Week 14: Children with Hematological and Oncological Alterations
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
Sickle cell anemia:
RBCs are C-shaped, making it easier for them to stick together, more rigid
-results in blockages in vessels, lower life span
-recessive disorder
-there are variety of sickle cell presentations (those with 2 S's is worst)
Iron deficiency anemia (IDA) causes:
body is unable to produce appropriate amounts of hemoglobin to support adequate oxygen circulation
-decreased iron intake (no Fe in breast milk)
-decreased iron absorption
-blood loss
Components that make up blood (3):
RBC (carry oxygen in blood, made up of iron)
WBC (least amount)
Plasma
What do platelets do?
control bleeding
-create a clot to prevent bleeding
-also called thrombocytes
Risk factors for iron deficiency anemia (IDA):
-endurance training
-vegan/vegetarian diets
-females
-drinking high levels of cows milk
-preterm or low birth weight
S/s for IDA:
-fatigue
-poor feeding
-tachypnea
-irritability
-pallor
Specific S/s of IDA:
-restless leg syndrome
-stomatitis
-glossitis
-pica
How is absorption of iron increased?
vitamin C foods
-citrus, berries, broccoli, dark green leafy vegetables
-Calcium decreases
Risk factors for sickle cell anemia:
-African, hispanic, mediterranean, asian descent
-where malaria is more common
Nursing considerations for sickle cell anemia:
-pain management
-oral hydration
-penicillin prophylaxis until 5 years, vaccines important
-fever is lifelong emergency
-AVOID COLD
-CURE: bone marrow transplant
Common triggers for sickle cell crisis:
dehydration
stress
menses
cold (temperature changes)
--do not use ice packs
Immune thrombocytopenia (ITP):
bleeding disorder characterized by low platelets
-acquired
S/s of ITP:
-sudden rash
-purple rash or spots caused by bleeding
-unusual bleeding
-epistaxis
Nursing considerations for ITP:
-ice and pressure cuts
-avoid ibuprofen or aspirin
-concern for hemorrhage from a wound
-assess for excess bleeding
Accessing and maintaining an implanted port:
-take child to treatment room
-minimize people in treatment room to minimize infection
-apply anesthetic prior
-wear mask and sterile technique
-aspirate 5 ml of blood after puncturing
Hemophilia
impacts clotting factors VIII and IX, which are important components in the coagulation cascade
-causes excess bleeding
-X-linked recessive disorder (males more at risk due to one X option)
S/s of hemophilia:
-Hemarthrosis: bleeding into joint cavity
-blood in urine
-easy bruising
-stiffness, warmth, swelling in joint
Nursing considerations for Desmopressin:
stops bleeding
-fluids need to be restricted for 18 to 24 hr, parameters will be provided by the prescribing provider
-fluid retention, tachycardia, hyponatremia
What is Factor VIII recombinant or Factor IX recombinant used for?
preventing/treating bleeding episodes
Von Willebrand Disease:
Low levels of, a lack of, or dysfunctional von Willebrand factor (factor VIII)
-low coagulation
-autosomal dominant (inherited)
-no cure
S/s of Von Willebrand Disease:
-gastrointestinal bleeding
-nose bleeds
-heavy menstrual bleeding
Nursing considerations for Von Willebrand disease:
-bleeding precautions
-administer vaccines with smallest needle
-avoid NSAIDs/ Aspirin
-treat RICE with injury
Epistaxis
nosebleed
Nursing steps for care of Epistaxis:
1) place in seated position
2) tilt head forward
3) apply pressure for 20 mins
4) apply ice to bridge of nose
Retinoblastoma
cancer that results from the unexpected growth of cells in the retina when they are missing both RB1 genes or have mutated
-can be hereditary and non-hereditary
Osteosarcoma
cancer of the bone
-creates osteoids in the bone
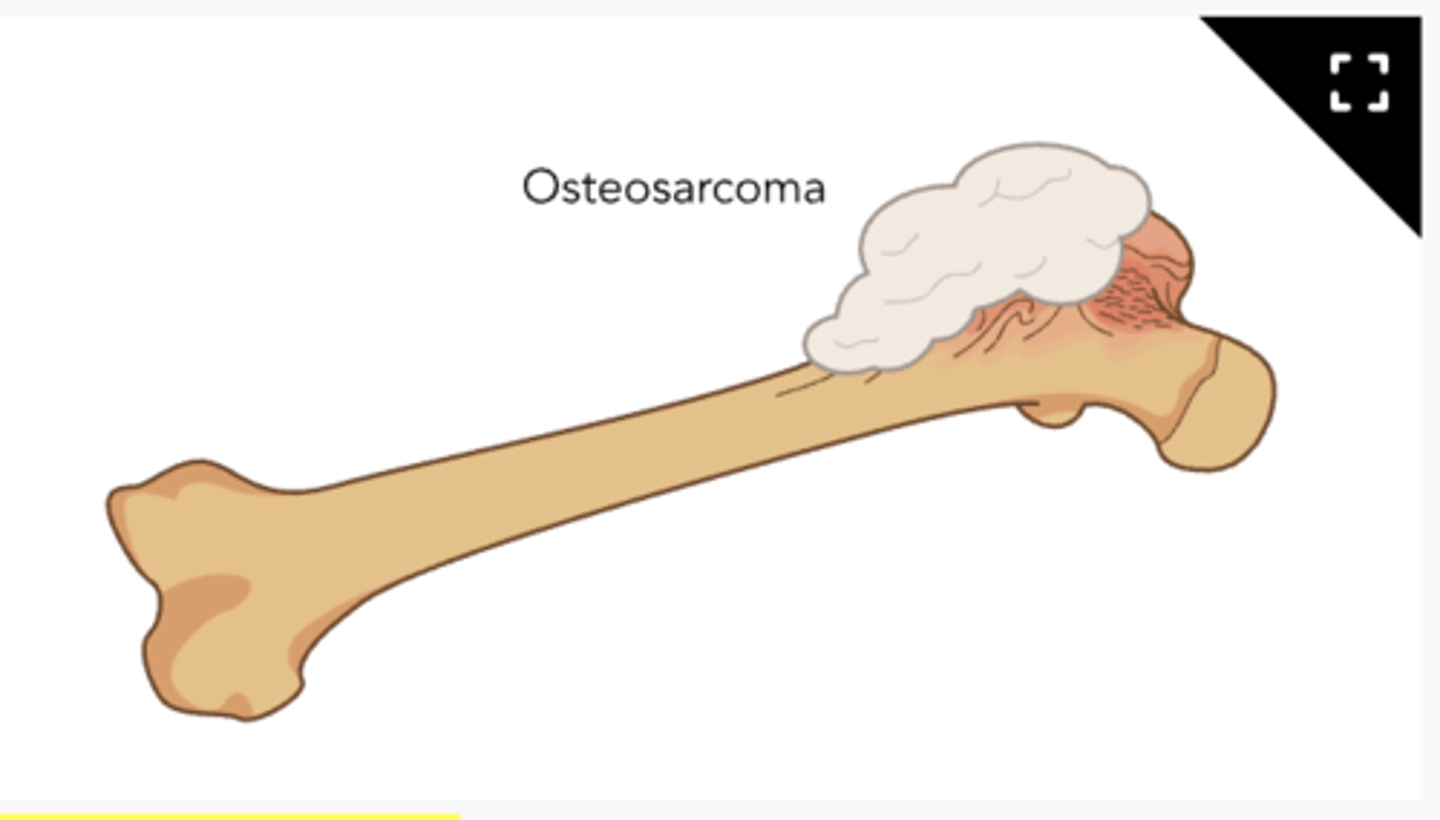
S/s of Osteosarcoma:
-swelling over cancer site
-pain w/increased activity
-lump at site
Wilms Tumors
also known as nephroblastomata, grow within the kidney
-may develop in one or both kidneys
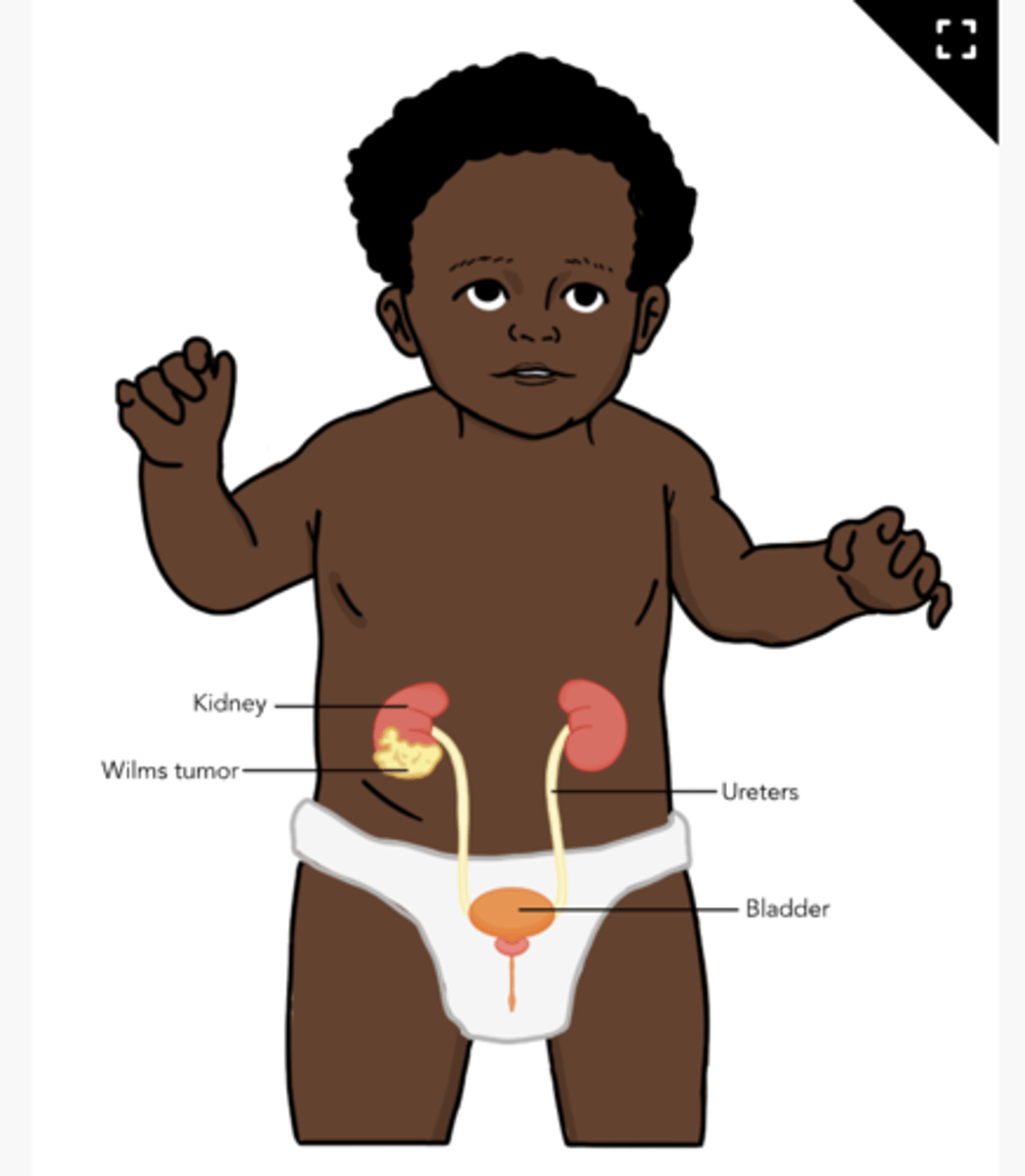
S/s of Wilms Tumors
-palpable, nontender abdominal flank mass
-swelling
-can be asymptomatic
Gliomas
tumors that come from glial precursor cells of the CNS
-can be low or high grade
-family history is biggest risk factor
Medulloblastoma:
embryonal brain tumor with differing cell origins that is fast-growing
-left over cells turned bad
Neuroblastoma:
solid cancerous tumor that starts in peripheral nerve cells in young children
-lump or pain in the abdomen, chest, neck, or pelvis
-begins in adrenal glands
-seen in children under 5
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL):
impacts immature white blood cells and bone also called lymphocytes
-overall body's defense is worse
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML):
-impacts bone marrow and non-lymphoid myeloblasts (immature WBC and RBC)
S/s of ALL and AML
-joint pain
-bleeding/bruising
-fever
-fatigue
Most common causes for low hemoglobin?
RBC loss (bleeding, ITP, hemophilia, epistaxis)
decreased production of RBC (iron deficiency)
destruction of RBCs
Lead exposure Screens:
universal at 1 - 2 years (blood lead level test)
-older if never screened
-thru interview as about when house was built? Renovating? How are siblings?
S/s of iron deficiency anemia:
SOB
hair loss
brittle, spoon shaped fingernails
decreased RBC and hemoglobin
ASK ABOUT LEAD EXPOSURE
Nursing considerations for iron deficiency anemia:
-obtain history of diet intake, lead exposure, pica, bleeding history
-craving for non food items
-administer iron supplementation (ferrous sulfate)
--make sure child brushes teeth/washes mouth (stains)
-provide screenings when young (1-2 yr)
When do children generally start to show s/s of sickle cell?
5 months
:) ur doing great, u got this
Nursing considerations for hemophilia:
-RICE for treatment
-GOAL IS TO PREVENT BLEEDING
-bleeding prevention
-NO NSAIDS or ASPIRIN
Where does childhood cancer origin in?
MESODERM
-bone marrow, lymph glands, bone, and muscle
What is the most common childhood cancer?
Leukemia and Brain and CNS
-survival rate is 85%
-S/s very broad, mostly advanced by the time they go to hospital
Major differences between child and adult cancer:
CHILD:
-no prevention
-80% metastatic at diagnosis
-very chemo receptive
ADULT:
-80% prevention
-local or regional spread at diagnosis
-less chemo receptive
Relationship between chemo and children's cells:
child's organ systems can tolerate higher doses
-chemo targets rapidly dividing cells to slow or stop growth
0-2 year old understanding of death:
little to no concept of death
3-6 year old understanding of death:
death is a reversible and temporary separation
-may be seen as punishment
7-12 year old understanding of death:
death is sad and irreversible but not necessarily inevitable
=responds to logic and facts
13-18 year old understanding of death:
death is inevitable and irreversible but often a distant event
-difficulty accepting death
To protect against the most prevalent form of anemia, the nurse advises parents to:
limit intake of cow's milk to <20oz/day for children >12mo old
A general description for the treatment effects in childhood cancer are:
Lower risk for acute toxicity, higher risk for long term effects
How long to breastfeed?
-start solid food at 6 months (increase iron food)
-can do formula up to 12 months
Bone marrow suppression as a result of chemotherapy may lead to which of the following conditions?
Neutropenia
Anemia
Thrombocytopenia