L16 Emotion and Motivation (Imported from Quizlet)
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Internal states
Behaviour is influenced by _________ _______
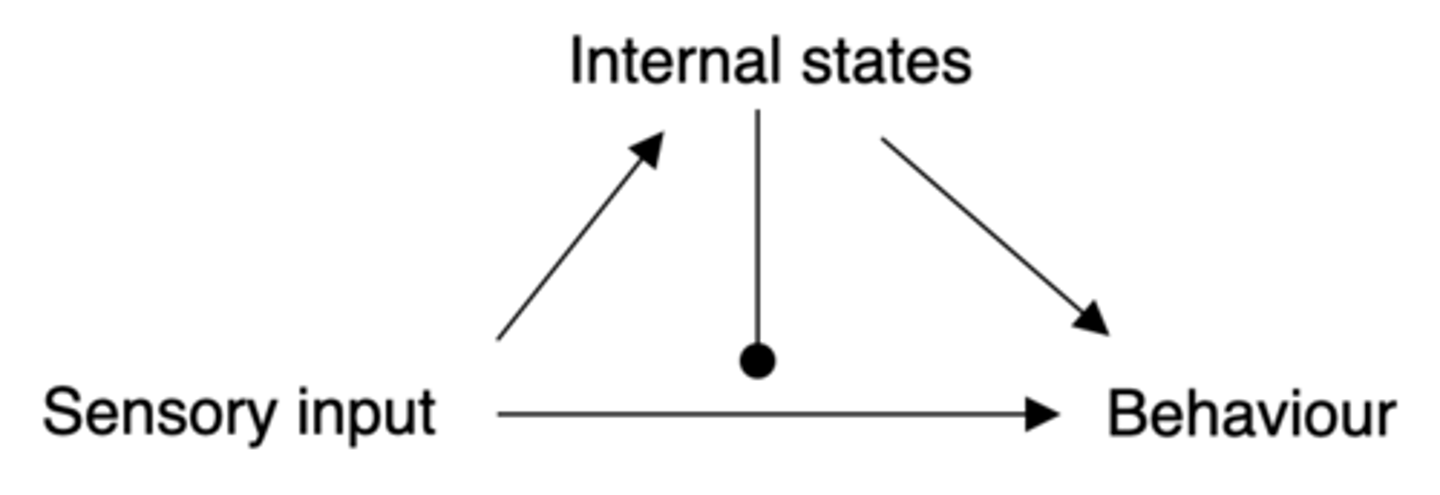
Feeding, fighting, fleeing, mating
What are the 4 basic internal states?
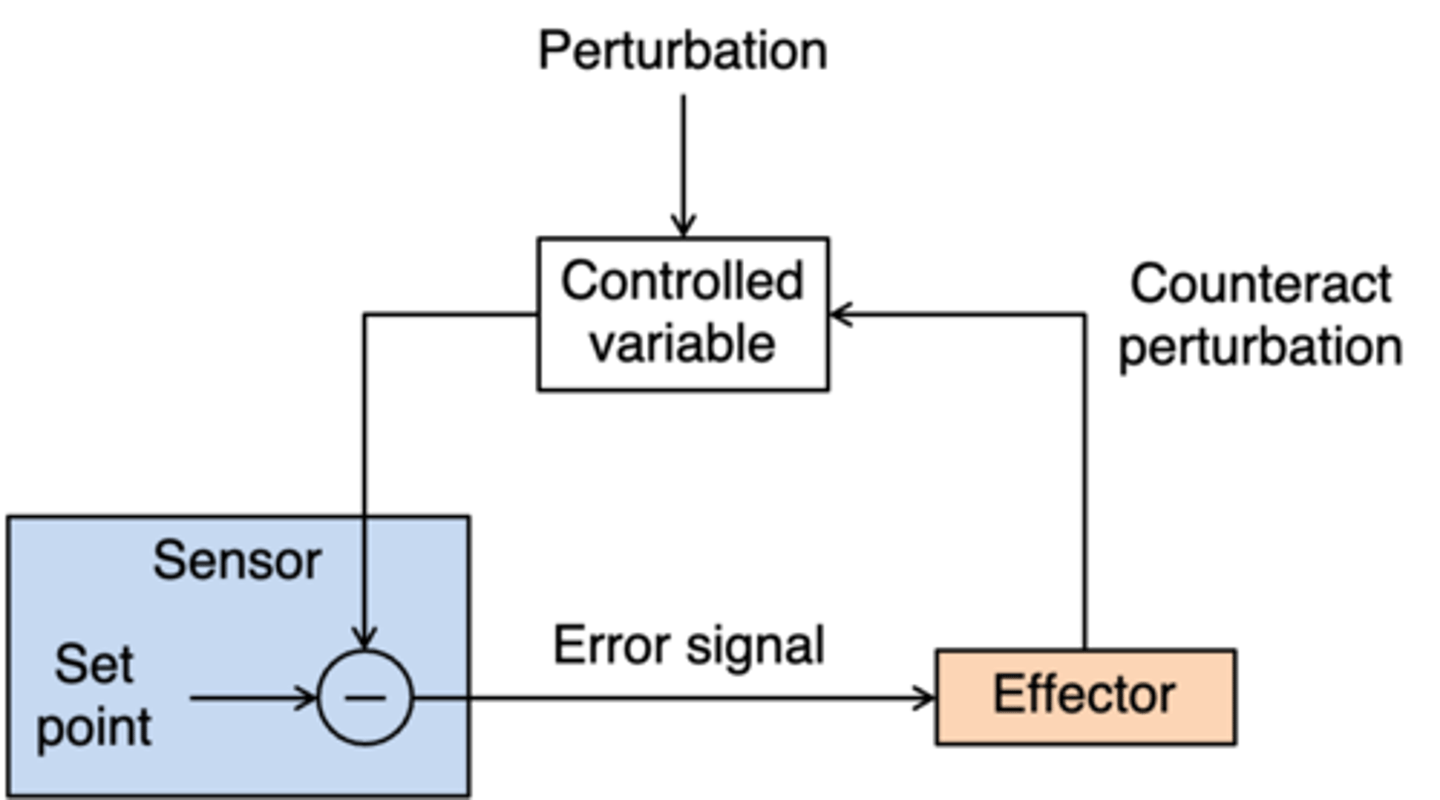
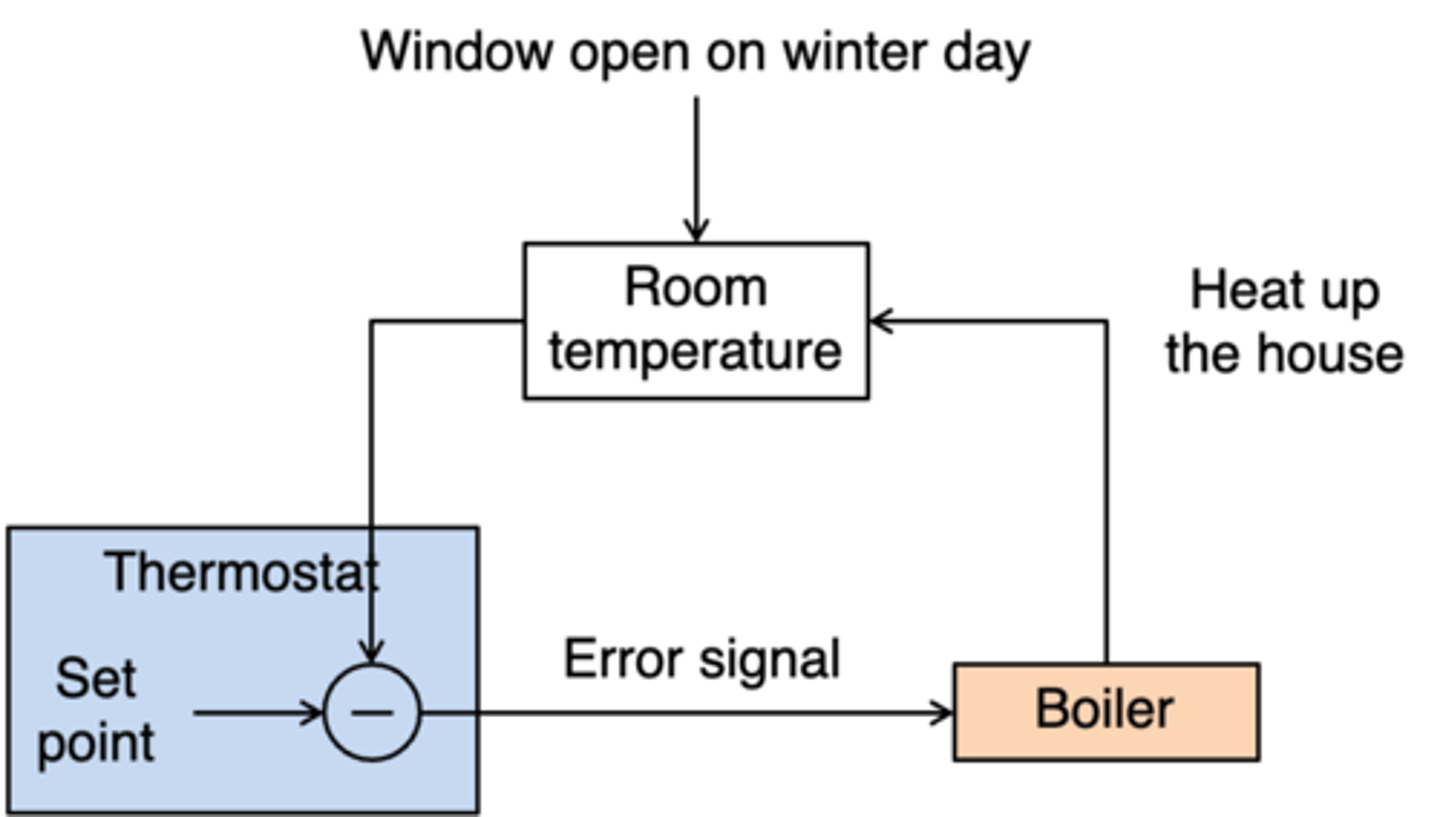
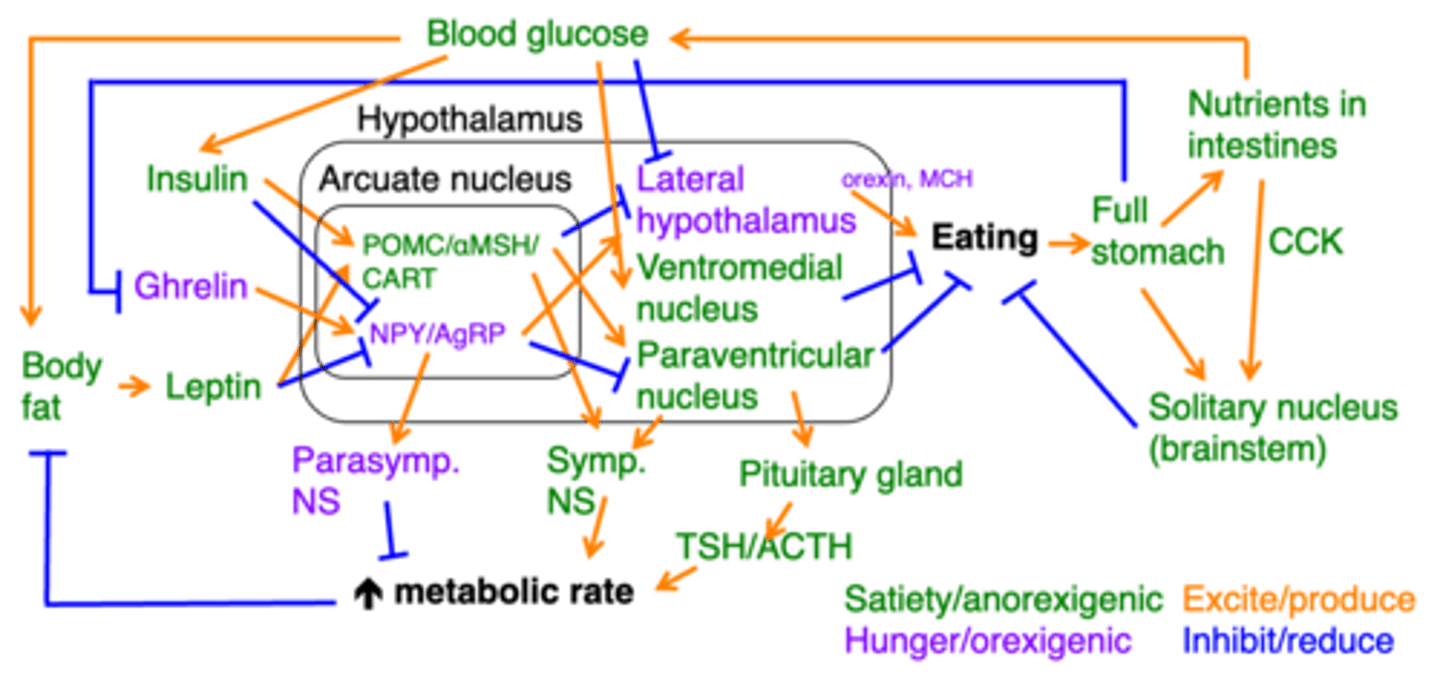
Basic structure of all homeostatic systems
What does this image represent?
Home central heating homeostatic system
Hunger/orexigenic
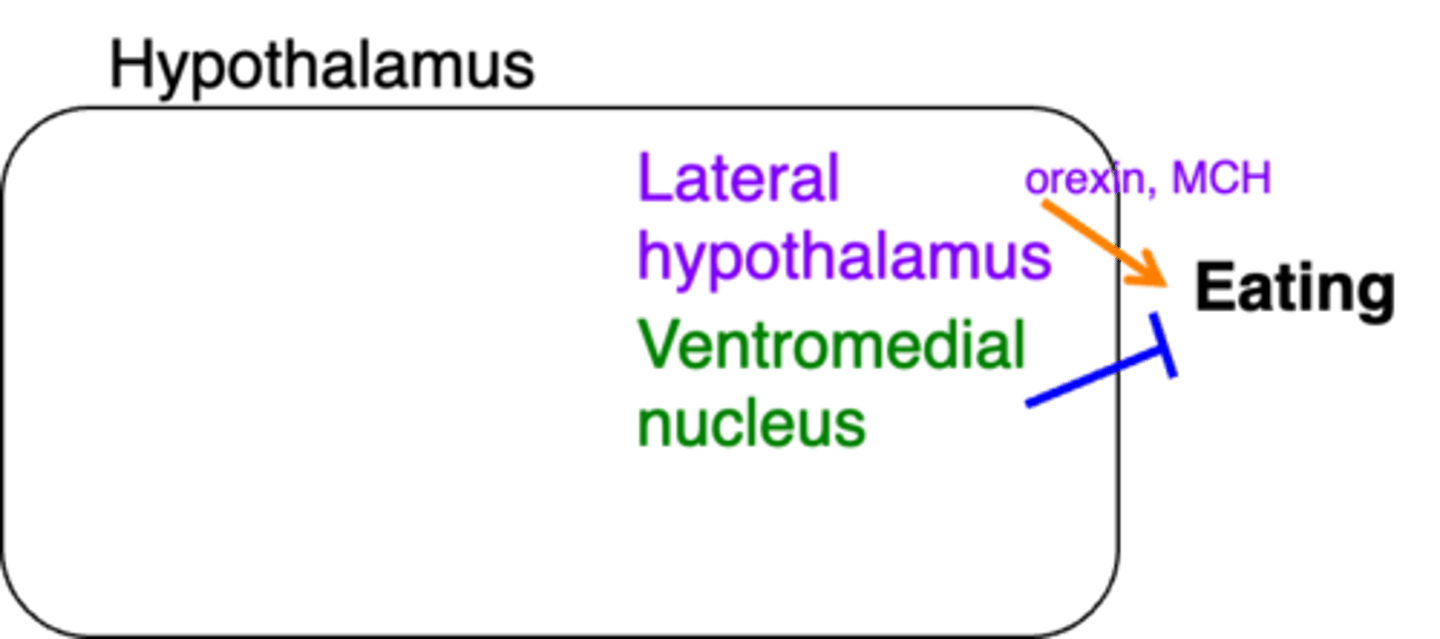
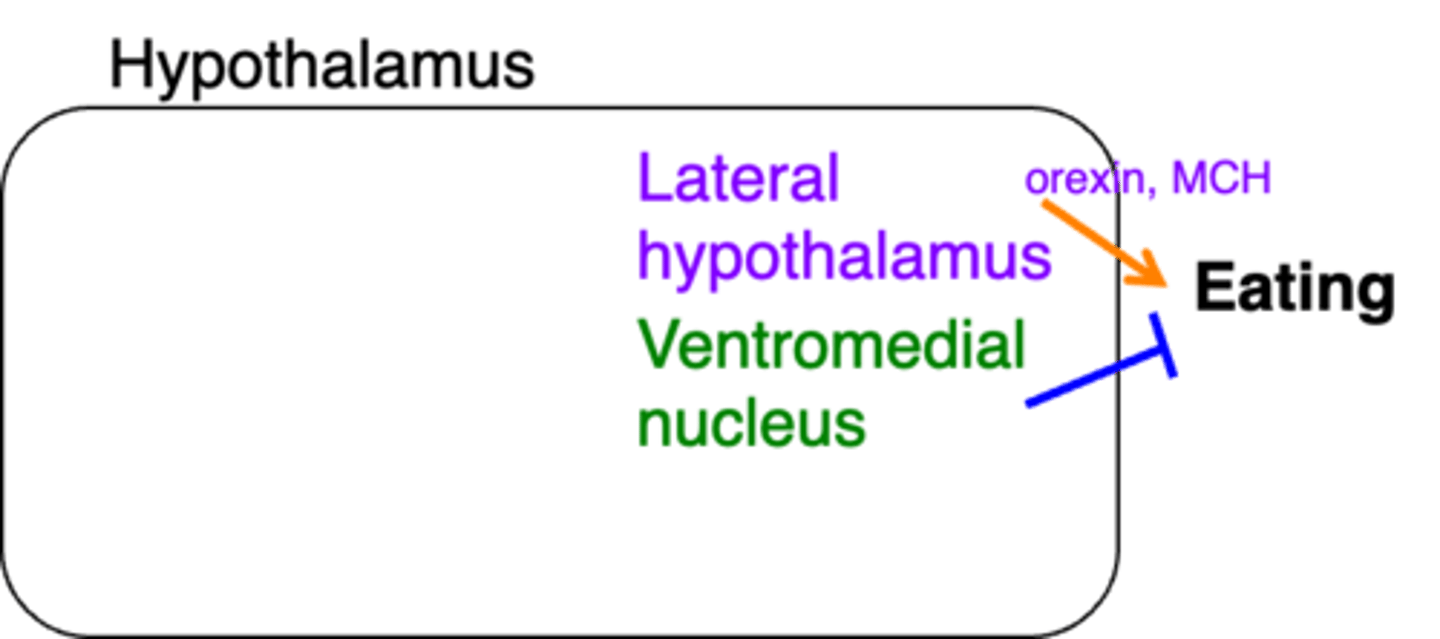
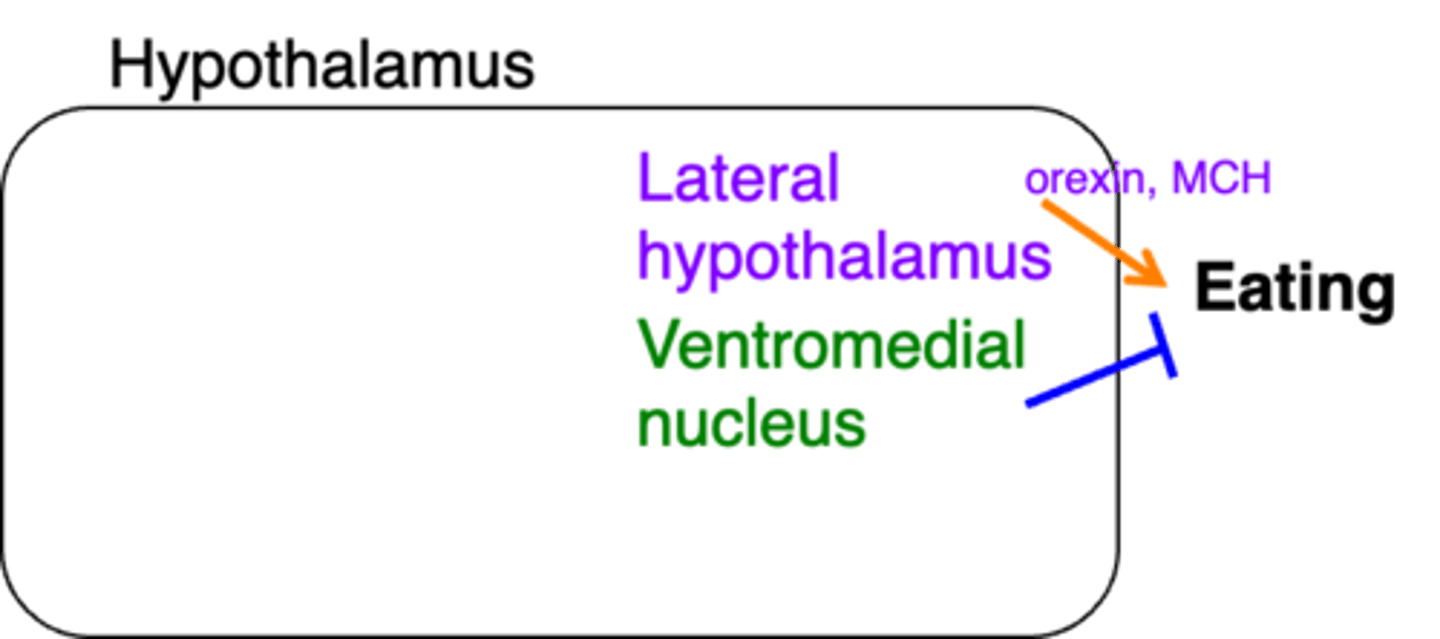
In this image, what does the colour purple represent?
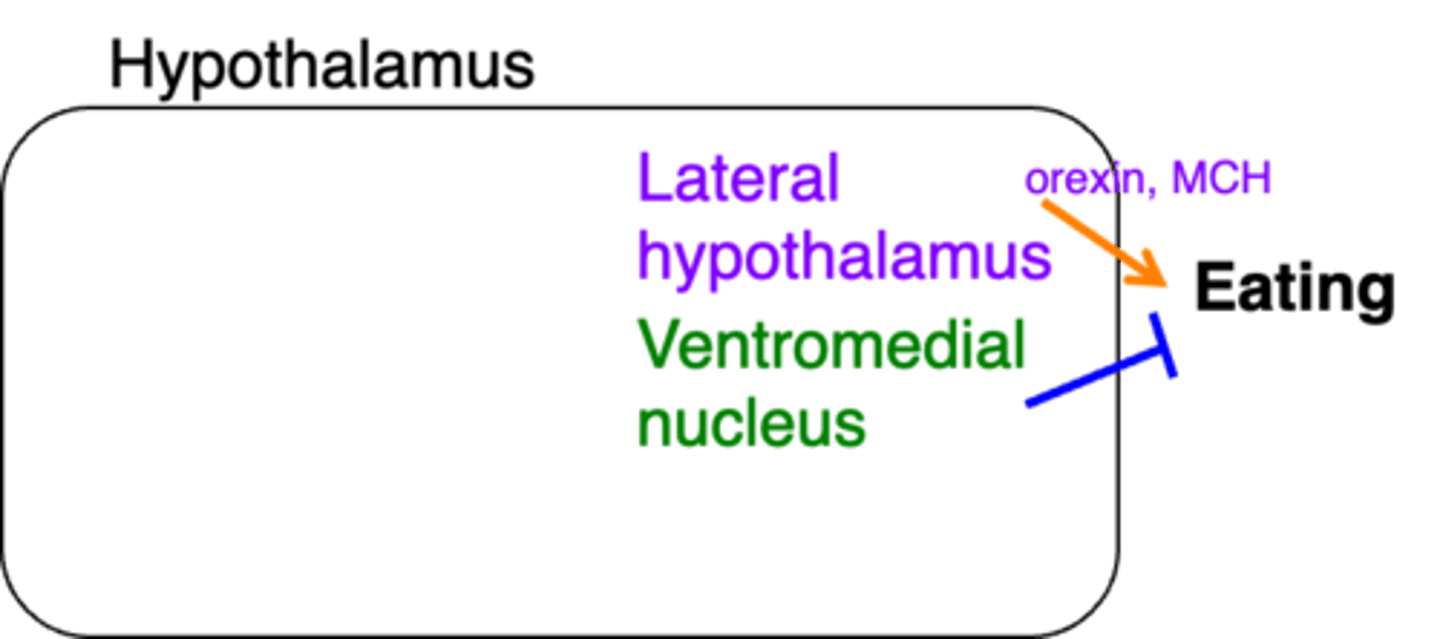
Satiety/anorexigenic
In this image, what does the colour green represent?
Excite/produce
In this image, what do the orange arrows represent?
Inhibit/reduce
In this image, what do the blue arrows represent?
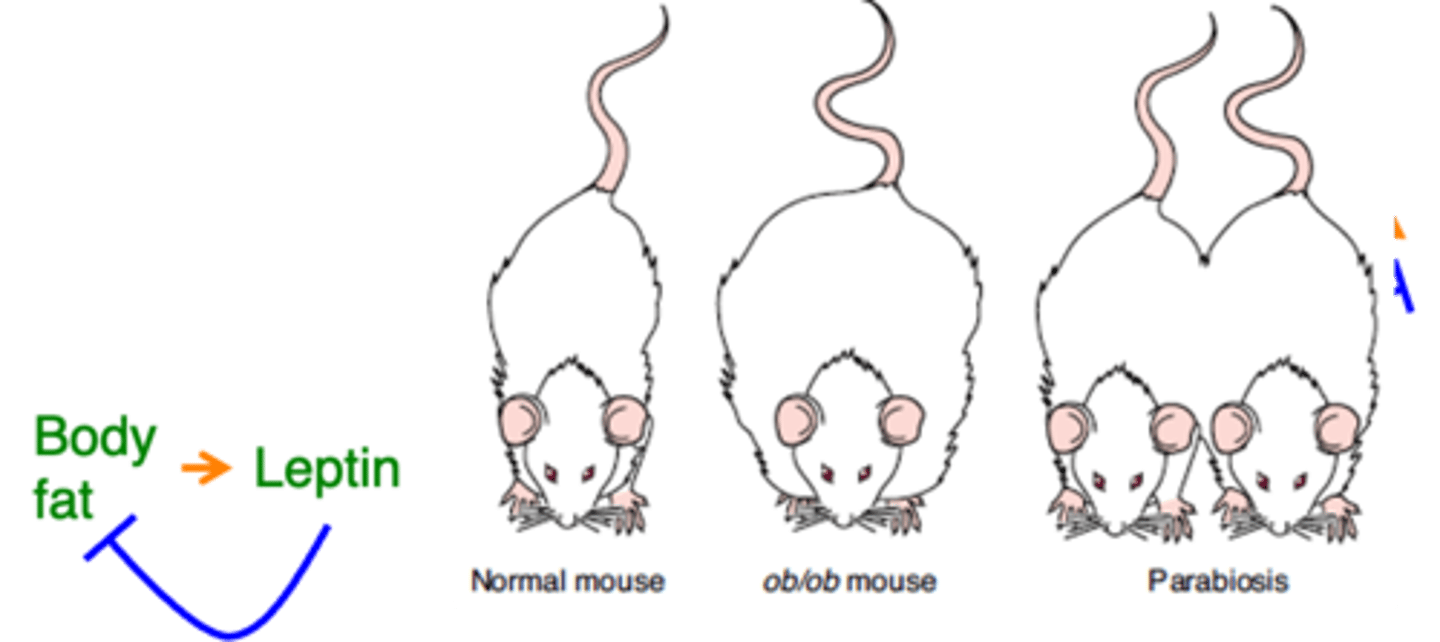
It is a hormone produced by fat that reduces fat
What is leptin and what does it do?
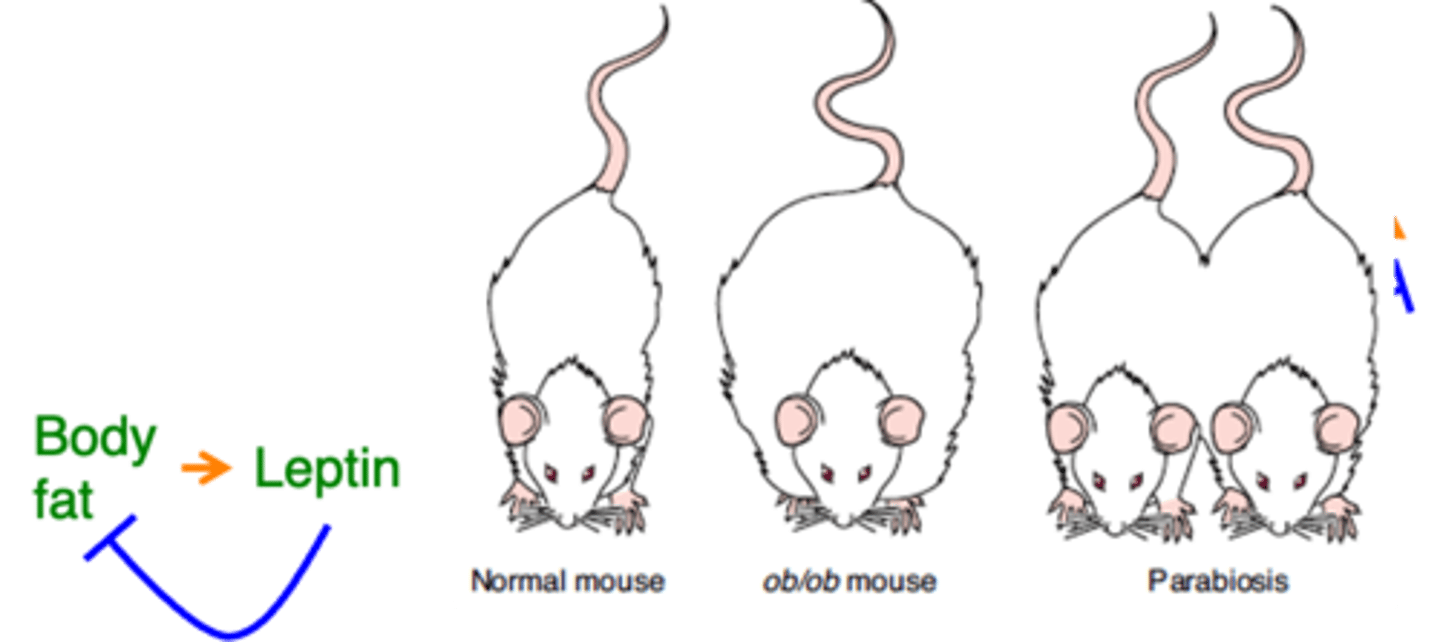
Get obese
Ob/ob mutant mice lack leptin and therefore ...?
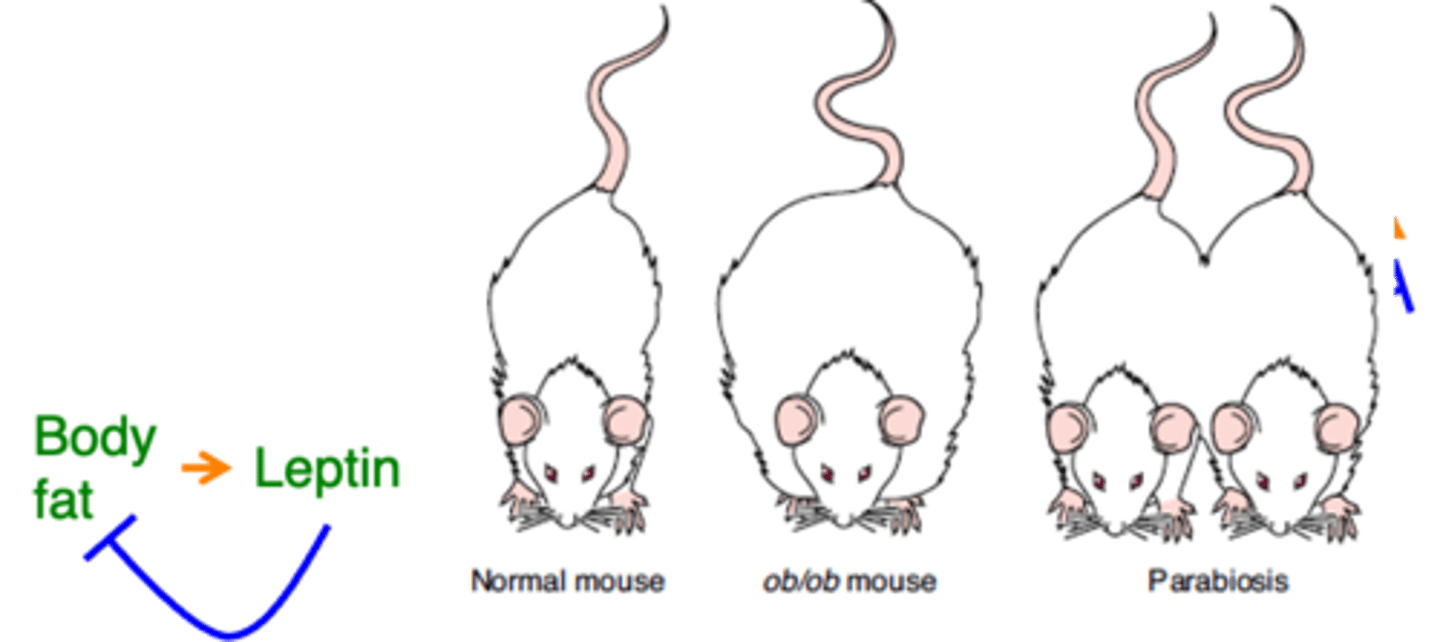
It gets thin again
If you link an ob/ob mouse's bloodstream with a normal mouse, what happens?
The mechanism regulating hunger
This image here represents what?
(must be able to know what hormones are satiety promoting or inhibiting)
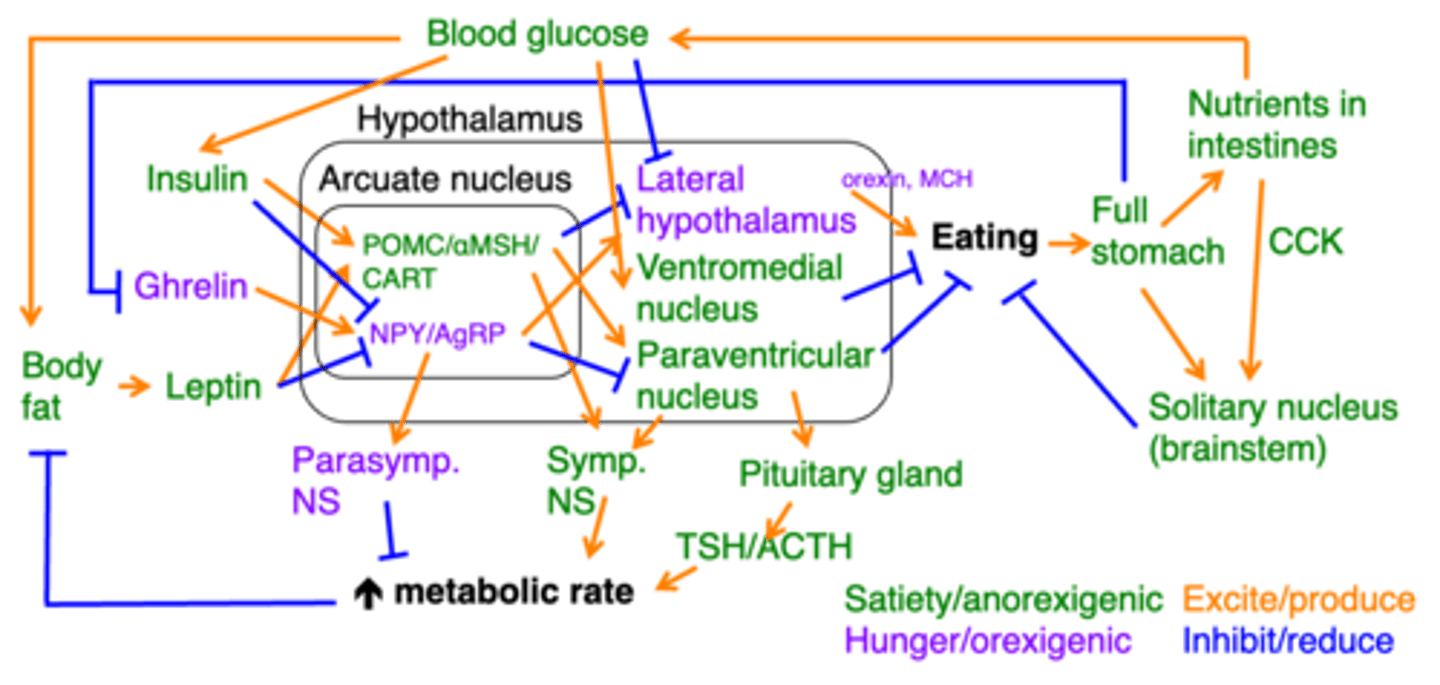
Ghrelin
An empty stomach produces what?
Negative feedback loops (an odd number of inhibitory arrows in the loop)
What is homeostasis governed by?
Adding or removing key peptides/hormones, activating or blocking/destroying brain regions
The feedback loops can be investigated by ...?
Neuropeptides, hormones
Signalling occurs by _______________ and ______________: slow (minutes - hours - days)
Multiple mechanisms
Hunger and metabolism are regulated by ____________ ______________
Amygdala
Which part of the brain, sitting anterior to the hippocampus, has an important role in fear?
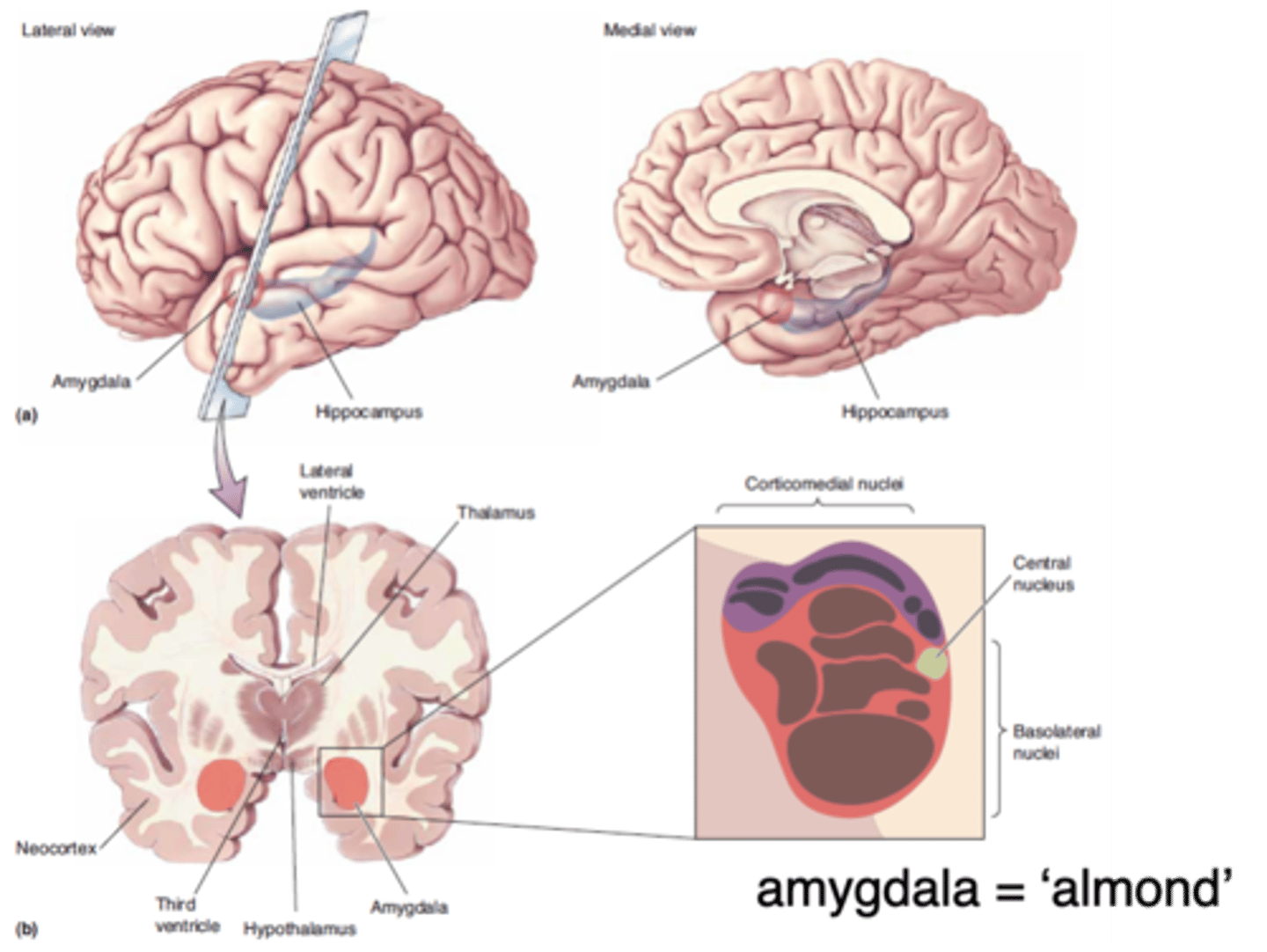
Fearful faces
When doing an fMRI, the amygdala is activated when people looked at what?
Less fear
Lesions in amygdala cause animals to show what?
Fear conditioning
Amygdala is required for _____ _____________
Amygdala and hypothalamus
What brain areas are involved in aggression?
Aggression
Electrical stimulation of the hypothalamus causes what?
Affective
The medial hypothalamus is important for ____________ aggression
Predatory
The lateral hypothalamus is important for ___________ aggression
Attack inanimate objects
Artificial activation of VMHvl by optogenetics caused a mouse to do what?
Dopamine
What encodes reward prediction error i.e. surprise?
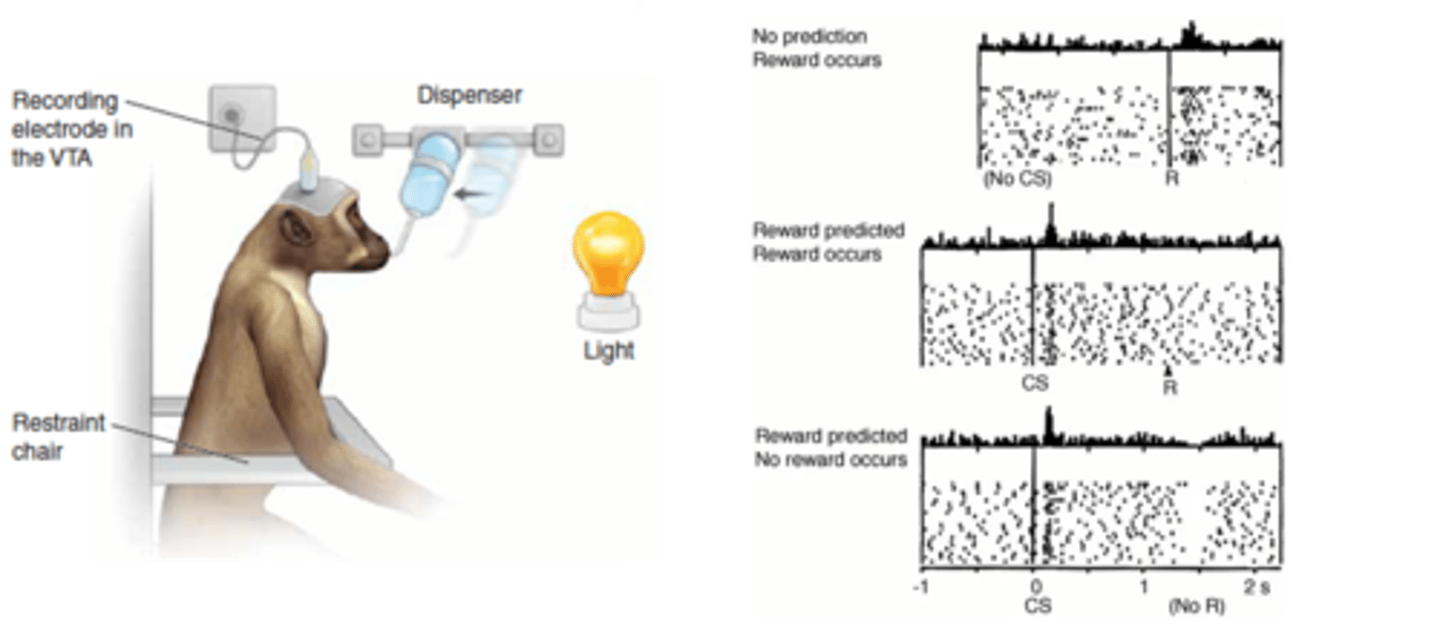
An action potential being fired
What does each black dot in the graphs represent?
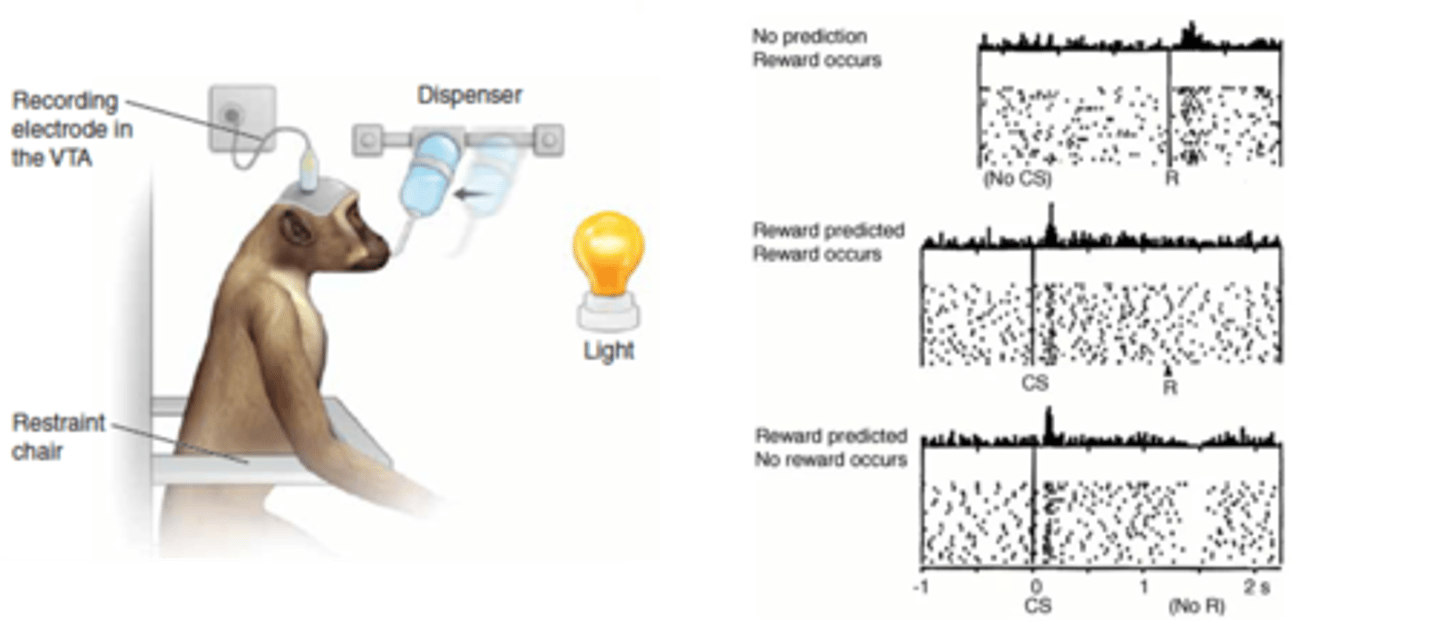
True
Dopamine can predict positive or negative prediction errors (True or False)
Lack motivation
Rats with destroyed mesolimbic dopaminergic projections still seem to enjoy tasty food but they ______ ________________ to seek food
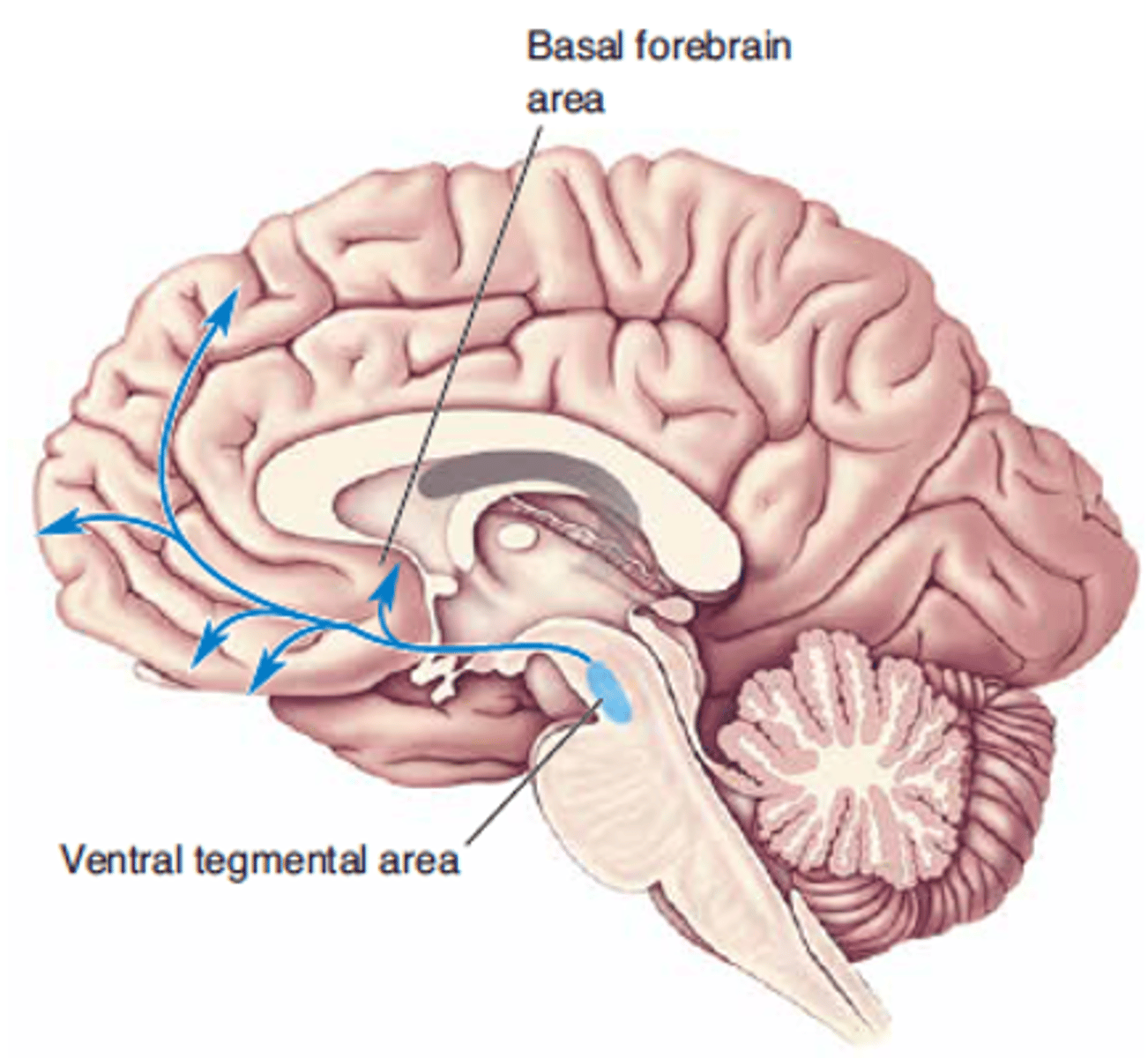
Wanting, motivation
Dopamine drives __________ or ___________ rather than pleasure
Embodied decision making - emotions as 'gut feelings'
What is the 'somatic marker hypothesis'?
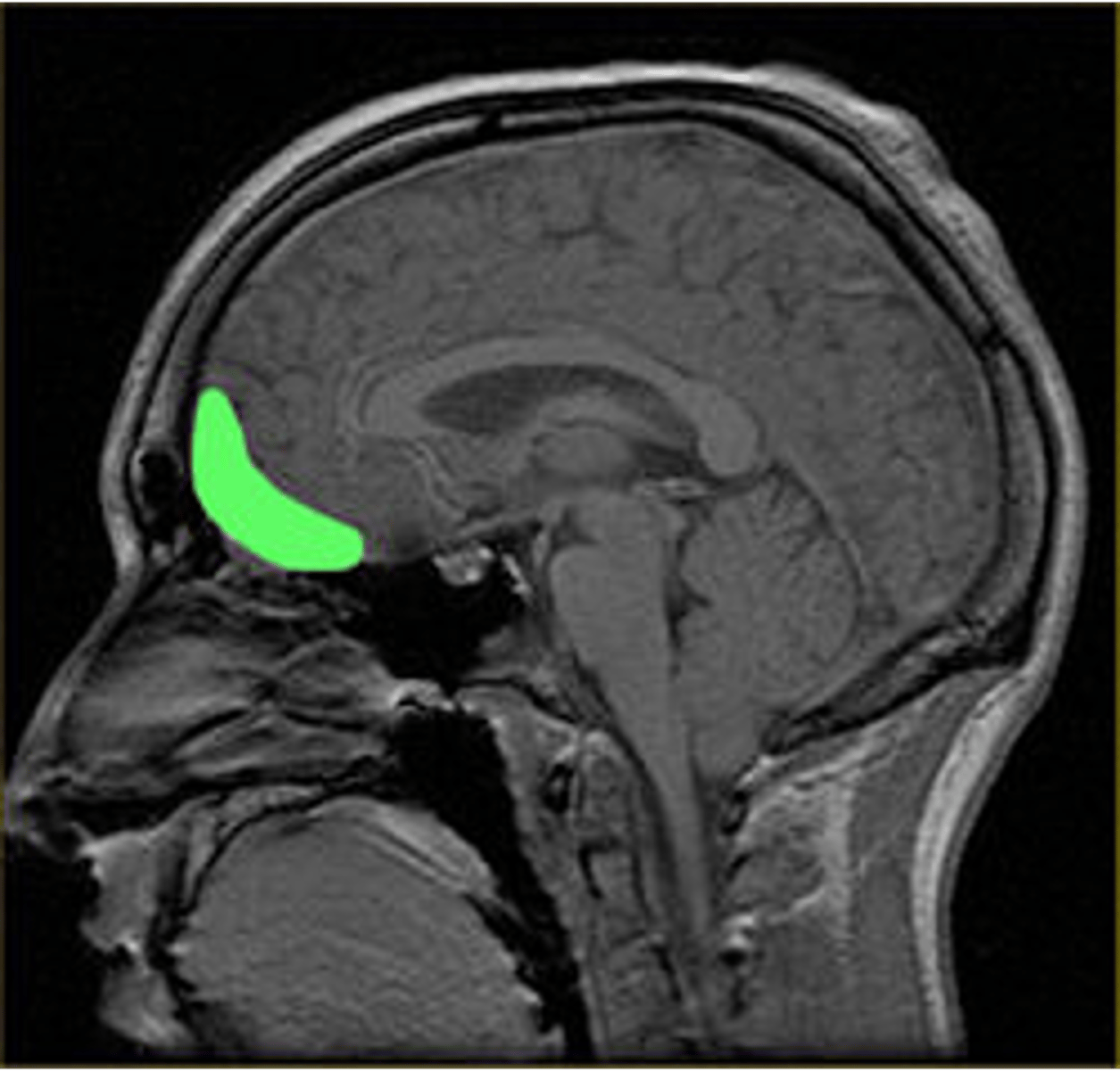
Orbitofrontal cortex aka ventromedial prefrontal cortex
What does the highlighted part of this image (in green) represent?
Stress response
Control patients learn to avoid Deck B and show a _______ ___________ (increased skin conductance) when hovering over Deck B
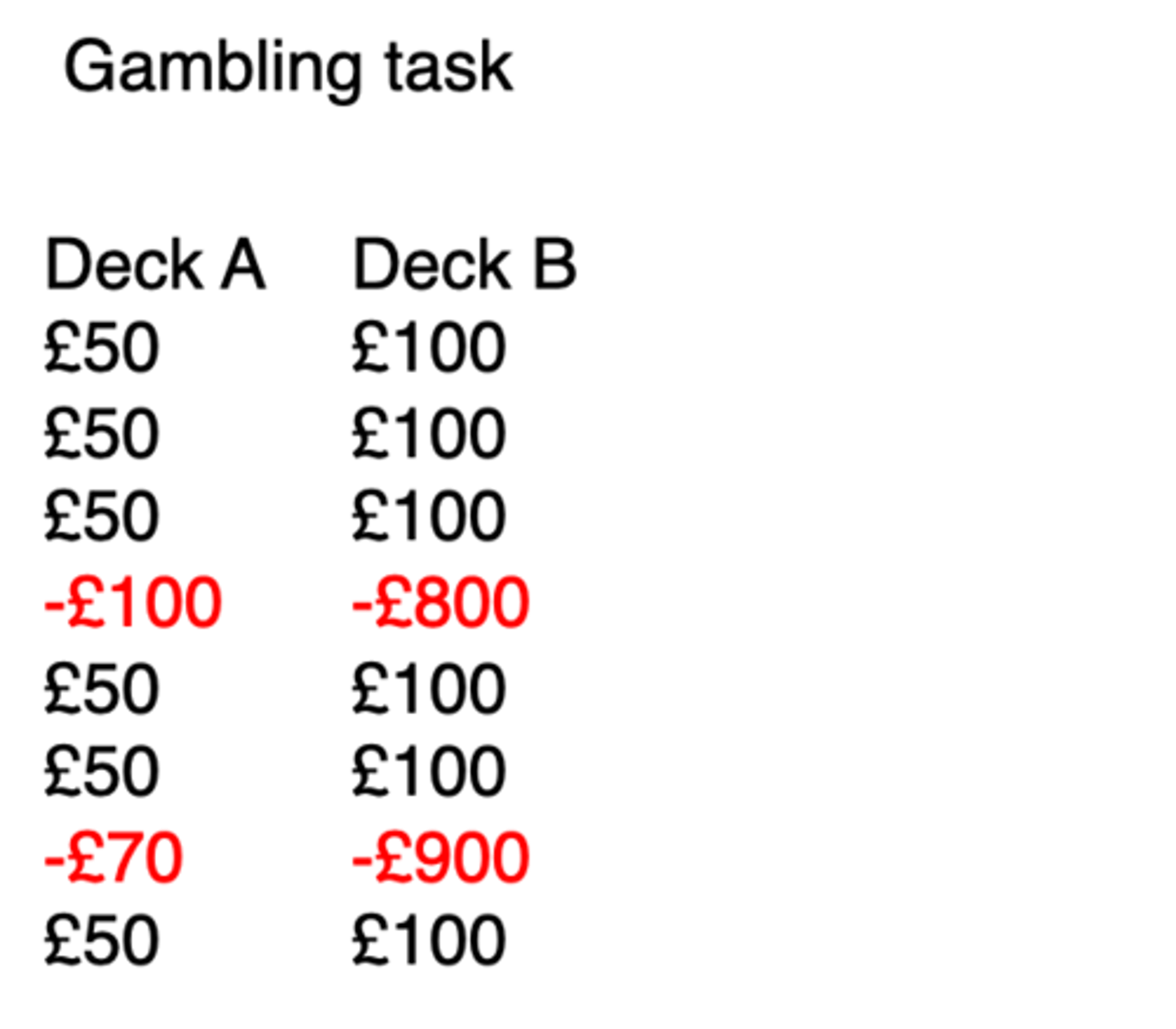
Anticipatory stress
Patients with orbitofrontal lesions don't avoid Deck B and don't show ______________ _________ for Deck B (but they do when they get a penalty)
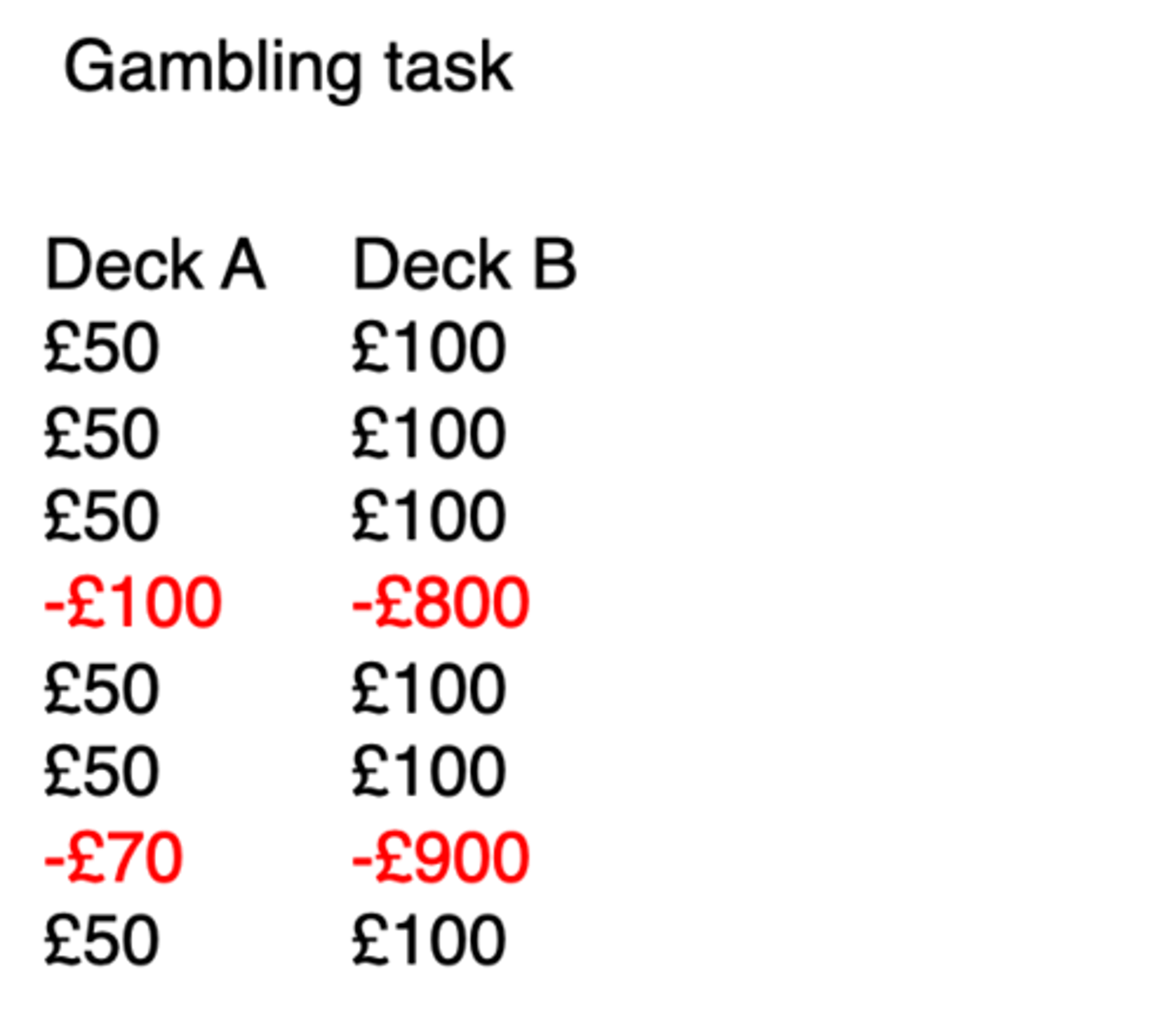
Common sense ('folk' theory)
Who's theory of how emotions are made is this?
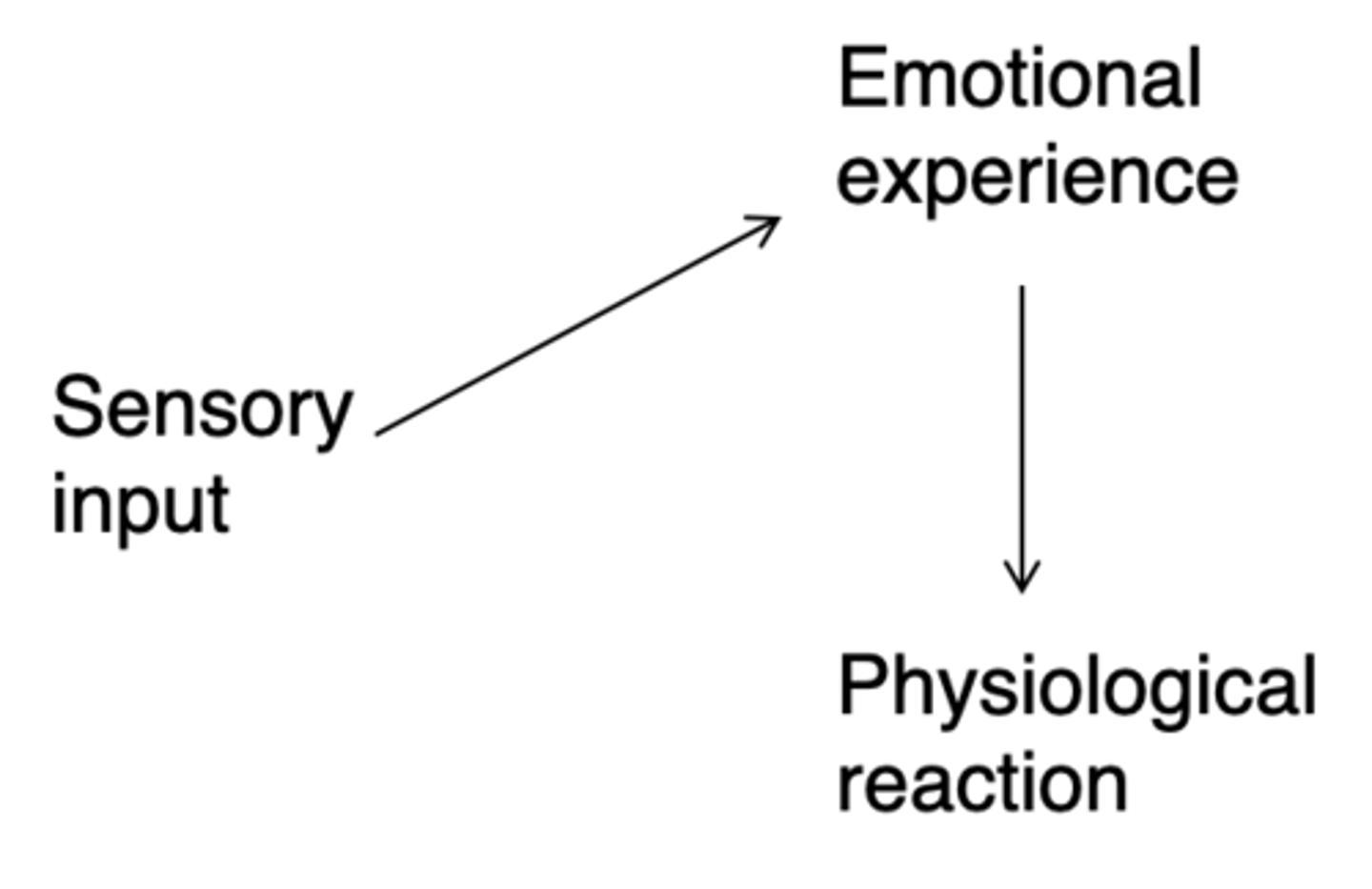
James-Lange theory (1880s)
Who's theory of how emotions are made is this?
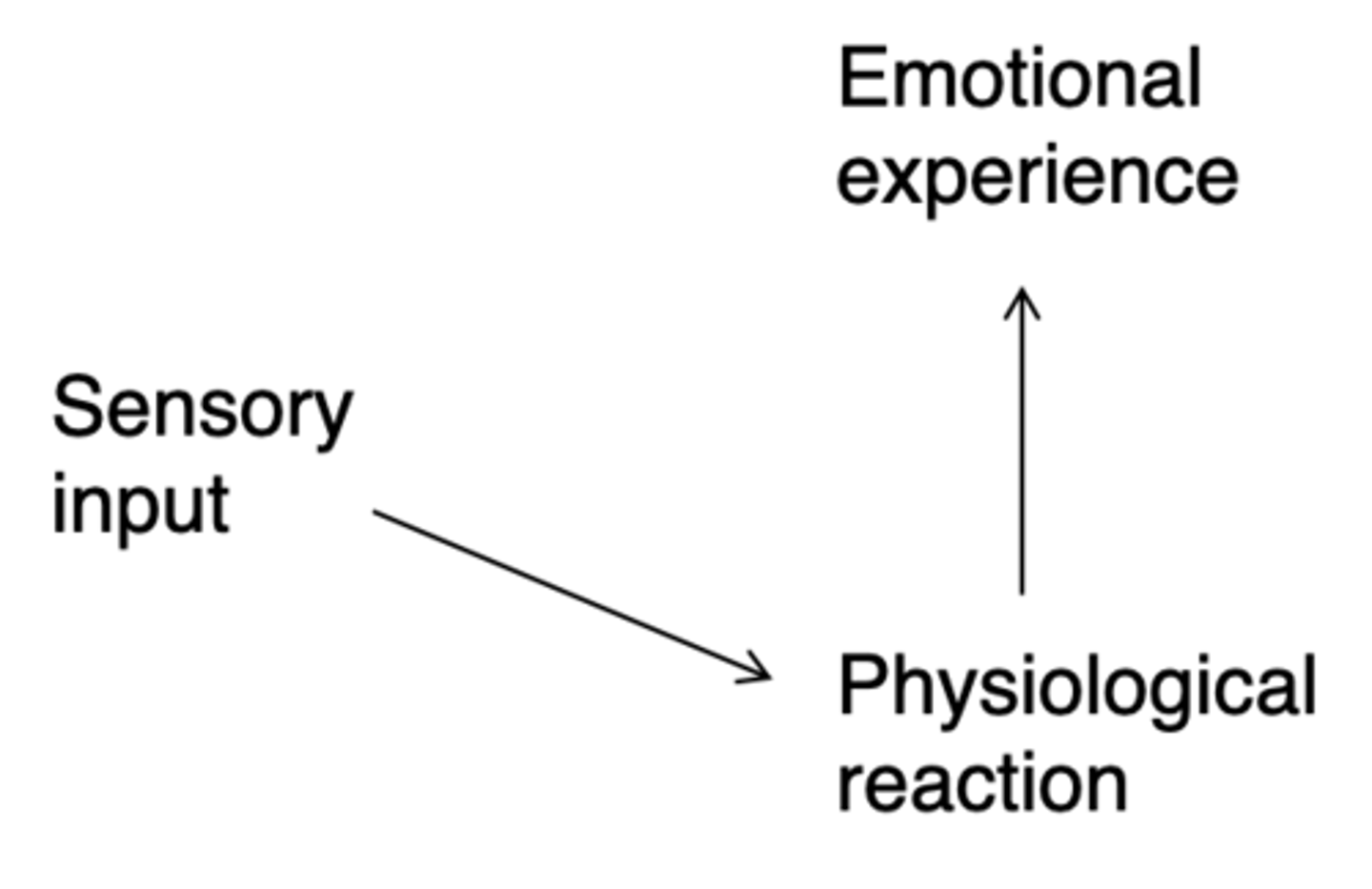
Cannon-Bard theory (1920s)
Who's theory of how emotions are made is this?
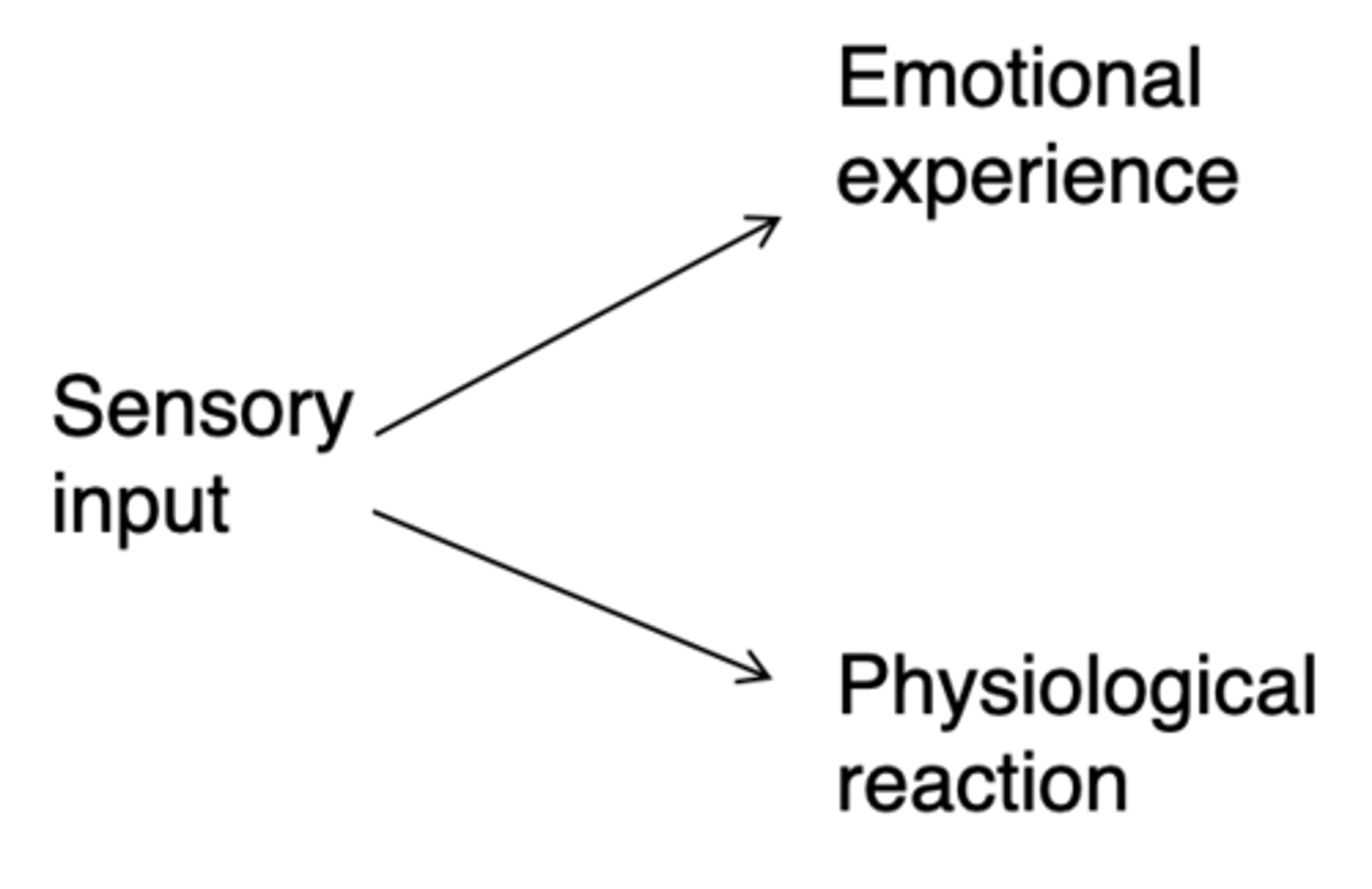
Emotional experience arises thalamus signalling to neocortex while the physiological reaction arises from thalamus signalling to hypothalamus
What did Cannon and Bard propose?
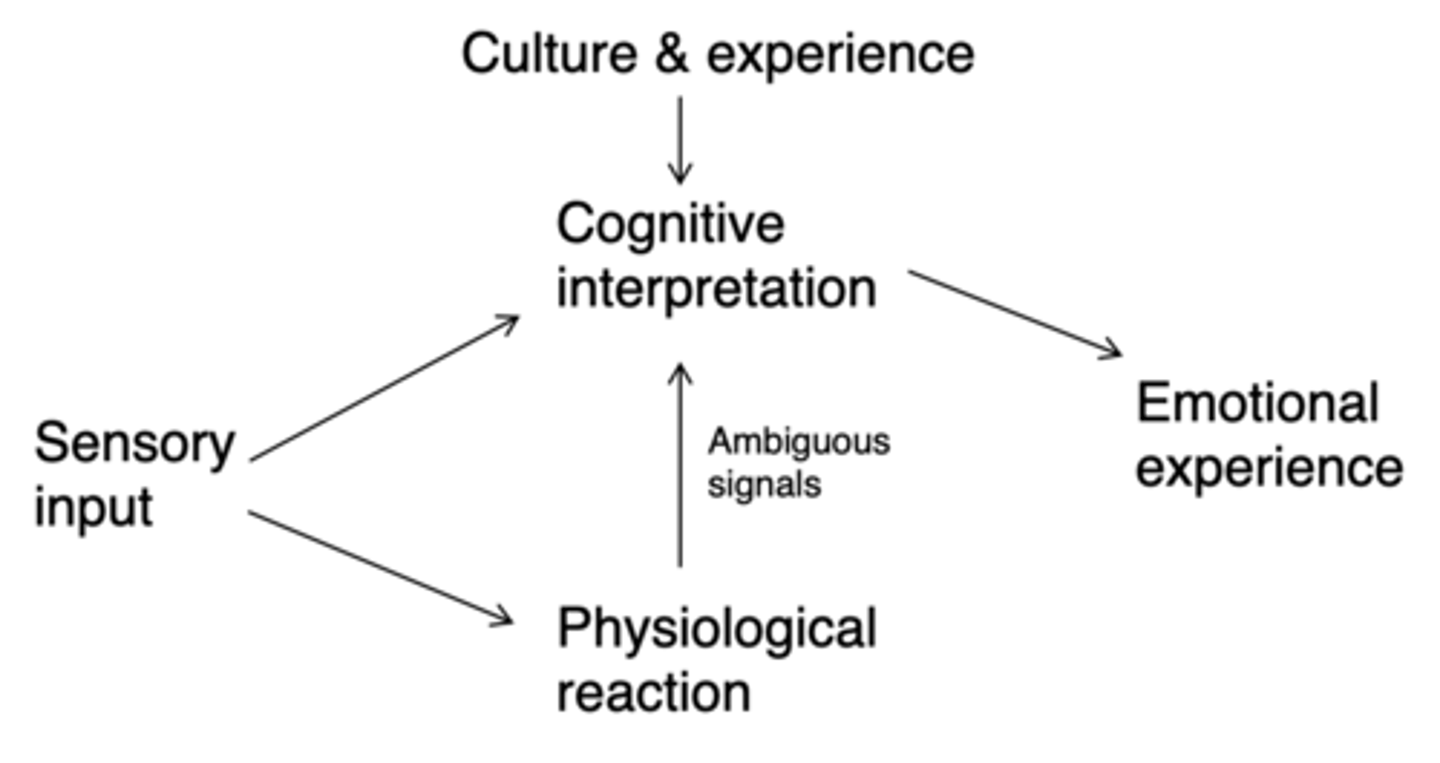
Singer-Schacter theory
Who's theory of how emotions are made is this?
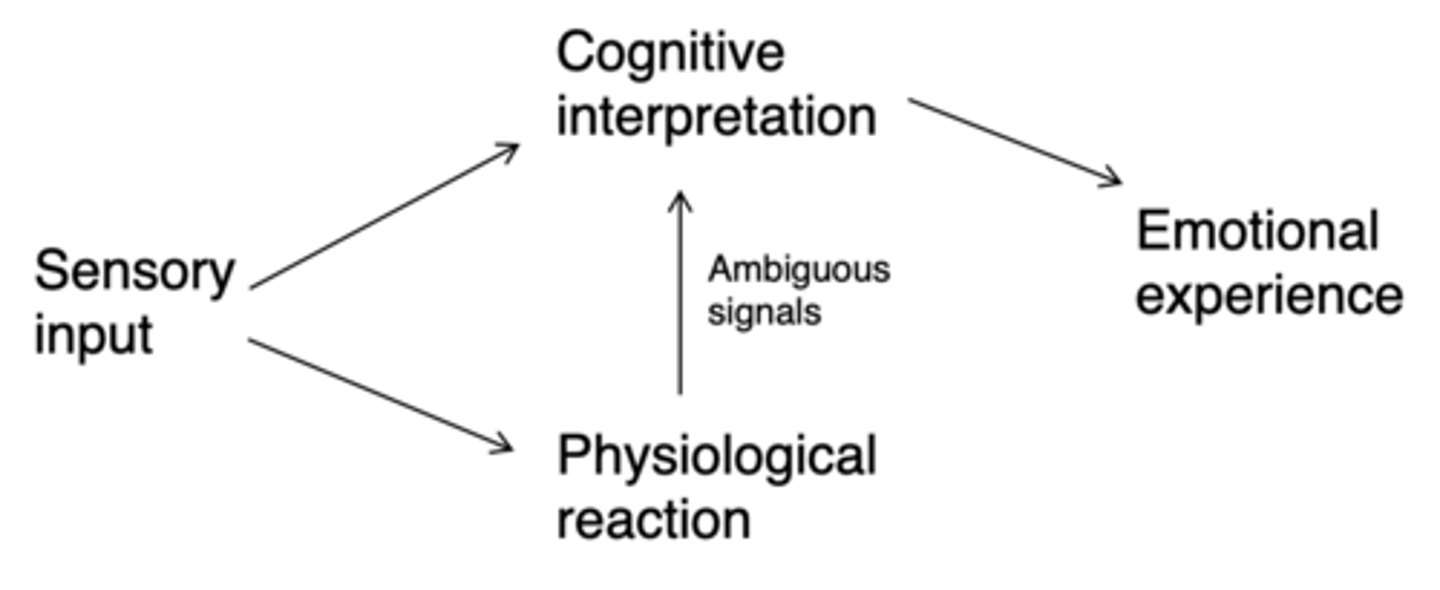
Constructivist theory
Who's theory of how emotions are made is this?
Dopaminergic neurons, mesolimbic pathway
Reward/addiction is mediated by ______________ _________ through the ___________ ___________