Organic Reactions
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
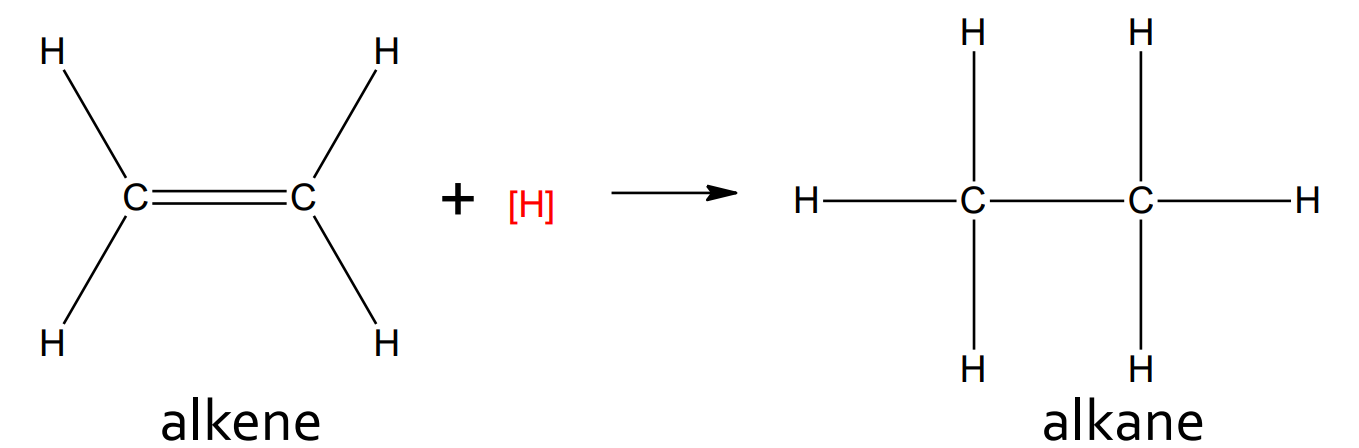
Addition - Hydrogenation
catalyst: Pt
product: alkane
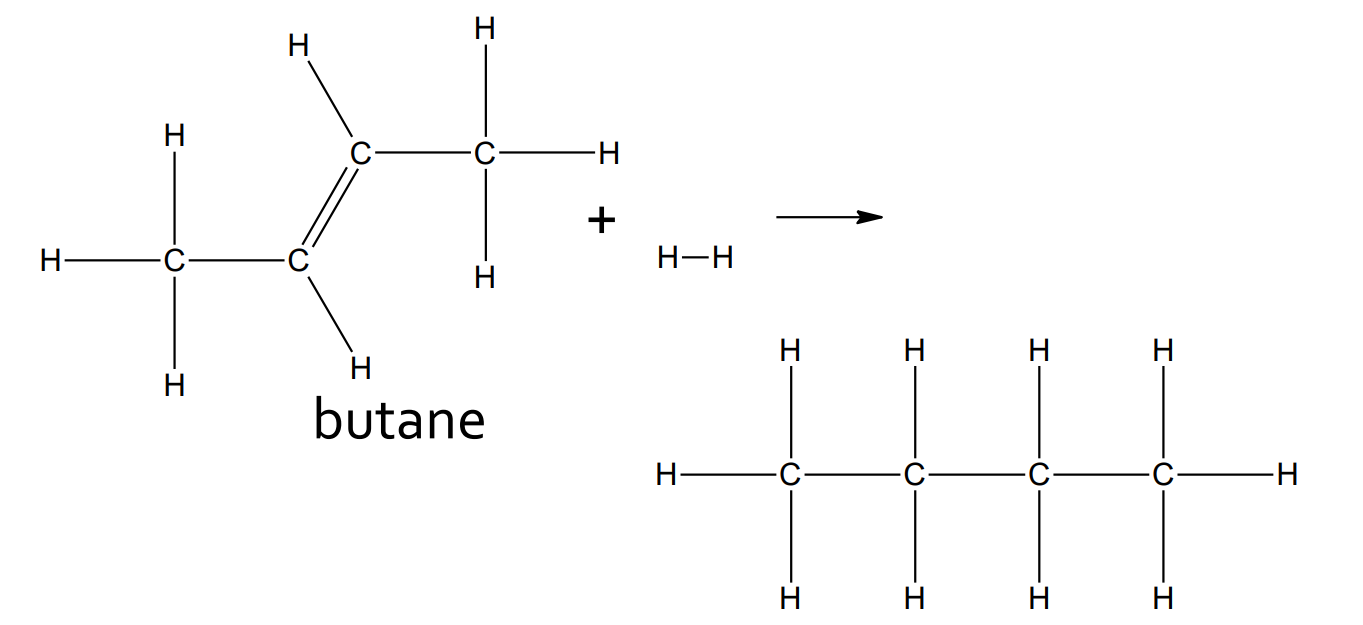
Addition - Hydration
catalyst: H2SO4 + 100 °C
product: alcohol
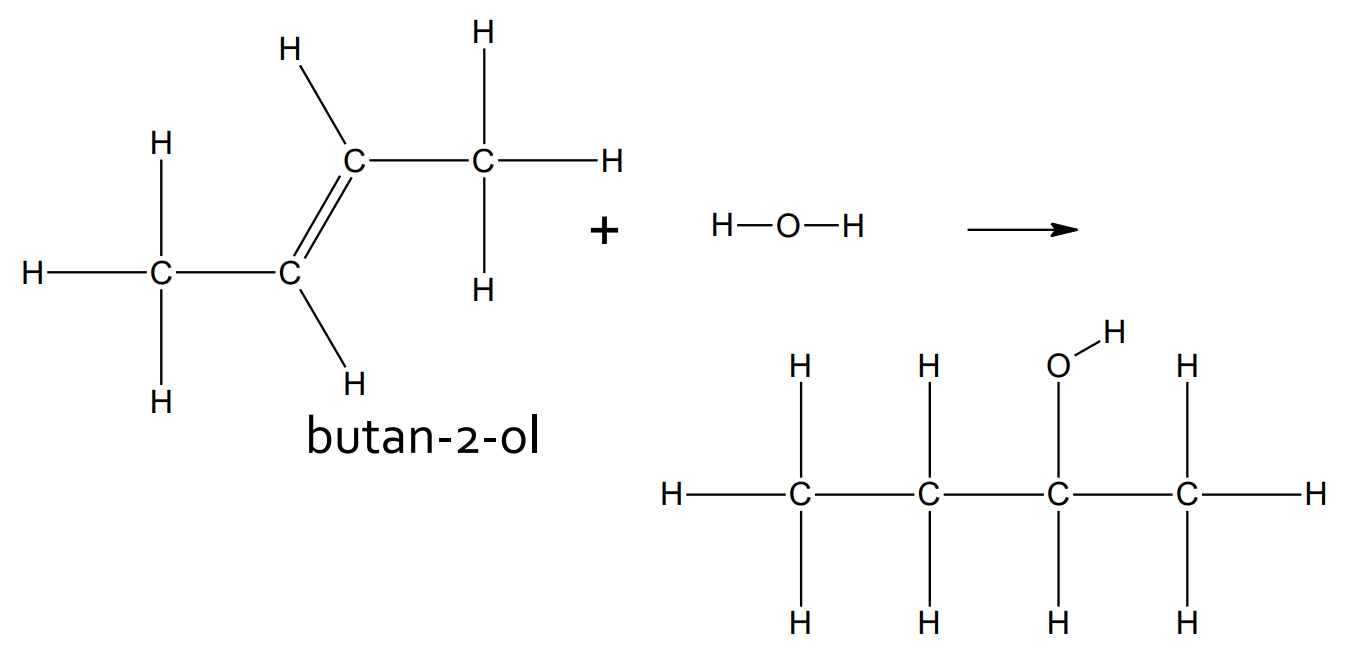
Addition - Hydrohalogenation
catalyst: N/A
product: haloalkane (with one halogen atom)
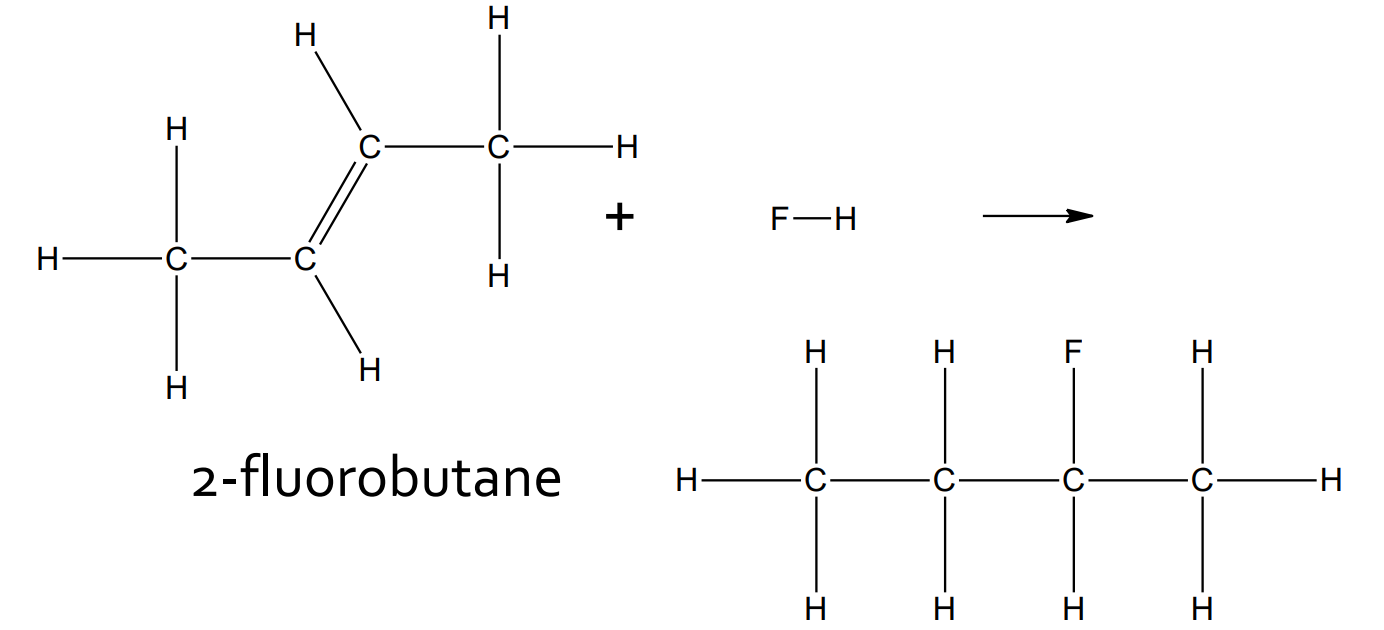
Addition - Halogenation
catalyst: CCl4
product: haloalkane (with two halogen atoms)
Elimination - Alcohols
catalyst: H2SO4 and 100 °C and heat (= ∆)
products: alkene and water
Elimination - Alkyl Halides
With hydroxide ion
products: alkene and water and halide ion base
Substitution - Alcohol with hydrogen halide
catalyst: ZnCl2 (Lucas Reagent)
products: alkyl halide and water
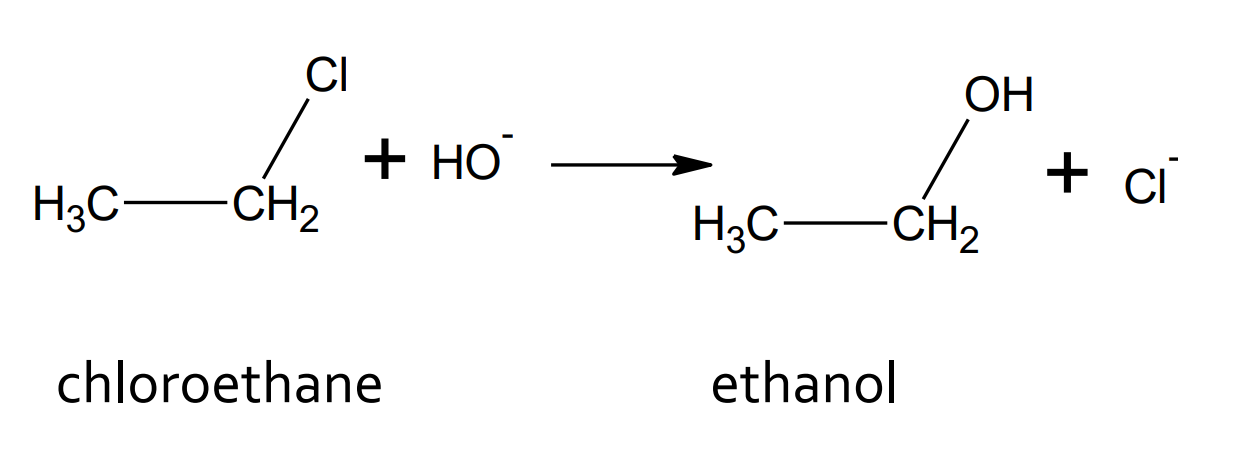
Substitution - Haloalkane + base (OH-)
catalyst: N/A
products: alcohol
unpredictable, might undergo elimination instead
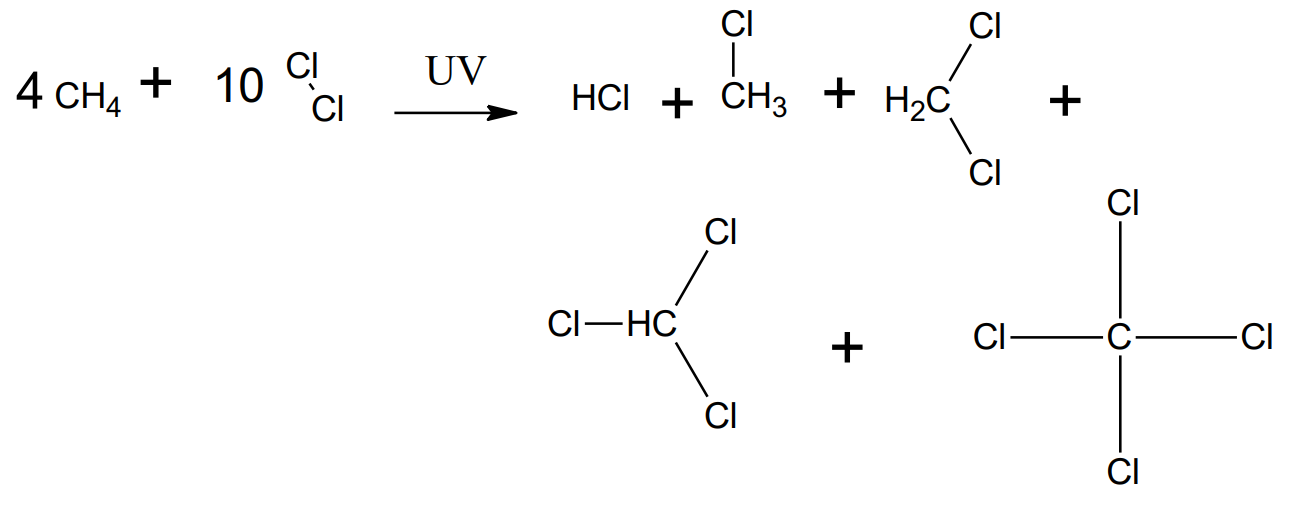
Substitution - Alkane with halogens
catalyst: UV light
products: haloalkane and hydrogen halide
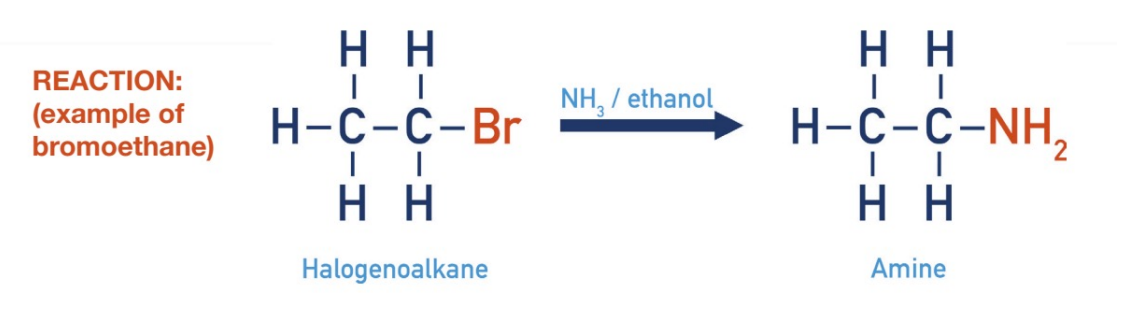
Substitution - Haloalkane with ammonia
catalyst: heat and ethanol
products: amine and ammonium halide salt
Substitution - Benzene and halogens
catalyst: FeBr3 or AlCl
product: halobenzene and hydrogen halide
addition does NOT occur
when substituting 2 atoms/groups onto benzene, the meta config is favoured
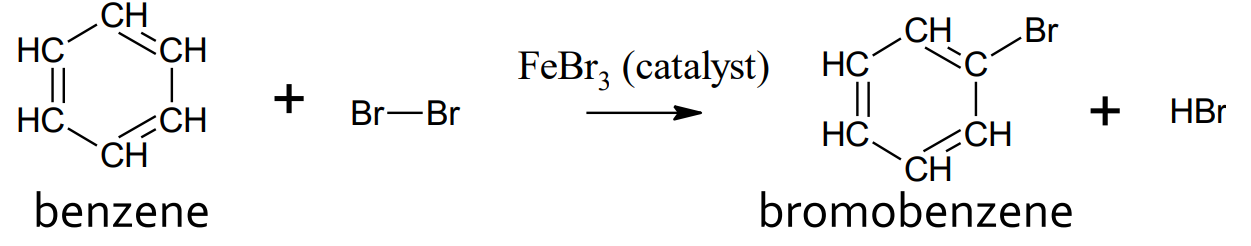
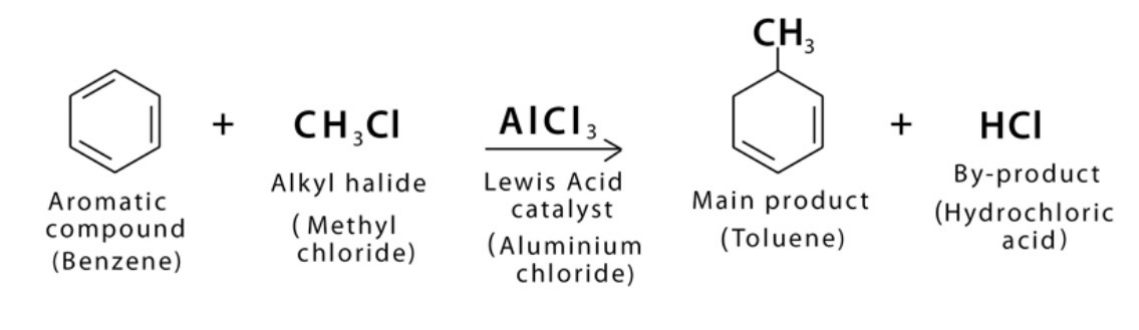
Substitution - Benzene with alkyl halide
catalyst: AlCl3
products: alkyl benzene and hydrogen halide
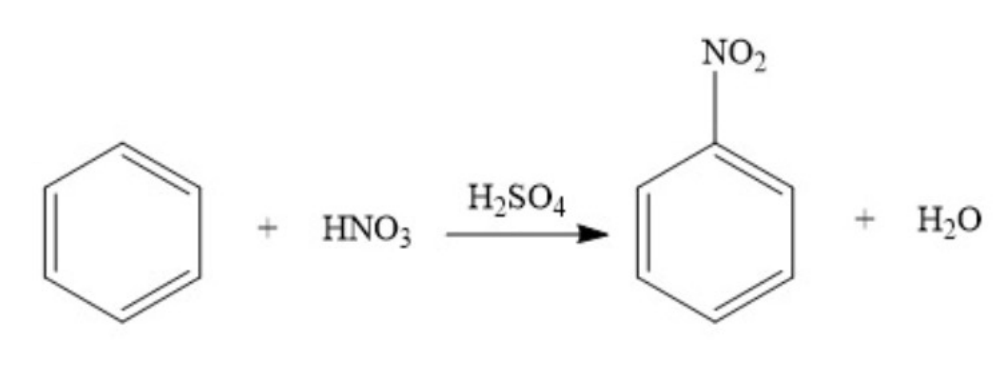
Substitution - Benzene with nitric acid
catalyst: H2SO4
products: nitrobenzene and water
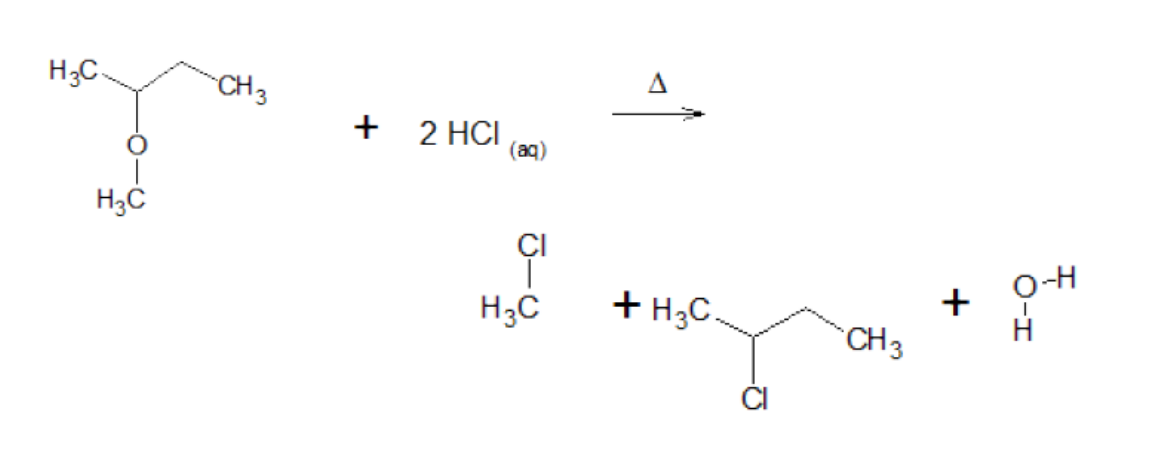
Substitution - Ethers with 2 binary acids
catalyst: heat
products: 2 alkyl halides + water
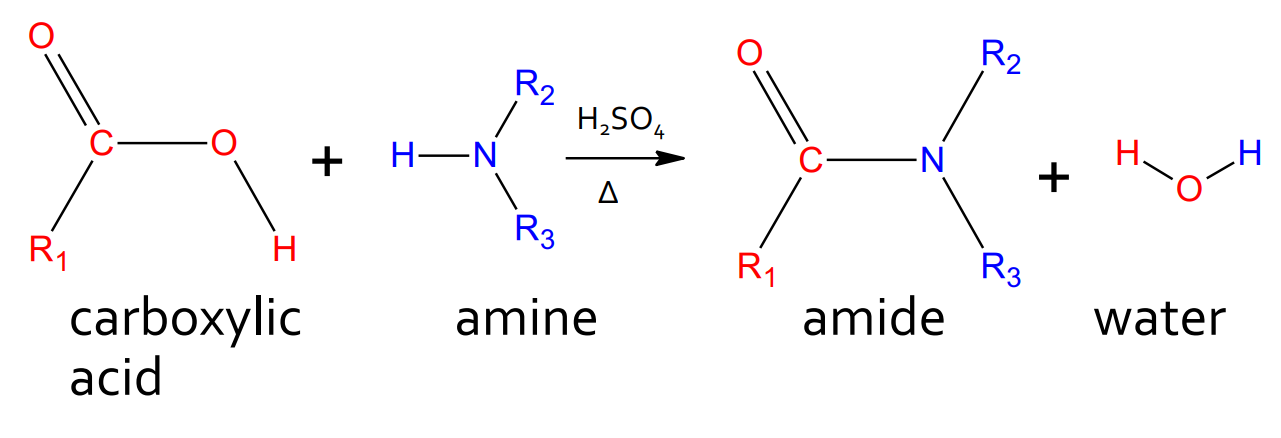
Condensation - Amine with carboxylic acid
catalyst: H2SO4 and heat
product: amide and water
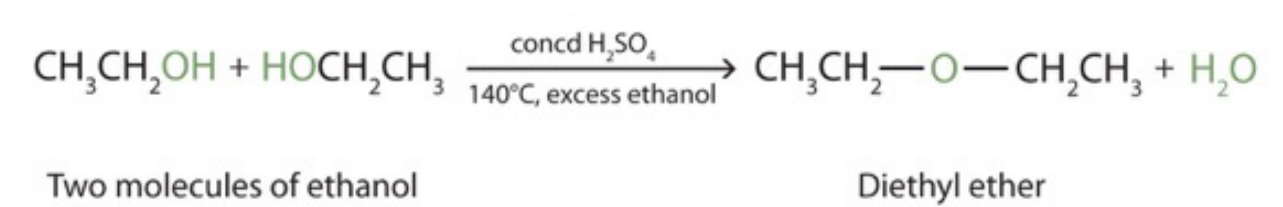
Condensation - Alcohol with another alcohol
catalyst: H2SO4, 140 ˚C
products: ether and water
could also form an alkene (elimination) if reaction occurred at 100 ˚C
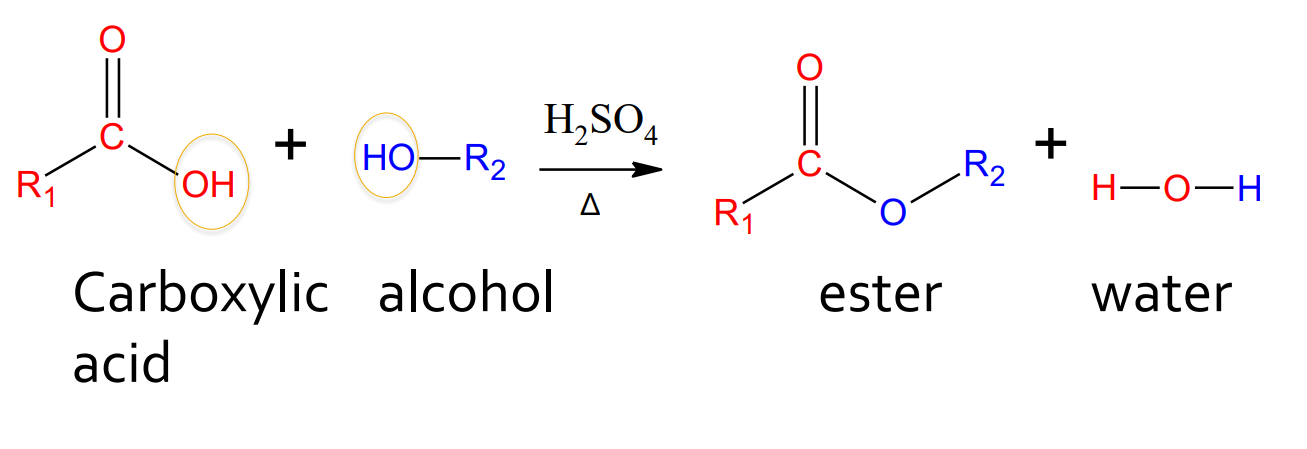
Esterification - Alcohol and carboxylic acid
catalyst: H2SO4 and water
products: ester and water
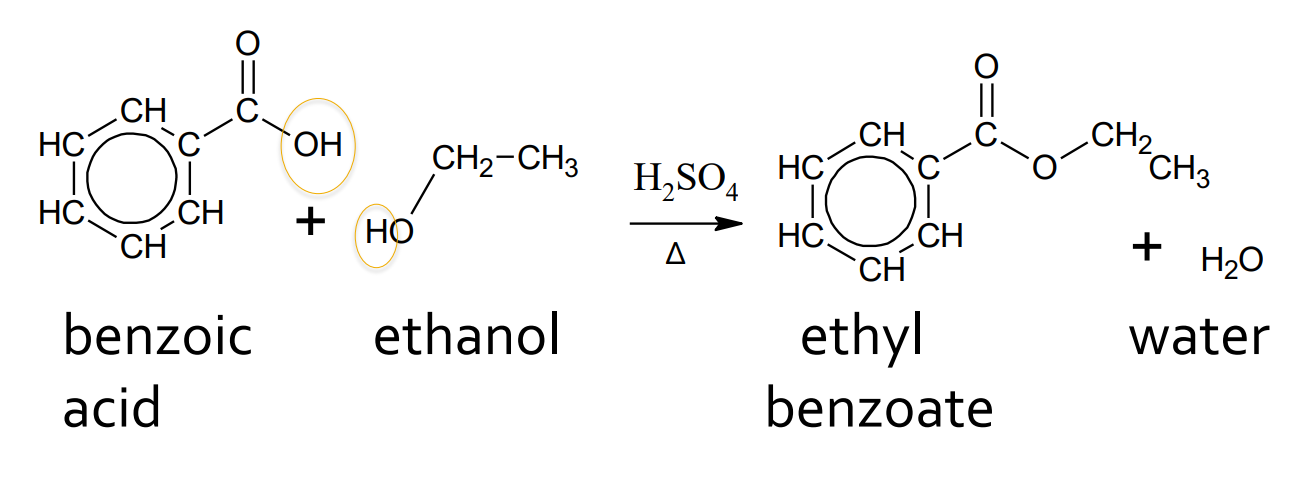
Esterification - Alcohol and benzoic acid
catalyst: H2SO4 and water
products: ester and water
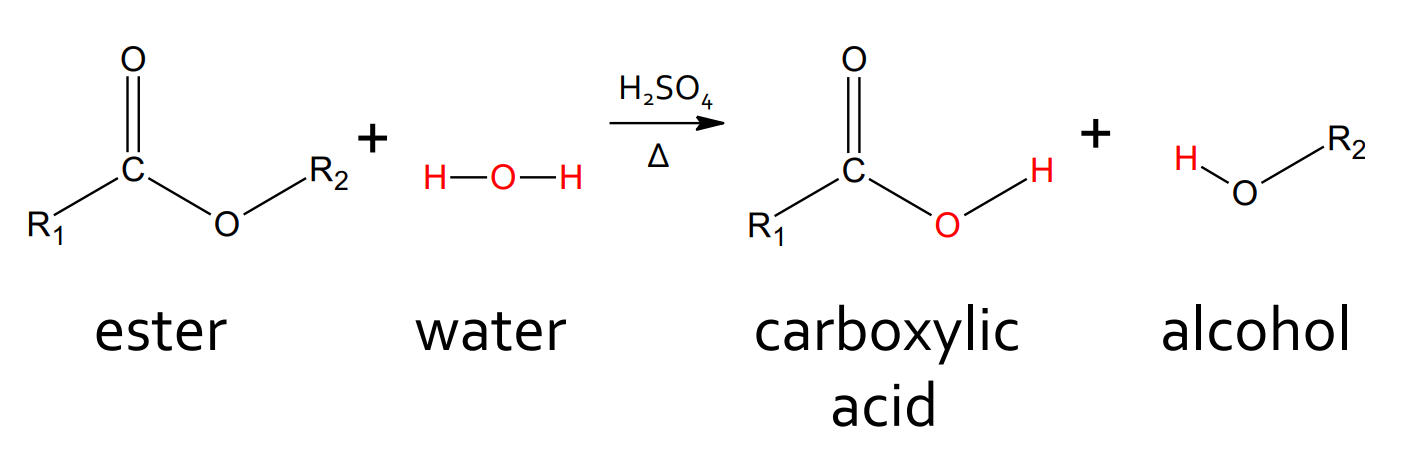
Hydrolysis - Ester and water
catalyst: H2SO4 and heat
products: alcohol, carboxylic acid
reversible
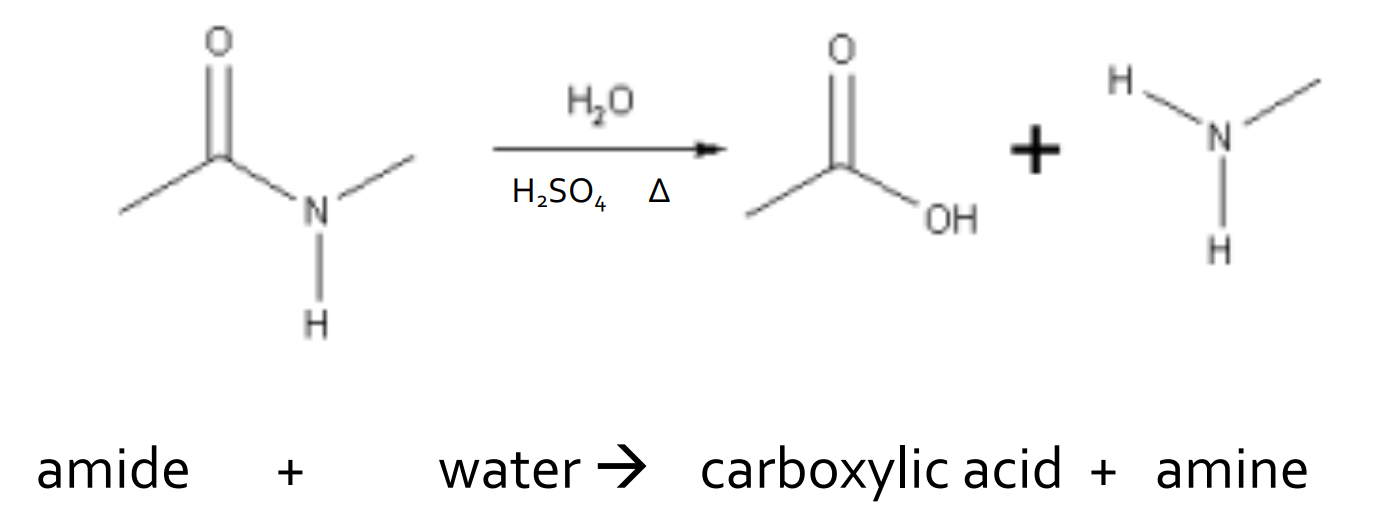
Hydrolysis - Amide and water
catalyst: H2SO4 and heat
products: amine and carboxylic acid
reversible
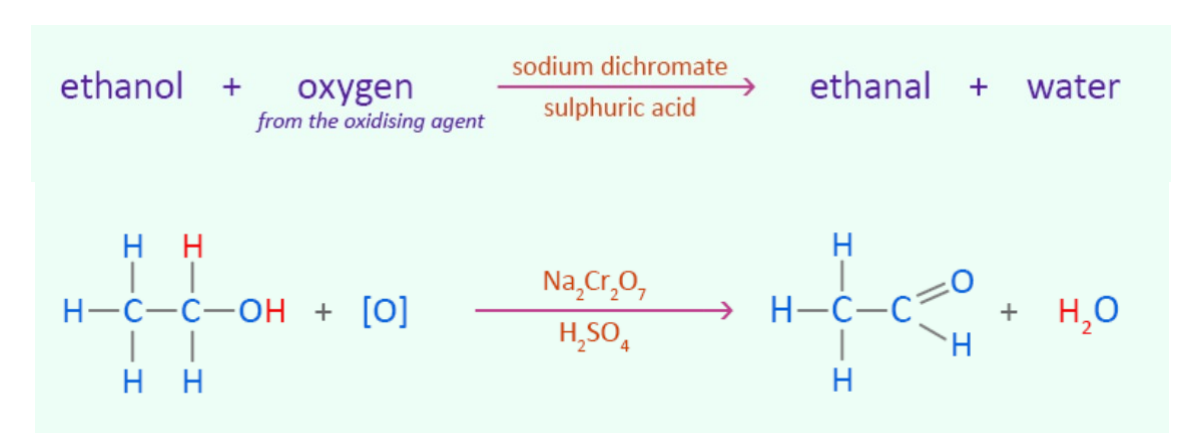
Oxidation - Primary alcohol and oxidizing agent
oxidizing agent: KMnO4 or K2Cr2O7
products: aldehyde + water
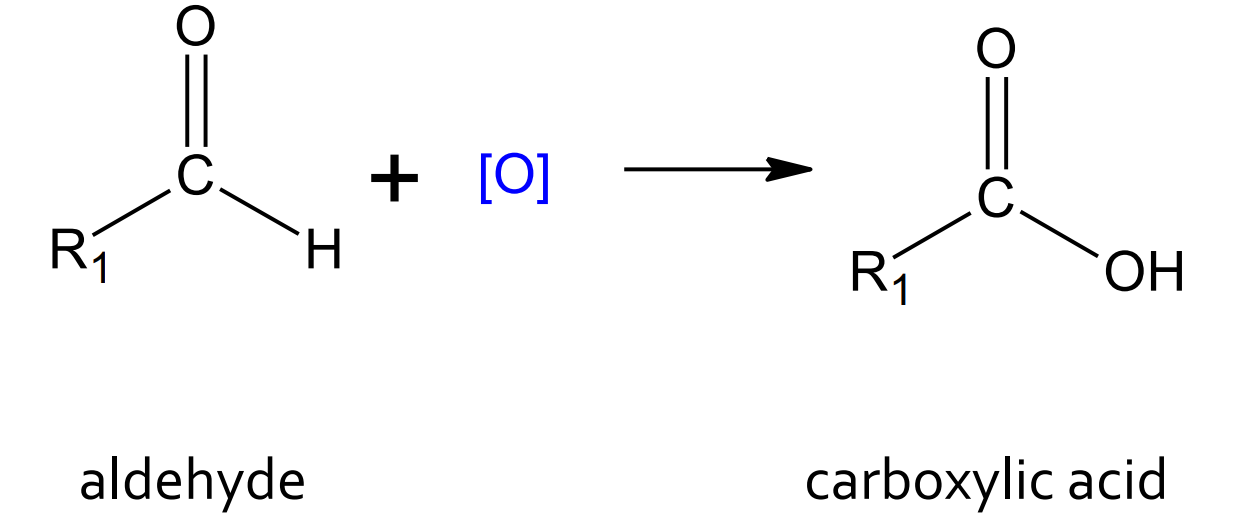
Oxidation of an aldehyde
product: carboxylic acid
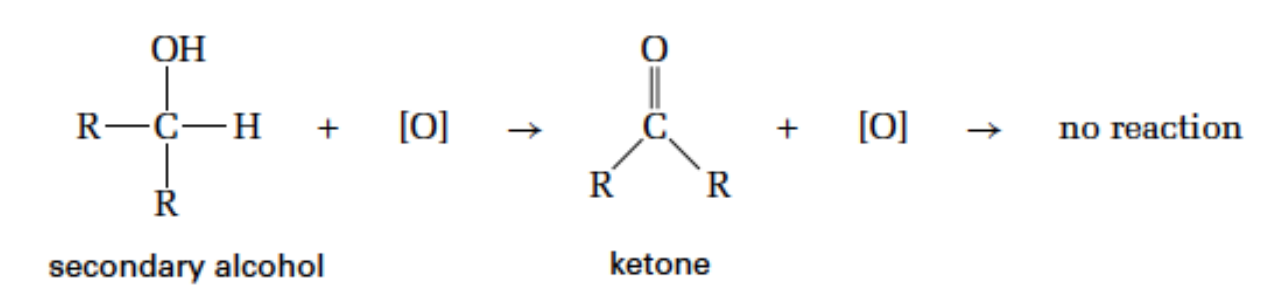
Oxidation - Secondary alcohol
product: ketone
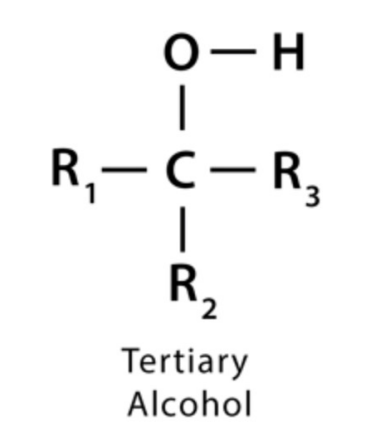
Oxidation - Tertiary alcohol
A tertiary alcohol cannot be oxidized. There is no hydrogen available to be removed. C-C bonds are too strong to be broken by an oxidizing agent.
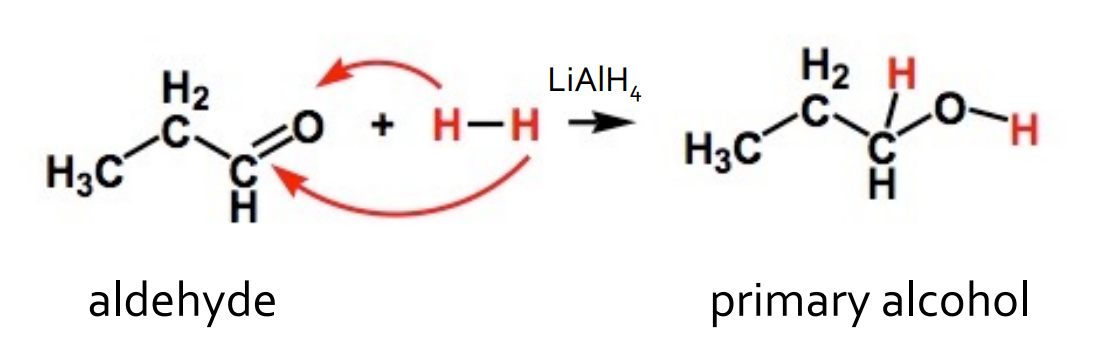
Reduction - Aldehyde with hydrogen
catalyst: LiAlH4 or H2/Pt
products: primary alcohol
Reduction - Ketone with hydrogen
catalyst: LiAlH4 or H2/Pt
products: secondary alcohol
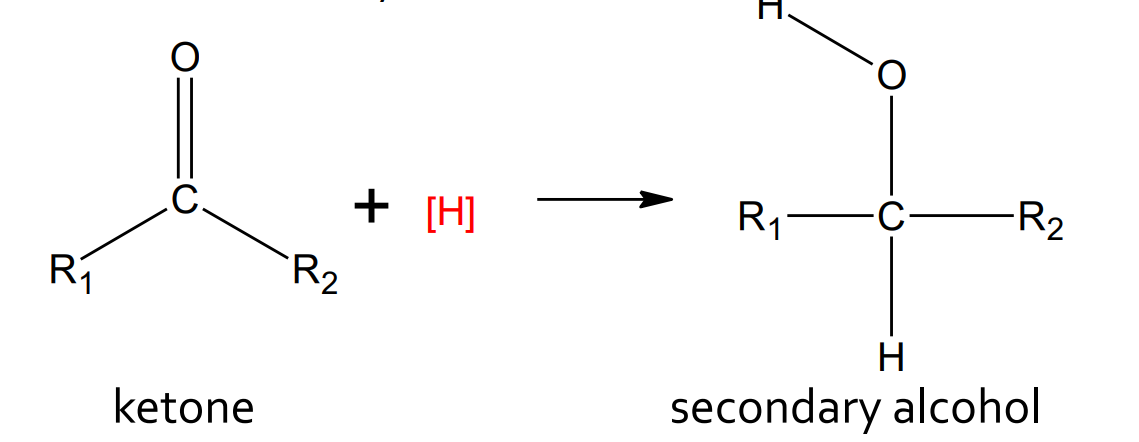
Reduction - Alkene with hydrogen
catalyst: LiAlH4 or H2/Pt
products: alkane