Cog: Decision Making & Reasoning
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
What are the 3 elements of a decision?
Judgment, reasoning, and decision
Judgement
To judge/form an opinion
Reasoning
The process of drawing conclusions
Decision
The process of choosing btwn alternatives
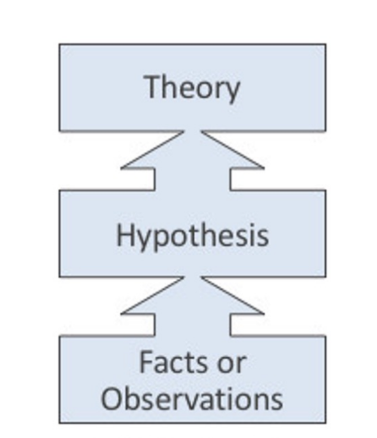
Inductive Reasoning
Process of drawing a general conclusion based on specific observations
Specific cases ——> board principles
Deductive Reasoning
Process of determining whether a specific conclusion logically follows from a general statement
broad principles —> specific cases

Where are inductive conclusions generalized from?
Conclusions generalized from premise

Inductive premises are stated as what?
Premise stated as observations of specific observations

Deductive conclusions are drawn from?
Conclusions drawn from logical rules applied to premise

Deductive premises are stated as?
Premise stated as facts or general principles
Inductive reasoning is what types of process?
Bottom Up
Deductive reasoning is what type of process?
Top down
Representativeness of Observations
How well observations about a particular category represent all members of that category
Number of observations
How many observations are made
Quality of Evidence
Observations can be supported by scientific evidence
Confirmation Bias
We look for information that supports our opinions and ignore information that refutes it
Inductive arguments are weakened by what?
Inductive arguments are weakened by bias to confirm/support our opinions
Myside Bias
We evaluate evidence in a way that’s biased toward our own opinions and attitudes
Backfire Effect
Our support for a given opinion can be stronger when faced with facts that oppose it
Heuristics
Educated guesses, intuitive judgments, or common sense used to solve a problem quickly
“rule of thumb”
Availability Heuristic
Events that come to mind more easily are judged as being more probable
our conclusions are biased by evidence that is more available
Undue weight is given to _________ that comes to mind more easily
Anecdotal Evidence
Illusory Correlations
When a relationship between 2 events appears to exist, but in reality, there’s little/no relationship
Stereotypes are a common form
Representativeness Heuristic
Events that are more similar to a given category more likely to be judged as being part of that category
Base Rate
Relative proportion of different classes in populations
T or F: we rely on representativeness to the occupation categories and ignore base rate
Truw
Conjunction Rule
Probability of a conjunction of 2 events cannot be higher than probability of events alone
Law of Large Numbers
More individuals that are randomly drawn from a population, the more representative the group will be drawn of an entire population
Syllogism
Consist of 2 broad statements (premises) and a conclusion
Categorical Syllogism
Statements with “all”, “no”, or “some”
Conditional Syllogism
1st premise has “if…then” format
Valid Syllogisms (Categorical)
Conclusion follows logically from premises
T or F: Not all valid Syllogisms are true
True

Invalid Syllogism
conclusion doesn’t follow logically from premises
T or F: all invalid syllogisms are false
False. Not all invalid syllogisms are not true.

Belief Bias
tendency to think a syllogism is valid if its conclusions are believable
Conditional Syllogisms
It’s easier to see the logic is invalid when using statements that also make it inaccurate
falsification principle
to test a rule, it’s necessary to look for a situation that would falsify it
T or F: real world problems are easier to solve than abstract problems
True
Decision
process of choosing between alternatives
Expected Utility Theory
Assumes if people have all relevant info, they’ll make a decision that results in outcomes that help to achieve their goals
Framing Effect
Decisions influenced by how choices are stated
Status Quo Bias
Tendency to do nothing when faced with making a decision
Risk Aversion
Tendency to avoid taking risks
Dual Systems Approach
Idea that we may have different systems for decision making