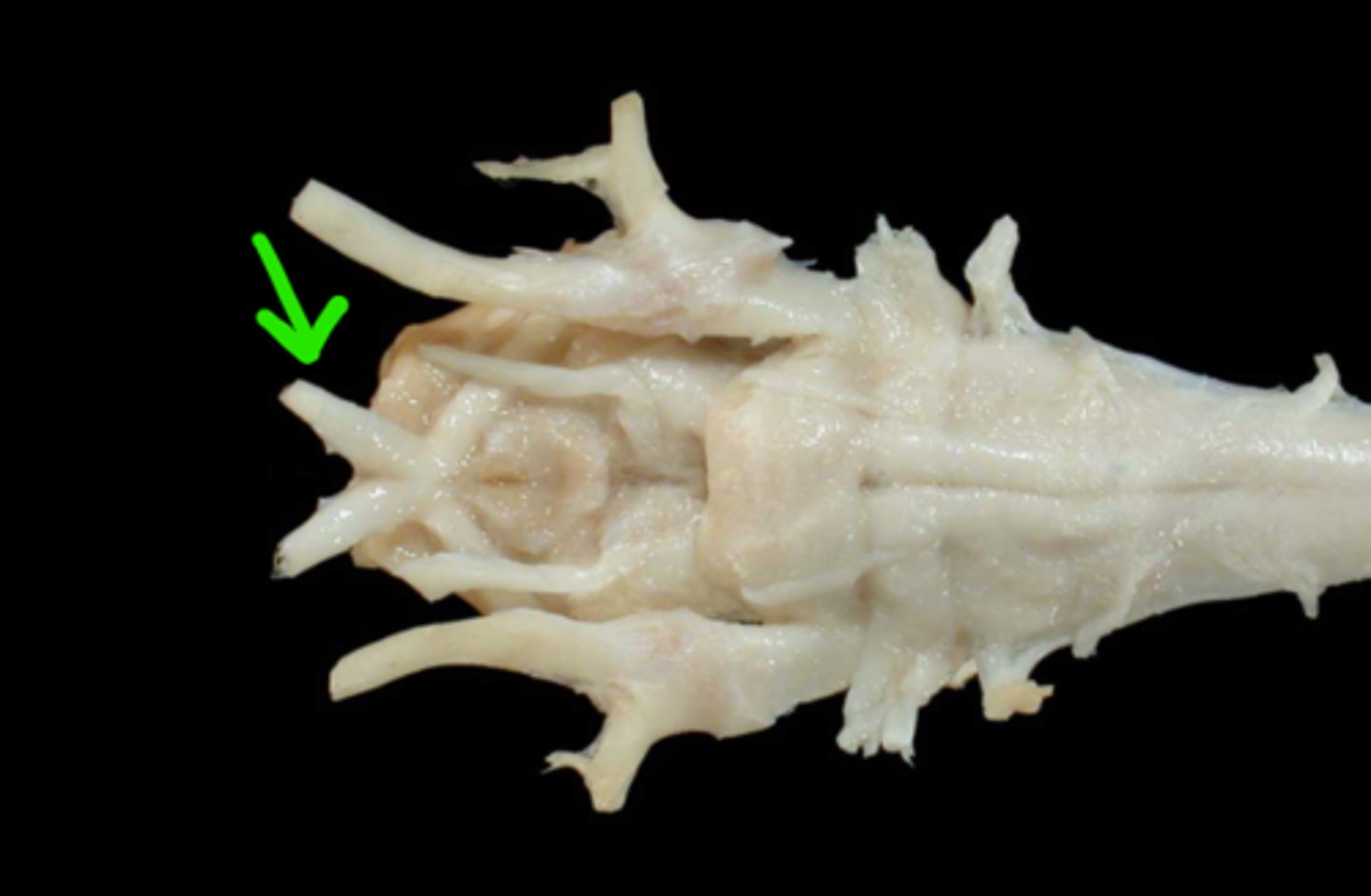
III. Oculomotor
This nerve is somatic efferent to the levator palpebrae superioris m. and the remaining 4 extrinsic muscles of the globe
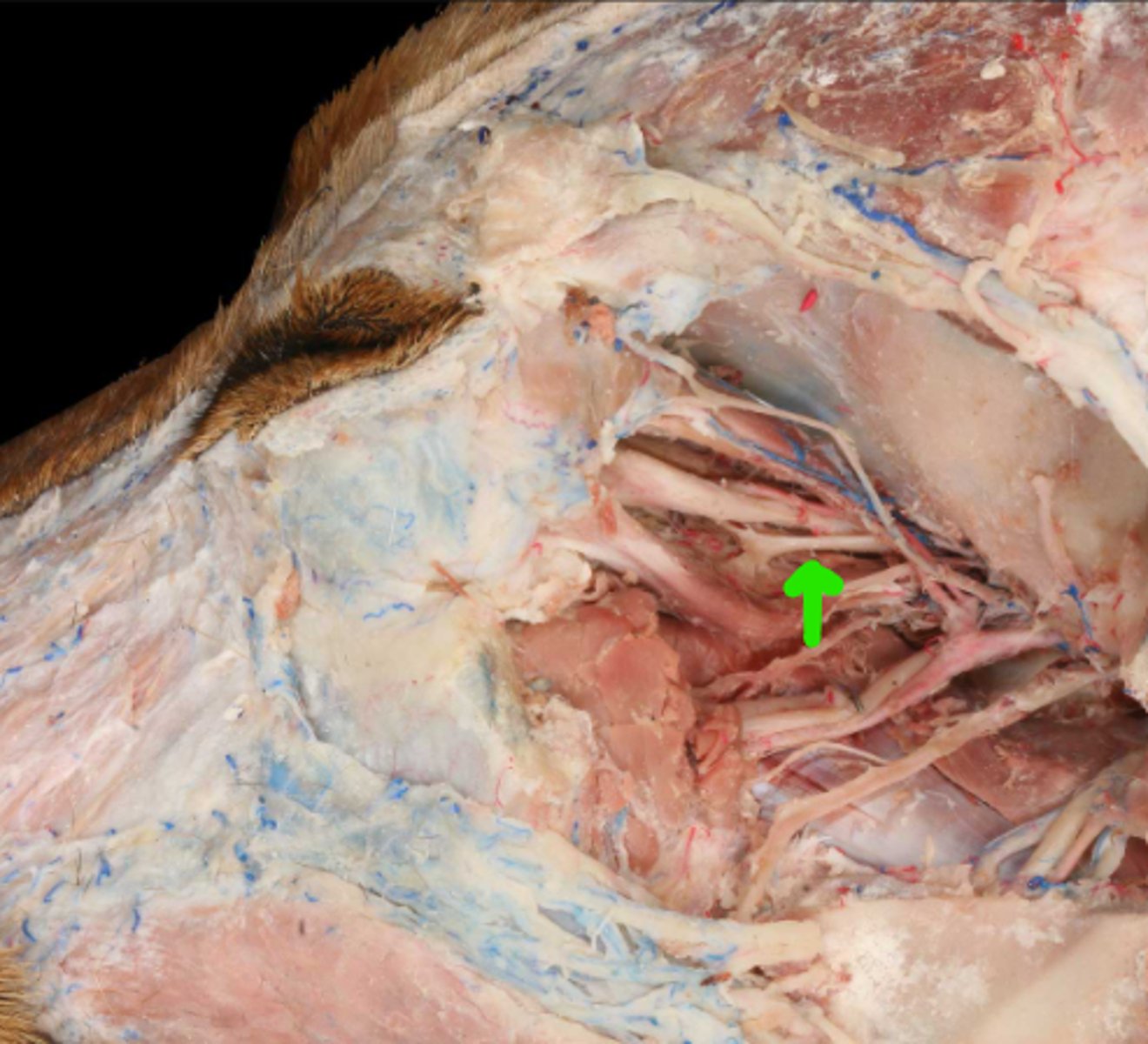
III. Oculomotor
This nerve is visceral efferent to the intrinsic muscles of the eye (constrictor pupillae m., ciliary m.)
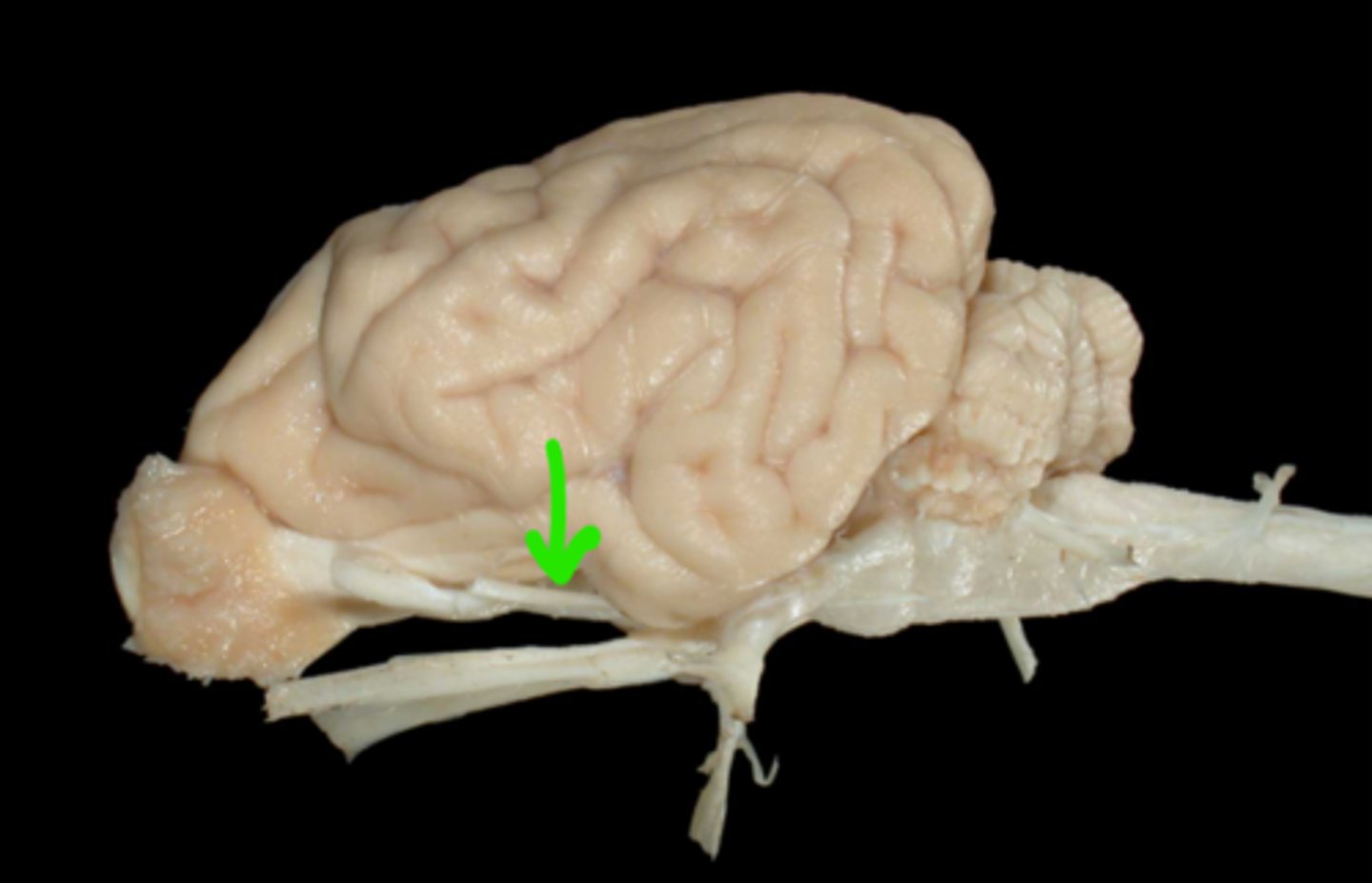
III. Oculomotor
This nerve extends through the orbital fissure
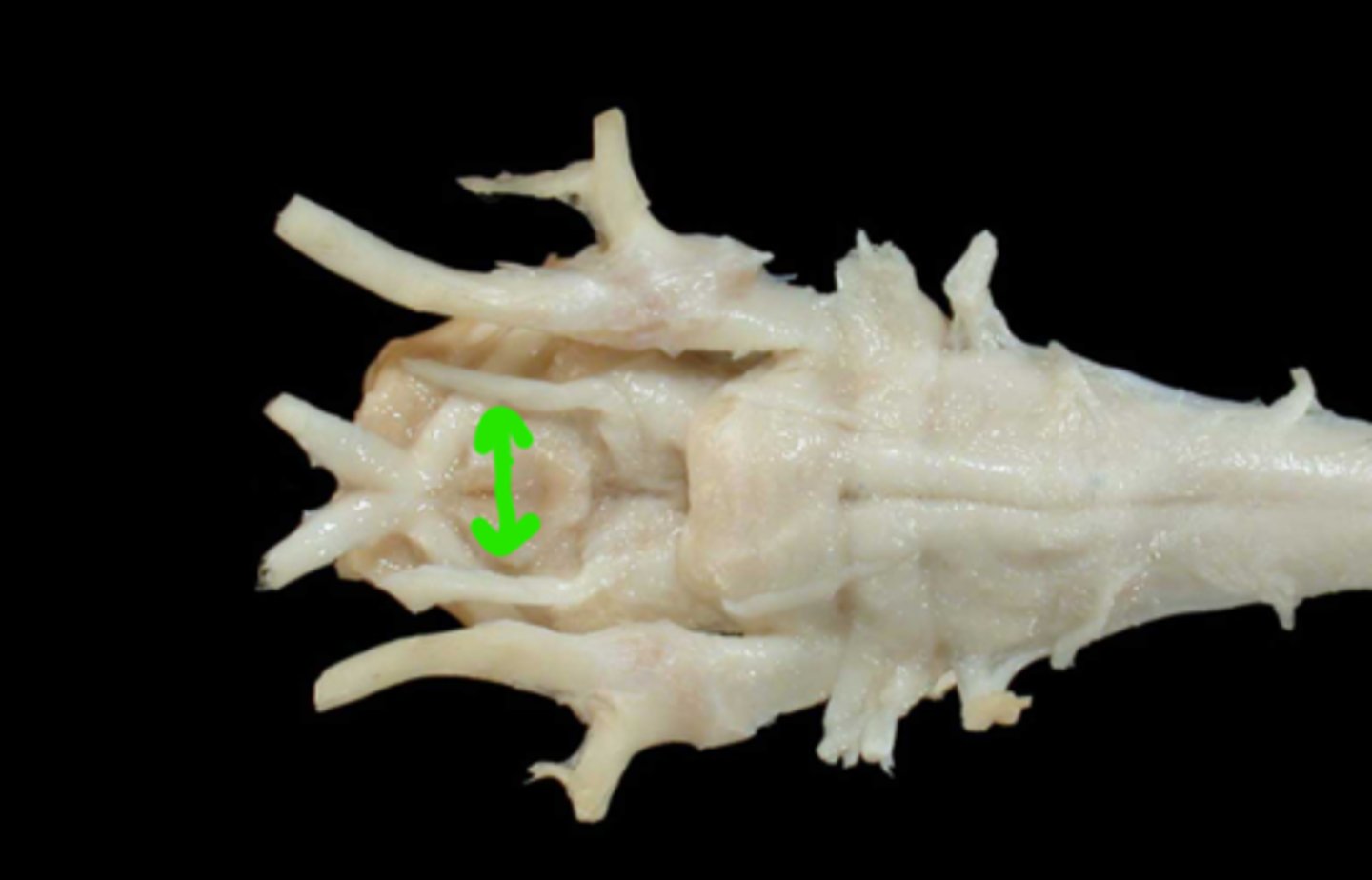
IV. Trochlear
This nerve innervates the dorsal oblique m. and extends through the orbital fissure
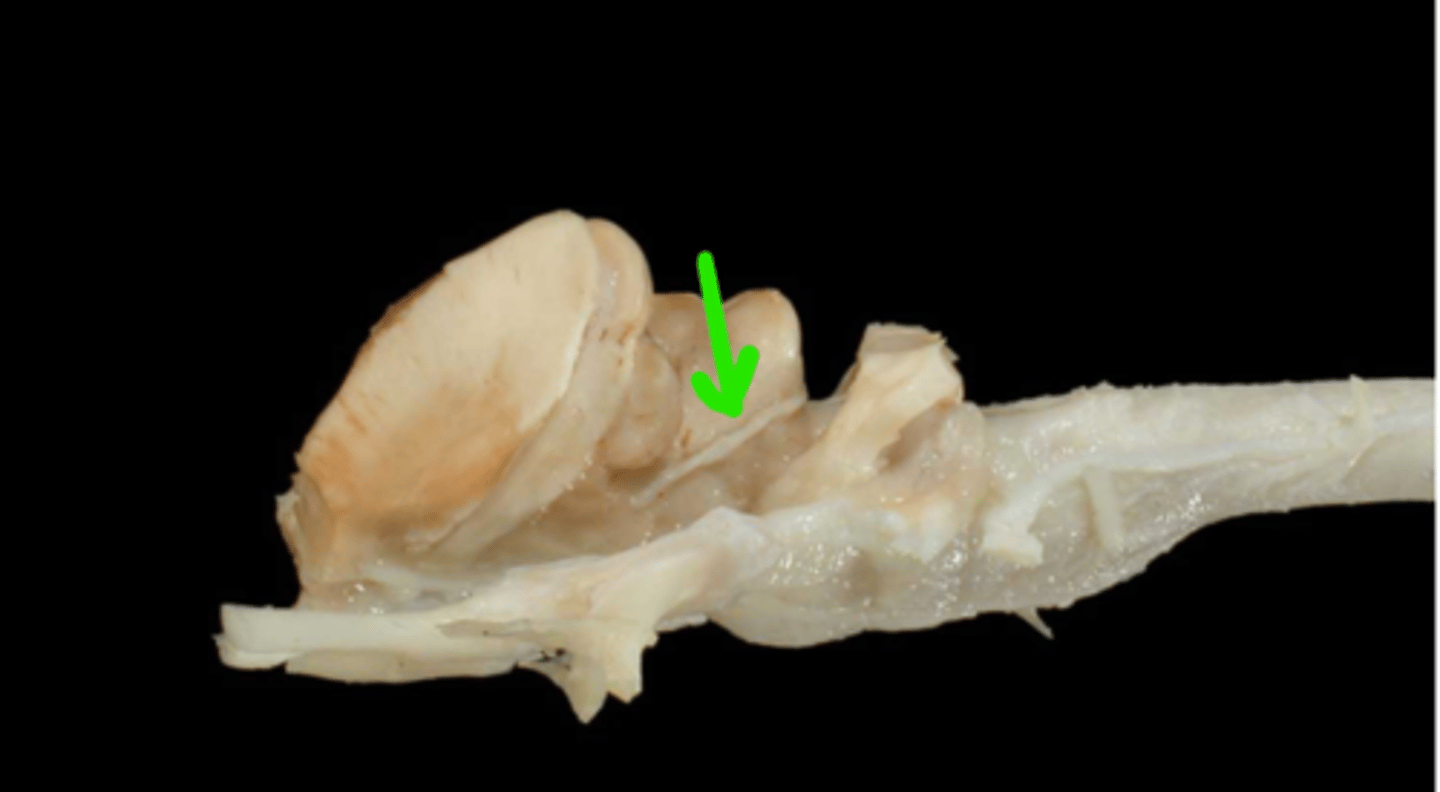
IV. Trochlear
This nerve innervates the dorsal oblique m. and extends through the orbital fissure
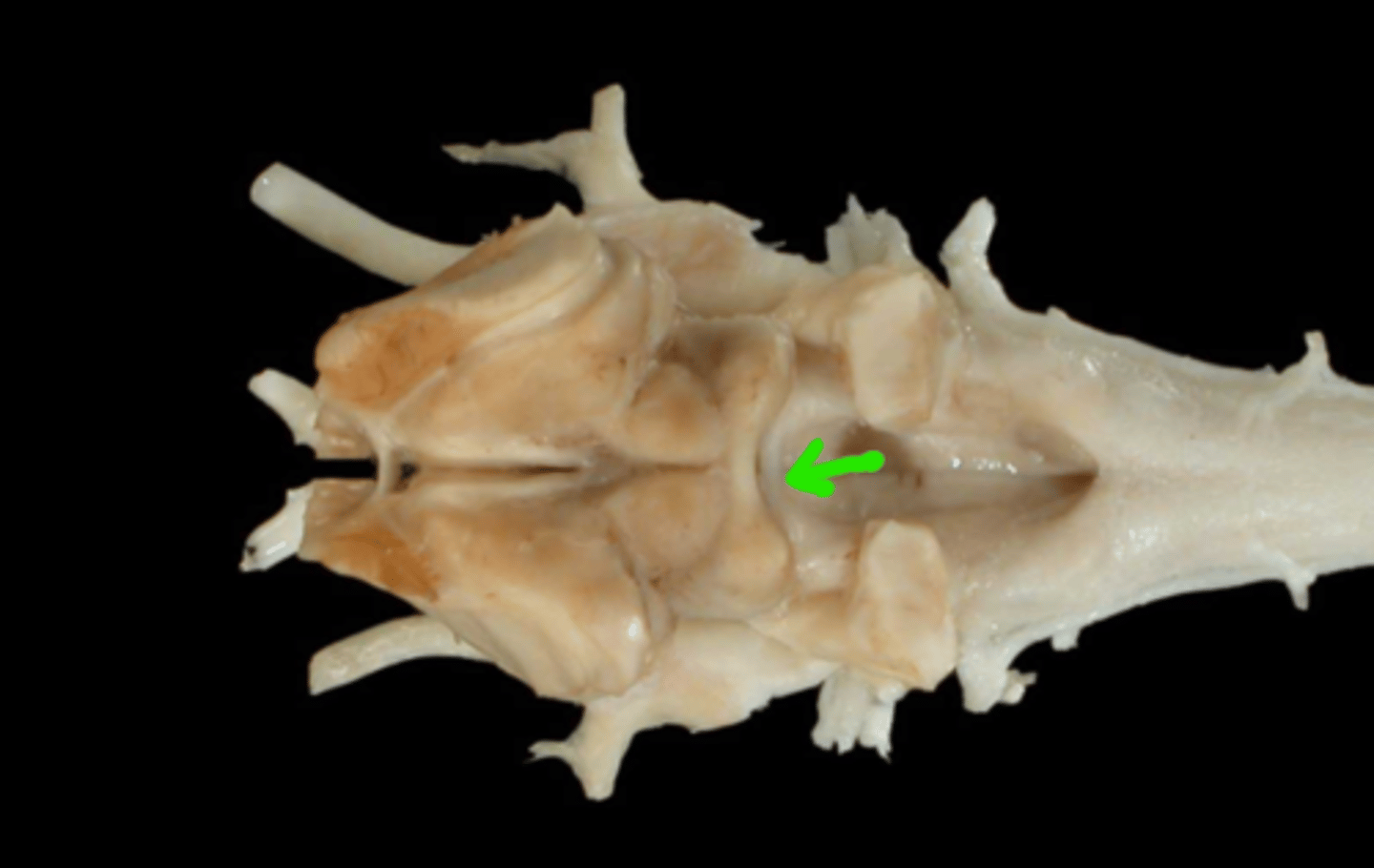
IV. Trochlear
This nerve innervates the dorsal oblique m. and extends through the orbital fissure
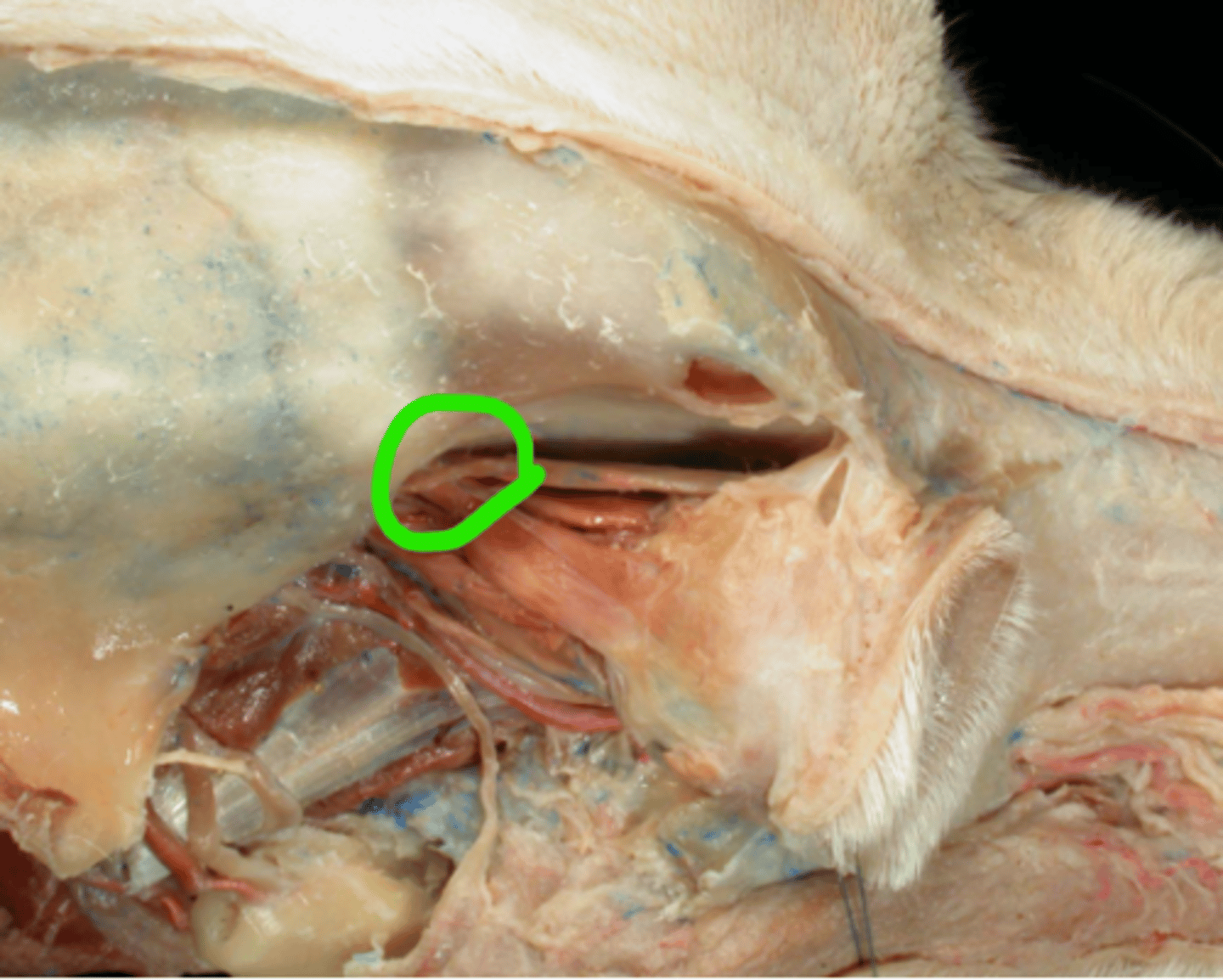
V. Trigeminal
Ophthalmic n (VI)
- orbital fissure
Maxillary n (V2)
-round foramen, alar canal, rostral alar foramen
Mandibular n (V3)
-oval foramen
This nerve has 3 divisions. What are they? Where do they pass through?
V. Trigeminal
Ophthalmic n (VI)
- orbital fissure
Maxillary n (V2)
-round foramen, alar canal, rostral alar foramen
Mandibular n (V3)
-oval foramen
This nerve has 3 divisions. What are they? Where do they pass through?
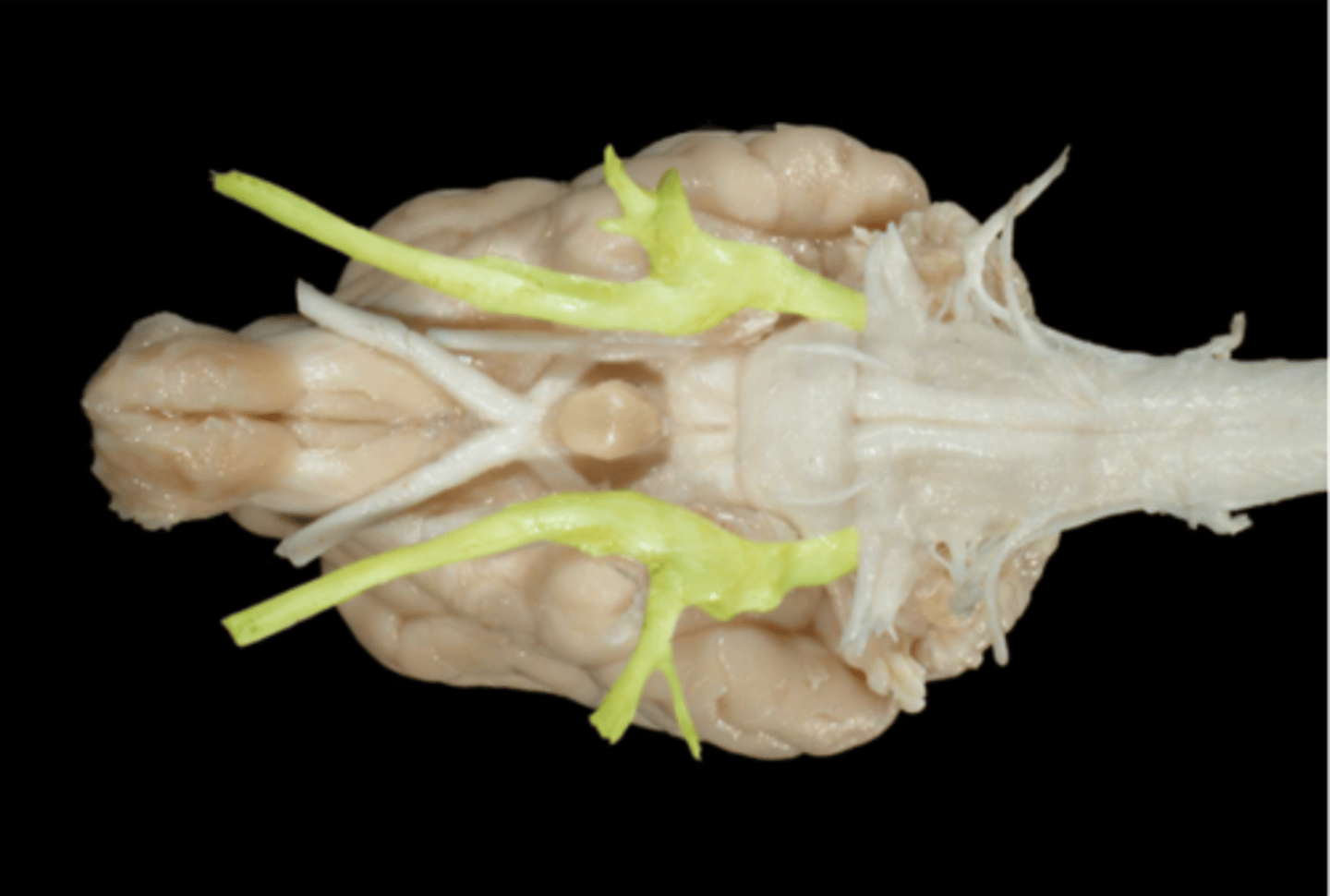
V. Trigeminal
Ophthalmic n (VI)
- orbital fissure
Maxillary n (V2)
-round foramen, alar canal, rostral alar foramen
Mandibular n (V3)
-oval foramen
This nerve has 3 divisions. What are they? Where do they pass through?
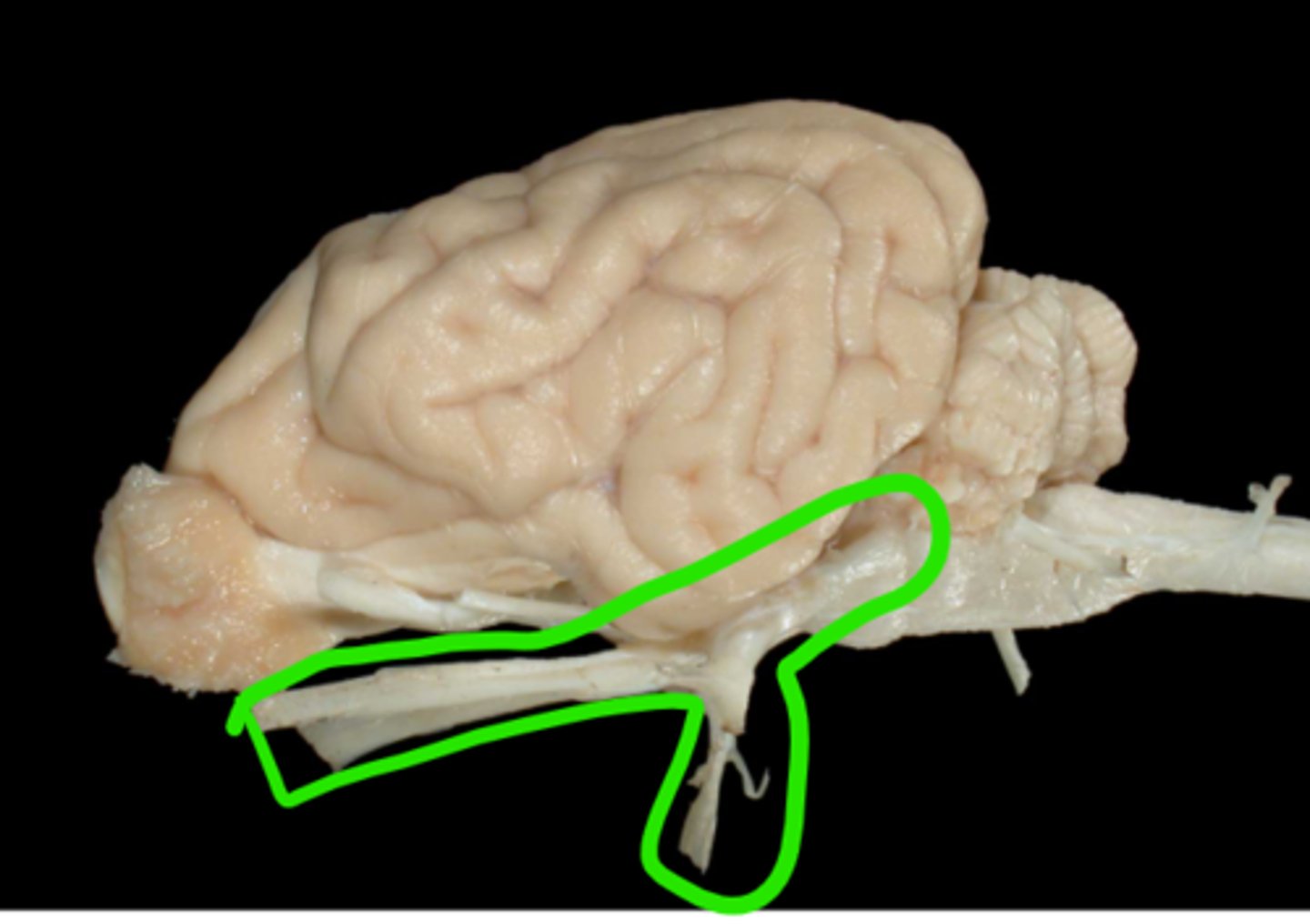
VI. Abducent
this nerve innervates the lateral rectus and retractor bulbi
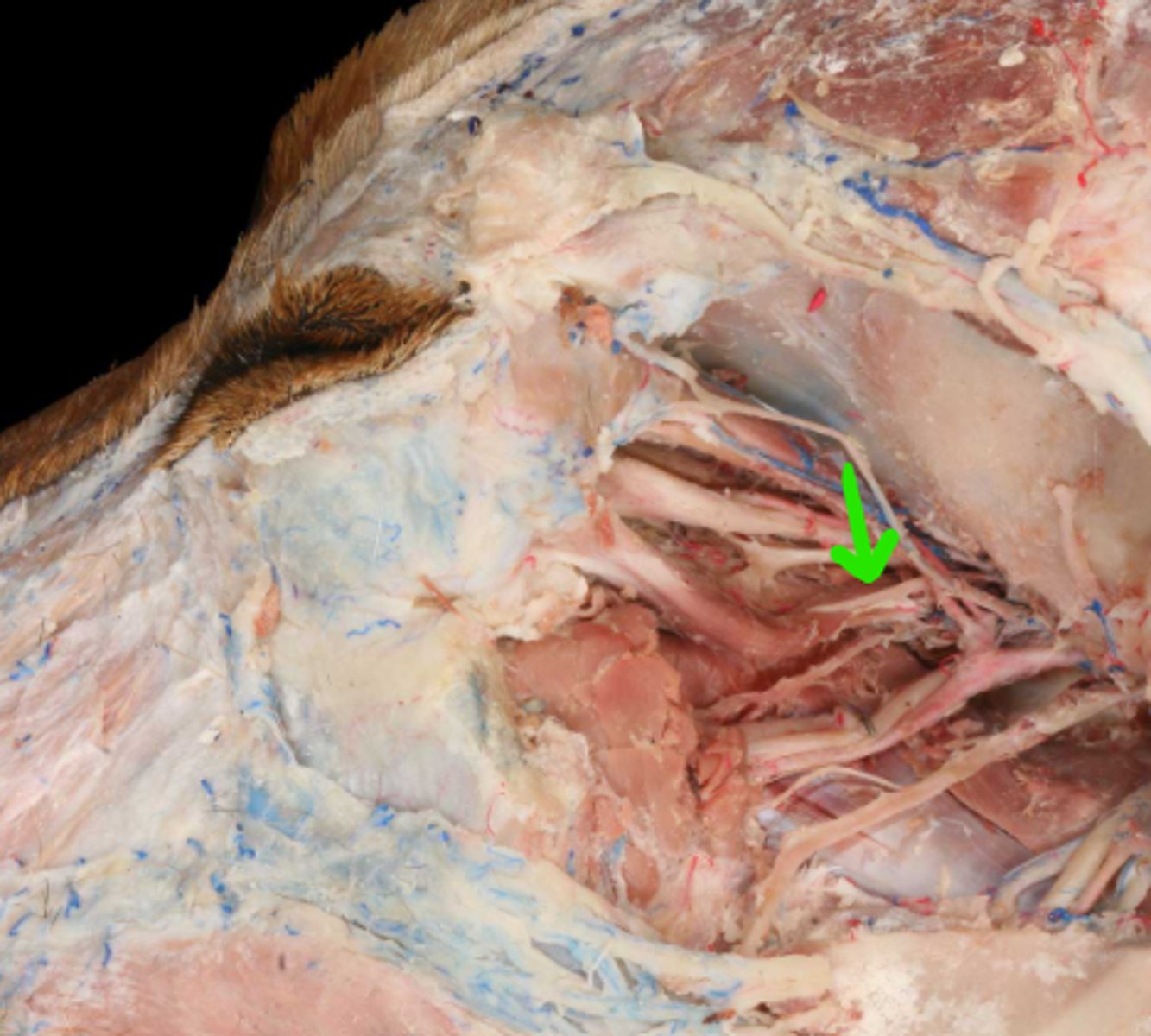
VI. Abducent
this nerve innervates the lateral rectus and retractor bulbi
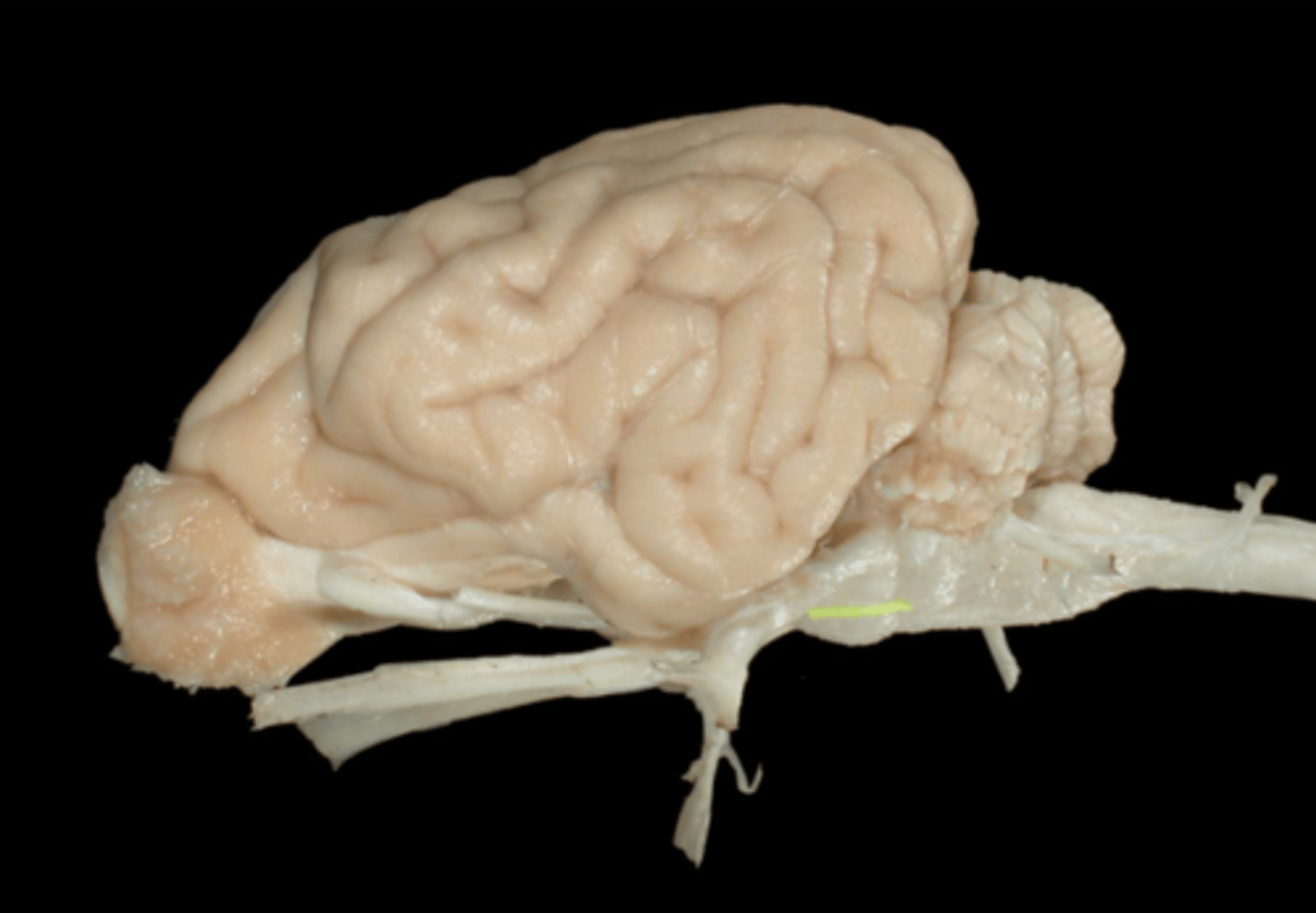
VI. Abducent
this nerve innervates the lateral rectus and retractor bulbi
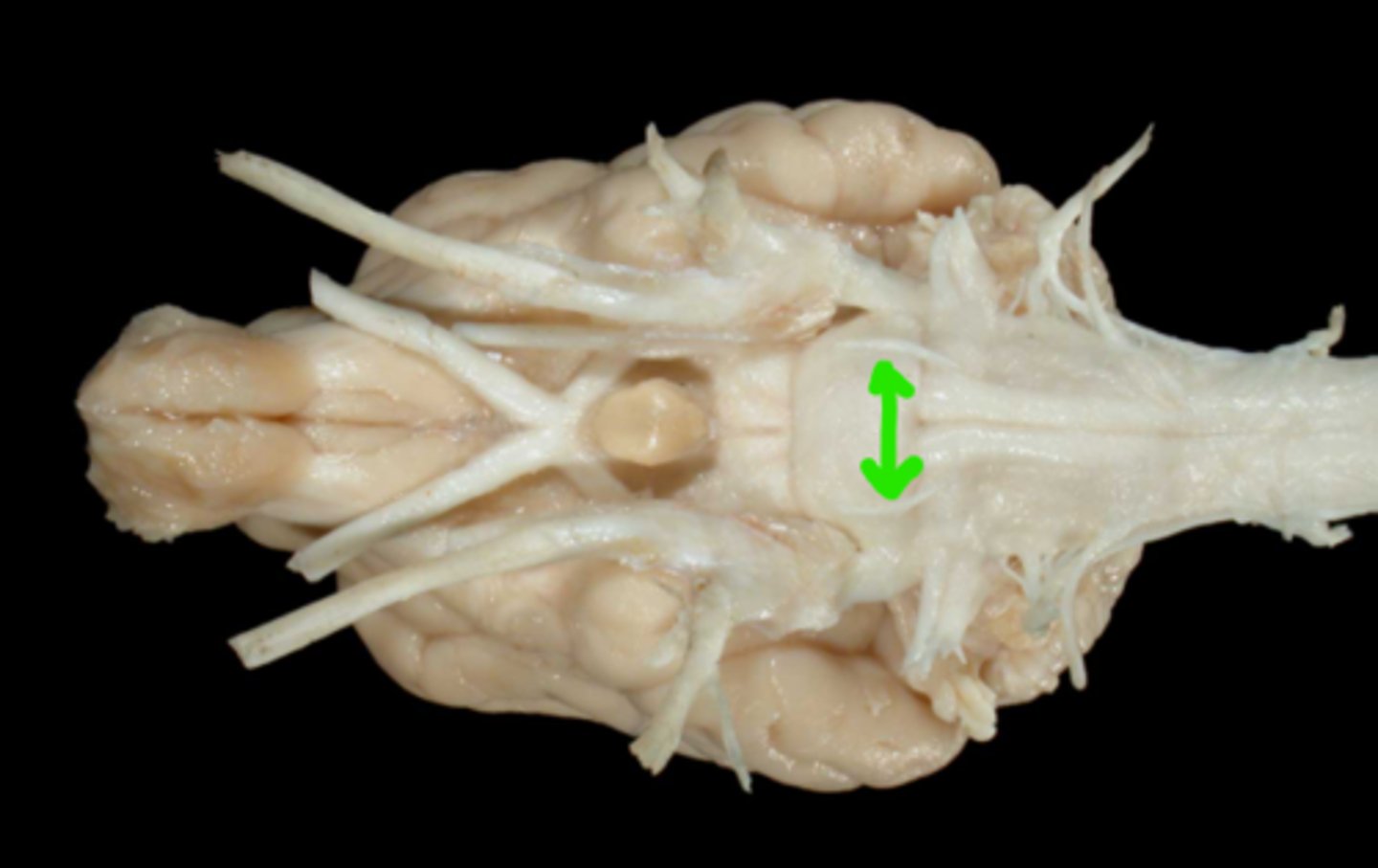
VII. Facial
This nerve enters the internal acoustic meatus, courses through the facial canal, and emerges from the stylomastoid foramen
VII. Facial
This nerve enters the internal acoustic meatus, courses through the facial canal, and emerges from the stylomastoid foramen
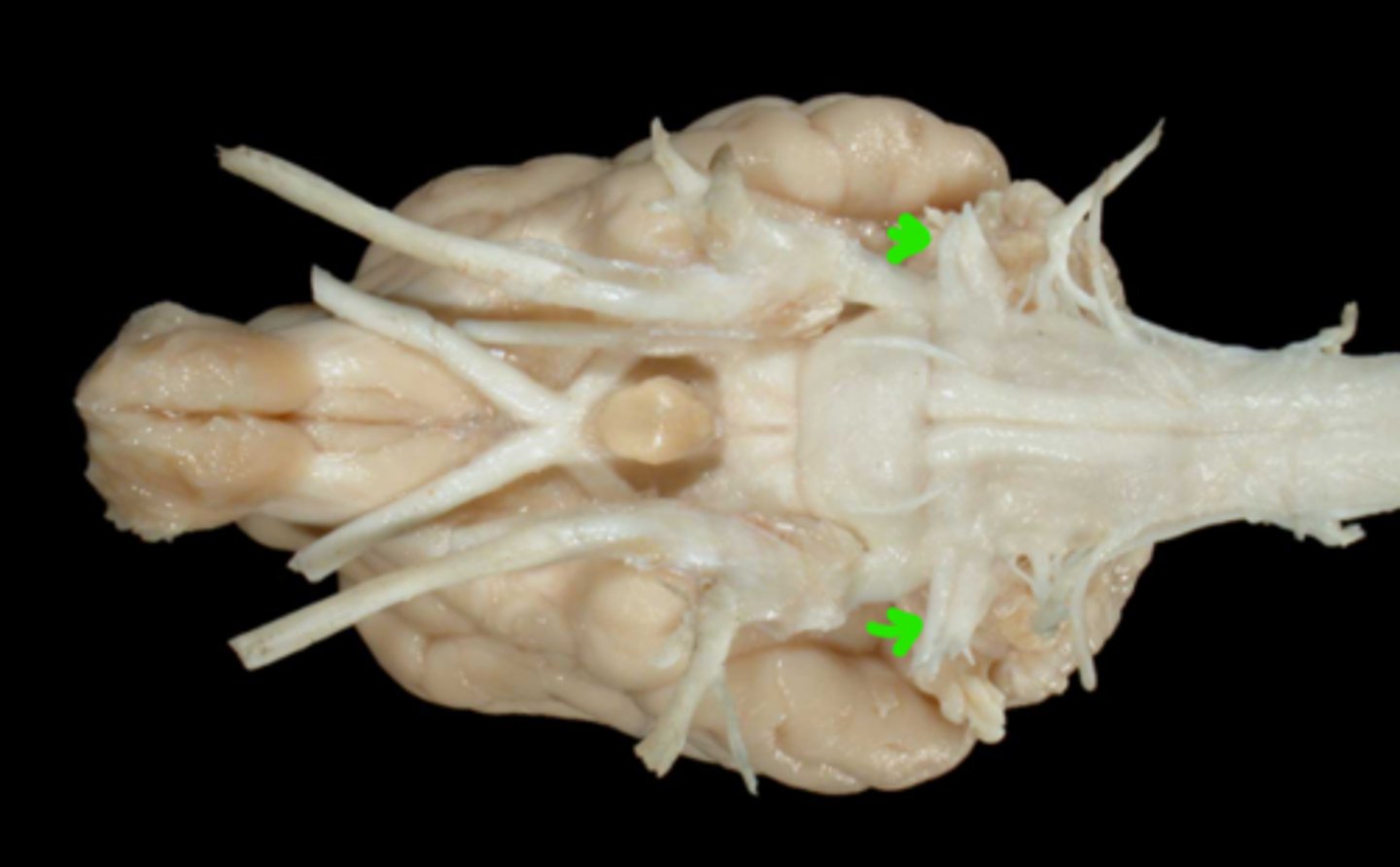
VII. Facial
This nerve enters the internal acoustic meatus, courses through the facial canal, and emerges from the stylomastoid foramen
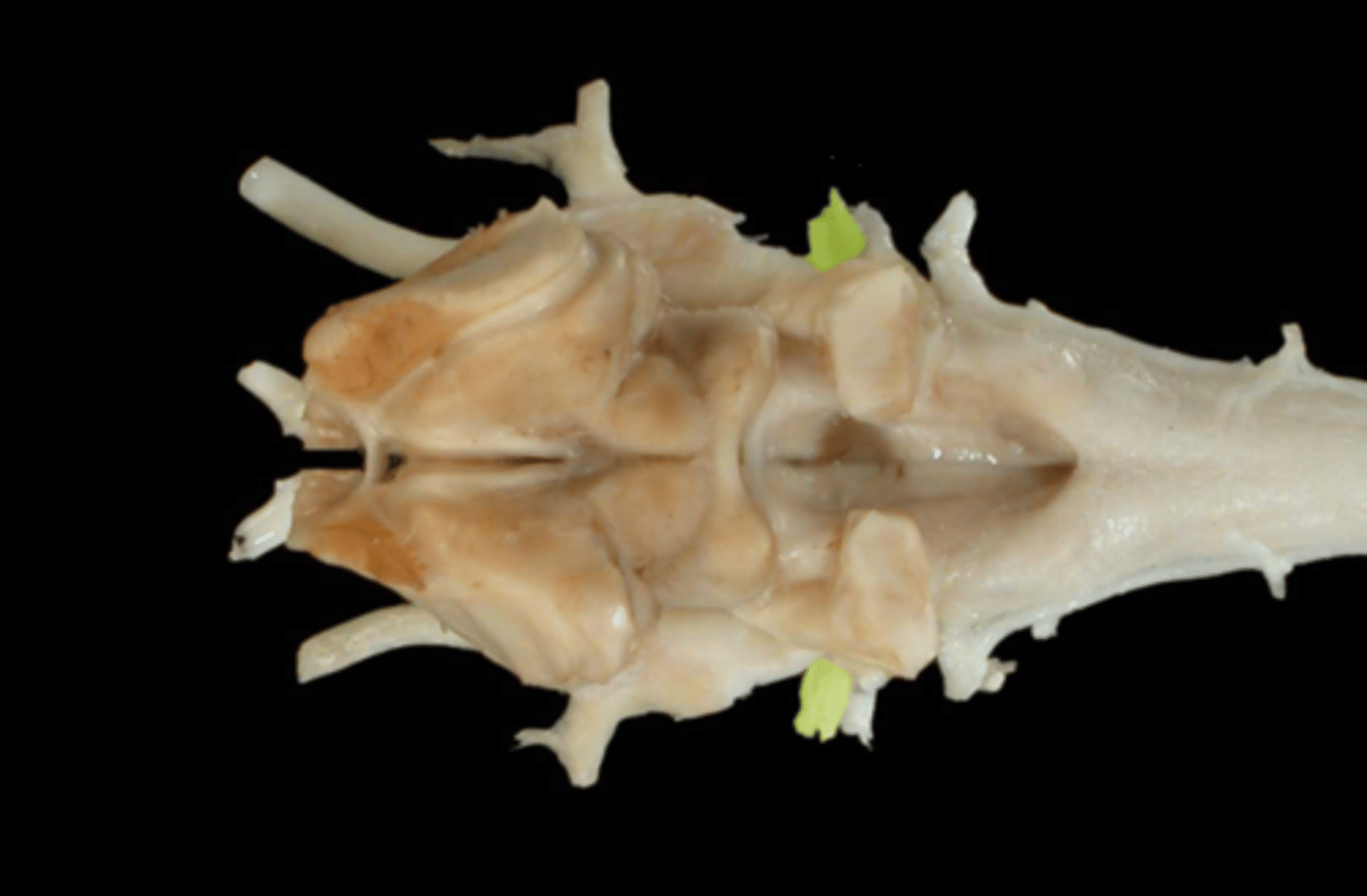
VII. Facial
This nerve enters the internal acoustic meatus, courses through the facial canal, and emerges from the stylomastoid foramen
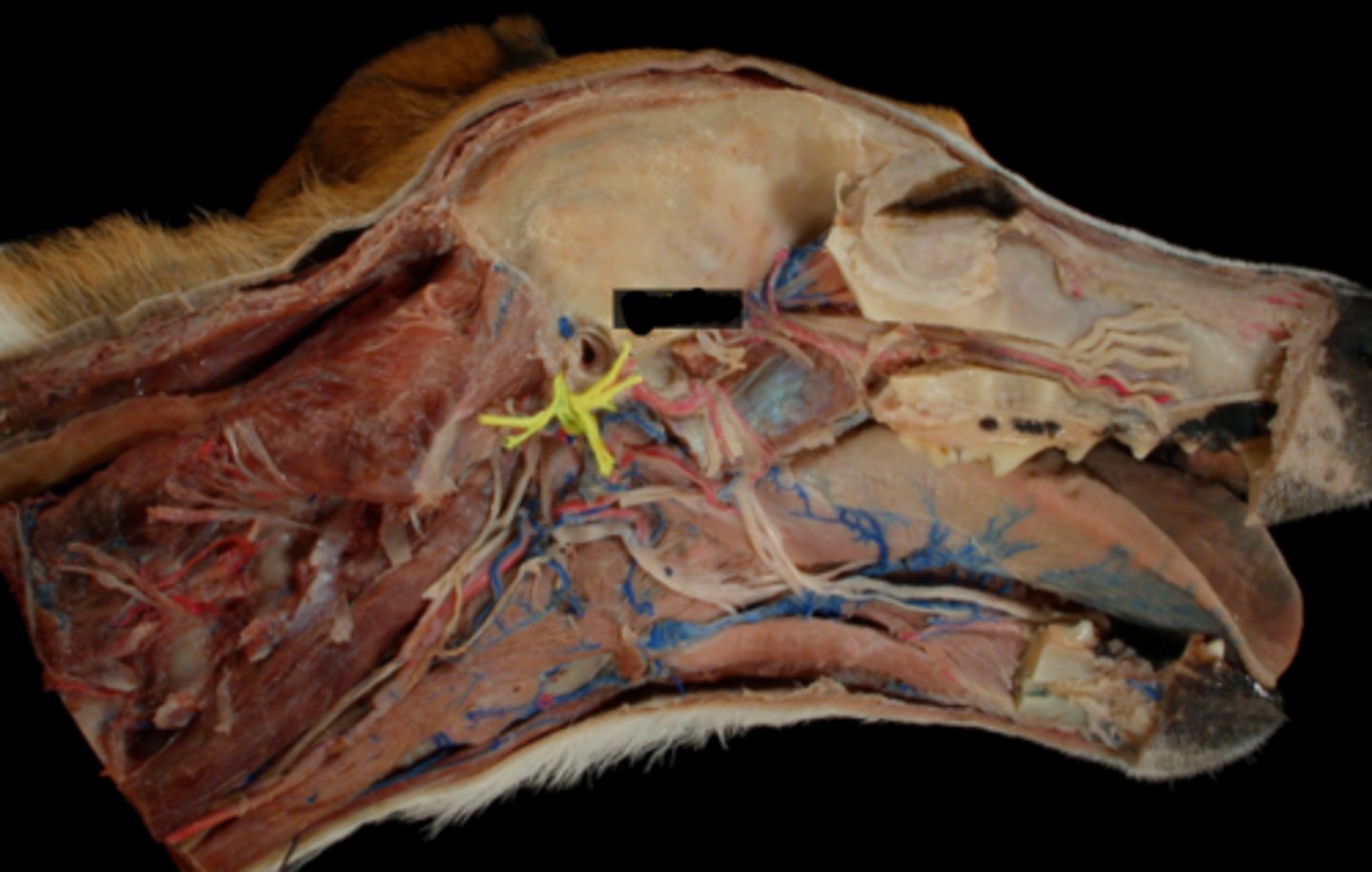
VIII. Vestibulocochlear
This nerve transmits impulses associated with equilibrium and hearing, has two branches, and courses through the internal acoustic meatus of the petrous temporal bone
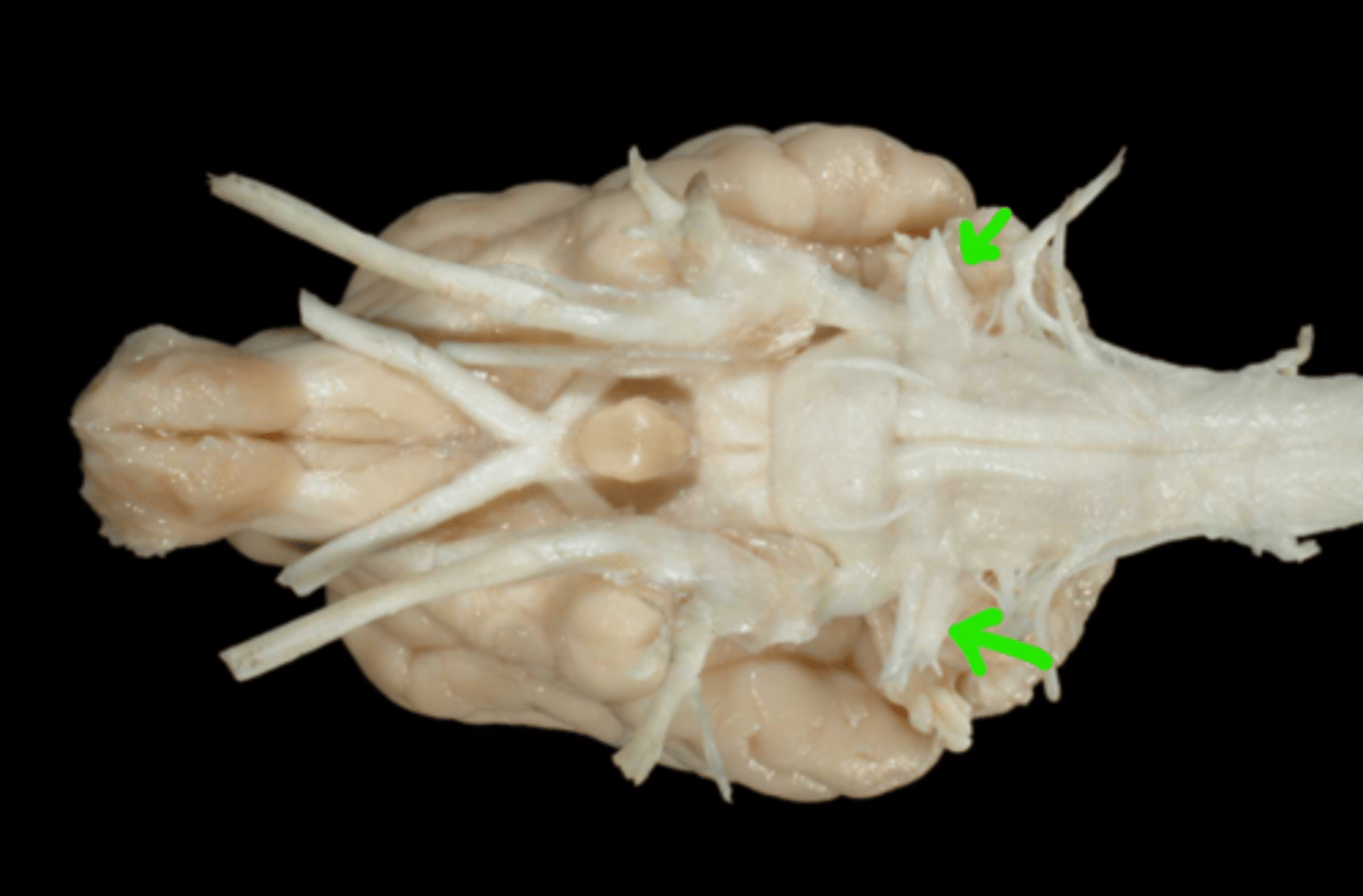
VIII. Vestibulocochlear
This nerve transmits impulses associated with equilibrium and hearing, has two branches, and courses through the internal acoustic meatus of the petrous temporal bone
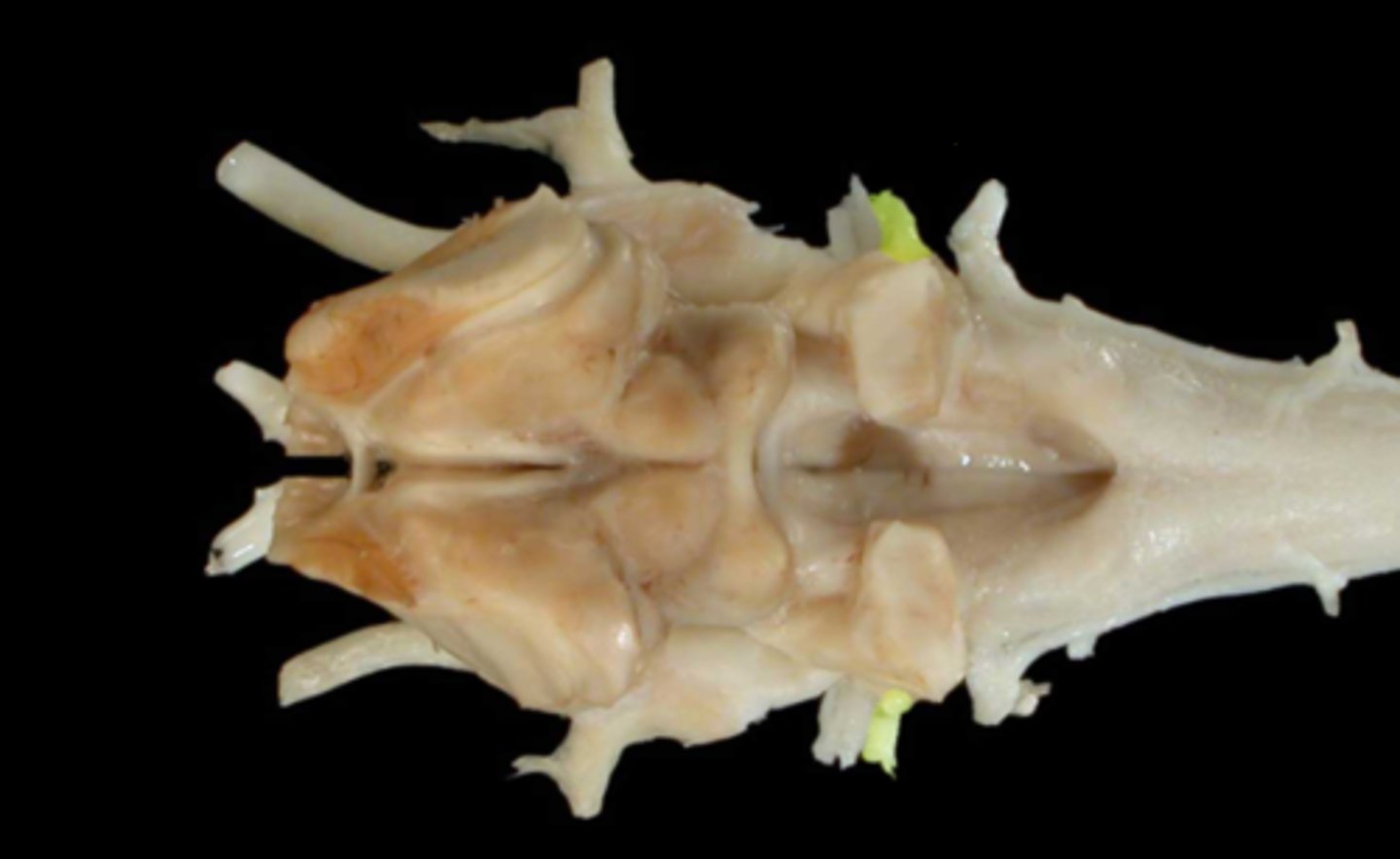
VIII. Vestibulocochlear
This nerve transmits impulses associated with equilibrium and hearing, has two branches, and courses through the internal acoustic meatus of the petrous temporal bone
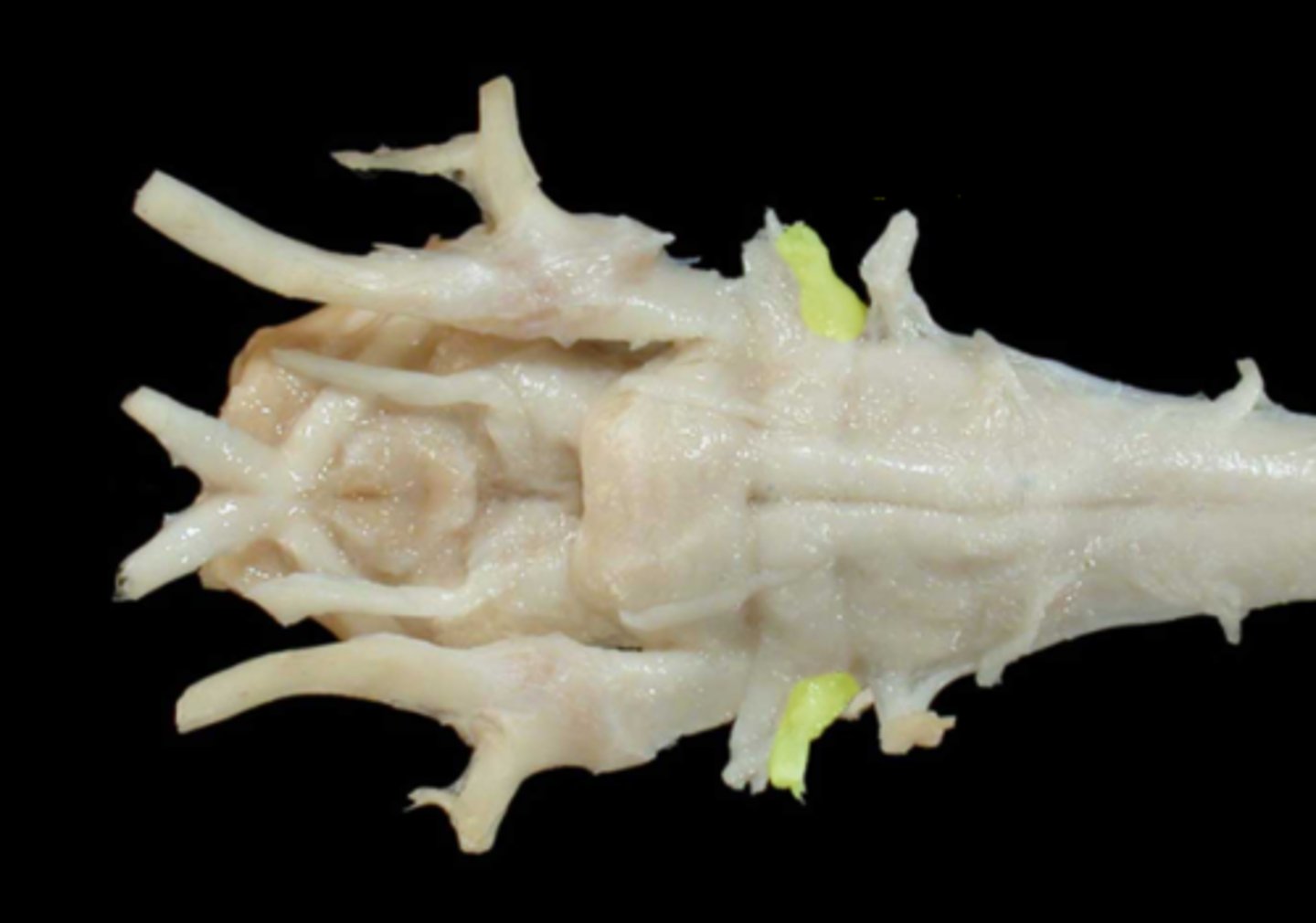
IX. Glossopharyngeal
-leaves via the jugular foramen & tympano-occipital fissure
-sensory: taste, pharyngeal mucosa, carotid sinus/body
-motor: stylopharyngeus m. , salivary glands
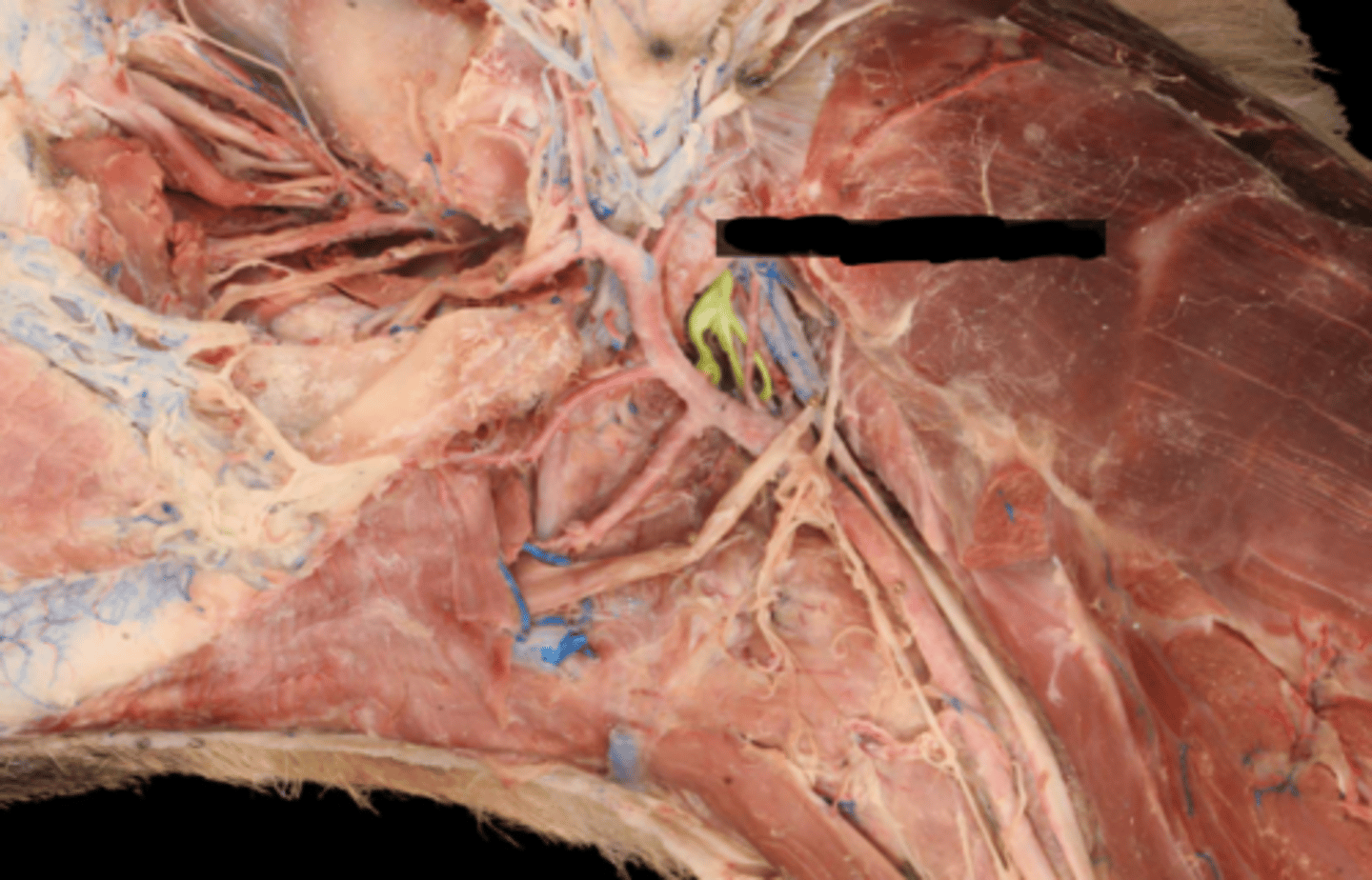
IX. Glossopharyngeal
-leaves via the jugular foramen & tympano-occipital fissure
-sensory: taste, pharyngeal mucosa, carotid sinus/body
-motor: stylopharyngeus m. , salivary glands
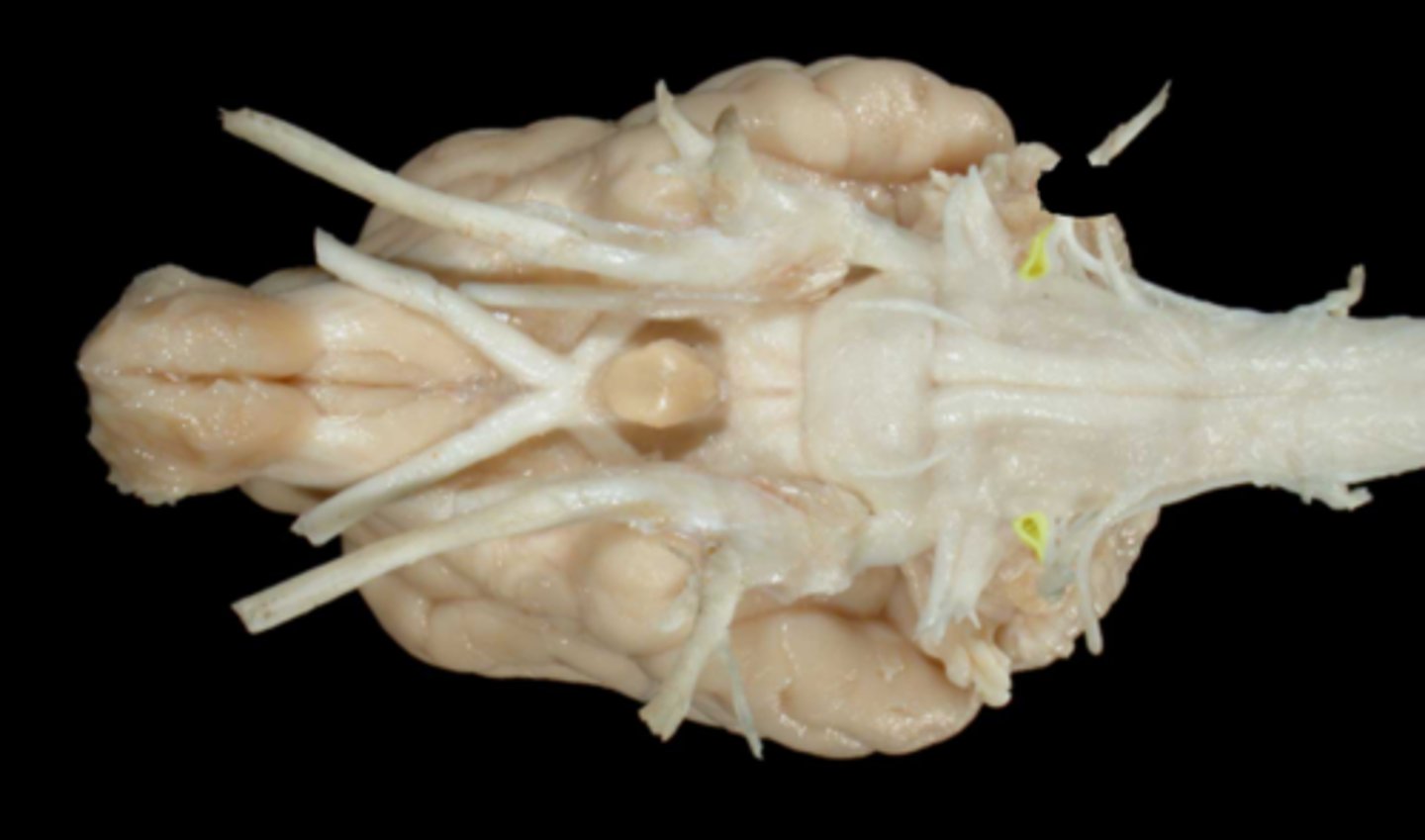
IX. Glossopharyngeal
-leaves via the jugular foramen & tympano-occipital fissure
-sensory: taste, pharyngeal mucosa, carotid sinus/body
-motor: stylopharyngeus m. , salivary glands
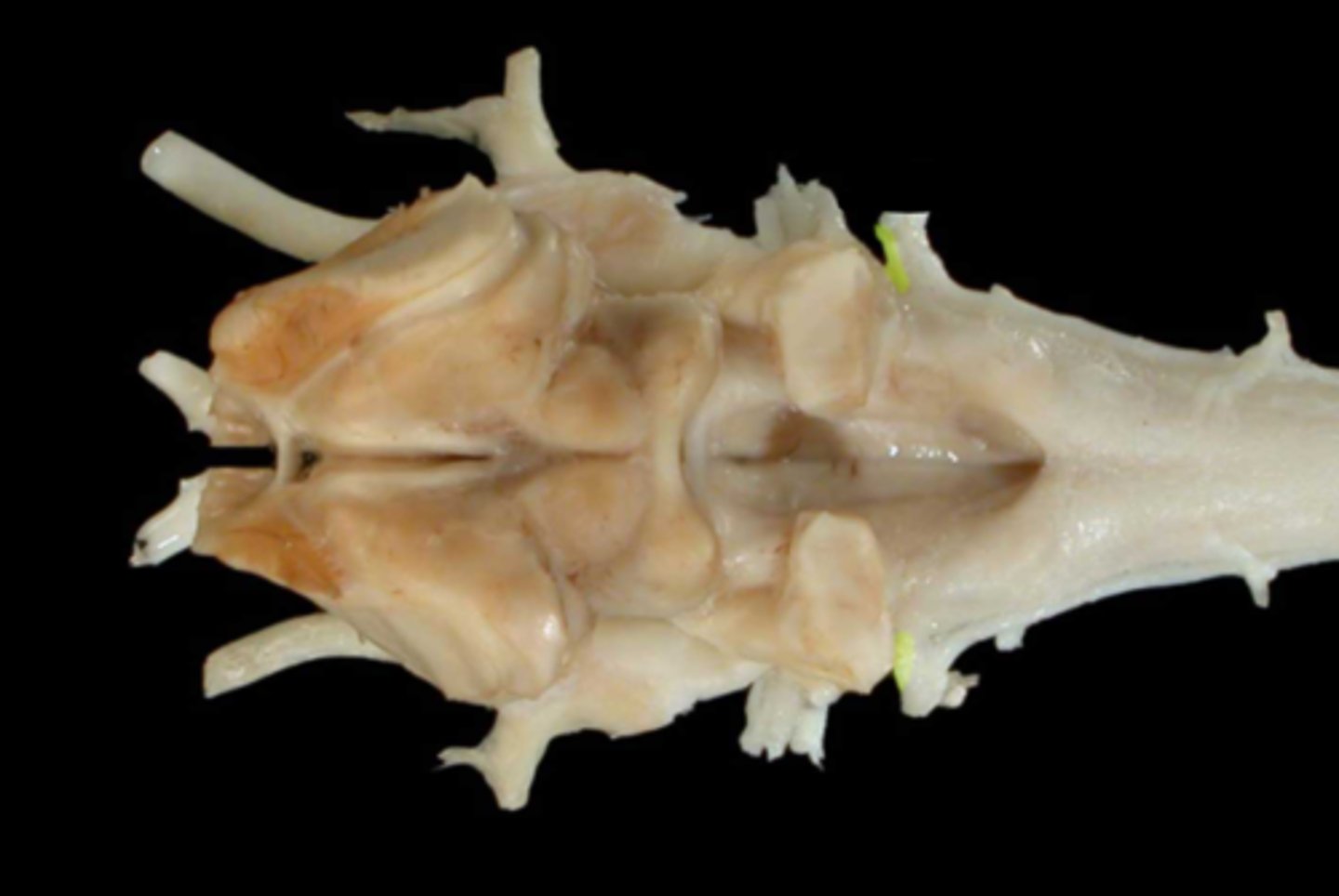
IX. Glossopharyngeal
-leaves via the jugular foramen & tympano-occipital fissure
-sensory: taste, pharyngeal mucosa, carotid sinus/body
-motor: stylopharyngeus m. , salivary glands
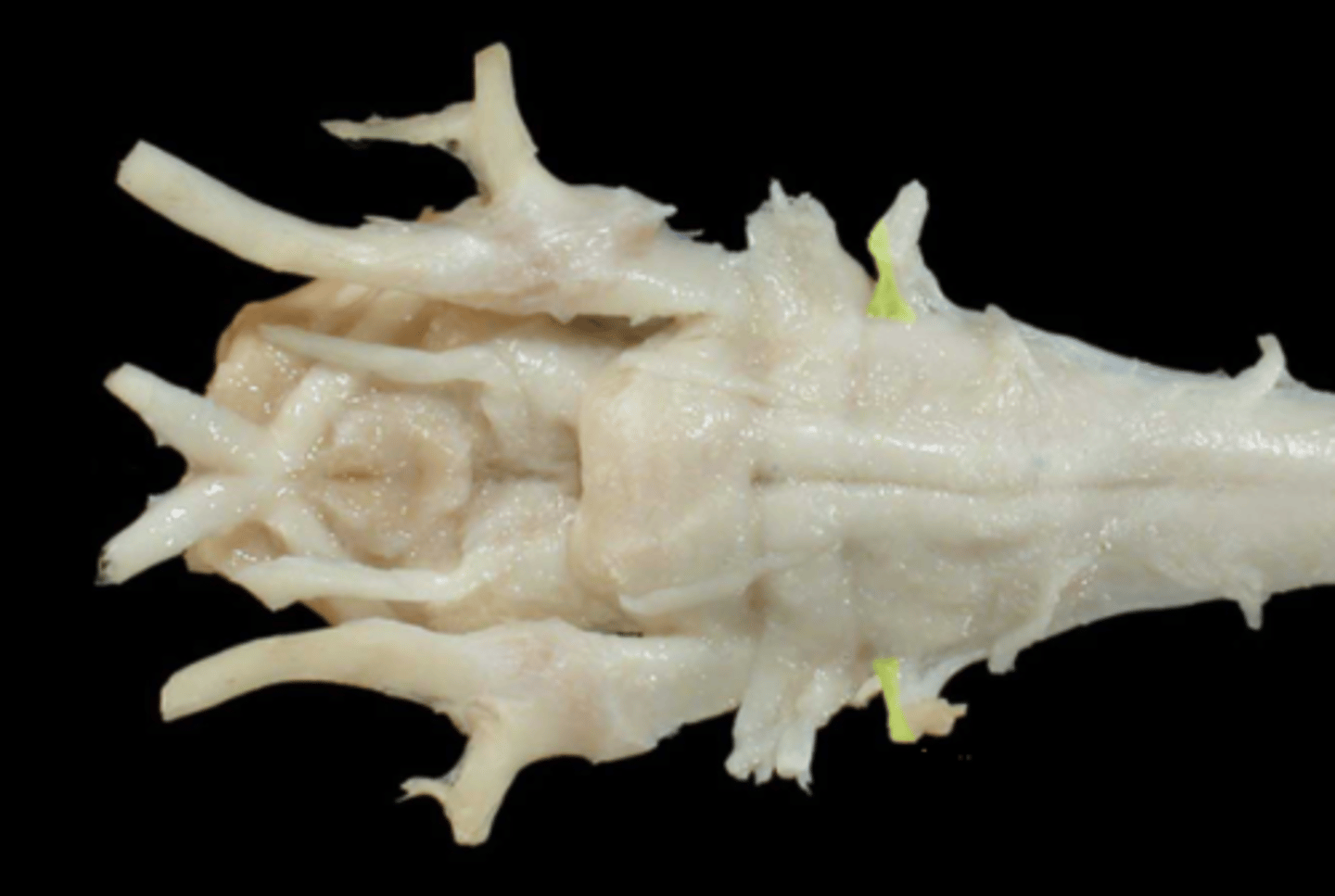
X. Vagus
-leaves via the jugular foramen & tympano-occipital fissure
-autonomic to thoracic & abdominal viscera
-somatic to pharyngeal muscles (swallowing)
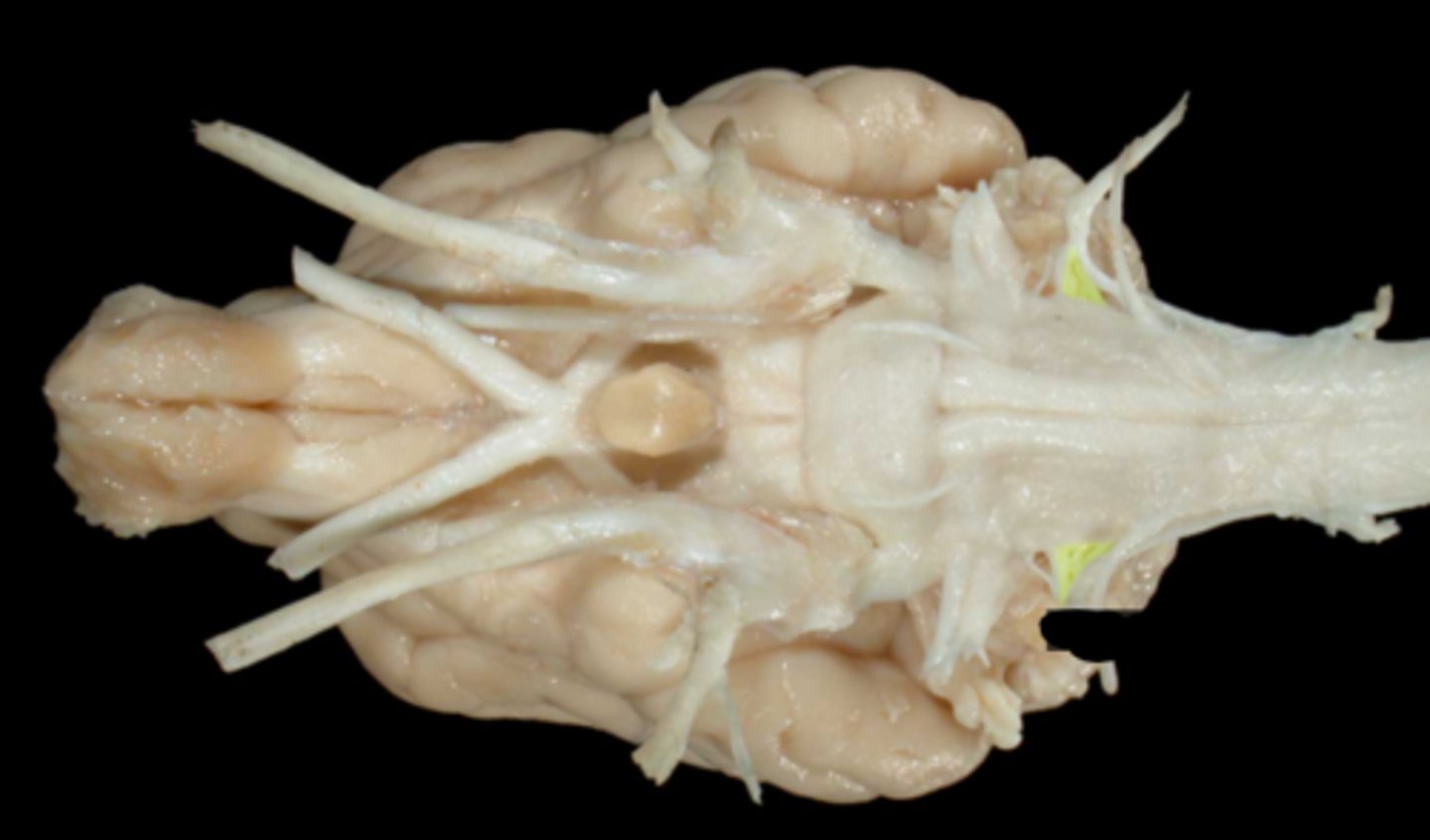
X. Vagus
-leaves via the jugular foramen & tympano-occipital fissure
-autonomic to thoracic & abdominal viscera
-somatic to pharyngeal muscles (swallowing)
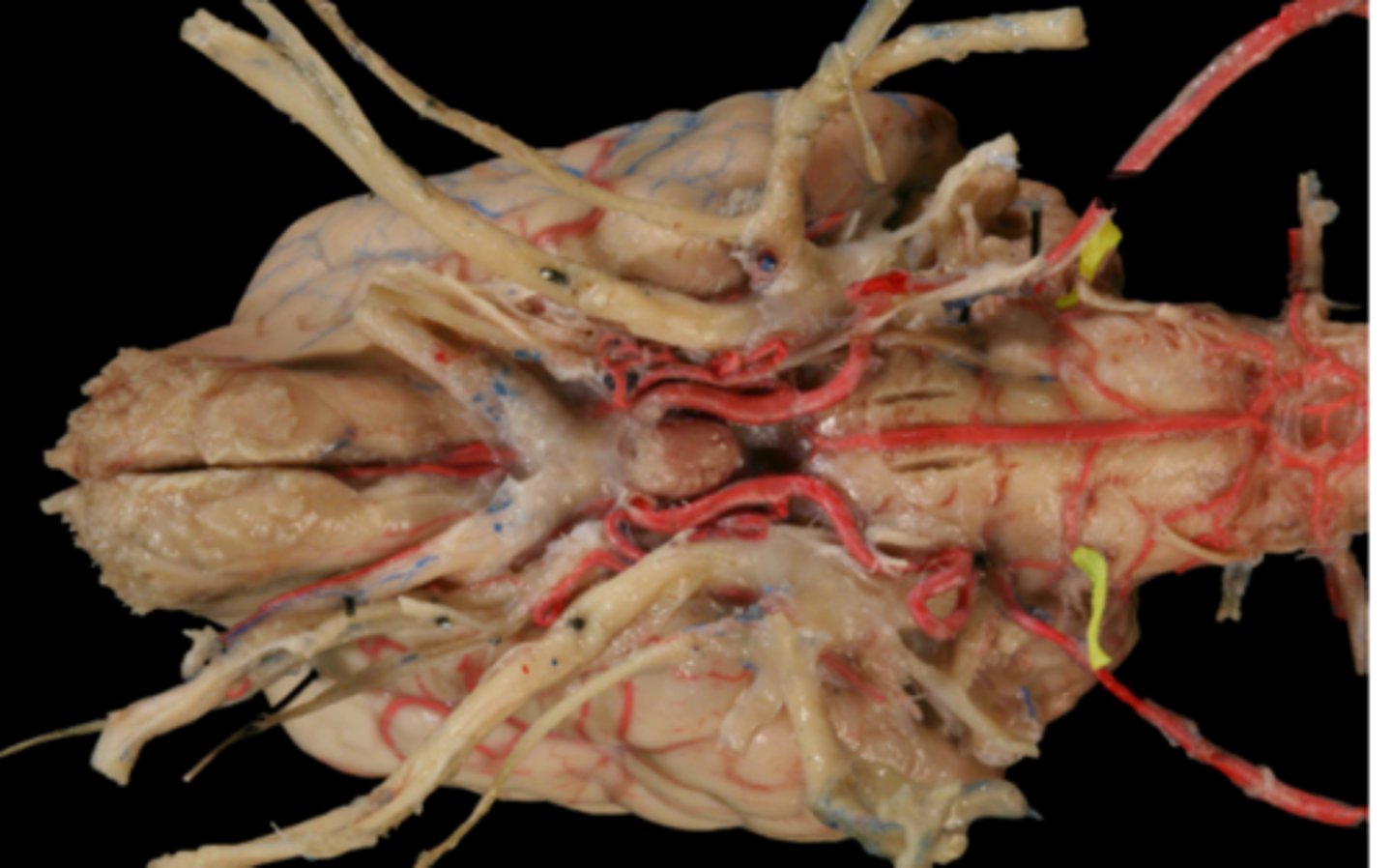
X. Vagus
-leaves via the jugular foramen & tympano-occipital fissure
-autonomic motor to thoracic & abdominal viscera
-somatic motor to pharyngeal muscles (swallowing)
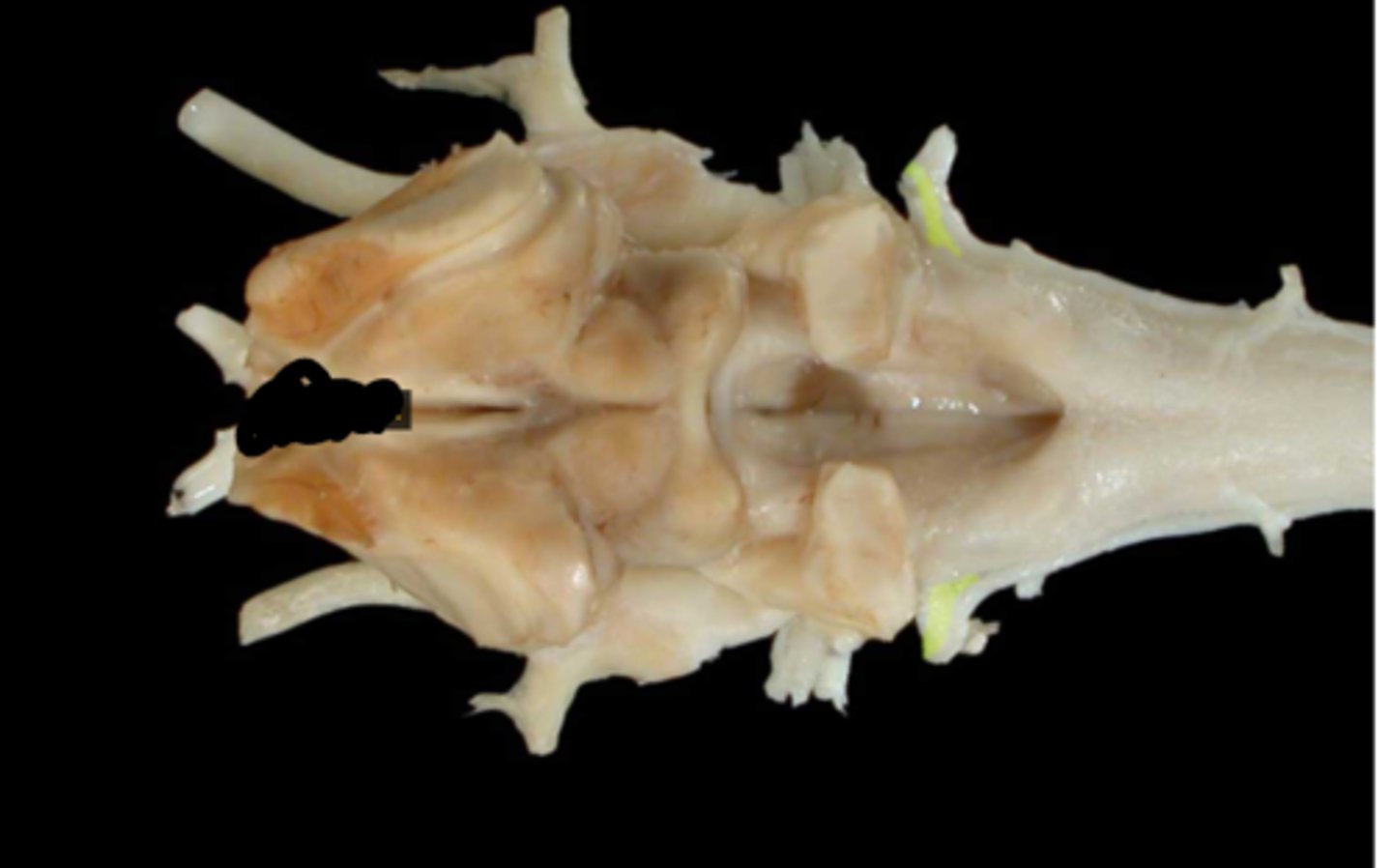
XI. Accessory
-leaves via the jugular foramen & tympano-occipital fissure
-primary motor to the muscles of the neck and larynx
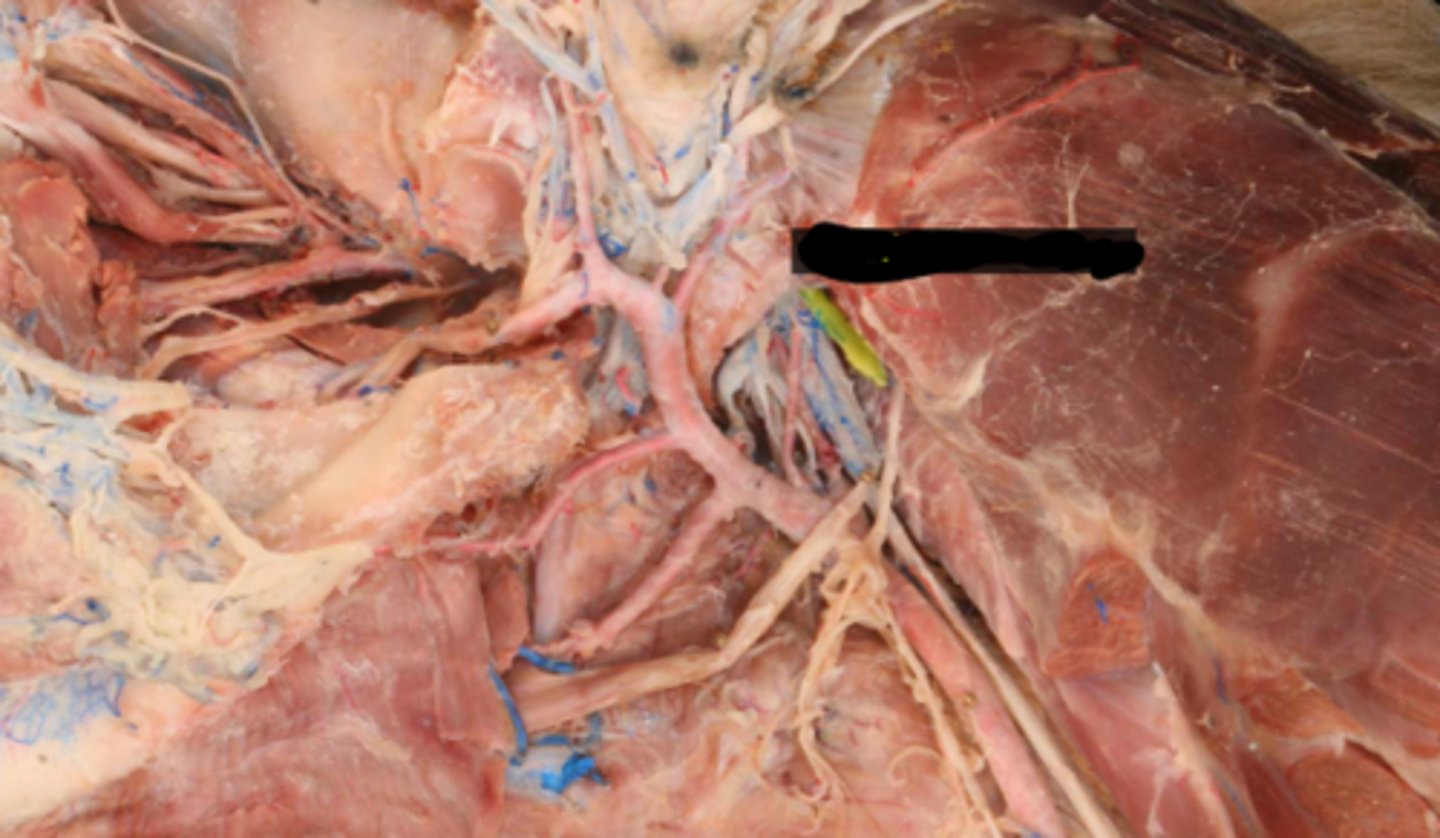
XI. Accessory
-leaves via the jugular foramen & tympano-occipital fissure
-primary motor to the muscles of the neck and larynx
XI. Accessory
-leaves via the jugular foramen & tympano-occipital fissure
-primary motor to the muscles of the neck and larynx
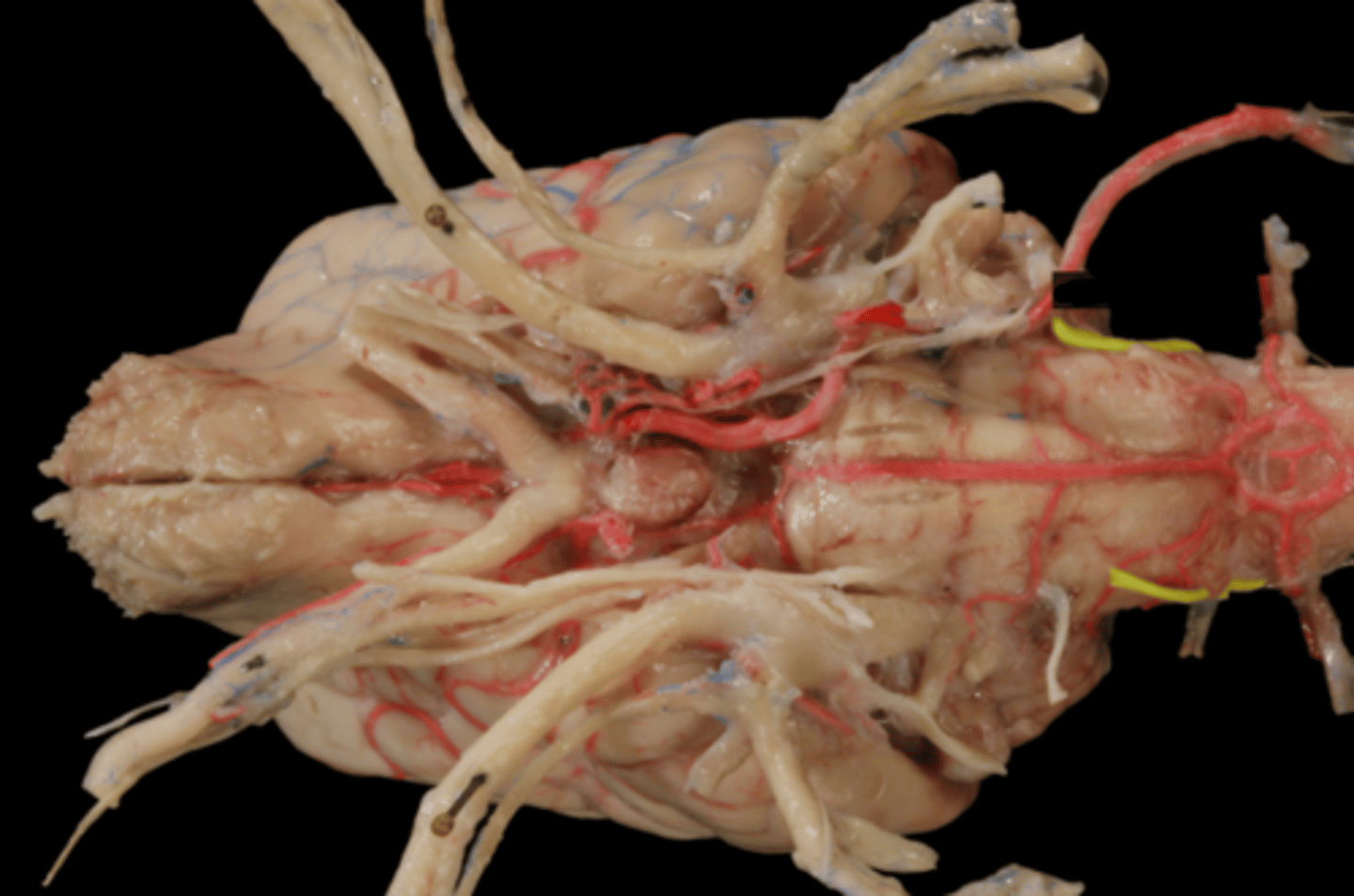
XI. Accessory
-leaves via the jugular foramen & tympano-occipital fissure
-primary motor to the muscles of the neck and larynx
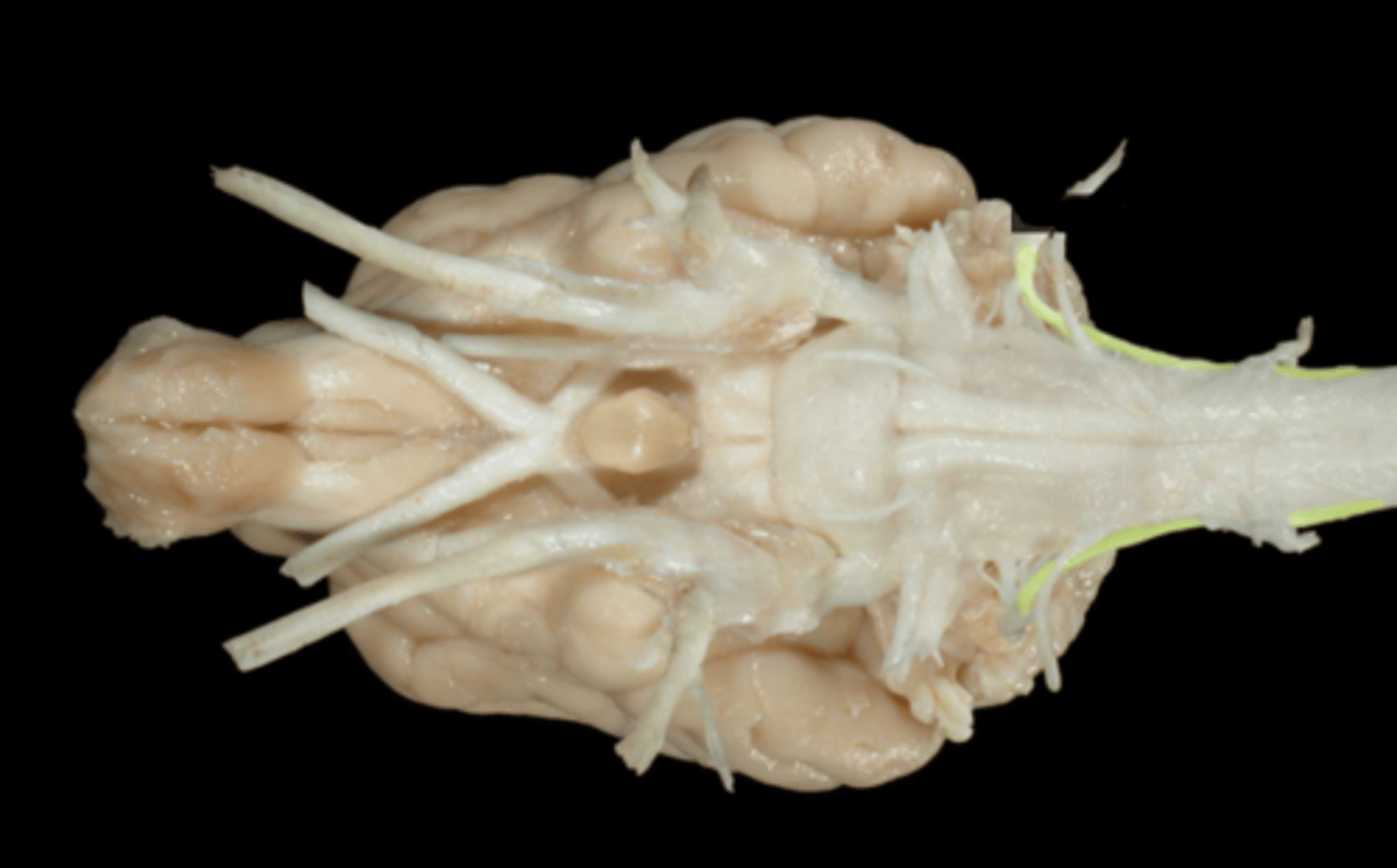
XI. Accessory
-leaves via the jugular foramen & tympano-occipital fissure
-primary motor to the muscles of the neck and larynx
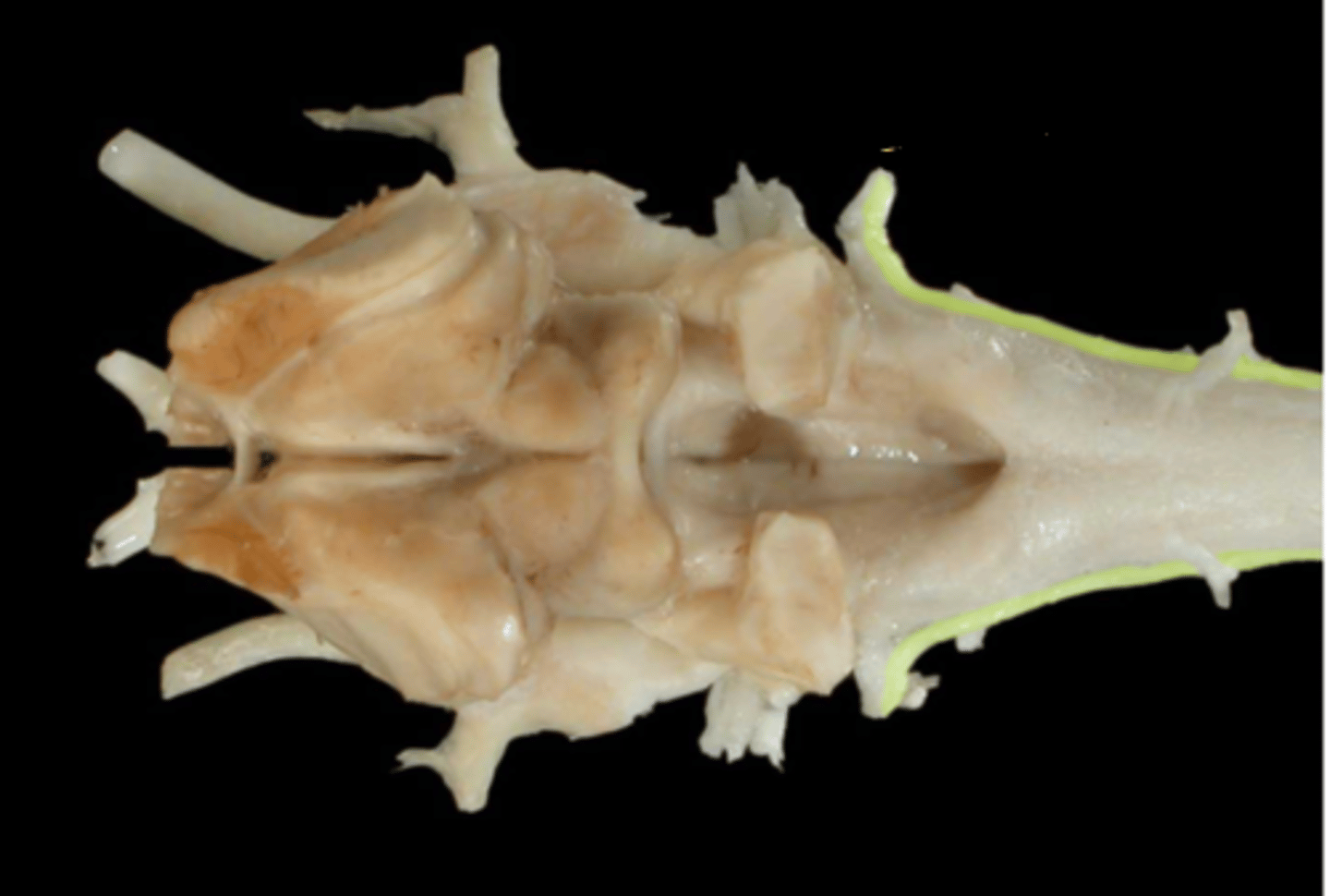
XI. Accessory
-leaves via the jugular foramen & tympano-occipital fissure
-primary motor to the muscles of the neck and larynx
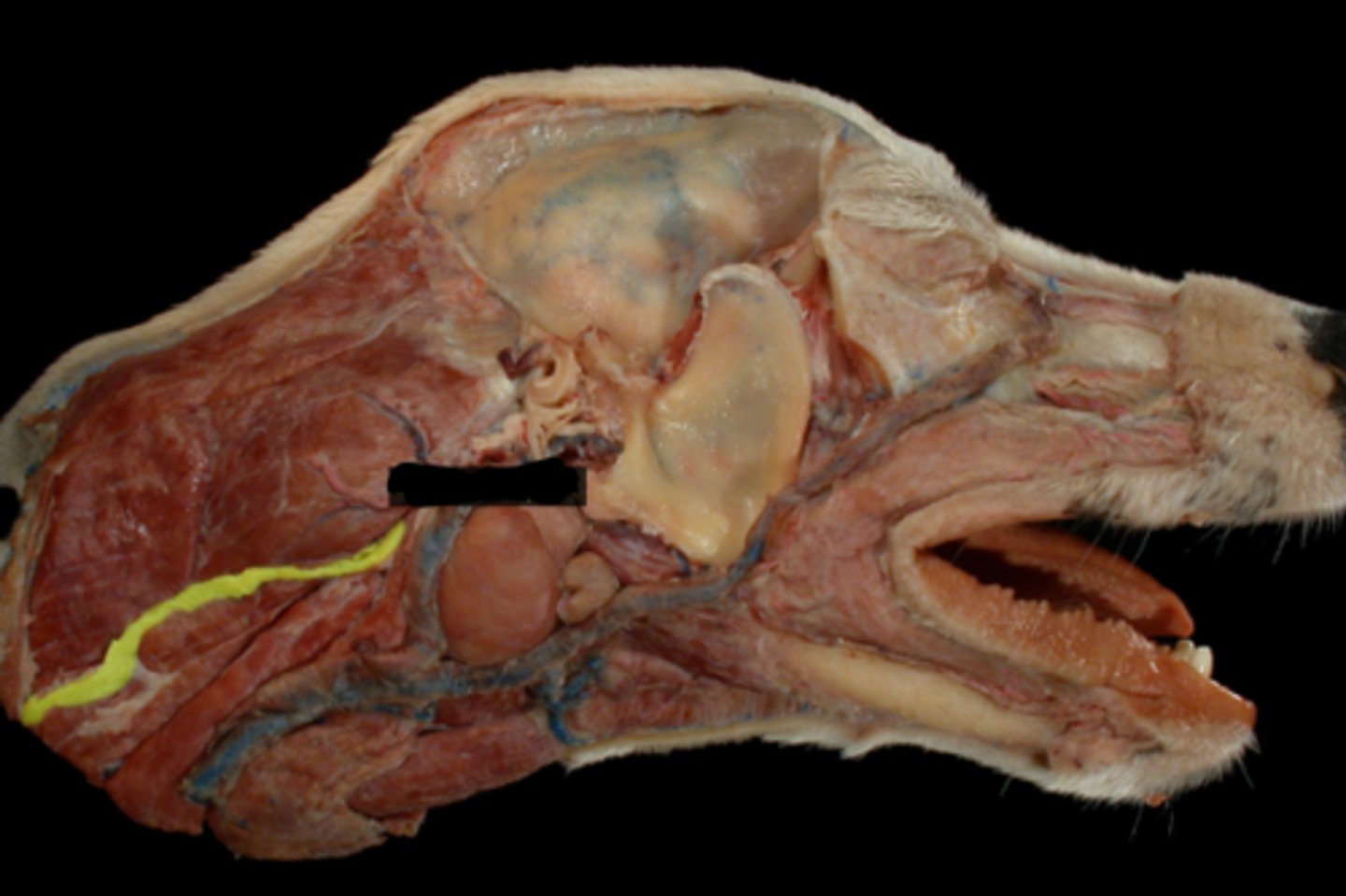
XII. Hypoglossal
-leaves via the jugular foramen & tympano-occipital fissure
-primarily motor to the muscles of the tongue
-leaves the cranial cavity via the hypoglossal foramen
-adjacent to lingual artery
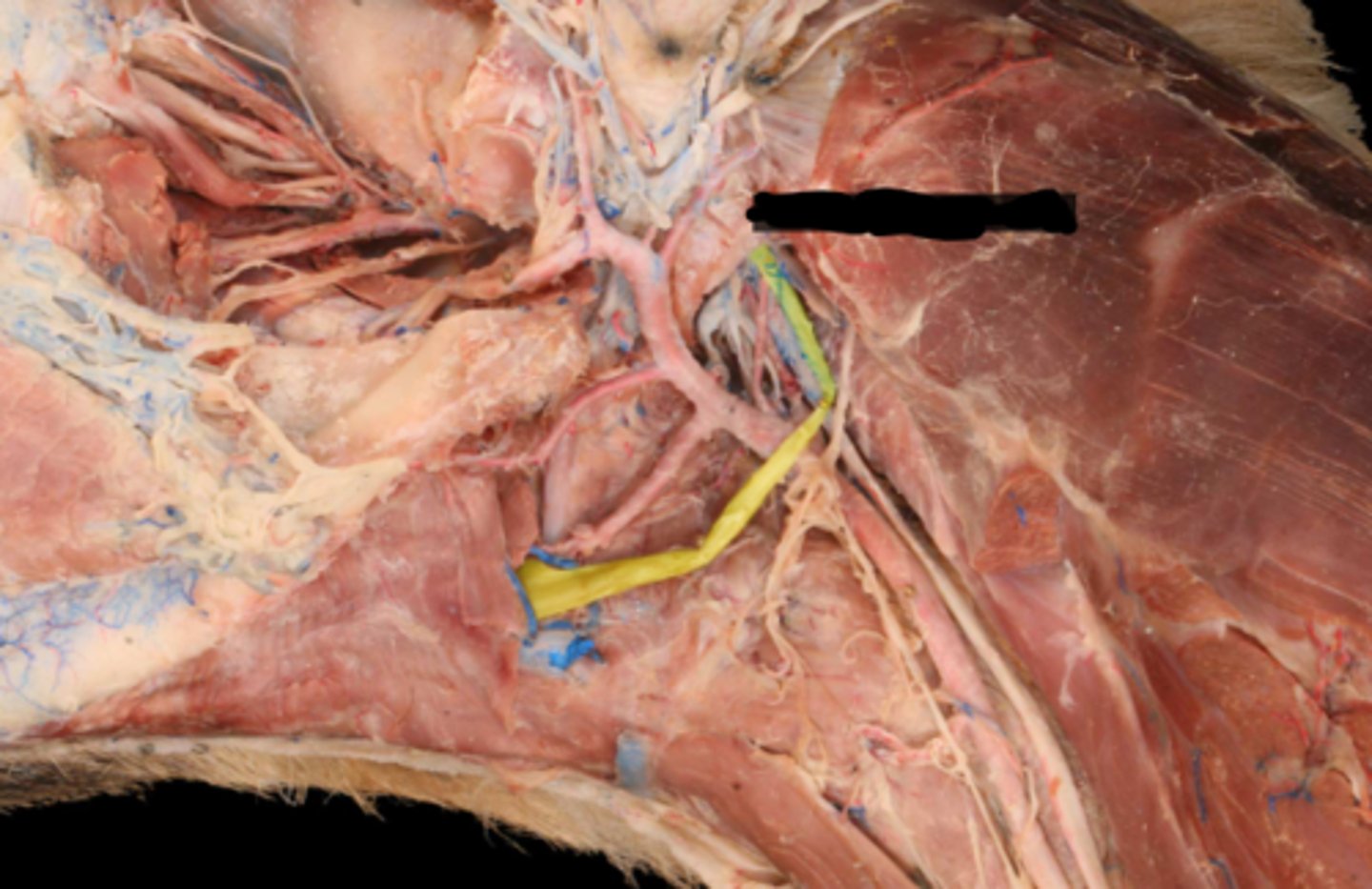
XII. Hypoglossal
-leaves via the jugular foramen & tympano-occipital fissure
-primarily motor to the muscles of the tongue
-leaves the cranial cavity via the hypoglossal foramen
-adjacent to lingual artery
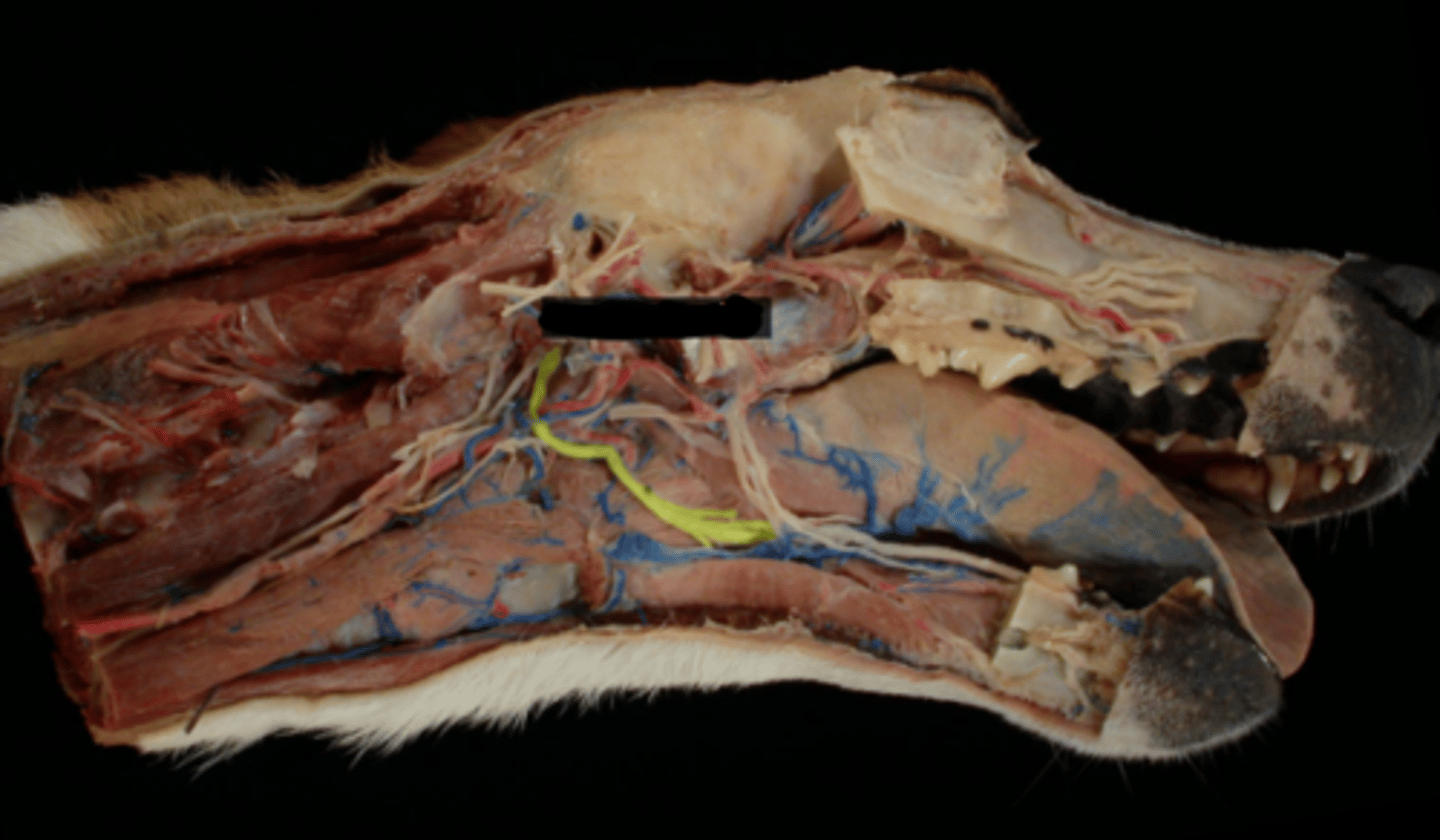
XII. Hypoglossal
-leaves via the jugular foramen & tympano-occipital fissure
-primarily motor to the muscles of the tongue
-leaves the cranial cavity via the hypoglossal foramen
-adjacent to lingual artery
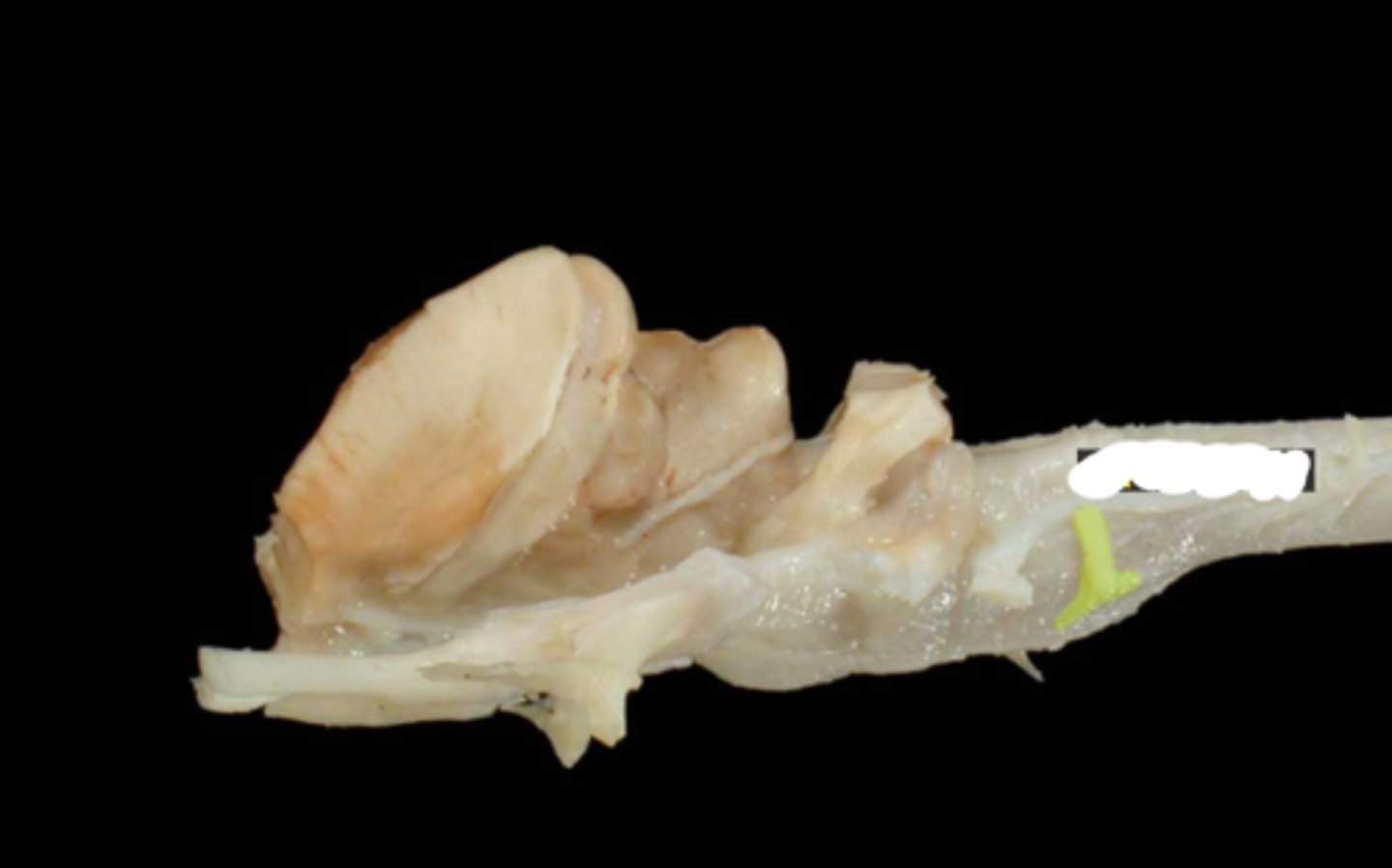
XII. Hypoglossal
-leaves via the jugular foramen & tympano-occipital fissure
-primarily motor to the muscles of the tongue
-leaves the cranial cavity via the hypoglossal foramen
-adjacent to lingual artery
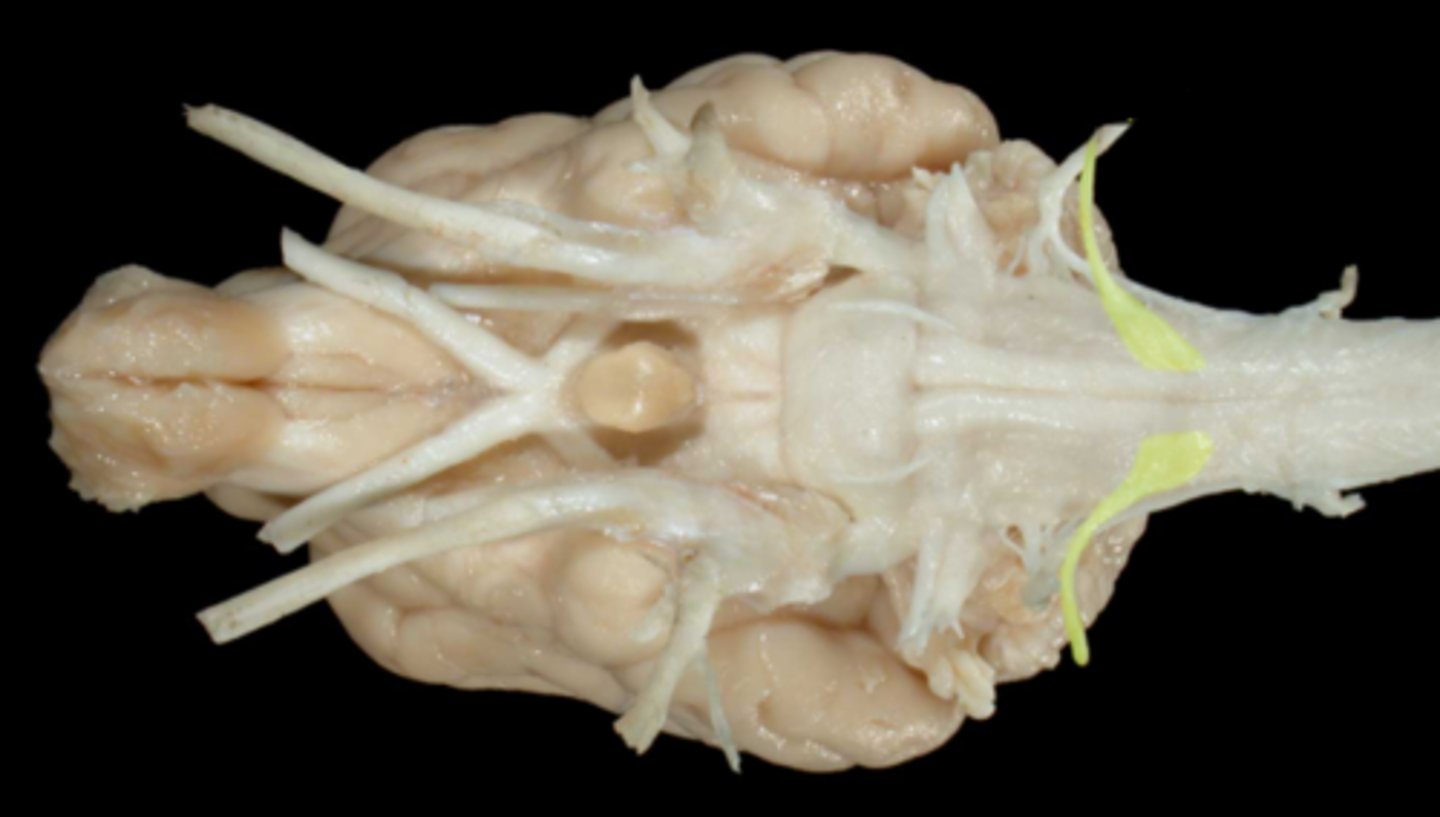
XII. Hypoglossal
-leaves via the jugular foramen & tympano-occipital fissure
-primarily motor to the muscles of the tongue
-leaves the cranial cavity via the hypoglossal foramen
-adjacent to lingual artery
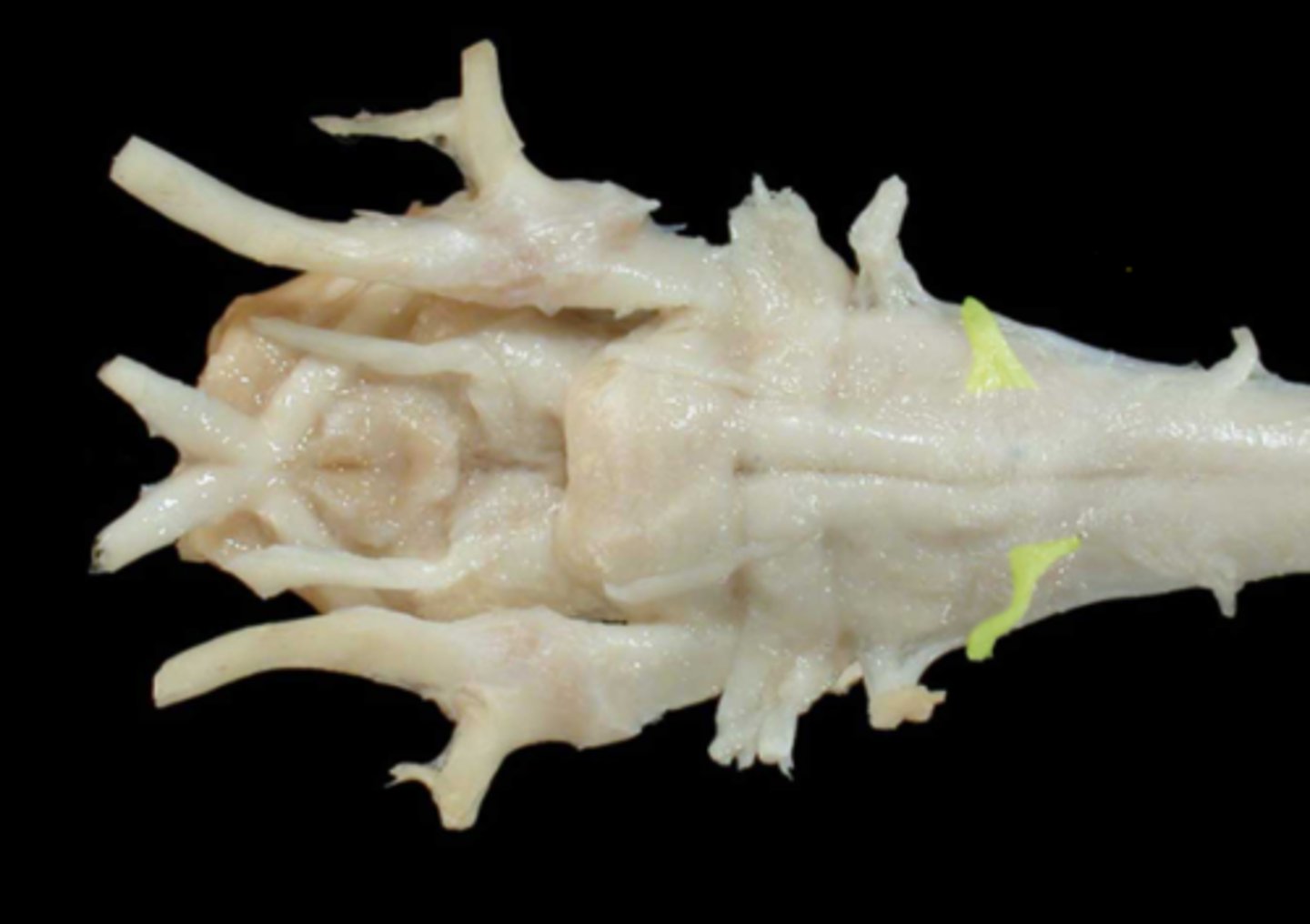
XII. Hypoglossal
-leaves via the jugular foramen & tympano-occipital fissure
-primarily motor to the muscles of the tongue
-leaves the cranial cavity via the hypoglossal foramen
-adjacent to lingual artery
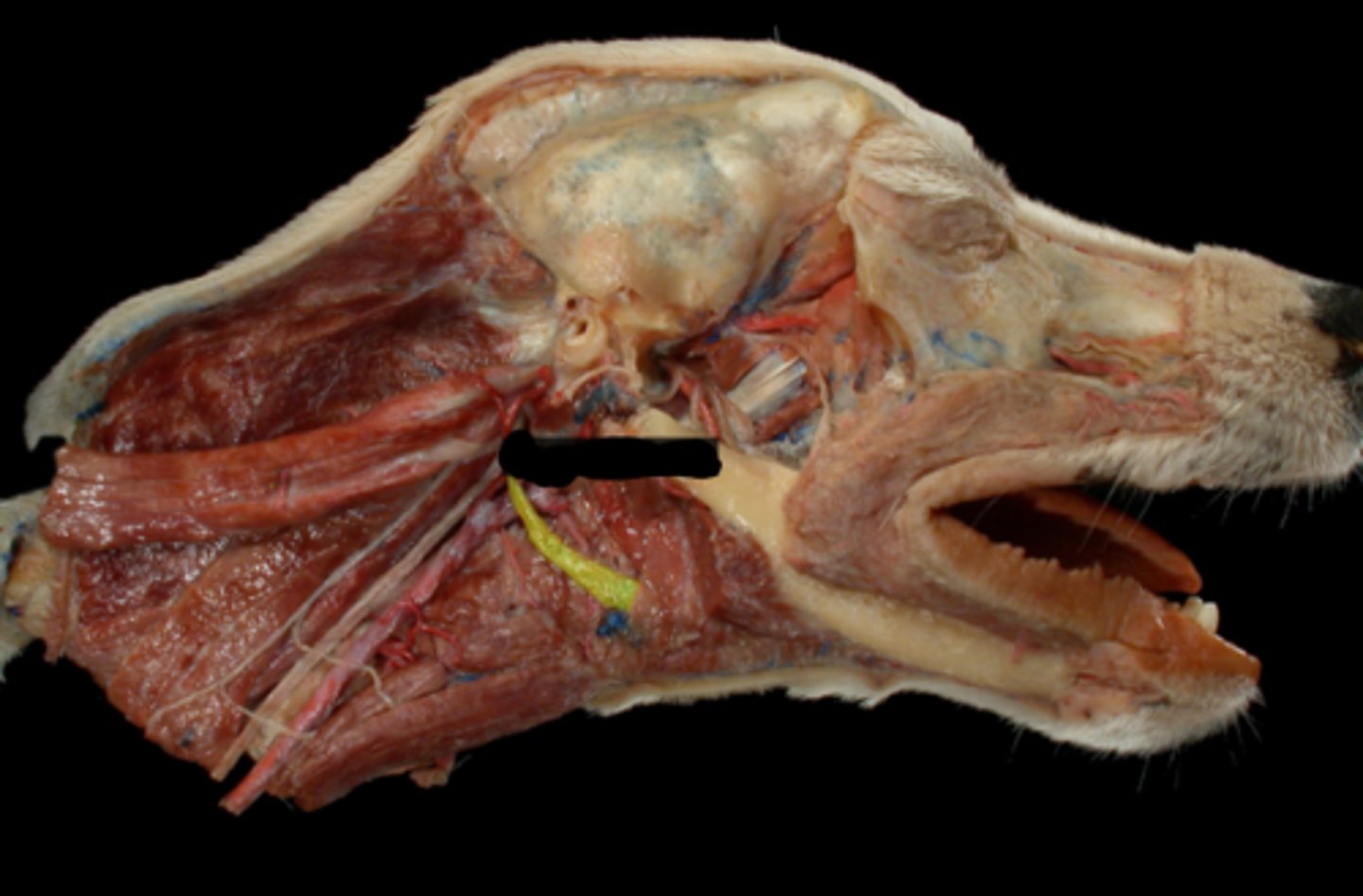
XII. Hypoglossal
-leaves via the jugular foramen & tympano-occipital fissure
-primarily motor to the muscles of the tongue
-leaves the cranial cavity via the hypoglossal foramen
-adjacent to lingual artery
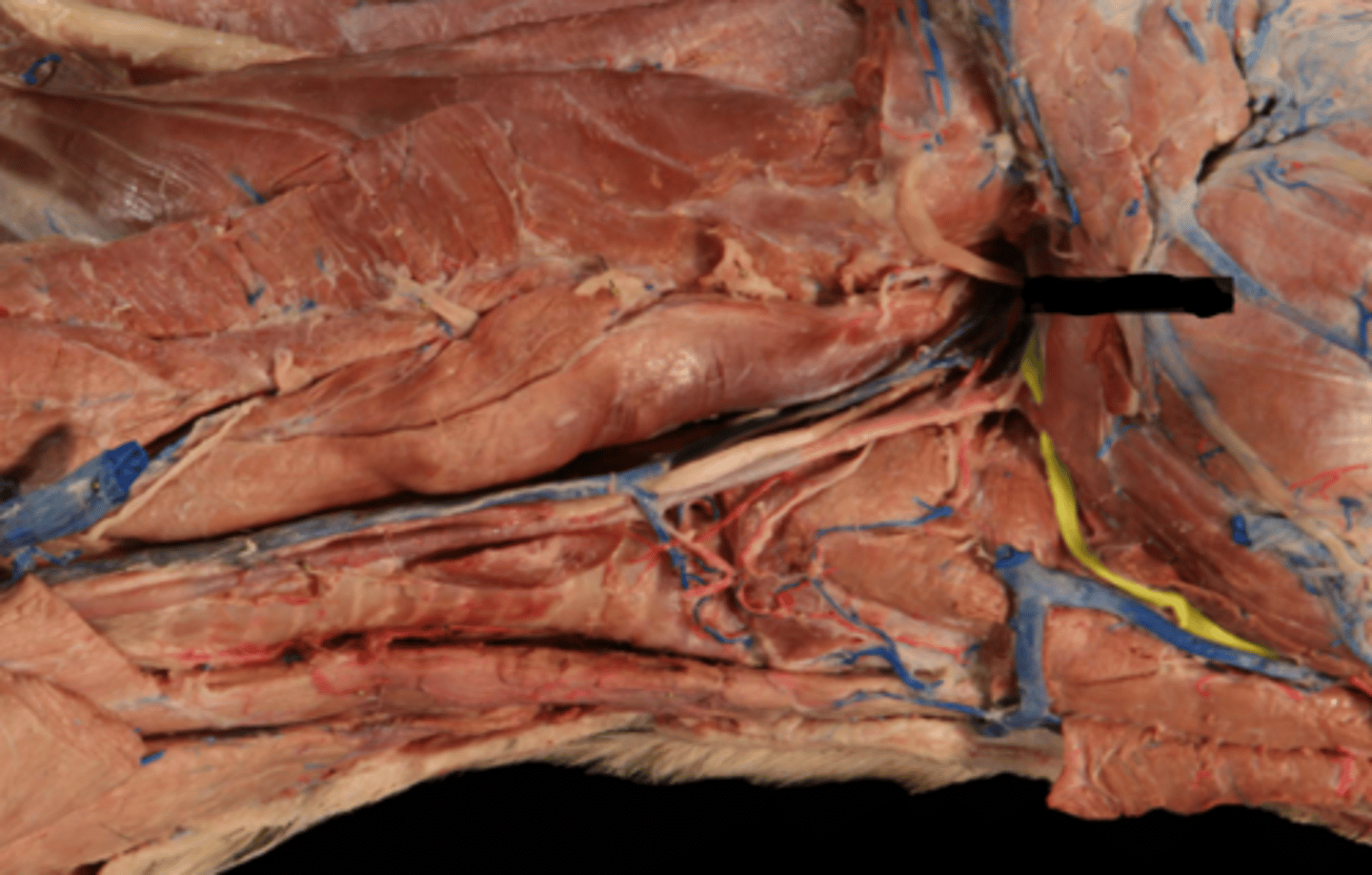
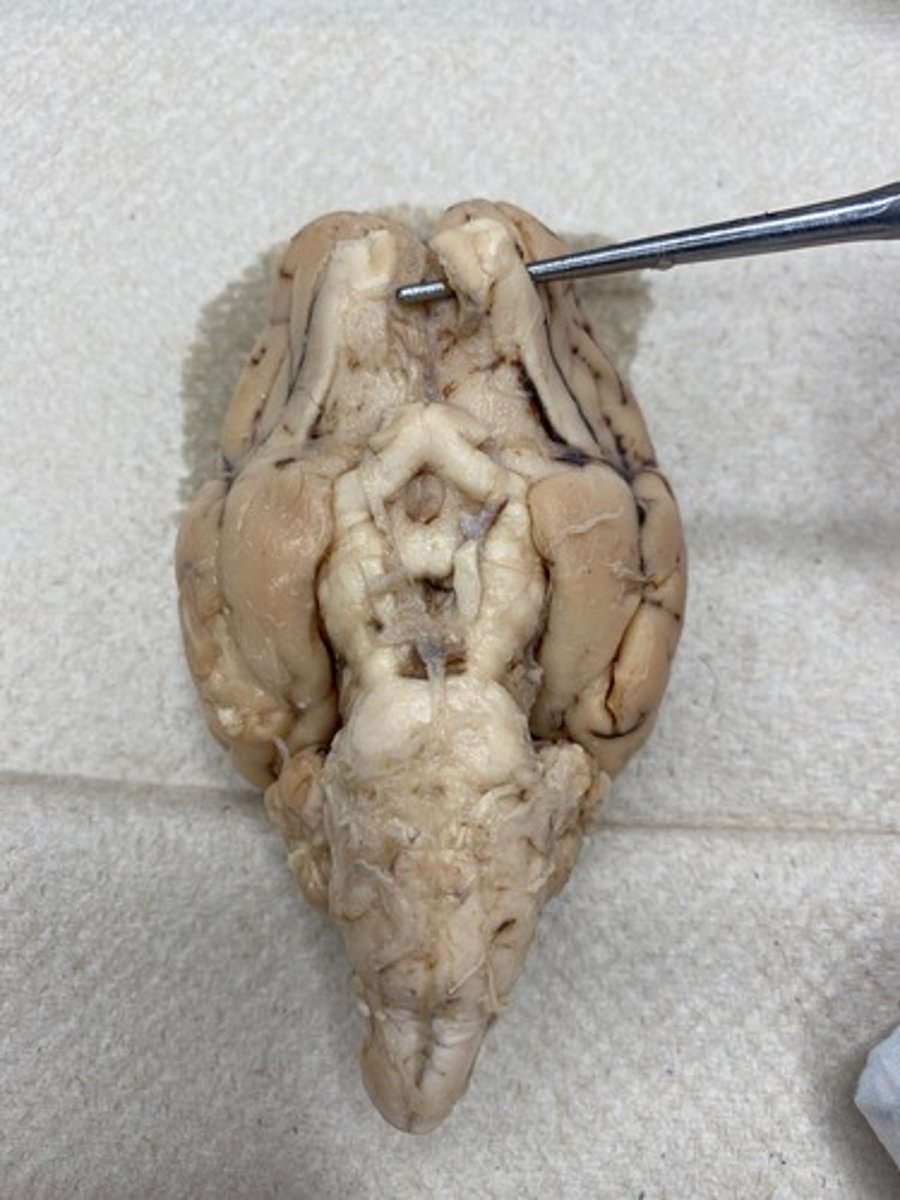
CN II (Optic)
Optic canal —> periorbita
CN III (Oculomotor)
Orbital fissure —> periorbita
CN IV (Trochlear)
Orbital fissure —> periorbita
CN V.1 (Ophthalmic)
Orbital fissure —> periorbita
CN VI (Abducent)
Orbital fissure —> periorbita
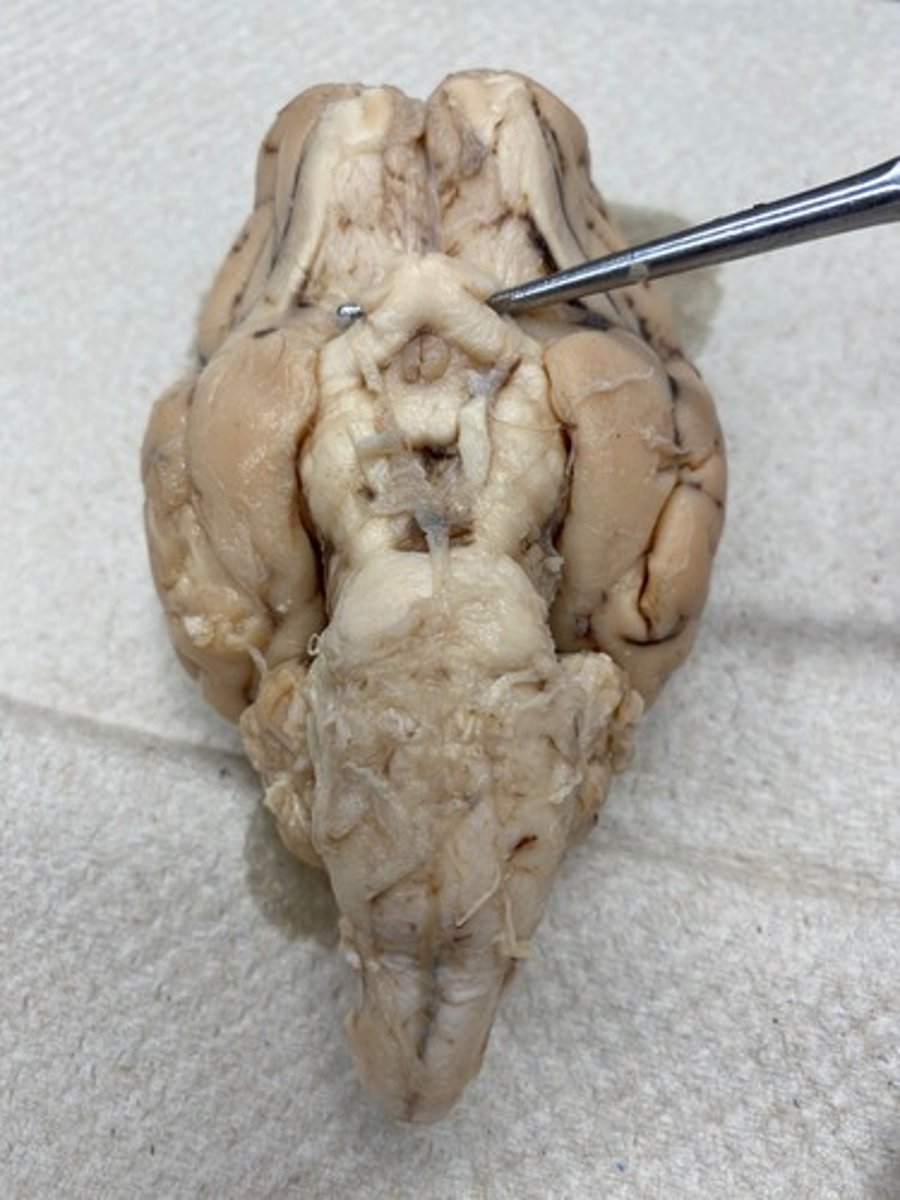
CN V.2 (Maxillary)
Round foramen —> rostrum alar canal —> maxillary foramen —> infraorbital foramen
CN V.3 (Mandibular)
Oval foramen & branches off
CN VII (Facial)
Internal acoustic meatus —> stylomastoid foramen
CN VIII (Vestibulocochlear)
Stays in internal acoustic meatus
CN IX (Glossopharyngeal)
Jugular foramen —> tympano-occipital fissure
CN X (Vagus)
Jugular foramen —> tympano-occipital fissure
CN XI (Accessory)
Jugular foramen —> tympano-occipital fissure