Biology - C5
1/115
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Enzymes, DNA structure and replication, protein synthesis, gene expression and mutations
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
116 Terms
Enzyme
Biological catalyst that speeds up chemical reactions in living organisms by lowering the activation energy. Reusable.
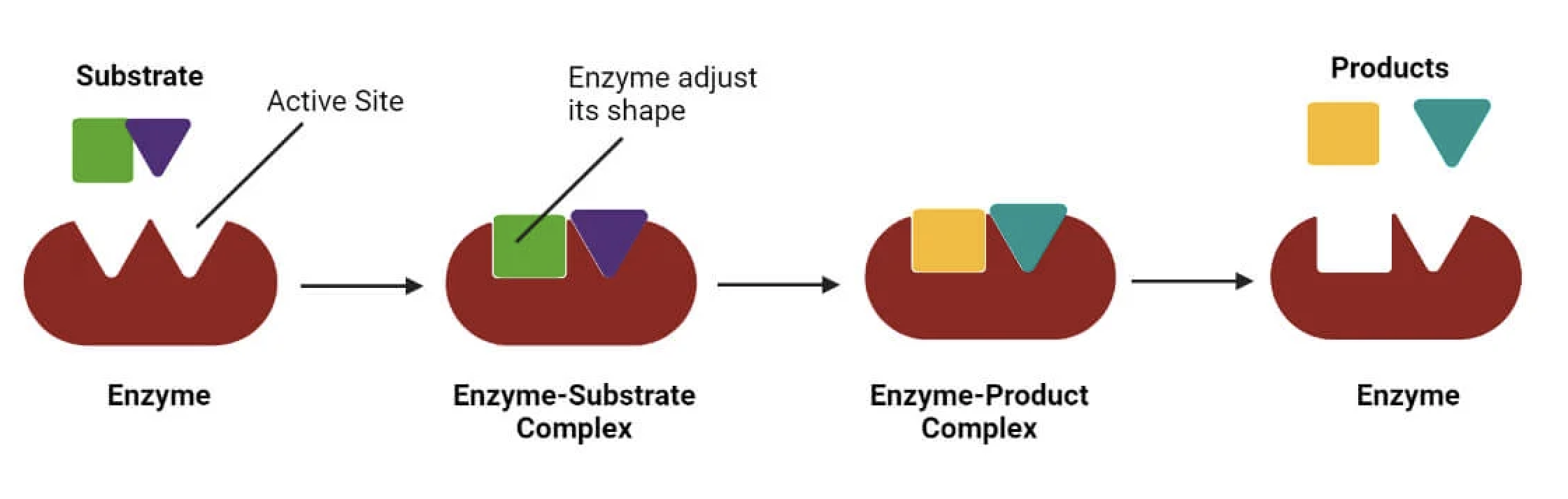
Substrate
Substance an enzyme acts on in a cellular reaction.
Active site
Where the substrate bonds to the enzyme (it is the same shape as the substrate).
Induced fit model
Model used to show the interaction between the substrate and enzyme - focus on how the enzyme changes shape to better fit the substrate.
Allosteric site
Area on the enzyme that is not the active site.
Anabolic
Substrates catalysed by enzymes to build complex molecules from simpler ones (two made into one).
Catabolic
Substrates catalysed by enzymes to make simple molecules from a complex one (one made into two).
Biochemical pathways
Multiple enzyme reactions done to break down a complex molecule into simpler products.
Rate of enzyme activity factors
Temperature, pH, substrate concentration, and enzyme concentration. RoEAF
Temperature
As it increases the kinetic energy of substrates and enzymes increases causing more frequent collisions, enhancing the rate of reaction. Too much can denature the enzyme so there is an optimum for enzyme activity.
Denatures
When the 3D structure of an enzyme deforms due to factors like extreme heat or incorrect pH.
pH
Affects the rate of reaction. Optimum is precise and different for each enzyme depending on the part of the body.
Concentration
More enzymes or substrates means the frequency of collision is higher, increasing the reaction rate.
Coenzyme
Organic non-protein needed for some enzyme reaction as they carry substrate to the enzyme. Can move between enzymes.
Cofactor
Inorganic non-protein that go in the active site and the substrate attaches to allow reaction. Often permanently bonds to enzyme.
Cofactor
Competitive inhibitor
Binds to enzymes active site to stop substrate. Substrate concentration will increase then increasing rate of reaction.
Non-competitive inhibitor
Binds to allosteric site of enzyme causing active site to deform so substrate can not bind. Not in competition with substrate so concentration increase has not affect.
Deoxyribonucleic acid
DNA stands for
DNA
Provides instructions for the formation of proteins.
Ribonucleic acid
RNA stands for
Double helix
Shape of DNA
Single strand
Shape of RNA
Nucleus
Where DNA is found.
Eukaryotic cells
Found in multicellular organisms and has a nucleus.
Prokaryotic cells
Single celled organisms like bacteria, has no nucleus so DNA is stored in the cytoplasm.
Cells
‘Building blocks of life’ - have different functions and shapes
Nucleus and cytoplasm
Where RNA is found
Nitrogenous bases
What does DNA have 4 types of?
Adenine
Nitrogenous base starting with A
Thymine
Nitrogenous base starting with T
Guanine
Nitrogenous base starting with G
Cytosine
Nitrogenous base starting with C
Thymine
Adenine’s base pair for DNA (two hydrogen bonds)
Cytosine
Guanine’s base pair for DNA (three hydrogen bonds)
Transfer
tRNA meaning
Messenger
mRNA meaning
Ribosome
rRNA meaning
Uracil
Nitrogenous base starting with U
Uracil
Adenine’s base pair for RNA instead of Thymine
Semi conservative
DNA replication is _ as half the old strand is maintained in the new strand.
Mutations
What is minimised because half the DNA strand is used in the new DNA.
Helicase enzyme
Unwinds the DNA forming the replication fork by breaking the hydrogen bonds between nucleotides (check)
RNA primase
Makes the RNA primer to start making another strand in DNA replication.
DNA polymerase
Attaches to primer and adds the rest of the complimentary base pairs during DNA replication.
DNA ligase
Joins gaps in new DNA strand (after primers removed) during replication.
Monomer
Molecules bonded together to form a polymer
Amino acids
Molecules that combine to form proteins.
Proteins
What are enzymes, haemoglobin, keratin and collagne all an example of?
Gene
Sequence of bases in DNA that code for proteins.
Amino acids
What do the triplets of nucleotides code for?
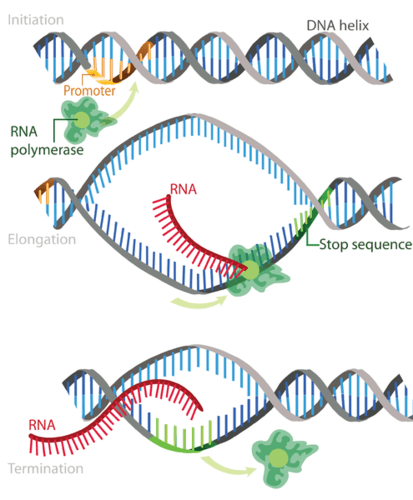
Transcription
When the gene sequences is copied onto mRNA in protein synthesis.
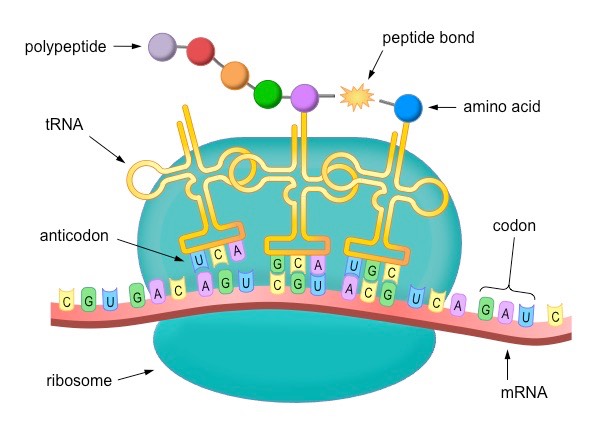
Translation
When mRNA is used by ribosomes to build proteins in protein synthesis.
RNA polymerase
Enzyme that unwinds and copies DNA during protein synthesis.
pre-mRNA
What the DNA is transcribe onto during protein synthesis (does not transcribe the promoter or terminator).
Introns
Non-coding regions removed in post transcription modification (splicing).
Mature mRNA
What pre-mRNA becomes after the introns are removed and the cap and tail added.
Ribosome
What mRNA goes to to start creating proteins.
tRNA
What brings the amino acid into the ribosome during protein synthesis.
Polypeptide chain
Chain of amino acids created during protein synthesis.
Codon
Group of 3 bases.
Peptide bonds
Bonds that form between amino acids during protein synthesis to create the polypeptide chain.
Transcribed
Environment and behaviour affects which and what genes are _
Gene expression
Process in which chosen genes are transcribed
Phenotypic expression
Observable characteristics or traits that result from an interaction of genes and environment.
Phenotype
What you see (traits).
Environmental factors
What are diet, temperature, O2 levels, etc
Gene regulation
Process used to control which and what genes get transcribed in the cell (expressed).
Energy conservation
Why is gene regulation a thing?
Chemical tags
How gene regulation is done by turning genes ‘off and on’ by binding to the DNA.
Transcription factors
Proteins that determine gene regulation by binding to the DNA.
Activators
Proteins that boost transcription by making it easier for RNA polymerase to bind to the promotor.
Repressors
Proteins that stop transcription by making it harder for RNA polymerase to bind to the promotor.
Promotor
Initiates the transcription of genes.
Gene
Segment of DNA that codes for a specific protein.
Exon
Coding region in mRNA.
Intron
Non-coding region in mRNA.
Pentose sugar
Main part of sugar-phosphate backbone.
Phosphate group
Small part of sugar-phosphate backbone.
Sugar-phosphate backbone
Holds nitrogenous base in the double helix.
Restriction enzymes
Protein that can cut DNA in a bacterial cell
restriction site
area of DNA that the active site of the restriction enzyme recognises
endonuclease
Another name for restriction enzymes
DNA sequence
Each restriction enzymes has a particular _ in the DNA that it cuts
restriction enzymes
the defence system of bacterial cells against harmful foreign DNA (viruses)
methylase enzyme
What the bacterial cell uses to protect its DNA from being cut by restriction enzymes
methyl group
What the methylase enzyme adds to the DNA to protect it
6-8
Amount of base pairs in the DNA sequence of a restriction site
Nucleotide
Organic molecule made of a nitrogenous base, a phosphate and pentose sugar
Mutation
A change in the sequence of bases in a DNA strand
DNA replication
When are mutations in DNA most likely to occur?
mutagen
An agent that causes induced genetic mutation
UV radiation, chemical exposure and heat
Things that can induce mutation (mutagens)
somatic
mutations that are not passed on - not in gametes
germ line
mutations that are passed onto offspring
point, block and chromosomal
Types of mutations
substitutions, insertions and deletions
types of point mutations
insertions and deletions
which point mutations are frame shift mutations
silent, missence and nonsense
types of substitution point mutations
point mutation
type of mutation where the nucleotide bases in the genome are affected