Ch. 8: The Central Nervous System
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
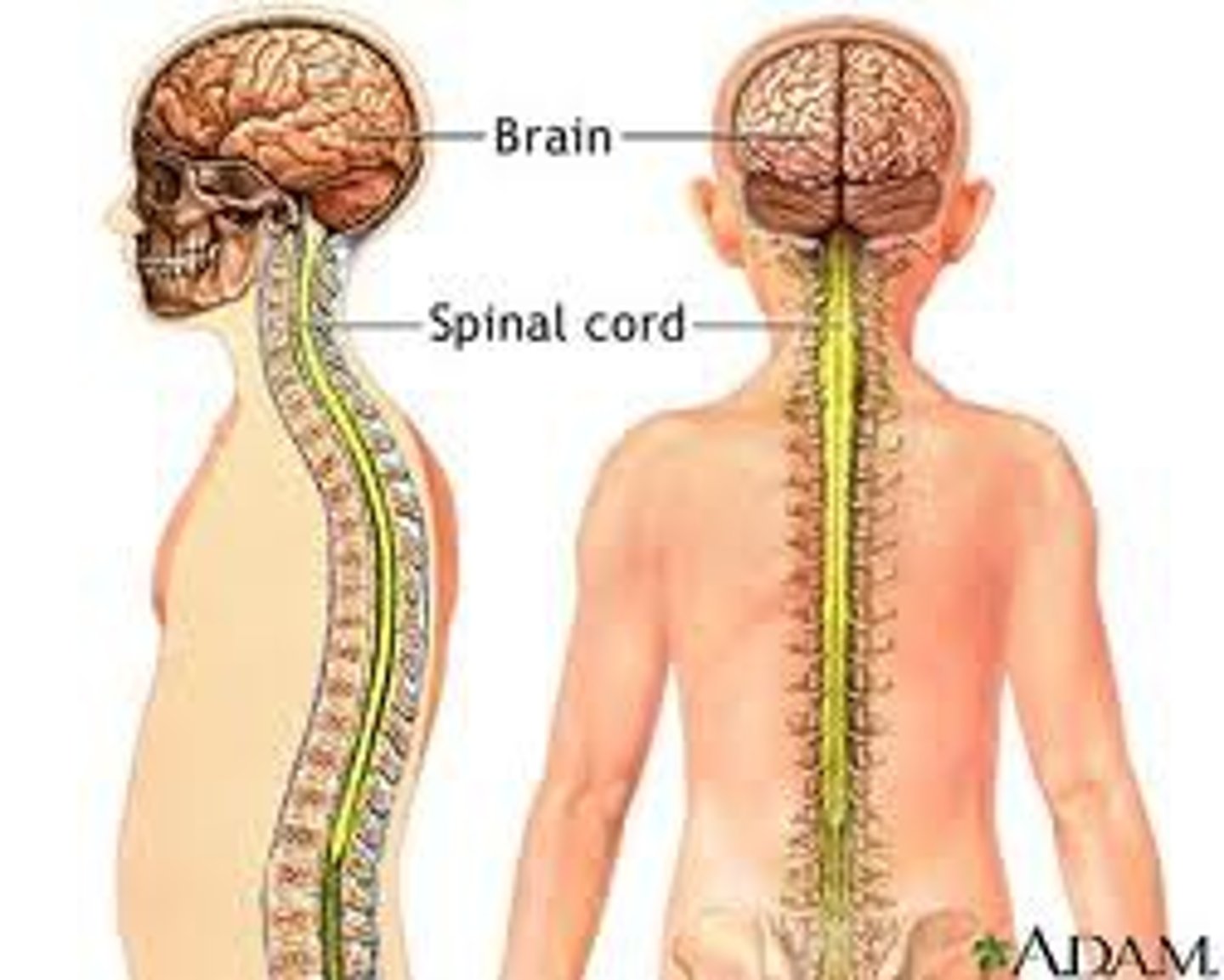
What does the CNS consist of
brain & spinal cord
What do the sensory neurons receive
input (afferent)
What do the motor neurons receive
output (efferent)
What do Association (interneurons) do
integrate sensory input and help direct response to maintain homeostasis
What is Grey matter (cities)
cell bodies: brain found in cortex and deep nuclei, spinal cord found deep (horns, central commissure)
What is White matter (highways)
tracts of axons (myelinated): brain found deep, spinal cord superficial (outside)
The neural tube is a part of the
CNS
The neural crest is part of the
PNS
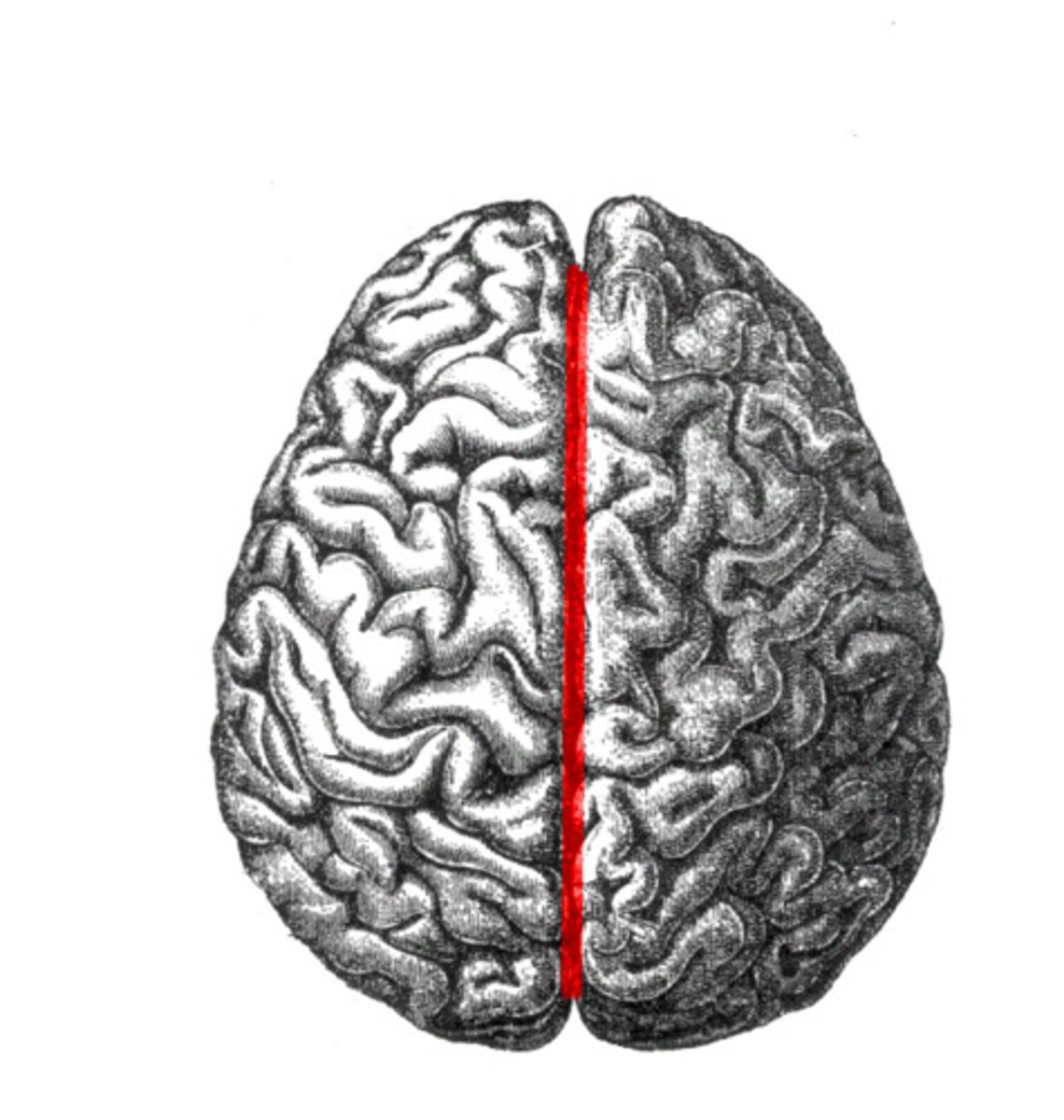
The R & L cerebral hemispheres connected by the
corpus callosum
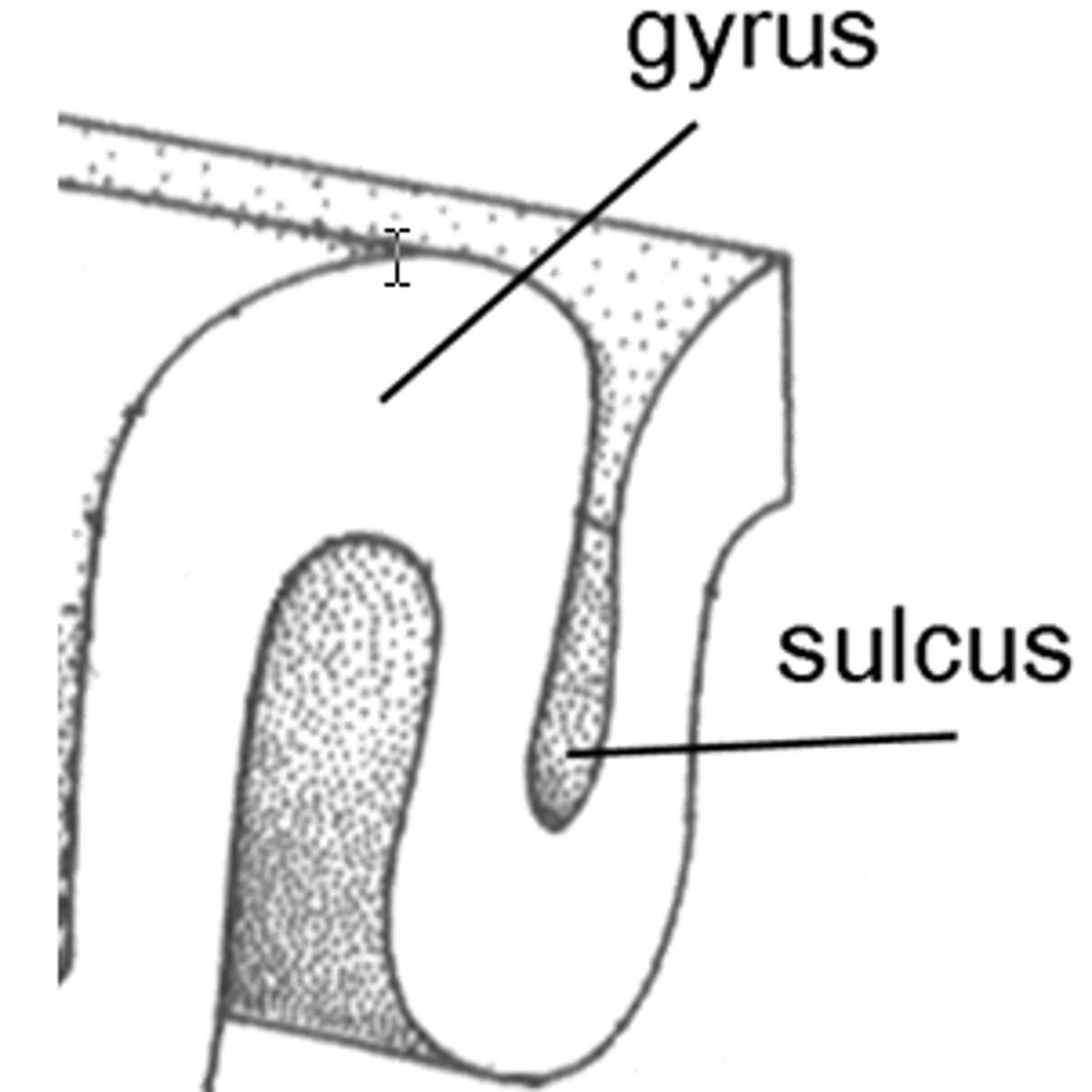
What is the Gyrus(Gyri) of the cerebrum
bumps
What is the Sulcus(Sulci of the cerebrum
invaginations
What's the purpose of the Gyri and Sulci
they provide more surface area of cortex
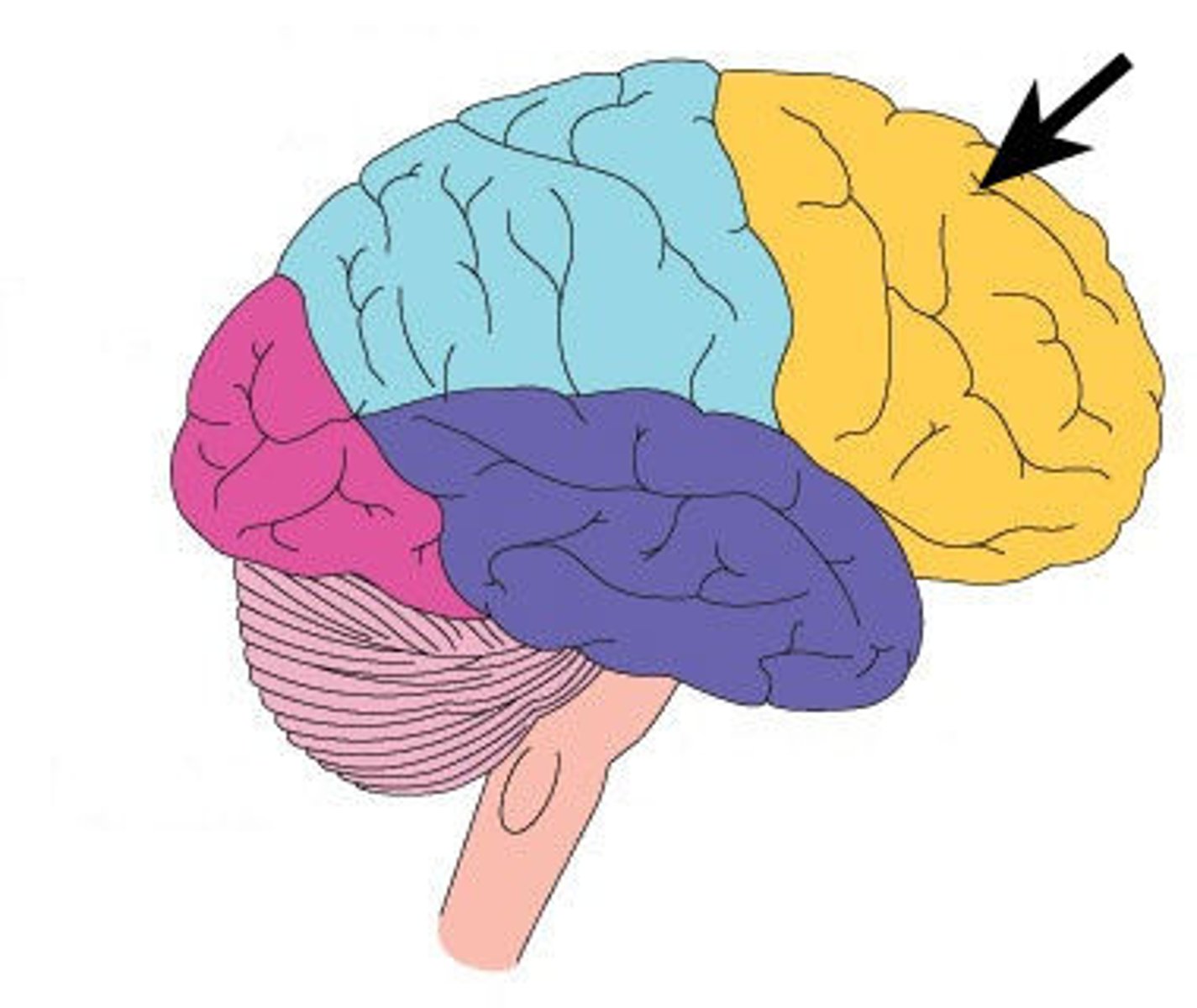
What are the 5 lobes of the brain
Frontal, Parietal, Occipital, Temporal, and Insular
What are the characteristics of the Frontal lobe
Contents: -primary motor cortex, premotor cortex, prefrontal cortex; Functions: motor planning, executive functioning, logic, emotion, judgement
What are the characteristics of the Parietal lobe
Contents: postcentral gyrus/primary (1o ) somatosensory cortex; Functions: somesthetic info (cutaneous, muscle, tendon, jt capsule)
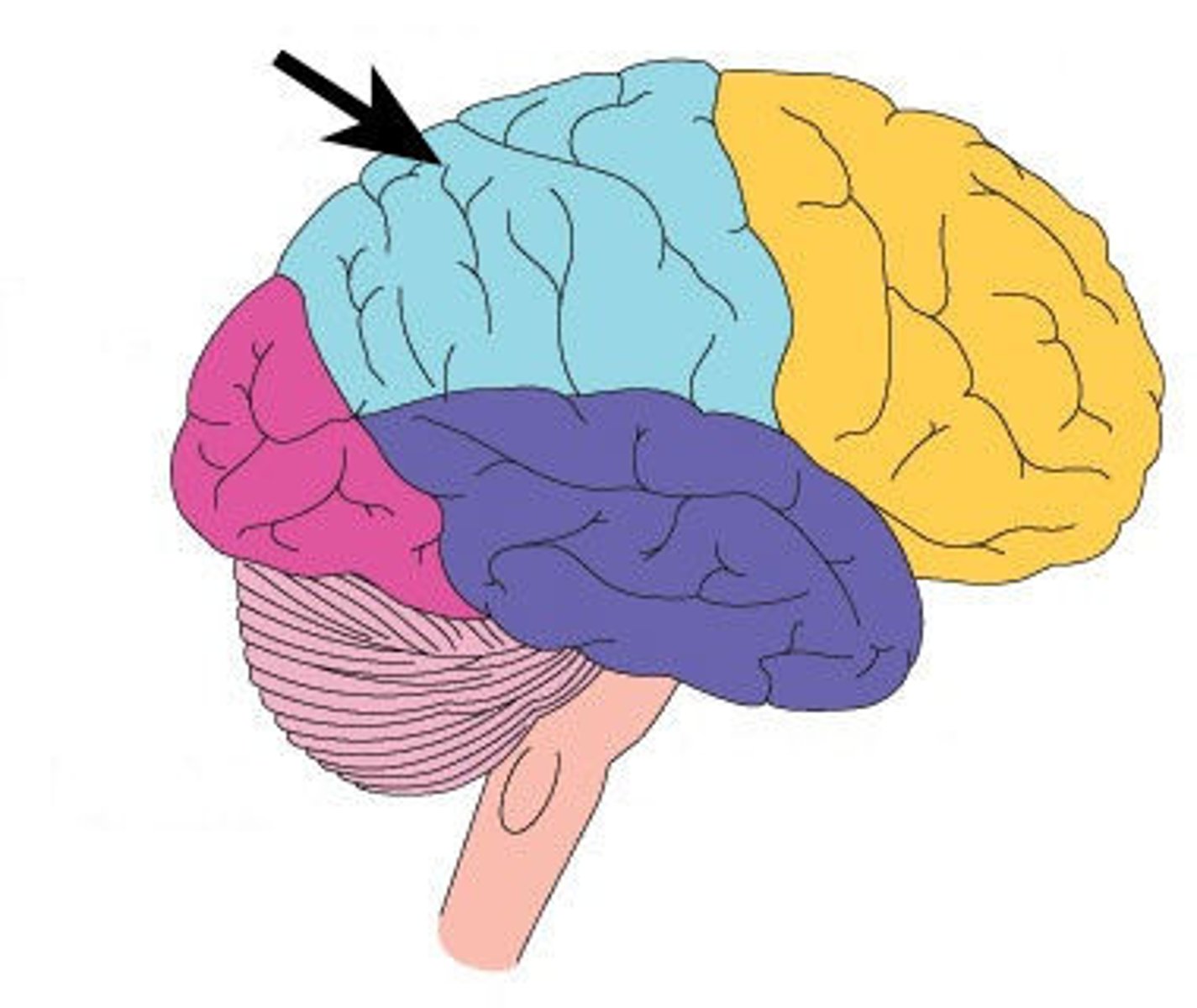
What does somesthetic mean
the senses related to touch, temperature, pain, and the body's position and movement
What is the frontal and parietal lobe divided by the
central sulcus
What's Homunculus
spatial mapping of body in 1o motor & somatosensory cortex
What are the characteristics of the occipital lobe
vision & coordination of eye mvmt
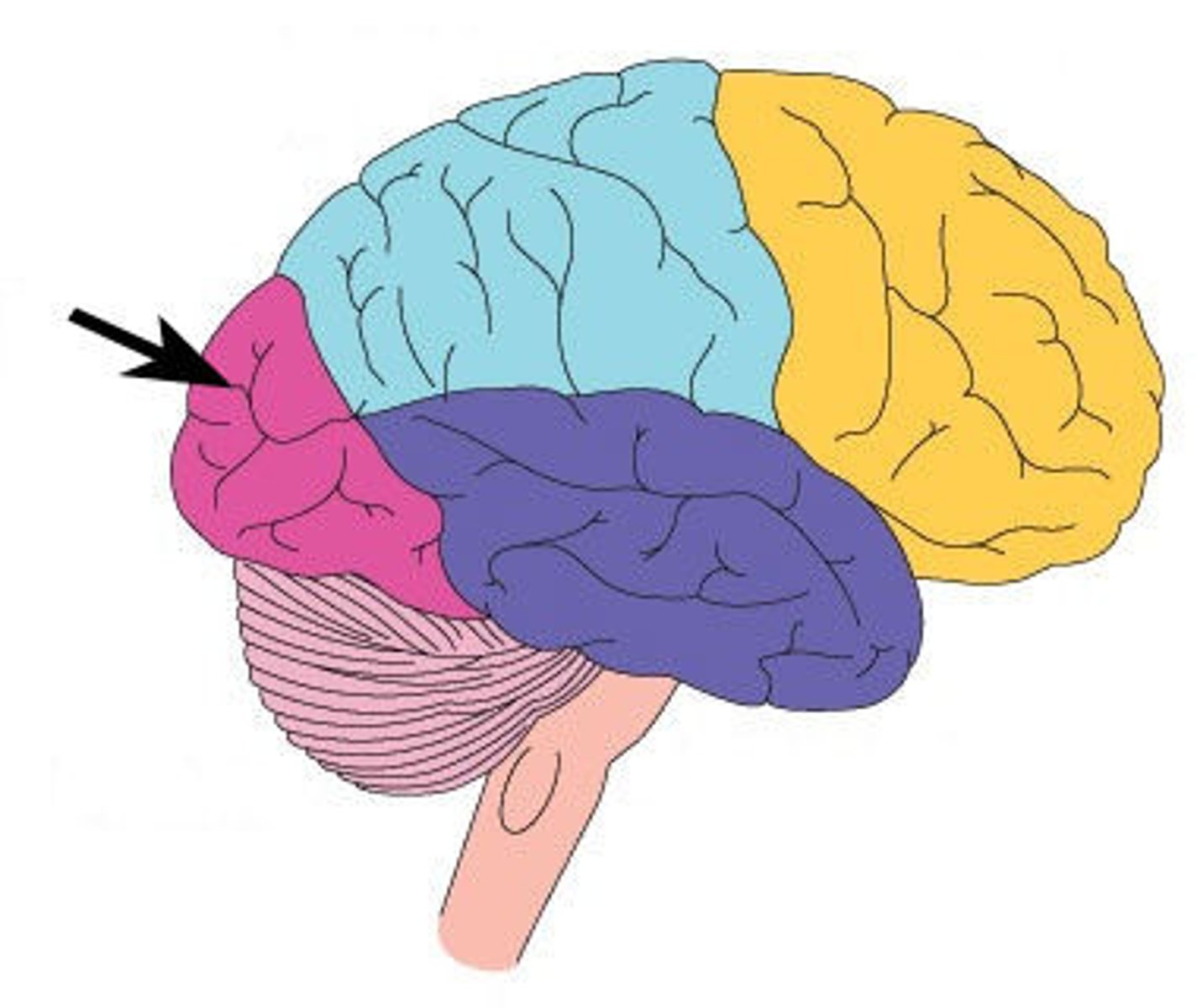
What are the characteristics of the temporal lobe
auditory sensation & interpretation of auditory & visual info
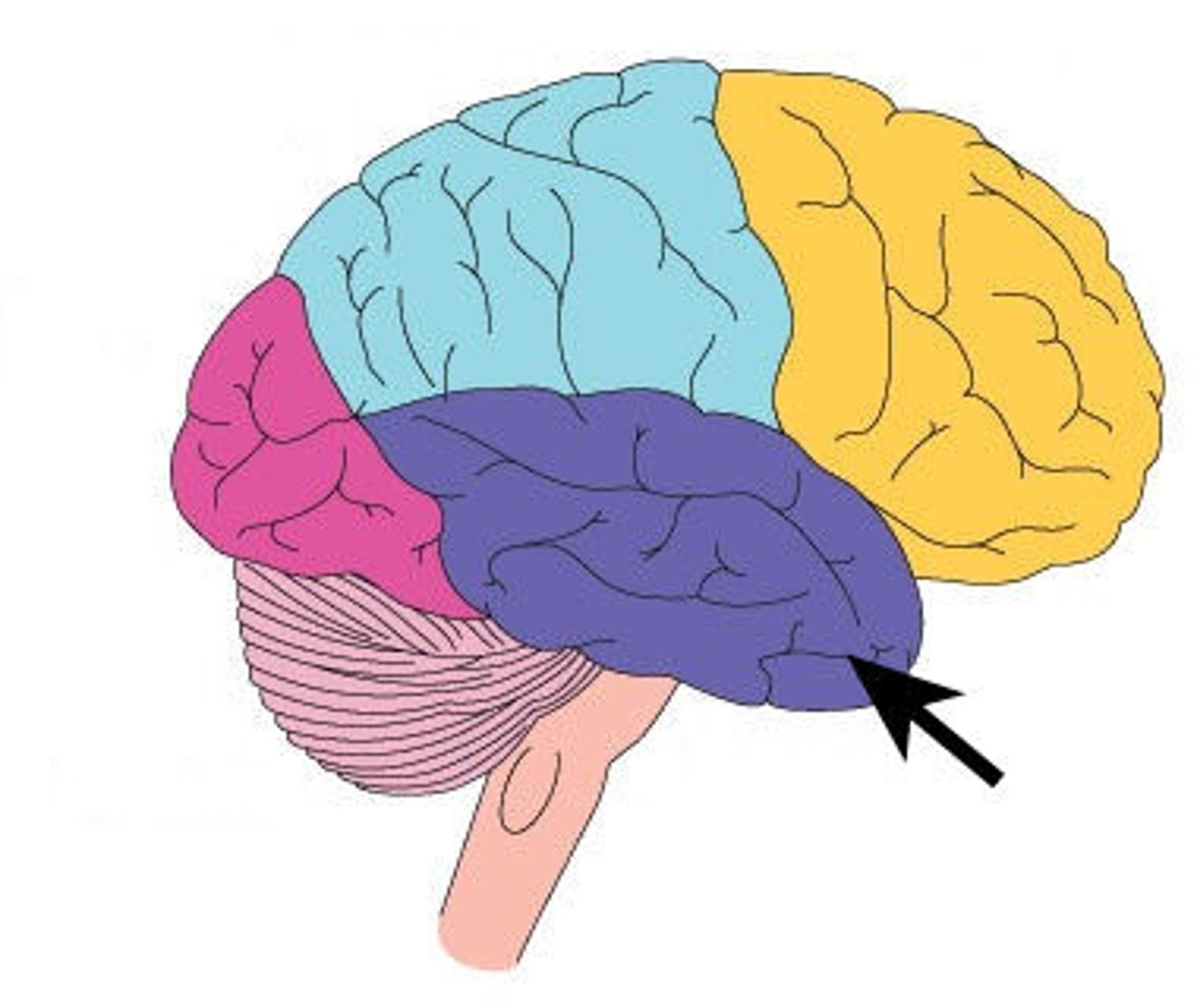
What are the characteristics of the insular lobe
memory & integration of sensory with visceral response (olfactory, gustatory, auditory, pain), controls autoimmune response
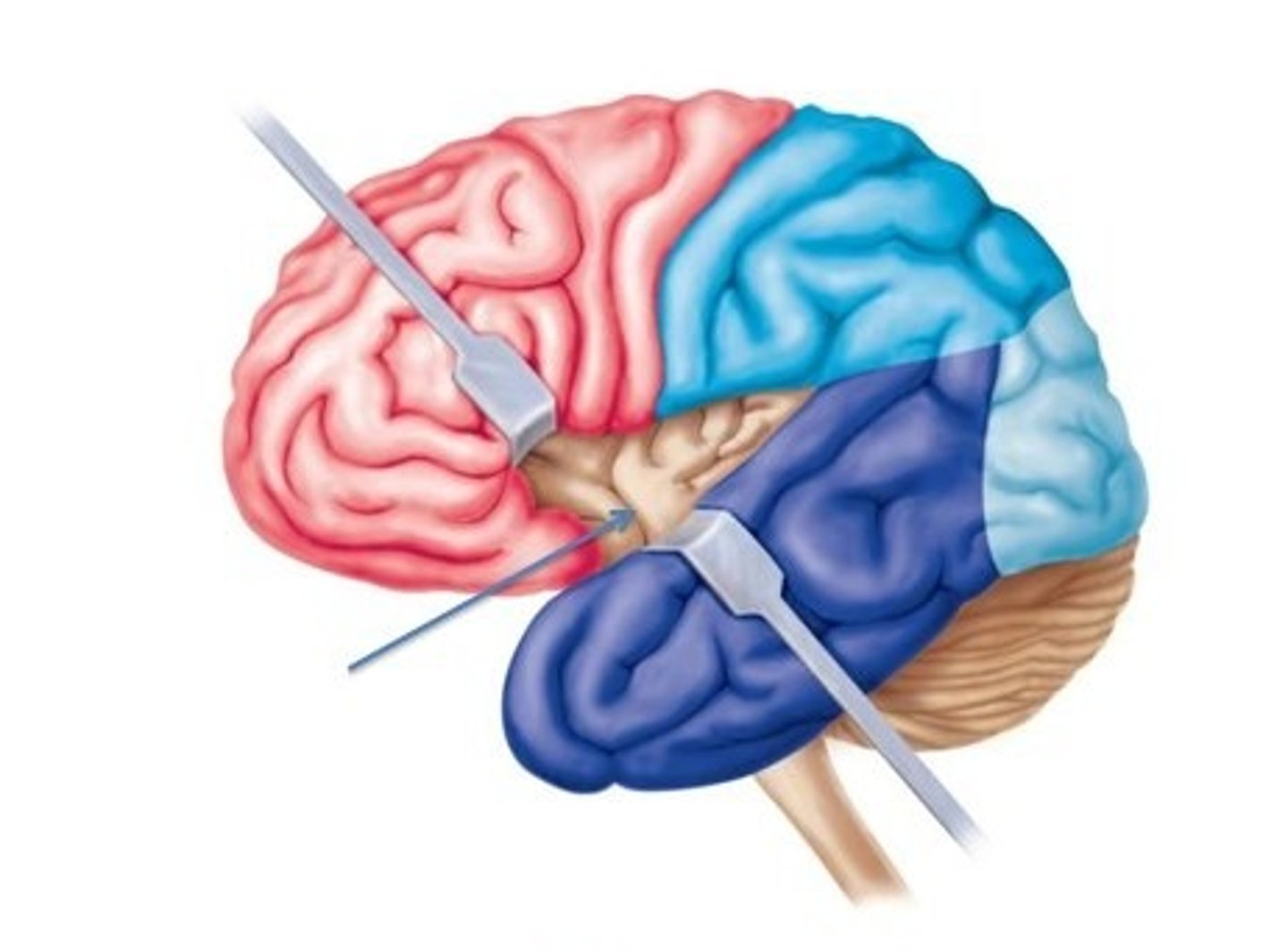
What are mirror neurons
motor & sensory neurons in frontal & parietal lobes, connected through the insula & cingulate gyrus to emotional centers of the brain. Activation by watching others: visual imagery, learning behaviors, imitation, understanding intention, empathizing with emotions of others (social skills - may be impaired with autism).
What are the basal nuclei
6 nuclei focused on motor control and behavior reward (influenced by substantia nigra)
What is the Corpus Striatum
a central component of the basal ganglia, a group of deep-brain nuclei involved in motor control, reward, habit formation, and decision-making
What does the reduction of dopamine from substantia nigra to corpus striatum cause
Parkinson's disease
What does the motor circuit do
it stimulates & inhibits appropriate movements
The premotor region sends Glutamate (excitatory) to
putamen
Putamen sends GABA (inhibitory) to
other basal nuclei
Globus pallidus sends GABA to
thalamus (normally sends excitatory signals to cerebrum)
Motor and sensory information in the pre/post-central gyrus is controlled/received from the
contralateral (opposite) side of the body
Communication between the two sides via the corpus callosum can be severed in severe forms of
epilepsy
What are the functions of the right hemisphere
visuospatial tasks, recognizing faces, composing music, arranging blocks, reading maps (Creativity)
What are the functions of the left hemisphere
Language, speech, writing, calculations, understand music (Logic)
What is aphasia
speech & language disorders from injury/stroke
What is Wernicke's area
left superior temporal gyrus, allows for understanding language
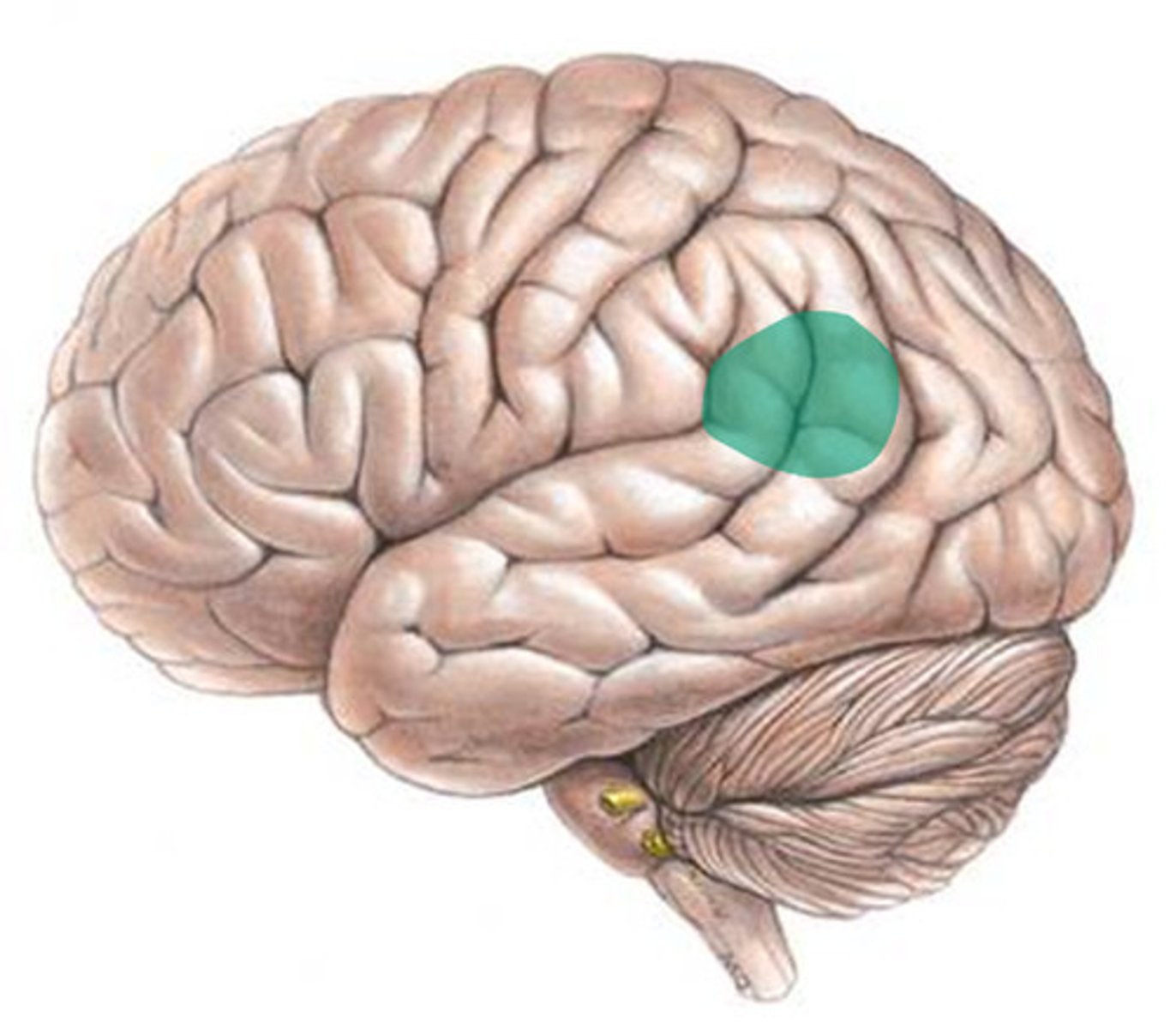
if damage is done to Wernicke's area (Wernicke's aphasia) it is characterized by
Difficulty understanding spoken and written language
Fluent but nonsensical speech (word salad)
Inability to produce grammatically correct sentences
May use made-up words or real words in the wrong context
Often unaware of their language errors
What is Broca's area
left inferior motor cortex, allows for speaking language correctly
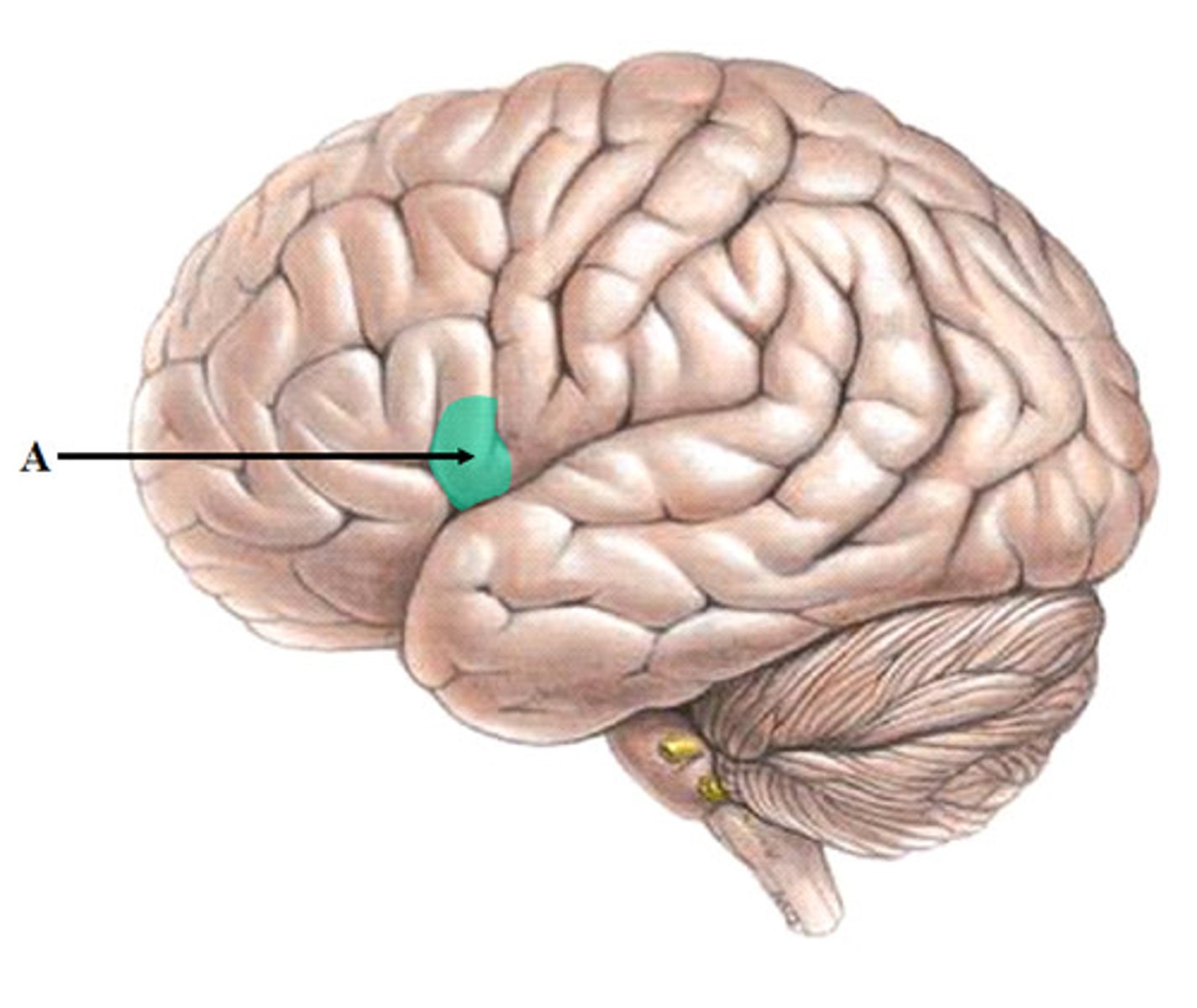
if damage is done to Broca's area (Broca's aphasia) it is characterized by
Difficulty speaking fluently
Use of short, grammatically incorrect sentences
Trouble finding words
Good comprehension of language
What is the limbic system composed of
Cingulate gyrus, amygdala, hippocampus, fornix, septal nuclei, anterior insula; parts of hypothalamus & thalamus
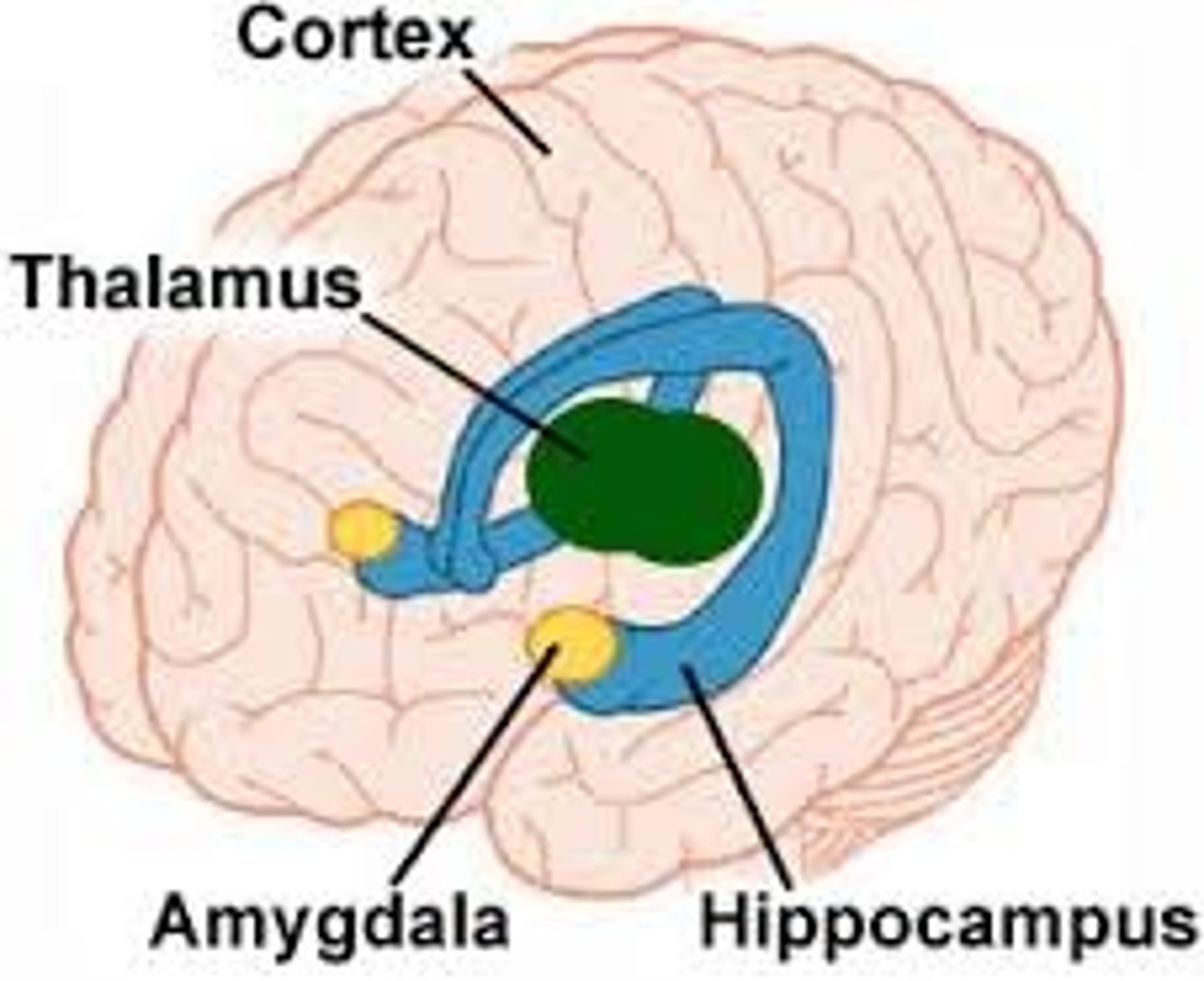
What is the limbic system responsible for
emotional drives such as Aggression & fear (amygdala & hypothalamus), hunger (hypothalamus), sex drive, goal-directed behaviors
The fornix connects hippocampus (memory) to
mammillary bodies (smell)
What's the function of the Hippocampus
formation and retrieval of memories, assists in consolidating STM > LTM, works with several other structures. stress can impair consolidation in hippocampus
What's the function of the Amygdala
learning fear response. Emotions influence/enhance memory encoding in amygdaloid
What's the ventricular system composed of
2 lateral ventricles, interventricular foramen, 3rd ventricle, cerebral aqueduct, 4 th ventricle to SC (central canal) & subarachnoid space.
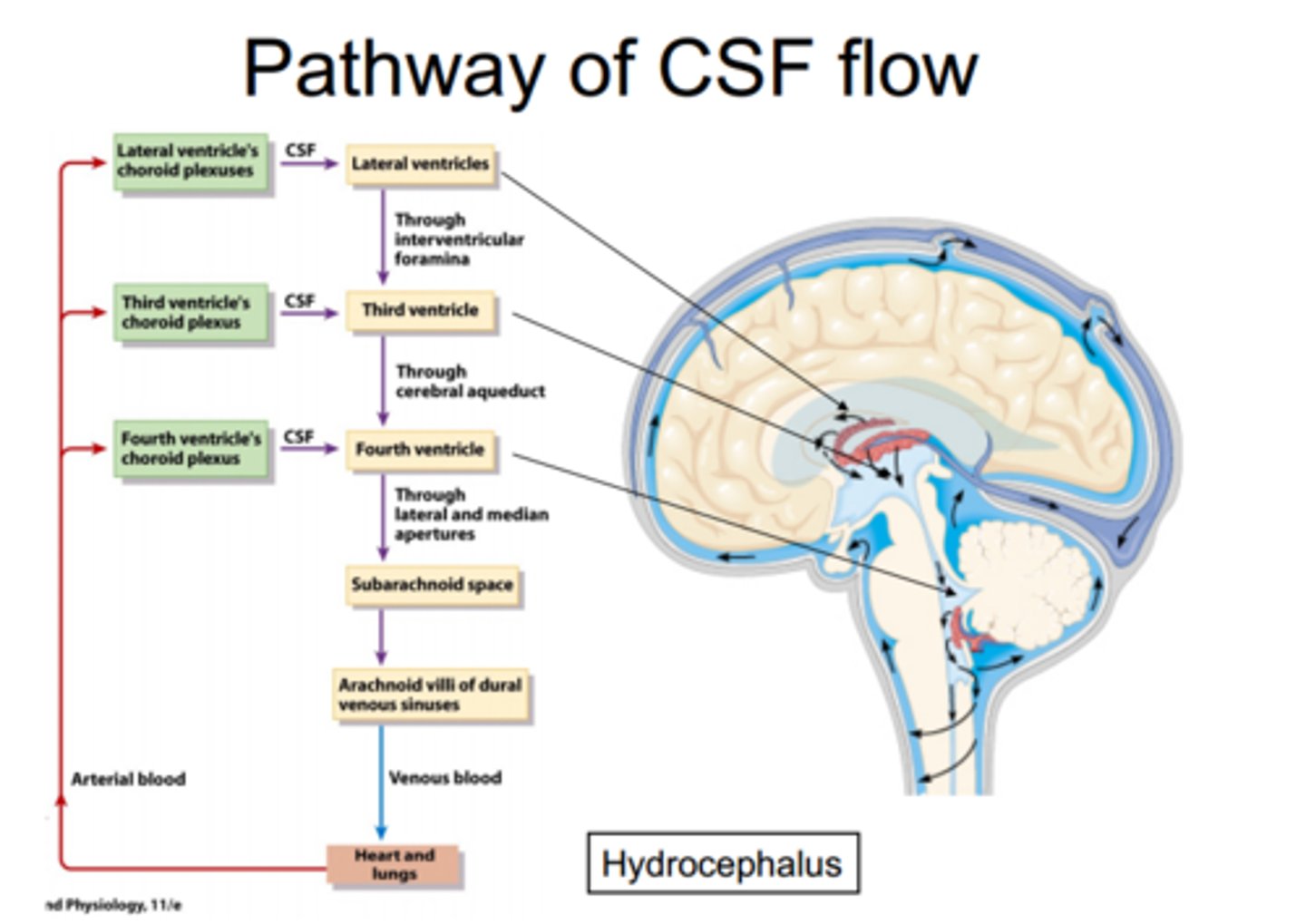
What's the choroid plexus & CSF do
Secretes cerebrospinal fluid (made from blood, returned to blood) Bathes cerebrum, 4th ventricle continues into spinal cord as central canal
a condition where there is an excessive buildup of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in the brain's ventricles is called
hydrocephalus
What are special functions involving the cerebrum
sleep and memory.
What is the Diencephalon (interbrain) composed of
The thalamus, Epithalamus, Hypothalamus, and Pituitary Gland
What is the thalamus, and what does it do
paired masses of grey matter (each thalamus has multiple nuclei) ii) relay center to cerebrum for sensory information iii) important for arousal from sleep &alertness
What is the Epithalamus
Contains pineal gland > secretes melatonin to regulate circadian rhythms (24 hr cycles)
What is the Hypothalamus (master gland) do
Hunger/satiety and thirst ii) Thermoregulation iii) Regulates sleep and wakefulness iv) Sexual arousal and performance v) Emotions of fear, anger, pain &pleasure vi) Controls endocrine system
What are the three nuclei of the hypothalamus
The Suprachiasmatic nuclei (SCN), The Supraoptic nuclei, and The Paraventricular nuclei
What does the suprachiasmatic nuclei do
maintains control of circadian rhythms, controls secretion of melatonin in pineal gland
What does the Supraoptic nuclei do
produced antidiuretic hormone
What does the Paraventricular nuclei do
produces oxytocin (childbirth, milk letdown, cuddling) and a little antidiuretic hormone. It directly controls hormone secretion from the pituitary gland
The Pituitary Gland is broken into a
anterior and posterior gland
What does the anterior pituitary gland do
produces many other hormones on it's own (growth, reproduction)
What does the posterior pituitary gland do
secretes antidiuretic hormone & oxytocin produced in the hypothalamus
What's the mesencephalon
the midbrain
What's the superior colliculi's reflex
the visual reflex
What's the inferior colliculi's reflex
the auditory reflex
What do the cerebral peduncles have
ascending & descending tracts
What does the red nucleus do
connects cerebrum & cerebellum (motor coordination)
What's the Nigrostriatal system involved in
movement initiation and coordination, projects to basal nuclei
What does Levodopa (L-dopa) do
mimics dopamine, difficult to pass through blood-brain barrier
What do MAO inhibitors do
keeps dopamine in synapse longer
What does the mesolimbic system do
limbic system & forebrain for behavioral reward system (addiction & psychiatric disturbances) Affected by nicotine, opioids, cannabinoids, benzodiazepines (valium & ambien), cocaine,amphetamines
What is the metecephalon composed of
The pons and the cerebellum
What is the pons
functions as a "bridge" for crucial communication between the forebrain and the cerebellum, while also housing important cranial nerves and centers that regulate unconscious, vital functions such as breathing and sleep.
What does the Apneustic center of the pons do
promotes inspiration (gas)
What does the Pneumotaxic center of the pons do
limits inspiration (brake)
What are some characteristics of the cerebellum
2nd largest brain structure: grey matter superficial, white matter deep (arborvitae) ii) Receives input from proprioceptors in joints, tendons & ms. iii) Coordinates mvmt with basal nuclei & motor cortex (via Red nucleus & thalamus)
disorder of mvmt, often associated with gait, balance, eye movement & swallowing is called
Ataxia
What does the Myelencephalon contain
the Medulla Oblongota
What does the medulla oblongota do
controls the involuntary, life-sustaining functions of the autonomic nervous system, including breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure.
What are the three vital centers of the medulla
The Vasomotor Center (VMC), Cardiac Control Center (CCC), and the Respiratory Rhythmicity Center (RRC)
What does the Vasomotor Center aid with
autonomic innervation of blood vessels
What does the Cardiac Control Center aid with
autonomic nerve control of the heart
What does the Respiratory Rhythmicty Center do
controls breathing with apneustic & pneumotaxic centers
What's the reticular activating system
a network of neurons in the brainstem responsible for regulating wakefulness and consciousness by filtering sensory information and modulating attention, arousal, and sleep-wake cycles
What is the order of the Dorsal Column - Medial lemniscus pathway
1 st order sensory neuron enters SC via DRG to fasciculus gracilis (LE) orfasciculus cuneatus (UE) to nucleus gracilis & cuneatus(M.O.) 2 nd order sensor neuron crosses (decussates) in pyramids of M.O., proceedsto thalamus 3 rd order sensory neuron extends to cerebral cortex (contralateral to original stimulus)
What's the order of the Anterolateral spinothalamic pathway
1 st order sensory neuron enters SC via DRG and immediately synapse in dorsal horn 2 nd order sensor neuron crosses (decussates) immediately and ascends on contralateral side from stimulus, synapsing on thalamus 3 rd order sensory neuron extends to cerebral cortex (contralateral to original stimulus)
what's the order of the Corticospinal (Pyramidal) tracts
1 st order motor neuron (UMN) - precentral gyrus > 80-90% decussate in pyramids (lateral CST), 10+% in SC (ant CST) > ventral horn of SC 2 nd order motor neuron (LMN) - ventral horn > muscle
What's extrapyramidal
many tracts from nuclei in brain stem directly to muscle, mostly controlled by basal ganglia Associated with substantia nigra, thalamus, red nucleus, reticular formation, cerebellum Can be motor or sensory
What does the Peripheral Nervous system contain
Cranial & Spinal Nerves
Characteristics of Cranial nerves
12 pairs with nuclei (cell bodies) in CNS ii) Most are mixed (optic, olfactory, & vestibulocochlear sensory only)
Characteristics of Spinal Nerves
Arise directly from spinal cord ii) Mixed motor and sensory iii) Cell bodies: sensory in DRG, motor in lateral & ventral grey horn
What does damage to spinal nerves cause
i) Sensory loss: dermatomal distribution ii) Motor loss: myotome distribution
The Quadriceps is innervated by the
Femoral nerve.
Semitendinosus is innervated by the
Sciatic nerve.
Tibialis anterior is innervated by the
Anterior fibular nerve (also known as the Deep fibular nerve).
Gastrocnemius is innervated by the
Tibial nerve.
What's the reflex arc
Unconscious motor response to a sensory stimulus
What are parts of the reflex arc
i) Sensory receptor ii) Sensory neuron iii) (Association neuron in CNS - not always) iv) Motor neuron v) Effector - muscle or gland that respond
What's the monosynaptic reflex
the most rapid and simplest reflex involving a two-neuron pathway: a single sensory neuron and a single motor neuron, with no interneurons Stretch reflex of ms. Spindles
What's the Disynaptic or polysynaptic reflex
a neural pathway involving two synapses and one interneuron between a sensory input and a motor output that prolongs stretch of GTO, or pain/temp, and may be inhibitory or excitatory
GTO is a
prolonged stretch, resulting in inhibition of the same muscle and excitation of its antagonist.
What does the dorsal column lemniscus pathway do
transmit sensory information related to light touch, vibration, and conscious proprioception (awareness of body position) from the body to the brain for conscious perception
What if the dorsal column lemniscus pathway was damaged
loss of light touch, vibration, proprioception (joint position sense), and pressure
What does the anterolateral spinothalamic pathway do
transmit sensory information, including pain, temperature, and deep touch, from the body to the brain for processing