Lecture 5- social influence, conformity, persuasion
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
94 Terms
What is social influence?
How others affect our beliefs, attitudes, values, or behaviour
What is social learning?
Capacity to learn from observing others
How do mirror neurons facilitate social learning?
Activated both when one does an action oneself
And when one simply observes another person perform that action
Describe Social learning theory (Bandura)
Observational learning
We are encouraged or discouraged to engage in new behaviours after viewing someone else engaging in these behaviours
According to social learning theory, what does the likelihood of replicating behaviours depend on?
Consequences
What study by Bandura supports social learning theory?
The bobo doll experiment
What is the chameleon effect?
Tendency to mimic nonverbal mannerisms of someone else
How does our attitude change when we like a person (chameleon effect)?
We shift attitudes towards what we think another person’s opinion might be
What is a strength of social learning?
It is adaptive- beneficial for survival
What is a limitation of social learning?
Can increase the likelihood of maladaptive/negative behaviours
e.g celebrity suicides → increases suicide among the general public
What is an injunctive norm?
What behaviours are generally appropriate in one’s culture
What is a descriptive norm?
A belief about what most people typically do
What is social cognition?
The phenomenon whereby ideas, feelings, and behaviours seems to spread across people like wildfire
What are some examples of socially contagious behaviours?
Yawns
Laughter
Applause
Moods
A confederate rubs their face.
Are participants more likely to rub their face or shake their foot as a result?
Rub their face
A confederate shakes their foot.
Are participants more likely to rub their face or shake their foot as a result?
Shake their foot
What is conformity as defined by Sherif?
Individual alters their beliefs, attitudes, or behaviour to bring them in accordance with those of a majority
Describe Asch’s (1951) conformity experiment
Participants were placed in a group of confederates
Confederates gave incorrect answers to a simple visual judgement task (judging length of lines)
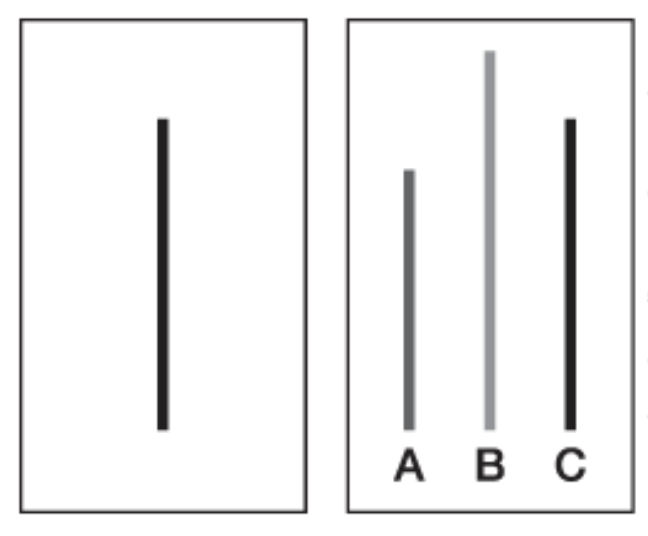
What does Asch’s (1951) conformity study find?
32% of participants conformed to the group’s incorrect answers
Even though the correct answer was obvious
Define public compliance
Conforming to fit in with a group, without changing beliefs
Define private acceptance
Conforming by altering private beliefs and public behaviour
Define informational influence
Others used as a source of information about the world
Why do people conform?
Normative influence
Define normative influence
Occurs when we use others to know how to fit in
What % of participants in Asch (1951) never conformed in at least one trial?
25%
Why may participants NOT have conformed to the group opinion in Asch (1951)?
Gender differences
Size of group exerting
Group member unanimity
Familiarity with task
How did the % of participants conforming change as the number of confederates giving wrong answer increased?
% of participants conforming increased
Describe the personality of those less likely to conform?
High need to achieve
Propensity to be leaders
Greater self-awareness
High self-esteem
Define obedience
Actions to fulfill the direct order or command of another person
The pressure to obey is direct and explicit
When is obedience sometimes essential?
Preserve societal health and functioning
e.g social distancing during COVID-19
What factors increased obedience in Milgram (1961)?
Separation from the ‘learner’ (confederate)
Legitimacy of authority of experimenter (wearing a lab coat)
What factors decreased obedience in Milgram (1961)?
Removing the experimenter from the room
What other factors influenced obedience in Milgram (1961)?
Closeness to authority figure
Closeness of the ‘learner’
Witnessing defiance
What % of participants obeyed when the participant only delivered the memory test (someone else administered the shocks) in Milgram (1961)?
92.5%
What % of participants obeyed in the original Milgram (1961)?
65%
What % of participants obeyed when Milgram’s (1961) study occurred in an unimpressive downtown office building?
48%
What % of participants obeyed when the learner was in the same room in Milgram (1961)?
40%
What % of participants obeyed when they had to physically place the learner’s hand on the shock plate in Milgram (1961)?
30%
What % of participants obeyed when the experimenter phones in the instructions in Milgram (1961)?
21%
What % of participants obeyed when the experimenter was replaced by another participant in ordinary clothes in Milgram (1961)?
20%
What % of participants obeyed in the presence of two defiant participants in Milgram (1961)?
10%
Are there gender differences in obedience?
No
Women show the same obedience as men
Are there culture differences in obedience?
No
People from different cultures show similar obedience
What individual differences influence obedience?
Submissive personality
Education
Does Milgram (1961) have temporal validity?
Some variations/replications suggest similar obedience today as in Milgram’s time
Yes?
Why do we obey?
Innate predisposition to obey authority
Socialised to obey authority
Gradual increases in obedience
Difficulty in defying a legitimate authority
Define persuasion
Intentional efforts to change other people’s attitudes to change their behaviour
What are attitudes?
Evaluation of a stimulus
Can range from positive to negative
What is the main target of persuasion techniques?
Attitudes
What is elaboration likelihood model?
Persuasive messages influence attitudes by 2 different routes
Central routes
Peripheral routes
What are the 2 routes according to the elaboration likelihood model?
Central routes
Peripheral routes
Describe the processing of central routes of persuasion
Effortful
Comparing arguments with prior knowledge
Generating thought
Direct, logic, and evidence based
What does the central route use to persuade?
Strong arguments
Describe the processing of peripheral routes of persuasion
Automatic and effortless
Indirect, emotional based
Use of irrelevant, peripheral cues and heuristics
What does the peripheral route use to persuade?
Peripheral cues
What persuasion route is used if the audience is motivated and able to elaborate on the message?
Central route
What persuasion route is used if the audience is NOT motivated and able to elaborate on the message?
Peripheral route
What is the role of motivation in the elaboration likelihood model?
Relevancy to goals and interests contributes to the level of effort we devote to thinking deeply (elaborating) about a message
What determines which persuasion route is taken?
Relevance to goals
What persuasion route do we use when we have strong motivation?
Central route
Rely on argument strength
When are peripheral routes effective?
Preventing maladaptive health behaviours from forming
e.g tobacco packaging
When are peripheral routes NOT effective? Why?
Not effective to change persistent behaviours
e.g as the evocative tobacco packaging did not stop everyone smoking
If we are motivated to continue smoking, we will discount peripheral routes of persuasion
Were participants who were mildly distracted more or less likely to disagree with the argument for a tuition cut?
Less likely
How does distraction influence elaboration?
Lots of distraction leaves us unable to elaborate
Describe attitudes formed through the central route
Stronger
More durable, longlasting
Resistant to contrary information
More likely to affect behaviour
Why are attitudes formed through the central route stronger?
They require deep thinking
What factors influence the source credibility of the persuasive messge?
Appearance
Perceived expertise
How does the appearance of trustworthiness influence source credibility?
Overheard conversation boost confidence in source
Argument of position opposes your self-interests
Display of authenticity and uniqueness
Describe DeBono and Harnish (1988)
Students were asked to react to issues on campus
Including the pom-pom squad’s calendar which included the cheerleaders dressed in bathing suits posing with university president
Listened to recorded opinions of campus community members
Either expert source or control source
Expert source
Psychologist ‘Dr Leonard Charles’
Nationally known
Well-published
Specialised in effects of print media on attitudes and beliefs
Control source
Leonard Charles
Active in student government
Conveys consensus of students
What was the strong argument in DeBono and Harnish (1988)?
Calendar promotes sexist attitudes
Reinforced gender stereotypes
Tarnished university image with presence of male staff
What was the weak argument in DeBono and Harnish (1988)?
Calendar gives free advertising to swimsuit manufacturers
People may focus on cheerleaders rather than athletes
Does the strong argument have high or low elaboration DeBono and Harnish (1988)?
Low elaboration
Does the weak argument have high or low elaboration DeBono and Harnish (1988)?
High elaboration
Does the expert source have high or low elaboration DeBono and Harnish (1988)?
Low elaboration
Does the control source have high or low elaboration DeBono and Harnish (1988)?
High elaboration
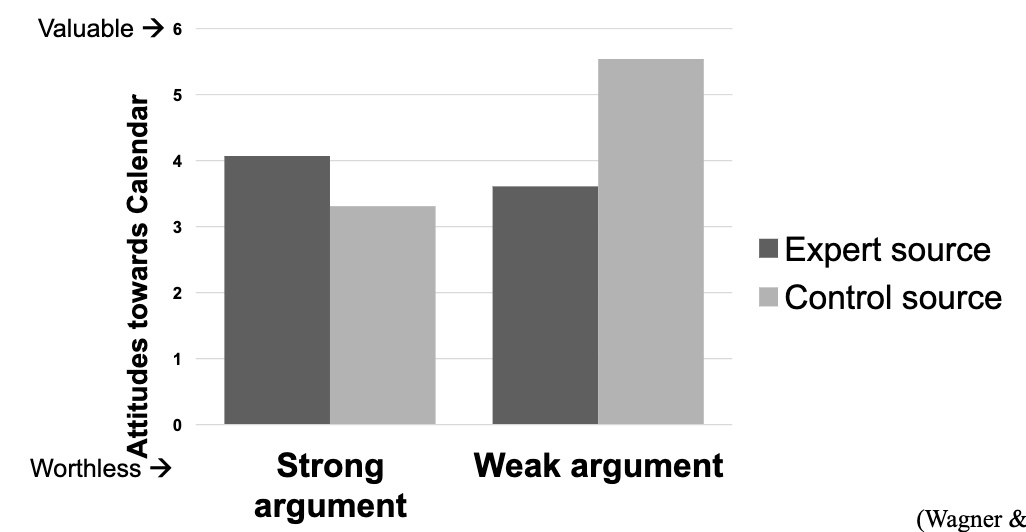
What did DeBono and Harnish (1988) find?
Expert source resulted in more positive attitudes towards the calendar for the strong argument
Control source resulted in more positive attitudes towards the calendar for the weak argument
Strong argument → expert source > control source
Weak argument → expert source < control source
What is the sleeper effect?
We remember a message but forget where it came from
How does source credibility affect attitudes over time (sleeper effect)?
Source credibility has a diminishing effect on attitudes over time
What is the primacy effect?
Initially encountered information primarily influences attitudes
What is the recency effect?
Recently encountered information primarily influences attitude
What does the likelihood of the primacy vs recency effect depend on?
Timing
Message 1 → message 2 → time delay =
Primacy effect
Message 1 → time delay → message 2 =
Recency effect
What are 2 peripheral routes of persuasion?
Classical conditioning
Mere exposure effect
How does classical conditioning act as a peripheral route of persusion?
We often associate pre-existing emotions with targeted stimuli
Transference of positive emotions with stimuli
What is the mere exposure effect?
Repetition and familiarity
e.g product placement
How does self-perception theory explain compliance?
Once we freely engage in a behaviour, we often adopt attitudes that are consistent with that behaviour
What is the foot-in-the-door effect?
People are more likely to comply with a moderate request after having initially complied with a smaller request
Describe the ‘norm for social commitment’
Once people make a public agreement, they tend to stick to it, even if circumstances change
What is an example of a norm for social commitment?
Lowballing
What is lowballing?
After agreeing to an offer, people find it hard to break that commitment, even if extra cost is later added to the deal
Describe the ‘norm of reciprocity’
Often used to induce compliance
Often plays a role in negotiations
What is the door-in-the-face-effect?
We are more likely to comply with a moderate request after first presented with and refused to agree to larger request
Who is Robert Cialdini?
Social psychologist made popular in 1980s
Wrote a book The Psychology of Persuasion
Worked on campaigns for Obama etc