Chapter 14: Firms in Competitive Markets
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Rank the market types from most competitive (& least concentrated) to least competitive (& most concentrated)
Perfect competition
Monopolistic competition
Oligopoly
Monopoly
Characteristics of perfect competition (PC) (4)
Lots of sellers
identical products
price takers
free entry and exit
Common examples of perfectly competitive markets
Agricultural markets
Commercial bakeries
Industrial markets
Screw, nut, and bolt manufacturers
Marginal revenue (MR)
MR = change in Total Revenue/change in Quantity
In perfect competition, MR =
Equilibrium price
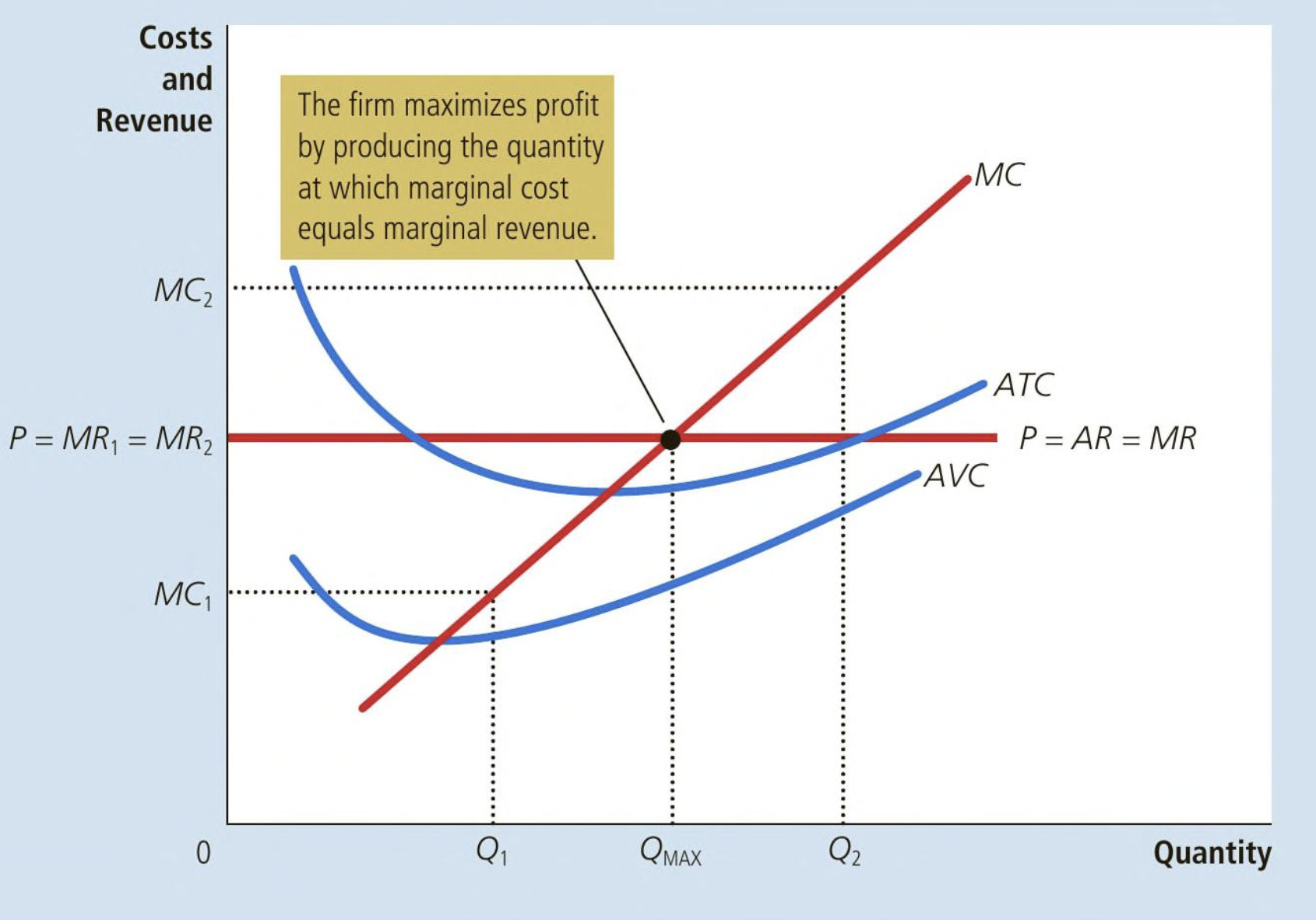
Profit-max rule & 3 rules for profit maximization
Keep producing until MR = MC
If MR > MC, firm should increase output
If MR < MC, firm should decrease output
At profit maximizing level, MR = MC
How to calculate/shade profit
profit = TR - TC
or profit = (P-ATC)q
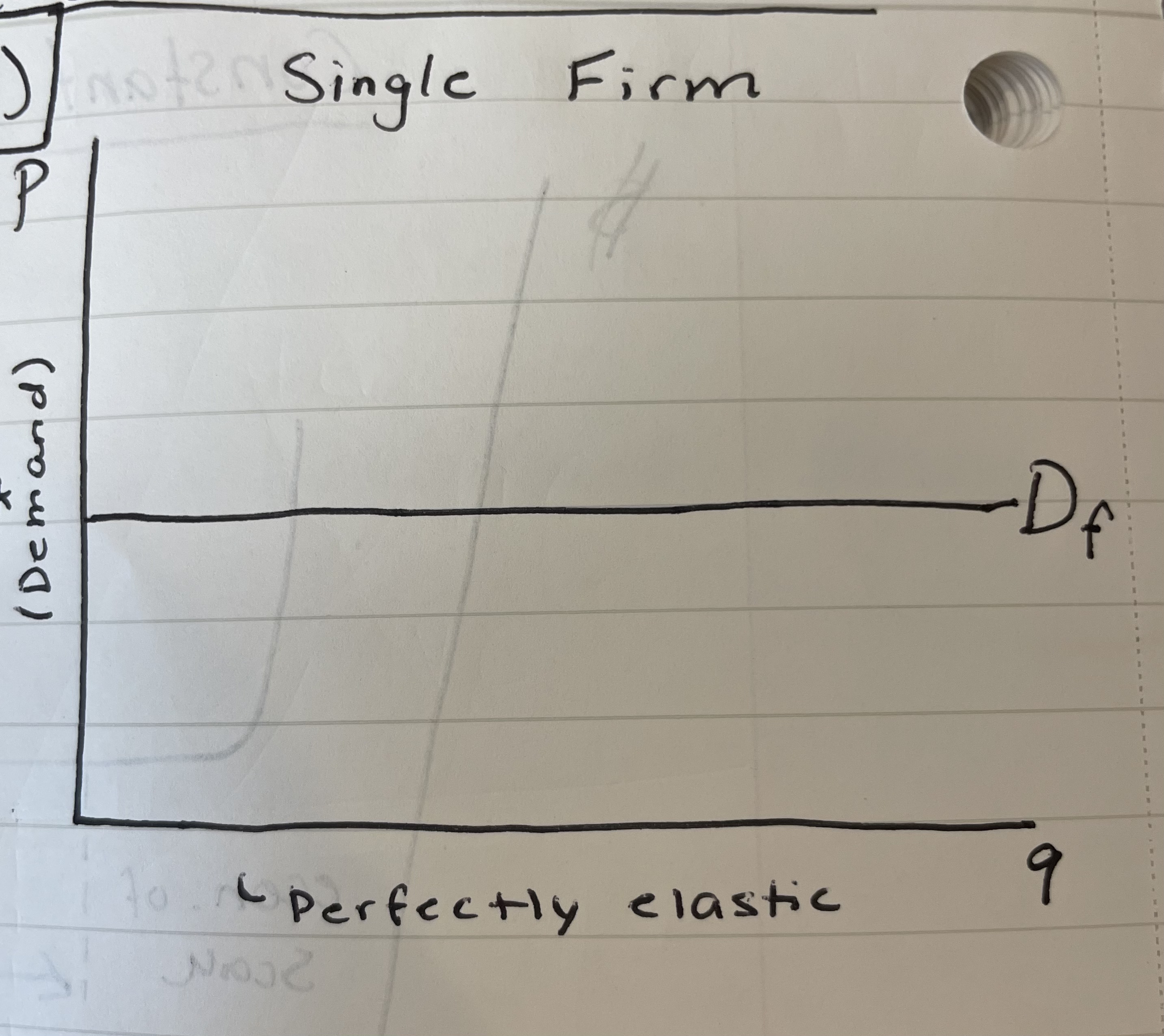
What does the demand for a single firm look like in perfect competition?
Perfectly elastic demand curve
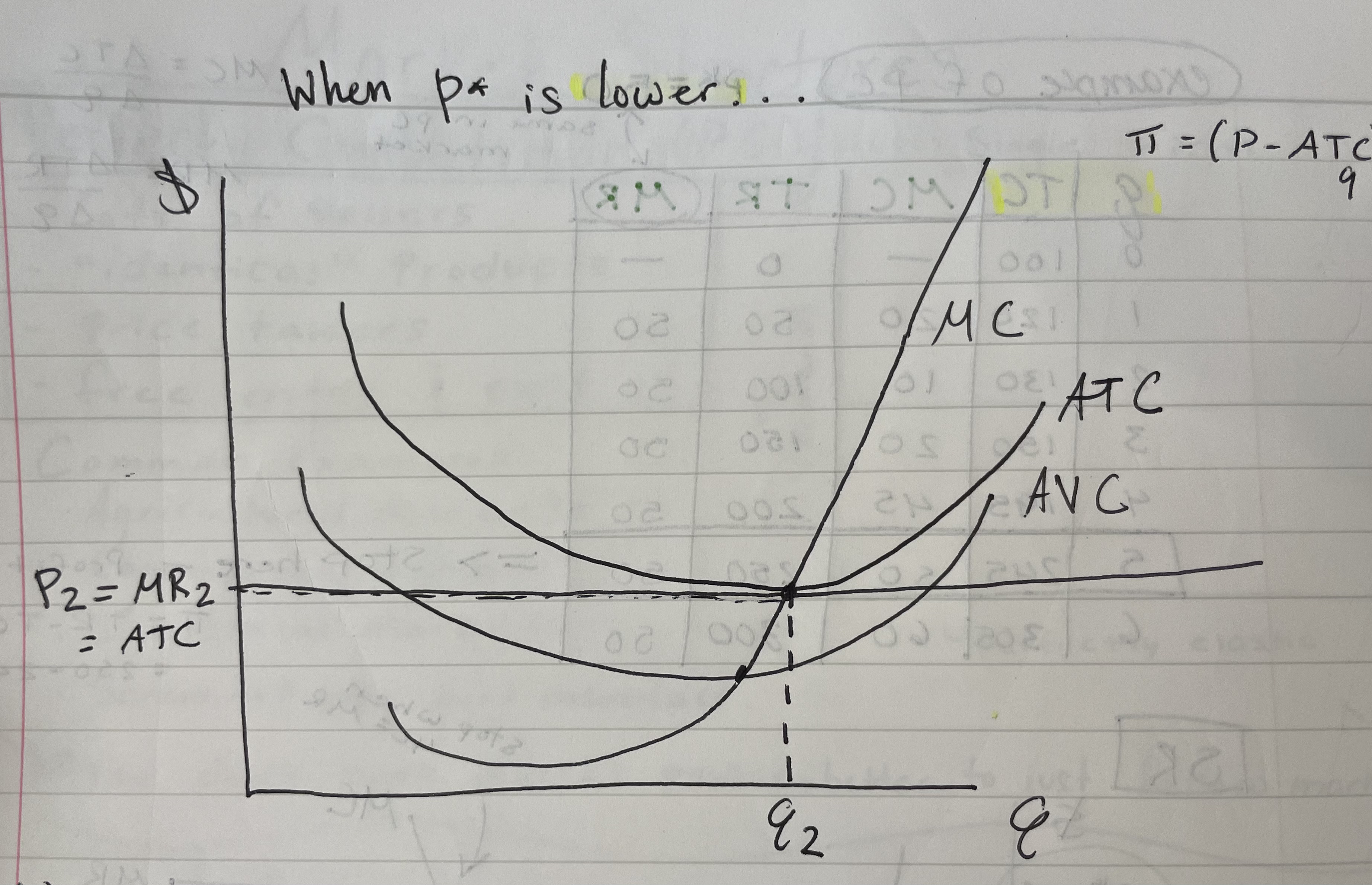
What happens when MR (marginal revenue)/price is equal to the ATC minimum?
Profit equals 0
When would you enact Tough Decision Time?
When price is below the ATC minimum
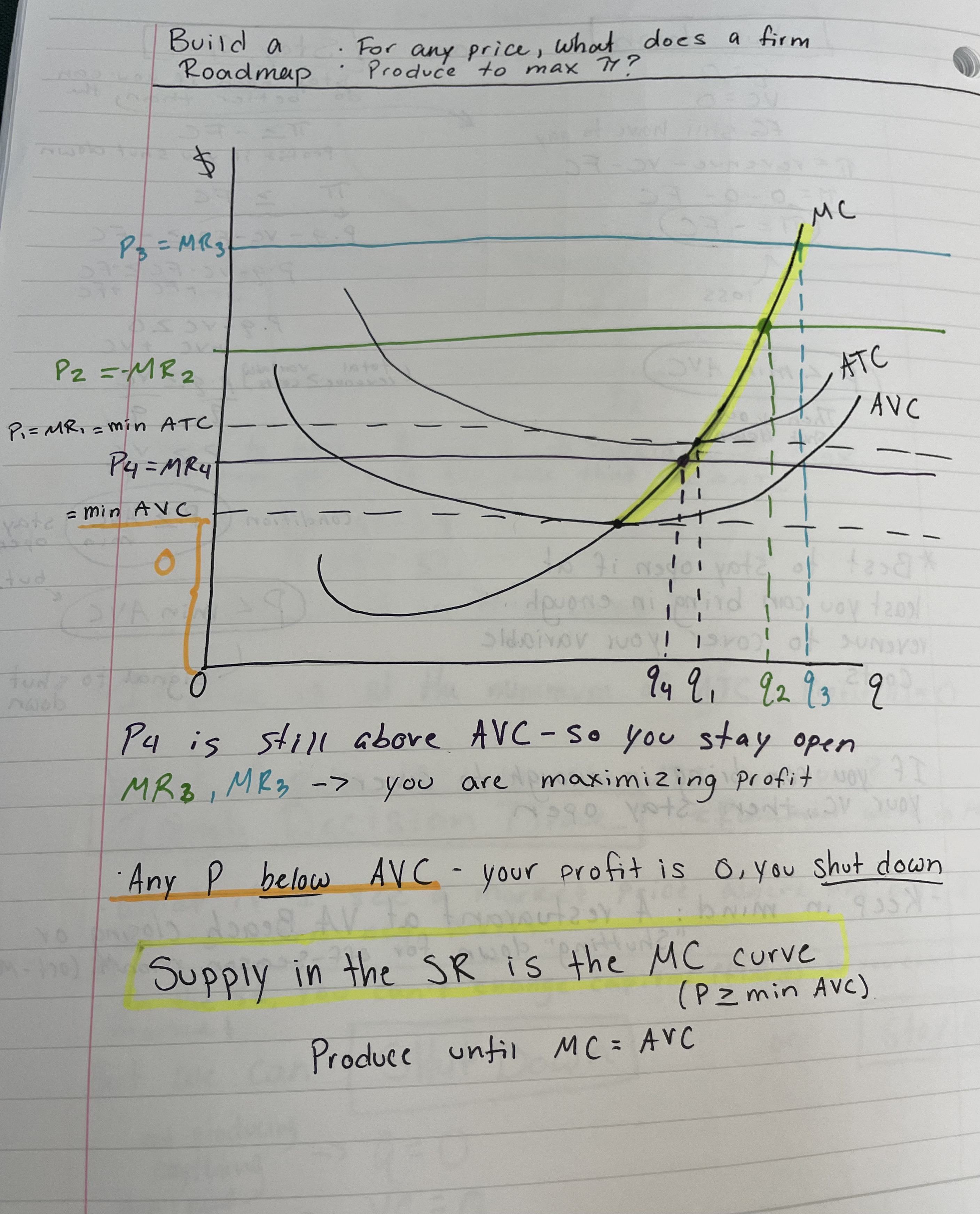
When should a firm shut down? How is this calculated?
q = 0
VC = 0
FC - still have to pay
profit = revenue - VC - FC
profit = 0 - 0 - FC
profit = -FC
Profit < minimum AVC, then you shut down
When should a firm stay open? How is this calculated?
If you can bring in enough profit to cover your VC, then stay open (profit ≥ -FC)
profit ≥ FC
p x q - VC - FC ≥ -FC
p x q - VC ≥ 0
p x q ≥ VC
p ≥ VC/q
(total revenue ≥ variable costs)
Stay open if p ≥ AVC min
For any price, what does a firm produce to maximize profit? (graph)
if firms are ____ and _____, the price of a good equals the ______ of making that good.
if firms are competitive and profit-maximizing, the price of a good equals the marginal cost of making that good.
if firms can freely enter and exit the market, the price also equals the _______________.
if firms can freely enter and exit the market, the price also equals the lowest possible average total cost (ATC) of production.
For all firms, ___ revenue equals the _____ of the good
For all firms, average revenue equals the price of the good
For competitive firms, ____ revenue equals the ____ of the good
For competitive firms, marginal revenue equals the price of the good
Profit maximizing for a competitive firm graph
In the long run, when should a firm exit the market?
P < ATC
A firm chooses to exit if the price of its good is less than the total average cost of production
If in the SR, profit is negative
Market supply shifts left, pushing prices up until profit = 0 again
In the long run, when should a firm enter the market?
P > ATC
In the SR, profit is positive
Market supply shifts right, pushing prices down until profit = 0 again
When does the process of entry and exit end in a market?
The process of entry and exit ends only when price and ATC are driven to equality.
In the long-run equilibrium of a competitive market with free entry and exit, firms must be operating at their _____.
In the long-run equilibrium of a competitive market with free entry and exit, firms must be operating at their efficient scale.
Because firms can enter and exit more easily in the long run than in the short run, the long-run supply curve is typically more elastic than the short-run supply curve.
True