Procedures (Shareable) - Ch. 2 Exam - General Anatomy and Radiographic Positioning Terminology (copy)
1/227
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
228 Terms
Anatomy
study of body structure
Physiology
study of body function
Osteology
detailed study of bone
Center the central ray (CR) for imaging
Why are surface (external) landmarks used for in radiography?
Anatomic position
When positioning, how do we always refer to the pt?
Sagittal
Type of body plane that divides the entire body or part into right and left segments
Mid-Sagittal (MSP)
Type of body plane that divides the body into equal right and left halves; most commonly used plane
Mid-Sagittal Plane (MSP)
What is the most commonly used body plane?
Coronal
Type of body plane that divides the body or part into anterior and posterior segments
Coronal Plane
Which plane is typically used for laterals?
Mid-Axillary or Mid-Coronal (MCP)
Type of body plane that passes through the midline to equally divide the body into equal anterior and posterior halves
Oblique
Type of body plane that passes through the body at any angle other than the previously mentioned planes
Transverse (Horizontal)
Type of body plane that passes crosswise through the body or part dividing the body into superior and inferior portions
Cuts or Slices
What may body “planes” also be called when imaging is performed in MRI, CT, or US?
Axillary
What’s another word referring to the armpit area?
Interiliac
Type of special body plane that skims or lies at the top of the pelvis at the top of the iliac crest (vertebral level L4)
Occlusal
Type of special body plane that is formed by the biting surface of the upper and lower teeth with the jaw closed (used for some head and neck positions)
7
How many cervical vertebrae?
12
How many thoracic vertebrae?
5
How many lumbar vertebrae?
C-7
T-12
L-5
How many of each vertebrae are there?
Aorta, Esophagus, Inferior Vena Cava
What are the 3 natural occurring openings in the diaphragm?
Diaphragm
This structure is a muscle that separates the thoracic and abdominal cavities
Thoracic and Abdominal
What are the 2 great body cavities?
Thoracic cavity
This cavity contains pleural membranes, lungs, trachea, esophagus, pericardium, heart and great vessels
Abdominal cavity
This cavity contains the peritoneum, liver, gallbladder, pancreas, spleen, stomach, intestines (small and large), kidneys, ureters, major blood vessels, and pelvic portion
Peritoneum
This is the lining of the abdominal cavity
Pericardium
What is the lining of the heart called?
Liver
What is the largest solid organ in the body?
RUQ
Which quadrant can the liver be found in?
RUQ
Which quadrant is the gallbladder in?
LUQ
Which quadrant is the spleen located in?
LUQ
Which quadrant is the stomach in?
Pelvic portion
This portion of the body contains rectum, urinary bladder, parts of reproductive system
Abdominal cavity
Which cavity is the pelvic portion (sometimes) considered to be a part of?
Quadrants
4 clinical divisions of the abdomen
Regions
9 clinical divisions of the abdomen; known as Addison’s Planes
Addison’s Planes
What is the name for the regions of the abdomen?
1 transverse, 1 mid-sagittal
What planes form the quadrants of the abdomen?
2 transverse, 2 sagittal
What planes form the regions of the abdomen?
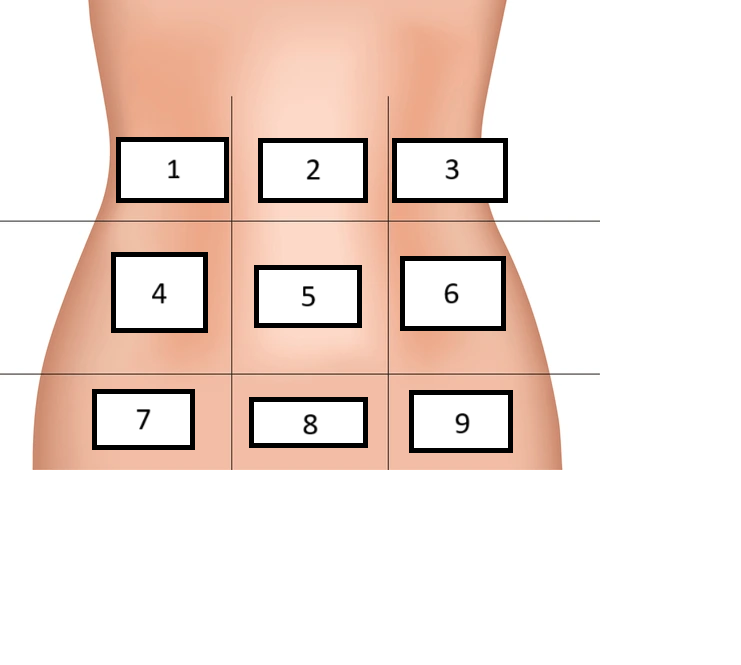
Right Hypochondrium
Label region 1
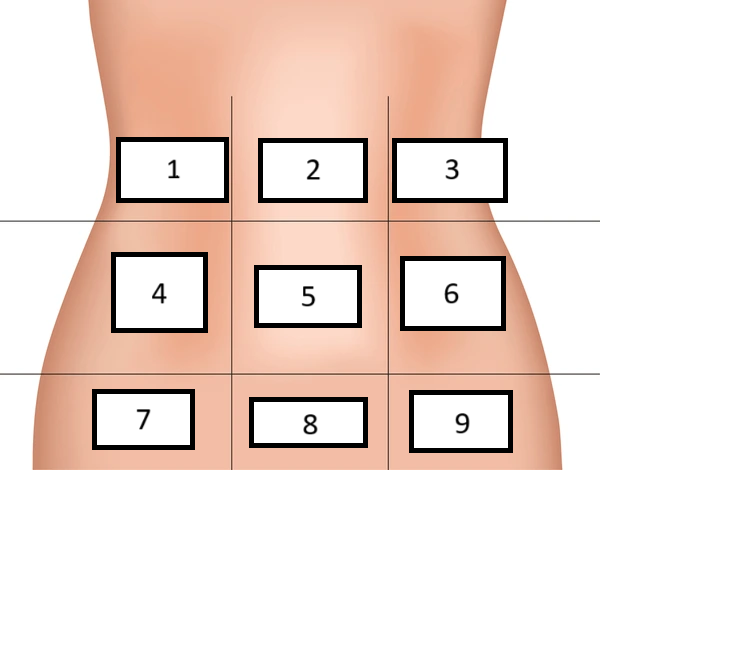
Epigastric
Label region 2
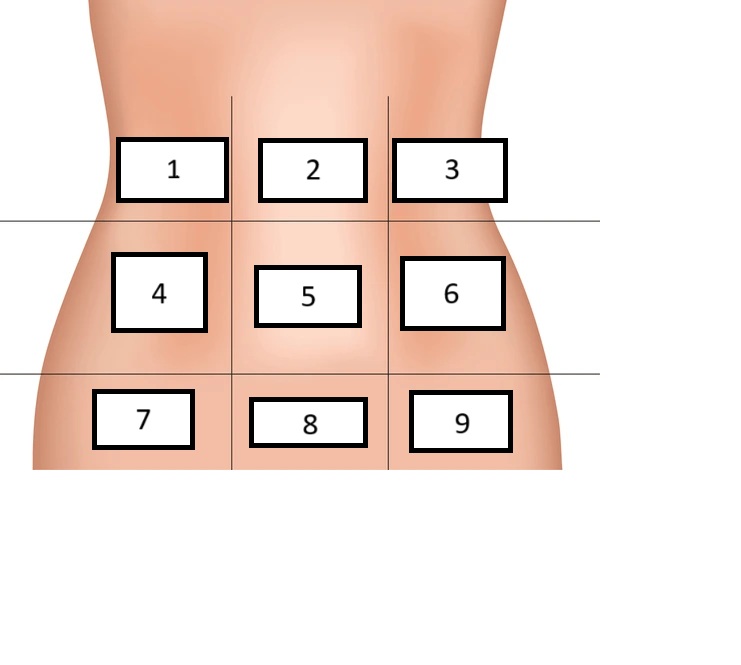
Left hypochondrium
Label region 3
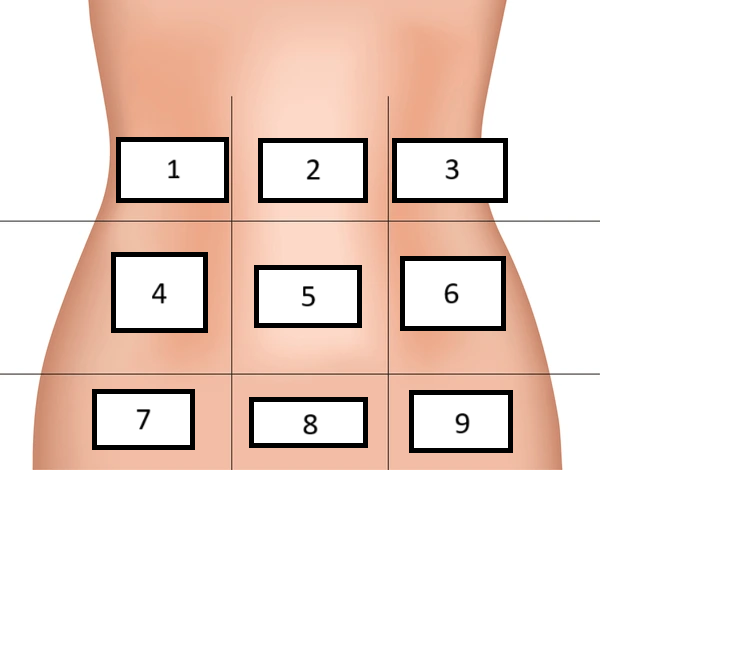
Right lumbar
Label region 4
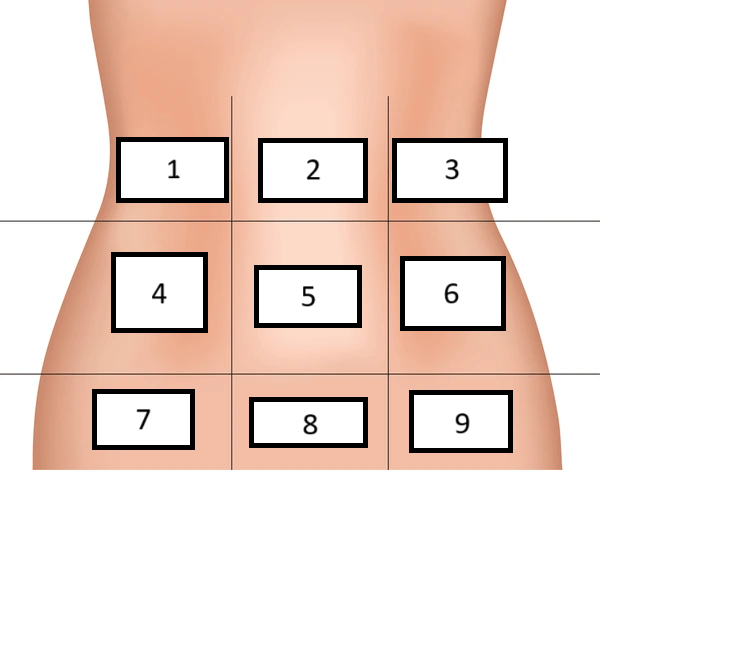
Umbilical
Label region 5
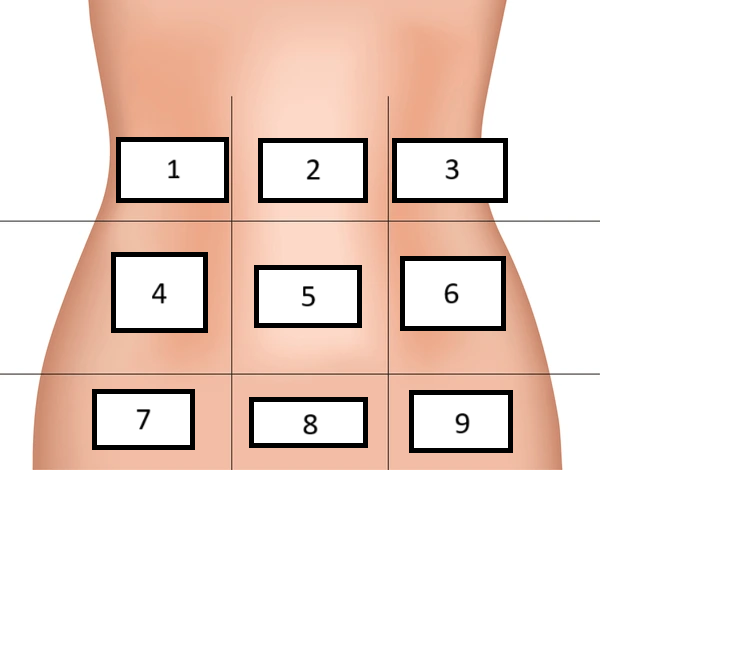
Left Lumbar
Label region 6
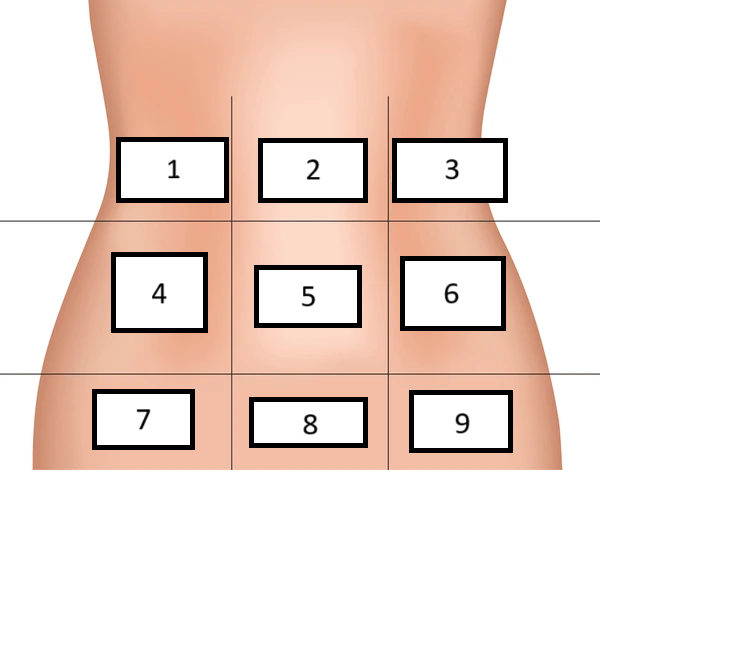
Right inguinal/iliac
Label region 7
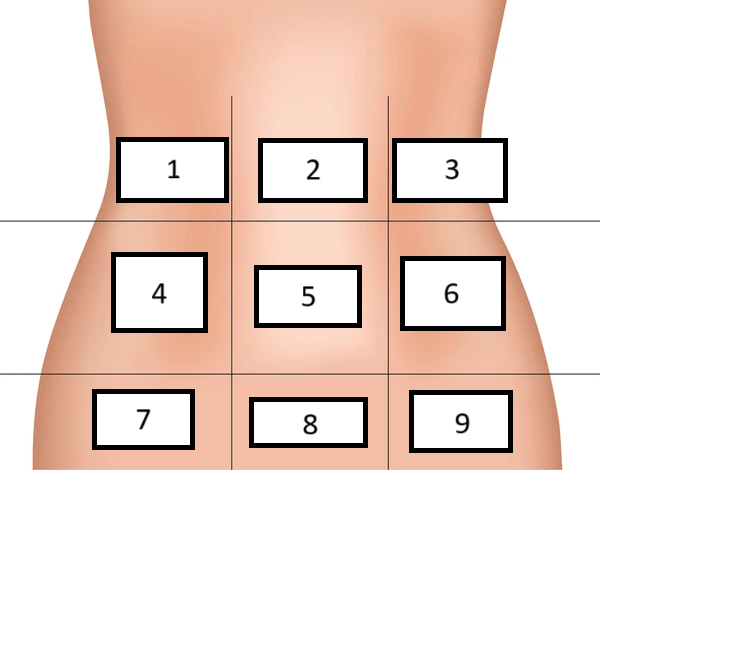
Hypogastric
Label region 8
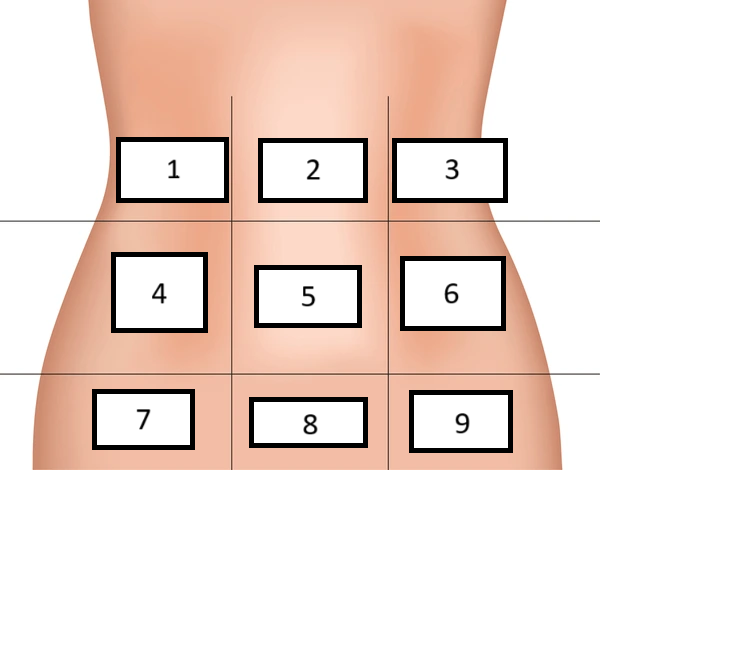
Left inguinal/iliac
Label region 9
protuberances and tuberosities
Most anatomic structures cannot be visualized directly with the naked eye, so _______________ and _______________ are used that are found externally to locate and image internal structures accurately
C3-C4
What anatomical landmark is aligned with the hyoid bone?
C5
What anatomical structure is used to find the thyroid cartilage?
C7-T1
Where can your vertebral prominens be found?
T2-T3
What landmark aligns with the jugular notch (space above sternum)?
Jugular notch
What is the space above your sternum called?
T7
What anatomic landmark is commonly used for chest positioning; aligns with bottom of scapula?
Diaphragm
Patients who are paralyzed can have issues breathing due to their difficulty controlling what muscle?
T9-10
What landmark can be used to find the xiphoid process?
L2-L3
What landmark can be used to find the Inferior Costal (Rib) cage and the stomach?
L4-L5
What landmark can be used to find the Superior most iliac crest?
Body Habitus
Very important concept in radiography as it directly affects centering and film placement; common variations in the shape of the human body; directly effects the location of the heart, lungs, diaphragm, stomach, colon, gallbladder
Hypersthenic
Largest body habitus; massive build, high diaphragm, organs are higher and more horizontal; away from the midline; 5% of the population
Sthenic
Type of body habitus that’s considered “ordinary” or “average”; diaphragm and organs will be moderately high and evenly spaced within the abdomen; 50% of the population
Hyposthenic
Type of body habitus that’s considered “ordinary” or “average”; similar to sthenic but slightly smaller space between organs; 35% of the population
Asthenic
Type of body habitus that’s very thin and frail; diaphragm is low; organs will be low and more vertical; towards the midline; not having any size normalcy; very small; 10% of the population
206
How many bones in the adult body?
Provide attachment for muscles, mechanism for movement, protection of internal organs, frame for support, storage of calcium, production of red and white blood cells
What are some purposes for bones?
Ligaments
These structures attach bone to bone
Tendons
These structures attach muscle to bone
Fractures
What heals faster: fractures or ligament/muscle injuries?
S1-S2
What anatomical landmark aligns with the ASIS (Anterior Superior Iliac Spine)?
Affects centering and film placement
Why is body habitus important to know?
Hypersthenic, Sthenic, Hyposthenic, Asthenic
What are the 4 body habitus types in order from largest to smallest?
80 bones
How many bones make up the axial skeleton?
Axial and appendicular
What are the 2 main divisions of bones in the body?
Axial
This skeleton division contains 80 bones including the skull, sternum, ribs, and spine; functions to support and protect the head and trunk of the body
Appendicular skeleton
Skeleton division that has 126 bones including the scapulae, clavicles, pelvis, and upper and lower limbs; functions to allow body to move in various positions
126
How many bones in the appendicular skeleton?
Trabeculae
What’s the term for bony detail?
Compact bone
The term for the strong, dense outer layer that is found on all bones that protects the bone and gives it strength
Spongy bone
The term for the inner less dense portion of all bones
Trabeculae
Found in spongy bone; filled with red and yellow bone marrow; bony detail
Red marrow
found in the trabeculae of spongy bones; produces red and white blood cells
Yellow marrow
found in the trabeculae of spongy bone that produces/stores adipose (fat) cells
Medullary canal
Inner channel of long bones
Medullary canal; epiphyseal ends
Where is yellow marrow found in long bones compared to where red marrow is in long bones?
Periosteum
Tough, fibrous connective tissue that covers all bony surfaces except joints covered by articular cartilage
Articular cartilage
This covers bones that are found in joints and are not covered in periosteum
Endosteum
The tissue that lines the medullary cavity inside bones
tubercles/tuberosities
Bones contain knoblike projects called ________________ or ________________ that are covered with periosteum and serve as attachments for muscles, tendons, and ligaments
Periosteum
Where do blood vessels and nerves enter and exit through in a bone?
foramen
blood vessels and nerves enter and exit bone through holes is called __________________
nutrient foramen
hole at the center of all long bones for nutrient artery which supplies the bone and marrow
ossification
development & formation of bone (starts in 2nd month of embryonic life)
starts in 2nd month of embryonic life
When does ossification begin?
intermembranous and endochondral
What are the two types of ossification?
Intermembranous
type of ossification; bones that develop from fibrous membranes of the embryo that produces flat bones such as skulls, clavicles, mandible, and sternum; fully form after birth
endochondral
type of ossification; develops from hyaline cartilage of the embryo to form short, irregular, and long bones; occurs at two distinct areas called the primary and secondary centers of ossification
Primary ossification
type of endochondral ossification; begins before birth, forms entire bulk of short and irregular bone; form the diaphysis
Secondary ossification
Type of endochondral ossification; occurs after birth; when separate bones begin to form at the ends of long bones; each end is called the epiphysis