geo lab final
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/114
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 10:20 PM on 11/29/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
115 Terms
1
New cards
imperial system
in the US, we use the ______________ with units such as feet, miles, and degrees F
2
New cards
2 feet
convert 24 inches to feet

3
New cards
distance/time
rate=
4
New cards
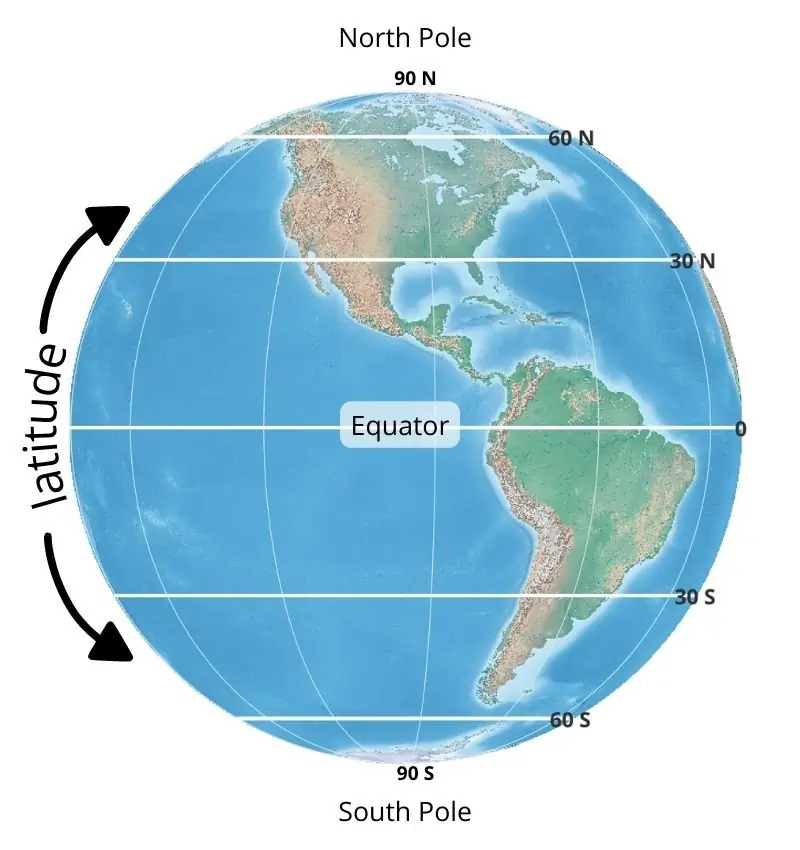
latitude
run horizontally; measure distance north or south of the equator
5
New cards
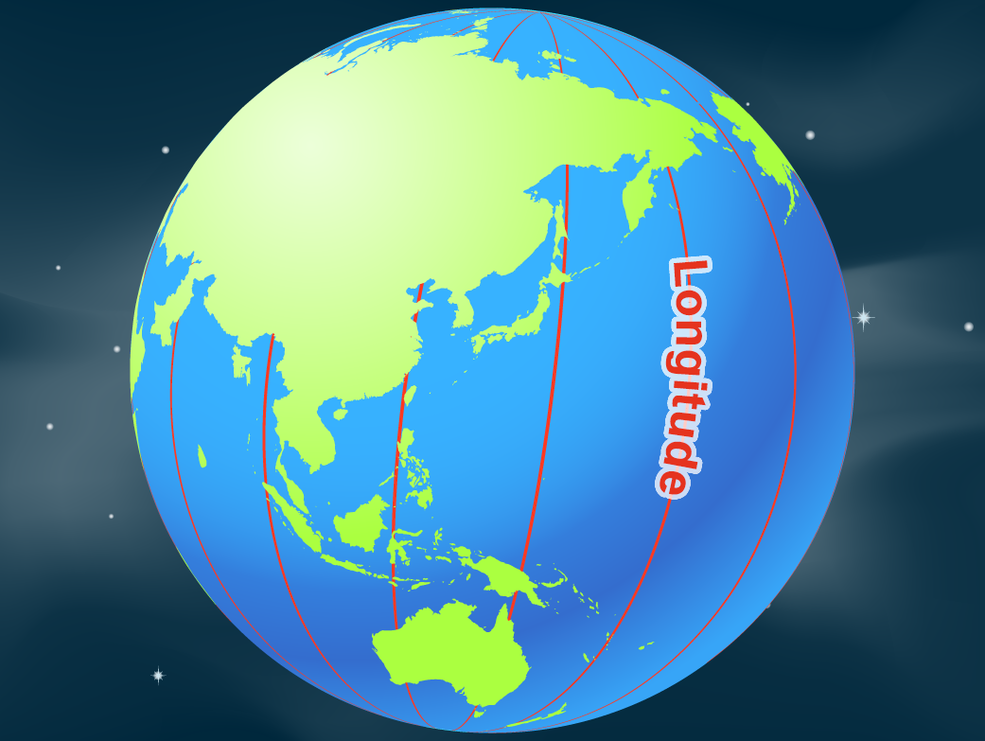
longitude
run vertically; measure distance east or west of the prime meridian
6
New cards
latitude and longitude
often used to form coordinates that describe locations on the surface of the earth
7
New cards
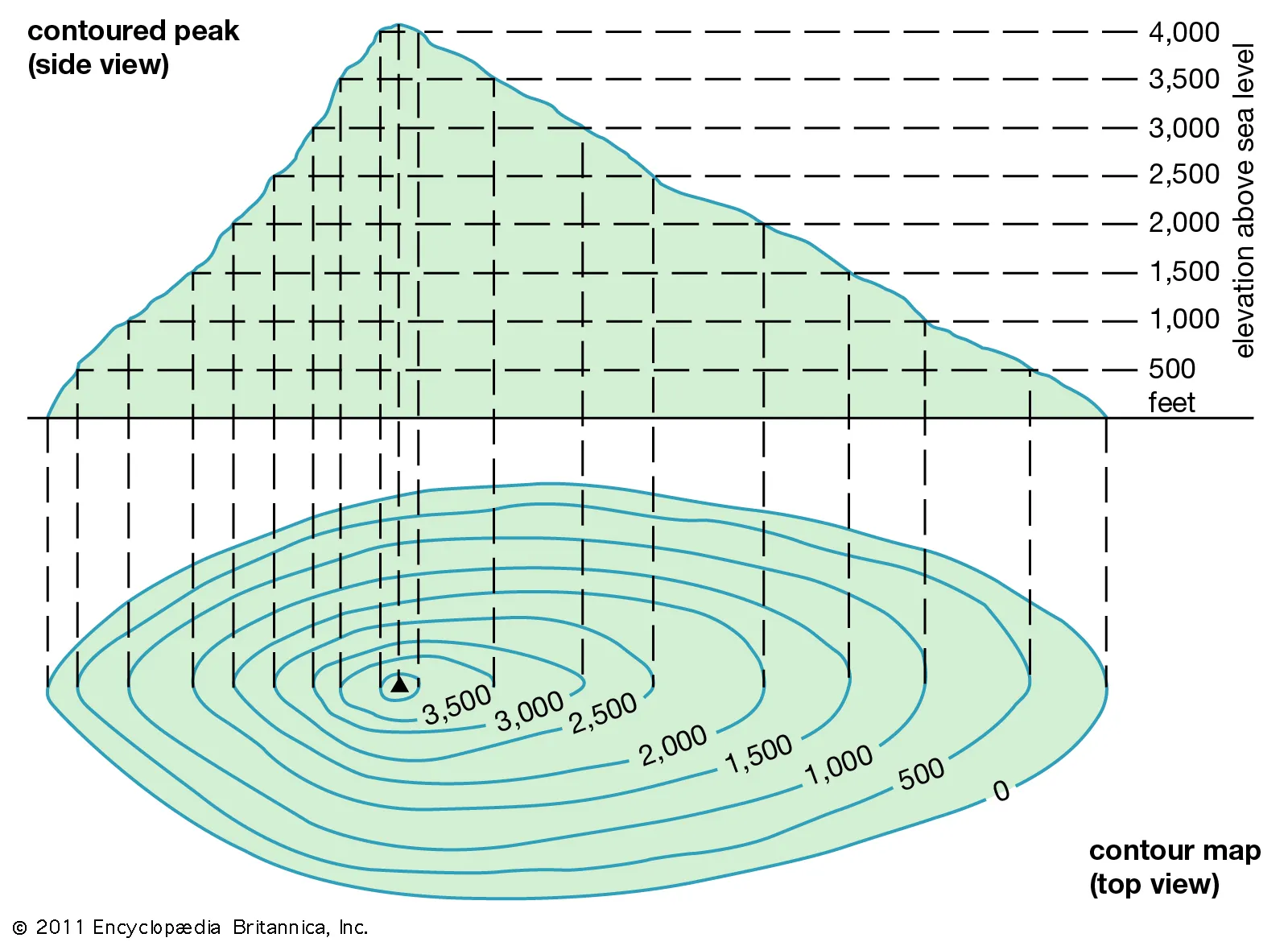
contour line
used on a topographic maps to show elevation of land surface; equal elevation
8
New cards
elevation
height of the land surface above sea level
9
New cards
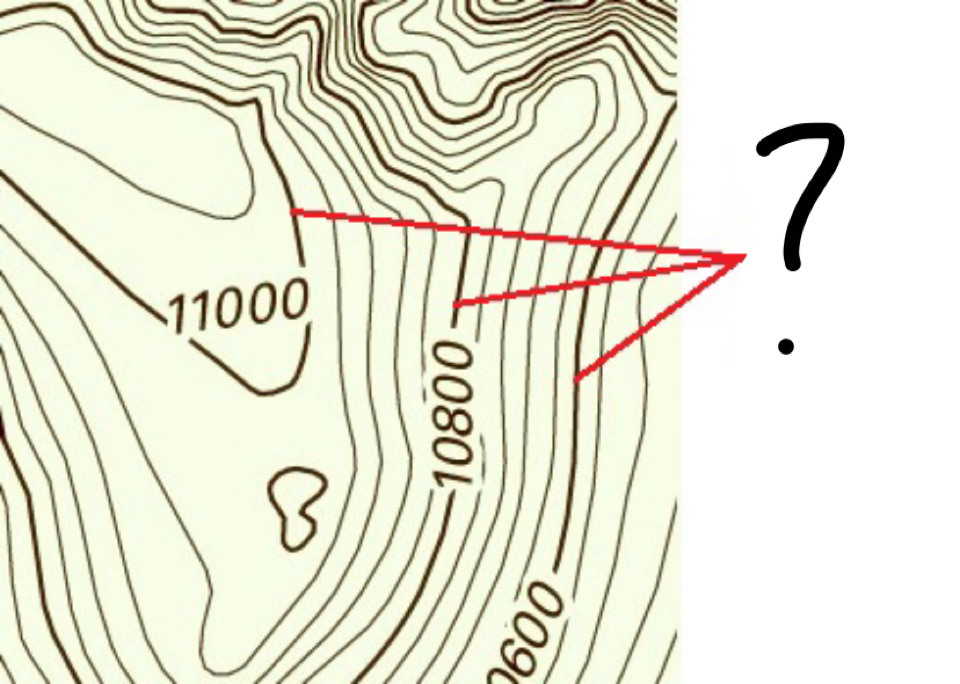
index contour
darker/bolder contour lines with elevation printed on them; every 5th line will be an ___________
10
New cards
contour interval
change in elevation between each adjacent contour line
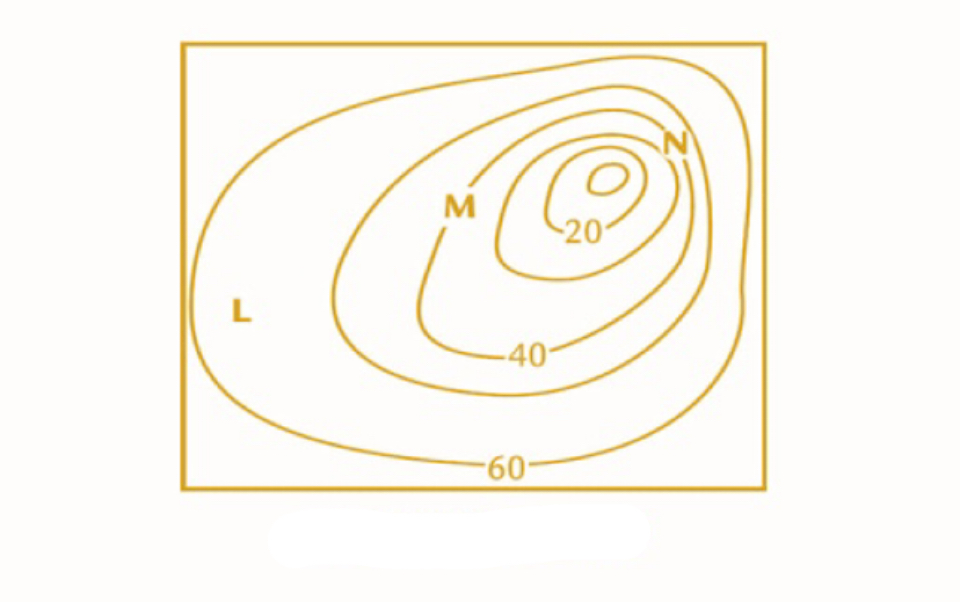
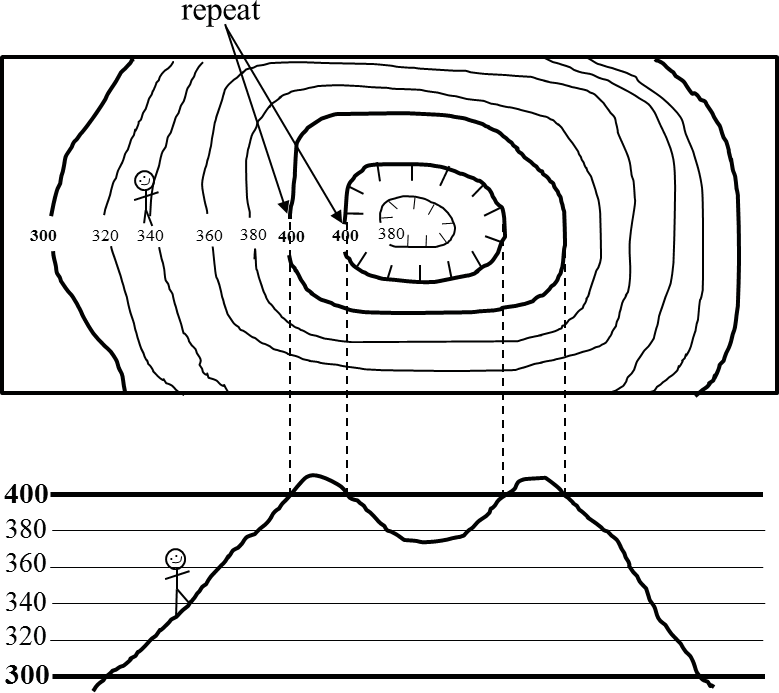
11
New cards
steep
contour lines that are bunch tightly together indicate a ________ slope
12
New cards
gentle
contour lines that are spaced apart indicate a _________ slope
13
New cards
hachure marks
indicate an isolated decrease in elevation, such as a sink hole or volcano crater

14
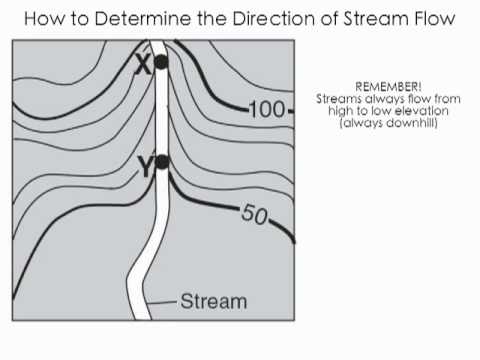
New cards
uphill
the pointy part of the V points
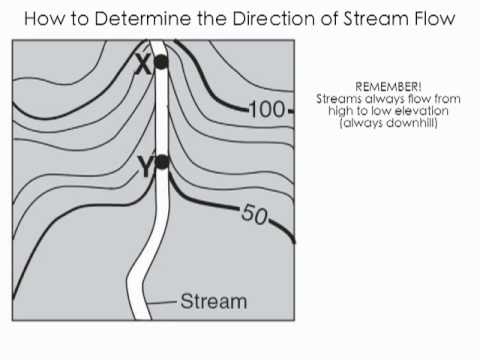
15
New cards
downhill
the mouth of the V opens up in the ________ direction
16
New cards
brown
color of topography: general shape of earths surface (ex. hills, valleys)
17
New cards
blue
color of water features: lakes, rivers, oceans
18
New cards
black and red
color of cultural features: buildings, roads, anything manmade
19
New cards
green
color of forested area/ tree cover
20
New cards
purple
color of new features since last update
21
New cards
relief
difference in elevation between two points on earth's surface
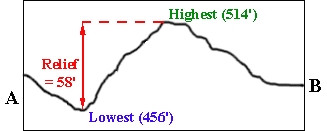
22
New cards
gradient
measure of steepness of a slope (the units can be FT/MI, M/KM, or DIMENSIONLESS
23
New cards
relief/horizontal distance
gradient=
24
New cards
coordinate system
is a method for describing the location of a point on the earth
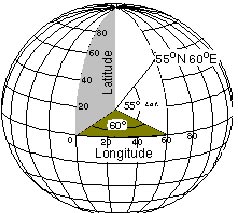
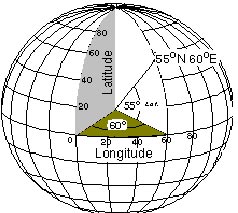
25
New cards
latitude-longitude
most common coordinate system used by civilians in the US
26
New cards
UTM (universal transverse mercator) and PLSS (public land survey system)
(besides lat-long) 2 major coordinate systems in the US
27
New cards
UTM
was devised for the military after WWII
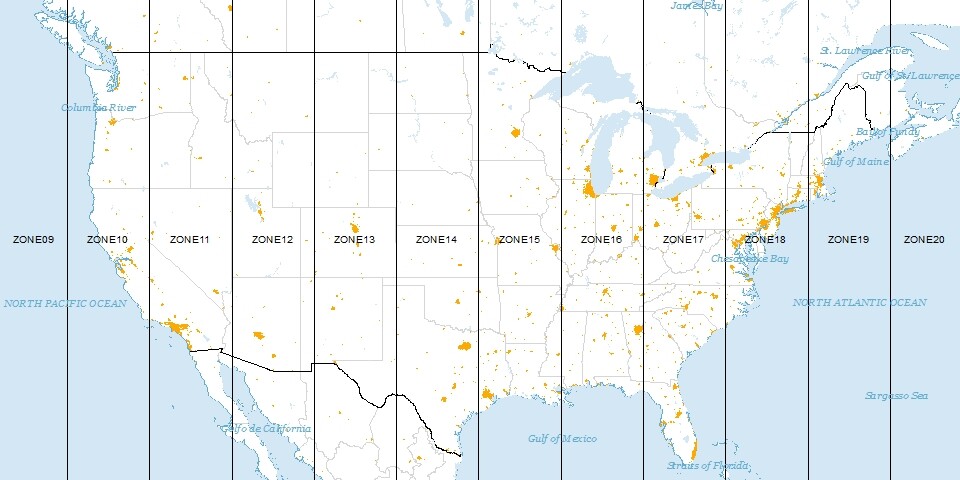
28
New cards
zones
UTM treats the globe like a rectangle and divides the earth into 60 _____
29
New cards
central meridian
in UTM, within each zone there is a _______________ : a north-south line that acts as a datum
30
New cards
datum
in UTM, a zero-point from which measurements are taken (like a starting point)
31
New cards
meters
in UTM, zones are broken into distances, all given in ______, "east" of central meridian and north of the equator
32
New cards
PLSS (public land survey system)
developed in 1785 to subdivide lands west of the original 13 US colonies into mappable (and sell-able) parcels
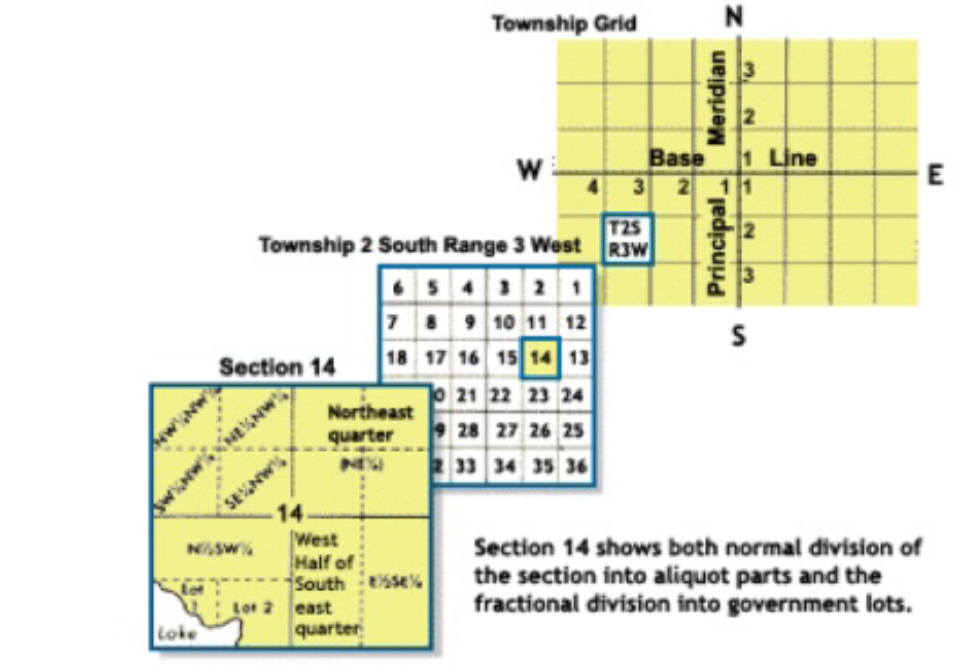
33
New cards
principle meridians and base lines
PLSS is a square grid system, centered on __________ (N-S lines) and ___________ (E-W lines)
34
New cards
townships
in PLSS, 6 mile by 6 miles squares
35
New cards
36
in PLSS, each 6 mile by 6 mile square is then divided into how many sections measured 1 mile by 1 mile?
36
New cards
GPS (global positioning system)
is a group of satellites that provides location and time information to a receiver anywhere on or near earth where there is an unobstructed line of sight to the satellites
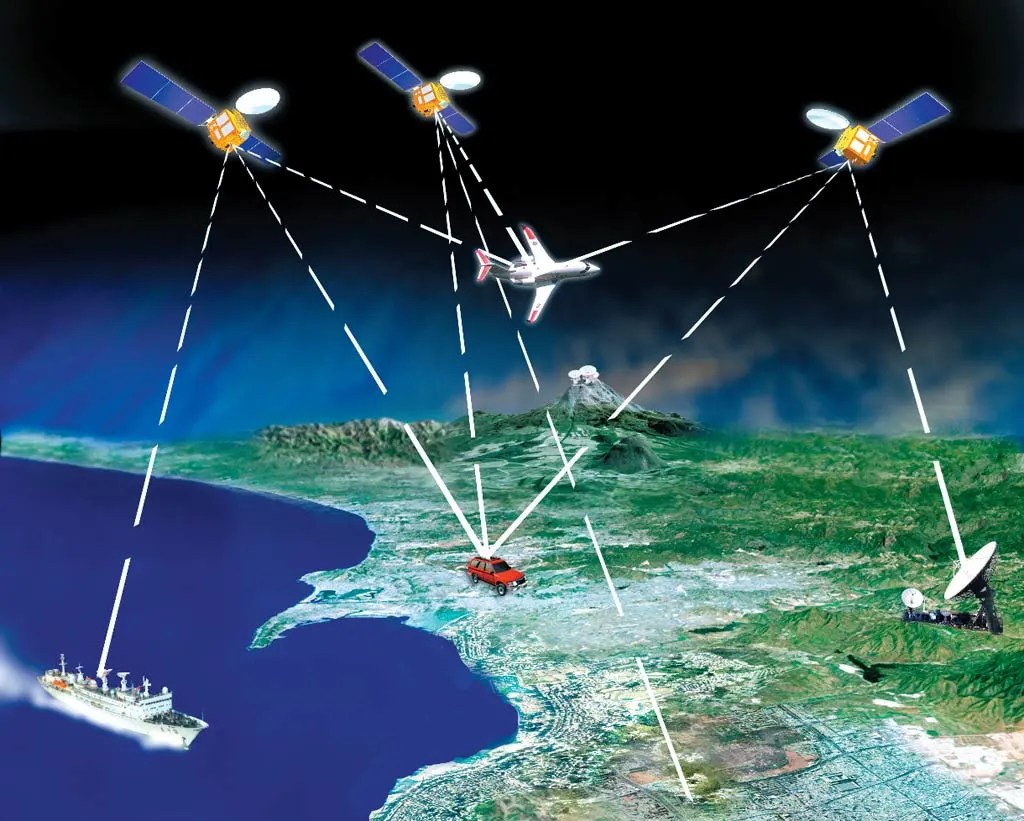
37
New cards
3
in GPS, location requires how many satellites?
38
New cards
4
in GPS, location and elevation requires how many satellites?
39
New cards
GIS (geographic information system)
is a computer software analyzes spatial location data and organizes layers of information into visualizations using maps and 3D images
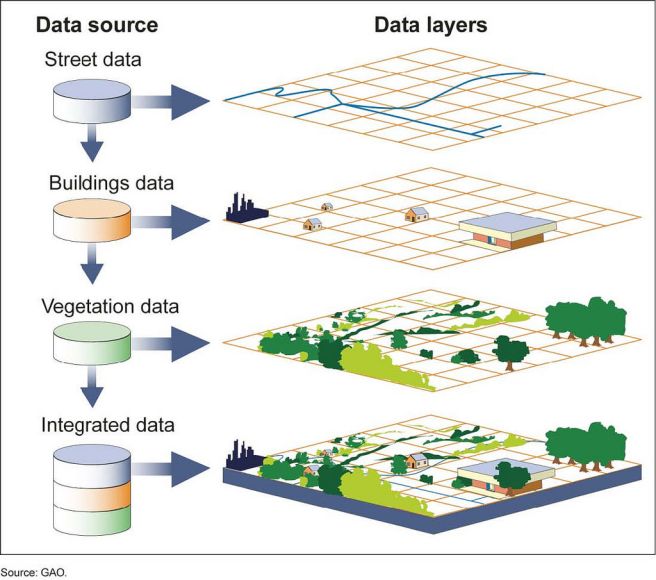
40
New cards
thermometer
what measures temperature?

41
New cards
barometer
what measures atmospheric pressure?

42
New cards
hygrometer
what measures moisture?

43
New cards
anemometer
what measures wind speed and direction?

44
New cards
precipitation gauge
what measures precipitation?

45
New cards
weather balloon
what measures upper level conditions?

46
New cards
evaluate the amount of moisture in the atmosphere
what does vapor pressure, relative humidity, and dew point have in common?
47
New cards
vapor pressure/saturation vapor pressure times 100
RH=
48
New cards
vapor pressure
is the amount of water vapor actually PRESENT in the air (mb or kPa)
49
New cards
saturation vapor pressure
is the MAXIMUM amount of water the air is capable of holding at a given temperature
50
New cards
moisture and temperature
relative humidity varies with both change in ________ and/or ____________
51
New cards
dew point
the temperature at which saturation would occur if the air was cooled (_______ is the temperature a parcel of air has to be for 100% RH)
52
New cards
saturated
when a parcel of air contains as much moisture as is possible at a given temperature, the air is said to be __________
53
New cards
cooling or addition of water vapor
air saturates through one of two processes
54
New cards
adiabatic
when the temperature of a parcel of air cools as a consequence of change in pressure
55
New cards
absolute stability
occurs when the air parcel is colder than its surroundings and will not rise, or it may sink
56
New cards
absolute instability
accurs when the parcel is warmer than the environment, and it will rise
57
New cards
conditional stability
the vertical motion of the parcel will be determined by whether it is saturated or not
58
New cards
convection
heating of the air; becomes less dense and rises
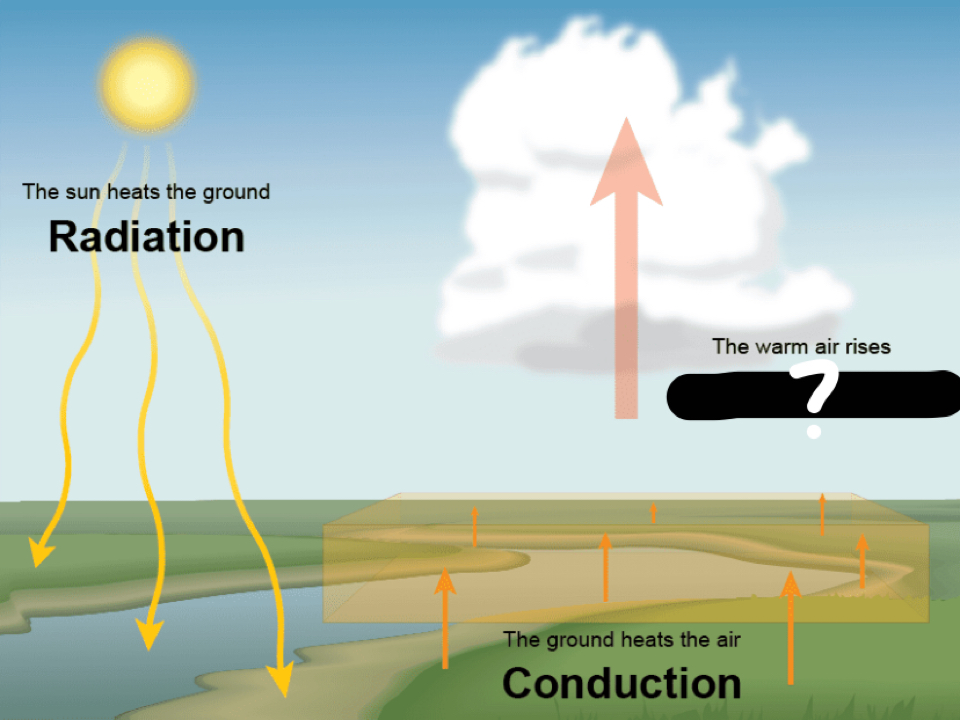
59
New cards
orographic
lifting by terrain; air rises as it passes over hills or mountains
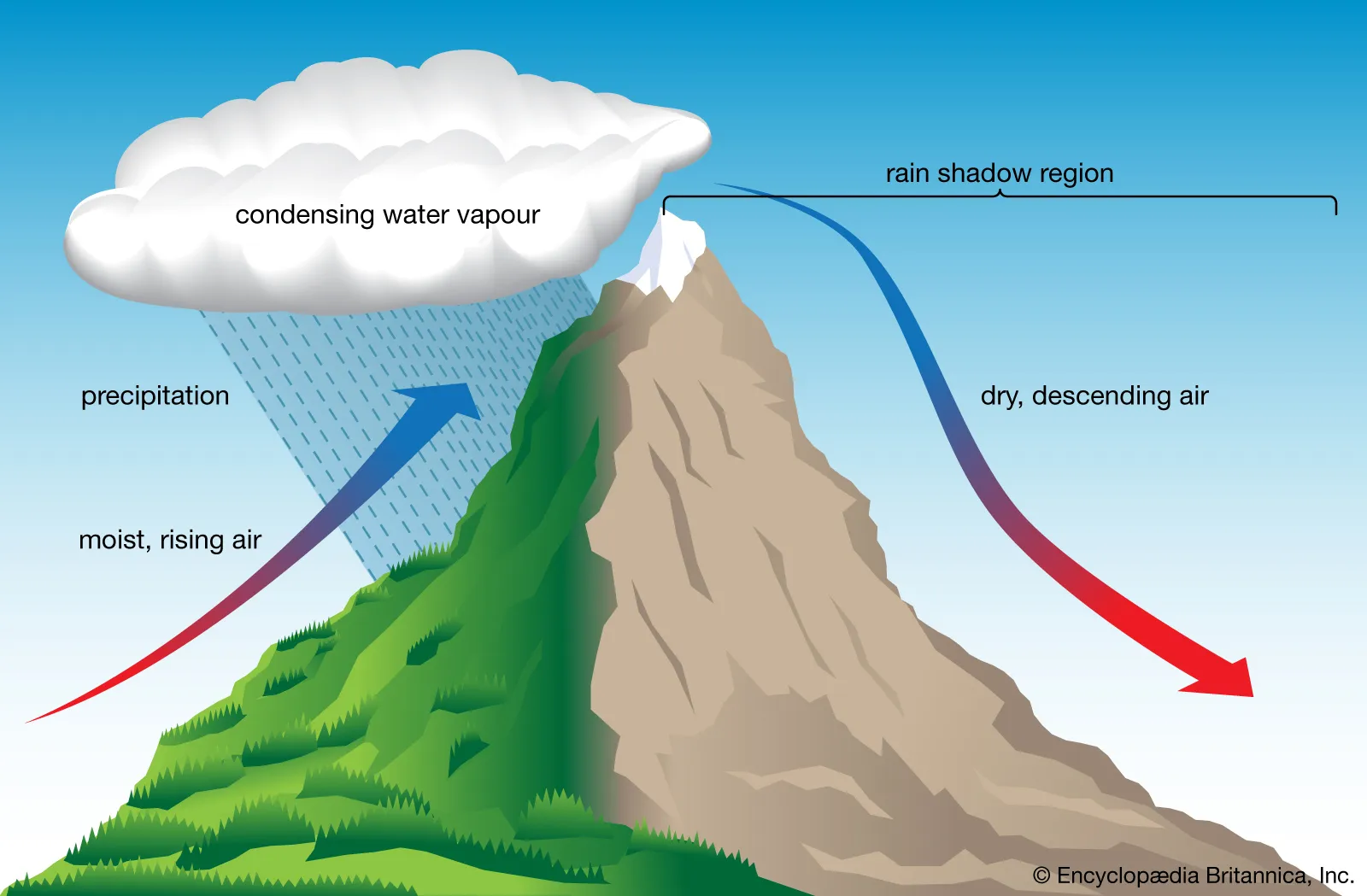
60
New cards
frontal
an air mass boundary forces air to rise
61
New cards
convergence
two air streams collide and air rises
62
New cards
LCL (lifting condensation level)
is the height where a parcel of air becomes fully saturated, and condensation occurs (clouds form)
63
New cards
ALR (adiabatic laps rate)
is the rate of warming or cooling of a parcel of air
64
New cards
temperature and moisture content
an air mass is a large body of air that is characterized by its _______ and _______
65
New cards
continental (c)
what forms over land (dry)?
66
New cards
maritime (m)
what forms over the ocean (humid/moist)?
67
New cards
polar (P)
what originates at high latitudes (cold)?
68
New cards
tropical (T)
what originates at lower latitudes (warm)?
69
New cards
mP and mT
what two air masses have the greatest impact on the pacific coast of north america?
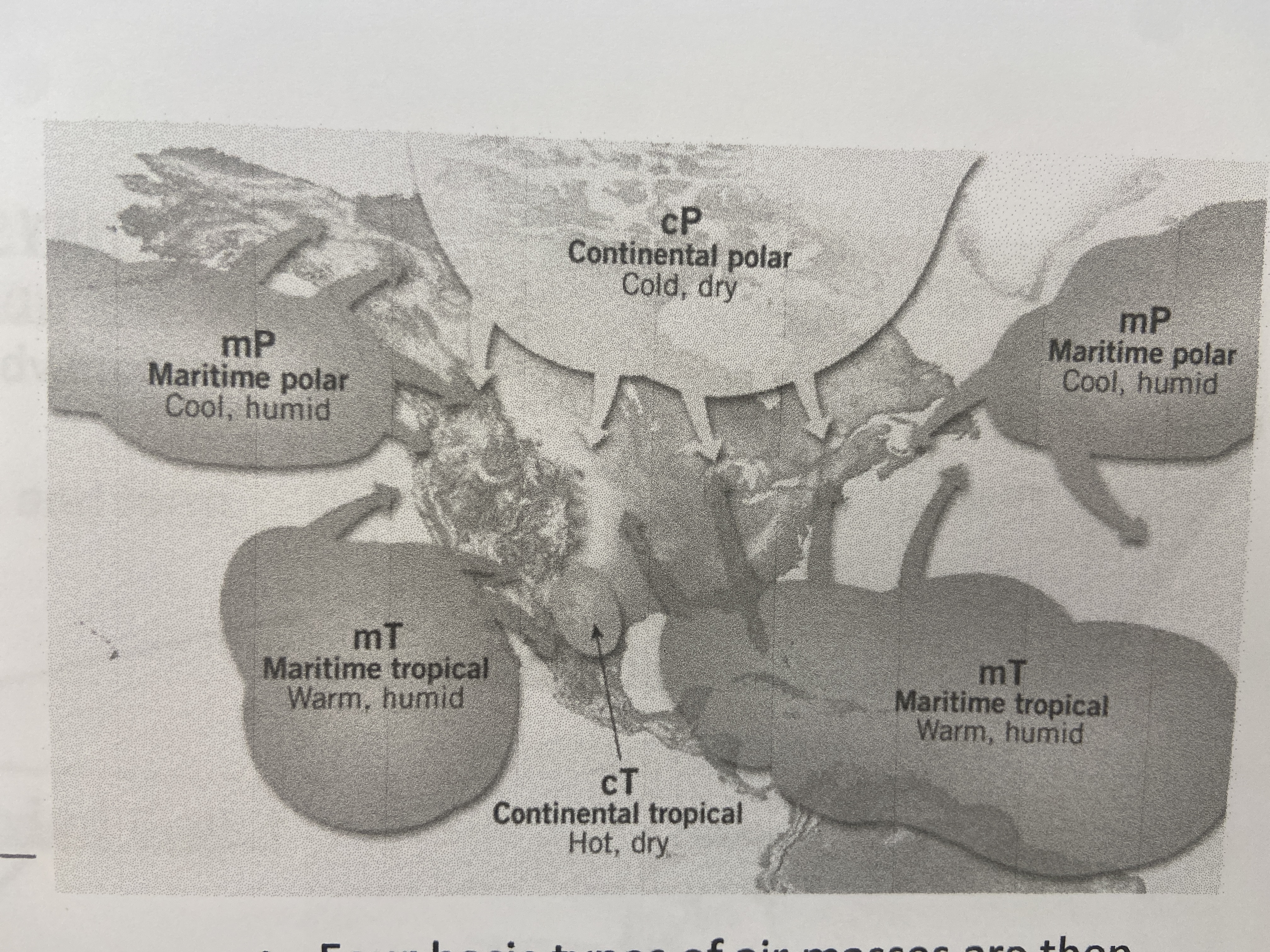
70
New cards
cT
the southwestern US and northwestern mexico is the source region for what type of air mass?
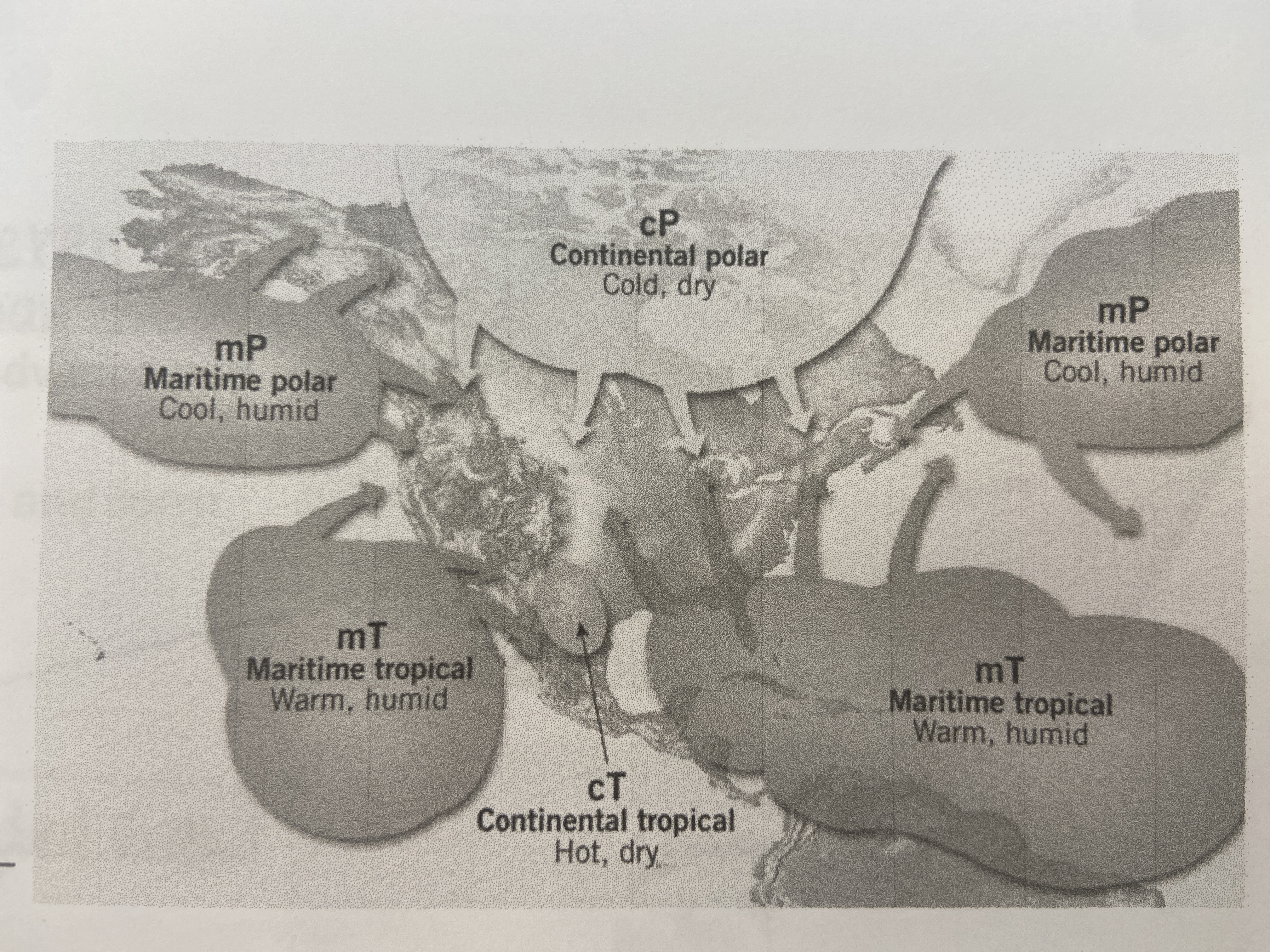
71
New cards
front
boundary that separate different air masses, where one mass is warmer than the other
72
New cards
warmer
will the warmer or colder air mass rise, cool adiabatically, and form clouds (and, potentially, precipitation)?
73
New cards
warm front
warm air overruns cold air
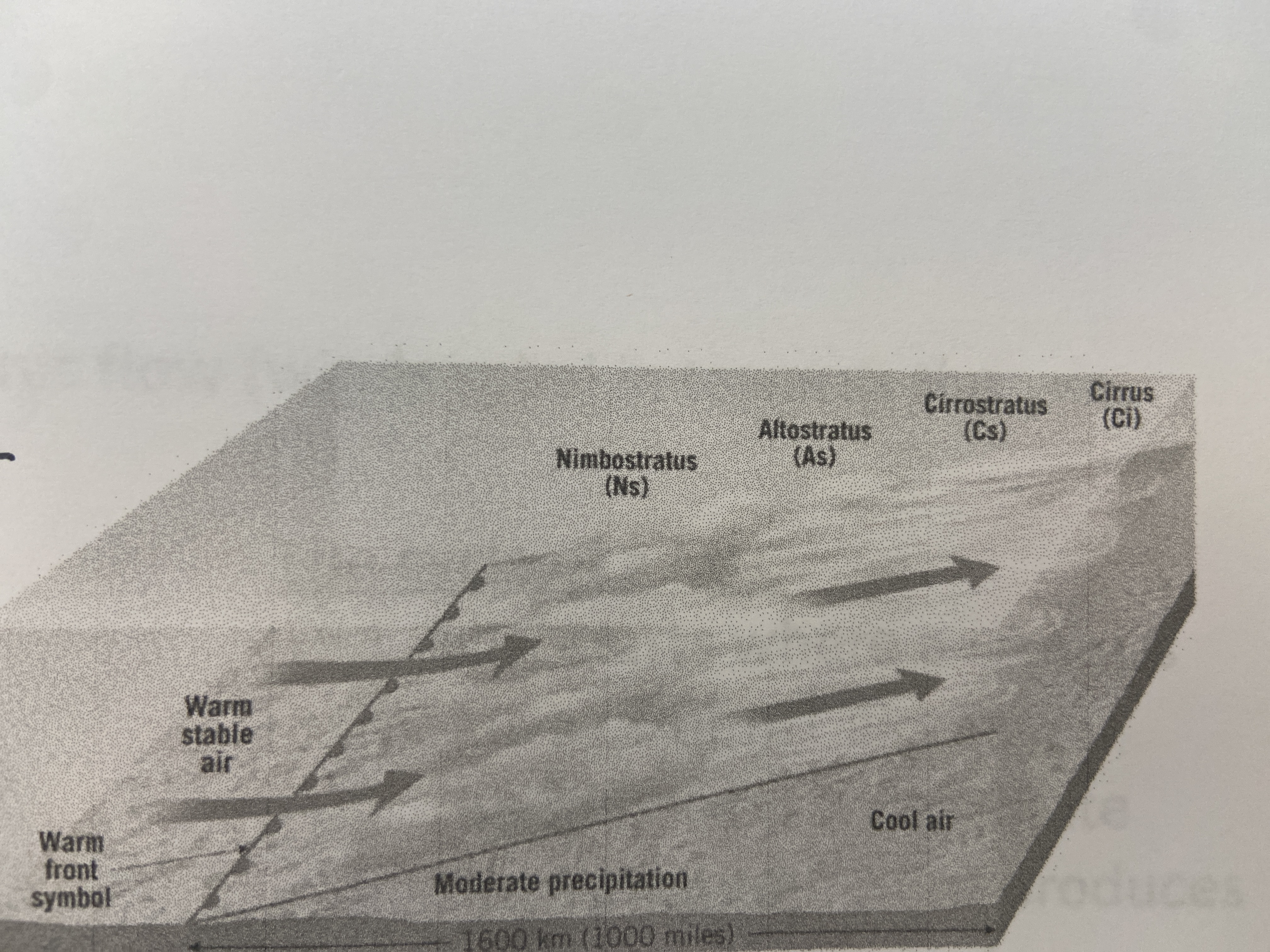
74
New cards
cold front
cold air overruns warm air
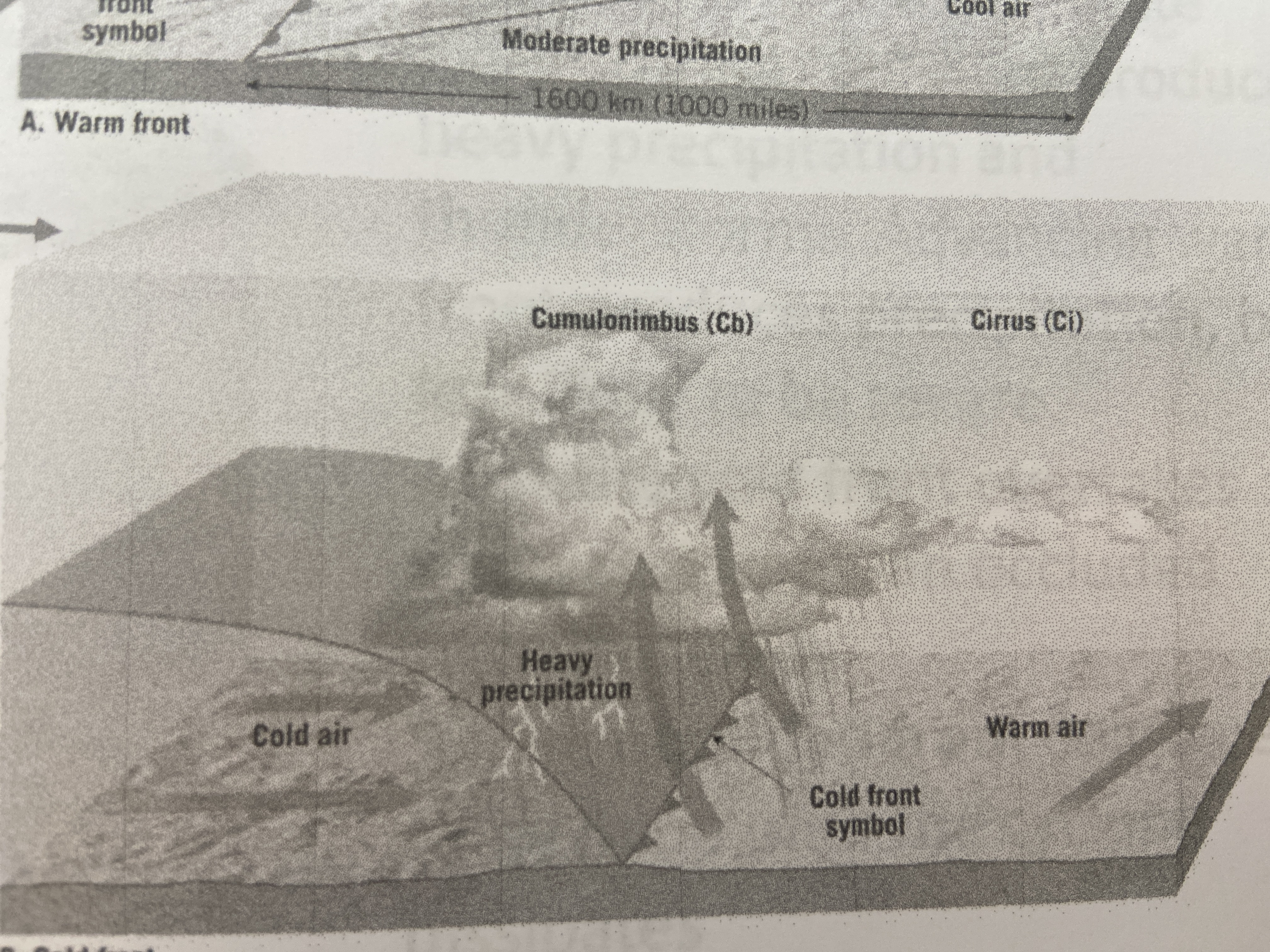
75
New cards
occluded front
cold front overruns a warm front
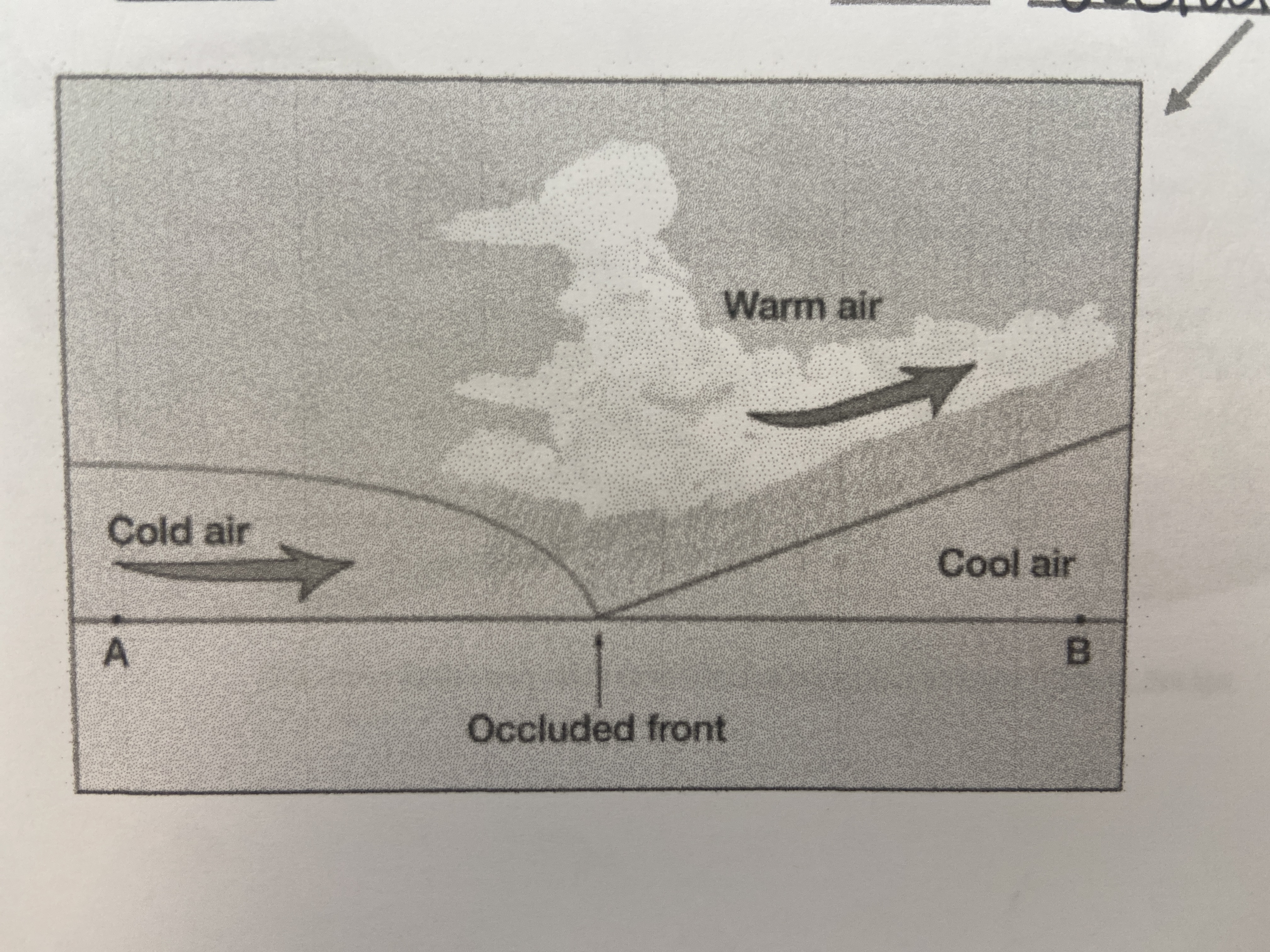
76
New cards
mid latitude cyclone (MCR)
low pressure system that has cyclonic flow (winds spiral in towards the center of low pressure) found in the middle-latitudes (~30-55°)

77
New cards
headwaters
where the stream starts; high elevations with steep slopes
78
New cards
mouth
where the stream flows into the ocean
79
New cards
stream channel
during normal conditions, water is contained within the ______ _______. they sit inside the floodplain
80
New cards
stream morphology
influenced by factors such as gradient (slope) and sediment load
81
New cards
sinuosity
how curvy or straight the channel is
82
New cards
straight
characterized by their single channel and low sinuosity; typically occur in high up mountainous areas due to very steep slopes and v-shaped bedrock valleys; usually has fast moving waters due to the steep slope, so they are capable of moving large particles
83
New cards
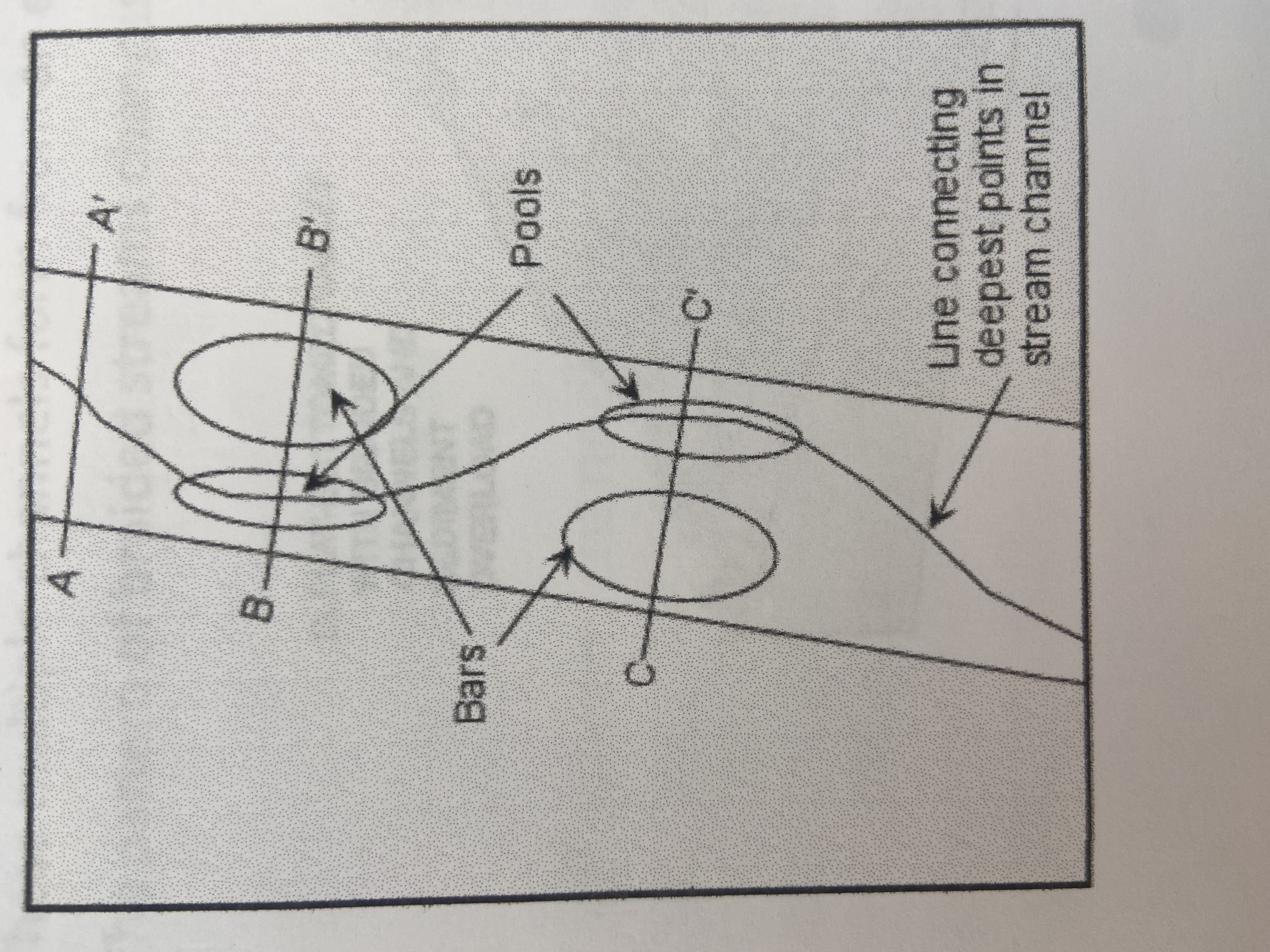
braided
form near the base of mountains; characterized by their multiple channels and tend to be wide and shallow; water slows down and it can no longer carry big boulders; we see gravel and sand on the beds of these streams; these multiple channels form from an excessive load of sand/gravel accumulating in CHANNEL BARS
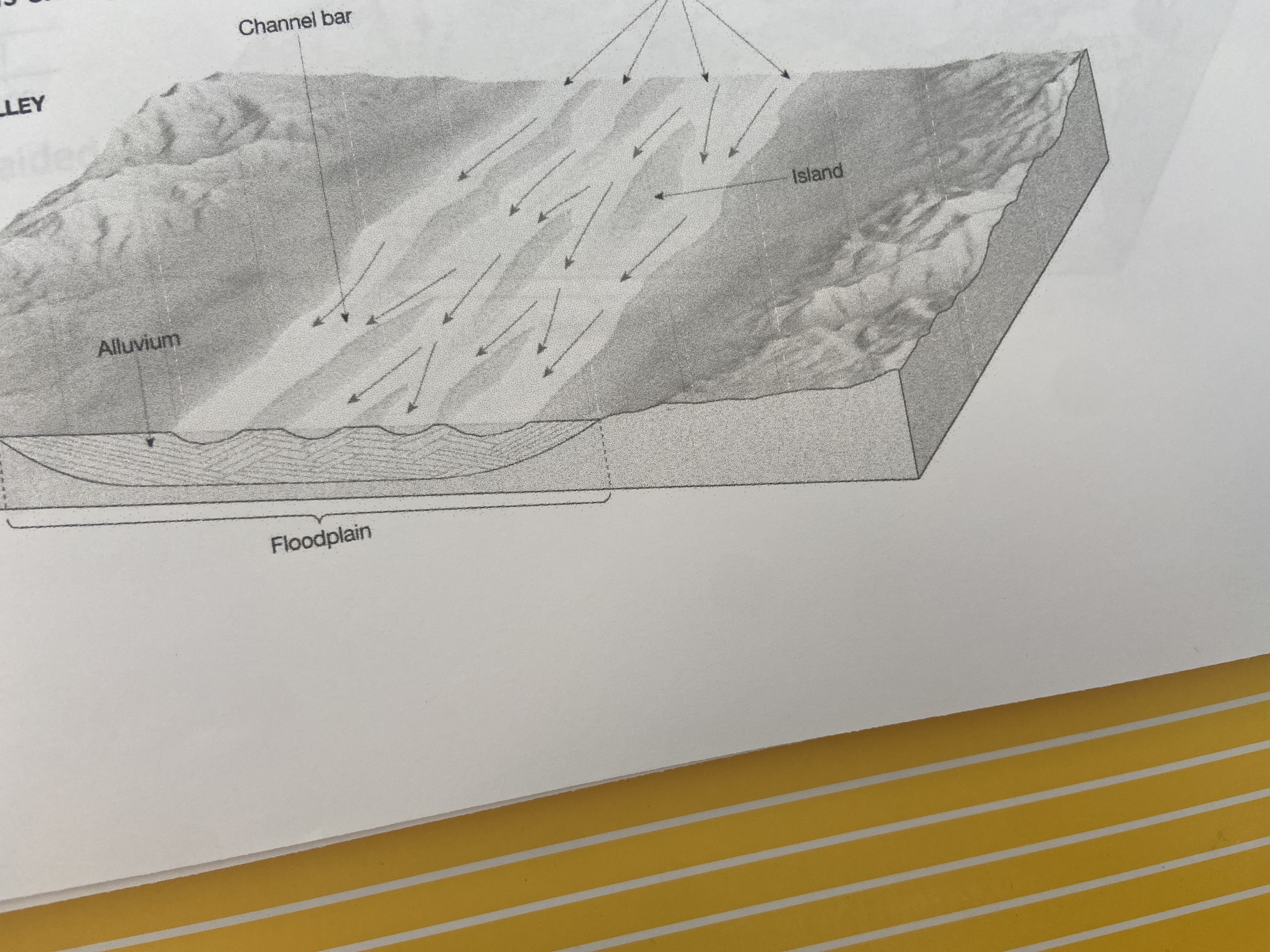
84
New cards
meandering
generally have a single, deep, sinuous channel with occasional sand bars; lower gradient than braided channels; the stream channel migrates back and forth over the floodplain over time due to continual erosion of the cutbank and deposition on the point bar
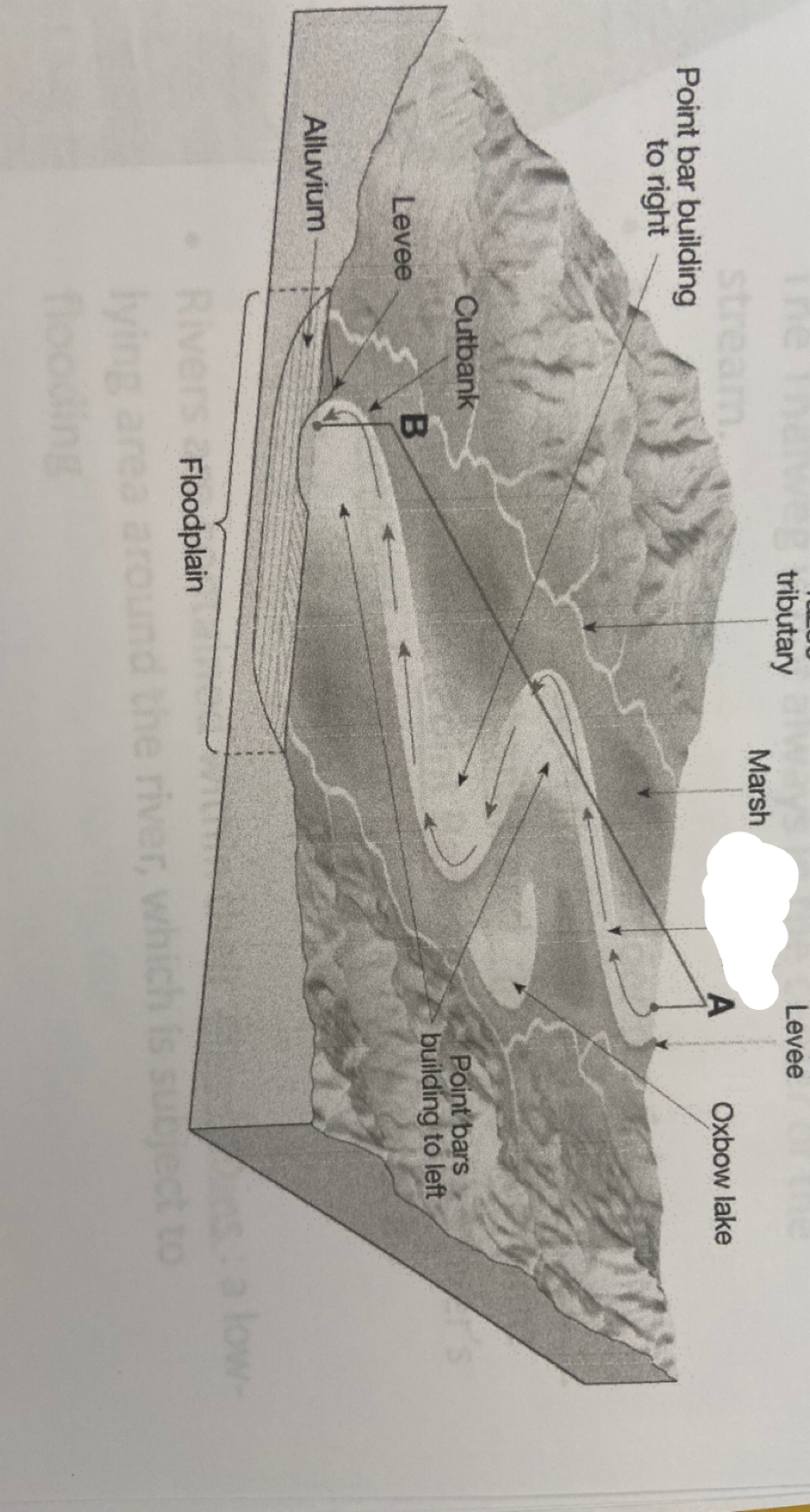
85
New cards
thalweg
deepest part of the river where the water moves fastest
86
New cards
cutbank
the outer side of the river that erodes
87
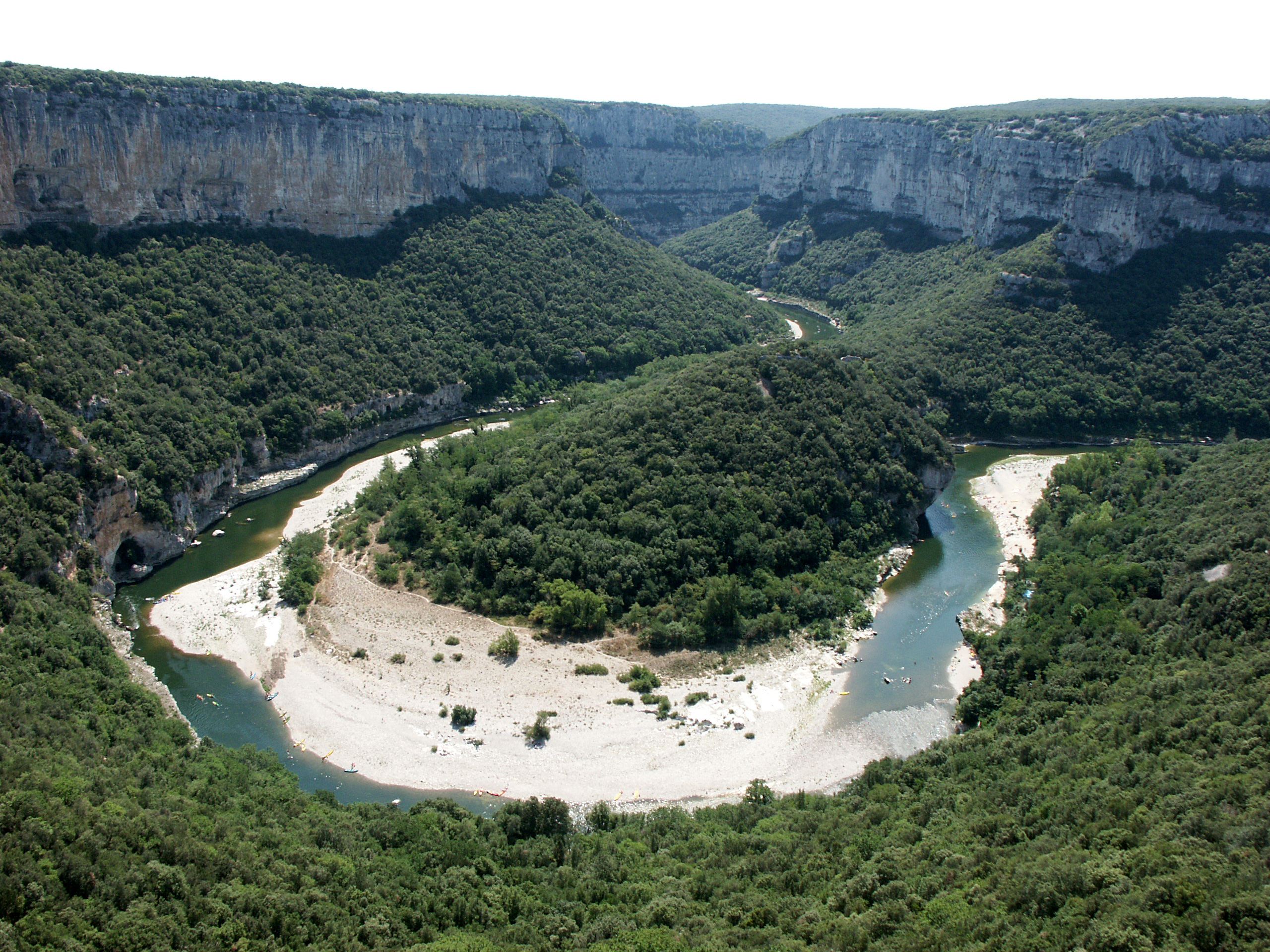
New cards
point bar
the inner side of the river that deposits sediment

88
New cards
floodplain
low-lying area around the river, which is subject to flooding

89
New cards
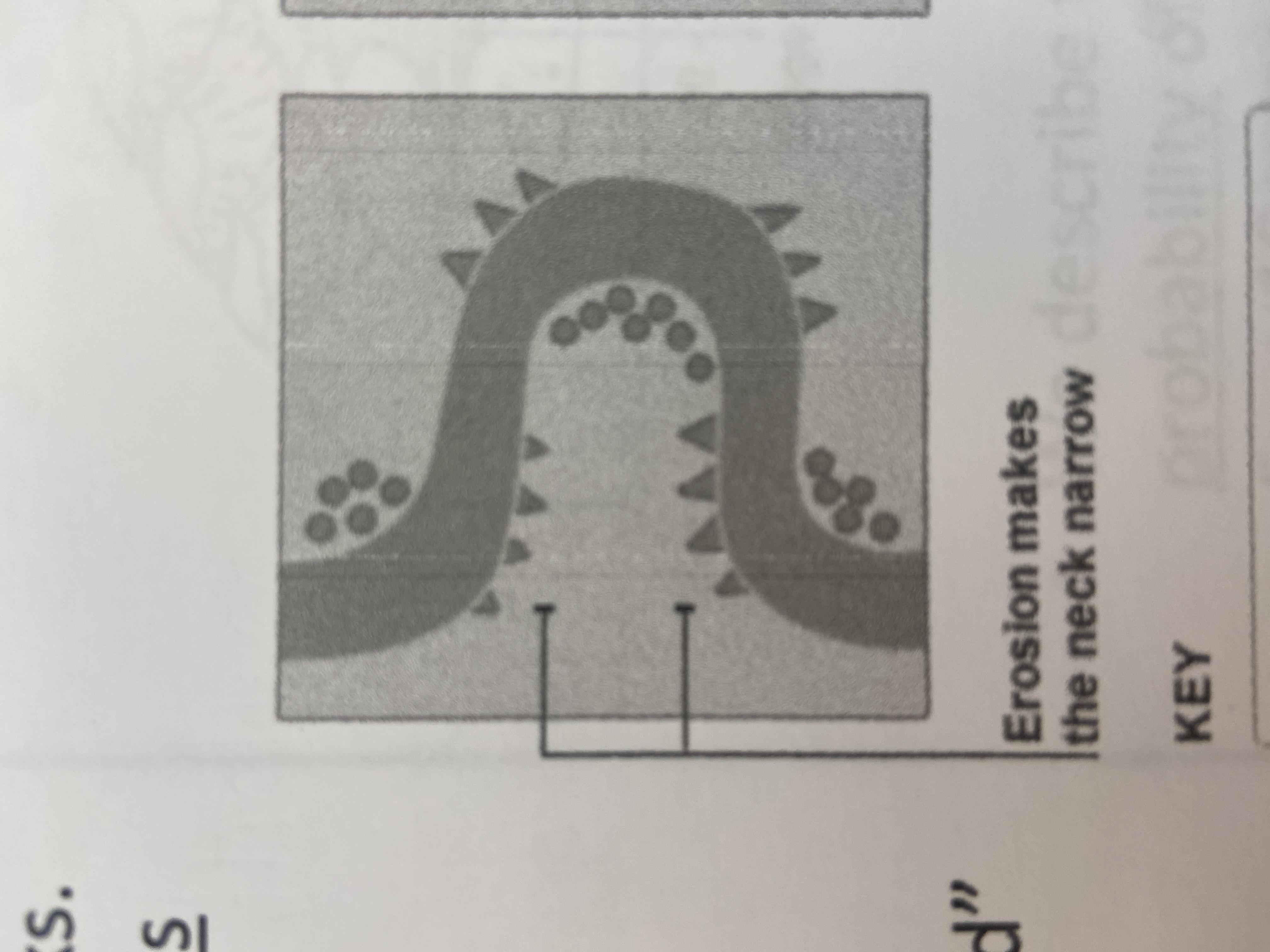
neck
narrow peninsula that is created from two cutbanks eroding towards each other
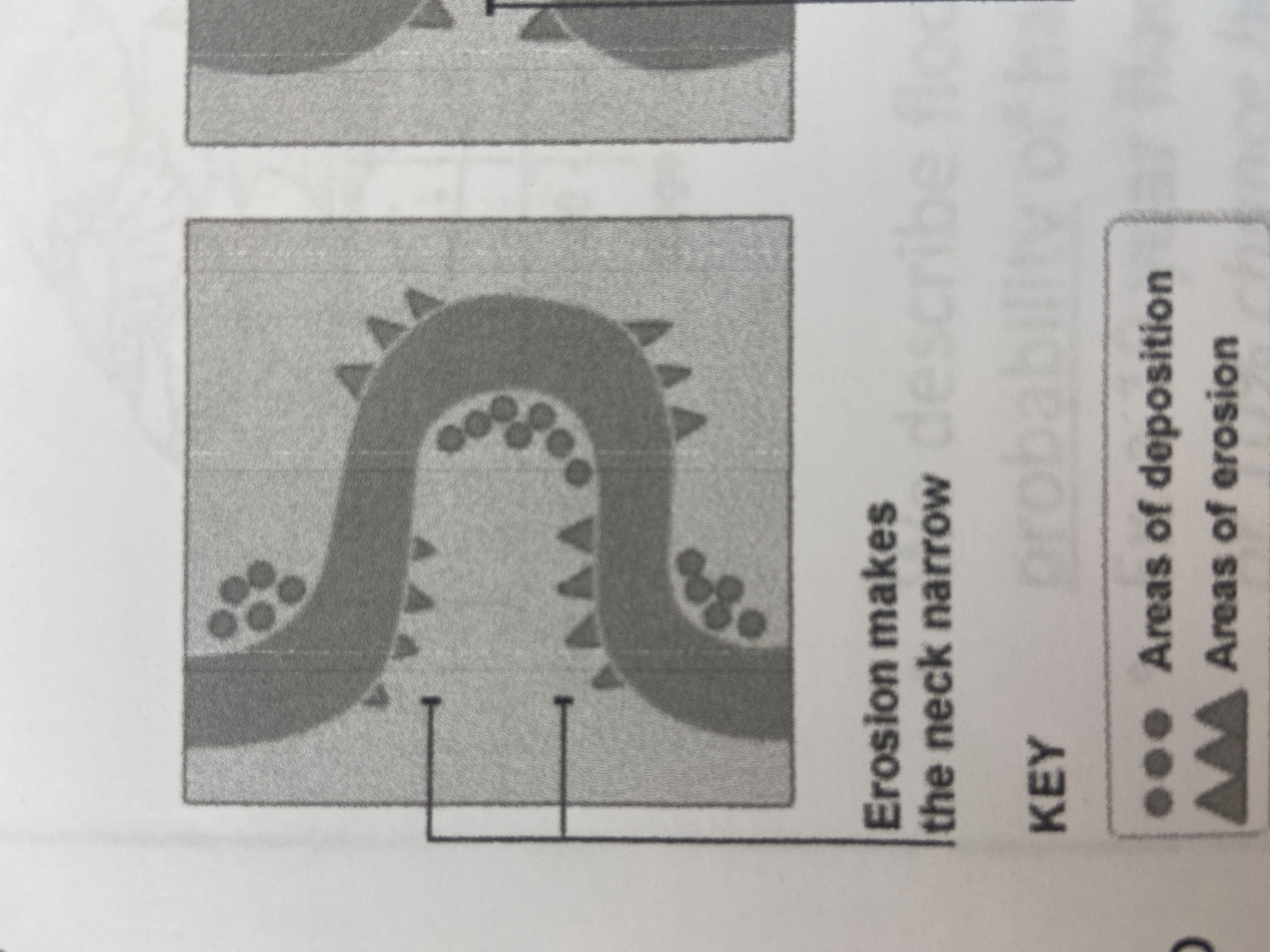
90
New cards
oxbow lake
when two cutbanks connect, and creates a shorter, more direct path for the river to follow. the abandoned meander is called a(n)
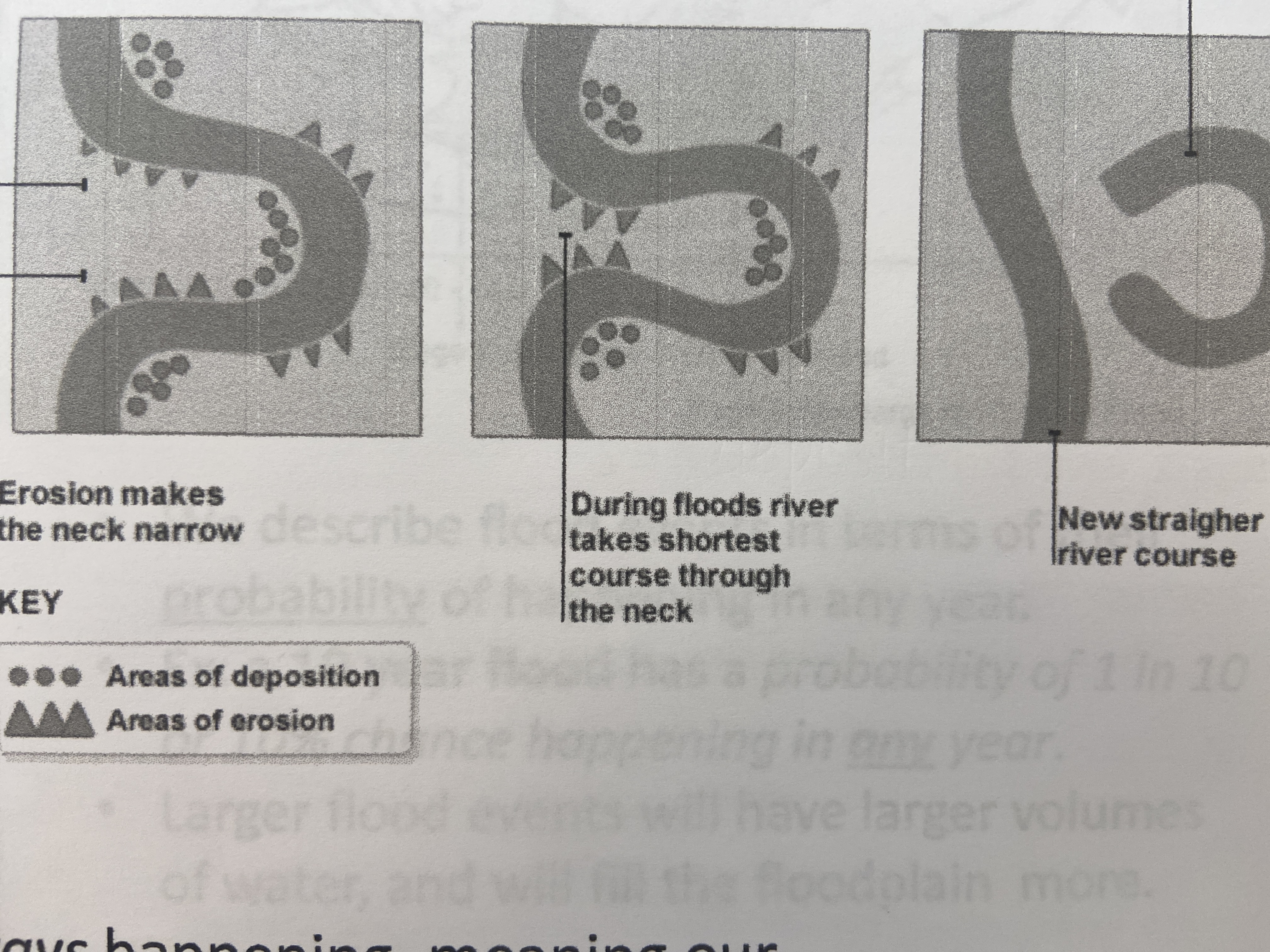
91
New cards
100
a 100 year flood has a 1 in ___ (1%) chance of happening in any given year
92
New cards
RI
(n+1)/s
93
New cards
lithosphere
all the solid rock components close to the surface of the earth (~top 100 km)
94
New cards
mineral
crystalline solids with fixed atomic structure and fixed chemical composition
95
New cards
cleavage
occurs when a mineral breaks easily along a plane of weakness—will have flat, smooth sides when broken
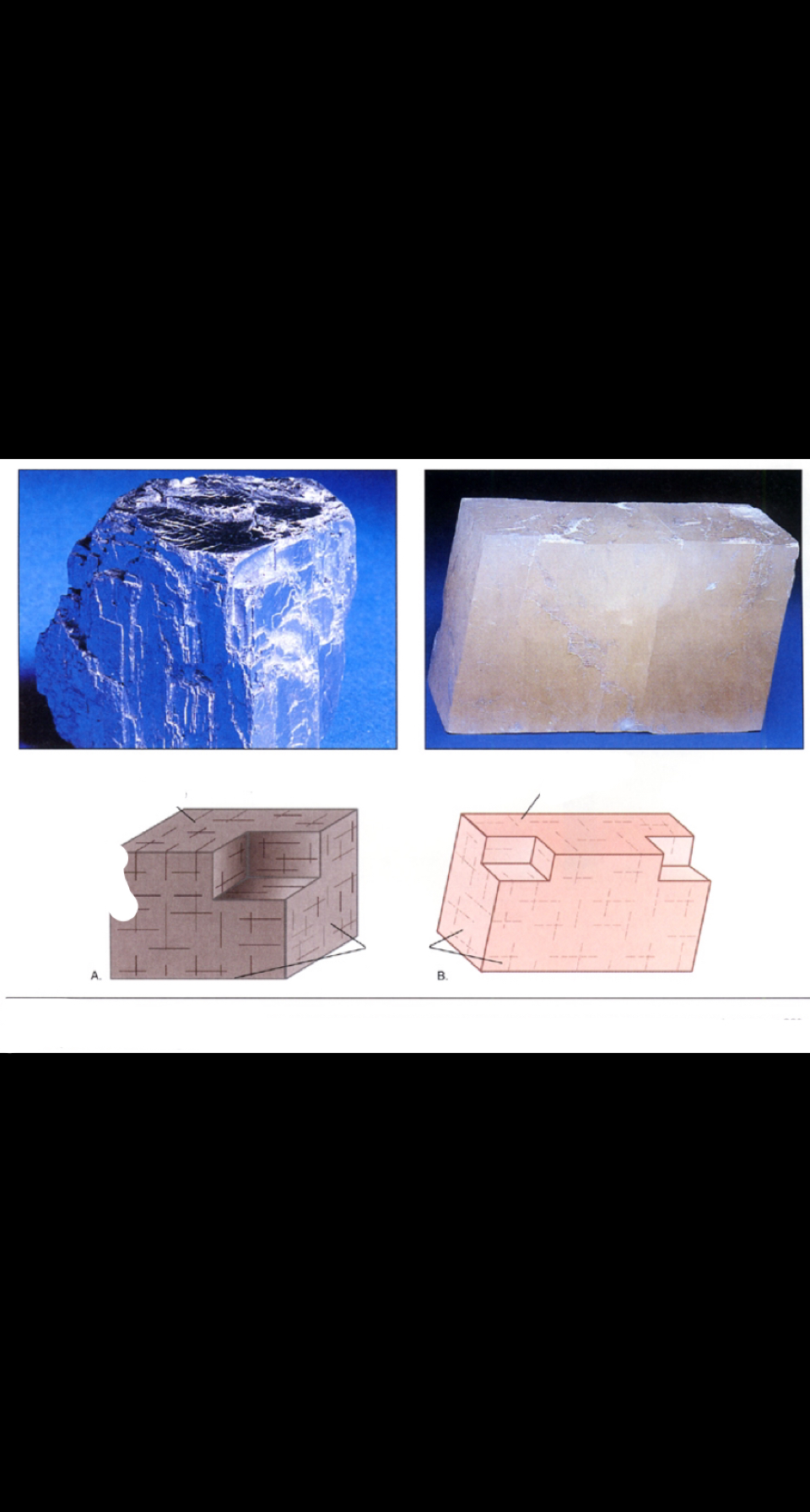
96
New cards
fracture
occurs when the sample breaks irregular, similar to broken glass; no flat smooth surfaces; no regular angle/direction to breakage
97
New cards
less than 2.5
if we can scratch a mineral with our fingernail, that mineral is fairly soft
98
New cards
greater than 5.5
if a mineral scratches the surface of glass, that mineral is pretty hard
99
New cards
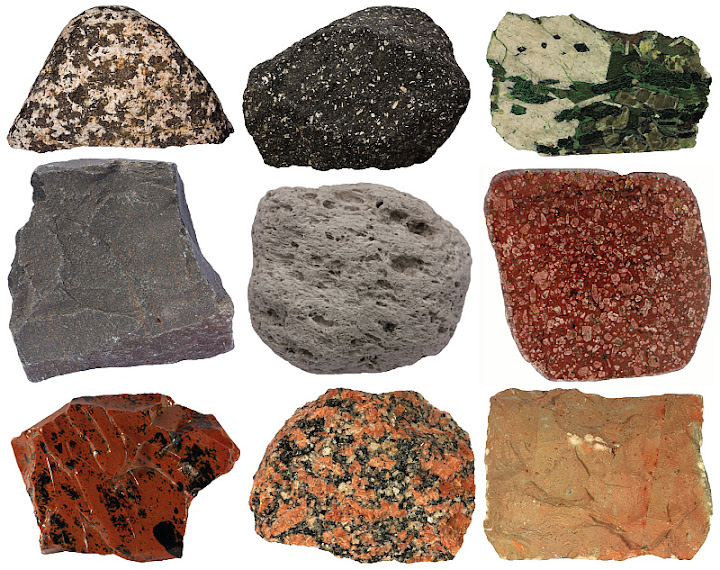
igneous
form from the cooling of melted/liquid rock (magma)

100
New cards
sedimentary
form from accumulation of sediment, or precipitation of minerals in water, at the surface of the earth
