Honors Chemistry Final - 2025
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
KMT (Kinetic Molecular Theory)
1. All matter is made of particles
2. The particles are in constant motion
3. As energy is added, the particles speed up
4. As the particles speed up, they spread apart
5. Different particles have different amounts of
intermolecular force
KMT in relation to solids
- Particles are fixed
- ordered
- least KE
- definite shape/volume
KMT in relation to liquids
- Particles are closely packed, but more space than in solids
- More KE than solids, enough so that particles can slide past each other
- weaker IMF
- definite volume/indefinite shape
Vapor Pressure and boiling point
the vapor pressure is the pressure exerted by a vapor over a liquid. Boiling point is when a liquid's vapor pressure is equal to the atmospheric pressure.
Types of IMF (Intermolecular Forces)
LDF
- weakest force
Dipole Dipole
- Polar bond
H-Bond
- hydrogen + highly electronegative
different types of solids and their relation to IMFs.
Ionic solids - high IMF
Molecular solids - weak IMF (LDF, H, D-D)
Covalent Network Solids - covalent bonds with crystal lattice
Metallic Solids - metalic bonds
volatility
a measure of how readily a substance vaporizes
Equilibrium
rate of evaporation = rate of condensation
Condensation
Gas to liquid
amorphous solid
A solid made up of particles that are not arranged in a regular pattern
five assumptions of KMT that relate to gases
1- Gas particles are in constant, random motion
2- gas particle volume is unimportant
3- Gas particles don't interact with each other
4- Gas particle collisions are completely elastic
5- Average KE of gas is proportional to temp.
difference between an ideal gas and a real gas
Ideal Gas - assumes gases have no IMF and volume
Real Gas - a gas that does have volume and IMF
conditions under which an ideal gas does not behave like a real gas
High pressure and low temperature
Boyle's Law
As Pressure Increases, volume decreases
P1xV1=P2xV2
Charles's Law
As temp. increases, volume increases
V1/T1 = V2/T2
Gay-Lussac's Law
As temp increases, pressure increases
P1/T1 = P2/T2
Combined Gas Law
The relationship between the pressure, volume, and temperature of a fixed amount of gas
P1xV1 = P2 x V2
T1 T2
Dalton's Law of Partial Pressure
states that the total pressure of a mixture of gases is equal to the sum of the pressures of all the gases in the mixture
Ptot= P1 + P2 + P3 + ...
STP (standard temperature and pressure)
T = 273 K
P = 1 atm
n = 1 mol of any gas
V = 22.4 L
Ideal Gas Law
PV=nRT
Properties of solutions
Solute - what gets dissolved
Solvent - what does the dissolving
Electrolyte Solution
a solution containing a solute that dissociates into ions. Conducts current when dissolving in water
dissolution
the breaking up or dissolving of something into parts; disintegration
Molarity (M)
moles of solute/liters of solution
Molality (m)
moles of solute/kg of solvent
Freezing point formula
ΔTf = (Kf)(m)(i)
Tf = change in freezing point
Kf = freezing constant
m = molality
i= vant hoff Factor
Boiling point formula
ΔTb = (Kb)(m)(i)
Tb = change in boiling point
Kb = boiling constant
m = molality
i= vant hoff factor
Properties of acids and bases
Acids-
Taste: Sour (vinegar)
Smell: Frequently burns nose
Texture: Sticky
Reactivity: Frequently react with metals to form H2
Bases-
Taste: Bitter (baking soda)
Smell: Usually no smell (except NH3!)
Texture: Slippery
Reactivity: React with many oils and fats
Arhenius Base and acid
Base - Ionizes to produce OH- Ions
Acid - produces H+
Bronsted-Lowry acid and base
Acid - a molecule or ion that is a proton donor
Base - proton acceptor
Lewis acid/base
acid: electron pair acceptor
base: electron pair donor
Strong Acids and Bases
A = H2SO4, HNO3 , HClO3, HClO4, HCl, HBr, HI
B= Group 1 with OH, Ba(OH)2
Weak Acids and Bases
A= HC2H3O2, H2CO3 (any other acids)
B= NH3 (any other bases)
monoprotic acid
an acid that can donate only one proton to a base
diprotic acid
an acid that can donate two protons per molecule in a base
polyprotic acid
an acid that can donate more than one proton per molecule
Hydronium
H3O+
hydroxide ion
OH-
self-ionization of water
H2O → H + OH-
or
H2O + H2O → H3O + OH-
pOH
the negative logarithm of the hydroxide ion concentration
pH
hydrogen ion concentration
Neutral/acidity
pH of 7 is neutral
[H+] = [OH-] = 1 x10-7 M = neutral
Ion product constant for water
[H+] x [OH-] = 1 x10-14 = Kw
If [H+] > [OH-] = acidic
If [H+] < [OH-] = basic
pH formula
pH=-log[H+]
pOH formula
pOH=-log[OH-]
Ka
acid ionization constant to tell how weak an acid is
Ka formula
Ka = [H+] x [A-] / [HA]
salt hydrolysis
a process in which the cations or anions of a dissociated salt accept hydrogen ions from water or donate hydrogen ions to water
How to tell in salt hydrolysis if a salt will produce a neutral, acidic, or basic solution.
salt of SA + SB= neutral Ex. NaCl
2. salt of SA + WB= acidic Ex. MgCl2
3. salt of WA = SB= basic Ex. NaF
4. salt of WA + WB= depends on Ka and Kb
If Ka > Kb then acidic
If Ka < Kb then basic
Specific Heat Formula
q=mc∆T
Enthalpy
energy transferred during a reaction as heat; symbol is ∆H
Enthalpy formula
∆H= Hprod – Hreac
How to tell if enthalpy is exo or endo
(exothermic= - ∆H)
(endothermic= + ∆H)
heat of reaction vs heat of formation
HOR = overall change in energy
HOF = change in enthalpy when one mole of a compound is formed
Hess's Law
the overall enthalpy change in a reaction is equal to the sum of enthalpy changes for the individual steps in the process
Entropy
A measure of disorder or randomness.
Free energy formula and sponteneity
ΔG = ΔH - TΔS
G= - then it is spon
G= + it is non-spon
collision theory
states that atoms, ions, and molecules must collide in order to react
Factors that influence reaction time
1: reactivity of reactants
2: surface area (more=faster)
3: Temp. (faster at higher temps.)
4: Concentration (Higher = faster)
5: Catalyst
Energy diagram
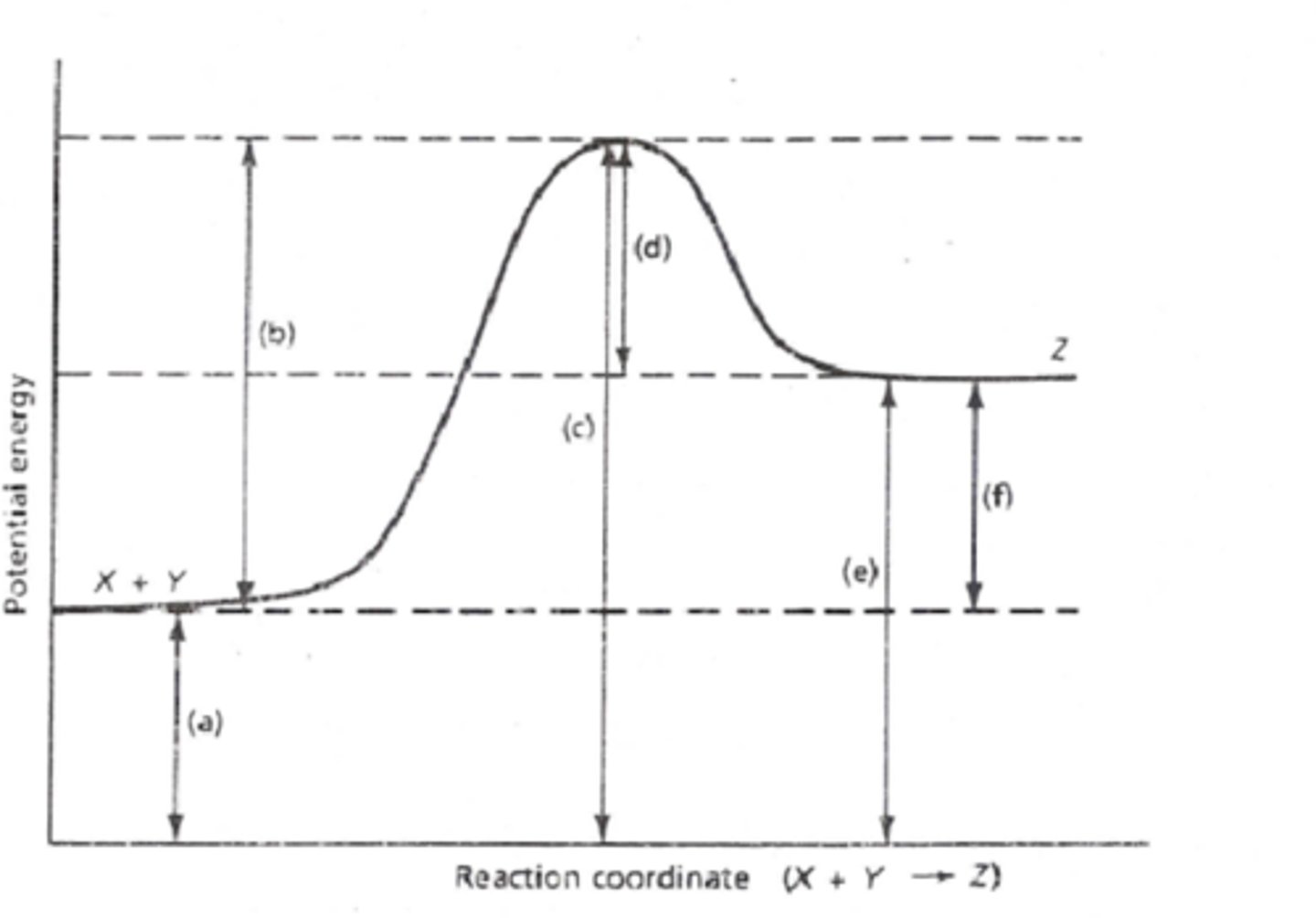
Activation Complex
transitional structure that results from a successful collision
Rate Law
R= k[react]n [react]m
k= rate constant, n and m= coefficients
Rate order
0 order = no effect on rate
1st order = 1 to 1 effect on the rate
2nd order = 1 to square ratio
Equilibrium reaction
K= [prod]^w[prod]^z / [react]^x [react]^y
K >1 (large) means prods favored
K <1 (small) means reacts favored
Le Chatelier's Principle
1. pressure= higher pressure will go to the side with fewer molecules and lower pressure will go to the side with more molecules
2. [concentration] = will favor the side with higher concentration
3. temp= higher temp favors endothermic, the lower temp favors exothermic
How to find q in equilibrium reaction
Q= [prod]^w[prod]^z / [react]^x [react]^y
How does q tell us which way we shift in equilibrium
K is given
If Q > K shifts left
If Q< K shifts right
Oxidation and reduction
oxidation: loss of electrons (LEO)
reduction: gain of electrons (GER)
galvanic cell
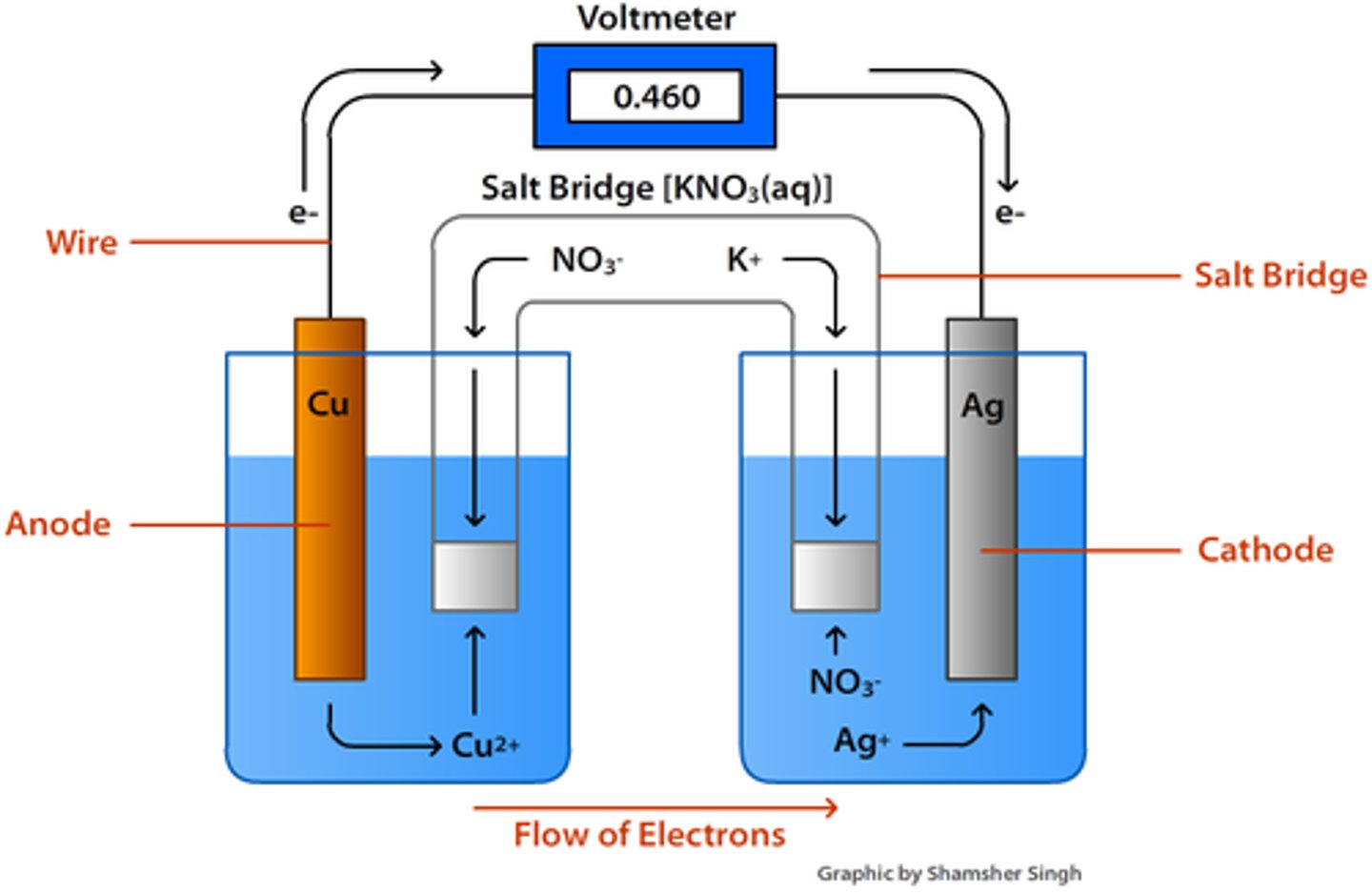
Anode
the electrode at which oxidation occurs
Cathode
the electrode at which reduction occurs