Psychology 101: Intro to Psychology Ch 8. Developmental Psychology Theories & Stages
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
developmental psychology
how we change over our lifespans
physical, intellectual, and emotional growth
Developmental psychology involves studying how we change
from birth until the cusp of adulthood
as we pass through adolescence
throughout our lives
throughout childhood
throughout our lives
How are the studies of Piaget, Kohlberg, and Erikson similar?
They all sought to understand continuities in development.
They all sought to understand moral development.
They all sought to understand emotional development.
They all sought to understand cognitive development.
They all sought to understand continuities in development.
Psychological development is influenced by
intellectual and emotional growth
physical and intellectual growth
physical, intellectual, and emotional growth
physical and emotional growth
physical, intellectual, and emotional growth
With regards to the nature vs. nurture debate, a child's development may be affected by nurturing if
he wears glasses like his mother
he is tall like his father
he is neglected by his parents
he is born with a birth defect
he is neglected by his parents
Which of the following is an example of a continuity?
Our ability to walk
Our ability to empathize
Our ability to daydream
Our ability to think abstractly
Our ability to daydream
prenatal
babies’ development inside their mothers
zygote
an egg cell that has been fertilized by sperm
differentiation
process where cells start to turn into all the different kinds of cells in our bodies — blood cells, skin cells, etc.
teratogen
substance that interferes with normal prenatal development
fetal alcohol syndrome
a set of abnormalities that include physical differences as well as mental retardation
mother’s voice
babies start to become familiar with this while still in the womb
once they’re born, they prefer it above other voices, which helps with mother-infant bonding
Rachel is pregnant with her first child and wants to be sure she is doing everything she can to help her baby grow and develop. Which of the following would most likely be recommended to Rachel to promote the psychological development of her baby?
Listen to classical music to increase the baby's intelligence.
Eat a protein-rich diet to promote fetal muscle development.
Exercise for the duration of pregnancy to maintain optimal weight.
Speak to the baby to promote mother-infant bonding.
Speak to the baby to promote mother-infant bonding.
Differentiation describes the process of _____.
an embryo attaching itself to the uterus
cells forming into various types of cells
the genes of the parents asserting themselves
an embryo turning into a fetus
cells forming into various types of cells
A zygote is an _____.
egg cell waiting to be fertilized
egg cell that has yet to begin dividing itself
embryo multiplying itself
egg cell that has been fertilized by sperm
egg cell that has been fertilized by sperm
Exposure to a specific teratogen during key developmental periods has been shown to cause which of the following?
Fetal alcohol syndrome
Difficult pregnancy and delivery
Increased intelligence of the child
Higher birth weight
Fetal alcohol syndrome
Why is the nine week mark important during fetal development?
At nine weeks the fetus begins the process of differentiation.
At nine weeks all of the major systems of the body have been established.
At nine weeks the risk of miscarriage increases.
At nine weeks the fetus can recognize the voice of the mother.
At nine weeks all of the major systems of the body have been established.
Harry and Margaret Harlow
decided to determine scientifically whether love is something we really need or just a feeling that we have toward things that satisfy our more basic, concrete, physical needs
wire mother
gave food
cloth mother
gave warmth and comfort
Through his research, Harlow concluded that the monkeys developed a preference for a certain surrogate mother based on _____.
nourishment
contact comfort
copying peers
survival
contact comfort
A monkey was raised in total isolation without contact with other monkeys. What is the most likely result of this experience?
The monkey will only display developmental impairment if frightened.
The monkey will be developmentally impaired but will recover later in life.
The monkey will be developmentally impaired throughout life.
The monkey will be no different from a monkey who experienced socialization.
The monkey will be developmentally impaired throughout life.
Harlow determined that maternal contact is not needed for survival, but is _____.
not important for female monkeys
not necessary for typical socialization
important for social development
connected with nourishment
important for social development
In Harlow's experiment, the wire monkey mother offered _____.
nourishment
security
comfort
safety
nourishment
Based on Harlow's research, which situation would result in monkeys developing typical social behavior?
Monkeys reared with wire surrogates.
Monkeys reared with mothers and peers.
Monkeys reared with cloth surrogates.
Monkeys reared with only mothers.
Monkeys reared with mothers and peers.
schemas
established patterns used to organize knowledge
Which of these statements about assimilation and accommodation is true?
All of these statements are true.
Assimilation helps kids gather information quickly.
They both help kids to learn with increasing sophistication.
Piaget believed they both drove intellectual growth.
All of these statements are true.
After a child calls a zebra 'horse,' an example of accommodation is when the child _____.
Learns that while a zebra might be similar to a horse, it's not the same
Starts calling all animals 'zebras'
Continues to call zebras 'horses'
Doesn't know what to call either animal
Learns that while a zebra might be similar to a horse, it's not the same
Adaptation is _____.
The ways in which children learn about and categorize the world
A set of patterns used to understand the world
An infant's desire to understand the world by sucking on objects
How children change what they believe in order to become adults
The ways in which children learn about and categorize the world
Examples of forming schemas include all of the following except _____.
Stereotyping by racial groups
Judging people based on gender
Seeing each stranger as unique
Expecting different football players to act alike
Seeing each stranger as unique
An example of assimilation is a child who has only seen brown horses seeing a white horse for the first time and _____.
Not knowing what to call it
Correctly identifying it as a horse
Calling it a zebra
Pointing out how it differs from other horses
Correctly identifying it as a horse
A game of peek-a-boo entertains infants because:
Babies understand the parent isn't actually disappearing
Babies are in the preoperational stage
Babies haven't developed object permanence
Babies are developing logic
Babies haven't developed object permanence
How have some studies of cognitive development challenged Piaget's four stage model?
Studies have found that there are more stages of cognitive development than Piaget first thought.
Studies have found that cognitive development is not always a linear progression.
Studies have found distinct differences in cognitive development in boys and girls.
Studies have found that Piaget was incorrect in the ages most children reach his defined cognitive stages.
Studies have found that cognitive development is not always a linear progression.
In the concrete operational stage, a child will learn that:
Language is the most appropriate way to communicate
They can use abstract thinking to solve problems
A taller, thinner glass can hold the same liquid as a fatter, shorter one
His or her mom has not disappeared when she plays peekaboo
A taller, thinner glass can hold the same liquid as a fatter, shorter one
A child who is just beginning to understand that others may think differently than them, is in which state of cognitive development?
Preoperational
Sensorimotor
Concrete Operational
Formal Operational
Preoperational
A child would be more successful in an algebra class if she had reached which stage of cognitive development?
Preoperational stage
Sensorimotor stage
Concrete operational stage
Formal operational stage
Formal operational stage
Lawrence Kohlberg
psychologist interested in how children develop their ability to make moral decisions
Carol Gilligan
criticized Kohlberg’s stages for being too focused on boys
A child hiding a cookie so he doesn't have to share it with the other kids is in _____ of moral development.
the second pre-conventional stage (stage two)
the second post-conventional stage (stage six)
the second conventional stage (stage four)
the first post-conventional stage (stage five)
the first conventional stage (stage three)
the second pre-conventional stage (stage two)
A child not stealing a cookie for fear of being punished is in _____ of moral development.
the second pre-conventional stage (stage two)
the first pre-conventional stage (stage one)
the second conventional stage (stage four)
the first conventional stage (stage three)
the first post-conventional stage (stage five)
the first pre-conventional stage (stage one)
A child who refuses to help a classmate cheat because the rules say cheating is wrong is in _____ of moral development.
the second pre-conventional stage (stage two)
the first pre-conventional stage (stage one)
the first post-conventional stage (stage five)
the first conventional stage (stage three)
the second conventional stage (stage four)
the second conventional stage (stage four)
A person who demonstrates against a law that they perceive as unjust, such as civil-rights advocates did in the 1960s, is in _____ of moral development.
the first pre-conventional stage (stage one)
the first conventional stage (stage three)
the second pre-conventional stage (stage two)
the second post-conventional stage (stage six)
the second conventional stage (stage four)
the second post-conventional stage (stage six)
A child who shares her lunch snack with a classmate she wants to make friends with is in _____ of moral development.
the first pre-conventional stage (stage one)
the second conventional stage (stage four)
the first post-conventional stage (stage five)
the first conventional stage (stage three)
the second pre-conventional stage (stage two)
the first conventional stage (stage three)
responsiveness & demandingness
the traits used to determine parenting style
authoritative
a healthy mix of demanding and responsive
children tend to have higher self-esteem, happiness, motivation & discipline
permissive
they are very responsive to their childs wishes and desires but not at all demanding
neglectful
not demanding of their child or responsive to their needs
Researchers have found that the benefits of authoritative parenting include _____.
children who score higher on IQ tests
children who have better decision-making skills
positive and free-thinking children
successful and disciplined children
successful and disciplined children
Jacob is not always in school. When he does come to school, his clothes tend to be dirty or ragged. He also never has lunch money, and when he does bring lunch, he tells his friends that he only brought what he could find. What type of parenting style does Jacob's parents have?
Neglectful
Permissive
Passive
Authoritarian
Neglectful
Which of the following best describes the actions of a parent with an authoritarian lifestyle?
Asking a child which club that he or she wants to join
Telling a child to complete a homework assignment in exchange for a reward
Pushing a child to participate in a sport that he or she does not want to play
Leaving a child home alone
Pushing a child to participate in a sport that he or she does not want to play
Which of the following describes the permissive parenting style?
Demanding but ultimately neglectful
Highly responsive but not demanding
A healthy mix of responsive and demanding
Neither demanding nor responsive
Highly responsive but not demanding
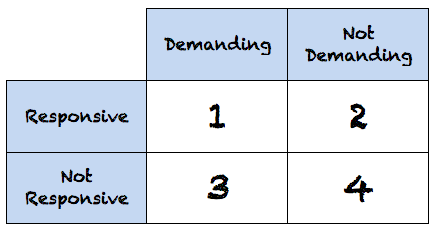
Anna drew the chart below to describe the main characteristics of parenting styles. Which parenting style belongs in box number 4?
Authoritarian
Neglectful
Demanding
Permissive
Neglectful
The struggle between intimacy and isolation is most common during the _____
adolescent stage
middle adulthood stage
young adulthood stage
late adulthood stage
latency stage
young adulthood stage
An elderly adult who feels content about her life is experiencing _____
despair
stagnation
generativity
autonomy
ego integrity
ego integrity
The conflict between trust and mistrust defines the _____
latency stage
locomotor stage
adolescent stage
muscular-anal stage
oral-sensory stage
oral-sensory stage
According to Erik Erikson, psychosocial identities involve the interplay between our _____.
emotional lives and our social circumstances
physiology and our social lives
biological development and our social lives
emotions and our physical development
emotional lives and our social circumstances
An identity crisis is most likely to take place during the _____
locomotor stage
young adulthood stage
middle adulthood stage
adolescent stage
latency stage
adolescent stage