Classical Greece: Culture, Politics, and Warfare
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
Nike
Goddess symbolizing speed, strength, and victory.
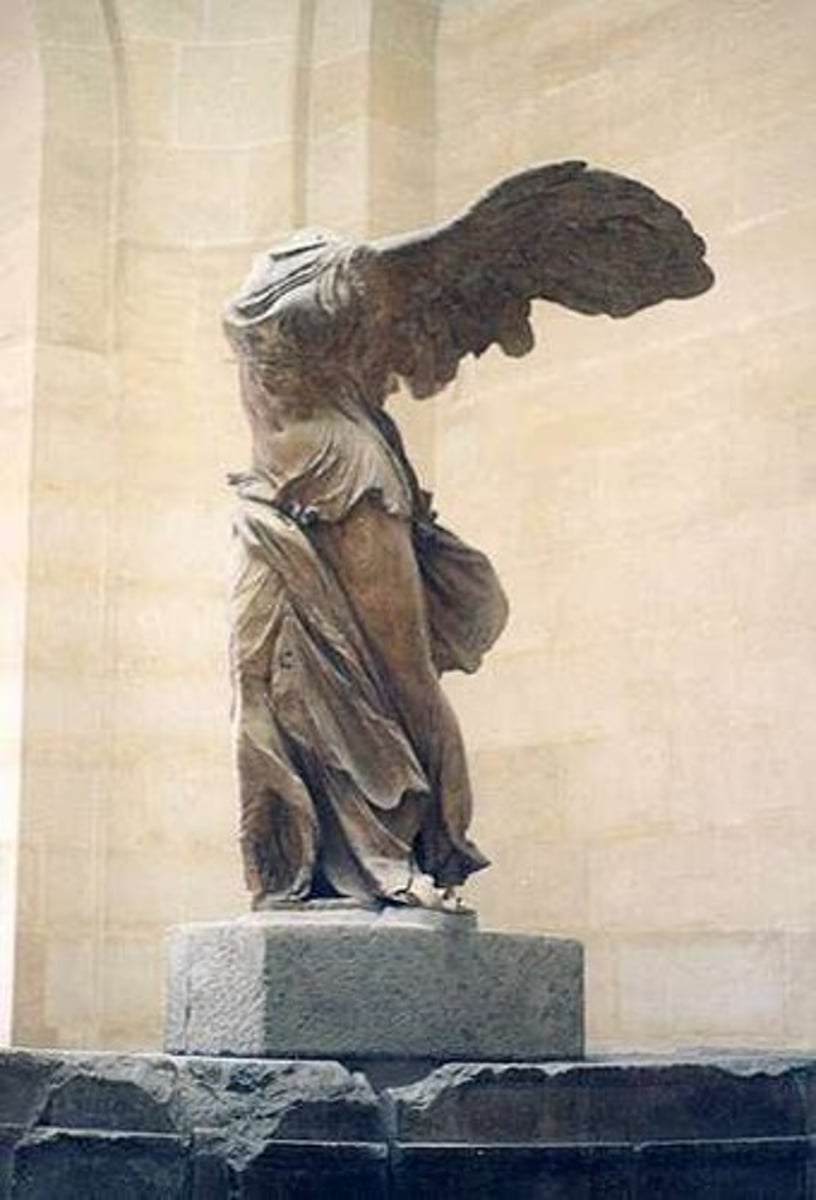

Victoria
Roman equivalent of the Greek Goddess Nike.
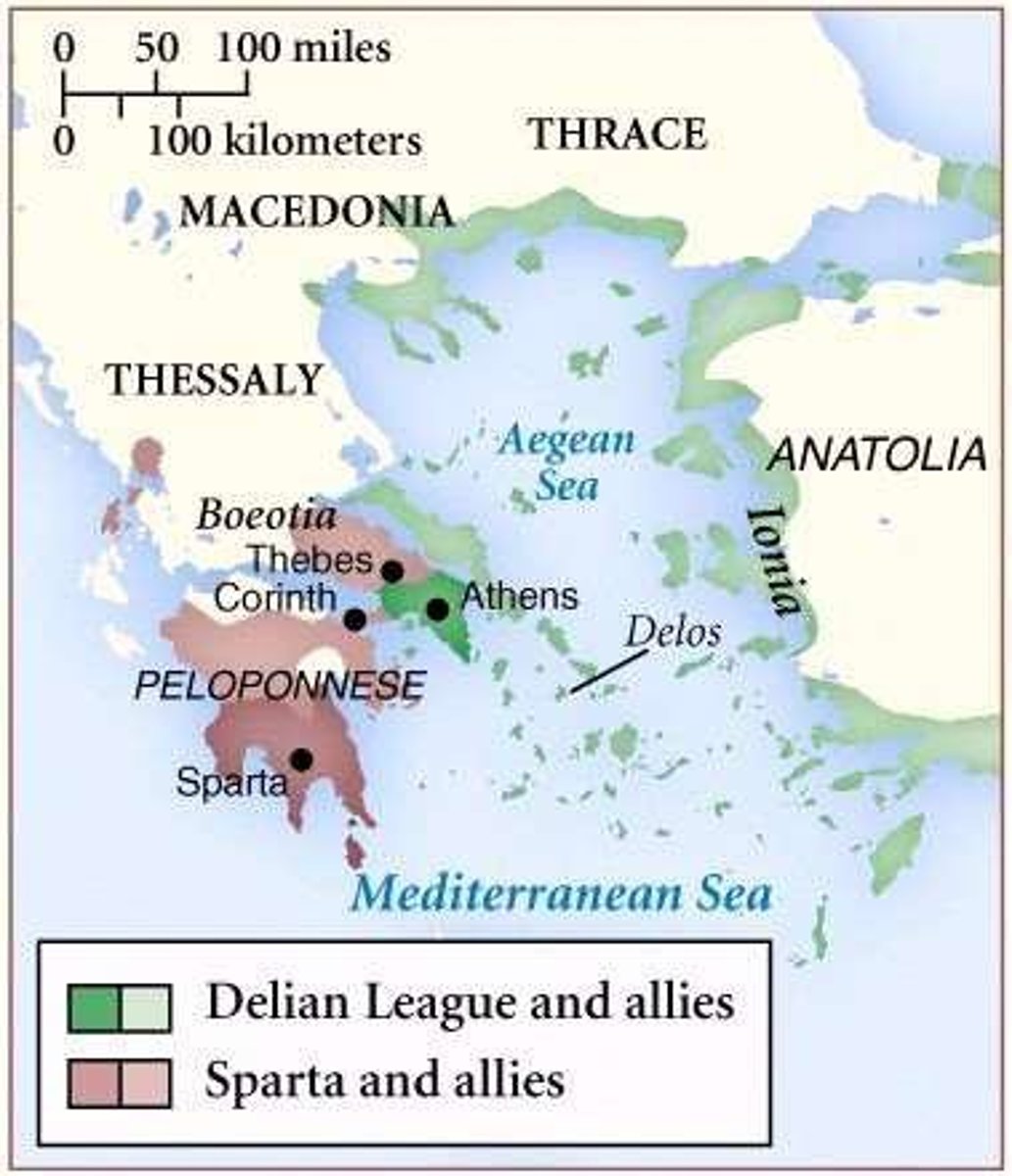
Delian League
Alliance formed to defend against Persian attacks.
Aristides the Just
Leader known for fair tribute assessments.
Kimon
General who shaped the Delian League's effectiveness.
Pericles
Leader during Athens' golden age of democracy.
Athenian Democracy
System allowing citizens to vote and hold office.
Archonships
One-year positions selected by lottery in Athens.
Jury Pay
Compensation enabling poor citizens to participate.
Ostracism
Exile of a citizen for political reasons.
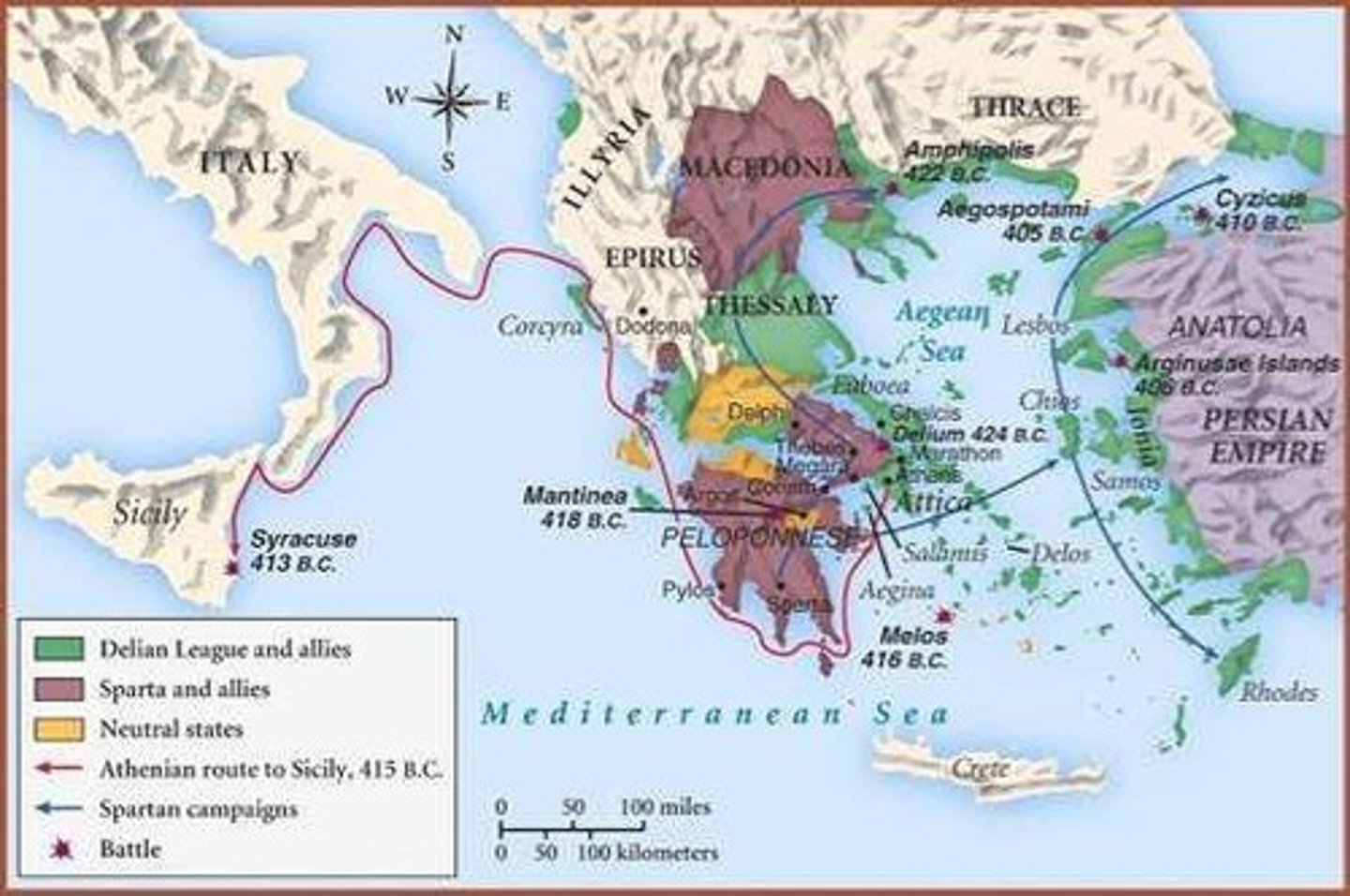
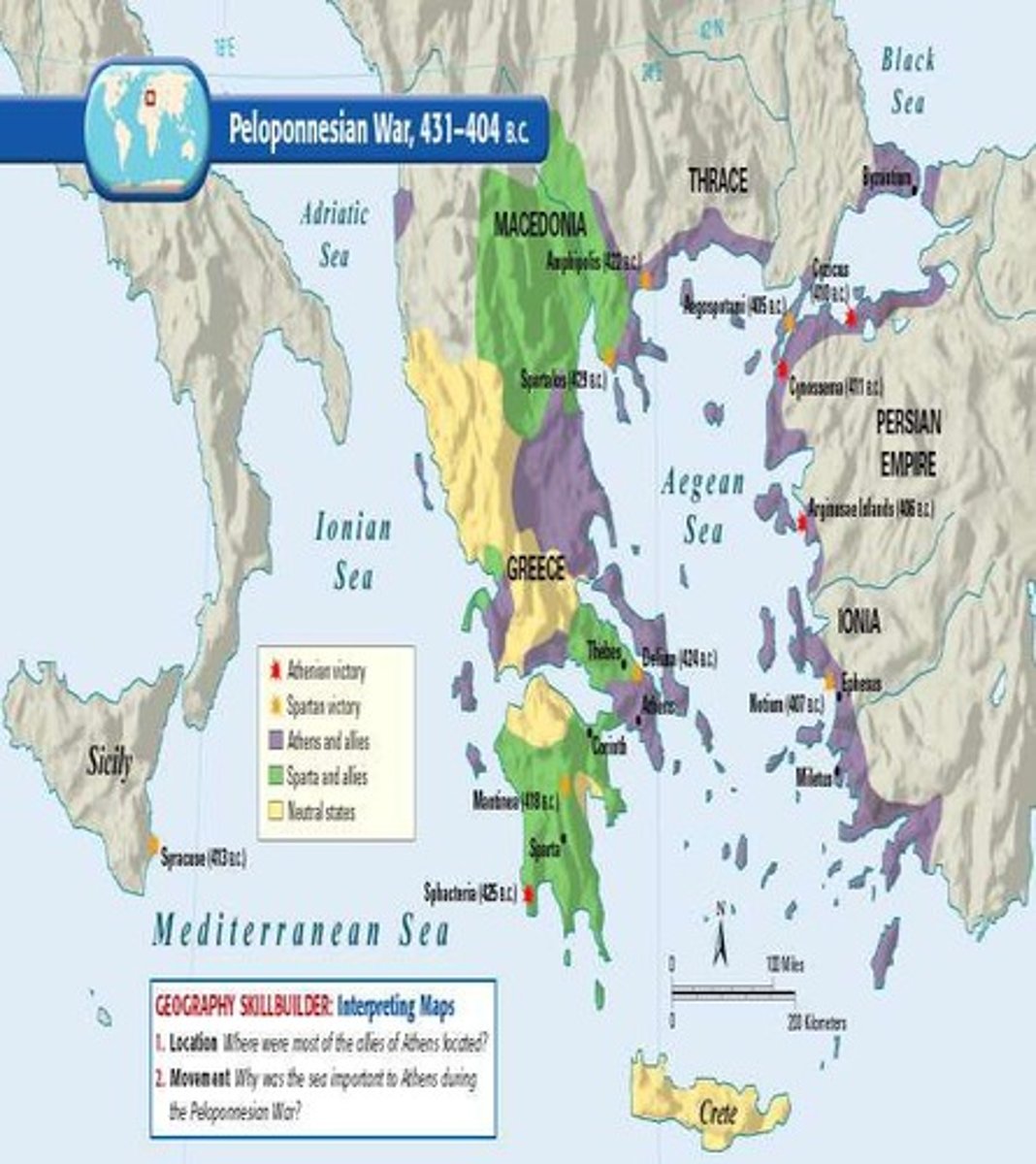
Peloponnesian War
Conflict between Athens and Sparta, longest in Greece.
Long Walls
Fortifications connecting Athens to its port Piraeus.
Helot Revolt
Spartan uprising leading to tensions with Athens.
Thirty-Year Peace Treaty
Agreement to avoid interference between Athens and Sparta.
Plague of Athens
Disease outbreak causing significant population loss in 430 BCE.
Corinth
Wealthy city-state allied with Sparta.
Persian Control
Dominance over Greek city-states, challenged by Athens.
Naval Victory Monument
Purpose of Nike's statue on Greek ships.
Tribute
Annual payment by states to maintain the Delian League.
Apollo Sanctuary
Location of Delian League treasury and meetings.
Aegean Sea
Region where Athens defended against Persian forces.
Public Responsibility
Criteria for government positions based on ability.
Citizenship Law
Limited citizenship to men with citizen fathers.
Radical Democracy
Political system emphasizing broad citizen participation.
Cultural Advances
Achievements in rhetoric, philosophy, and literature in Athens.
Spartan Government
Conservative oligarchy focused on land power.
Athenian Empire
Expansion driven by the Delian League's influence.
King Brasidas
Spartan leader killed in battle, leading to temporary peace.
Alcibiades
Athenian general who shifted allegiances and strategies.
Syracuse Campaign
Failed Athenian attempt to conquer Sicily's powerful city.
Lysander
Spartan general who innovated naval combat tactics.
Aegospotami
Site of decisive 405 BCE battle leading to Athenian defeat.
Thirty Tyrants
Spartan-installed rulers who terrorized Athens post-war.
Thucydides
Historian who documented the Peloponnesian War objectively.
Parthenon
Iconic temple in Athens, symbolizing wealth and power.
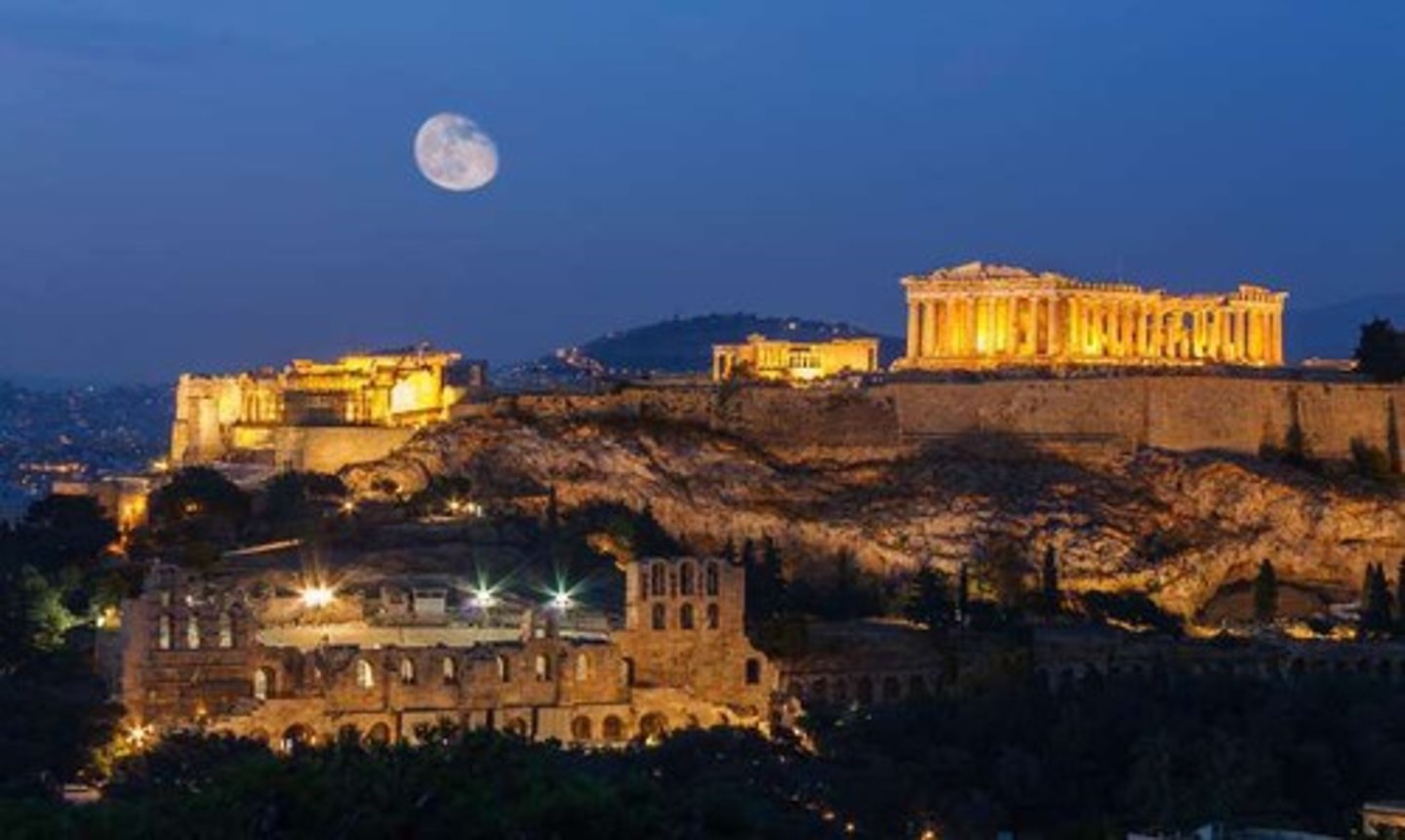

Phidias
Sculptor who designed the Parthenon and Athena's statue.
Sophocles
Playwright who expressed Greek ideals through drama.
Acropolis
High city in Athens, location of the Parthenon.
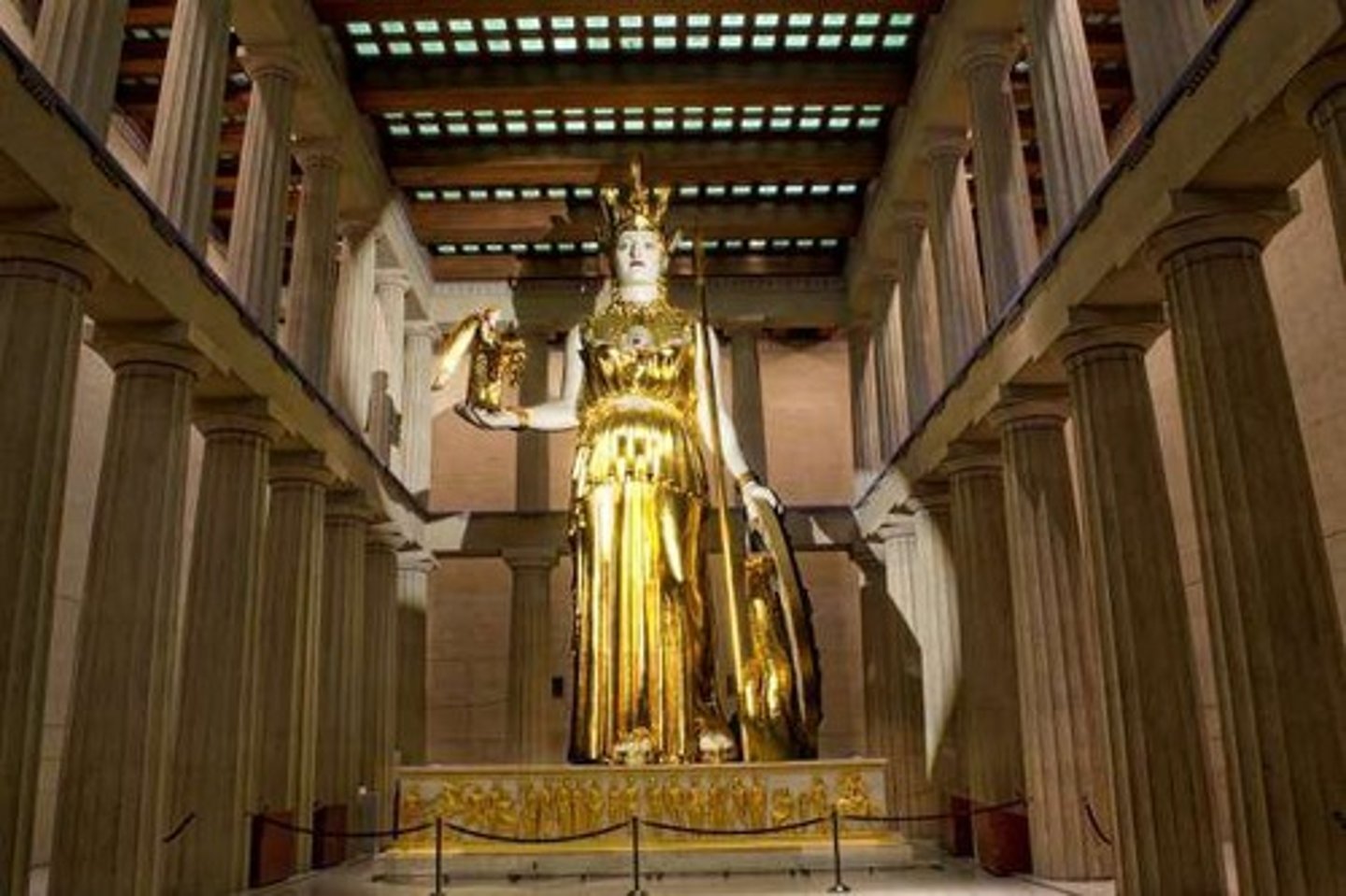
Cella
Inner chamber of the Parthenon housing Athena's statue.
Hubris
Excessive pride leading to downfall, avoided in art.
Aeschylus
Playwright addressing justice and societal issues.
Euripides
Dramatist exploring themes of human experience and morality.
Aristophanes
Comic playwright who critiqued society through humor.
Masonry Techniques
Advanced building methods learned from ancient Egyptians.
Frieze
Decorative panel on the Parthenon depicting historical scenes.
British Museum
Current location of many Parthenon sculptures.
Statue of Athena
12-meter tall statue made of ivory and gold.

Cultural Peak
Fifth Century BCE Athens' height of artistic achievement.
Persian Support
Provided ships to Spartans, aiding their naval efforts.
Exile of Alcibiades
Forced departure impacting Athenian military leadership.
Melos
Island attacked by Athens, leading to its population's enslavement.
Corinth and Thebes
City-states that encouraged Spartan actions against Athens.
Thebes
City-state that briefly defeated Sparta and led Greece.
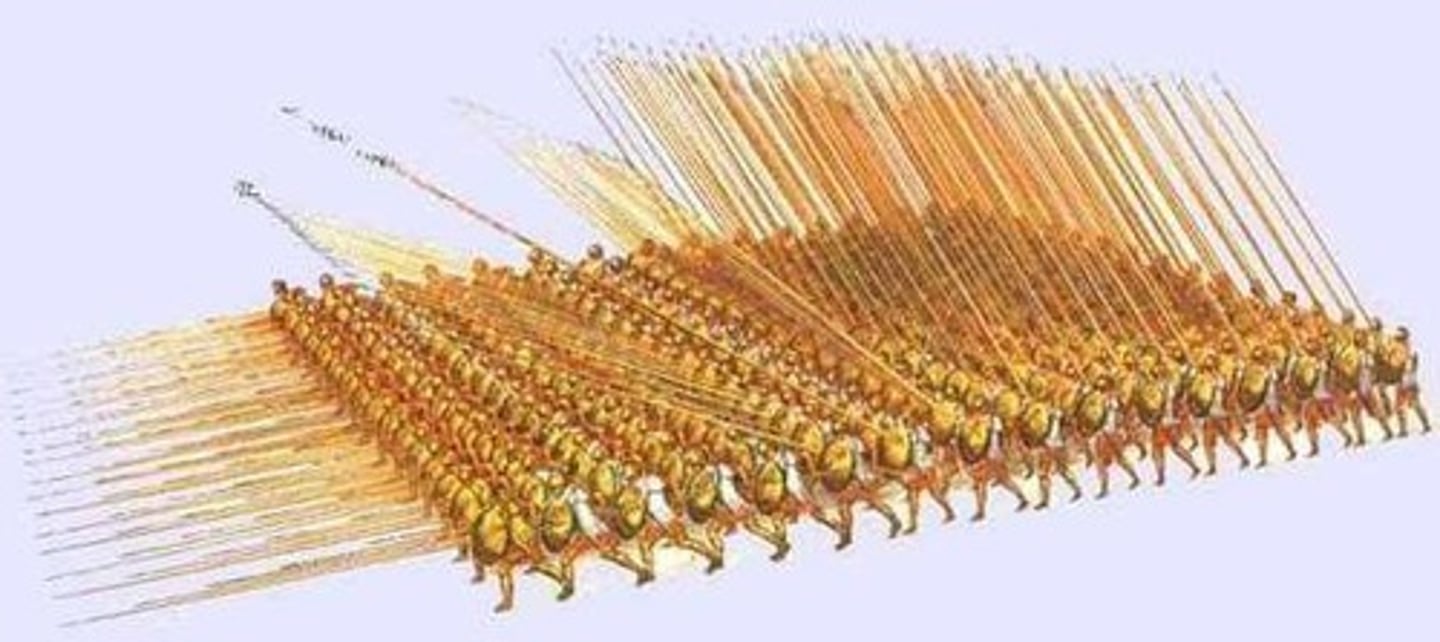
Phalanx
Military formation using deep ranks and long spears.
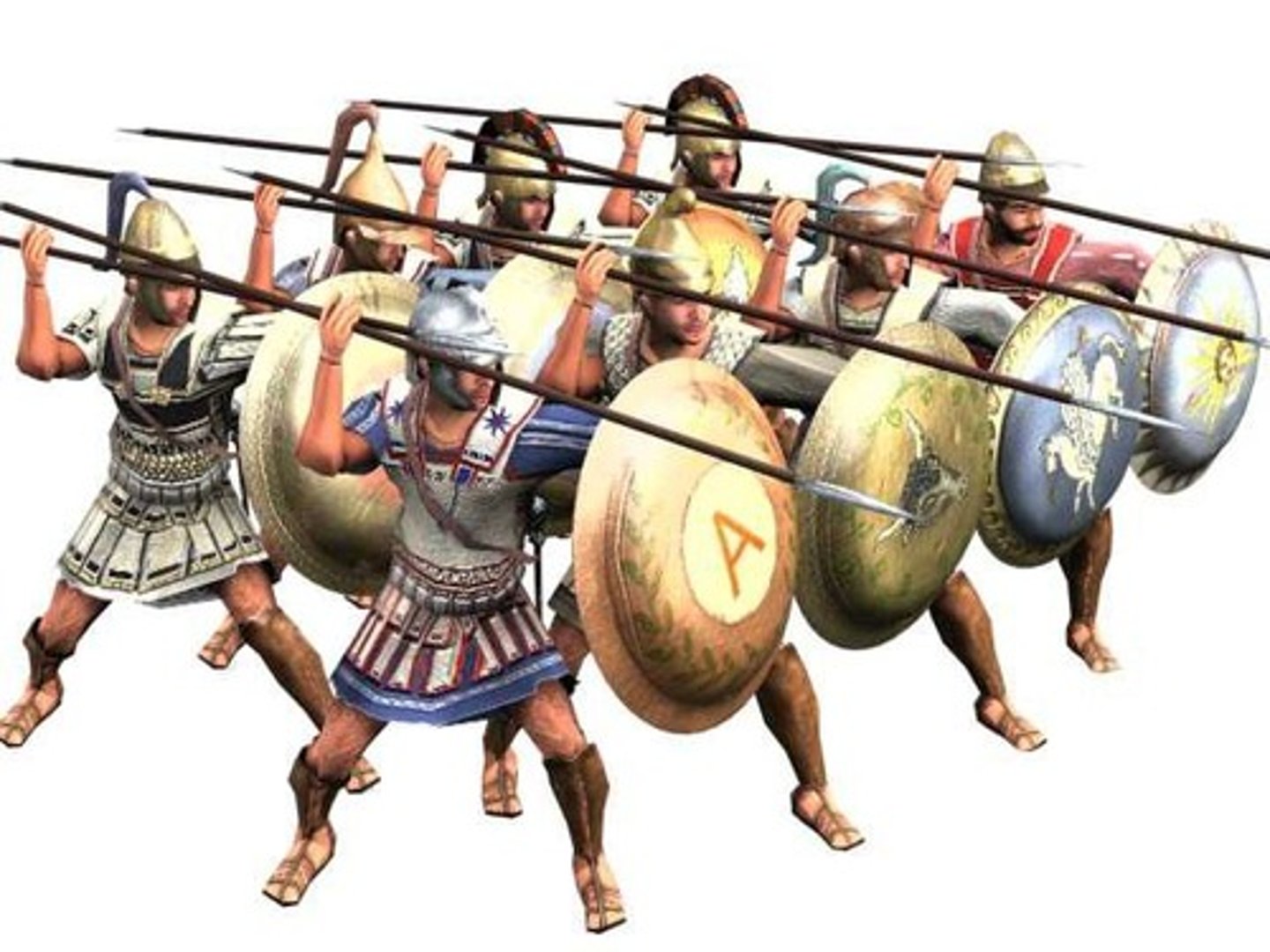

Epaminondas
Theban general who innovated military tactics.
Philip of Macedon
King who united Macedonians and defeated Greeks.
Battle of Chaeronaea
338 BCE battle where Philip defeated Greek forces.
Alexander the Great
Son of Philip, renowned for vast military conquests.
Persian War
Conflict where Alexander defeated the Persian Empire.
Battle of Gaugamela
Decisive 331 BCE battle leading to Persian defeat.

Hoplite Phalanx
Greek infantry formation emphasizing close combat.
Hellenistic Age
Period after Alexander's death, marked by cultural diffusion.
Alexandria
Cities founded by Alexander, centers of Greek culture.
Seleucus
General who ruled the Asiatic region post-Alexander.
Ptolemy
General who established a dynasty in Egypt.
Cleopatra
Last ruler of the Ptolemaic Kingdom in Egypt.
Antigonus
General who seized control of Macedonia and Greece.
Citizenship
Only men held citizenship rights in ancient Greece.
Metics
Foreign residents in city-states, treated like women.
Slavery
Institution where individuals had no rights or freedoms.
Greek Philosophy
Early thought focused on nature and truth.
Socrates
Philosopher who shifted focus to ethics and knowledge.
Cultural Diffusion
Spread of Greek culture through Alexander's conquests.
Greek Art
Influential style admired and imitated across cultures.
Greek Language
Unifying force in Alexander's diverse empire.
Military Innovation
Advancements in tactics and formations during Greek wars.
Legacy of Warfare
Men's roles in warfare shaped citizenship and rights.
Cultural Resistance
Local customs preserved despite Greek cultural influence.
Atom
Tiny particles that make up matter.
Sophists
Teachers of logic and rhetoric in ancient Greece.
Socratic Method
Inquiry method using questioning to challenge beliefs.
Plato
Socrates' student who founded the Academy.
Dialogues
Plato's writings featuring Socratic discussions.
The Good
Concept influencing Christian ideas of God.
Aristotle
Plato's student who founded the Lyceum.
Lyceum
Aristotle's school for scientific research.
Hellenistic Architecture
Architecture reflecting non-religious public buildings.
Foreshortening
Technique making objects appear larger than distant ones.
Greek Ideals
Artistic focus on calmness, youth, and proportion.
Halicarnassus
Location of Mausolus' famous tomb, a wonder.
Seven Wonders
Famous ancient constructions, including Mausoleum.
Doric Order
Simplest architectural column style in ancient Greece.
Ionic Order
Column style characterized by scroll-like capitals.
Corinthian Order
Most ornate column style with elaborate capitals.
Arch of Constantine
Roman arch featuring Doric, Ionic, and Corinthian styles.
Sculptors
Artists creating lifelike statues of young men.
Public Buildings
Structures like theaters and gymnasiums in Hellenistic period.
Private Architecture
Buildings reflecting wealth, such as tombs.
Asclepius
The healing god associated with Greek hospitals located at sanctuaries.
Hippocrates
The most famous Greek doctor known for his oath for caring for the sick and studying the body as a whole.