Psychology in Your Life: Chapter 1, 2, 3
1/304
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
305 Terms
Psychology
Study of mental activity/behavior; based on brain processes.
-Mental activity lets us perceive world(use senses) to take in info from outside ourselves
Behavior
All our actions that result from sensing/interpreting info
Critical Thinking
Systematically evaluating info to reach responsible conclusions supported by evidence.
1.) What am I being asked to believe or accept?
2.) What evidence is provided to support claim?
3.) What are the most reasonable conclusions?
Structuralism
-EDWARD TITCHENER & Wilhem Wund
-Early school of psychology that explored structures of the mind through introspection
-Based on idea that conscious experience can be broken down into underlying parts
-Components of conscious mind
Functionalism
WILLIAM JAMES & Charles Darwin
Concerned with adaptive purpose/function of mind/behavior
James argued that the mind is much more complex than its elements and couldn't be broken down
Goal to describe how conscious mind aids adaption to an environment
Psychoanalytic Theory
Sigmund Freud
Try to understand connection between psychology and physical problems
Used psychoanalysis to treat unconscious mental forces that conflicted with acceptable behavior and produce psychological disorders
Goal to understand how unconscious though cause psychological disorders
Unconscious conflicts
Gestalt Theory
Max Wertheimer & Wolfgang Kohler
Developed in opposition to structuralism
Idea that whole of personal experience is different from simply the sum of its parts
Experiencing the "whole"
Different people view some object and have perceptual experience and then seeing the same object differently each time
Behaviorism
JOHN B. WATSON & B.F. Skinner
Stimuli and responses
Emphasizes role of environmental forces in producing behavior
Investigate observable environmental effect on human and animal behaviors
Dominated psychological research into early 1960s
View furthered by thousands of psychologists including Skinner
Humanistic Psychology
Abraham Maslow & Carl Rogers
Focus on positives
Investigates how people grow to become happier and more fulfilled; focuses on people's basic goodness
How people are free to choose activities that make them fulfilled or happy
"Positive psychology"
Cognitive Psychology
George Miller & Ulric Neissler
Mental Activity
Learning not as simple as behaviorists believed
Study or how people think, learn, and remember
Language, attention, problem solving, decision making
Cognitive Neuroscience
Consists of cognitive psychologists, philosophers, computer scientists, and brain researchers
Biological Level of Analysis
How the physical body influences over our thoughts and behaviors
-Brain systems
-Neurochemistry
-Genetics
Individual Level of Analysis
Individual differences in personality and mental processes that affect perception and understanding
-Individual differences
-Perception and cognition
-Behavior
Social Level of Analysis
Investigating how groups affect people's interactions and people's influence on each other
-Interpersonal behavior
-Social cognition
Culture Level of Analysis
Explores how people's thoughts, feeling, and actions are similar or different across cultures/societies
-Norms,beliefs, values, symbols, ethnicity, religion
-Common language and environment transmitted through learning passed from generation to generation
Institutional Review Boards (IRB)
Groups of people responsible for reviewing proposed research to ensure that it meets accepted standards of science and provides for the physical and emotional well-being of research participant
-Privacy, confidentiality, informed consent, deception, and risks
Scientific Method
Systematic procedure observing and measuring observable things to answer questions about what happens, when it happens, what causes it, and why
Involves dynamic interaction between theories, hypotheses, and research methods
-Theory, hypothesis, testing hypothesis, analyze data, and report results
Theory
Model of interconnected ideas or concepts that explains what's observed/makes predictions about future events
Hypothesis
Specific prediction of what should be observed if a theory is correct
Descriptive Method
"Research method"
Provides systematic and objective description of what's occuring
Self-Report
Descriptive method consisting of obtaining self-reports from research participants
Questionnaires or surveys used for data from large group in short time
-Bias must be considered
Observational Study
Specific type of descriptive method involving systematically assessing/coding observable behavior
-Can be used in lab or natural environment
-Qualitative research
Case Studies
Involve intensive examination of a few unique people or organizations
-Commonly use people with psychological disorders
Correlational Methods
Examine how variables are naturally related in real world. Researchers make no attempt to alter variables or assign causation between them
-Measure 2 factors then determine degree of association between them
-Real world setting; not causality; directionality problem, third variable problem
Experimental Method
Test casual hypotheses by manipulating independent variable and measuring effects on dependent variables
-Provide control over dependent variables
Independent Variable
Variable that experimenter manipulates to examine its impact on dependent variable
Dependent Variable
Affected by manipulation of independent variable
Operational Definition
Detailed description of variables
Control Group
Comparison group in experiment
-No intervention given or receive intervention unrelated to independent variable being investigated
Experimental Group
1 or more treatment groups in experiment
-Receive intervention of independent variable being investigated
Confound
Anything that affects dependent variable that may unintentionally vary between the study's different experimental conditions
Random Assignment
Placing research participants in conditions of experiment so each participant has an equal chance of being assigned to any level of independent variable
Random Variable
Sample that fairly represents the population by allowing each member of population an equal chance of being included
Freud's thought about psychological and physical problems
Large extent of behavior is directed by mental processes that operate at a subconscious level
Empiricism
Approach to gaining knowledge about behavior and metal processes by observation and measurement only
Untrue about Modern Psychology
Few cognitive psychologists recognize the importance that the brain plays in cognition
Cycle of Scientific Method
Statistics help you determine whether your hypothesis is supported
Biological Psychology
Study how biological systems give rise to mental activity
"How do brain cells change during learning?"
"How do brain chemicals influence sexual behavior?"
Cognitive Psychology/Neuroscience
Study attention, perception, memory, problem solving, and language, often based on brain processes
"How do cell phone distract people when they drive?"
"What makes some problems harder to solve than other?"
Developmental Psychology
Study how people change from infancy through old age
"How do children learn to speak?"
"How can older adults maintain mental abilities as they age?"
Personality Psychology
Study enduring characteristics that people display overtime and across circumstances
"Why are some people shy?"
"How do genes, circumstances, and culture shape personality?"
Social Psychology
Study how people are affected by others
"When do people form impressions of others?"
"How do people form or dissolve intimate relationships?"
Cultural Psychology
Study how people are influenced by societal rules that dictate behavior in their culture
"How does culture shape the sense of self?"
"Does culture create differences in perception?"
Clinical Psychology
Study the factors that cause psychological disorders and the best methods to treat them
"What factors lead people to feel depressed?"
"How does the brain change as a result of therapy for depression?"
Industrial/Organizational Psychology
Study issues pertaining to industry and workplace
"How can building morale help motivate workers?"
"How can equipment be designed so workers can easily perform duties and avoid accidents?"
Pons
Hindbrain structure above medulla
Regulates sleep, arousal, and coordinates movements of the left and right sides of the body
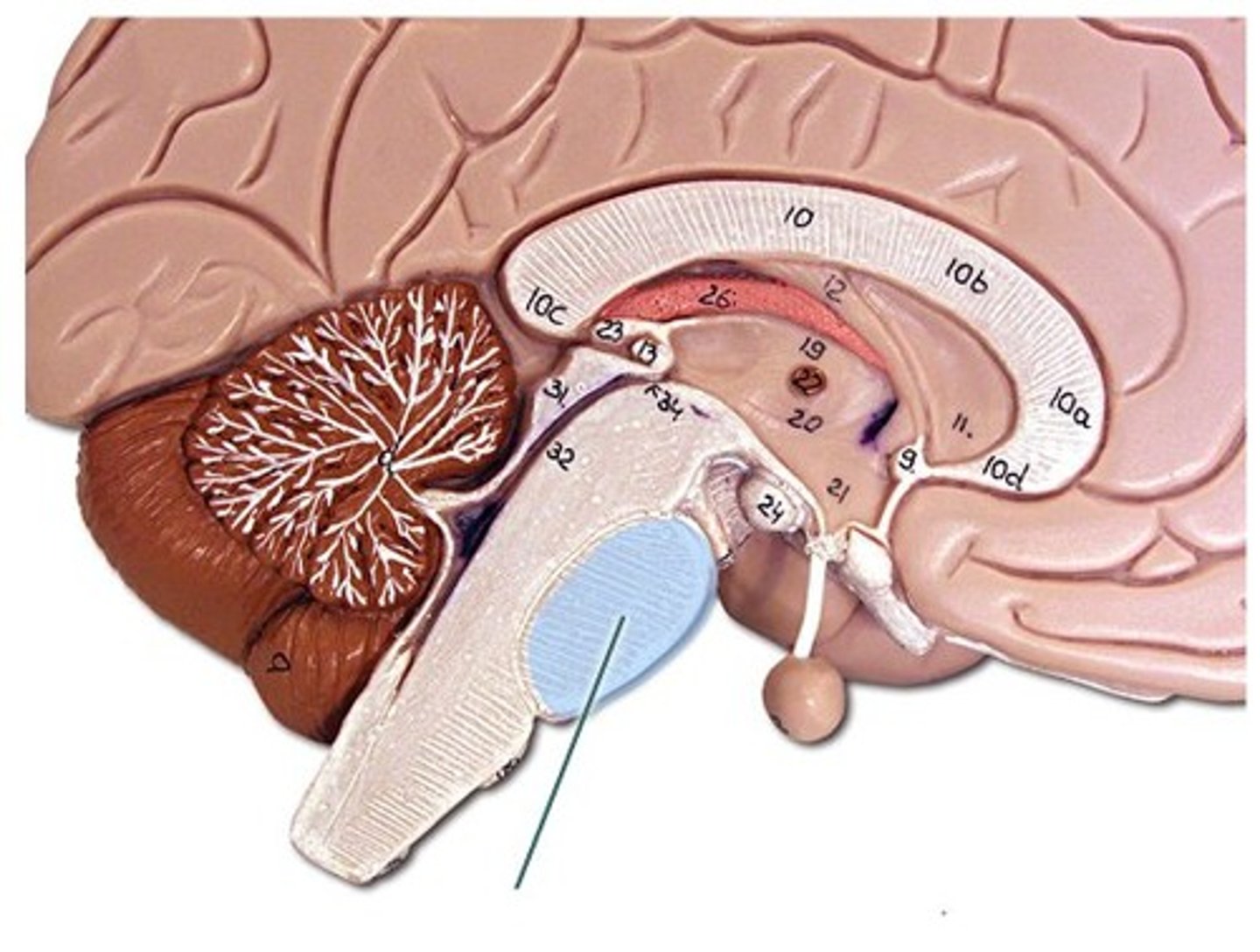
Temporal Lobes
Regions of cerebral cortex below parietal lobes and in front of occipital lobes
Important for processing auditory info and for perceiving objects and faces
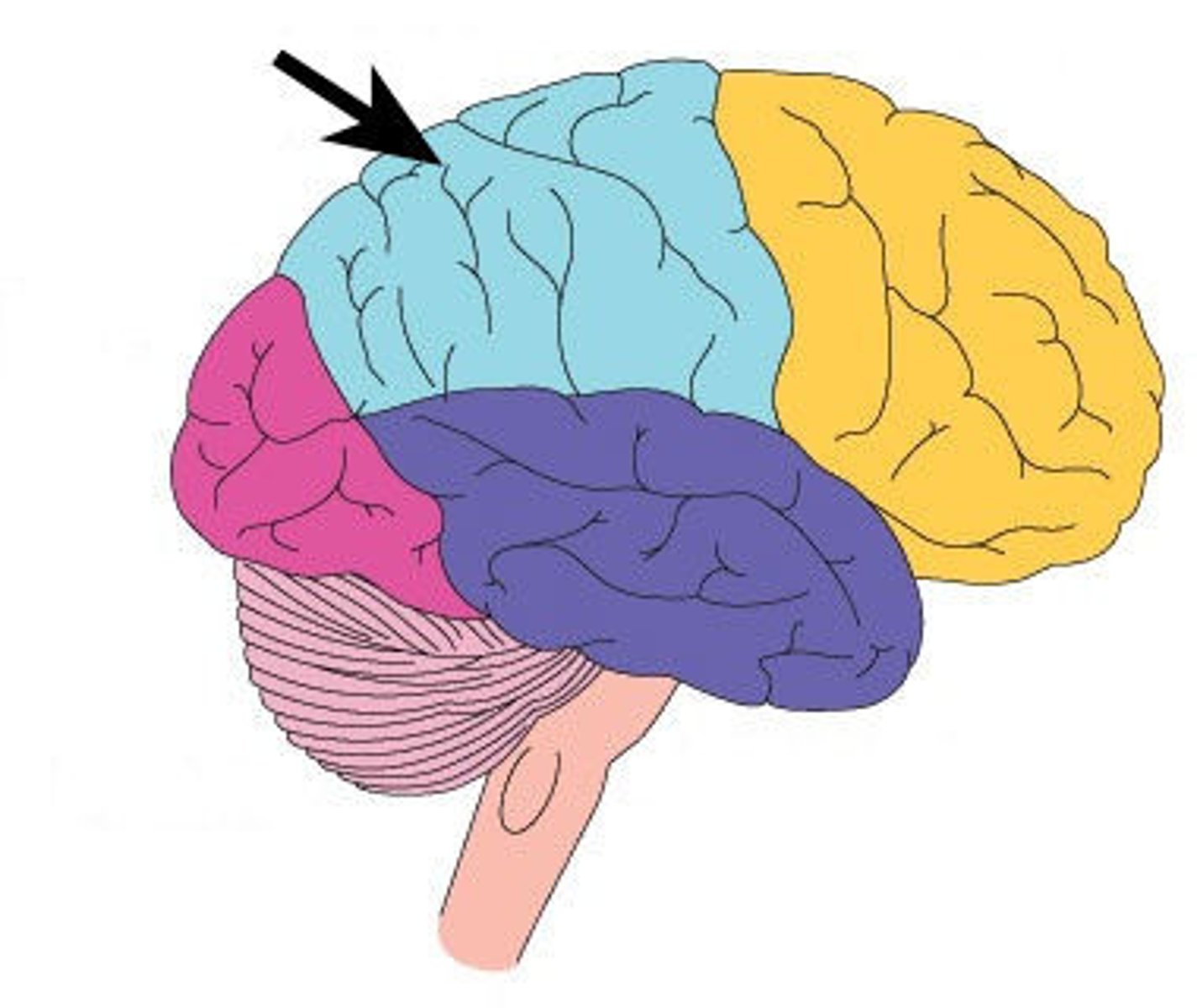
Occipital Lobes
Regions of cerebral cortex at back of brain
Important for vision
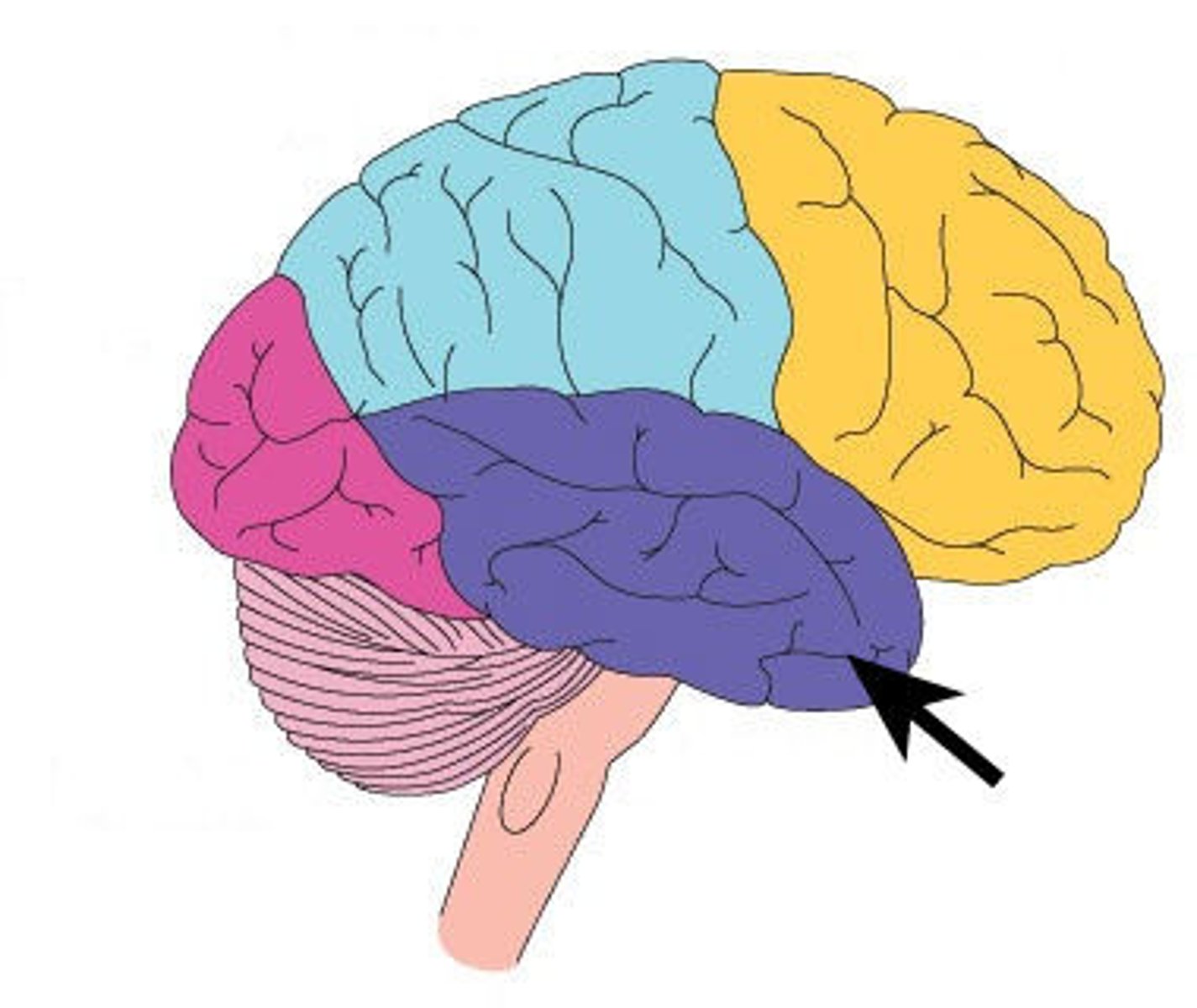
Parietal Lobes
Regions of cerebral cortex in front of occipital lobes and behind frontal lobes
Important for sense of touch and for picturing layout of spaces in an environment
"Homunculus"
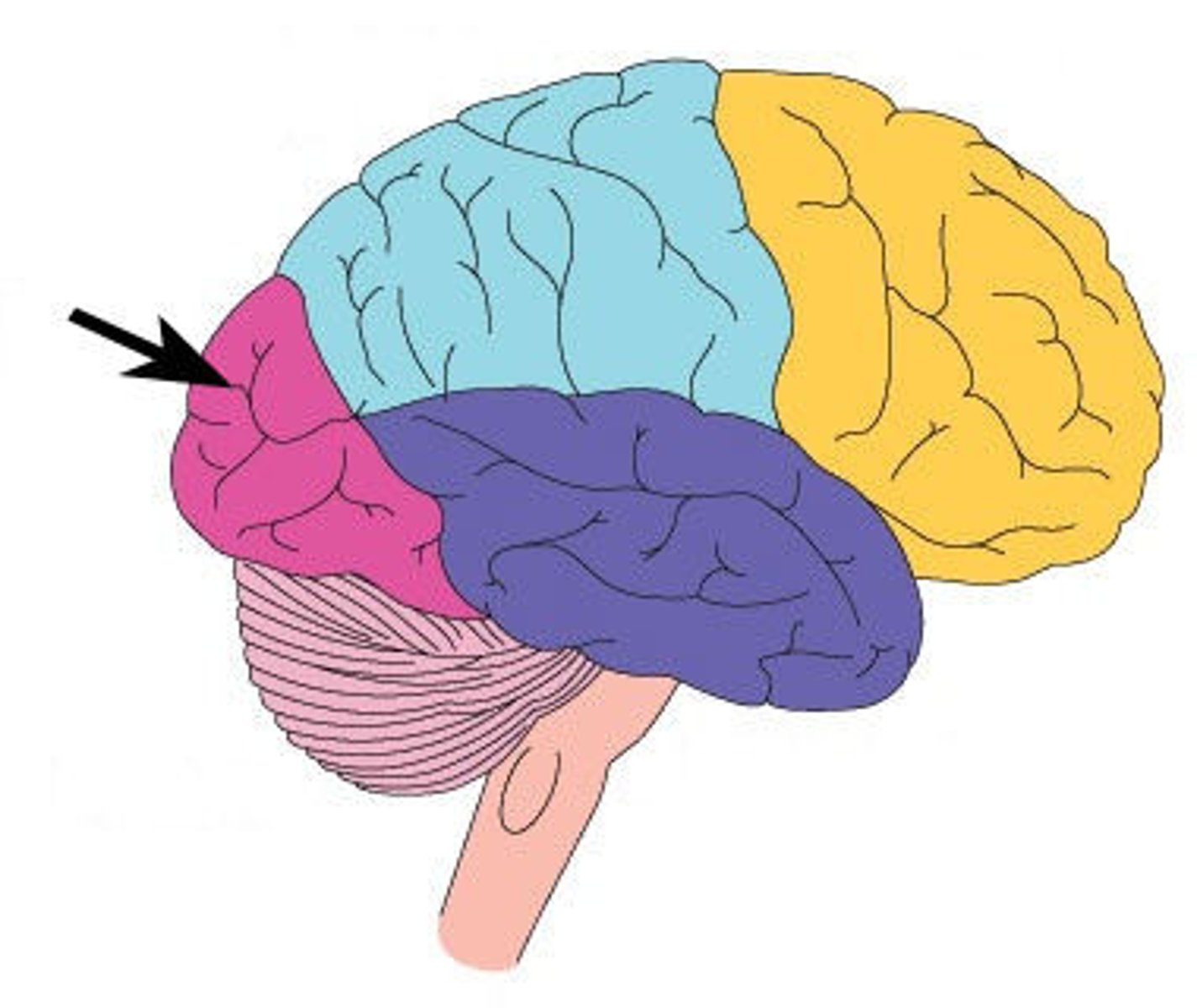
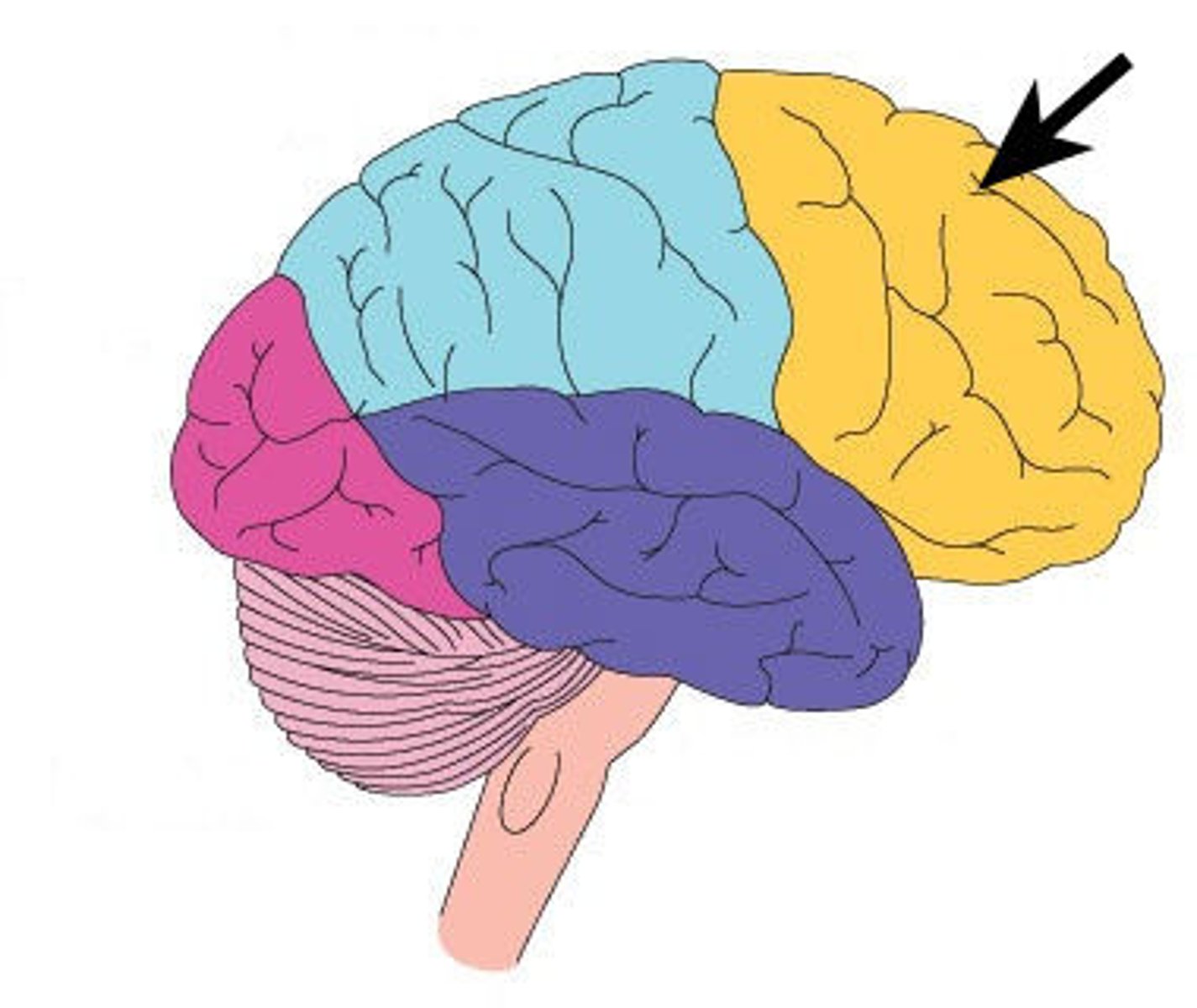
Frontal Lobes
Regions of cerebral cortex at front of brain
Important for movement and complex processes
-Rational thought, attention, social processes
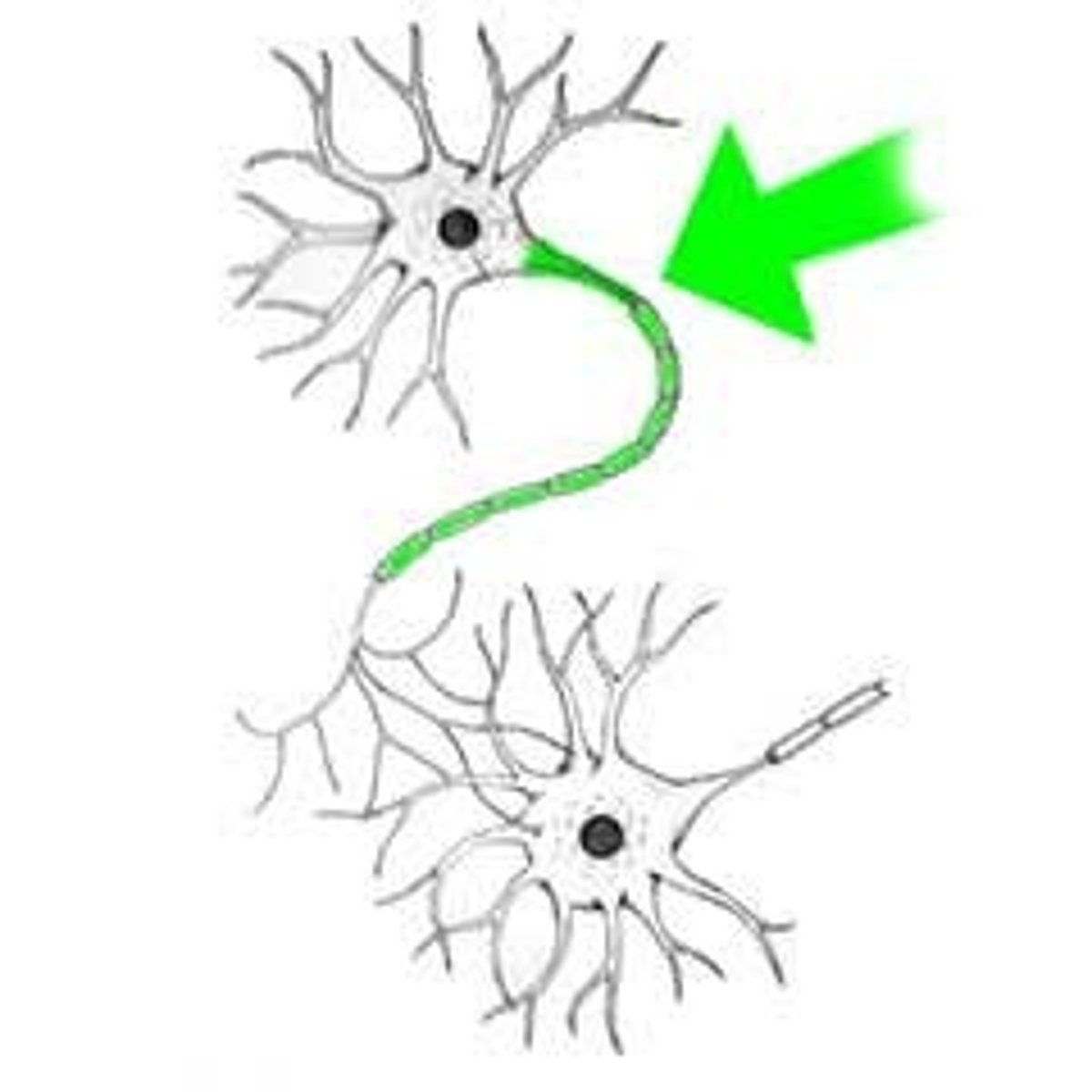
Neuron Communication
Transmission~ When enough stimulation in presynaptic neuron to create action potential travels quickly down myelinated axon to terminal button
Reception~ Action potential causes neurotransmitters to be released from terminal buttons at end of the axon. Neurotransmitters cross synapse and fit into receptors in dendrites of postsynaptic neuron
Integration~ Each neurotransmitter has either excitatory or inhibitory effects on post synaptic neuron that's summed up in cell body. If enough action it'll lead to another action potential
Neurons
Basic unit of nervous system; cells that receive, integrate, and transmit info in nervous system
Operate through electrical impulses, communicate with other neurons through chemical signals, and for neural networks
-Can't fire only a little bit, either fires or doesn't at all
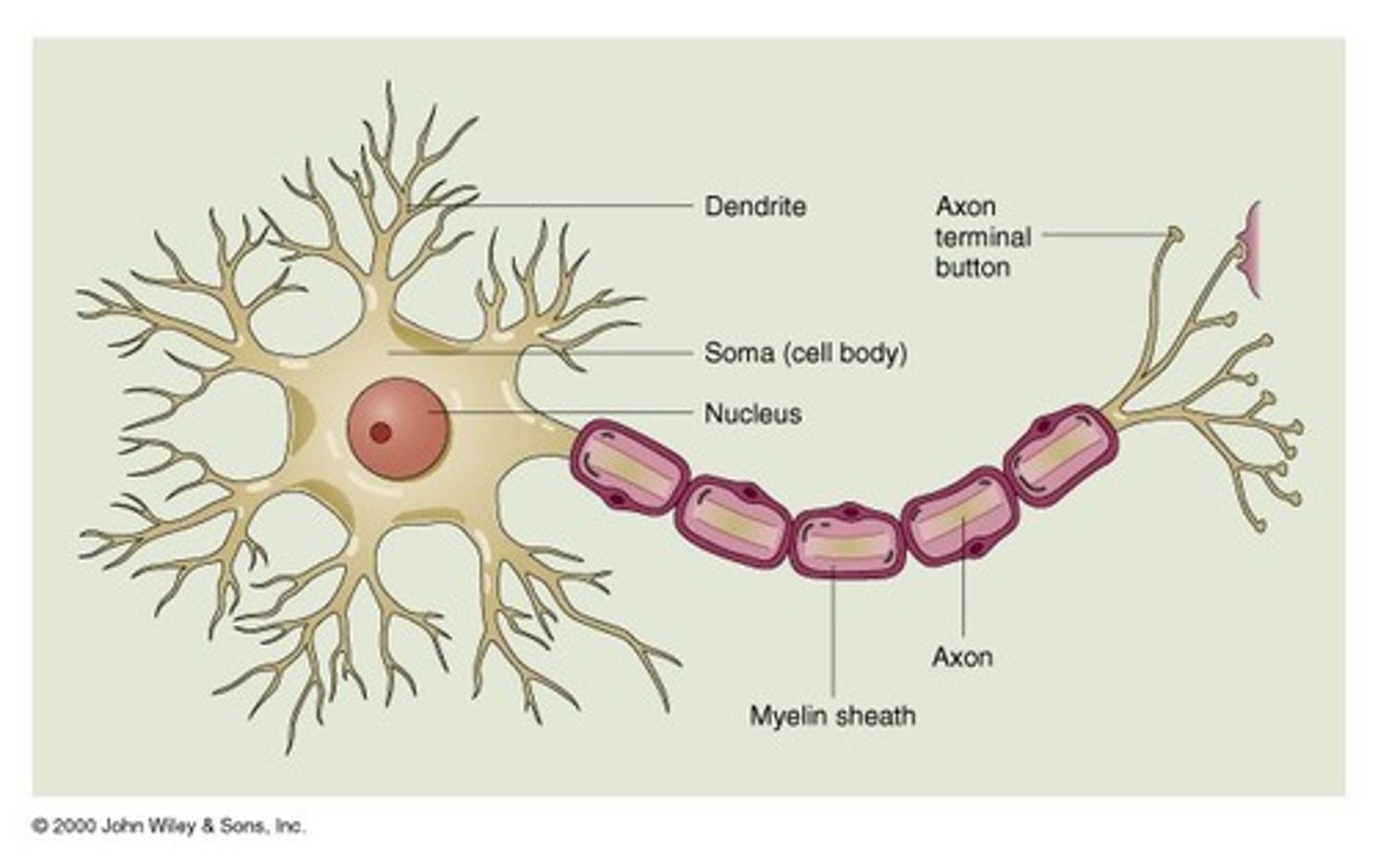
Cell Body
Part of neuron where info from thousands of other neurons are collected and integrated
Axon
Long, narrow outgrowth of neuron that enables it to transmit info to other neurons
Myelin Sheath
Fatty layer that insulates the axon
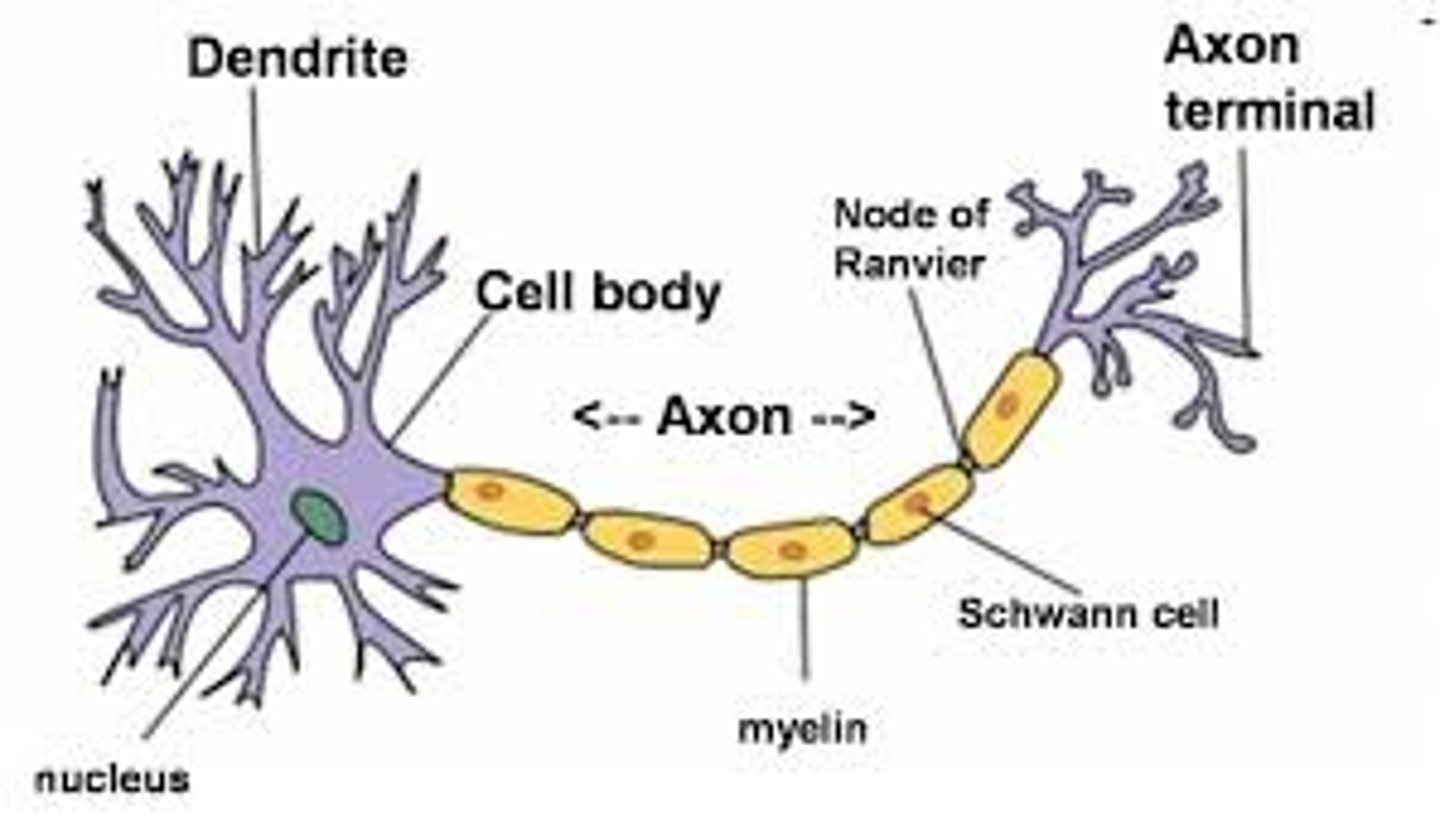
Dendrites
Branchlike extensions of neuron with receptors that detect info from other neurons
Synapse
Site of communication between neurons through neurotransmitters
-Don't actually touch
Action Potential
Neutral impulses that travel along axon then causes release of neurotransmitters into synapse
-During, sodium ions continue to enter neuron and potassium ions leave neuron
Action Potential Communication
1. Pass signals to receive neurons
2. Receive signals from neighboring neurons
3. Assess incoming signals
Pasticity
Property of brain that allows it to change as a result of experience, drugs, or injury
Reflects interactive nature of biological and environmental influences
Subjective Opinions
People have unique perspectives on events and ideas
Possible that some people find traits admirable and others not share shame opinion
Genetic Diseases
Huntington's disease is a genetic disorder that damages nervous system/ specific parts of the brain
Affects thoughts and behavior
Hormones
Chemical substances, released from endocrine glads, that travel through bloodstream to targeted tissues
Tissues are later influenced by hormones
Genes
Units of heredity
Partially determine an organism's characteristics
Monozygotic Twins
Identical Twins
Result from one zygote splitting in two
Share same genes
Dizygotic Twins
Faternal twins
Result from two separately fertilized eggs
No more similar genetically than non-twin siblings
Endocrine System
Communication System that uses hormones to influence thought and actions
Central Nervous System
Part of nervous system that consists of the brain and spinal cord
Nervous System
Network of billions of cells in brain and body that are responsible for all aspects of what we think, feel, and do
-Receive sensory input through senses
-Process info in brain by paying attention, perceiving, and remembering it
-Respond to info by acting on it
Peripheral Nervous System
Part of nervous system that enables nerves to connect central nervous system to muscles, organ, and glands
-Somatic
-Autonomic
-Sympathetic
-Para-sympathetic
Autonomic Nervous System
Part of peripheral nervous system
Transmit sensory signals and motor signals between central nervous system and body's glands and internal organs
Two divisions-sympathetic and parasympathetic
Sympathetic
Control activity of organs and glands
Prepares body for action
Parasympathetic
Control activity of organs and glands
Returns body to resting state
Somatic Nervous System
Part of peripheral nervous system
Transmits sensory signals and motor signals between central nervous system and skin, muscles, and joints
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI)
Measures changes in blood oxygen level
-A technology that uses magnetic fields to detect activity in the brain by monitoring blood flow.
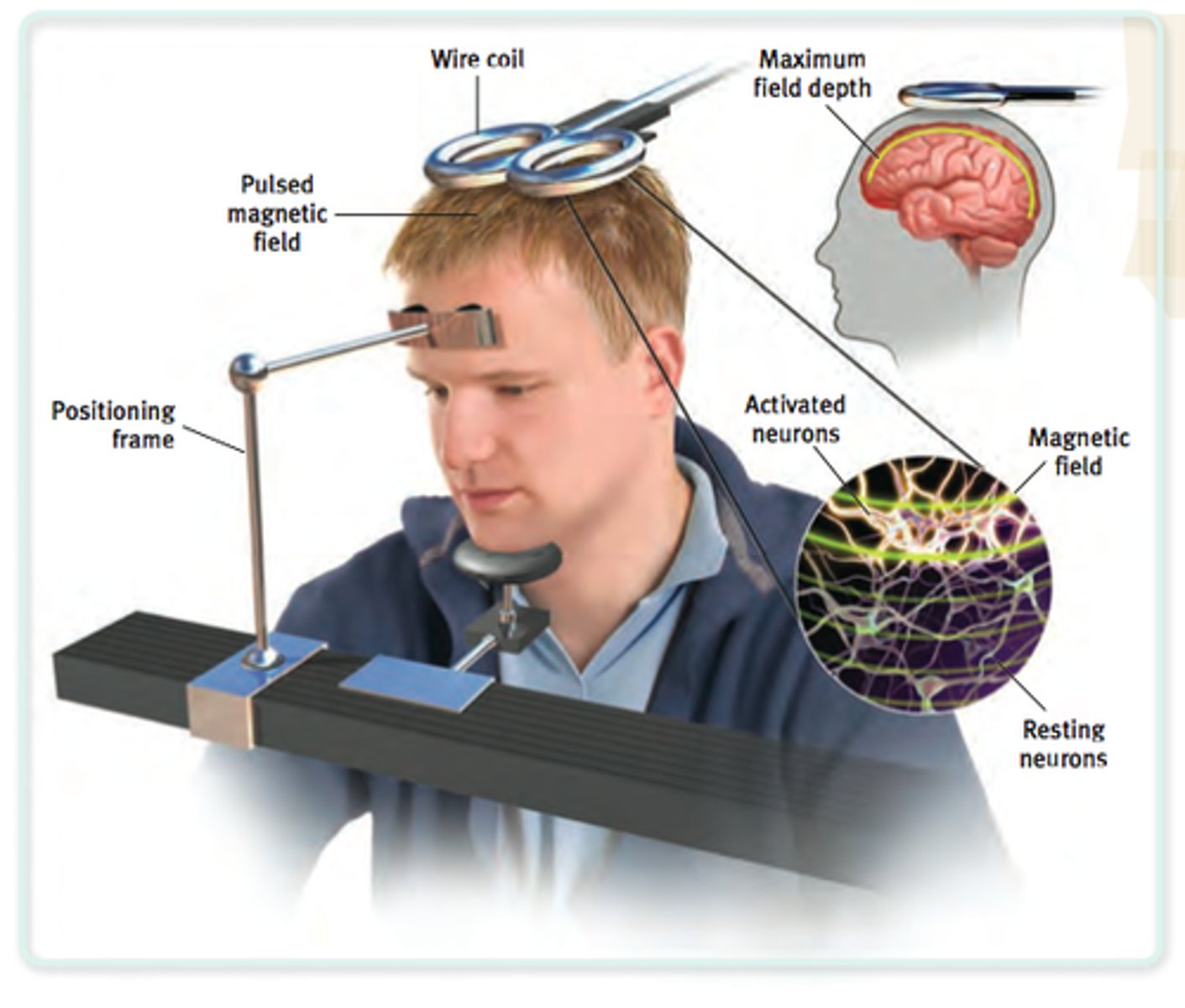
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS)
Uses very fast and powerful magnetic field to momentarily disrupt activity in specific brain region
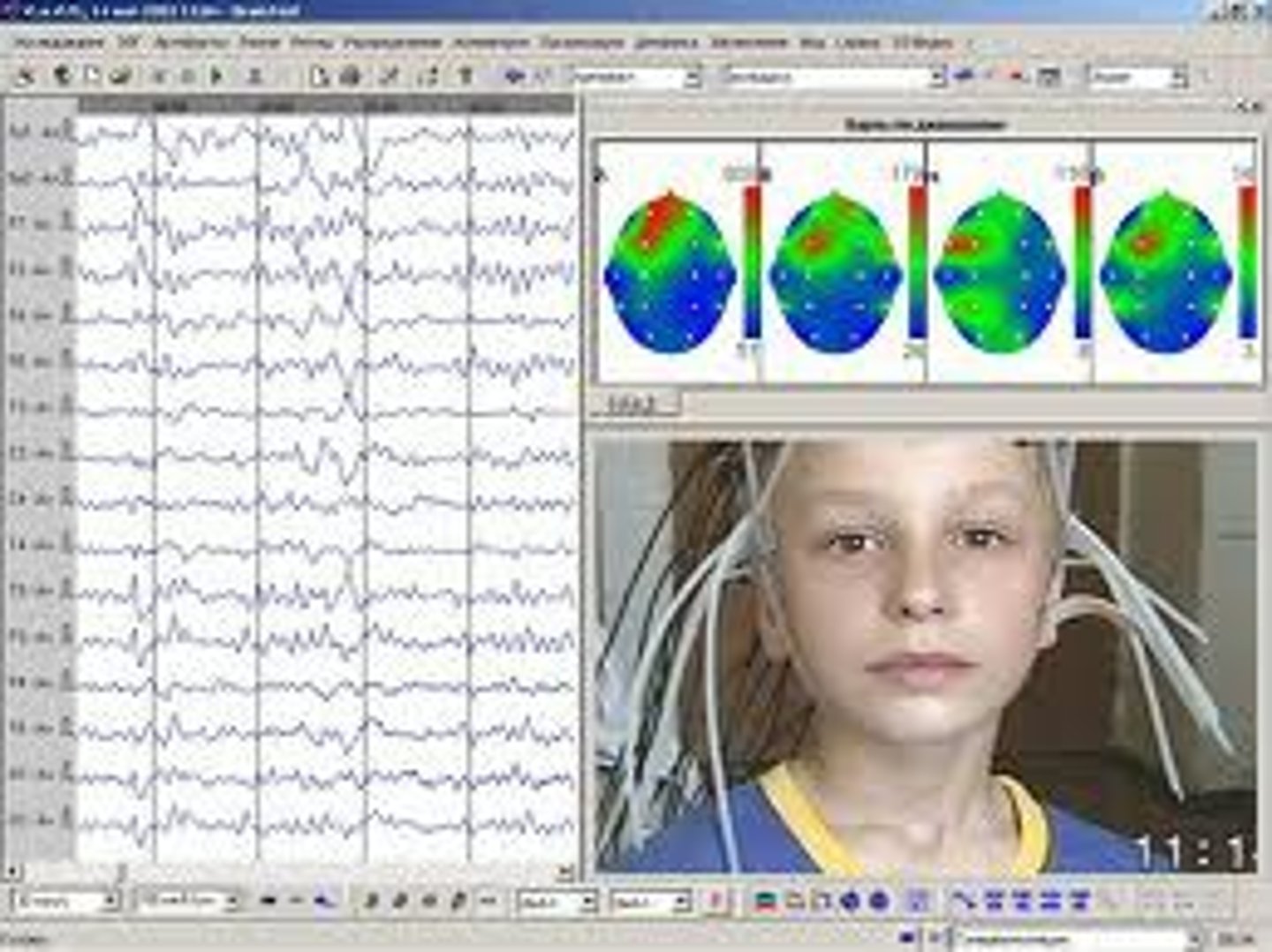
Electroencephalograph (EEG)
instrument used to record the electrical impulses of the brain
-different behavioral states produce different and predictable EEG patterns
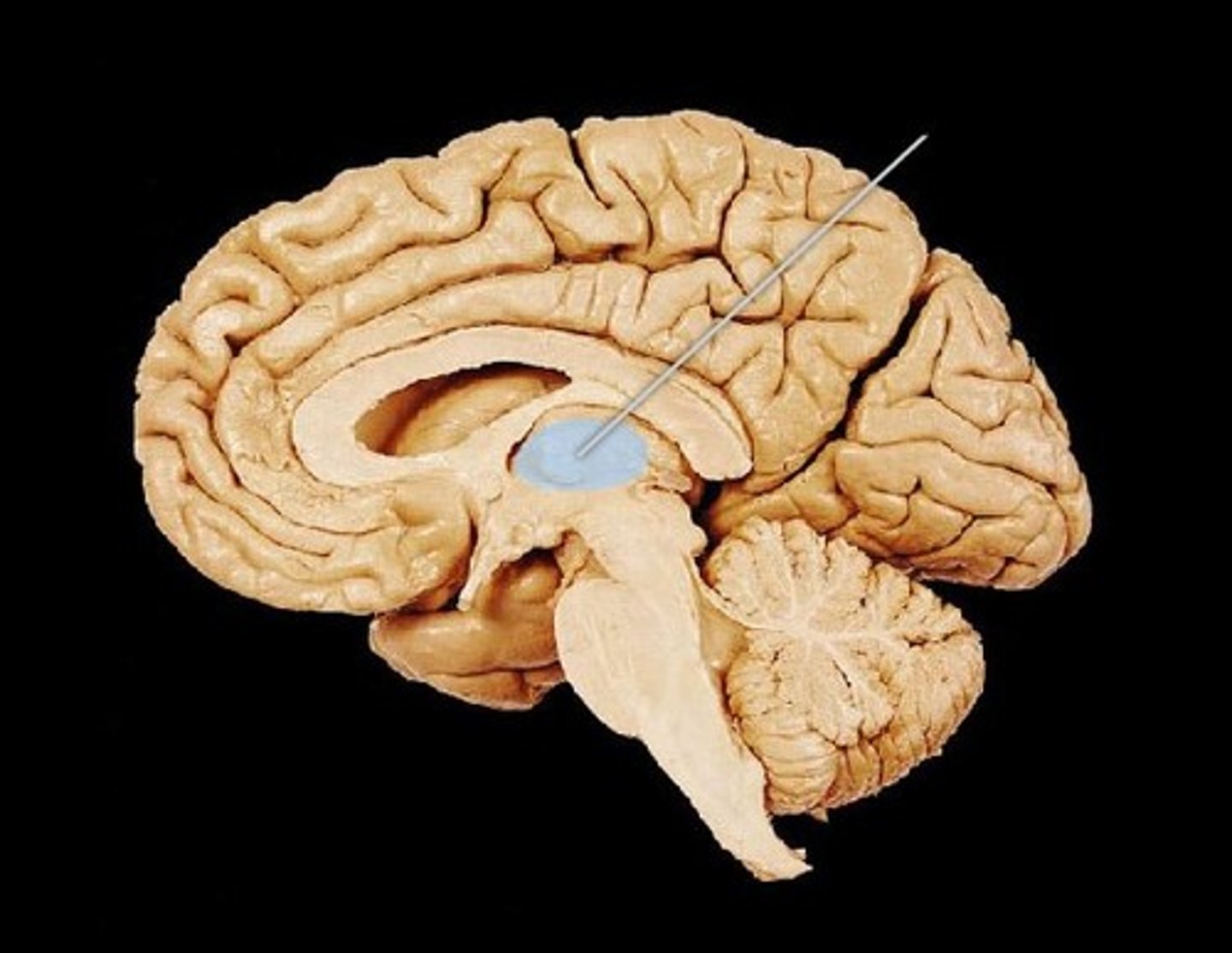
Thalamus
Subcortical forebrain structure
Gateway to brain for almost all incoming sensory info before that info reaches cortex
Cerebral Cortex
Outer layer of forebrain
Hemispheres are connected by corpus callosun
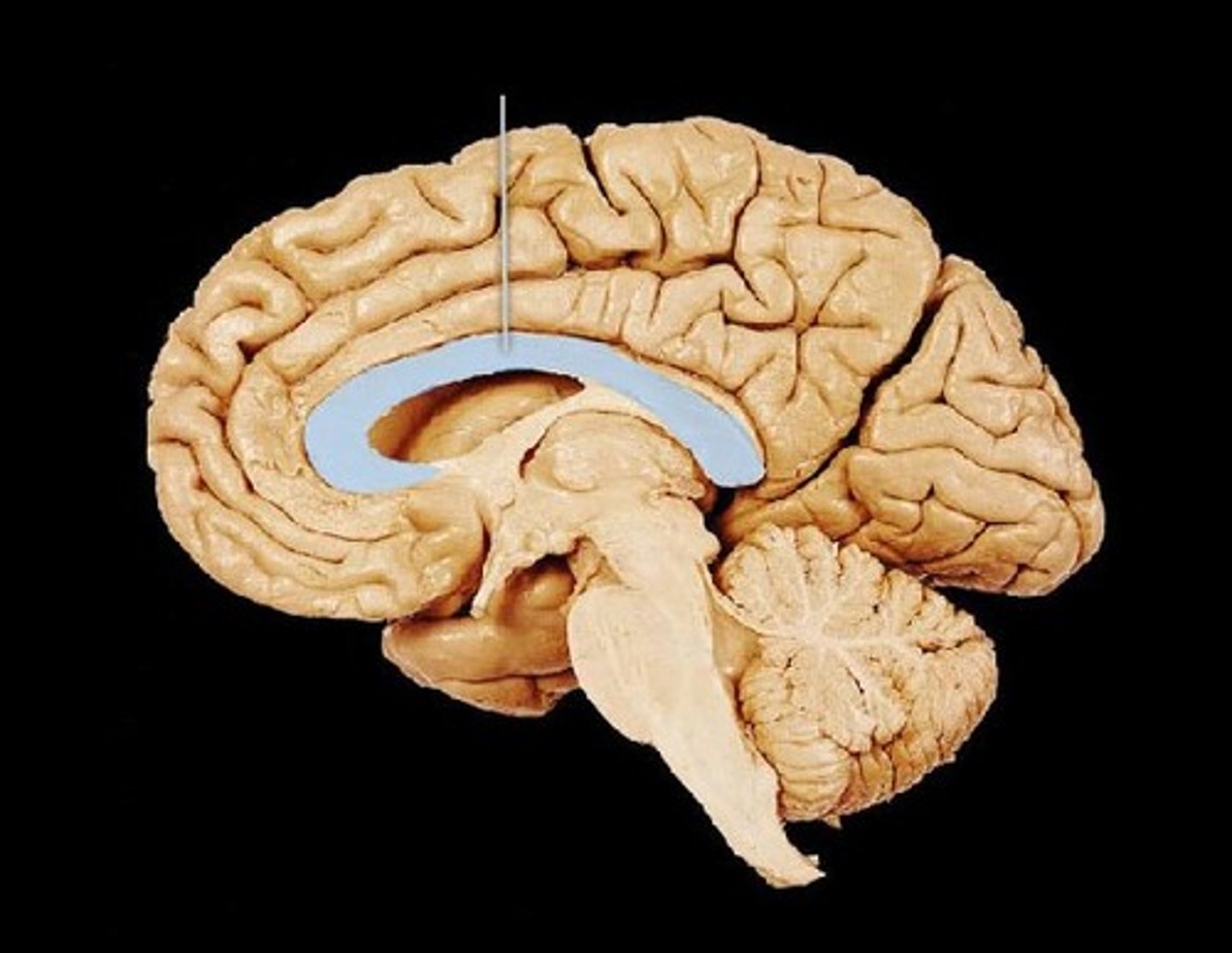
Corpus Callosum
Massive bridge consisting of millions of axons
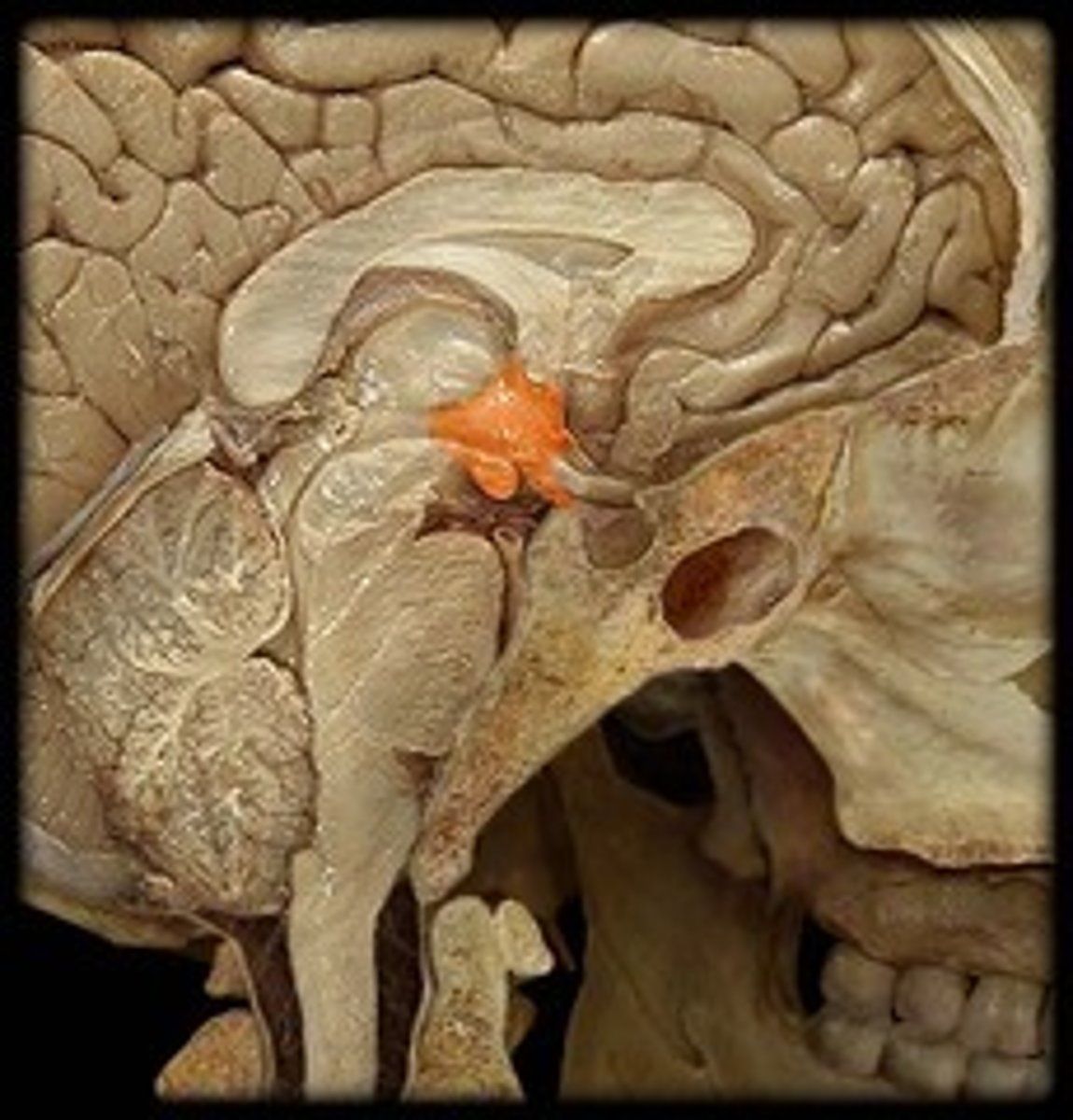
Hypothalamus
Subcortical forebrain structure involved in regulating bodily functions
Influences basic motivated behaviors
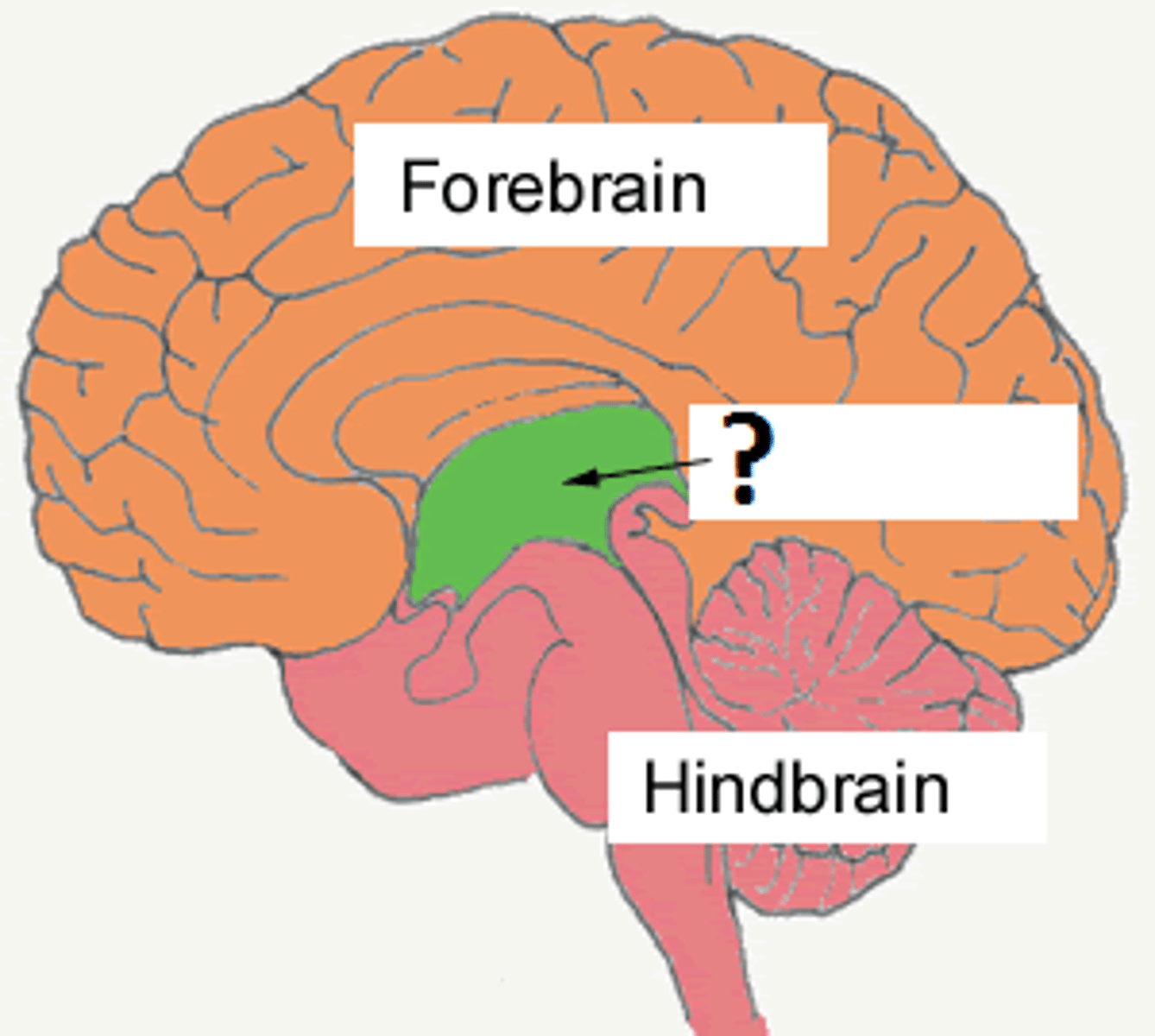
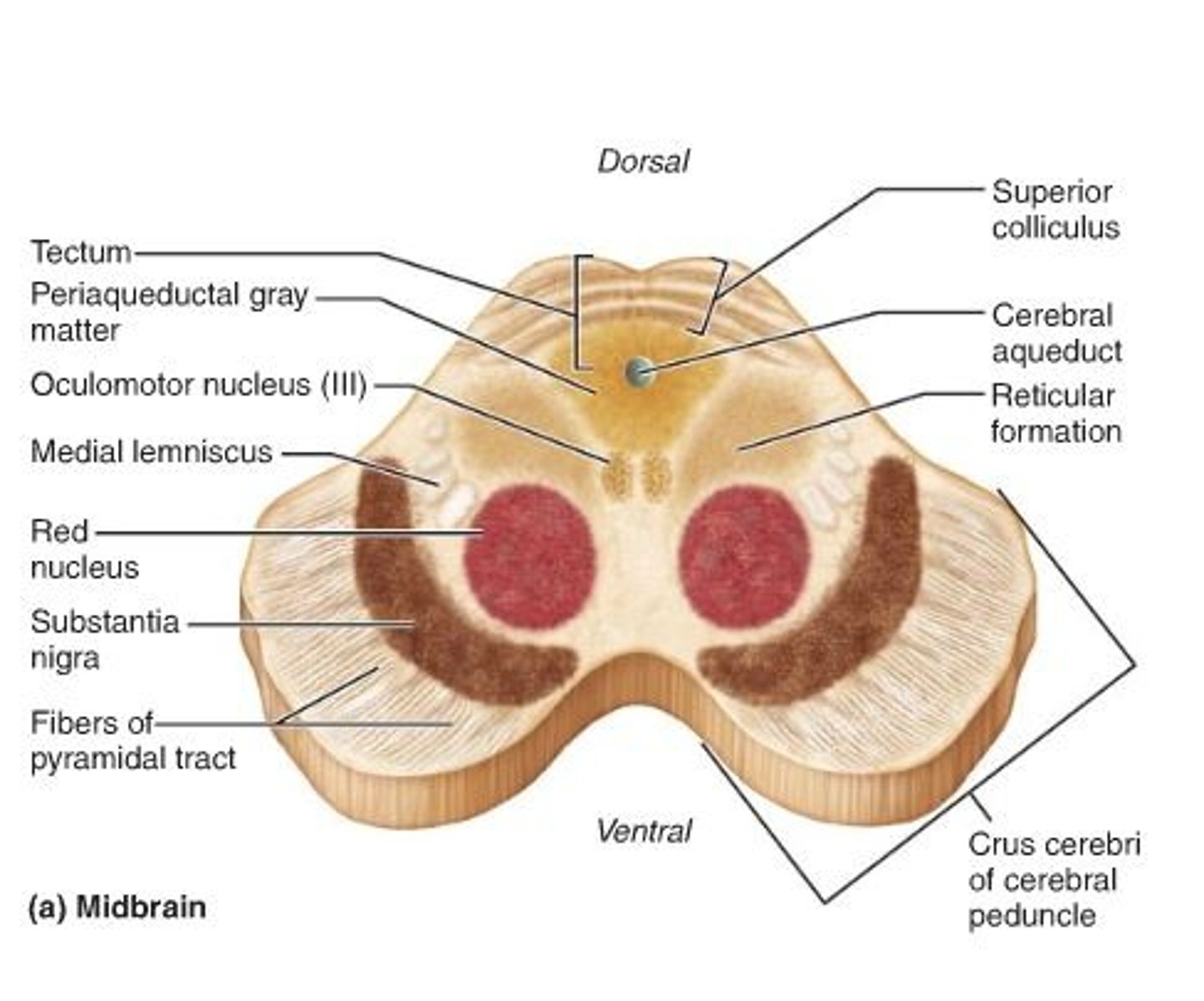
Midbrain
Involved in reflexive movement of eyes and body
Substantia Nigra
Initiation of voluntary motor activity
Region is critical for production of dopamine
Parkinson's caused by death of these cells and resulting in loss of dopamine produced by these cells
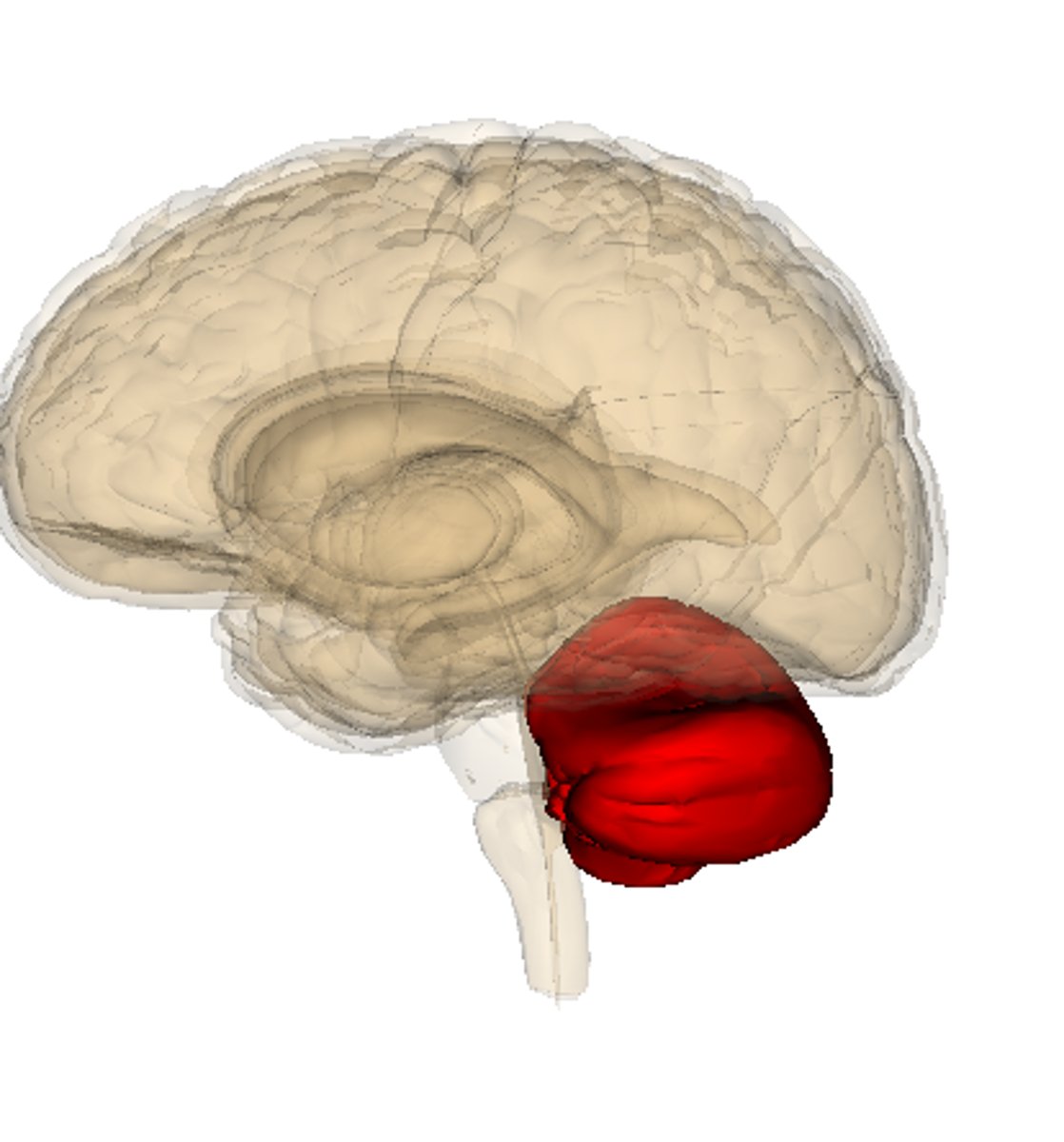
Cerebellum
Hindbrain structure at back of brain stem
Essential for coordinated movement and balance
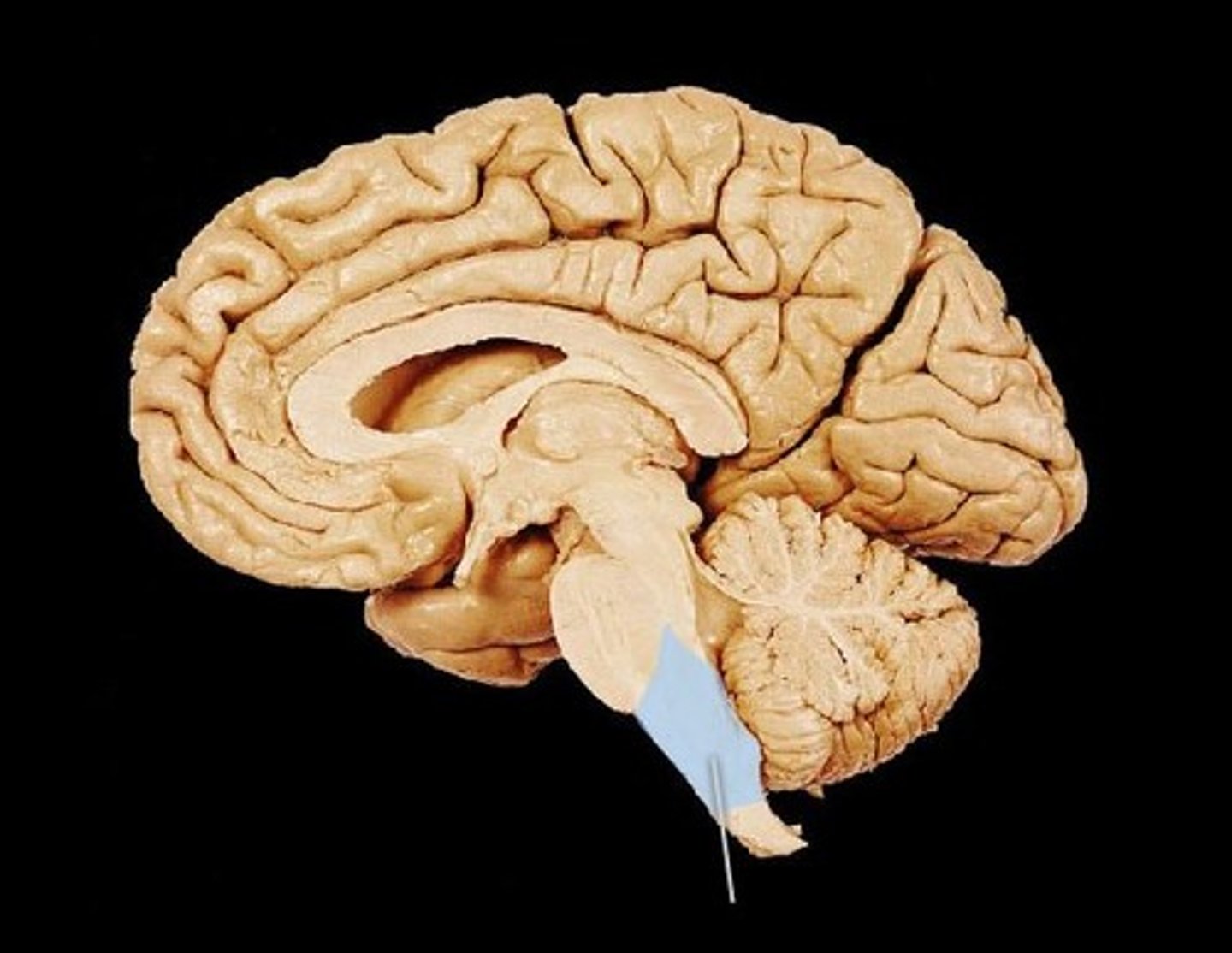
Medulla
Hindbrain structure at top of spinal cord
Controls survival functions such as breathing and heart rate
Hippocampus
Subcortical forebrain structure
Associated with formation of memories
Amygdala
Subcortical forebrain structure
Vital role in learning to associate things with emotional responses and in processing emotional info
Neurotransmitters
Chemical substances that carry signals from one neuron to another
Receptors
Removed from synapse~Reuptake and enzyme degradation
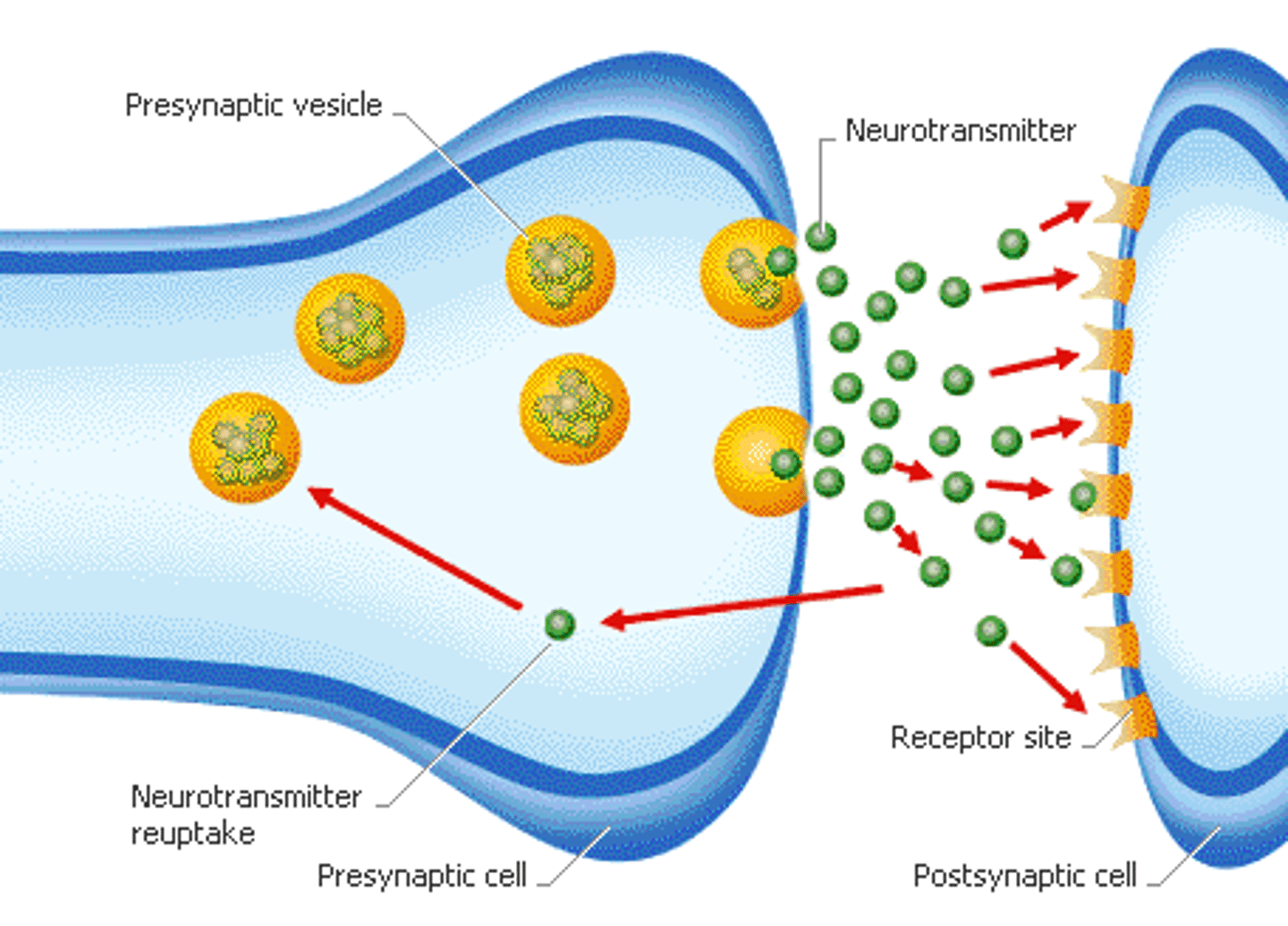
Receptors
Specialized sites that specifically respond to certain types of neurotransmitters
Norepinephrine
Precursor of epinephrine that is secreted by the adrenal medulla and also released at synapses.
Neurotransmitter involved in arousal, as well as in learning and mood regulation (alertness)
Epinephrine
Formally known as adrenaline
Neurotransmitter involved with energy
Dopamine
Motor control over voluntary movement
Reward and motivation
Neurotransmitter associated with movement, attention and learning and the brain's pleasure and reward system.
Seratonin
Emotional states, impulse control, dreaming
Neurotransmitter that affects mood, hunger, sleep, and arousal; linked to depression
GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid)
Inhibition of action potentials, anxiety reduction, intoxication (through alcohol)
Glutamate
Major excitatory neurotransmitter
Learning and memory
Enhancement of action potentials
Endorphins
Chemical substance that involves pain reduction
Reward
Phrenology
Franz Gall
Analysis of personality based on location and size of skull bumps
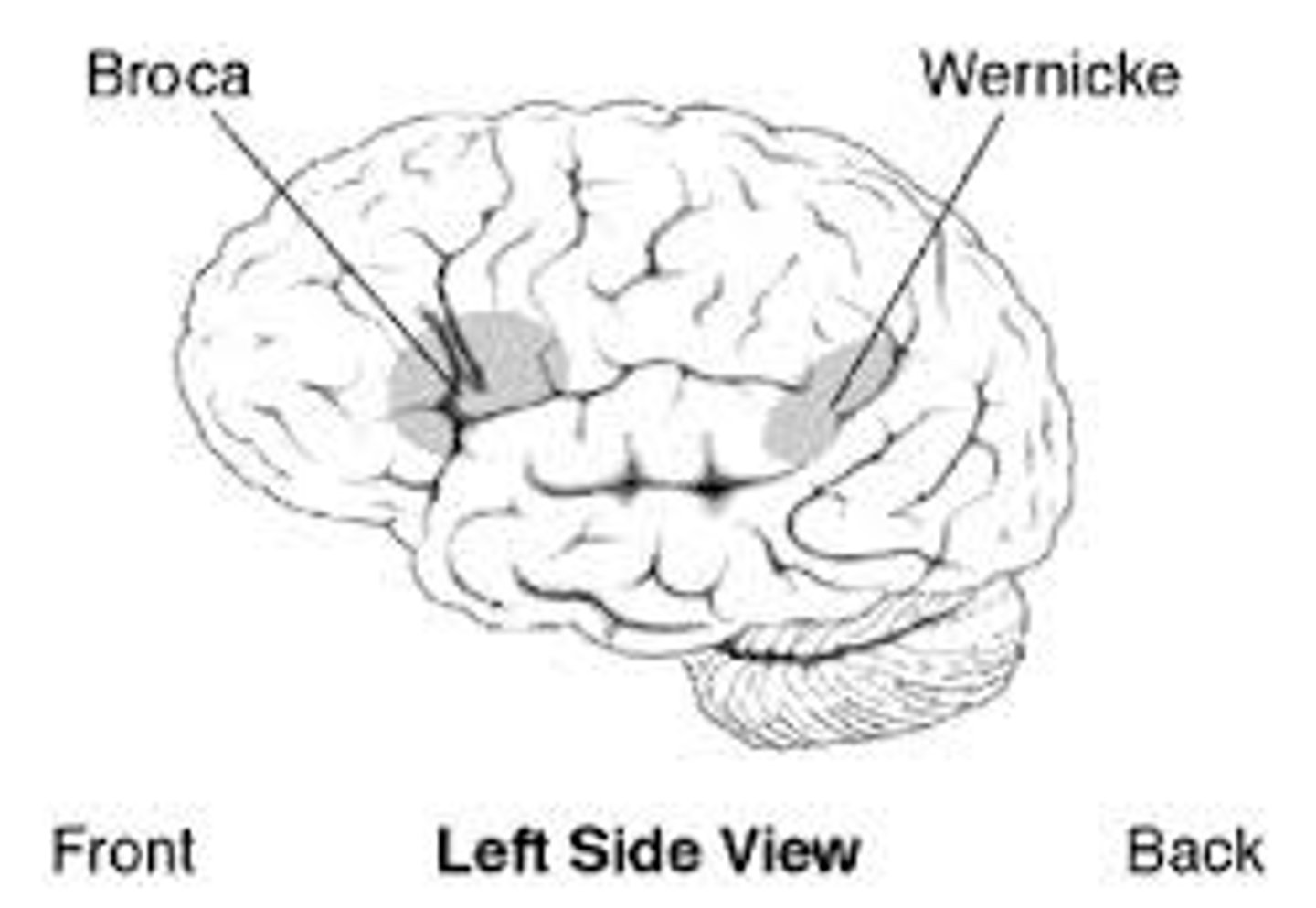
Broca's Area
Paul Broca
Small portion of left frontal region of brain
Crucial for producing speech
Acetylcholine
A neurotransmitter that enables learning, attention, sleeping, and memory and also triggers muscle contraction
Excitatory
Signal produced by postsynaptic neurons
Increase likelihood that it'll fire