Clin Path - New Info
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
What are the five stages of the estrous cycle. Name them in order.
Proestrus, Estrus, Metestrus, Diestrus, & Anestrus
What physical exam finding is consistent with a bitch that is attractive to males but not permitting males to mate?
A swollen vulva with a reddish discharge present.
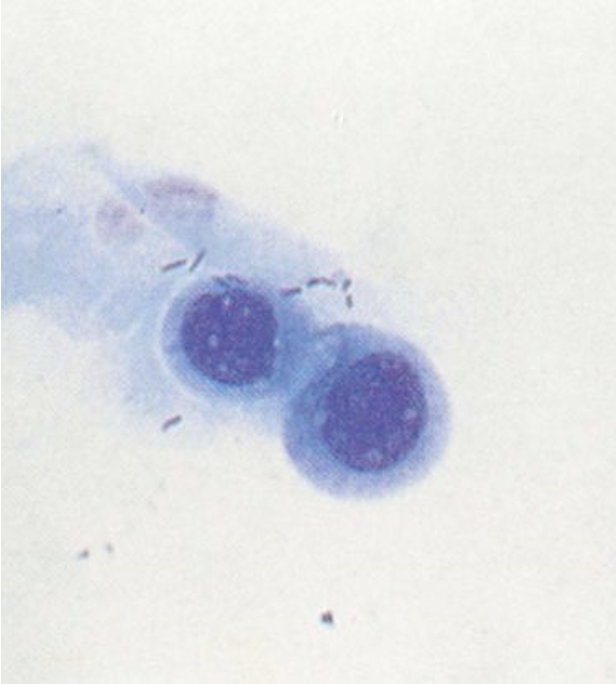
Which epithelial cell type is characterized as round, small, and containing a large nucleus? It looks similar to a WBC but is significantly larger than a WBC.
Parabasal epithelial cells
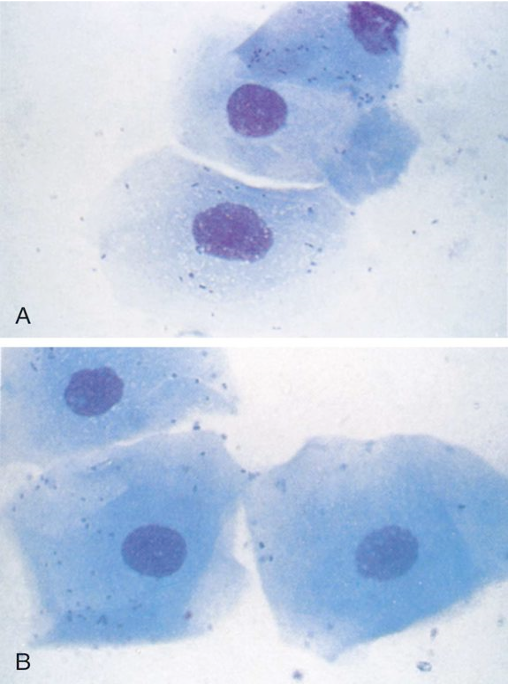
Which epithelial cell type is characterized as larger than parabasal cells, less nucleus, more cytoplasm?
Intermediate epithelial cells
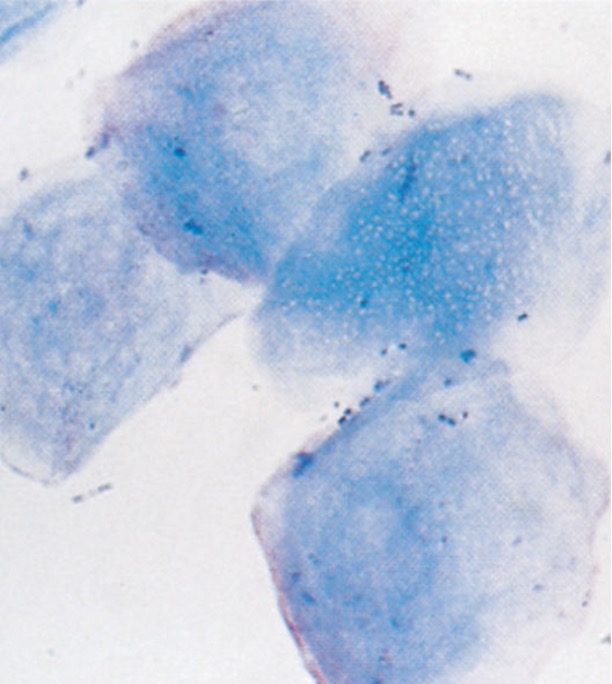
Which epithelial cell type is characterized as the largest, pyknotic nucleus, irregular, flat, or boxy borders?
Cornified epithelial cells
If you are performing the Live:Dead Sperm Ratio, which sperm are counted as dead?
The sperm which appear pinkish-red.
Sperm defects which occur during sperm production are classified as what?
Primary defects
•Female is attractive to males
•Female is not receptive to attempts to mate
•On PE: swollen vulva with reddish discharge is present
Which stage of the estrous cycle is the bitch in?
Proestrus
•Female is attractive to males
•Female is receptive to mating with males
•On PE: pinkish/reddish discharge from the vulva is present becoming whiter as metestrus approaches
Which stage of the estrous cycle is the bitch in?
Estrus
•No longer attractive to males
•No longer receptive to mating by males
•On PE: decreased vulvar swelling and discharge is present
Which stage of the estrous cycle is the bitch in?
Metestrus (post-estrus)
•No longer attractive to males
•No longer receptive to mating by males
•On PE: no vulvar swelling or discharge is present
Which stage of the estrous cycle is the bitch in?
Diestrus
•Female is not attractive to males
•Female is not receptive to mating by males
•On PE: no vulvar swelling or discharge is present
Which stage of the estrous cycle is the bitch in?
Anestrus
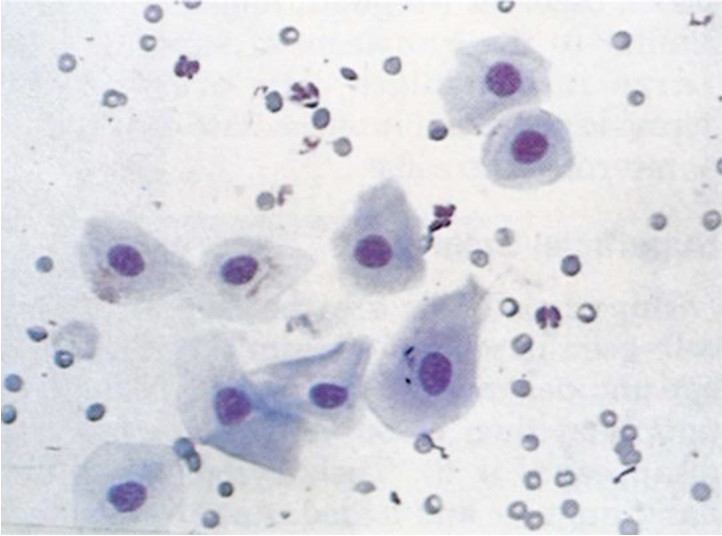
•Parabasal epithelial cells predominate
•RBCs are present in large numbers
•A small number of neutrophils may be present
What stage of the estrous cycle is found via the vaginal cytology?
Early Proestrus
•Parabasal epithelial cells predominate
•Increasing numbers of intermediate epithelial cells appear
•RBC numbers decrease
•A small number of neutrophils may be present
What stage of the estrous cycle is found via the vaginal cytology?
Late Proestrus
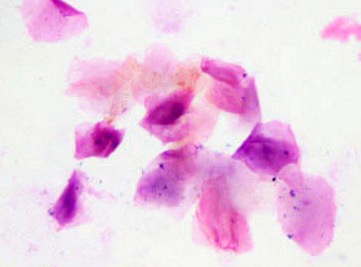
•Squamous epithelial cells predominate.
-Some cells may have pyknotic nuclei present while most others will have no nucleus at all.
•Abundant bacteria is present.
•A few RBCs may be present.
•No WBCs are present.
What stage of the estrous cycle is found via the vaginal cytology?
Estrus
•Intermediate and parabasal epithelial cells predominate.
•Few squamous epithelial cells are present.
•Abundant bacteria and other debris is present.
•Neutrophils increase but then decrease greatly as debris and bacteria are removed.
•RBCs are absent so discharge should be white in appearance.
What stage of the estrous cycle is found via the vaginal cytology?
Metestrus
•Parabasal epithelial cells predominate.
•Few bacteria is present
•Few WBCs are present.
•No RBCs are present.
What stage of the estrous cycle is found via the vaginal cytology?
Diestrus
•Parabasal epithelial cells predominate
•Bacteria may be present.
•A few neutrophils may be present.
•No RBCs are present.
What stage of the estrous cycle is found via the vaginal cytology?
Anestrus
On a cytology what all cannot be differentiated from one another because they look the same?
Diestrus, anestrus, & pregnancy
What conditions should sperm samples not come into contact with?
Extremes in temperature (especially cold), water, disinfectants, and pH variations
What all components should be included for a complete semen evaluation?
•Volume of ejaculate (mls)
•Gross appearance (color and clarity)
•Wave motion
•Microscopic motility
•Concentration of sperm on the slide
•Ratio of live to dead sperm
•Morphological features of sperm cells
•Presence of any foreign material or cells
What other information should be included for a complete evaluation?
•Method of collection
•Signalment (breed, age, species)
•History and relevant PE findings
•Any suspected abnormalities
A semen sample should have what percentage of progressive motility of sperm to be adequate for fertility?
≥60%
What percentage of motility is poor with very slow erratic activity?
20-40%
What percentage of motility is fair with slow linear or erratic activity?
40-60%
What percentage of motility is good with moderate linear activity?
60-80%
What percentage of motility is very good with rapid linear activity?
80-100%
Which defects occur during production and are more significant because it indicates fertility issues?
Primary
Which defects occur sometime between storage in the epididymis and sample evaluation?
Secondary
For adequate fertility what should the percentage be for normal morphology?
≥80%
What are the primary defects of the sperm’s head?
•Double
•Too large
•Too small
•Odd-shaped: pear, round, twisted, knobby
What are the primary defects of the sperm’s midpiece?
•Swollen
•Kinked
•Twisted
•Double
•Eccentrically attached to the head
What are the primary defects of the sperm’s tail?
•Coiled
•Short
•Double
•Terminal droplet
What are the secondary defects of a sperm?
•Tailless heads
•Protoplasmic droplets on the midpiece
•Bent or broken tails
For stained sperm, ____ will appear white while ____ will take up the stain used.
Live & Dead
Which technique is most commonly used in veterinary medicine for performing agar diffusion?
Bauer-Kirby technique
If you want to determine the minimum concentration of a specific drug required to effectively treat a microbial infection, you should perform what tests?
Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) testing
What is the zone of inhibition?
Clearing of growth around the disc on the media surface
What is the best location for collecting samples for fungal culture from a skin lesion?
Collect samples from the outside edge of the lesion
Which two (2) dermatophytes of veterinary importance are zoonotic?
Trichophyton mentagrophytes & Microsporum canis
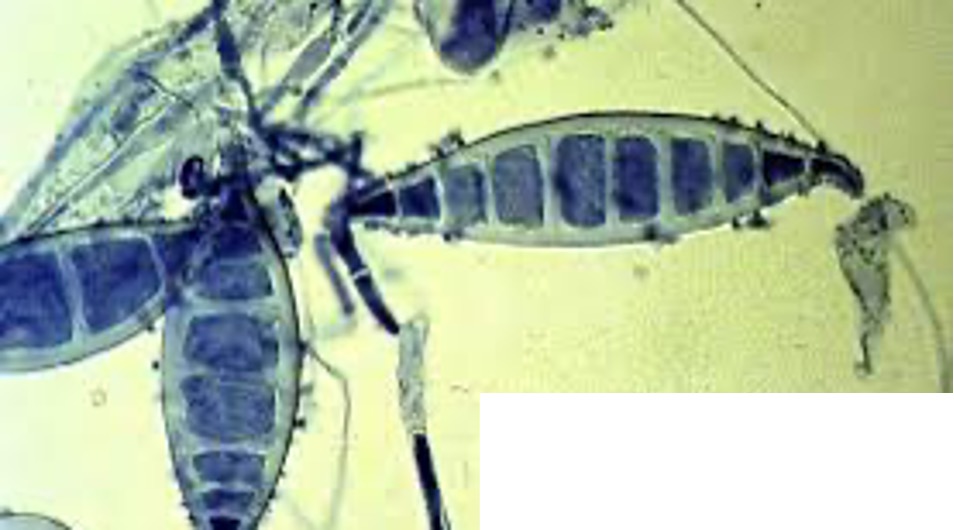

What is the parasite shown in the image?
Utilize the following characteristics:
•There are usually more than 6 partitions (cells) within each macroconidia – commonly 9.
•Note the thick walls around each macroconidia.
Microsporum canis
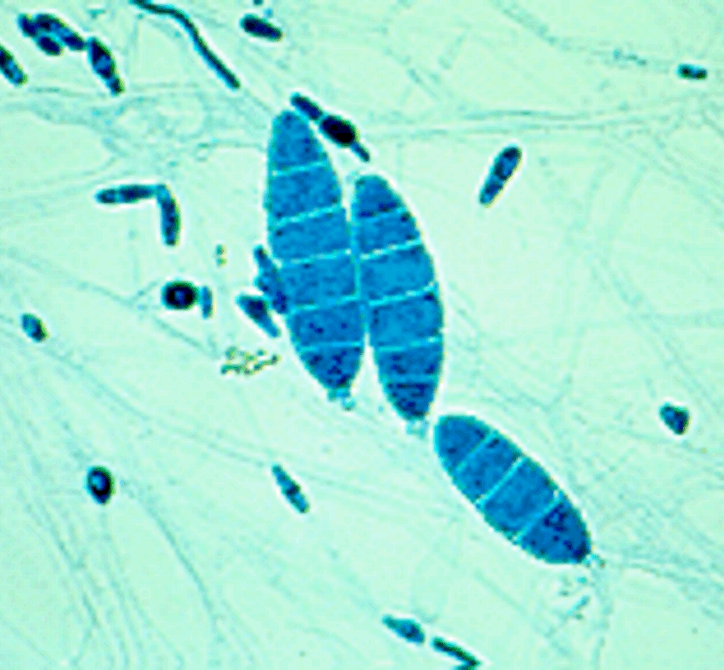
What is the parasite shown in the image?
Utilize the following characteristics:
•This is a thin-walled macroconidia with no more than 6 cells - commonly has 6.
•Both humans and pets can be infected with this parasite.
•Infection occurs due to contact with the environment.
•Treating the pet alone does not prevent recurrence of this infection.
•Usually not an issue unless the animal and/or human is immunocompromised.
Microsporum gypseum
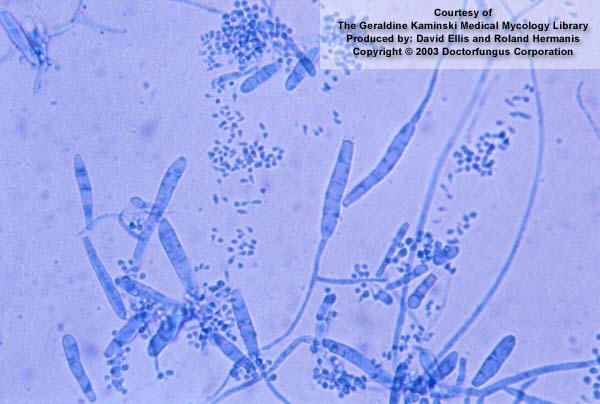
What is the parasite shown in the image?
Utilize the following characteristics:
•Macroconidia have NO terminal appendages.
•Thin – walled macroconidia usually have fewer than 6 cells commonly.
•Grows on DTM within 5 to 7 days
Trichophyton mentagrophytes
This type of microbiological test is performed to determine the MOST appropriate drug and/or the MOST appropriate concentration of the drug to treat the organism of interest. What is the name of this test?
Antimicrobial Sensitivity Test (AST)
If an organism is effectively killed or inhibited from further growth by the drug, what is it?
Susceptible
If an organism is NOT effectively killed or inhibited from further growth by the drug, what is it?
Resistant
When is the best time to collect a sample for any antimicrobial sensitivity testing?
Before treatment begins
After allowing the test media to warm to room temperature, how much of the media’s surface should be inoculated?
The entire surface to create a lawn of growth.
What are the guidelines for manually placing the paper discs in the media for antimicrobial drug testing?
•Place disks at least 24 mm apart.
•Place discs at least 10-15 mm from the edge of the plate.
•Discs must be tamped down firmly to provide good contact with the media surface.
•The discs cannot be moved in any way once they touch the media surface.
What type of media is used when preforming the agar diffusion method of AST?
Mueller-Hinton agar with and without blood
For agar diffusion method with AST what is being tested and how?
•Each paper disc is infused with a different type of drug at therapeutic concentrations.
•The test will determine the drug to select for treatment.
For agar diffusion method with Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) what is being tested and how?
•Each paper disc is infused with the same drug but at different therapeutic concentrations.
•The test will determine the lowest concentration of the drug required for effective treatment.
What is the area immediately surrounding the disc where growth of the organism is inhibited by the presence of the drug contained within the disc?
The Zone of Inhibition
What is the study of fungal organisms?
Mycology
What type of media is described below?
•Media of choice for dermatophytes.
•Contains an indicator that turns RED in the presence of most dermatophytes.
•Available in plate and tube forms.
Dermatophyte Test Medium (DTM)
What type of media is described below?
•Media of choice for non-dermatophytes.
•Promotes earlier formation of fungal structures for identification.
•Contains no color indicator.
Sabouraud Dextrose Agar (SDA)
Blood agar media is classified as what categories of culture media?
Differential & Enriched
What are sites considered to be sterile?
Bladder, Cerebrospinal Fluid, & Stifle Joint
MacConkey agar test media is categorized as both __________ and _________ types of media.
Selective & Differential
What type of microbiological test media is differential ONLY?
SIM tubes
If you observe pink colonies of growth on MacConkey agar test media, what does this mean?
The organism is gram-negative and ferments lactose.
Of a gram stain what solution is the primary stain that stains the slide purple?
Crystal Violet
Of a gram stain what solution is the mordant that forces the primary stain to adhere to the cell wall?
Gram’s Iodine
Of a gram stain what solution is the decolorizer?
95% Ethanol or Acetone
Of a gram stain what solution is a counter stain that stains the slide pink?
Basic Fuchsin or Safranin
What is the order of the solutions used when performing the gram stain?
Crystal Violet, Gram’s Iodine, 95% Ethanol or Acetone, & Basic Fuchsin or Safranin
What is reported during a gram stain?
Gram Reaction, Arrangement, & Morphology
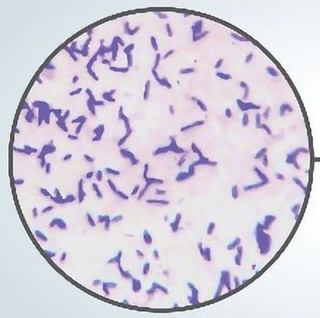
The following gram reaction is purple/blue in color. What is it?
Gram-positive
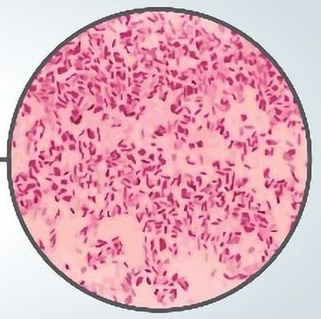
The following gram reaction is pink/red in color. What is it?
Gram-negative
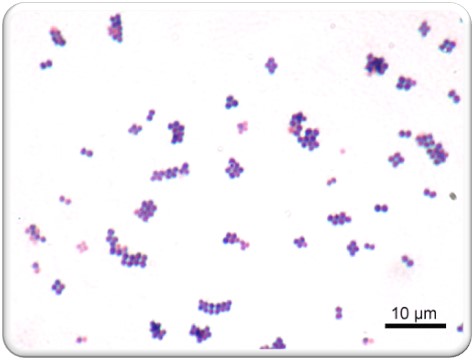
What is the Gram reaction, arrangement, and morphology of the organisms shown in the image below?
Gram positive cocci in pairs, tetrads, and clusters
The KOH test is used when:
When a variable gram reaction is obtained on Gram stains.
If an organism is acid-fast positive, what color will the organisms stain on the slide when viewed under the microscope?
Red
What can cause gram-variable reaction on your gram stain?
Over-decolorizing, gram staining using older cultures, & excessive heat fixation
Which of the stains used for Gram staining is also referred to as the 'mordant'?
Gram's Iodine
What are the sterile sites?
Bladder, peritoneum, pleural cavity, joint spaces, CSF fluid, & eye
What are the contaminated sites?
Vaginal/preputial swabs, ear swabs, distal urinary tract, skin, go tract, upper respiratory tract, & oral swabs
What is the test media that usually contains basic nutrients with blood, serum, or egg nutrients added? All gram-positive and gram-negative organisms will grow on this test media.
Enriched media
What are examples enriched media?
•Chocolate agar
•Blood agar (most used enriched test media in veterinary medicine)
•Thioglycollate broth
This type of test media places bacteria into specific groups based on biochemical reactions taking place on the media. What type of media is it?
Differential media
What are examples of differential media?
•Simmons citrate
•Urea tubes
•Sulfide-Indole Motility tubes
•TSI (triple sugar iron) agar
This type of test media contains substances like bile salts and antimicrobial drugs which inhibit the growth of all but a few types of bacteria. It is useful when you need to isolate specific organisms from a mixed sample of growth. What type of media is it?
Selective media
What are examples of selective media?
•MacConkey Agar (most used selective test media in veterinary medicine)
•Eosin-methylene blue agar (EMB)
•Hektoen agar
If you are reading a histology report for an excisional biopsy specimen that states that the lesion has 'complete surgical margins', this means that:
There were no tumor cells along the margin where the scalpel cut the tissue from the body.
What is an incisional biopsy?
A portion of tissue is collected from a lesion or mass for evaluation

What is the tool in the image shown used for?
Skin punch biopsy
What is NOT an appropriate site for bone marrow biopsy sample collection in a 35 lb. dog with a normal body condition?
Proximal tibia
If you are using a Jamshidi needle, what are you most likely performing?
Bone marrow biopsy
What is the preferred method of marking surgical margins?
Inking
What is cytology?
The study of cells to determine type, number, and character
A histology report would include information about complete or incomplete surgical margins for what types of samples?
Excisional biopsy
Which biopsy collection methods requires the use of a scalpel and forceps?
Wedge biopsy
What is NOT a reason to choose to perform an incisional biopsy instead of an excisional biopsy?
The mass or lesion is superficial
Which type of biopsy is when a portion of the lesion is sampled?
Incisional
Which type of biopsy is where the entire lesion is removed?
Excisional
What is any region of the biopsy specimen that was adjacent to or contiguous with tissue that remains in vivo (in the body)?
Surgical margin
What are the ways to mark margins on excisional biopsies?
Inking & Suturing
What are examples of incisional biopsies?
Needle core technique, Punch biopsy technique, & Wedge biopsy technique
What are the preferred sites of bone marrow biopsies in dogs?
•Dorsal crest or lateral face of the wing of the ileum
•Proximal femur
•Proximal humerus
What are the preferred sites for bone marrow biopsies in cats?
•Proximal femur
•Proximal humerus

What is the tool in the picture shown?
Jamshidi Needle