Disease Detectives 2025 Outbreak Investigation
1/117
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
118 Terms
Step 1: Collect Data
Gather surveillance data on time, place, person.
Step 2: Assessment
Make inferences based on collected data.
Step 3: Hypothesis Testing
Determine how and why the outbreak occurred.
Step 4: Action
Implement interventions to control the outbreak.
Experimental Studies
Research involving controlled experiments on subjects.
Clinical Trials
Experimental studies on individuals for treatment efficacy.
Community Trials
Experimental studies conducted on community populations.
Cohort Study
Tracks exposed participants to assess disease development.
Case Control Study
Compares exposure history between diseased and non-diseased.
Cross Sectional Study
Measures exposures and outcomes simultaneously in a population.
Ecological Study
Analyzes group-level data to compare health outcomes.
Scientific Method
Systematic approach for investigating phenomena and hypotheses.
Obtain Background Information
Gather existing knowledge relevant to the outbreak.
Define the Problem
Clearly articulate the health issue being investigated.
Formulate Hypothesis
Develop a testable statement based on observations.
Develop a Study
Create a method to test the hypothesis effectively.
Collect Data and Observations
Gather empirical evidence to support or refute hypothesis.
Evaluate Results
Analyze data to determine hypothesis validity.
Modify Hypothesis
Adjust hypothesis based on lab verification results.
Formulate Conclusions
Summarize findings and implications of the study.
Report Results
Communicate findings to relevant stakeholders and authorities.
Prepare for Field Work
Gather supplies and research before investigation begins.
Establish Existence of Outbreak
Assess severity and potential spread of health issue.
Verify the Diagnosis
Confirm diagnosis through proper testing and interviews.
Construct Case Definition
Define criteria for identifying affected individuals.
Case Definition
Criteria to determine disease presence.
Clinical Information
Details about the disease or condition.
Characteristics
Traits of affected individuals.
Location
Specific area of outbreak occurrence.
Time Sequence
Specific period of outbreak occurrence.
Identification of Cases
Counting specific cases of disease.
Confirmed Case
Diagnosis with lab verification present.
Probable Case
Diagnosis suggested but lacks lab verification.
Possible Case
Some evidence points to diagnosis.
Line Listing
Chart of specific cases with details.
Identifying Information
Case ID and personal identifiers.
Demographic Information
Age, sex, race, and occupation details.
Clinical Information (Line Listing)
Diagnosis, symptoms, and lab results.
Descriptive Time
Date and time of onset and report.
Descriptive Person
Age, sex, and other characteristics.
Descriptive Place
Specific location details of cases.
Risk Factors
Specific factors related to disease and outbreak.
Case Finding
Systematic search for cases.
Passive Reporting
Cases reported without active investigation.
Data Collection Form
Form for gathering case information.
Reporter Information
Source of case report details.
Descriptive Epidemiology
Analysis of data by time, place, and person.
Outbreak Investigation Forms
Documents used during outbreak analysis.
Epidemic Curve
Histogram showing disease outbreak over time.
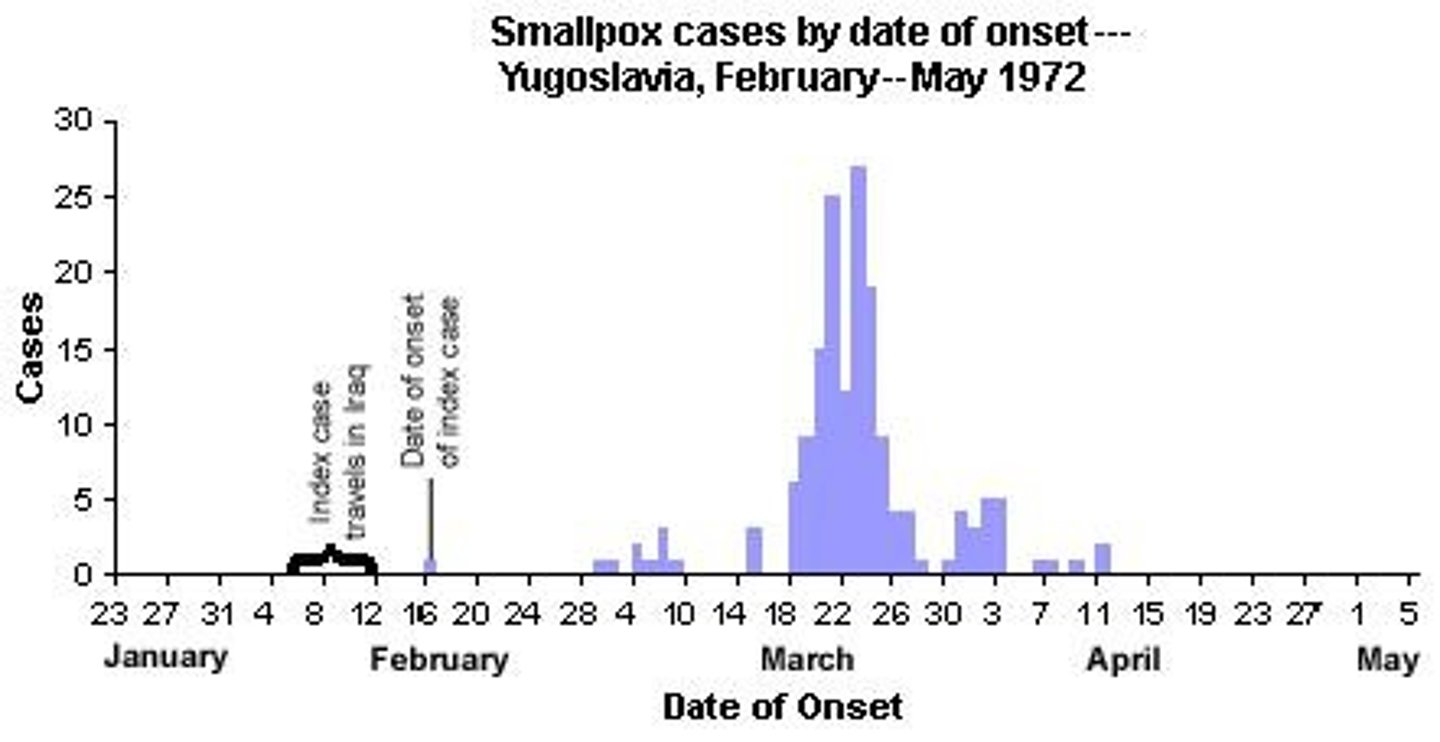
Epi Curve
Visual representation of disease incidence.
X-axis
Represents time units in Epi curve.
Y-axis
Represents number of cases in Epi curve.
Single Peak
Indicates a single source of exposure.
Plateau
Shows continuous common source of infection.
Uniform Peaks
Indicates a propagated outbreak from person to person.
Geographic Extent
Area affected by the disease outbreak.
Spot Map
Visual tool to identify case locations.
Affected Population
Group identified by demographics or exposures.
Agent/Host/Environment Triad
Framework for understanding disease transmission.
Testable Hypothesis
Hypothesis must be verifiable through experimentation.
Cohort Study
Follows exposed and unexposed groups over time.
Retrospective Cohort
Looks back at past exposures to determine outcomes.
Prospective Cohort
Follows current exposures to future outcomes.
Attack Rate
Rate of illness in a specific group.
Relative Risk
Comparison of disease risk between exposed and unexposed.
Incidence Rate
Frequency of new cases in a population.
Control Group
Group not exposed, used for comparison.
Lab Verification
Scientific confirmation of hypothesis through testing.
High Attack Rate
Indicates significant illness in exposed group.
Low Attack Rate
Indicates minimal illness in unexposed group.
Positive Association
Increased risk indicated by relative risk > 1.0.
Negative Association
Decreased risk indicated by relative risk < 1.0.
Relative Risk
Used in cohort studies to measure risk.
Odds Ratio
Compares odds of exposure in cases vs controls.
Case-Control Study
Analyzes backward from effect to suspected cause.
Control Group
Similar characteristics to case group, not ill.
Odds Ratio Formula
Calculated as (a/c) / (b/d).
Case Patients
Individuals with the disease under study.
Control Patients
Individuals without the disease, used for comparison.
Random Error
Chance fluctuations affecting measurement precision.
Systematic Error
Consistent deviation from true population values.
Internal Validity
Accuracy of measurements within the study.
External Validity
Generalizability of study findings to the population.
Selection Bias
Bias from unmeasured variables affecting subject selection.
Information Bias
Systematic error in variable assessment.
Confounding
Extraneous factors affecting disease and exposure relationship.
False Relationships
Incorrect associations due to various errors.
Sample Size
Larger size reduces random error variability.
Hepatitis A Example
Case-control study linked infection to Restaurant A.
2x2 Table
Organizes data for case and control comparisons.
Odds of Exposure
Probability of exposure among case or control.
Bias Types
Different problems affecting study organization.
Measurement Validity
Degree of accuracy in study results.
Epidemiologic Study
Research examining health-related events and exposures.
Data Collection Errors
Mistakes during data gathering or analysis.
Information Bias
Systematic error in data collection affecting results.
Response Bias
Participants provide inaccurate or misleading responses.
Interviewer Bias
Interviewer influences participant responses unintentionally.
Recall Bias
Participants' memory affects accuracy of reported information.
Confounding
Mixing effects of extraneous factors on outcomes.