ScholarRX: Bones and Joints of the Arm, Forearm, and Hand
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
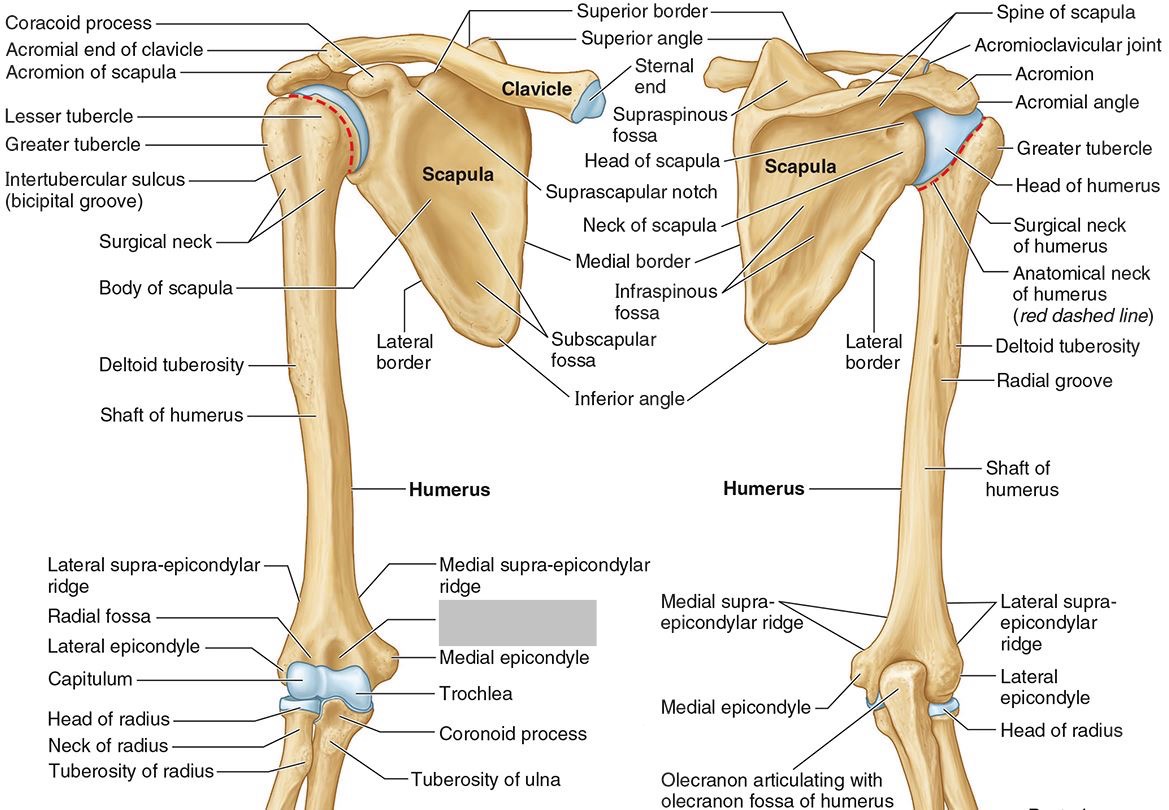
What is the only bone in the upper arm?
The humerus
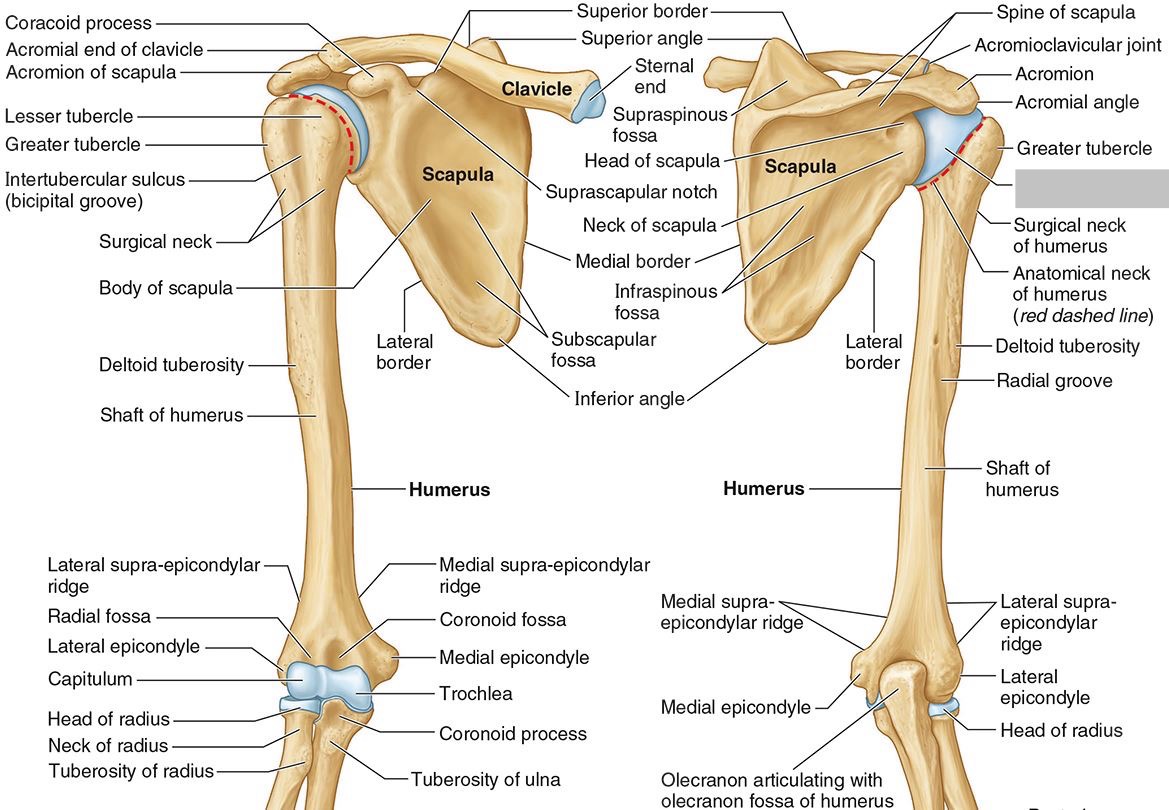
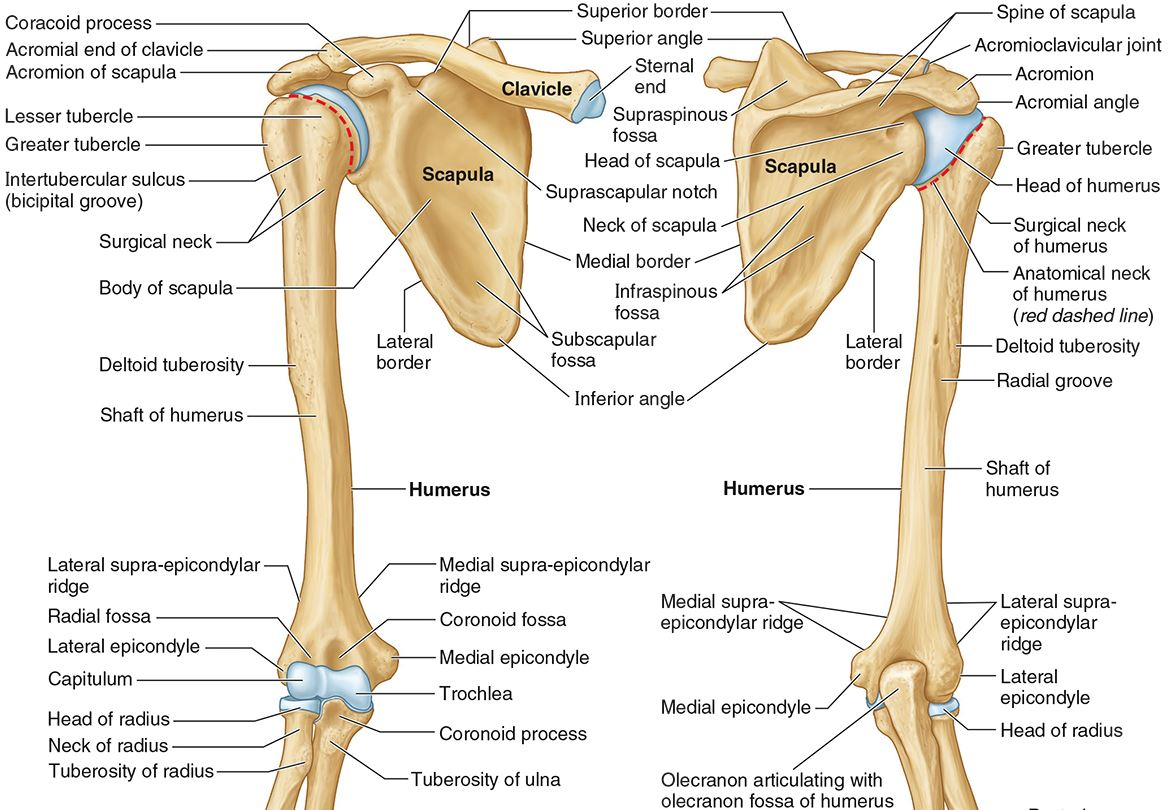
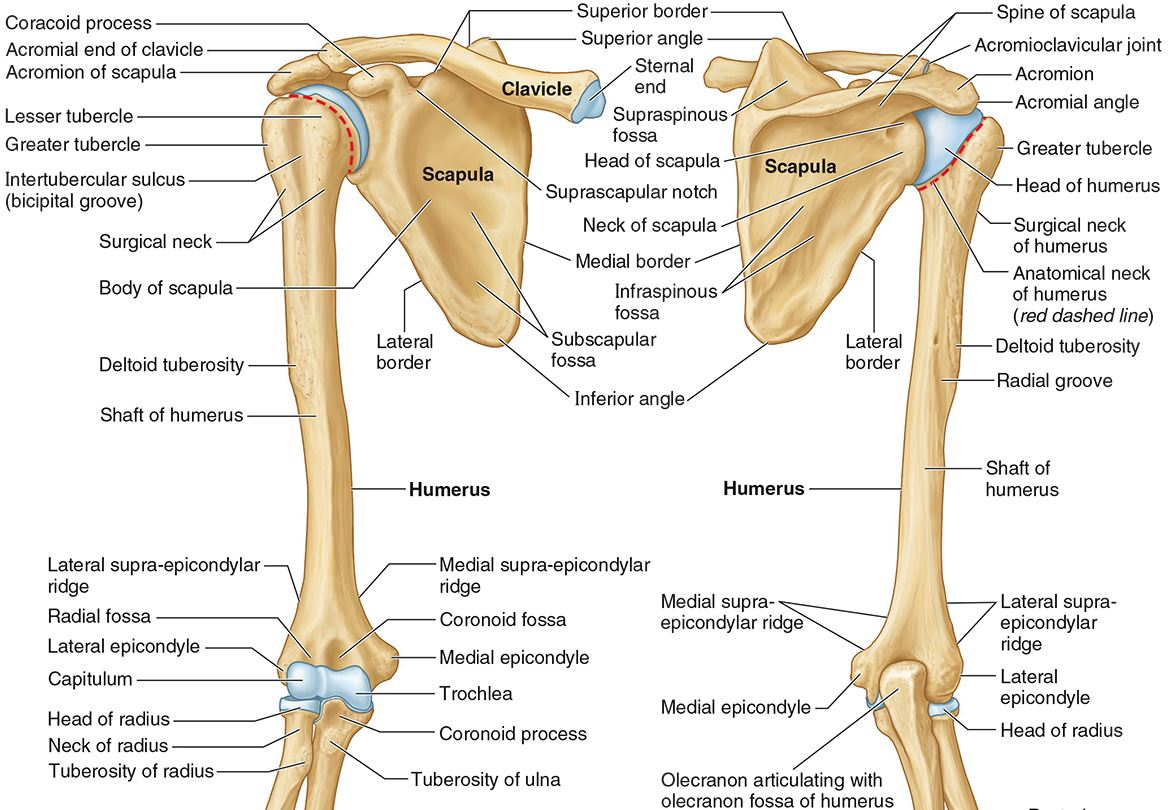
What part of the humerus is this?
The head of the humerus articulates with the scapula at the glenohumeral joint.
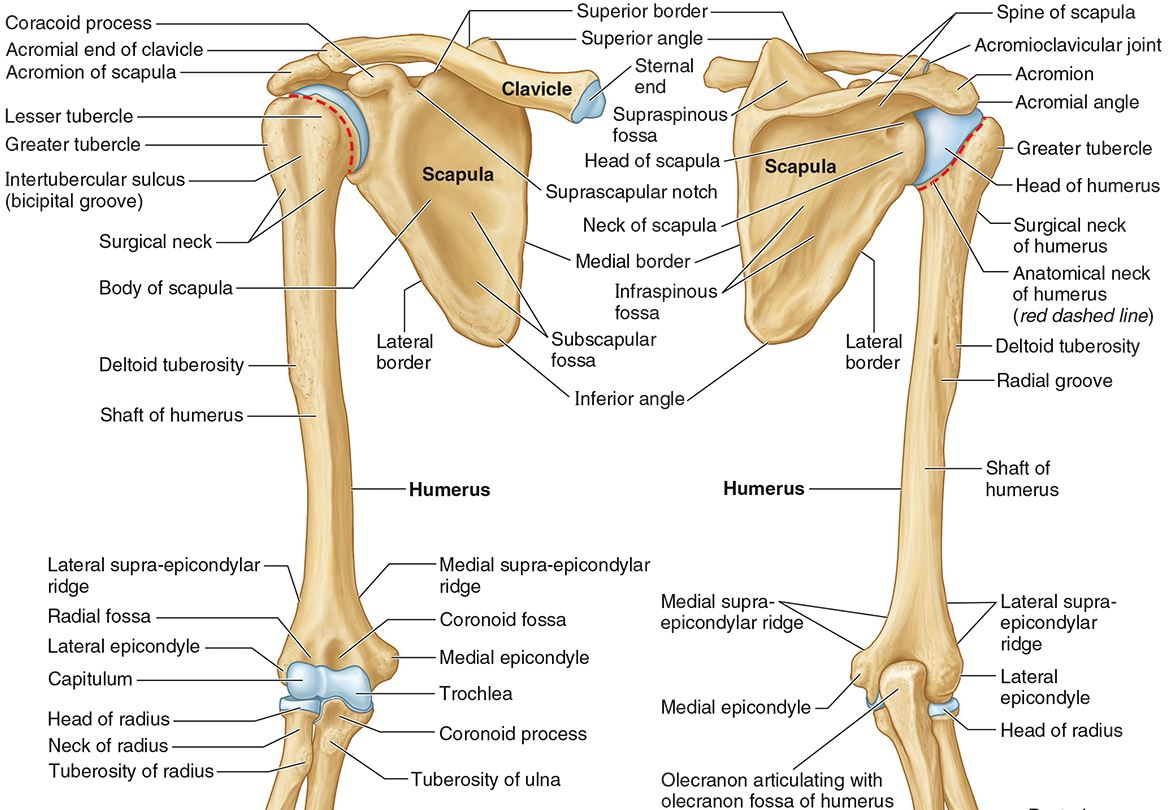
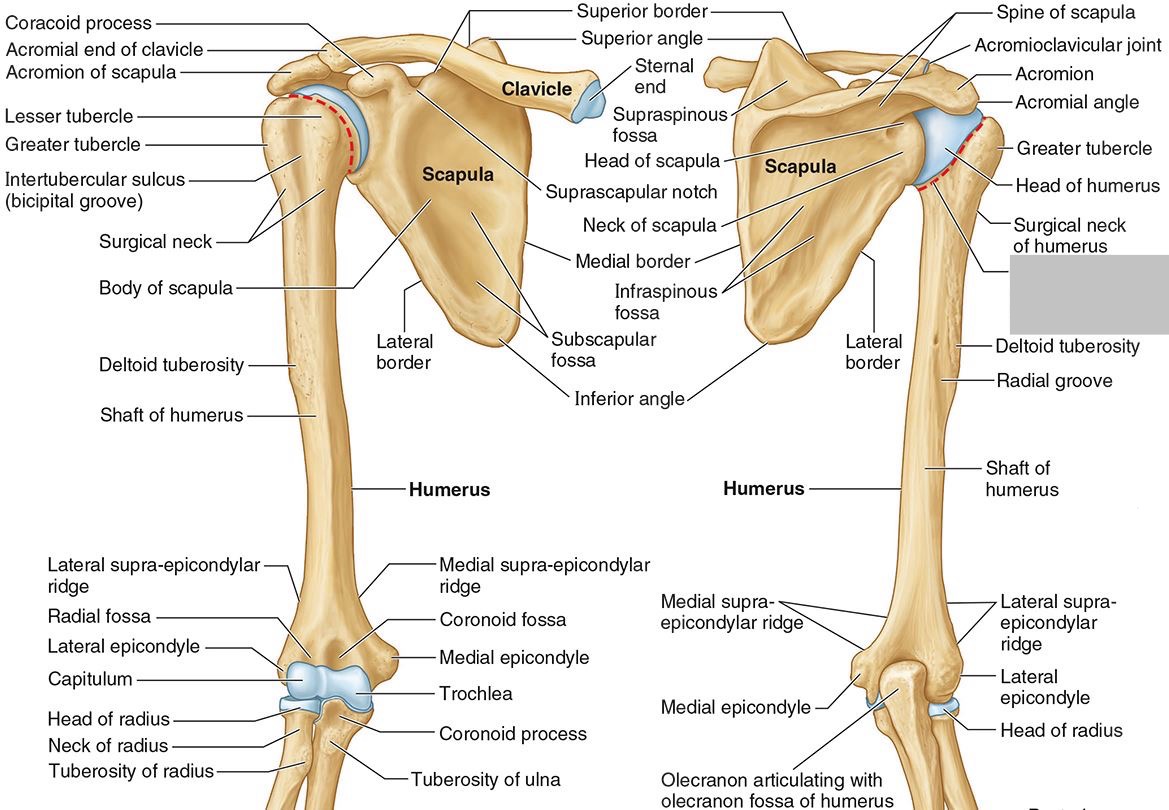
What part of the humerus is this?
The anatomic neck is an indentation distal to the head and provides an attachment for the fibrous joint capsule of the glenohumeral joint.
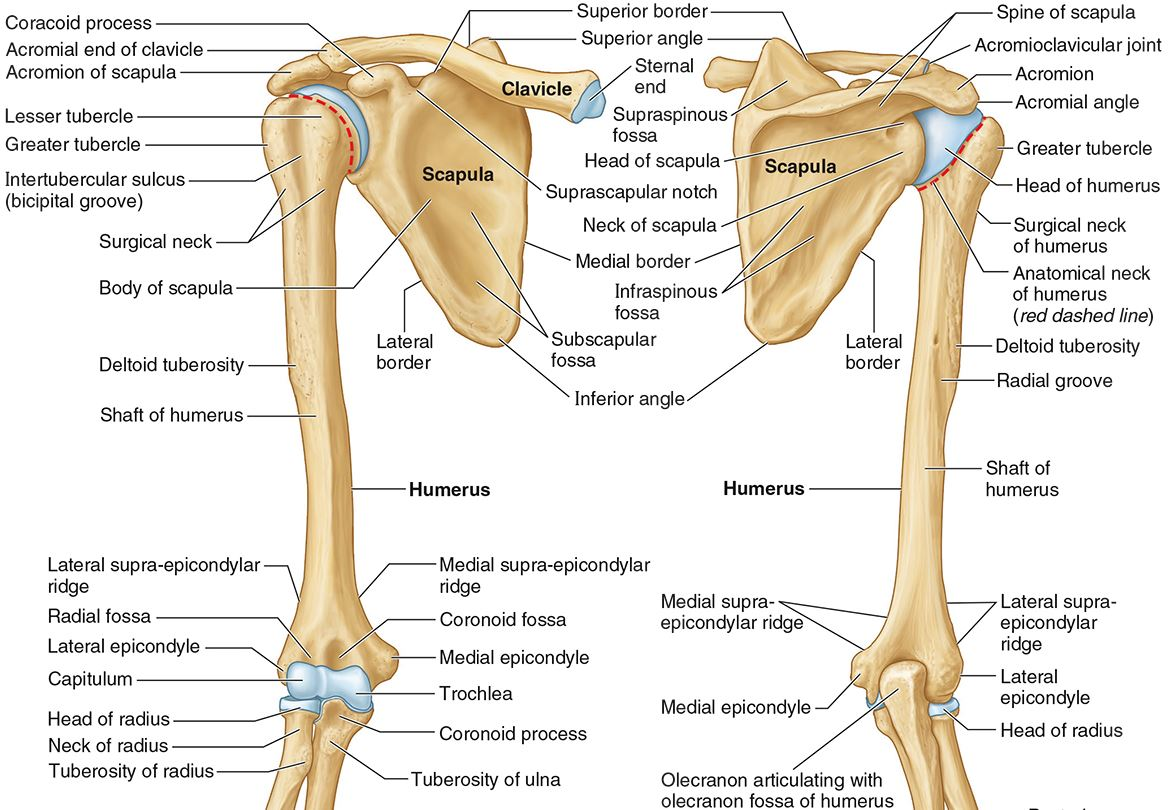
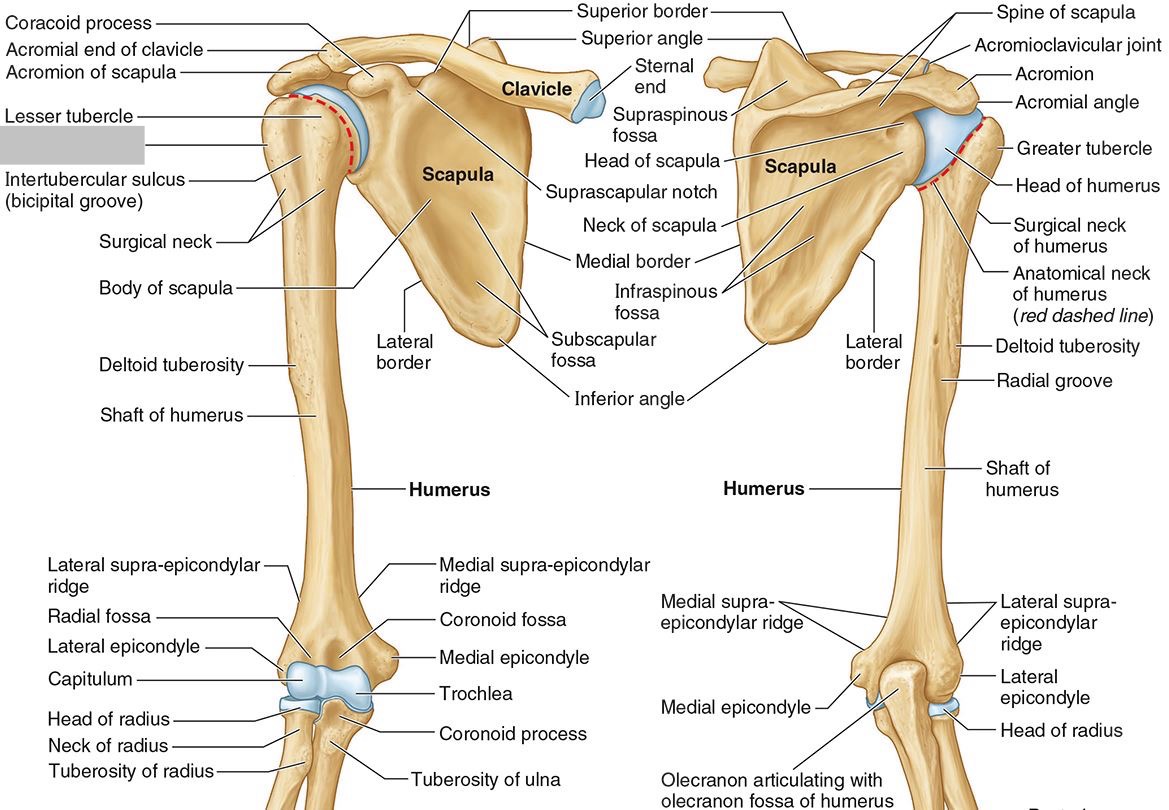
What part of the humerus is this?
The greater tubercle lies lateral and distal to the anatomic neck.
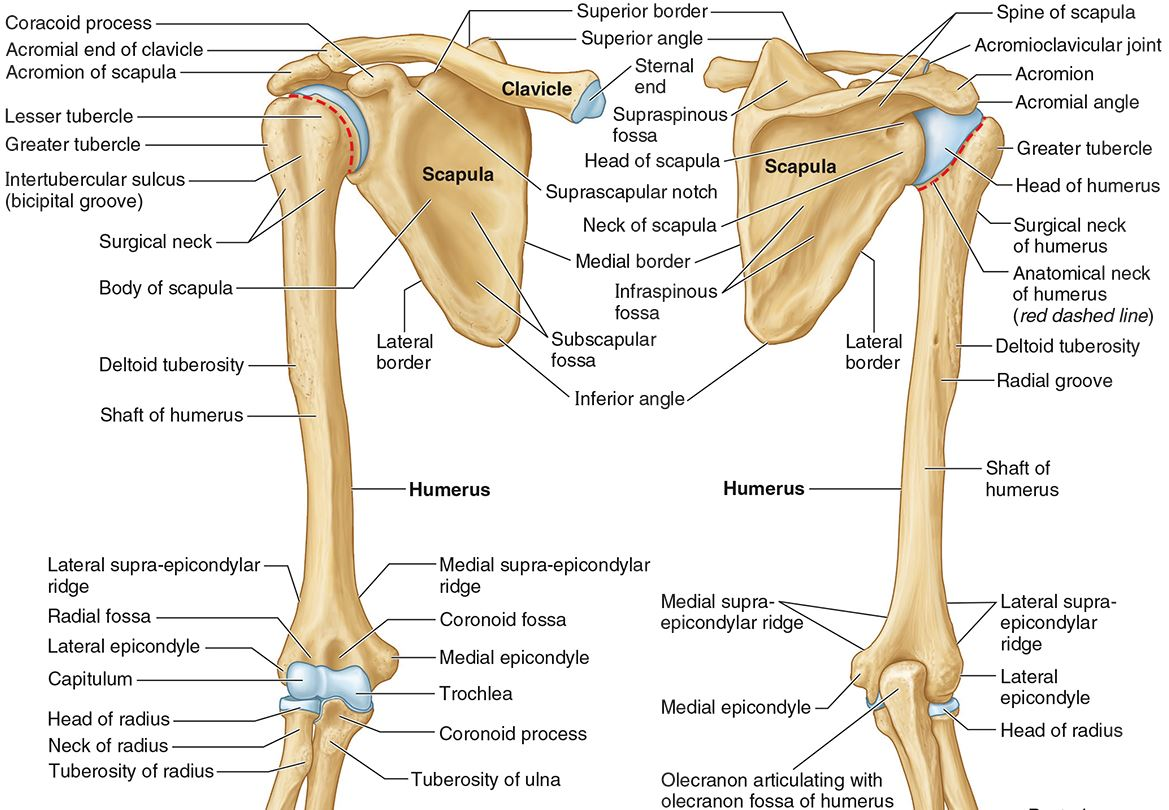
What part of the humerus is this?
The lesser tubercle lies on the anterior/medial side of the humerus, just distal the anatomic neck.
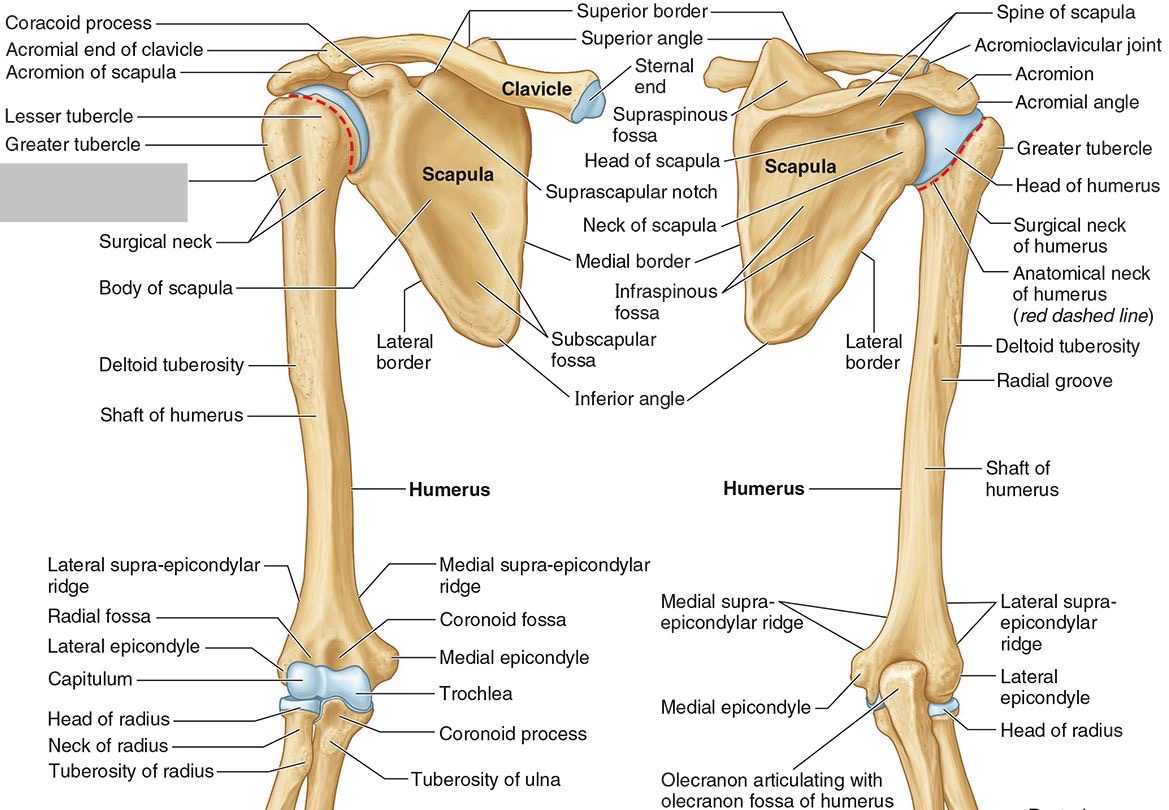
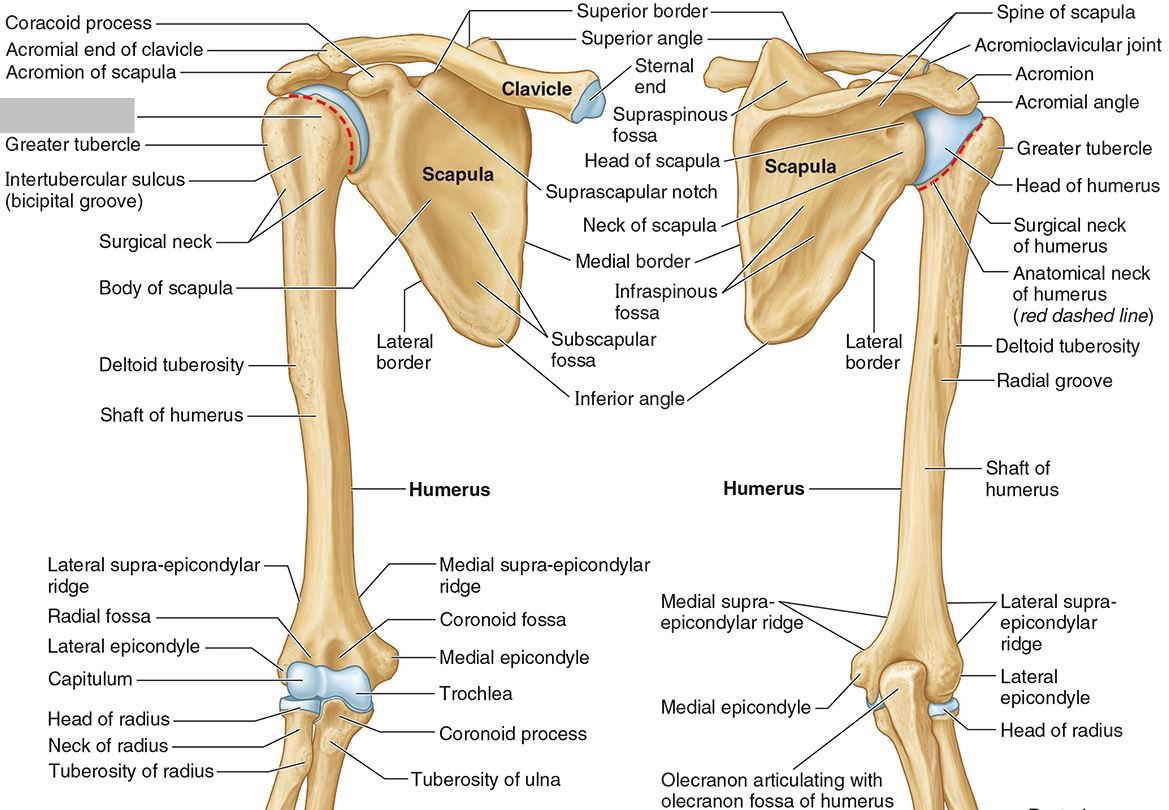
What part of the humerus is this?
The intertubercular (bicipital) groove lies between the greater and lesser tubercles.
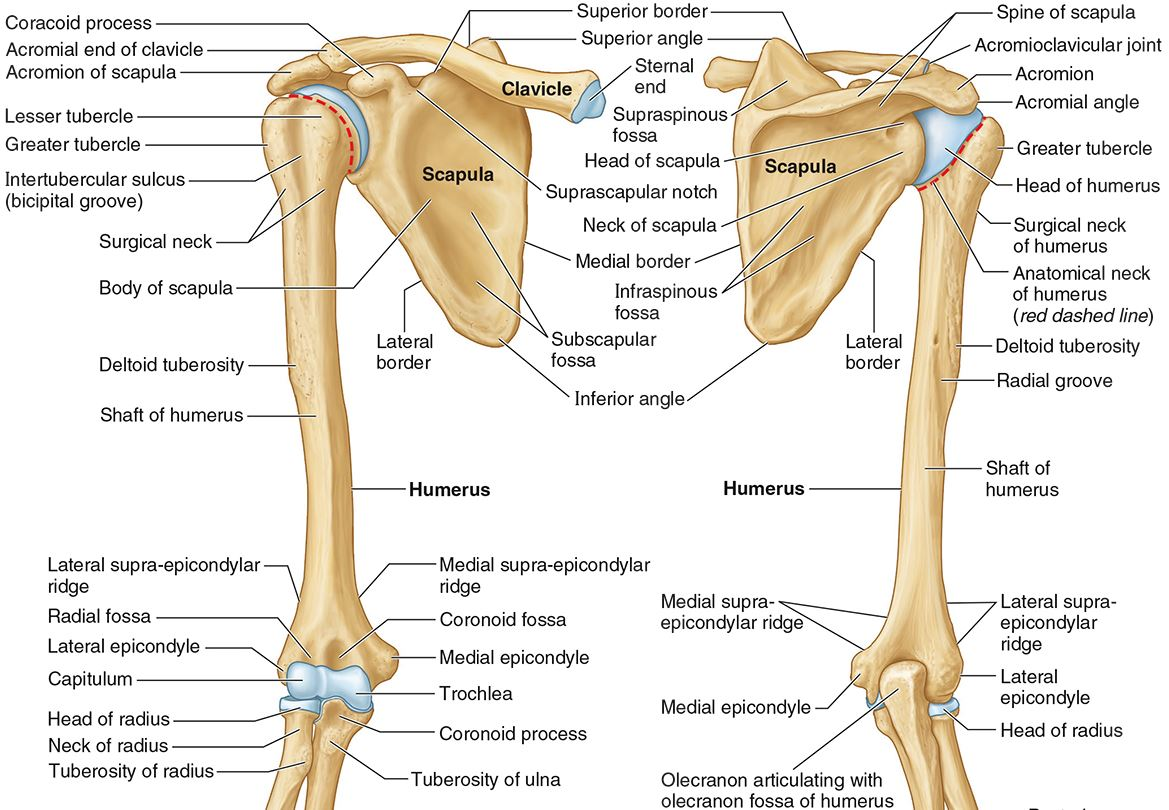
What part of the humerus is this?
The surgical neck is a narrow area distal to the tubercles. It is a common site for proximal humerus fractures.
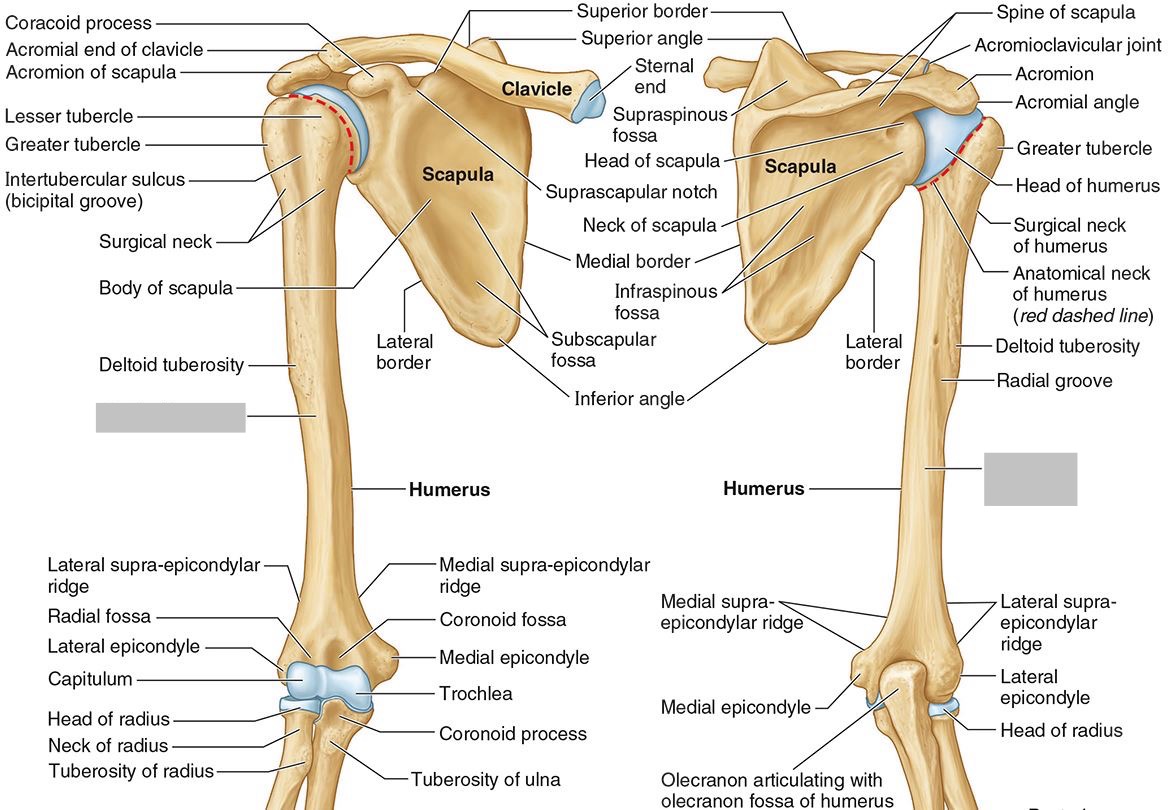
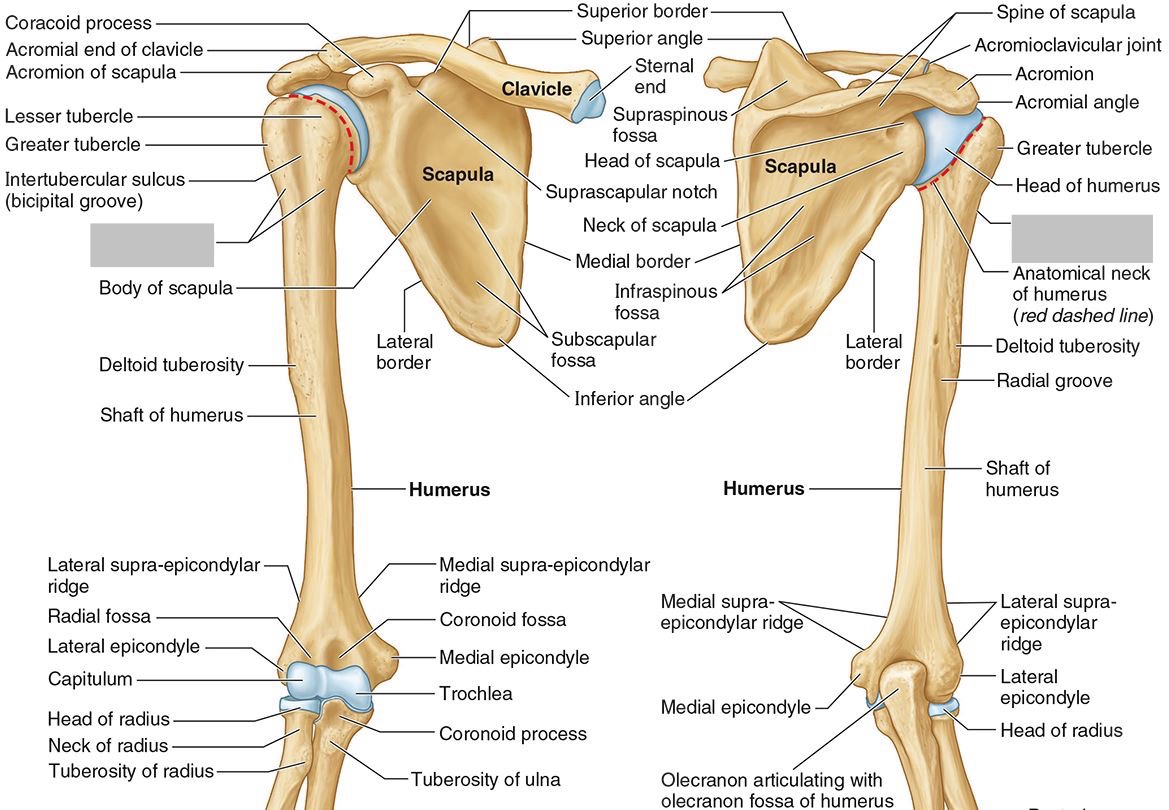
What part of the humerus is this?
The humeral shaft features the deltoid tuberosity laterally for the distal insertion of the deltoid muscle.
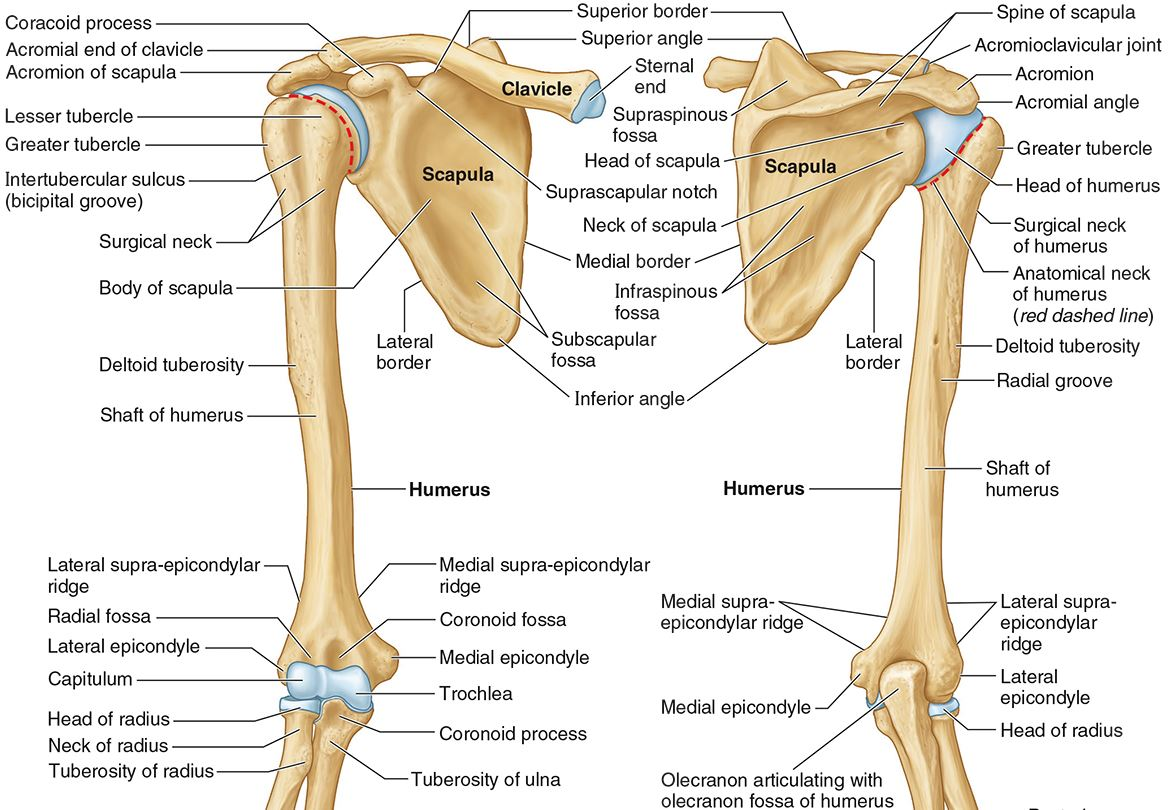
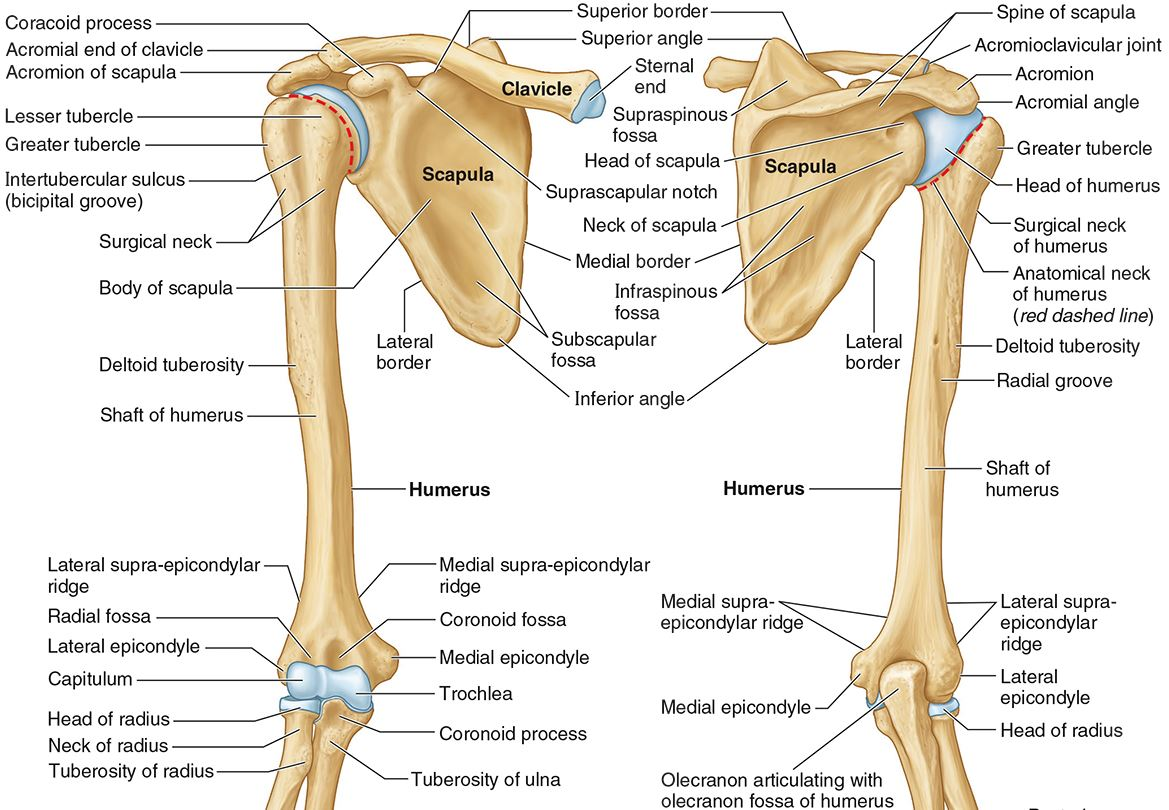
What part of the humerus is this?
The radial groove is an oblique depression that contains the radial nerve and deep brachial artery.
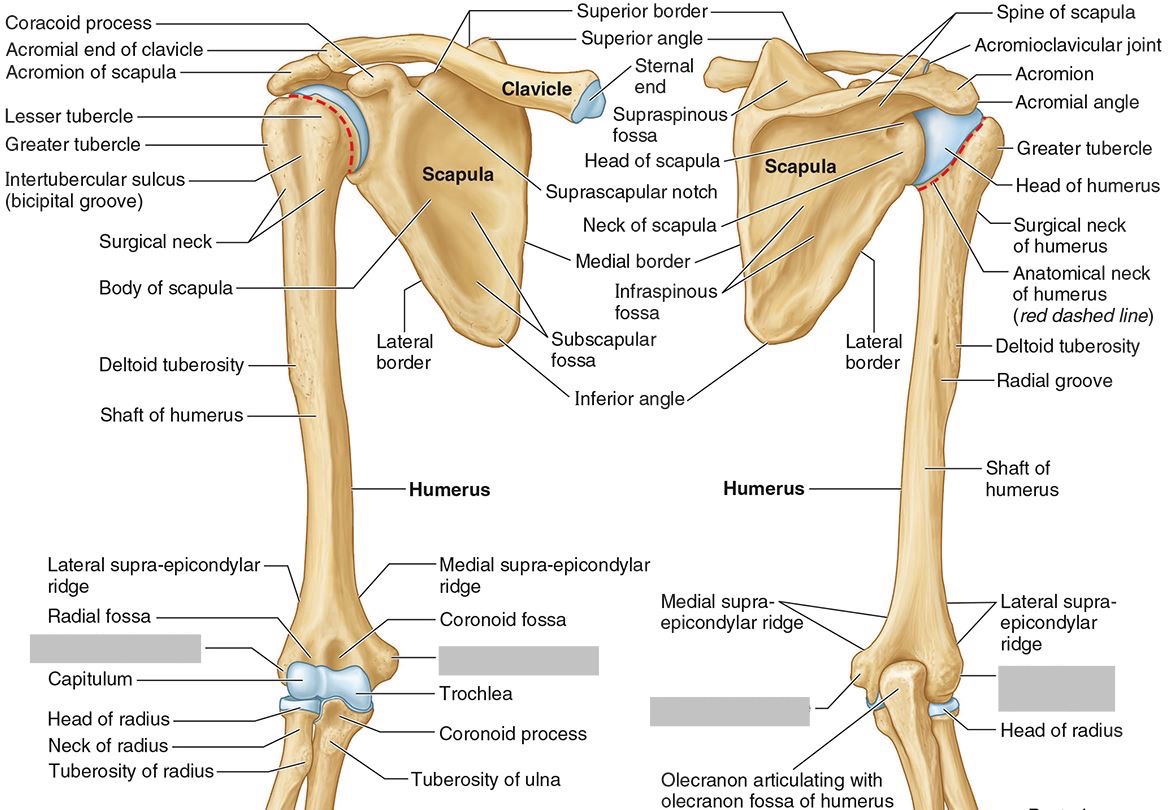
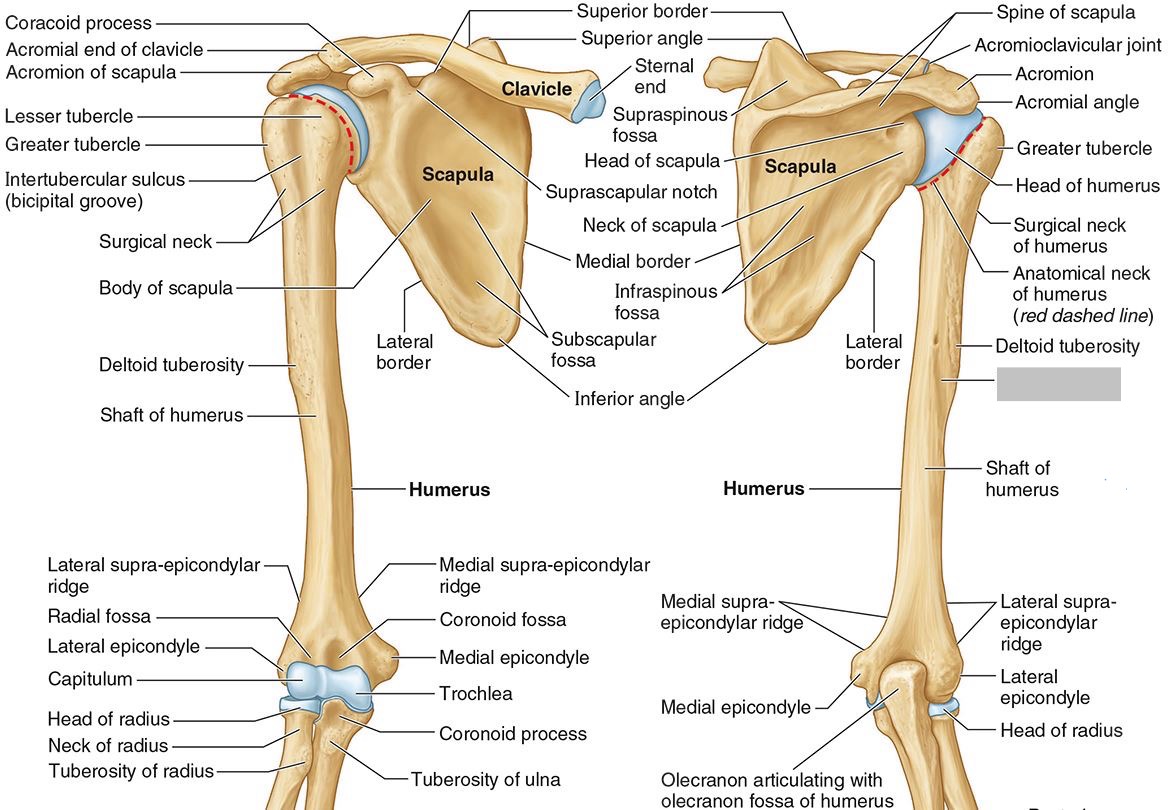
Which parts of the humerus is this?
The medial and lateral epicondyles are distal prominences to which many forearm tendons attach, near the elbow joint.
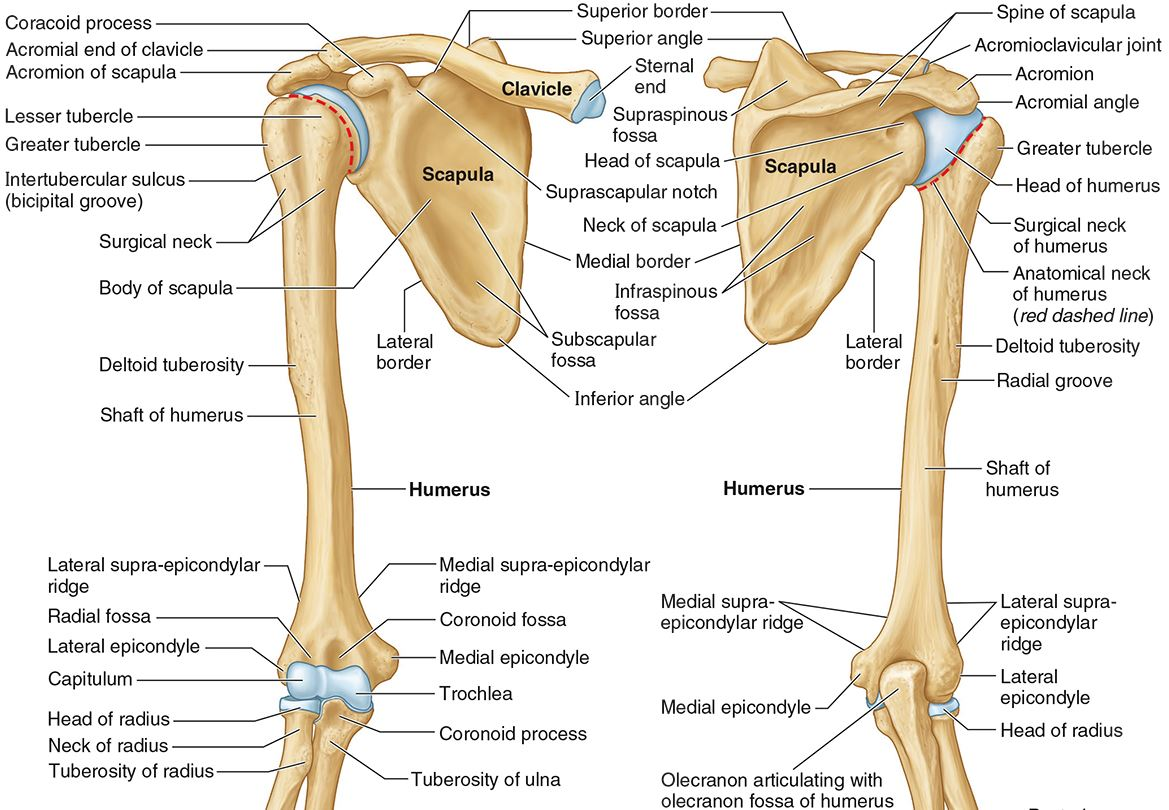
Which parts of the humerus is this?
The medial and lateral supracondylar ridges extend superiorly from the medial and lateral epicondyles.
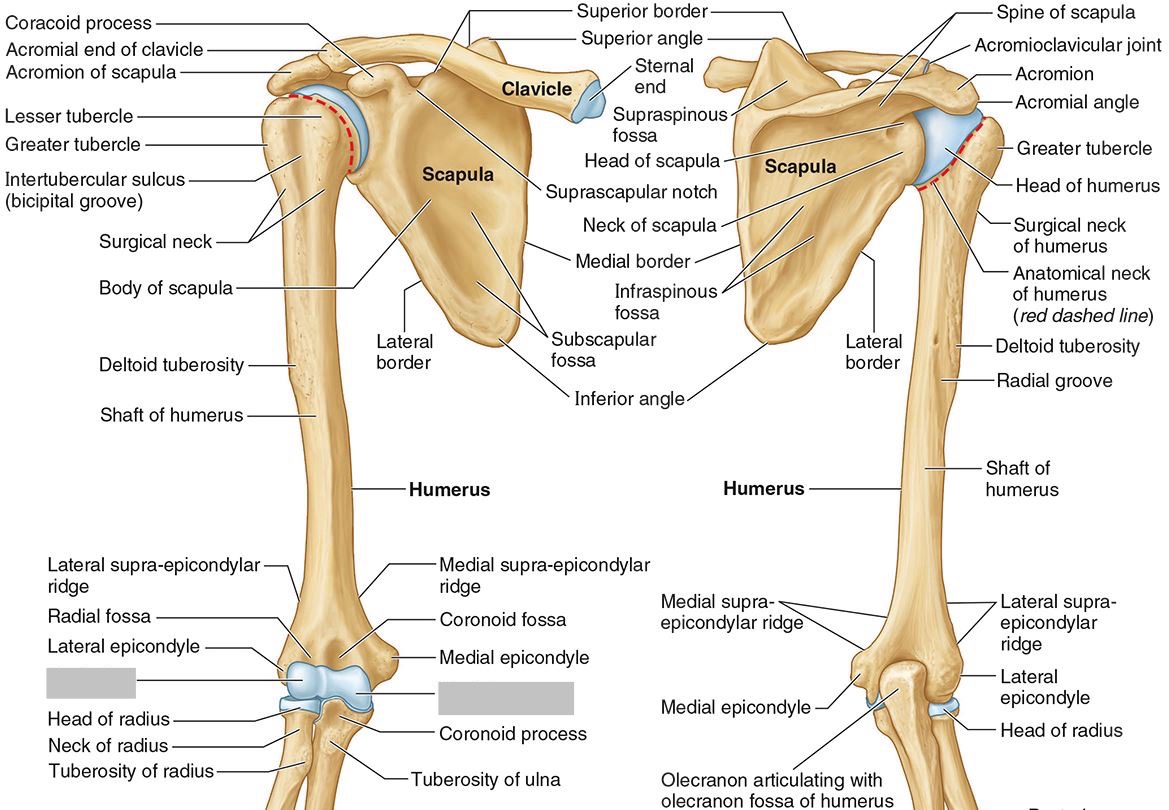
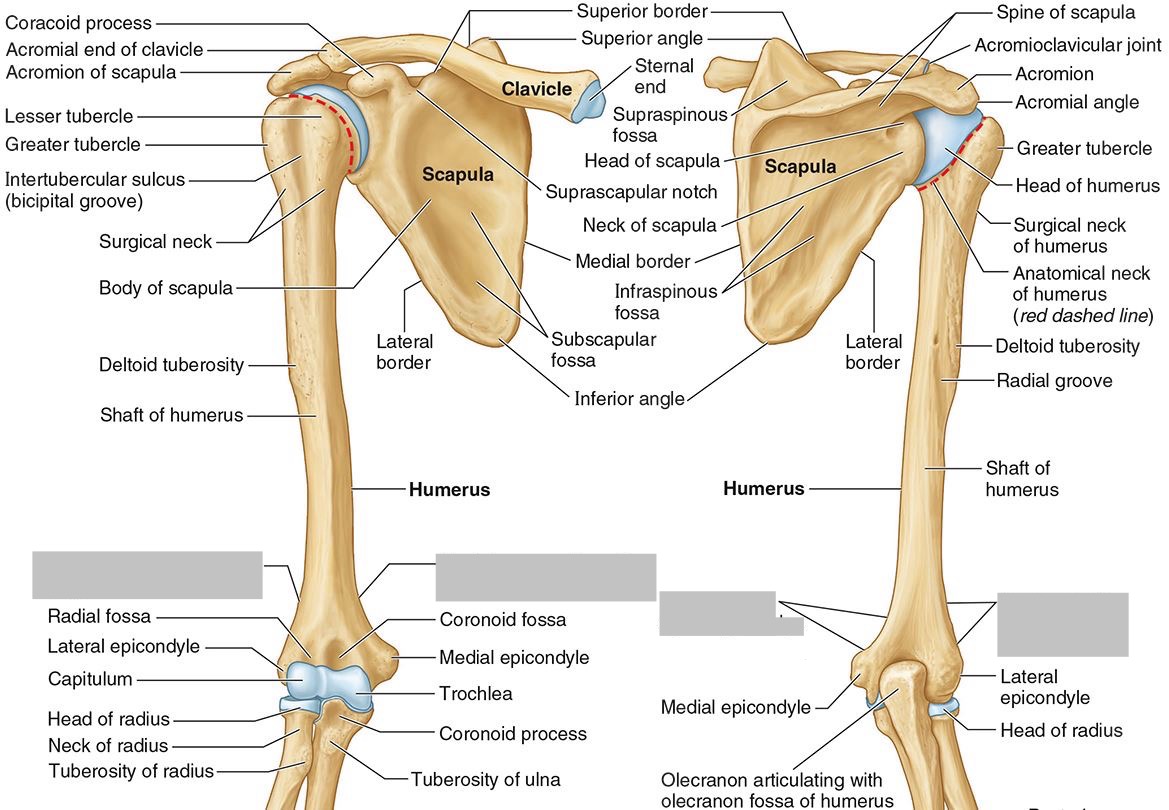
Which parts of the humerus is this?
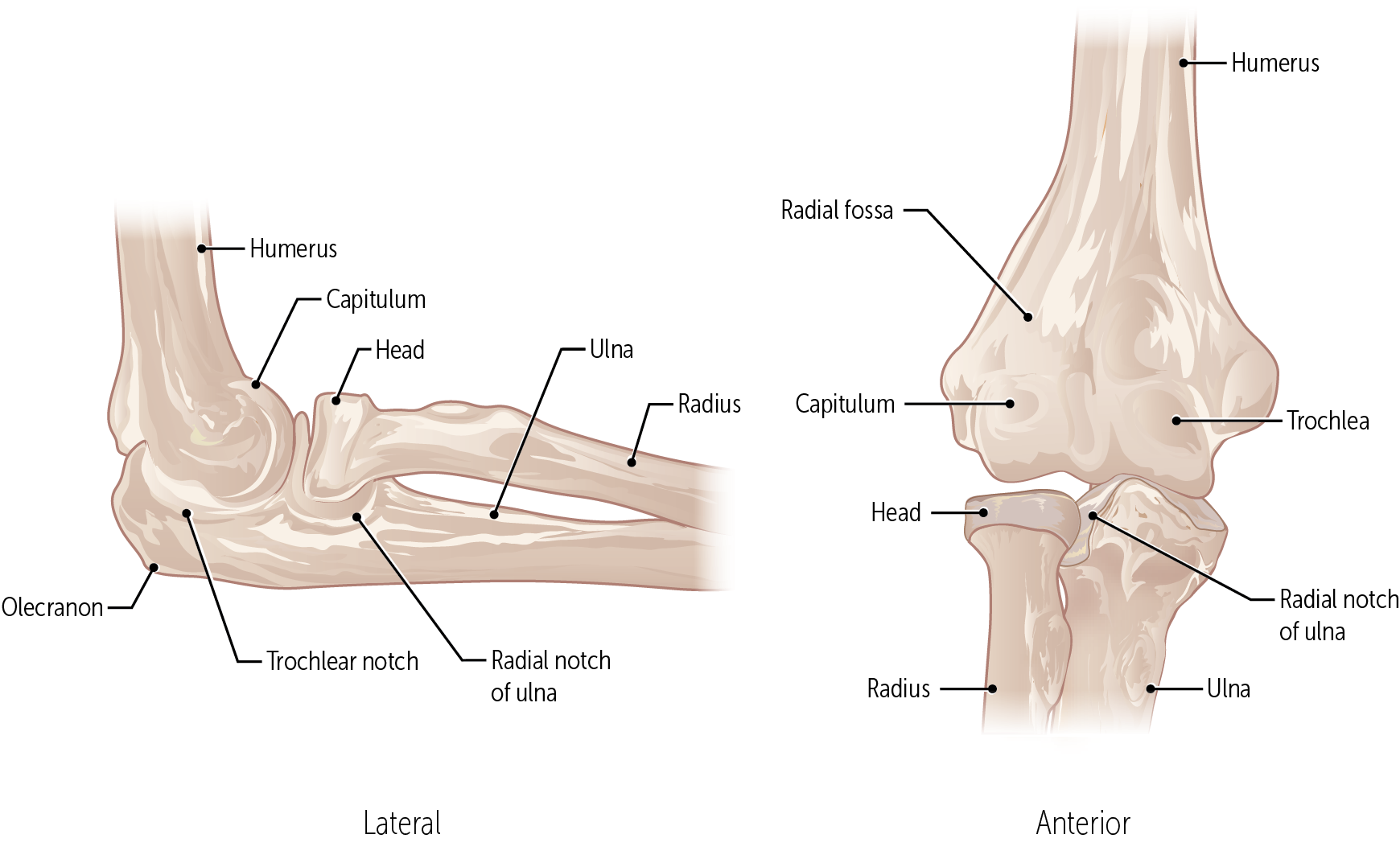
The trochlea and the capitulum (the condyles) are the most distal surfaces of the humerus, where it articulates with the forearm bones at the elbow joint
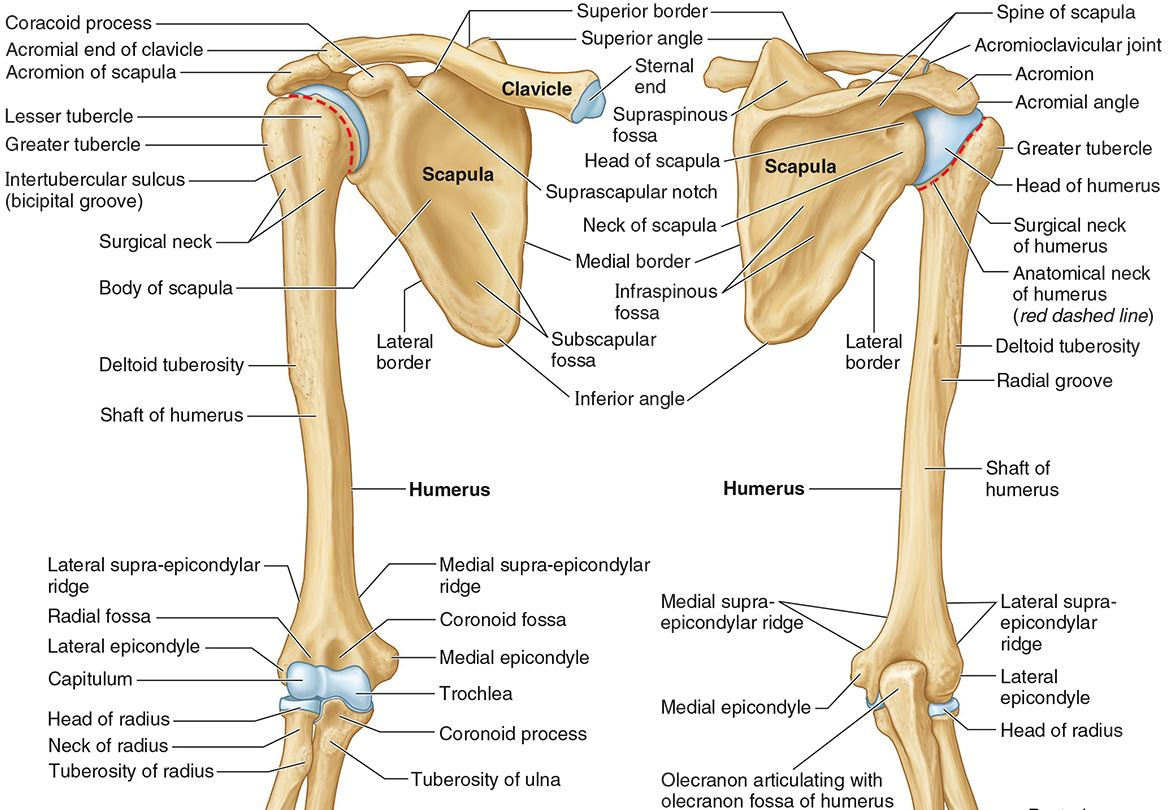
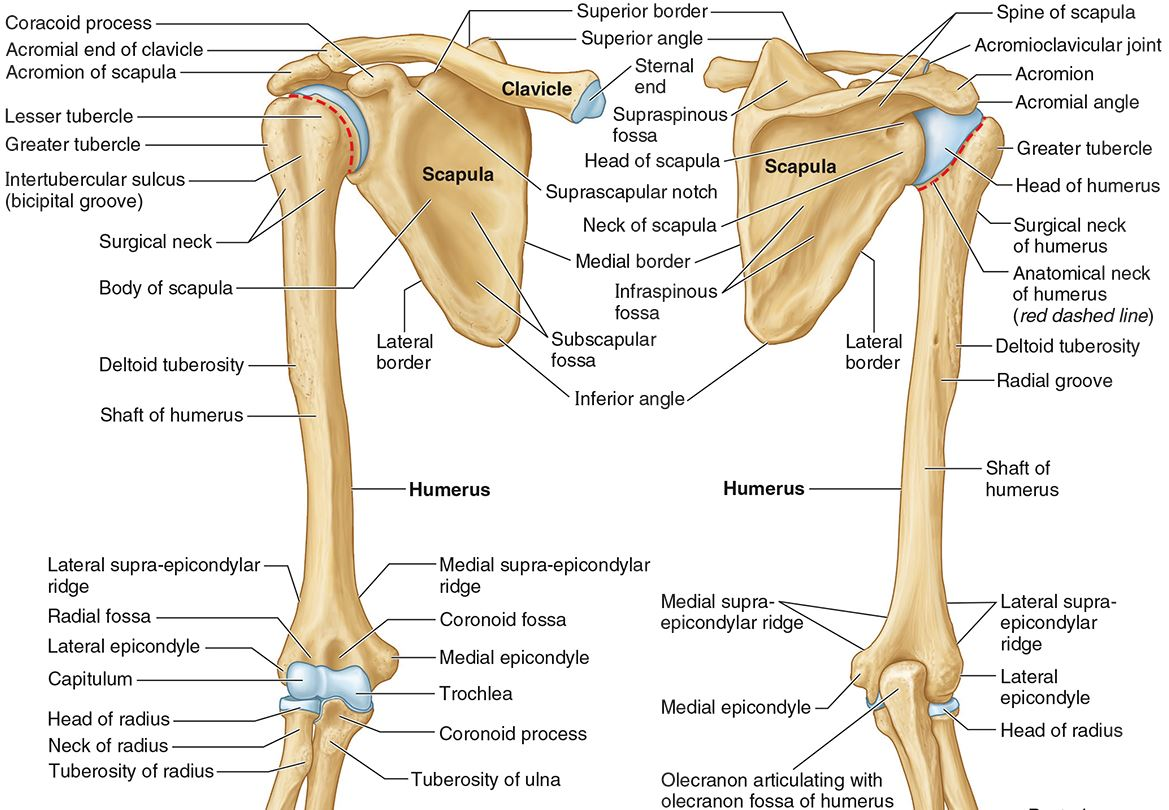
What part of the humerus is this?
The olecranon fossa is a posterior depression above the trochlea that receives that olecranon process of the ulna
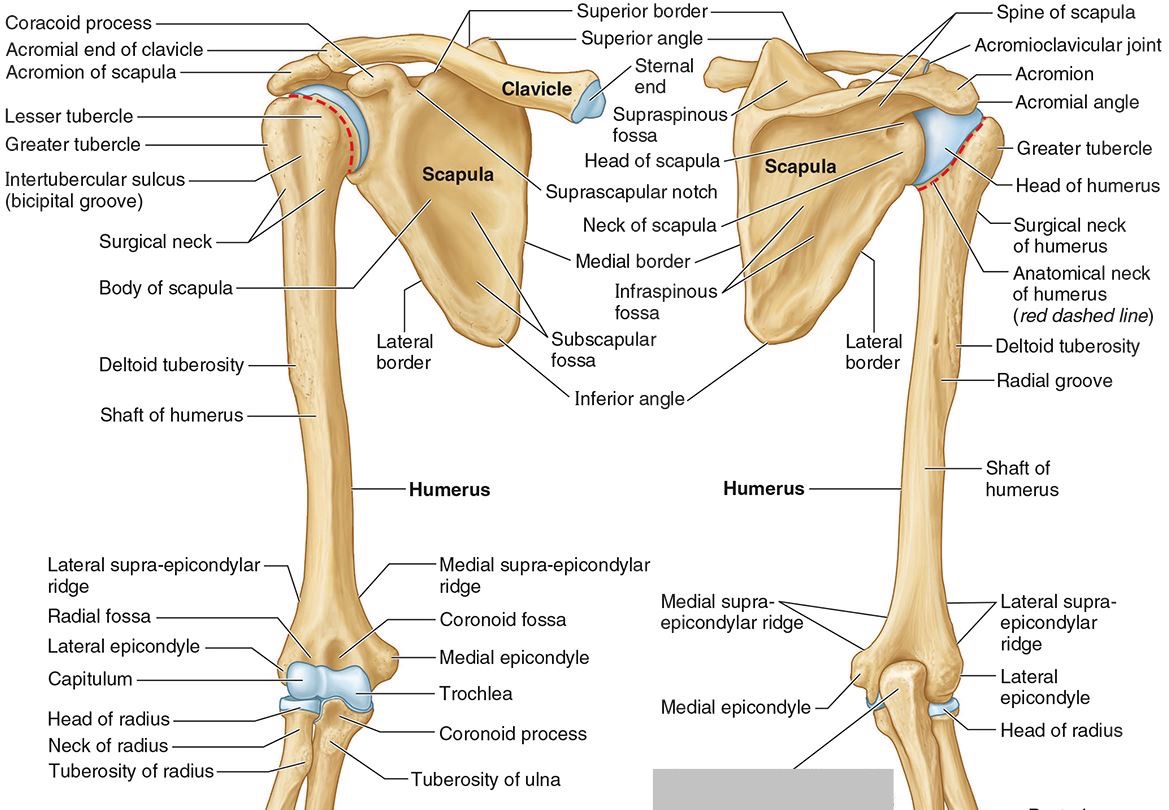
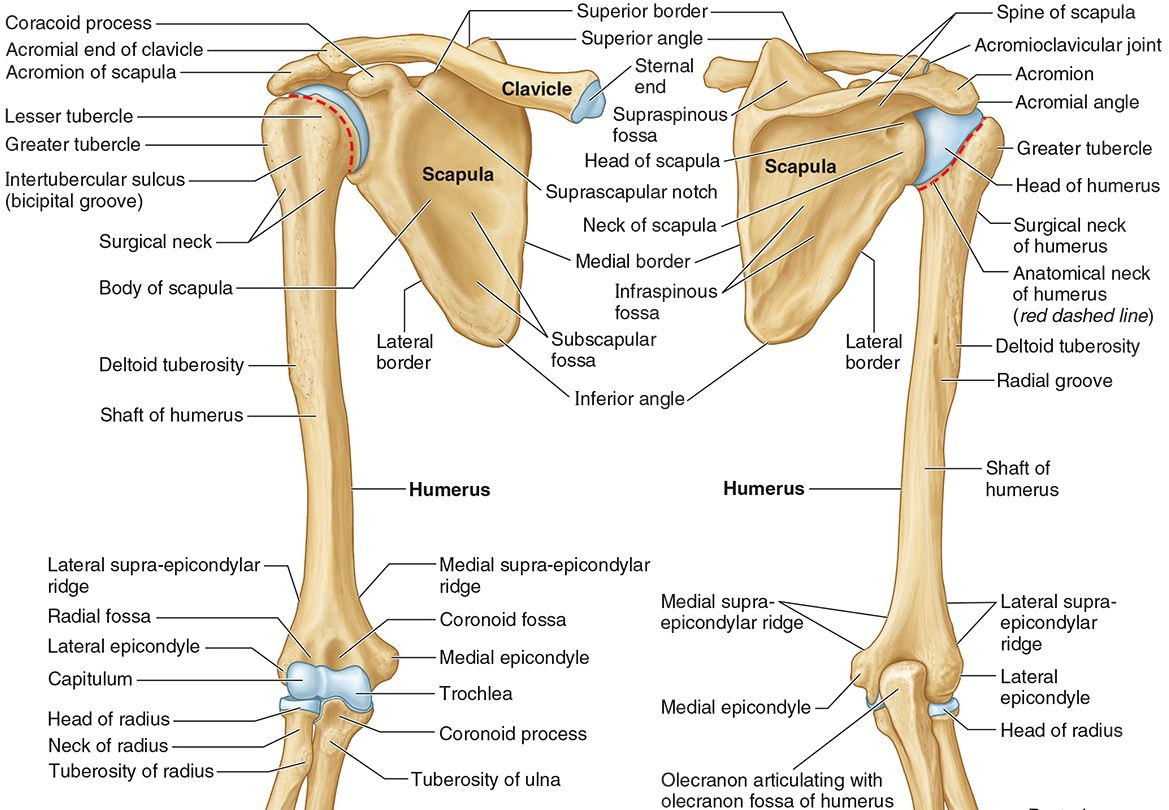
What part of the humerus is this?
The coronoid fossa is an anterior depression above the trochlea that receives that coronoid process of the ulna.
What nerve and vascular injuries are associated with Midshaft humerus fracture?
Radial nerve (N.) & deep brachial artery (A.)
What nerve and vascular injuries are associated with Surgical neck humerus fracture?
Axillary N. & posterior humeral circumflex A.
What nerve injury is associated with Supracondylar humerus fracture?
Median N.
What nerve injury is associated with Medial epicondylar fracture?
Ulnar N.
What nerve injury is associated with Lateral epicondyle fracture?
Radial N.
What nerve and vascular injuries are associated with Anterior shoulder dislocation?
Axillary N. & axillary A.
What nerve and vascular injuries are associated with Posterior shoulder dislocation?
Axillary N.& subscapular N.7
What bones connect to the humerus at the elbow?
The radius and ulna
The ______ connects to the carpal bones of the hand at the wrist joint. The _____ widens distally to provide the proximal articular surface of the wrist (remember, the _____ is on thumb side of the wrist!)
(all the blanks are the same word)
Radius
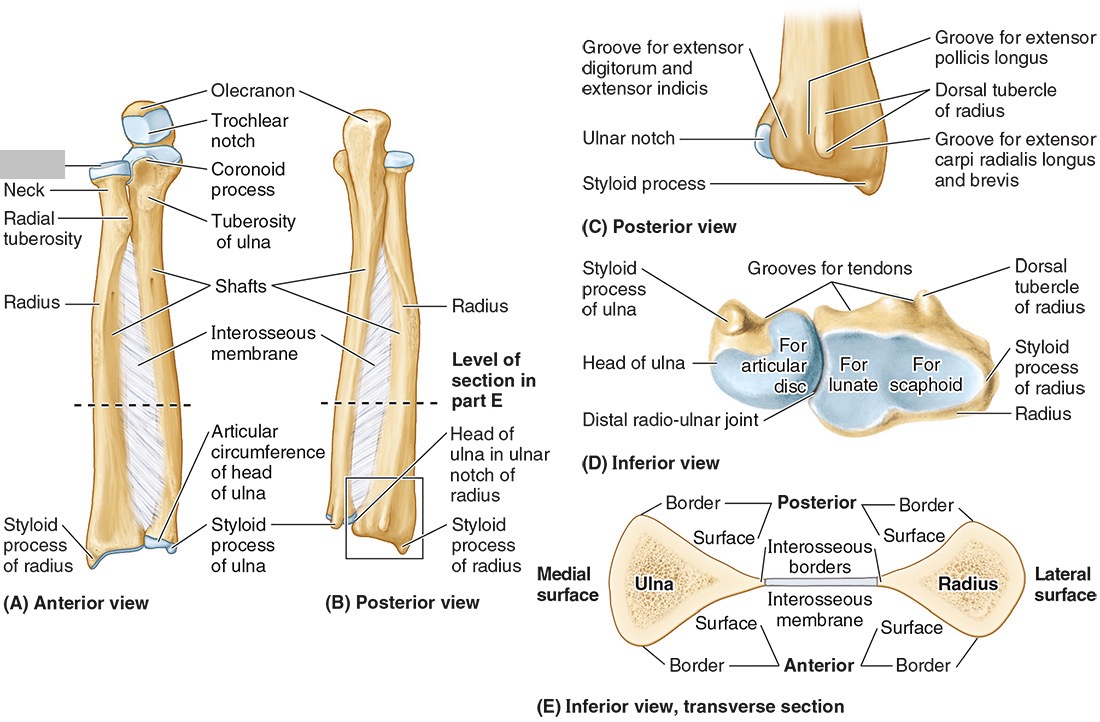
The head of the radius
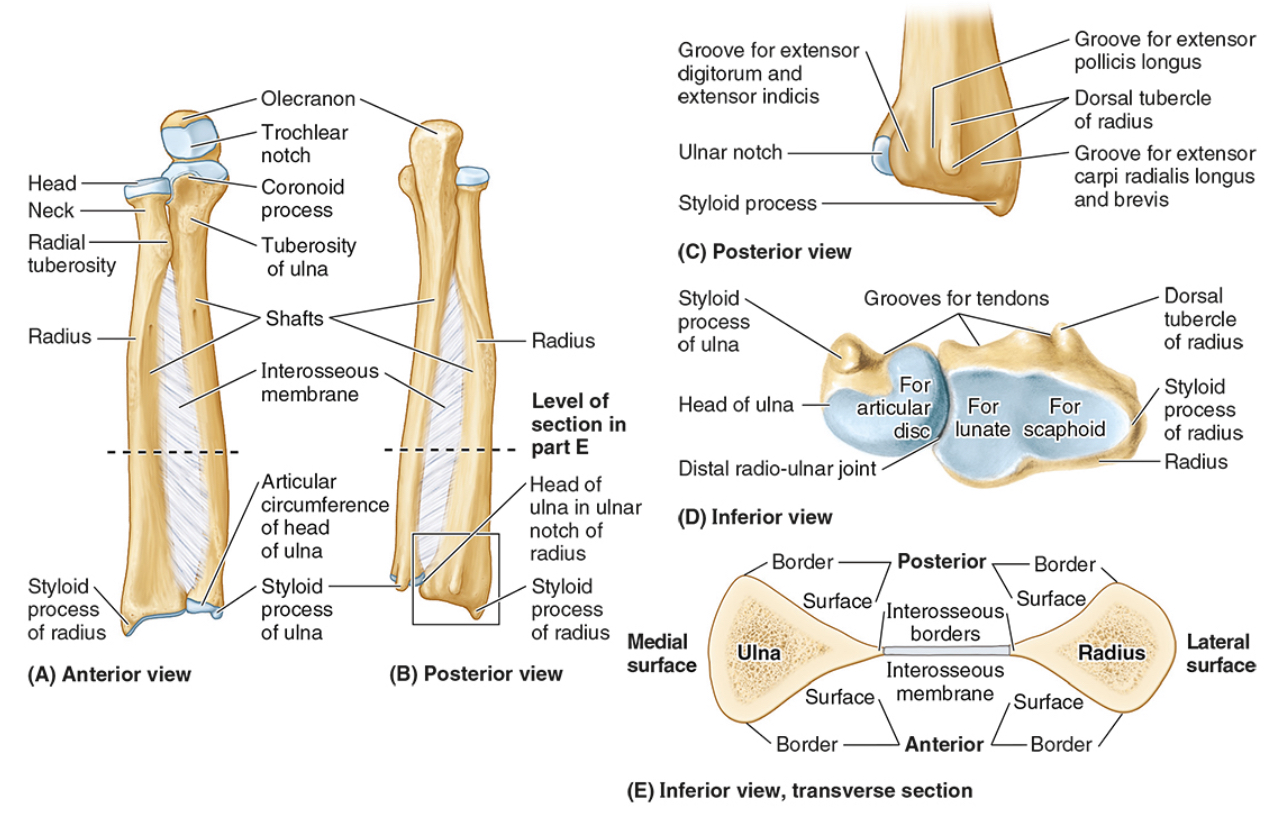
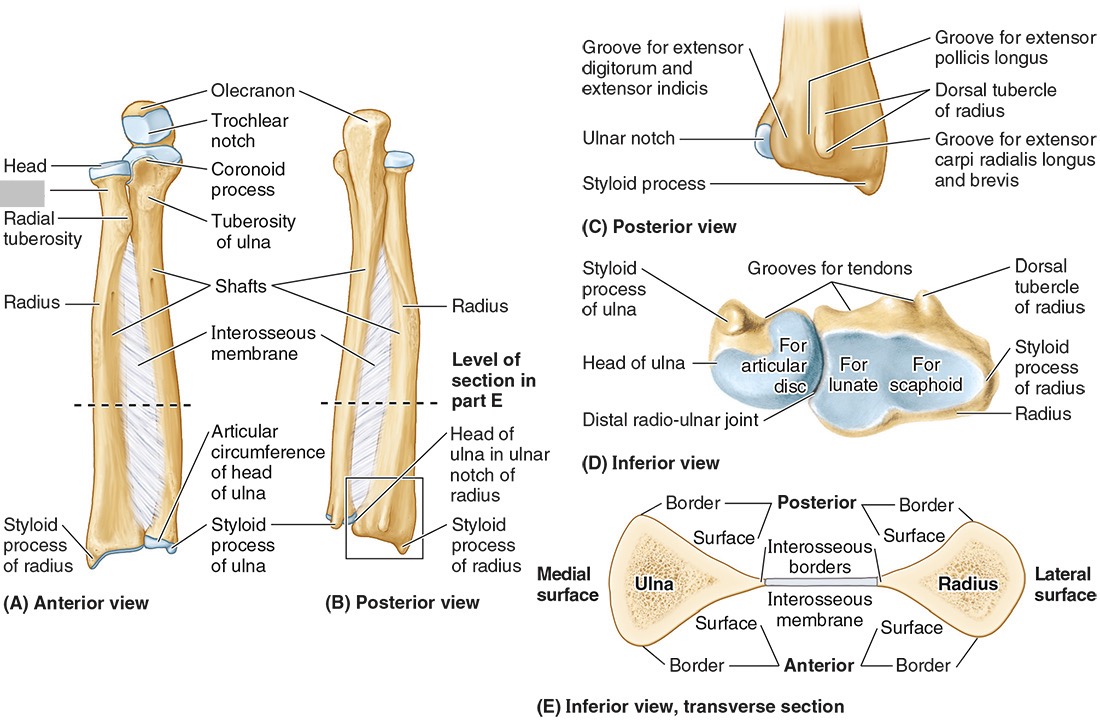
The neck of the radius
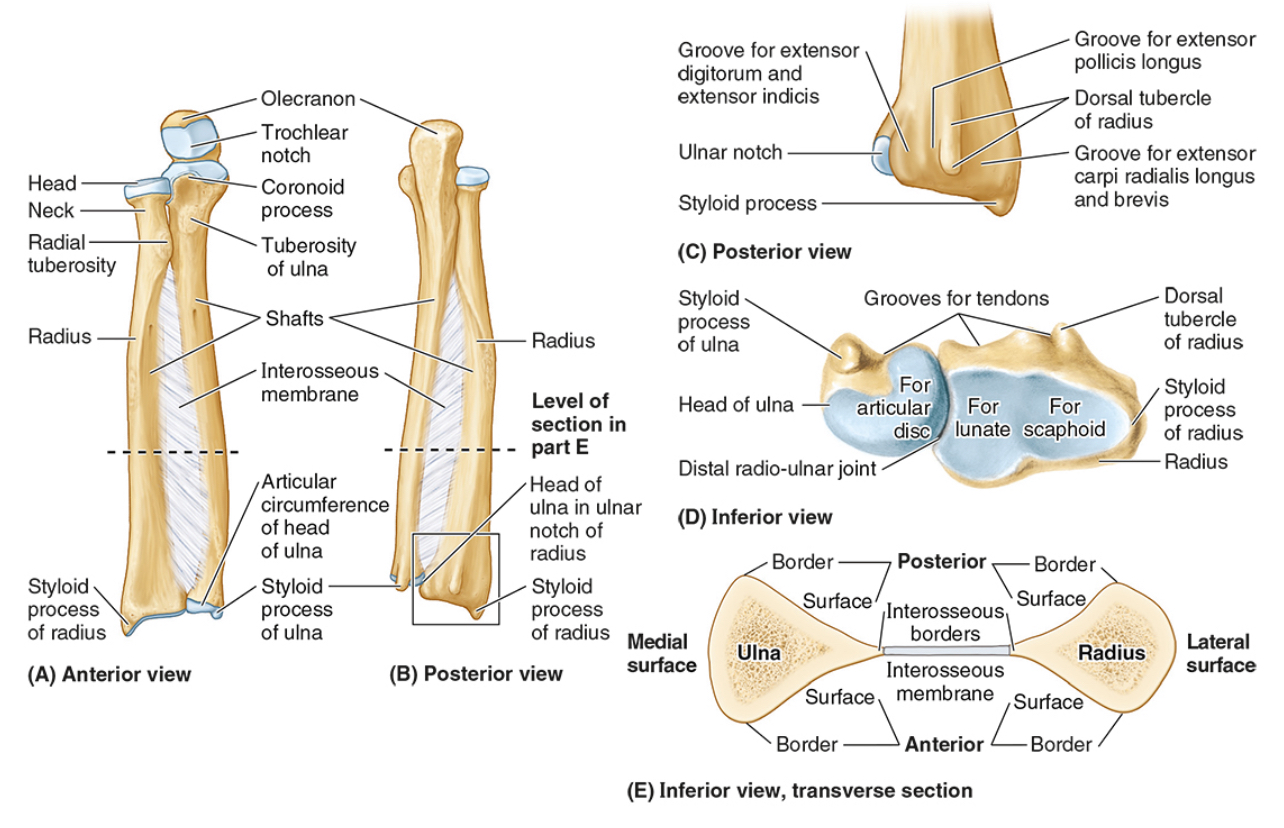
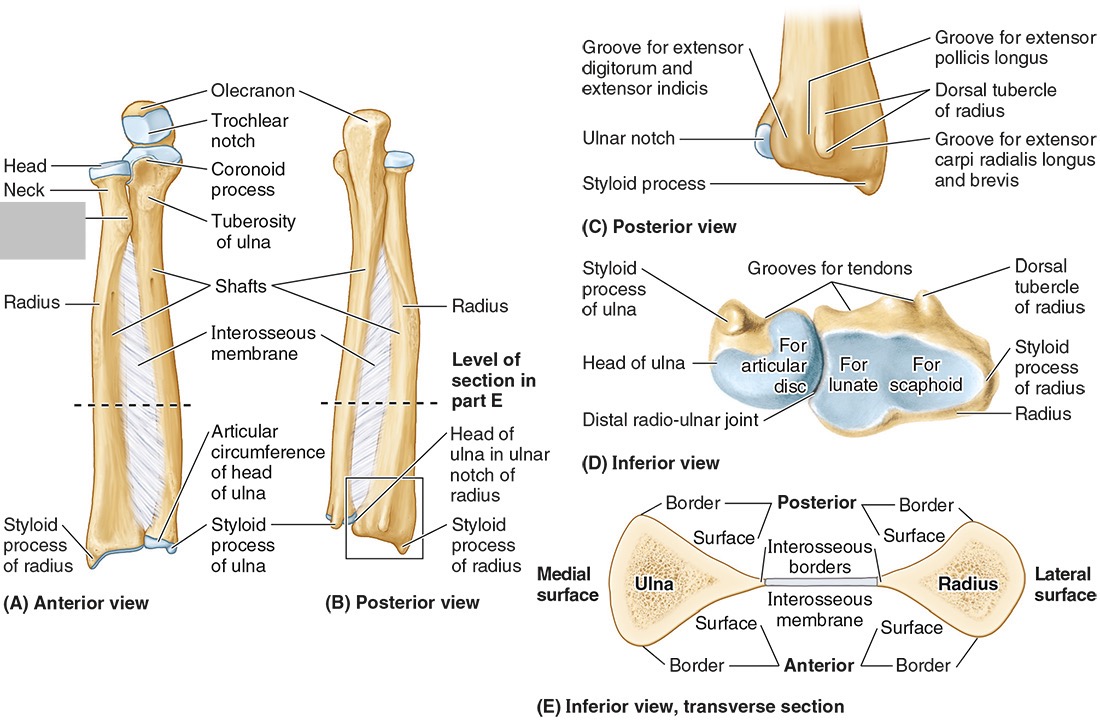
The radial tuberosity
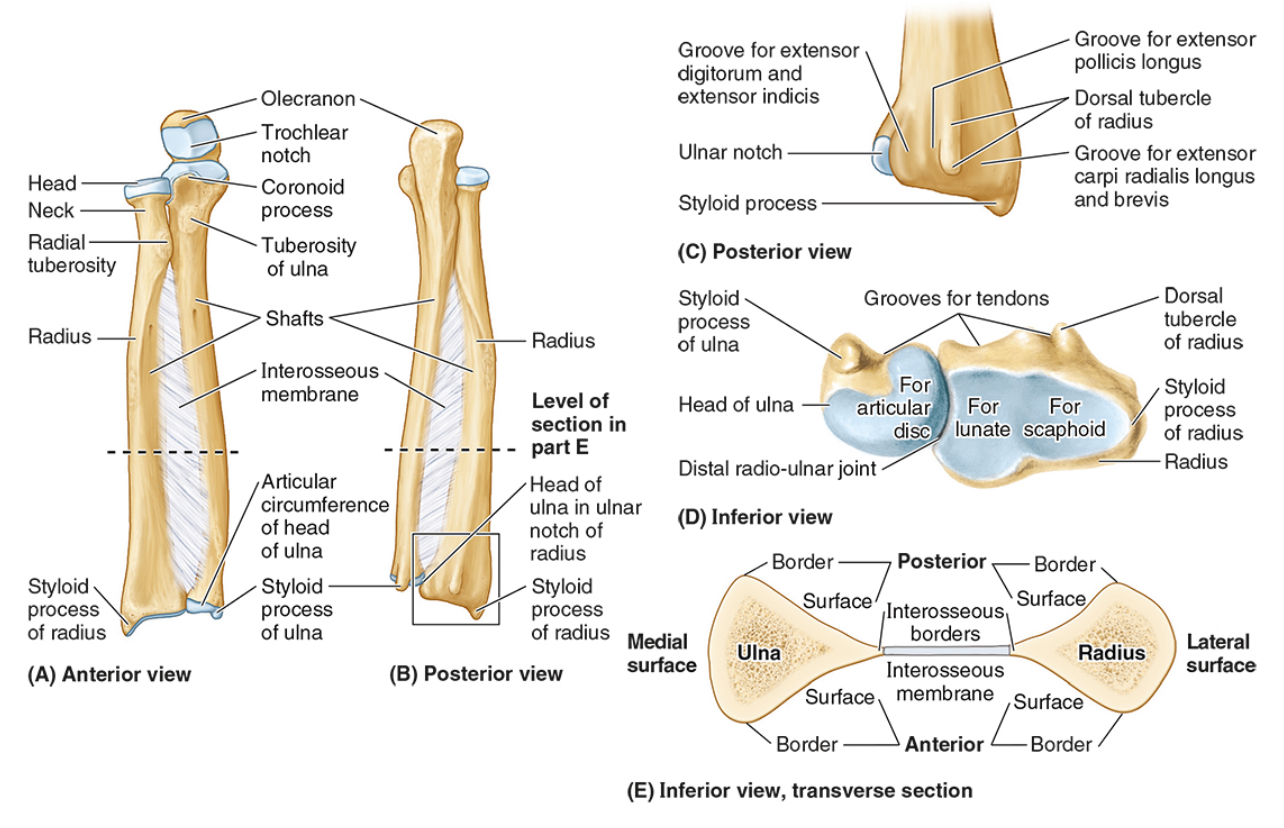
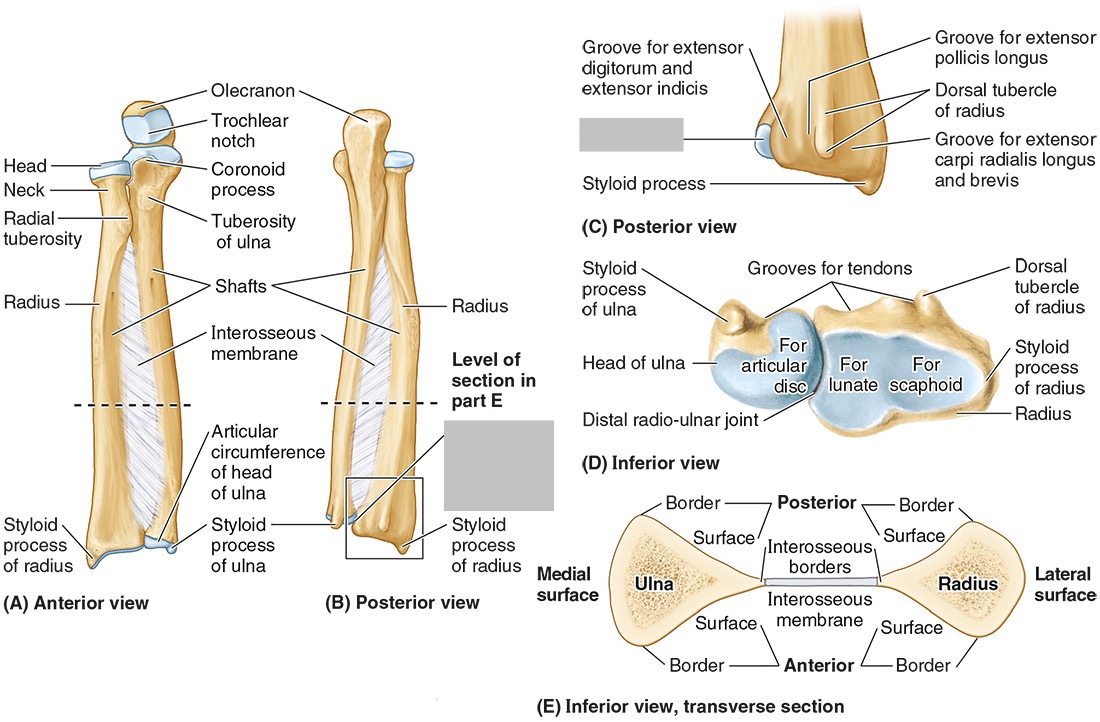
The ulnar notch
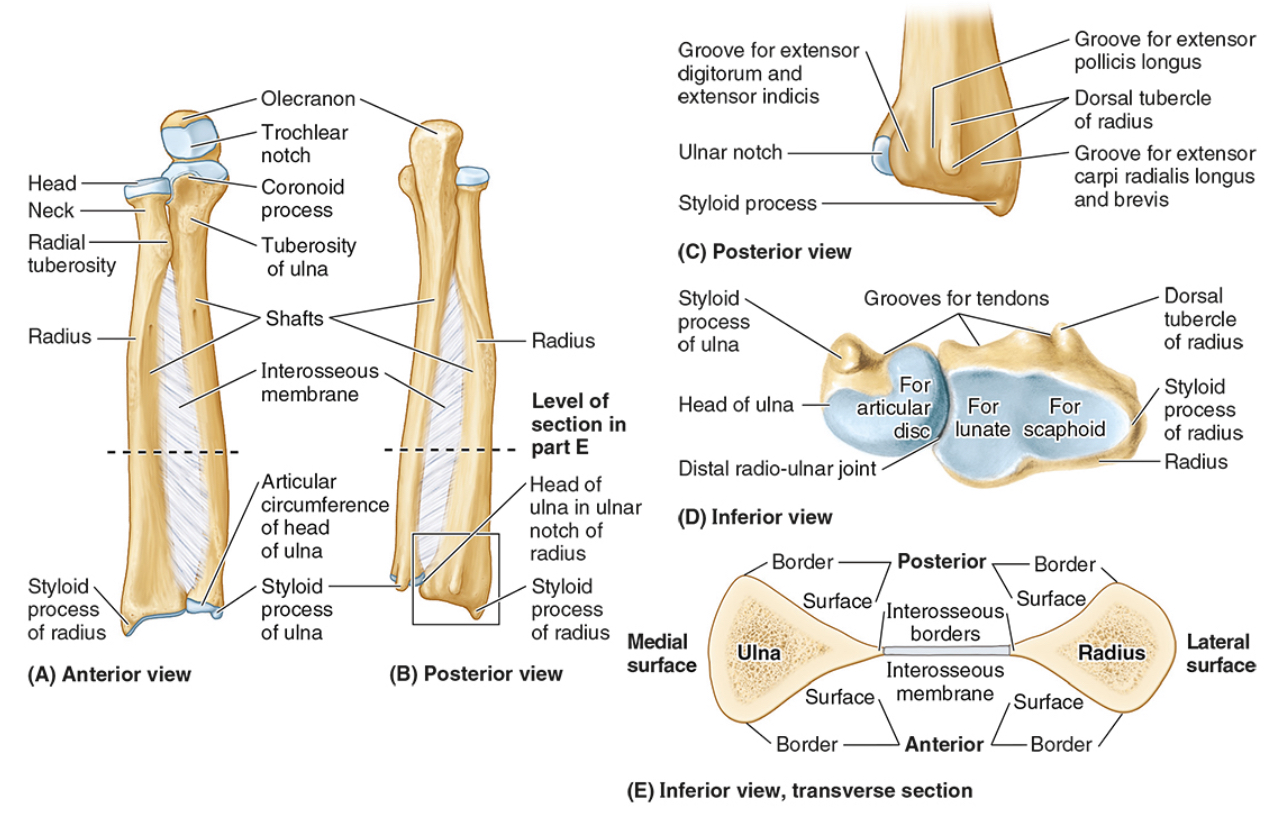
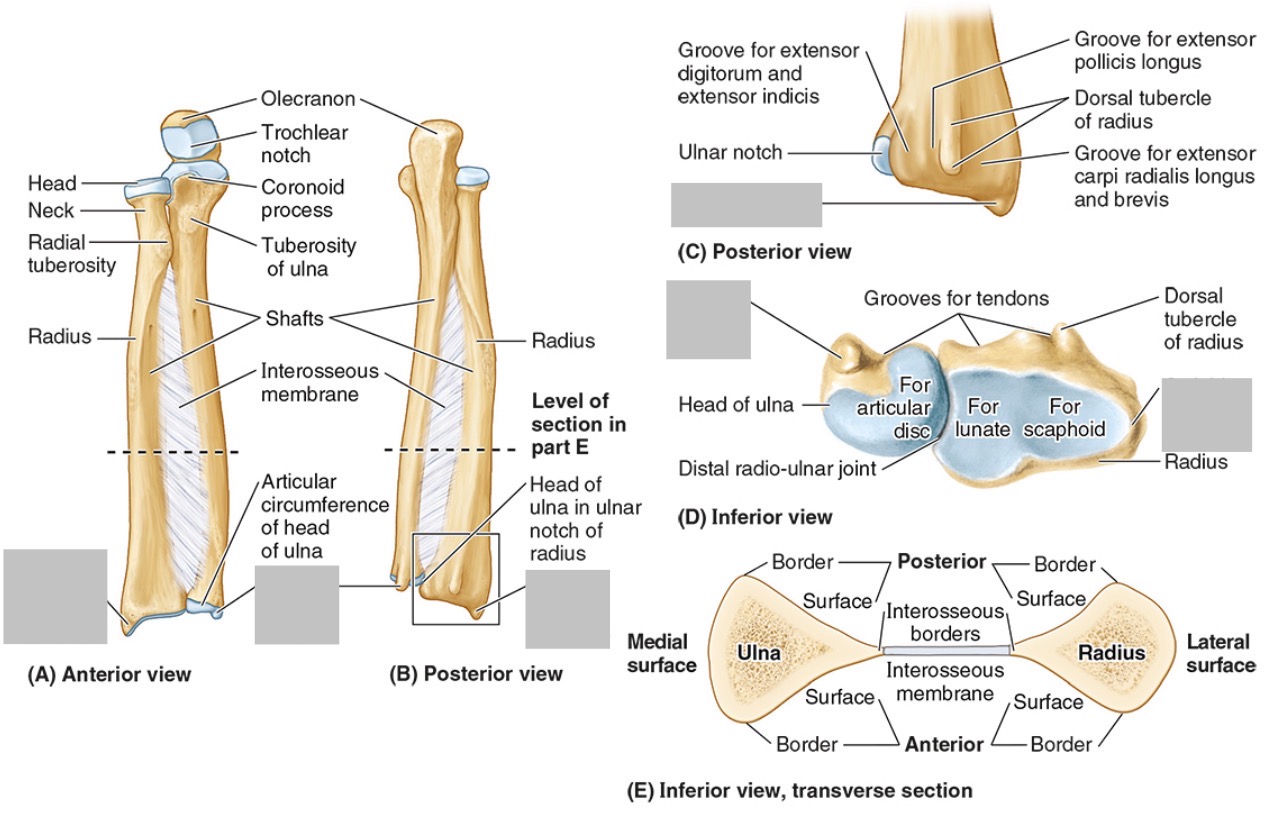
The styloid process
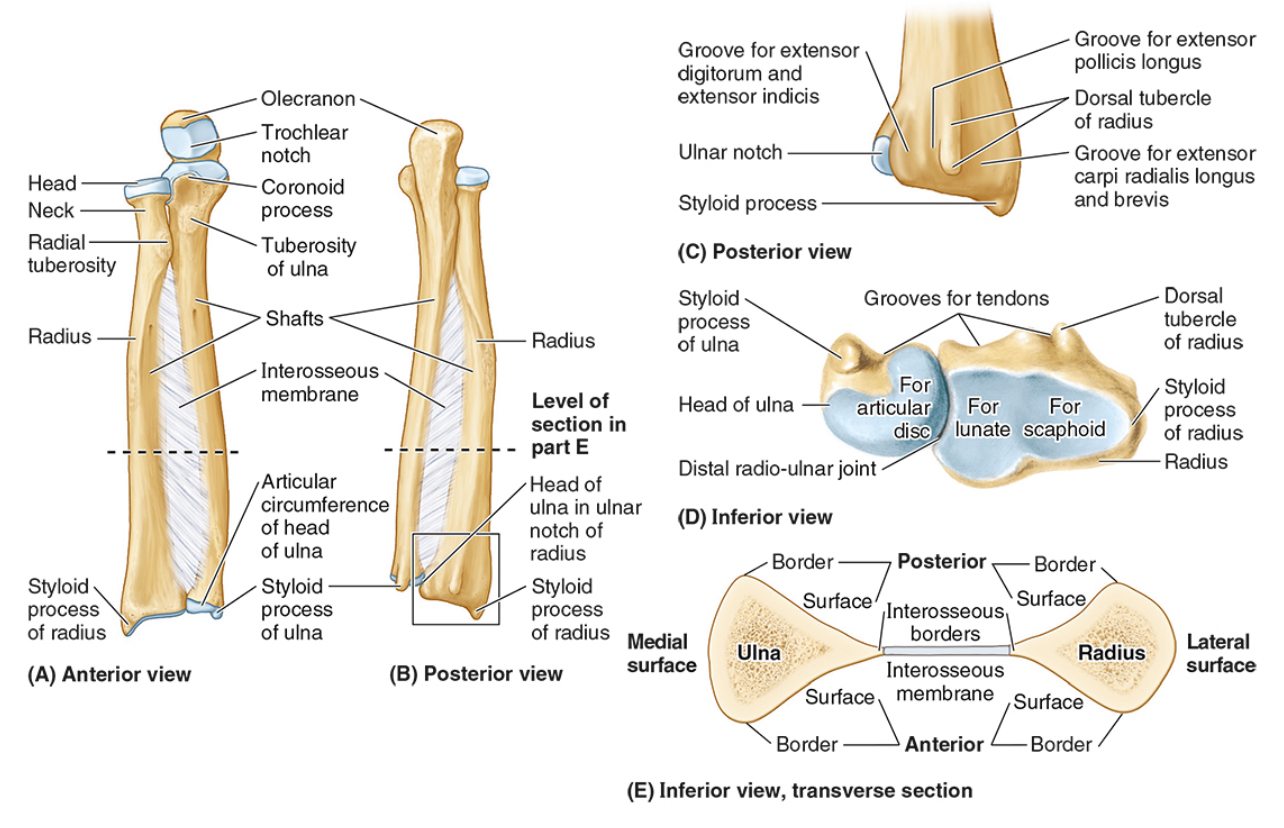
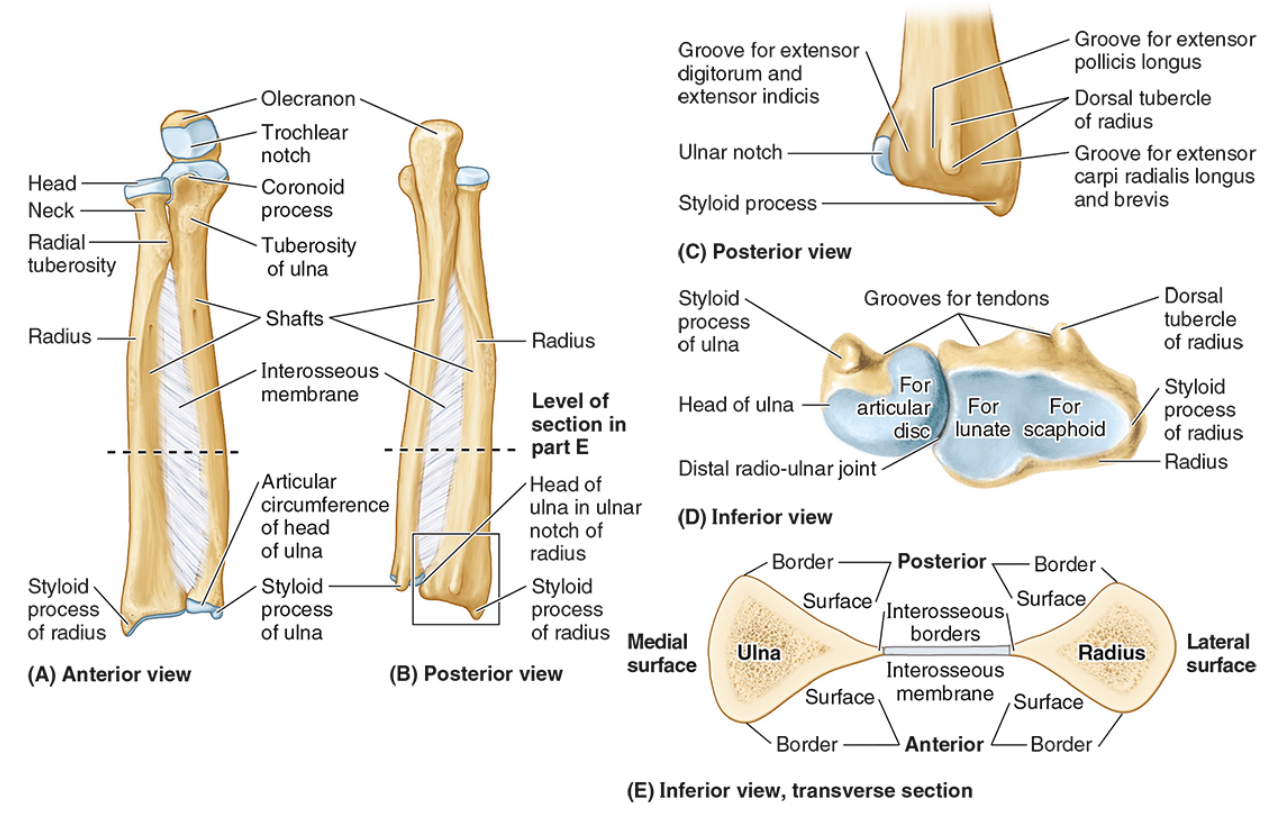
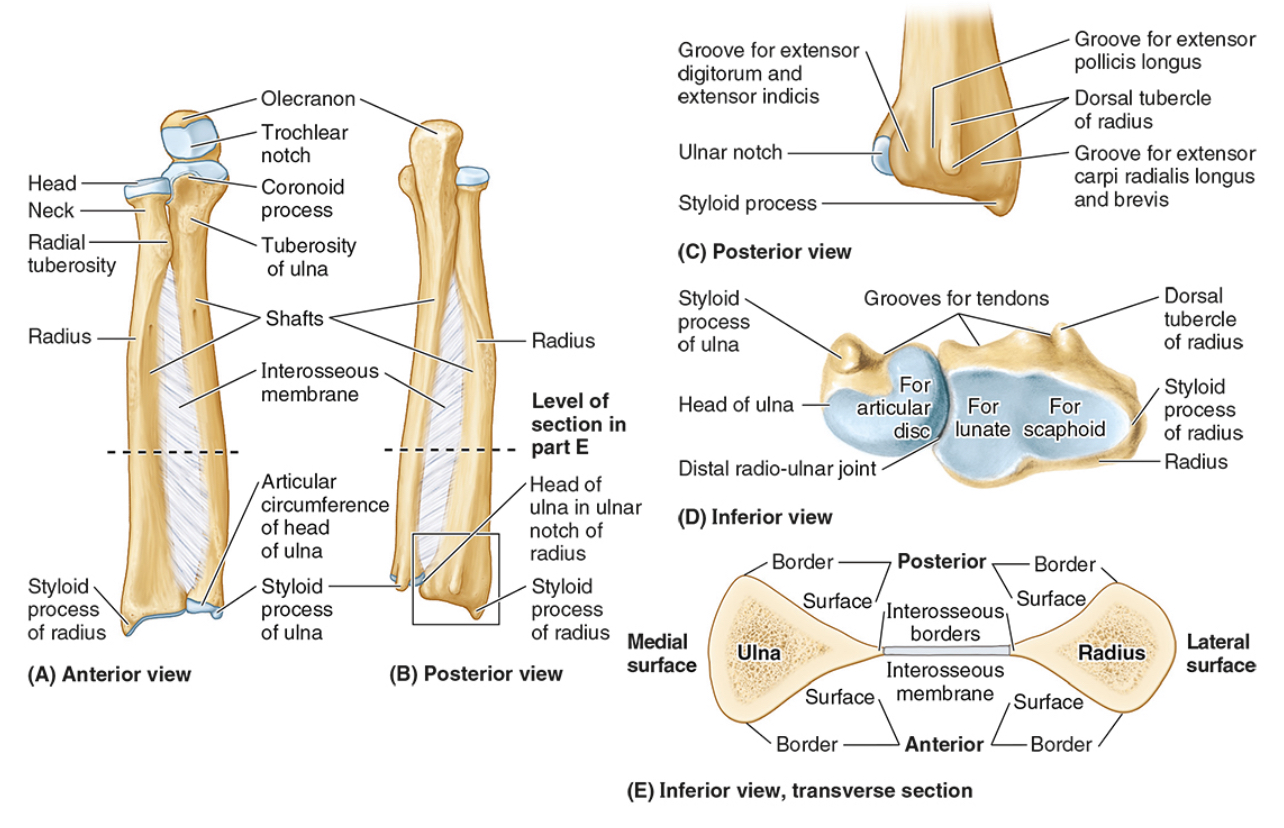
The ____ is the medial forearm bone
Ulna
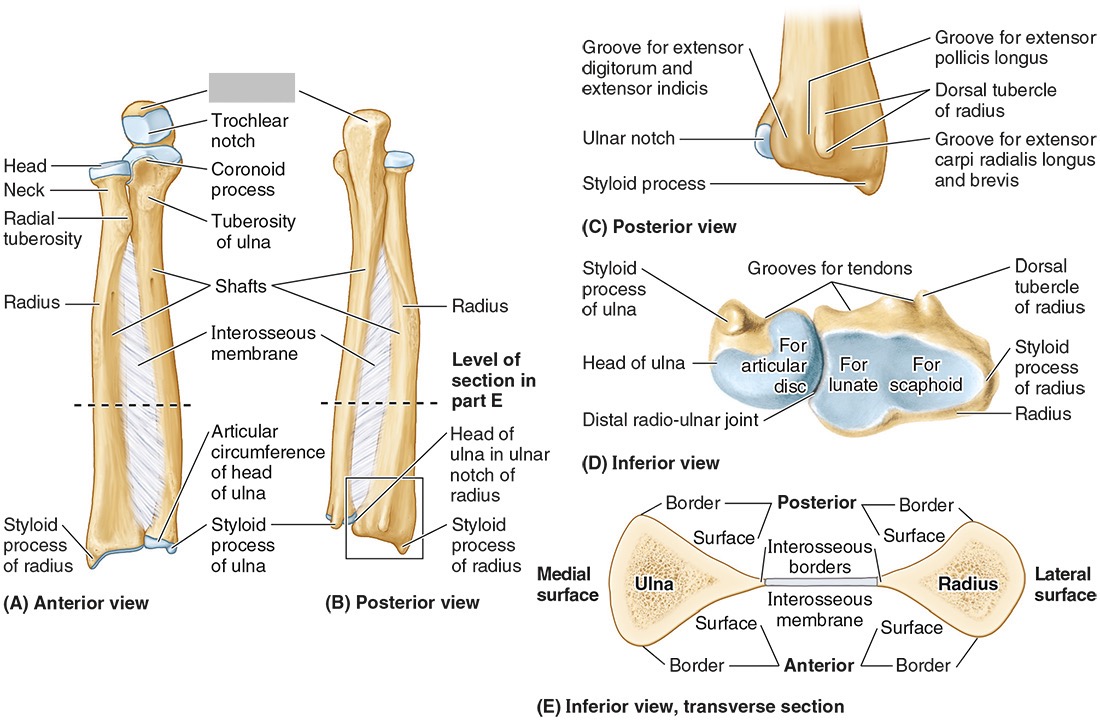
the olecranon (superior)
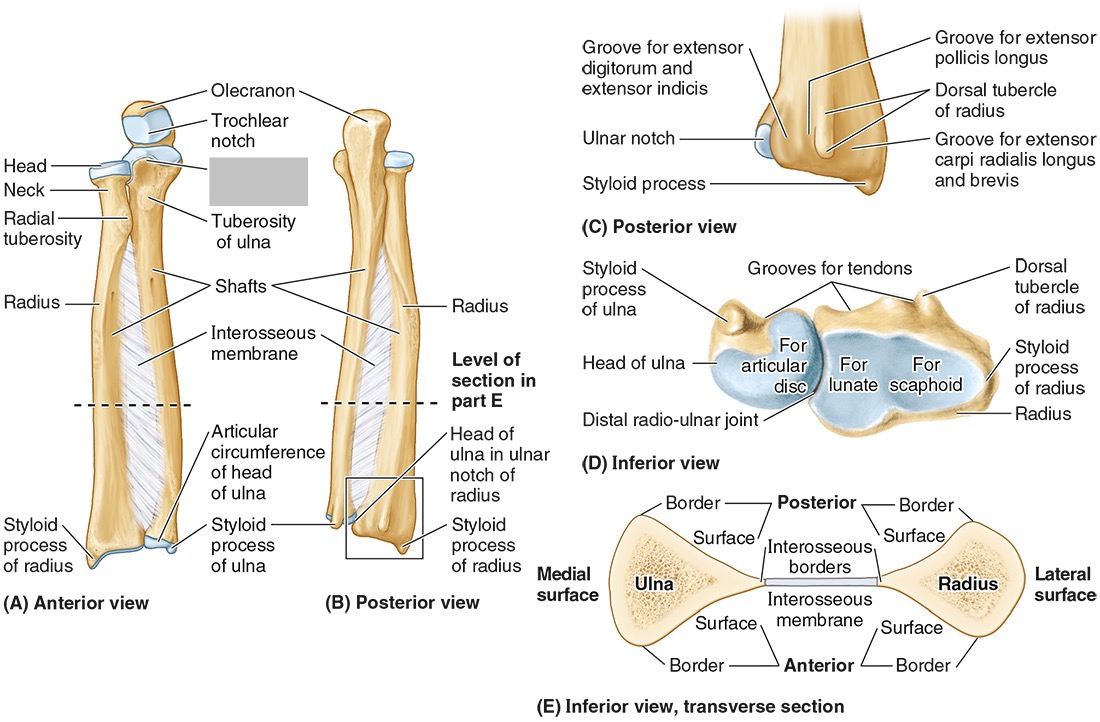
The coronoid processes (inferior)
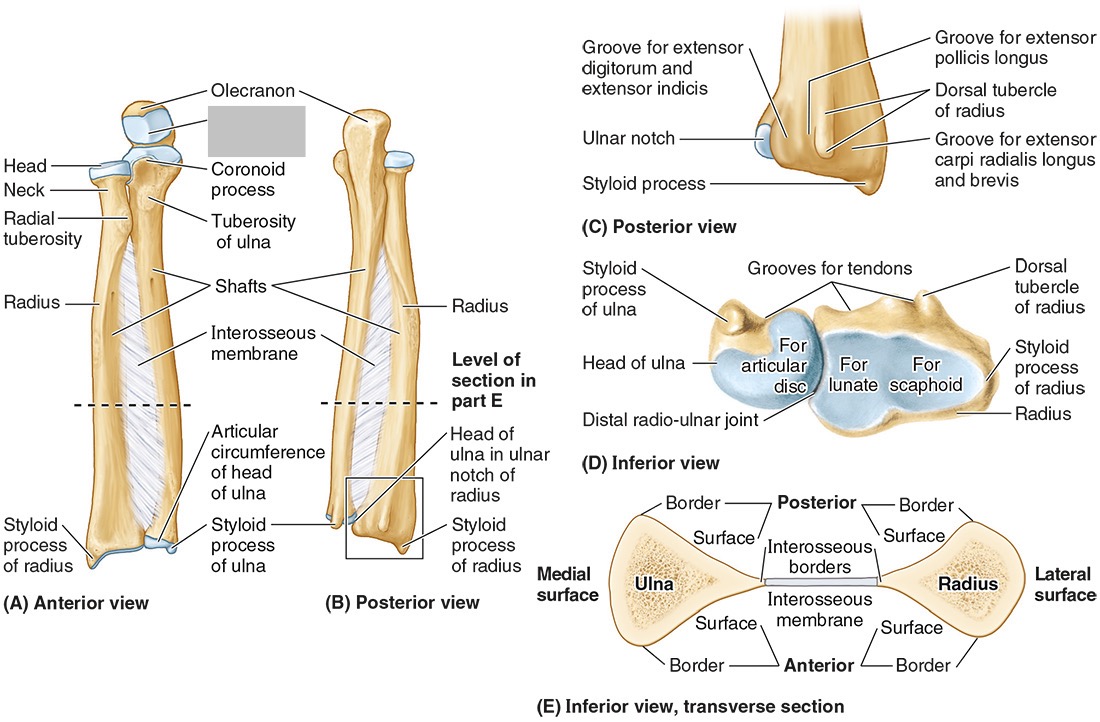
The trochlear notch
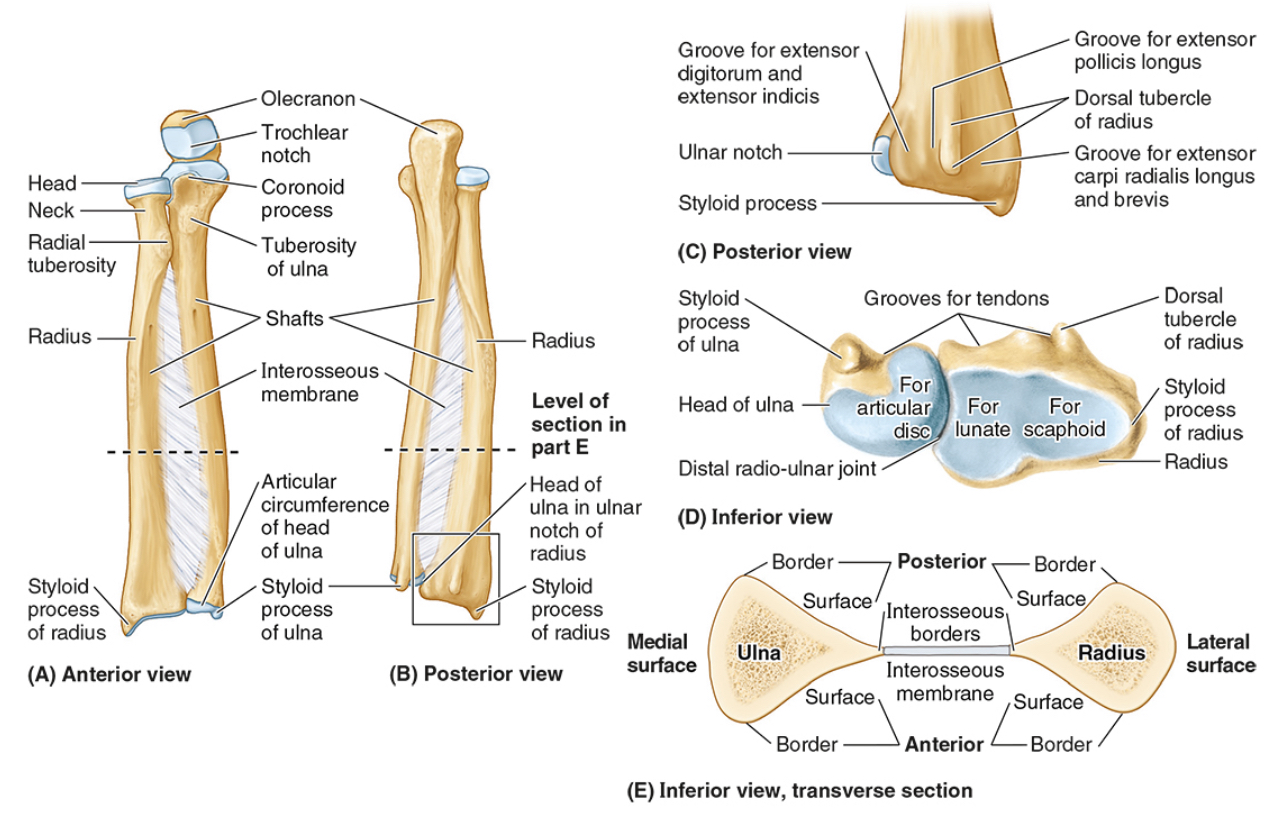
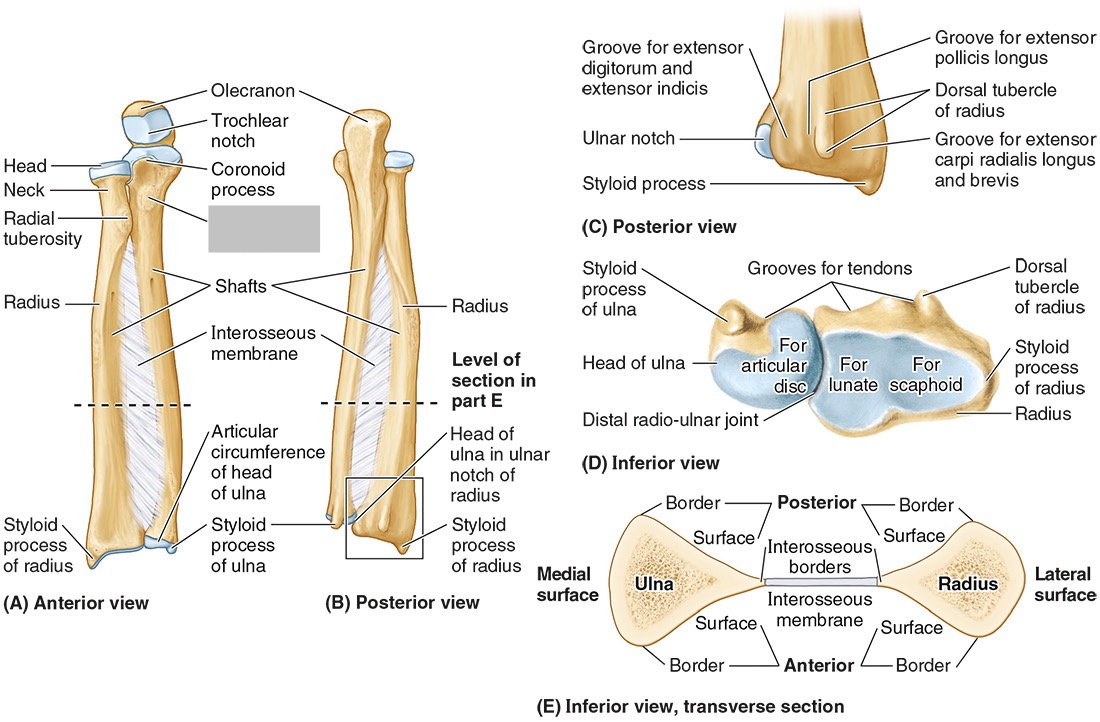
The tuberosity of the ulna
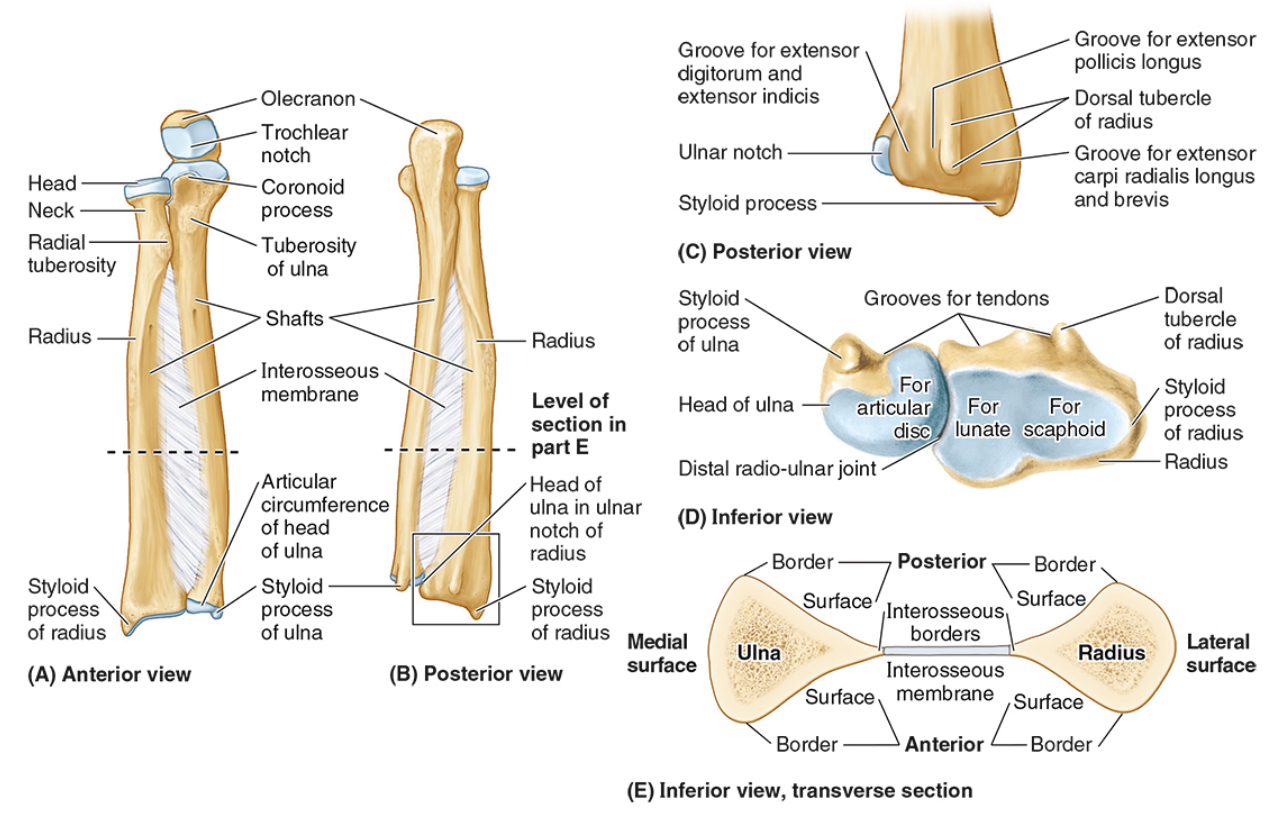
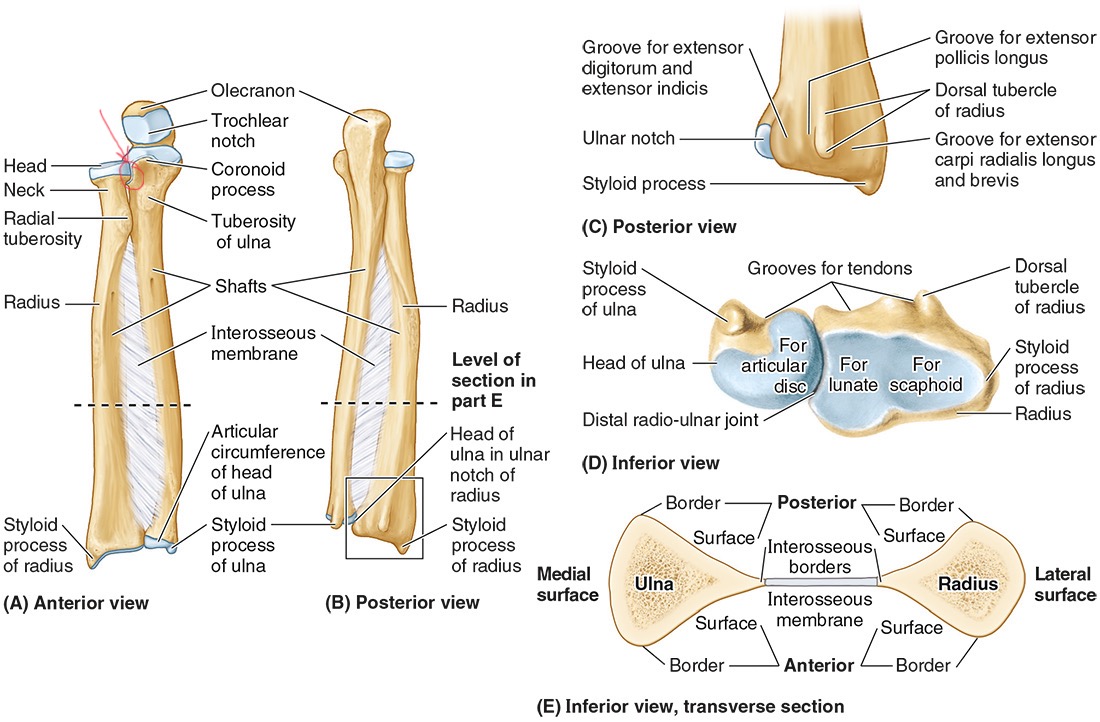
The radial notch
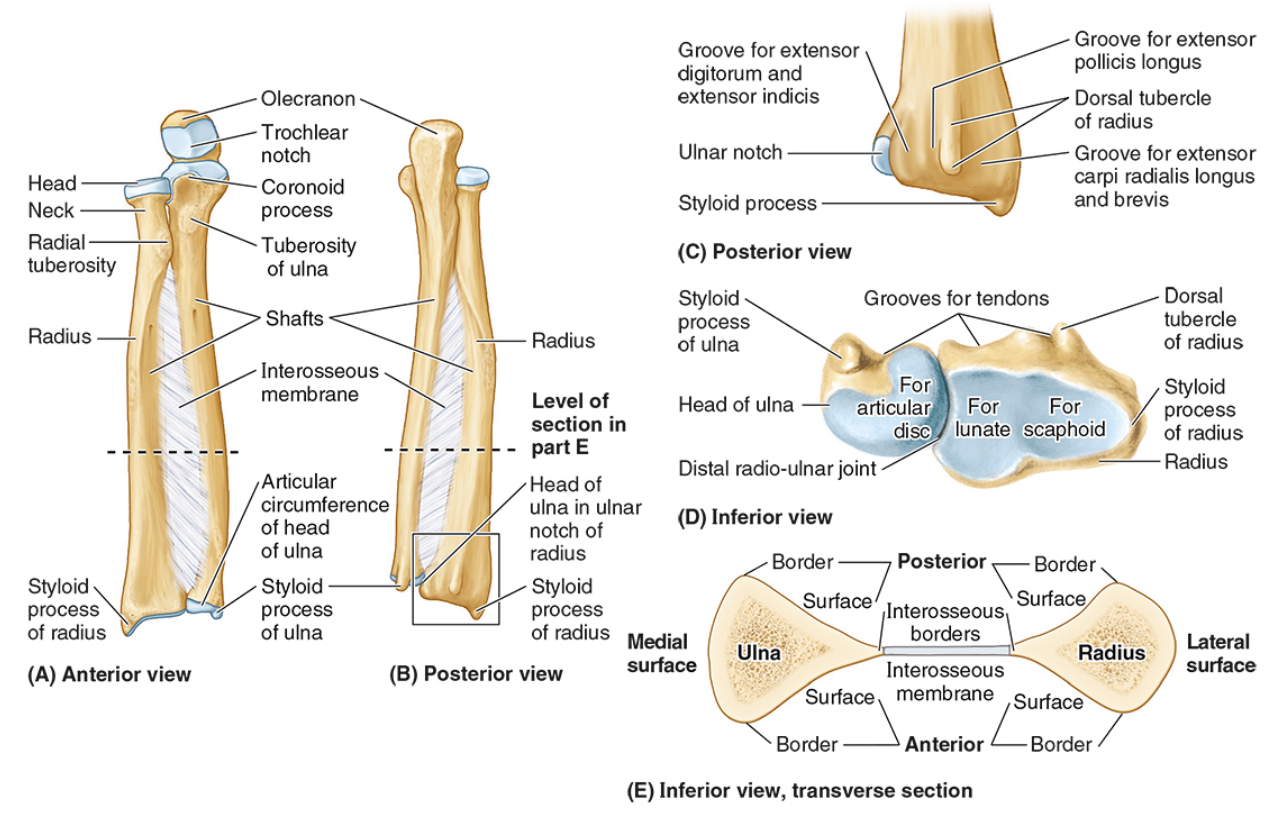

The head of the ulna
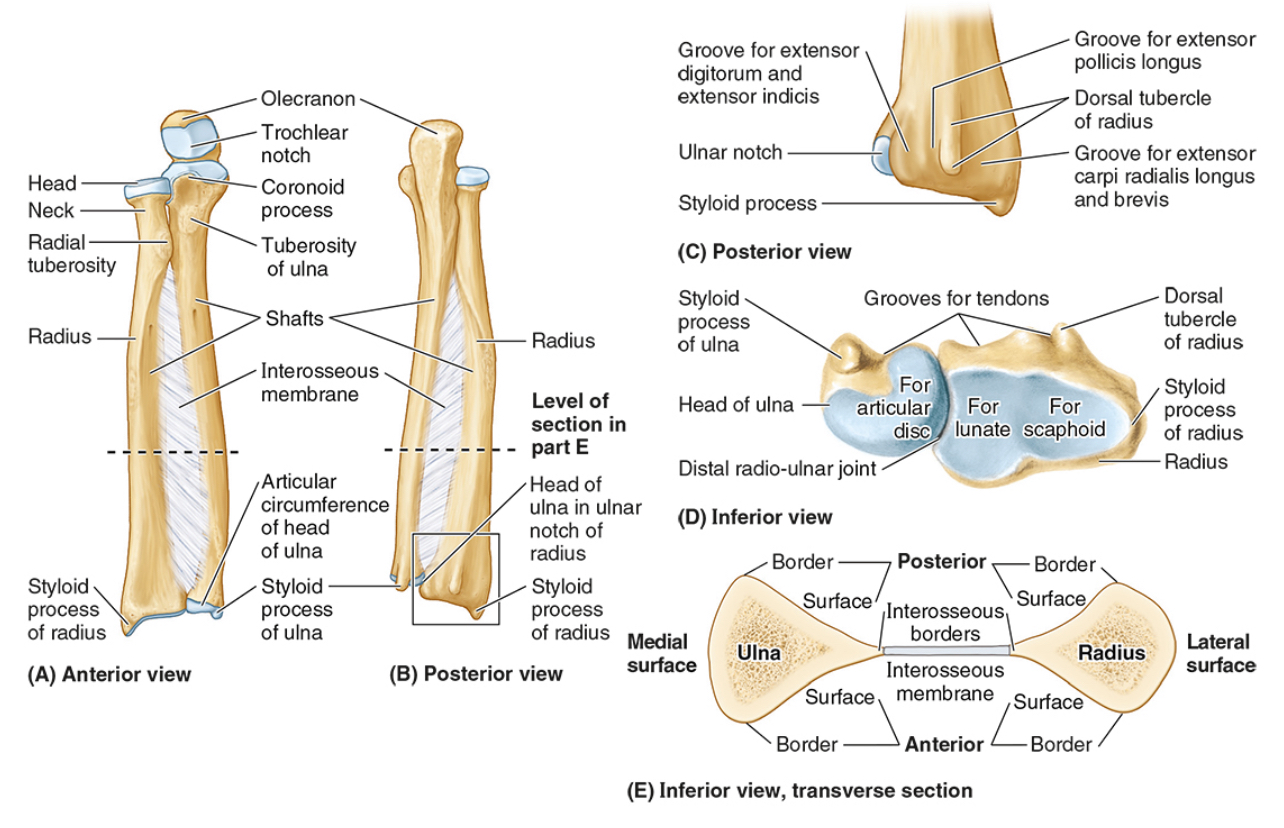
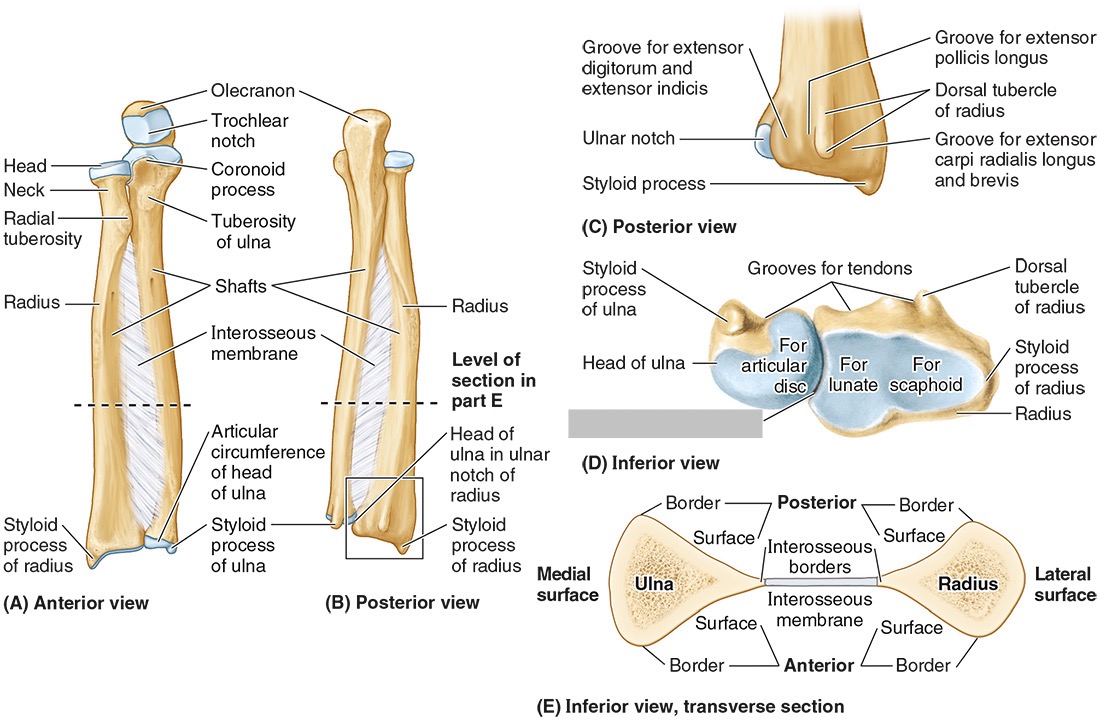
Distal radio-ulnar joint
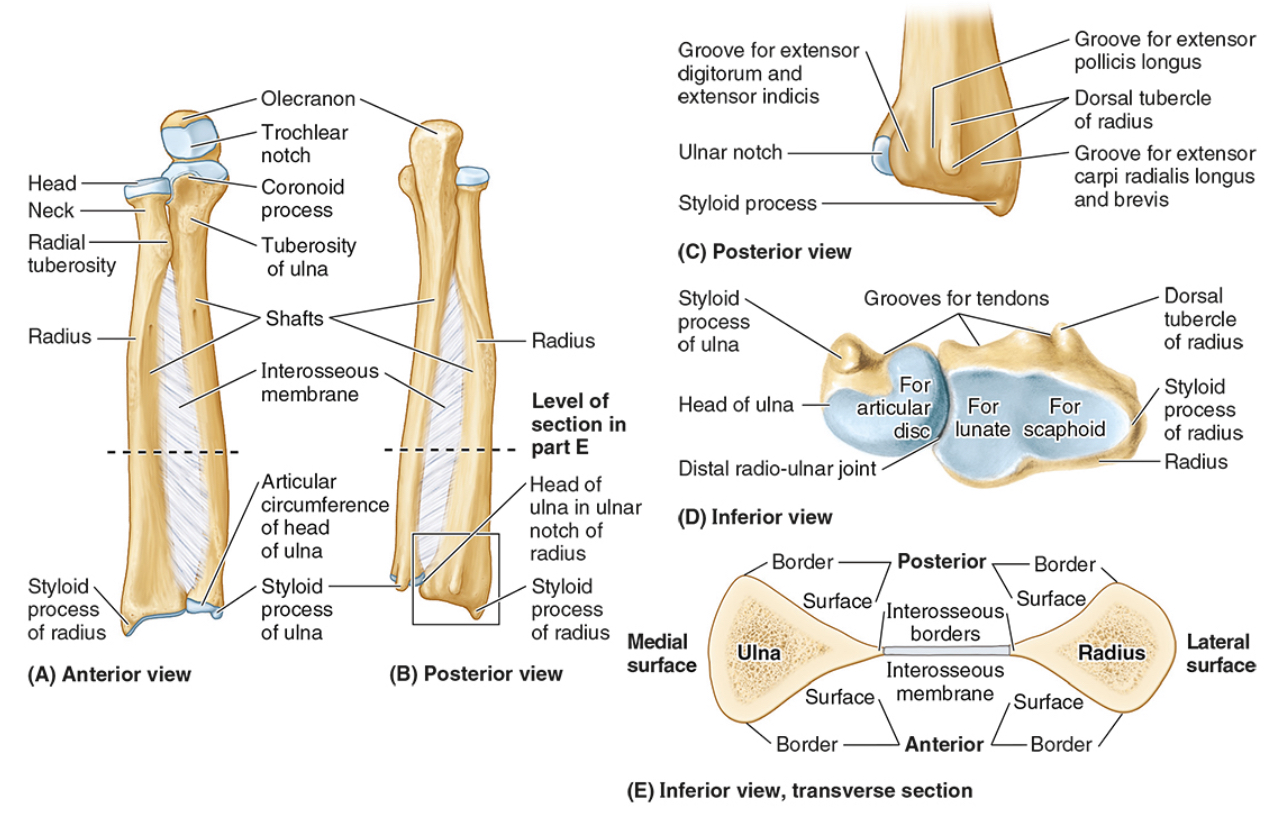
What are the three articulations in the elbow joint?
The humerus-ulna articulation
The humerus-radius articulation
The proximal radius-ulnar articulation
The __________ forms a hinge joint, used to flex and extend the forearm
humerus-ulna articulation
The __________ allows the radius to rotate because the concave head of the radius fits onto a round humoral capitulum.
humerus-radius articulation
The __________ is a articulations in the elbow joint that does not directly contribute to motion at the elbow.
proximal radius-ulnar articulation
__________ is palm up to hold your soup bowl
Supination
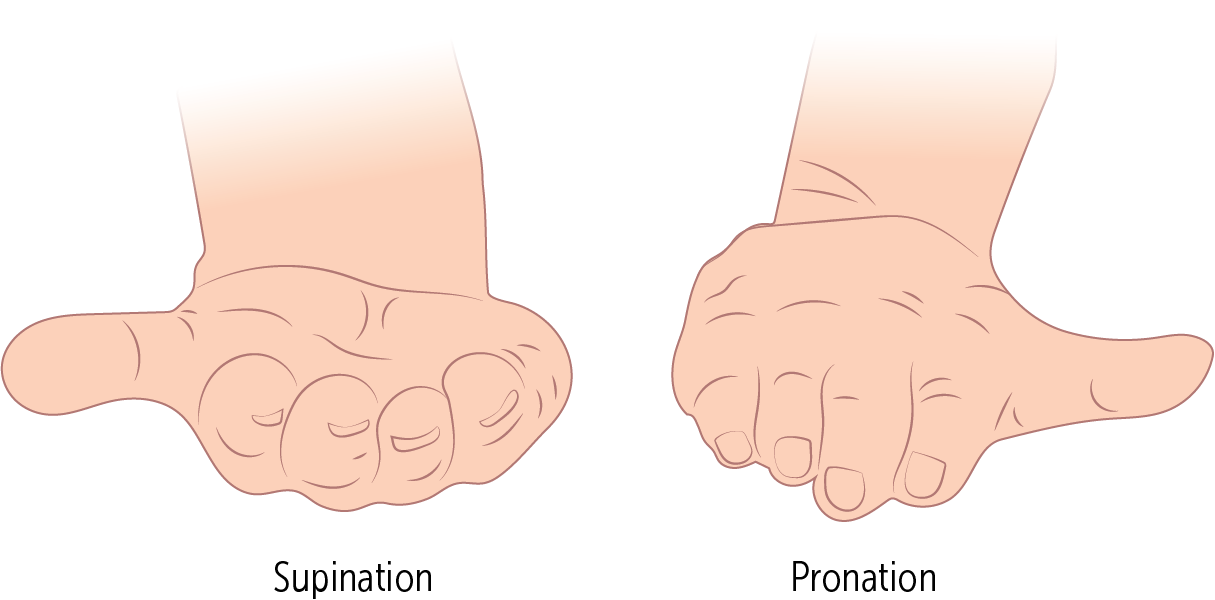
__________ is palm down to push off the ground
Pronation
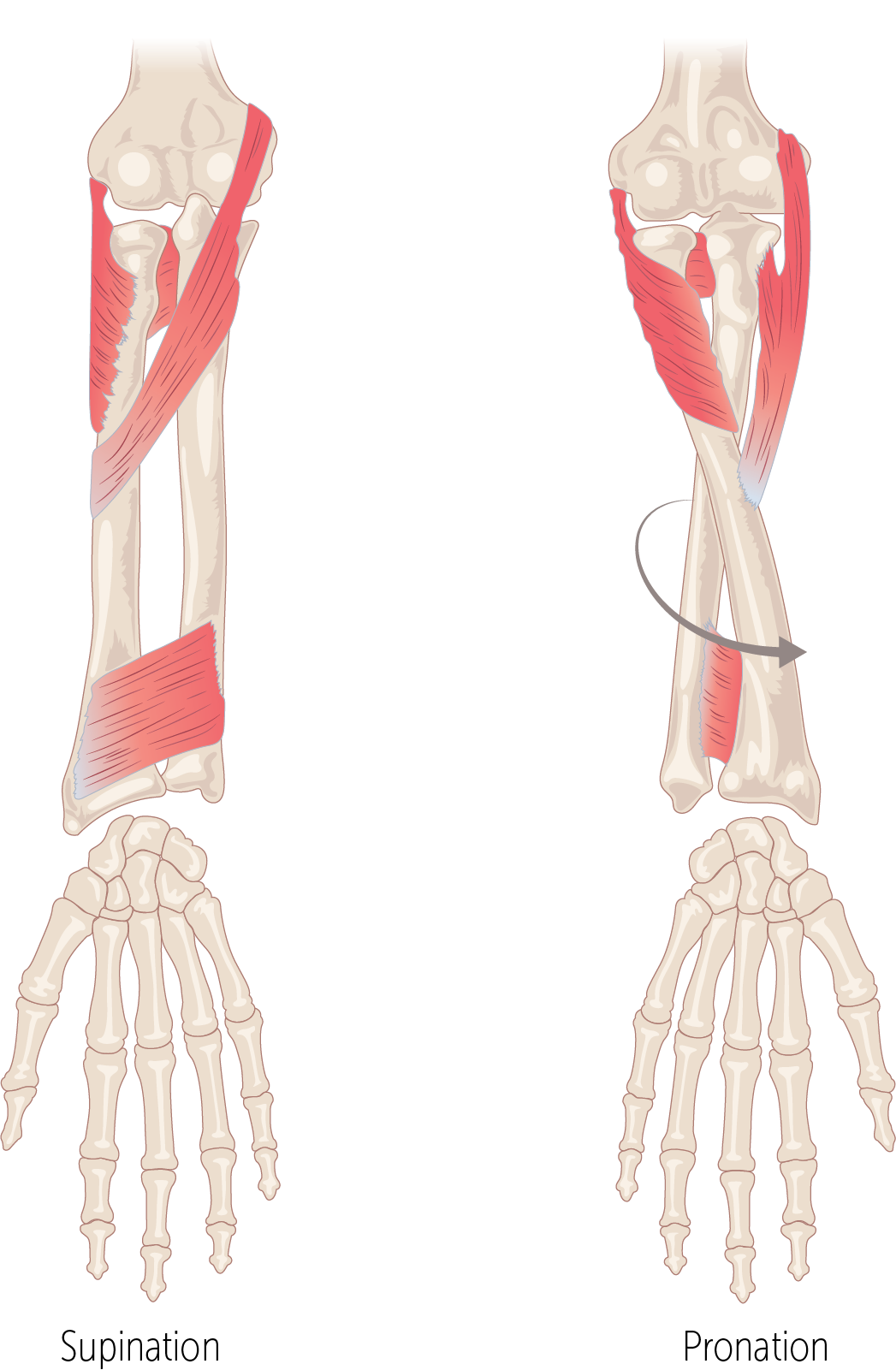
When _________ occurs, the radius twists over the front of the ulna.
Pronation
The rounded __________ of the humerus allows the head of the radius to rotate within the radial notch of the ulna
capitulum
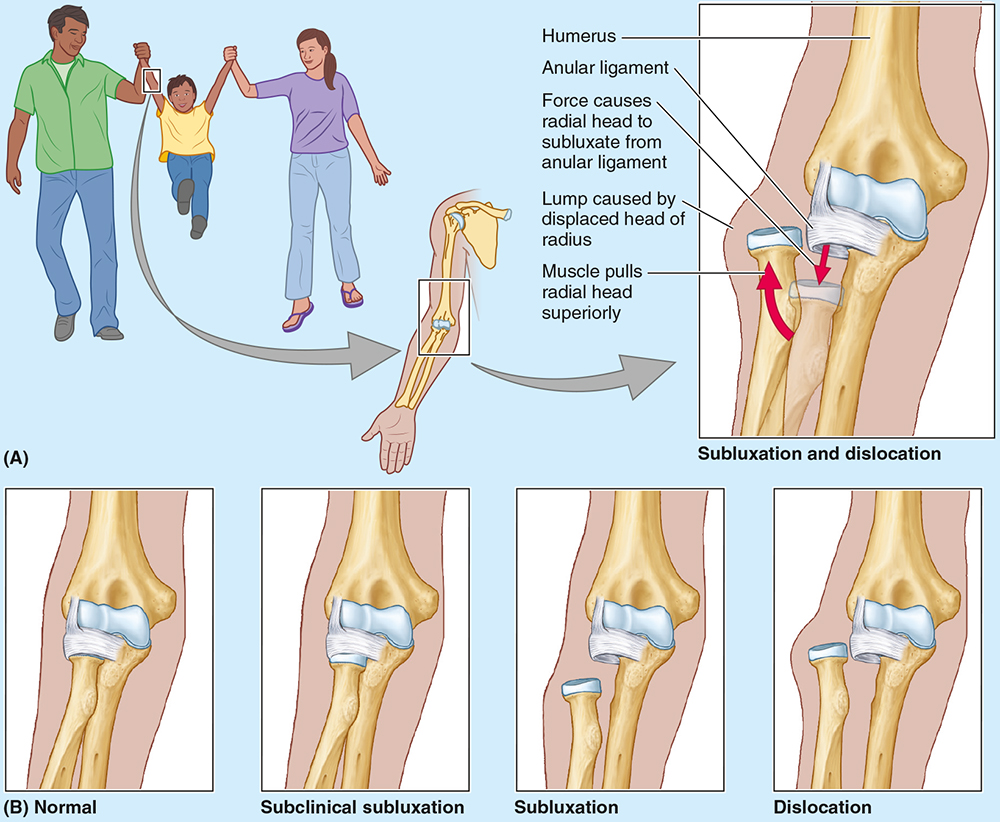
Nursemaid’s elbow is a common injury in preschool children, especially girls, caused by sudden pulling of the pronated forearm (e.g., lifting a child). The _________ tear causes subluxation of the radial head.
annular ligament
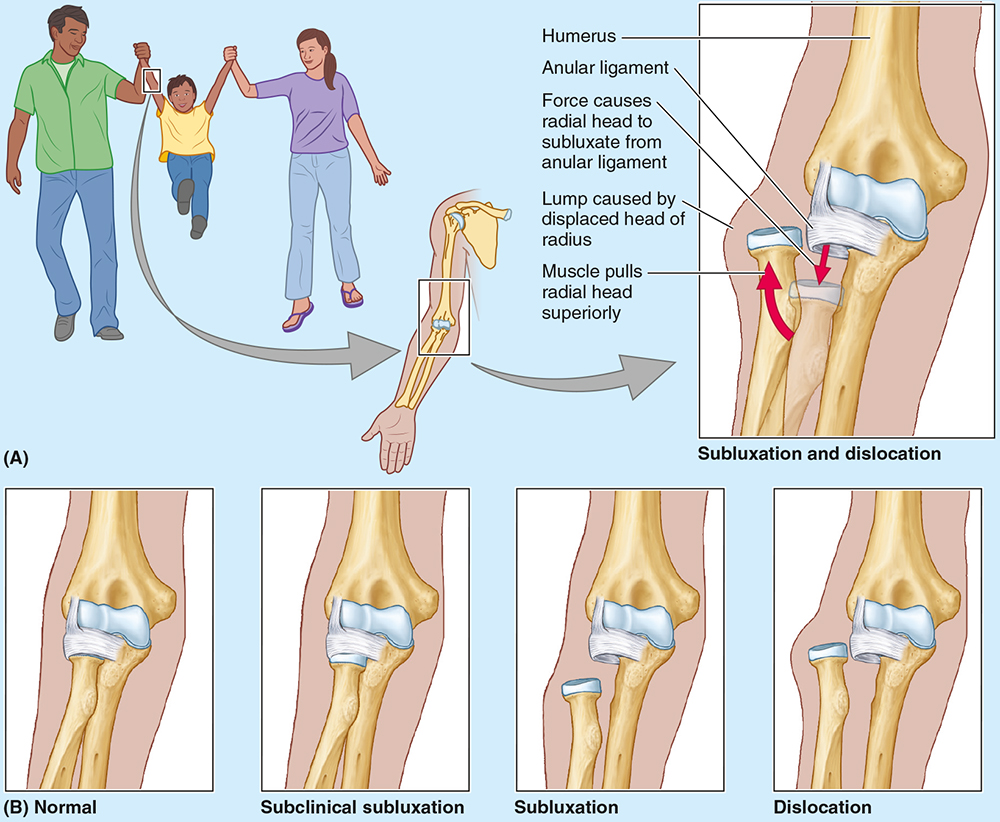
Nursemaid’s elbow is a common injury in preschool children, especially girls, caused by sudden pulling of the pronated forearm (e.g., lifting a child). The annular ligament tear causes __________ of the radial head.
subluxation
Treatment of nursemaid’s elbow involves?
Treatment involves supination with elbow flexion; healing occurs with sling use for 2 weeks.
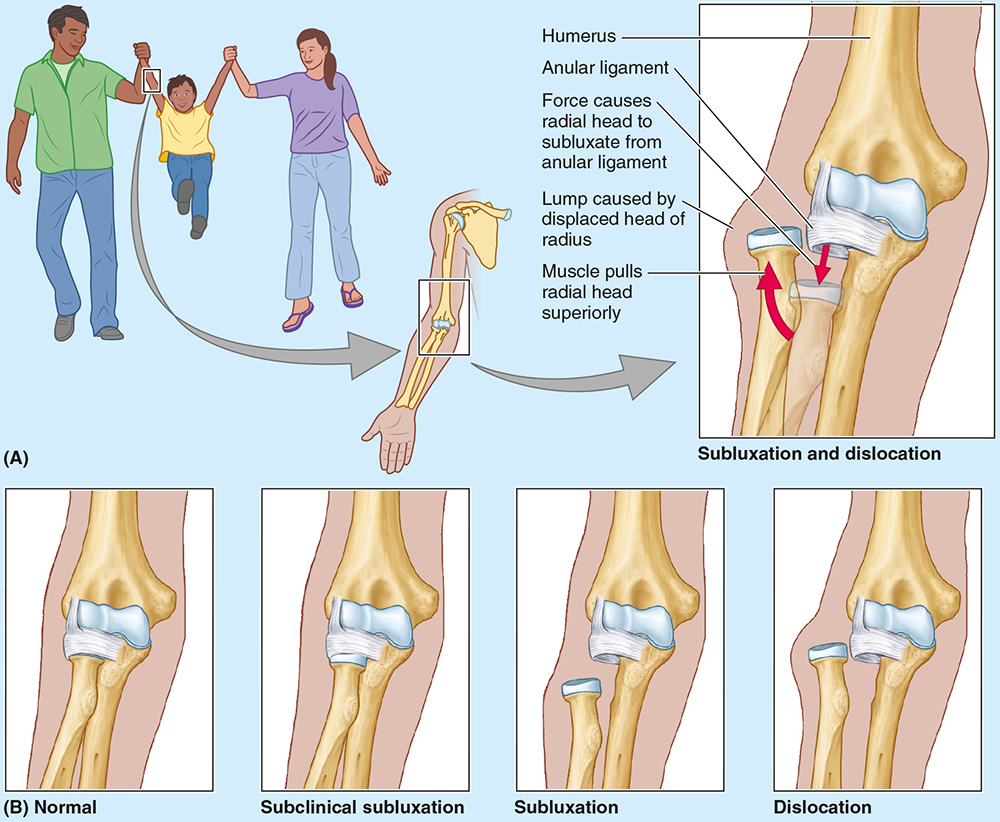
The elbow is stabilized by the ulnar and radial collateral ligaments, whereas the _____________ holds the radius against the ulna for rotation.
annular ligament
The hand comprises__ bones: __ carpal bones, __ metacarpal, and __ phalangeal bones
27, 8, 5, 14
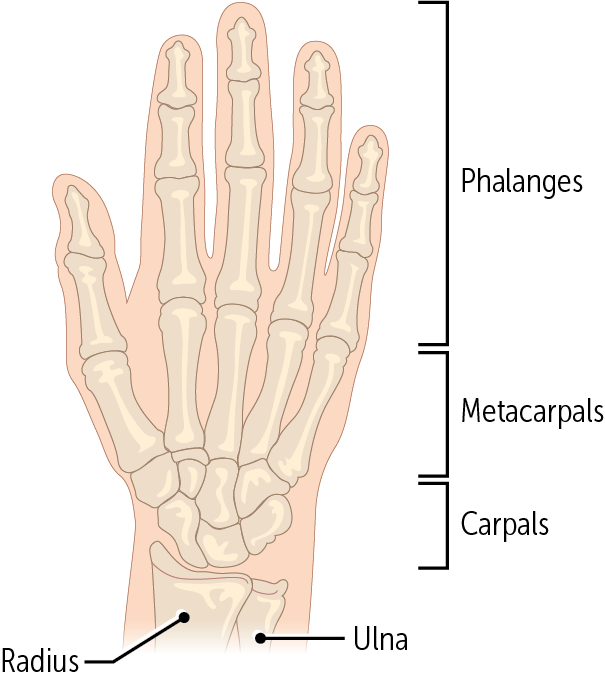
Every digit is made up of a metacarpal bone and three phalanges, except for the ___________, which only has two phalanges.
thumb (aka the pollux - Latin for thumb)
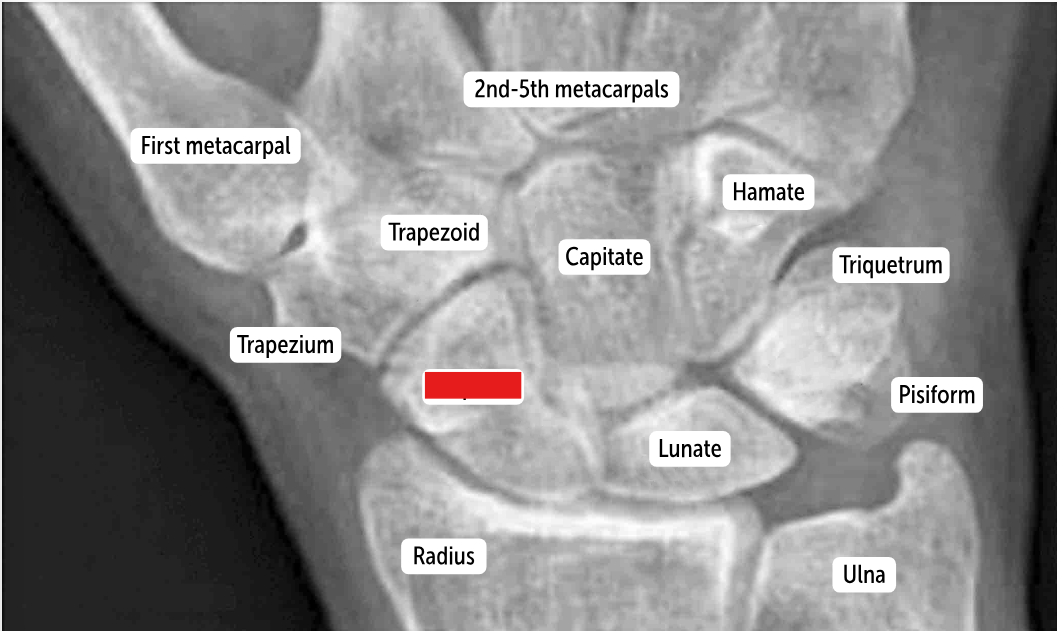
The most commonly fractured carpal bone by falling on an outstretched hand, which has a risk of avascular necrosis, is the __________.
Scaphoid bone
The most commonly dislocated bone after a fall on an outstretched hand is the ___________.
Lunate bone
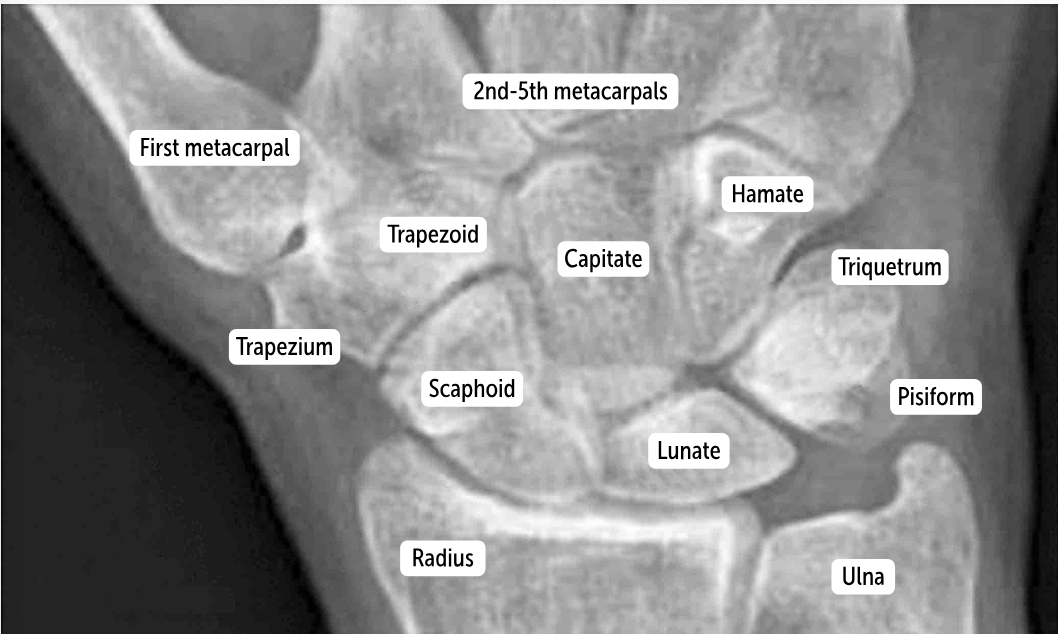
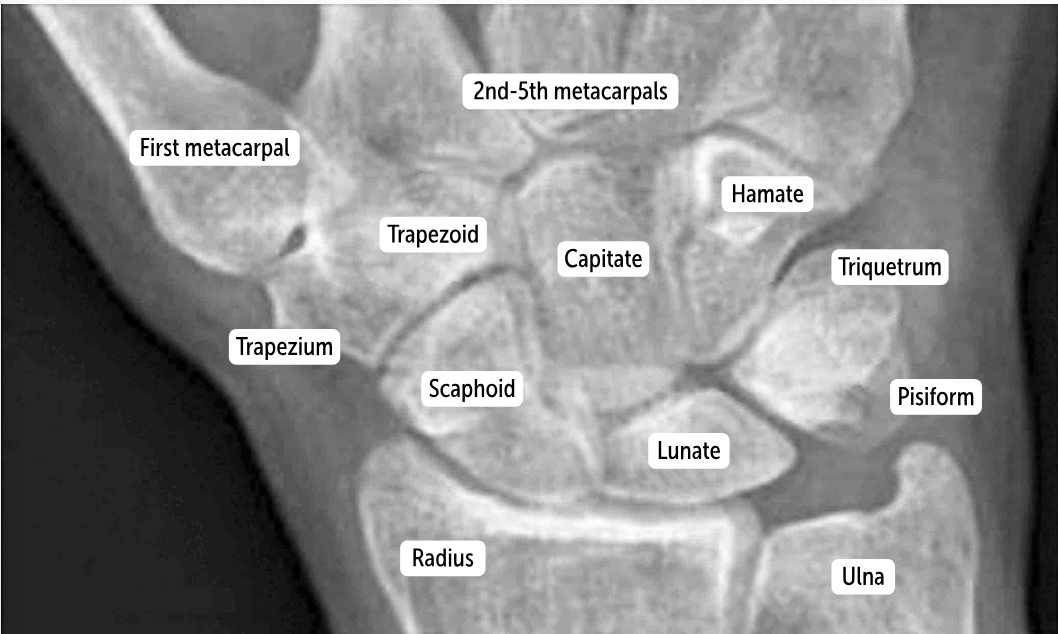
Carpal bones by row:
So Long To Pinky, Here Comes The Thumb
Scaphoid, Lunate, Triquetrum, Pisiform, Hamate, Capitate, Trapezoid, Trapezium
Scaphoid
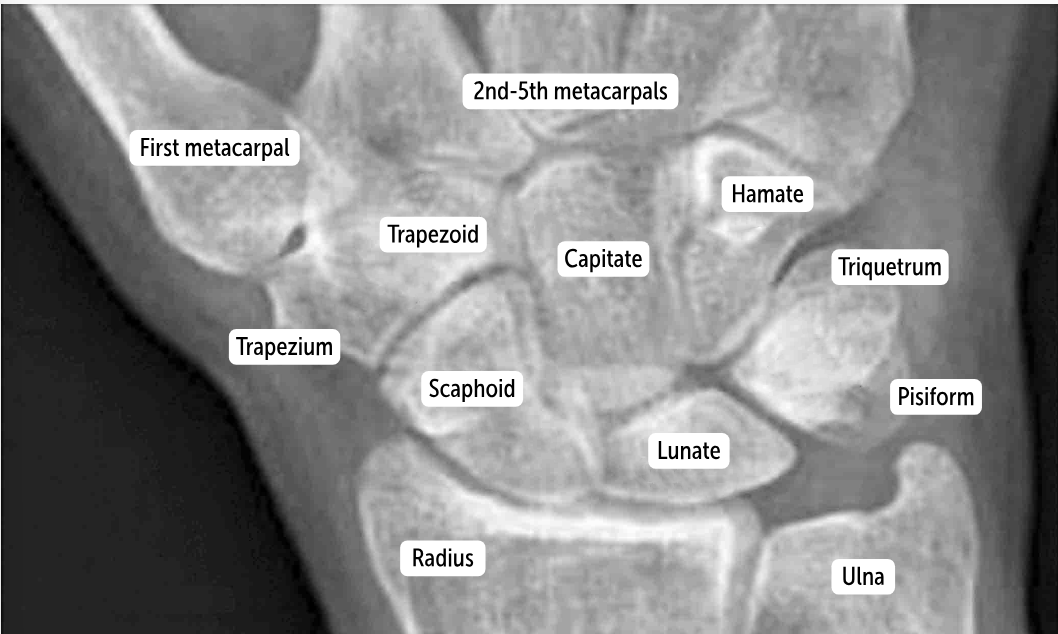
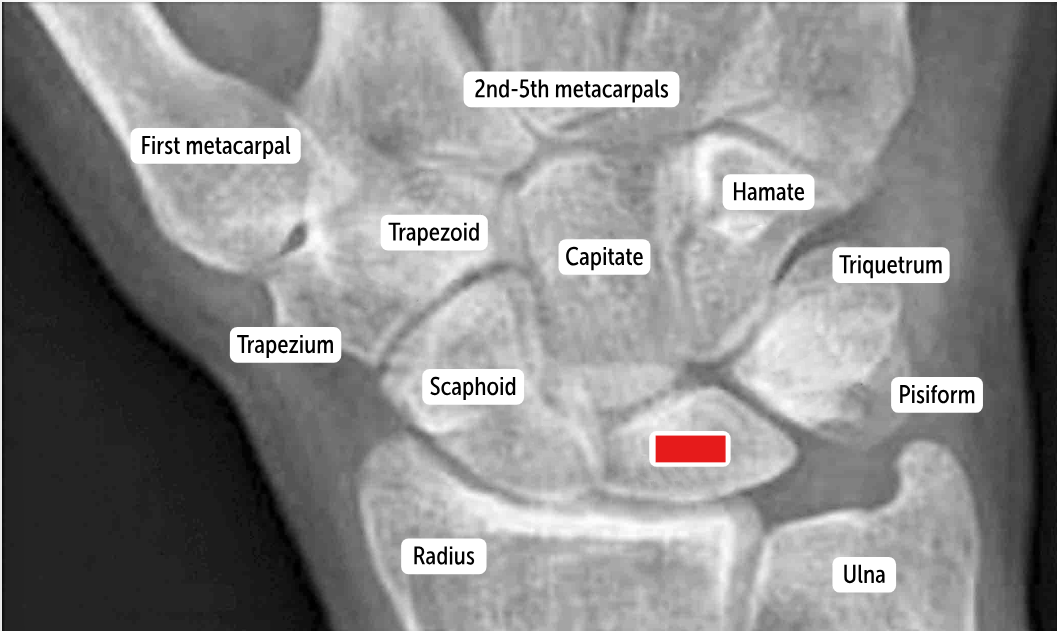
Lunate
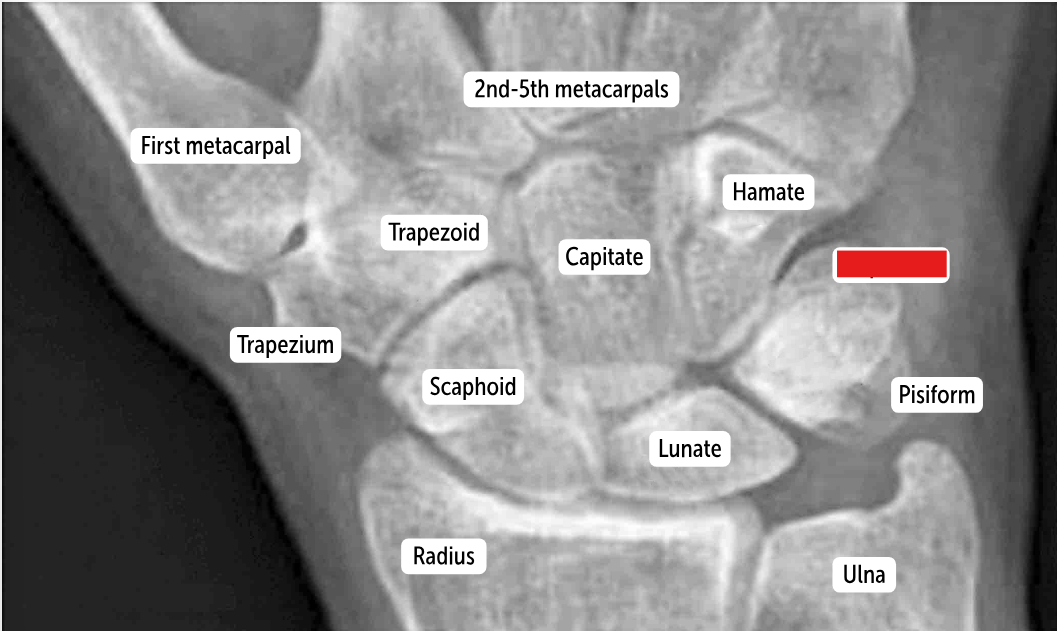
Triquetrum
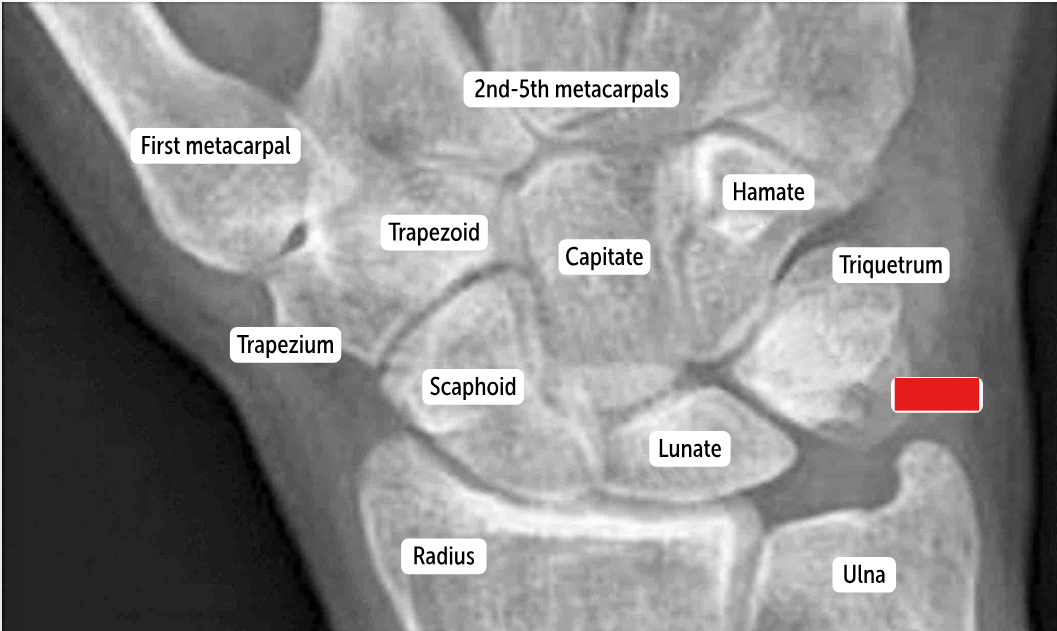
Pisiform
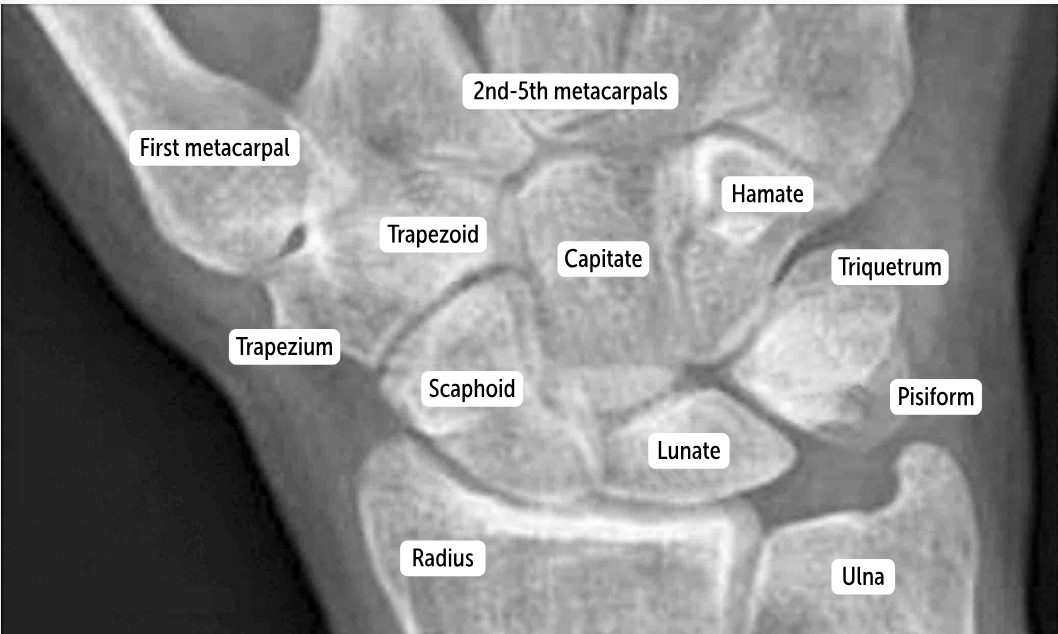
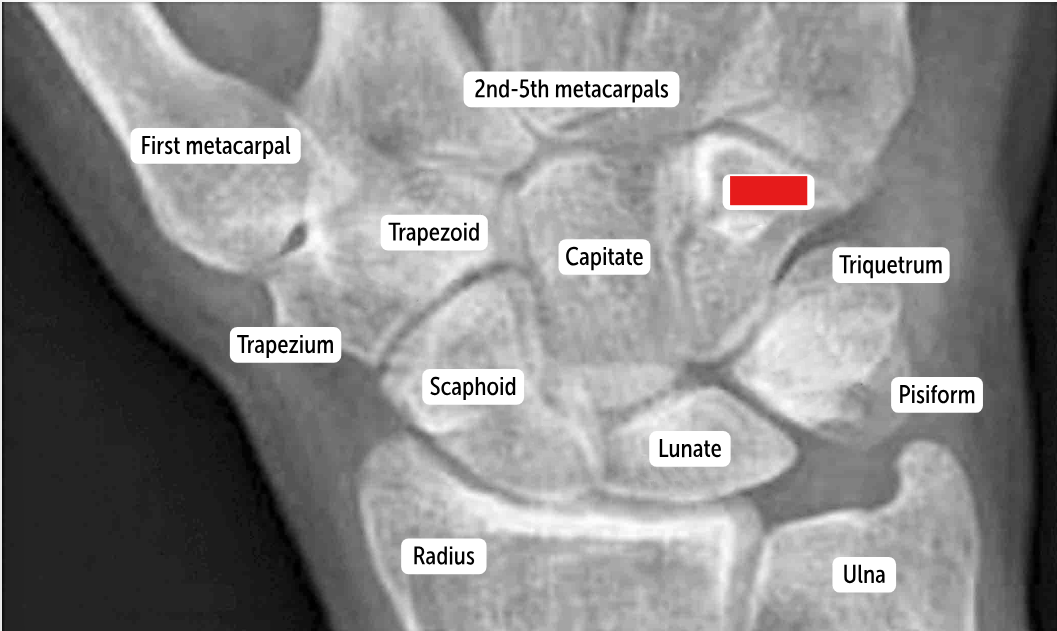
Hamate
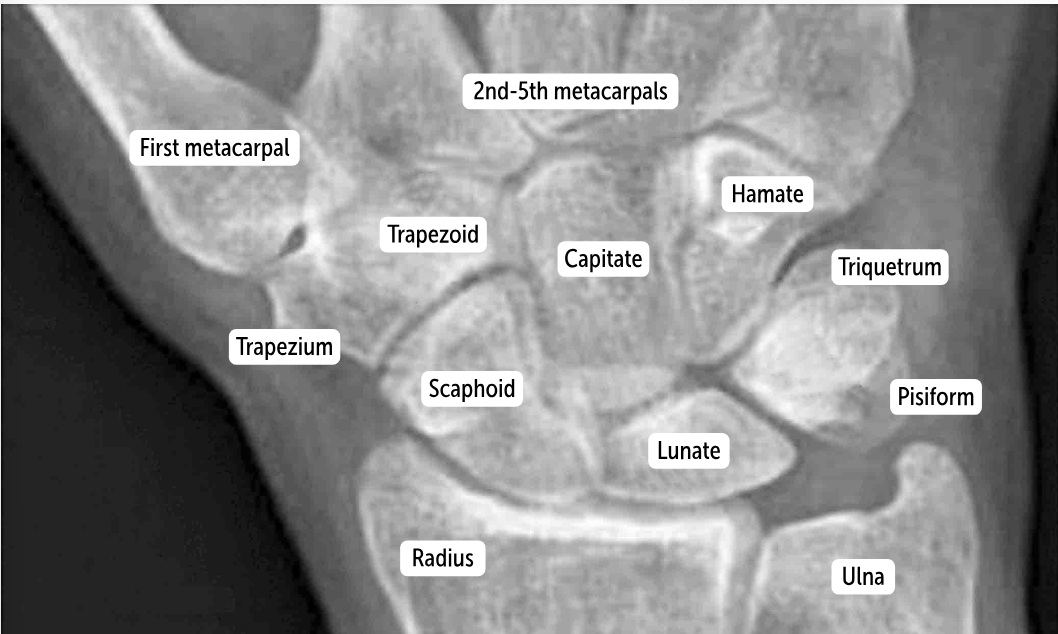
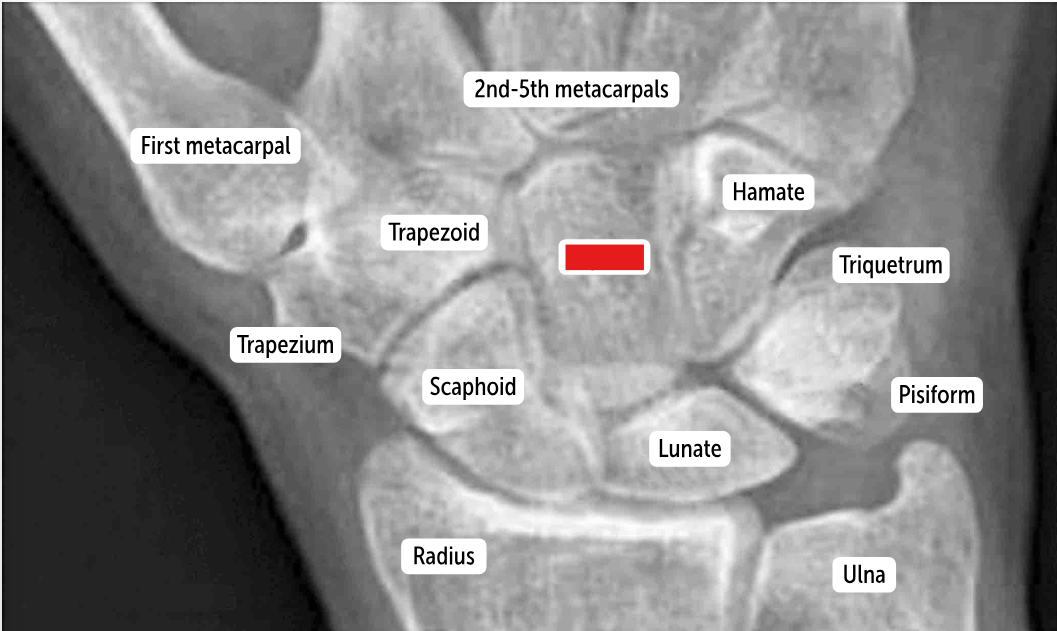
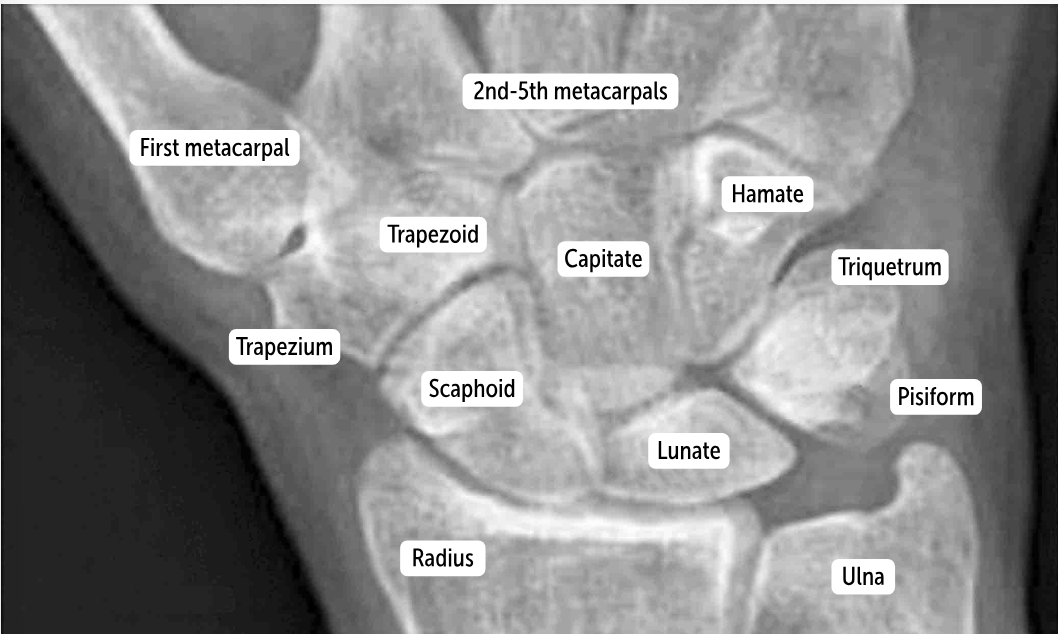
Capitate
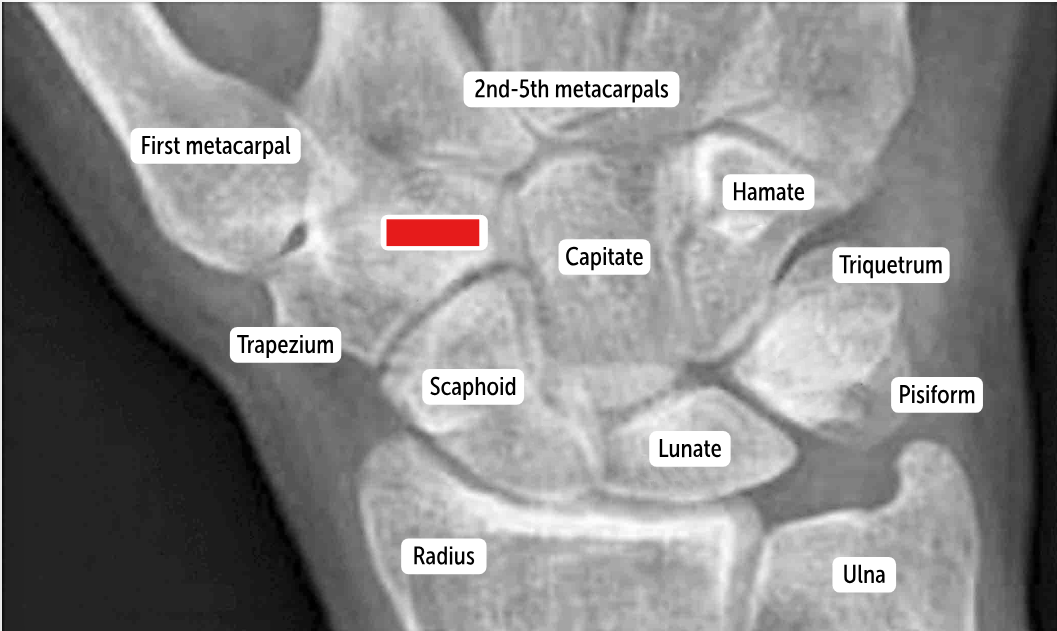
Trapezoid
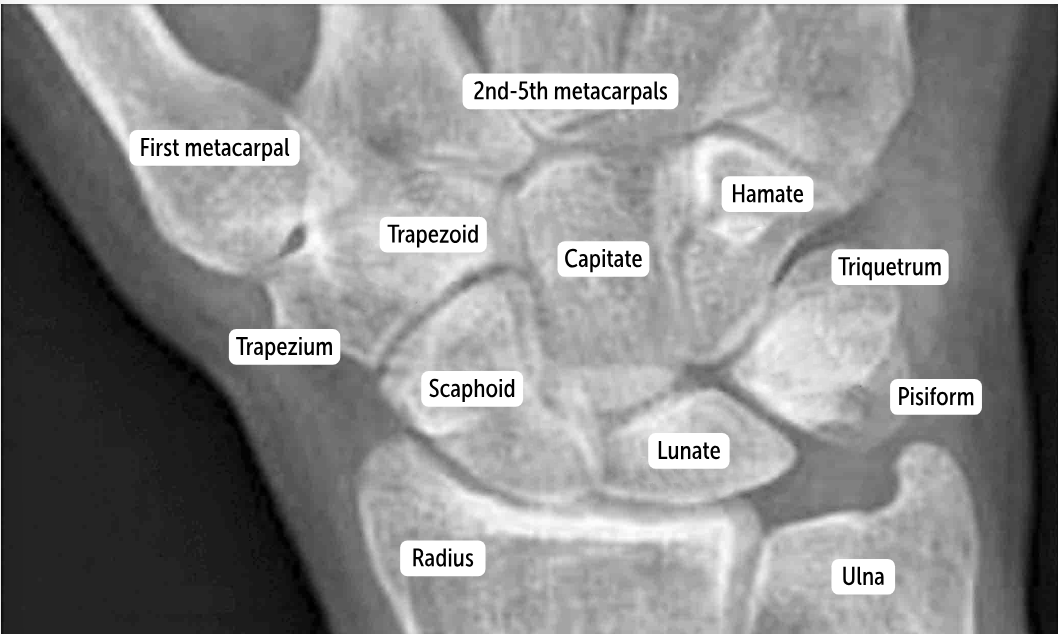
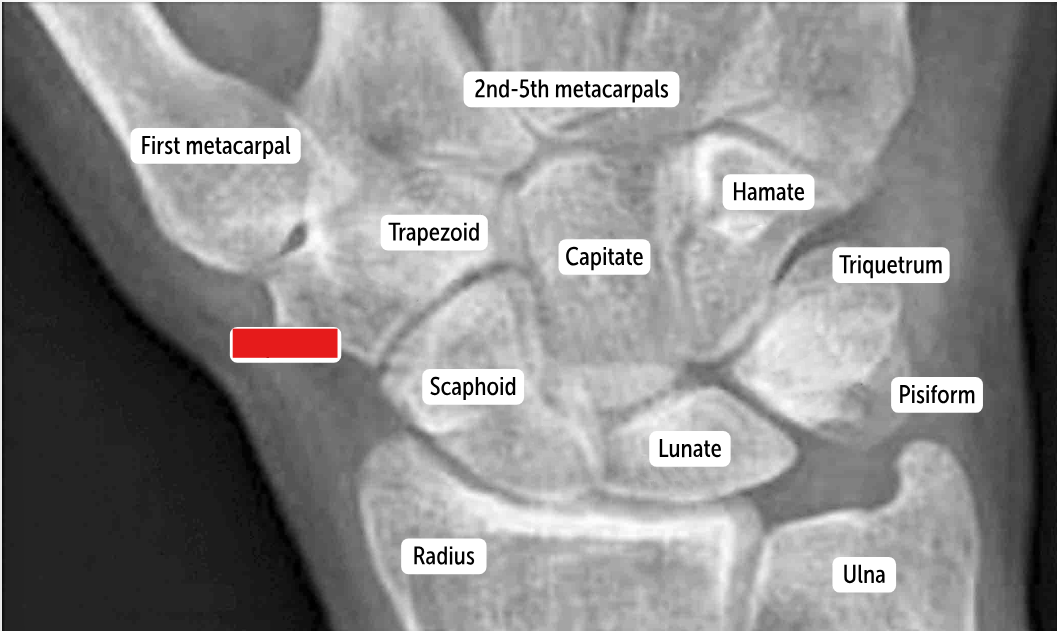
Trapezium
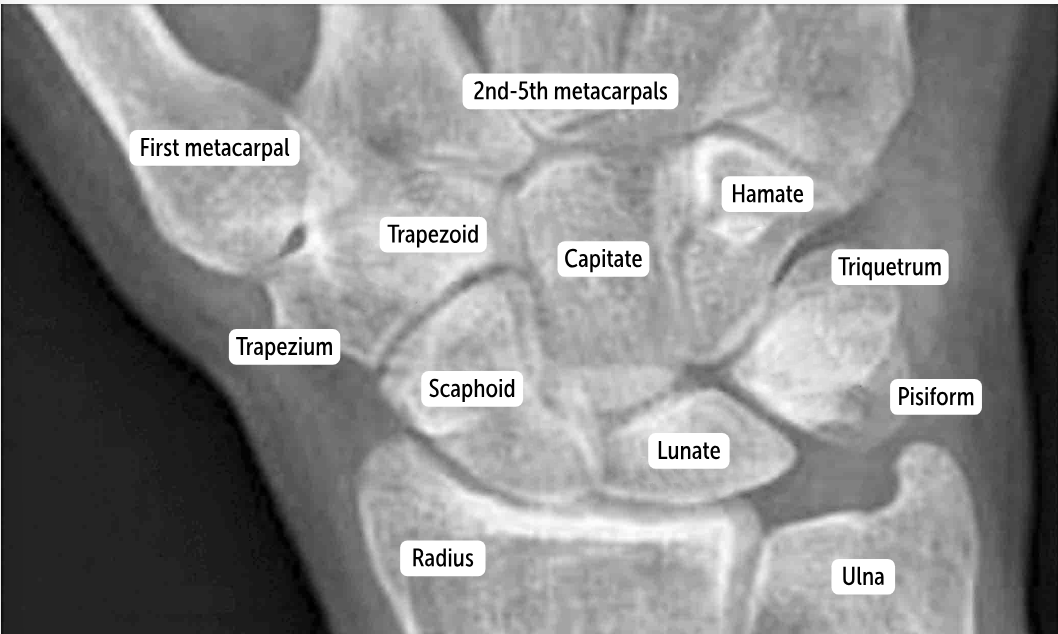
The two distinct rows articulate with each other at the __________. It’s a plane (simple sliding) joint that acts to amplify all the other wrist actions.
midcarpal joint
Which carpal bones articulate with the metacarpal bones?
The bones of the distal row (hamate, capitate, trapezoid, and trapezium) articulate with the metacarpal bones.
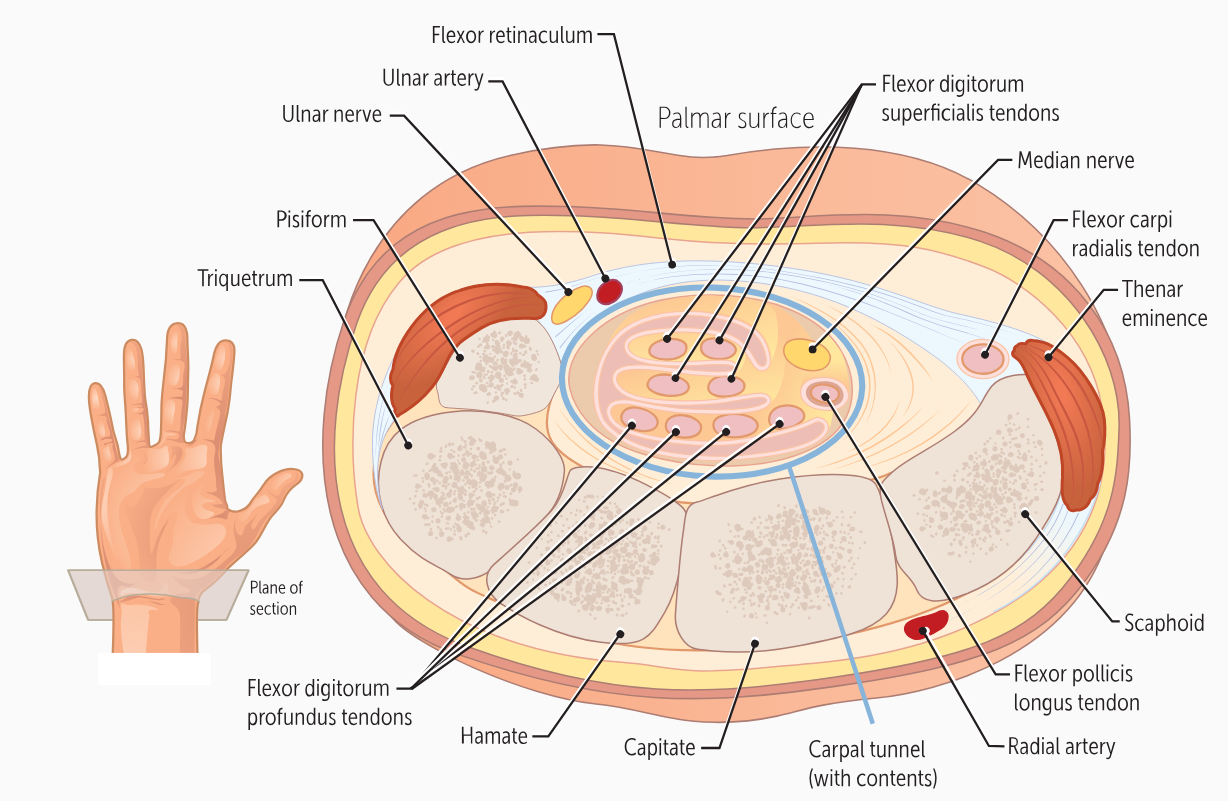
The carpals form the floor of a “tunnel” covered by a ligament called the ______________. This carpal tunnel allows tendons, nerves, and blood vessels to cross the wrist and enter the hand.
flexor retinaculum
The bone forms the floor of the ____________, an anatomic landmark formed by the tendons of the extensor pollicis longus, the extensor pollicis brevis, and the abductor pollicis longus muscles
anatomic snuff box
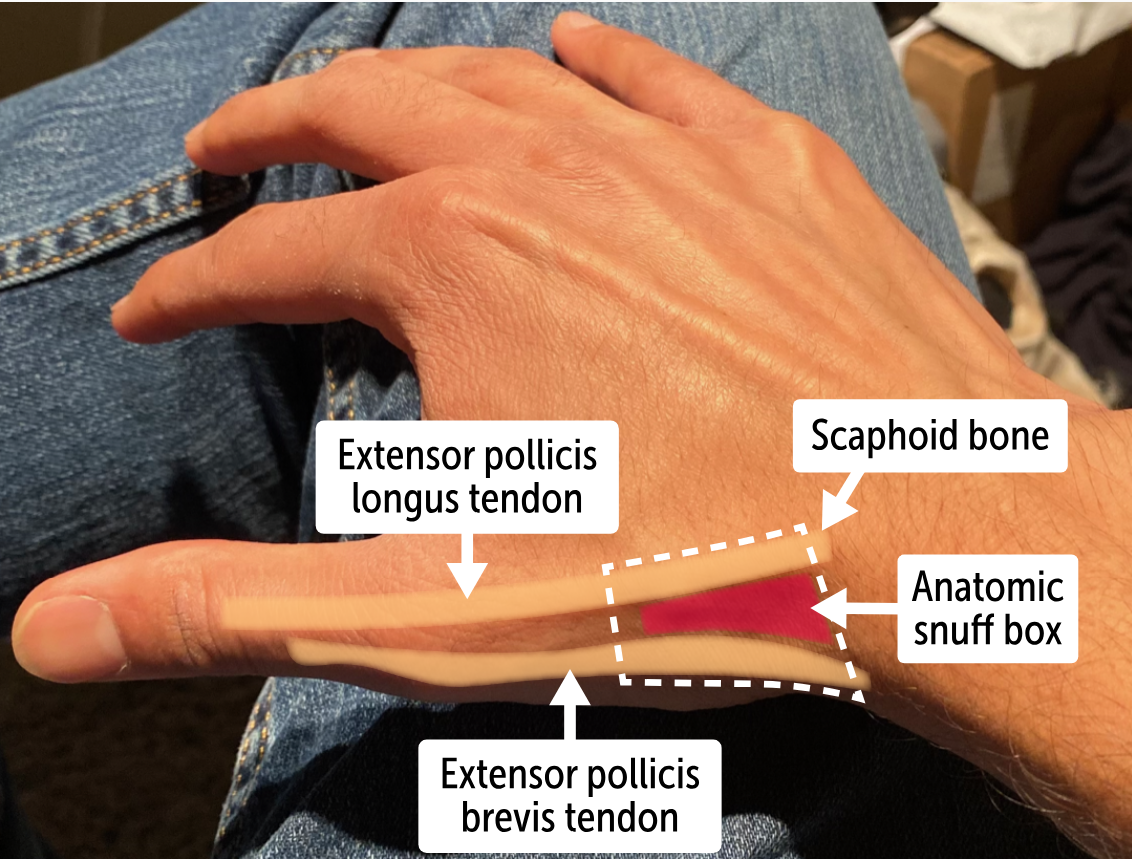
What bone lies in the anatomic snuff box?
The carpal scaphoid bone is found in the anatomic snuff box.
The true wrist joint is better called the radio-carpal joint. It is an __________ formed by the articulation of the distal radius and its articular disk to the scaphoid and lunate bones in the first row of carpals.__________ can move in two dimensions.
(Both are the same term)
Ellipsoidal joints
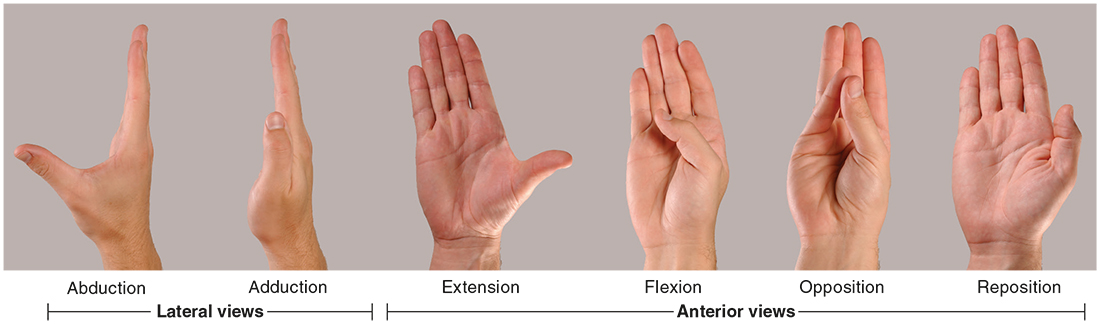
The wrist’s main action is simple ________and _________, it also moves in the plane of the palm, during _________ and _________.
flexion, extension, abduction, adduction
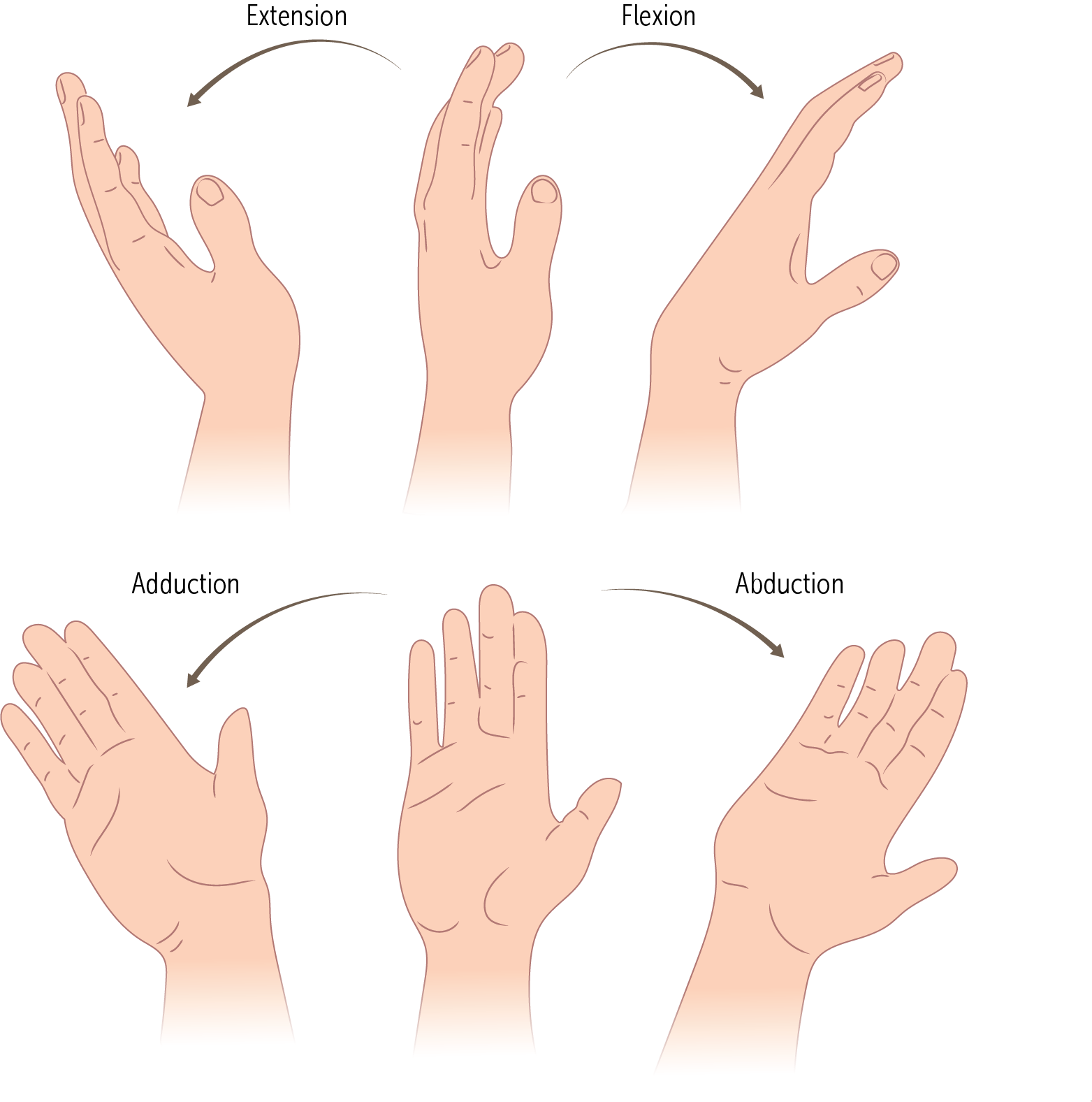
_________and _________are also known as radial deviation and ulnar deviation, respectively
Abduction, adduction
The metacarpals are the most proximal bones of the digits (Figure 14). These bones—numbered 1 through 5, with 1 being the _____—connect the carpals to the proximal phalanges
thumb
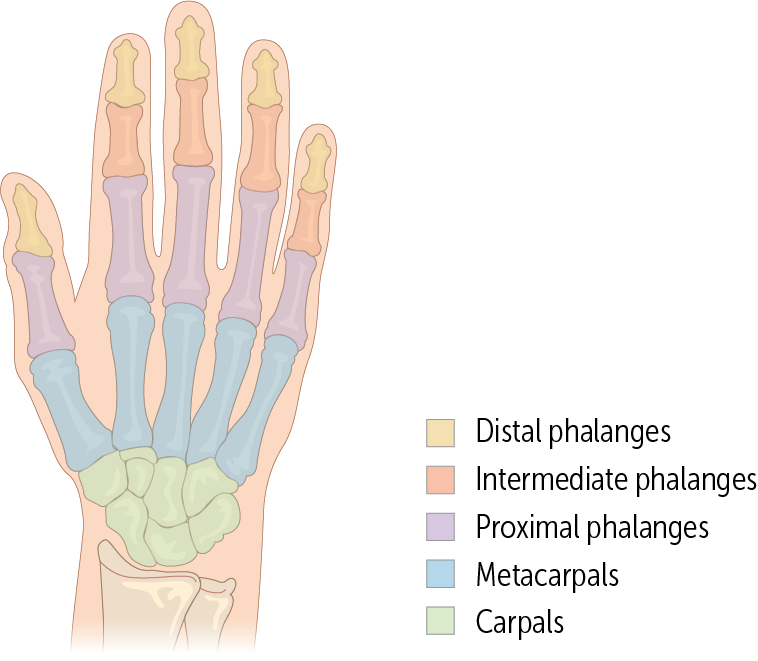
________ are the longest bones in the hands. They have a base, body, and head; like the ulna, their head is distal and their base is proximal.
The metacarpals
The metacarpals connect to the carpal bones via ______________
carpometacarpal (CMC) joints
The joints for _______ are simple plane joints that only allow limited sliding motion.
digits 2-5
The joints of _______ are mostly immovable because of very strong attached ligaments.
digits 2 and 3 (index and middle finger)
The joint of ______ is a saddle joint allowing extensive motion along three dimensions: flexion/extension, abduction/adduction (in the plane of the palm), and opposition, bringing the thumb against the pinkie finger.
digit 5
Every finger has three phalanges (proximal, medial, and distal) except for the _____, which only has two (the proximal and distal).
thumb
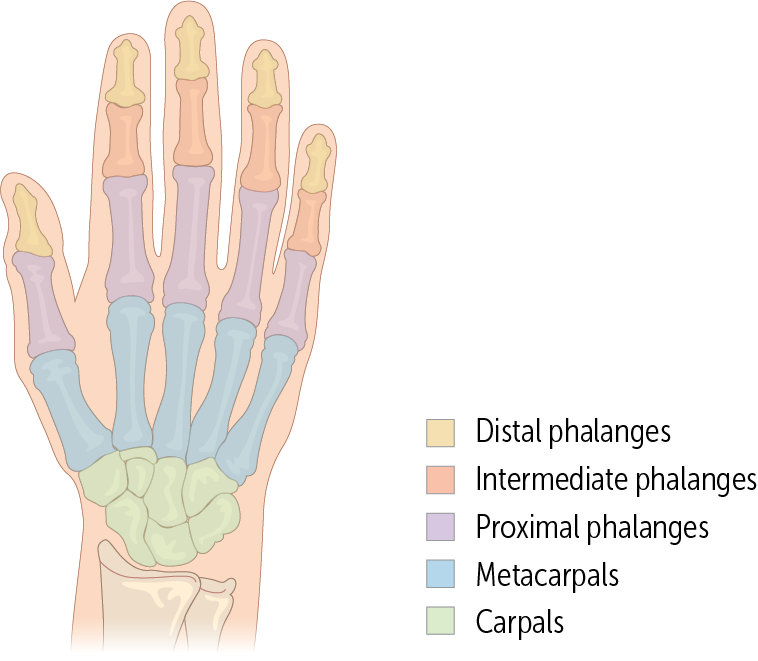
The proximal phalanges are connected to the metacarpals by the _________ joints. These are ellipsoidal joints, allowing movement in two planes (flexion/extension and abduction/adduction in the palmar plane).
metacarpophalangeal (MCP)
The phalanges connect to one another by the ___________ joints. These are hinge joints that allow only flexion and (minimal) extension.
(There are two)
proximal and distal interphalangeal joints (PIP and DIP)
The thumb only has _______ joints because it only has two phalanges
proximal interphalangeal joints (PIP)
The PIP and DIP joints are very stable laterally, since the joints have strong _____________ supporting them.
collateral ligaments
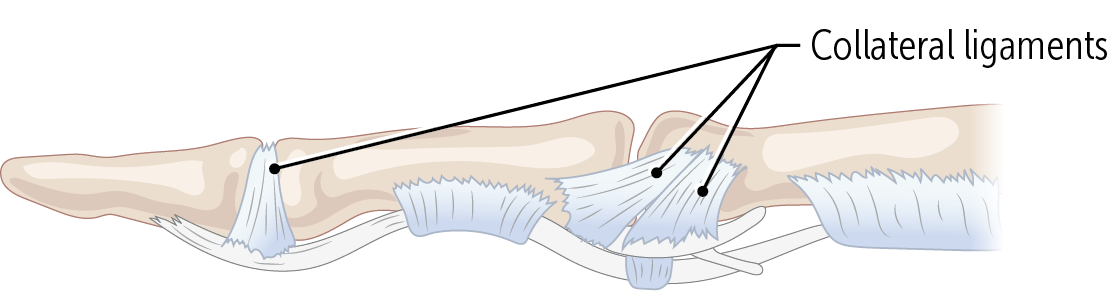
Finger sprains are often caused by jamming the finger against something, hyperextending the _________ joint.
PIP or DIP (proximal and distal interphalangeal joints)
The ____________ are involved in arthritis. Rheumatoid arthritis, an autoimmune disease in which the immune system attacks the body, spares the DIP joints but affects the MCPs and PIPs
interphalangeal joints
Osteoarthritis, a common degenerative disease of older age, affects _______ joints and can lead to severe hand and finger deformities.
The DIP, PIP, and MCP