Research Methods and Data Interpretation Ap Psych
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
How is psychology a Science?
Psychology is a science because it employs the scientific method to study human behavior and mental processes
What are the three Key elements of the Scientific Attitude?
Curiosity, Skepticism, and Humility
What is Critical Thinking
thinking that does not automatically accept arguments and conclusions. Rather, it examines assumptions, appraises the source, discerns hidden biases, evaluates evidence, and asses conclusions
What can Critical Inquiry do?
Surprise us and debunk popular assumptions, by checking intuitive fiction with scientific fact.
What do we need to overcome to think critically?
Hindsight Bias, Overconfidence, Perceiving Order in Random Events
Hindsight Bias
the tendency to believe, after learning an outcome, that one would have foreseen it (also known as the I knew it all along phenomenon)
Overconfidence
the tendency to be more confident than correct - to overestimate the accuracy of our belief and judgments
Perceiving Order in Random Events
the tendency to make sense of a random, unpredictable world.
What components does the scientific process have?
Theory (mere hunch) , Hypothesis (can be confirmed or refuted), Replication (can be repeated), and Peer Review (feedback before and after)
Peer Reviewers
scientific experts who evaluate a research article’s theory, originality, and accuracy
Theory
an explanation using integrated set of principles that organizes observations and predict behaviors or events
Hypothesis
a testable prediction, often implied by a theory
Falsifiable
the possibility that an idea, hypothesis, or theory can be disproven by observation or experiment
Operational definition
a carefully worded statement of the exact procedures (operations used in a research study.
Replication
repeating the essence of research study, usually with different participants in different situations, to see whether the basic finding can be reproduced
These terms are examples of constructing. ______
Theories
Descriptive Methods
describe behaviors -methods are the Case Study, Naturalistic Observation and Surveys
Case Study
A descriptive technique in which one individual or group is studied in depth in the home of revealing universal principles.
What are examples of case study?
Brain damage, Children’s minds, and Animal intelligence
Naturalistic Observation
a descriptive technique of observing and recording behavior in naturally occurring situations without trying to manipulate or control the situation
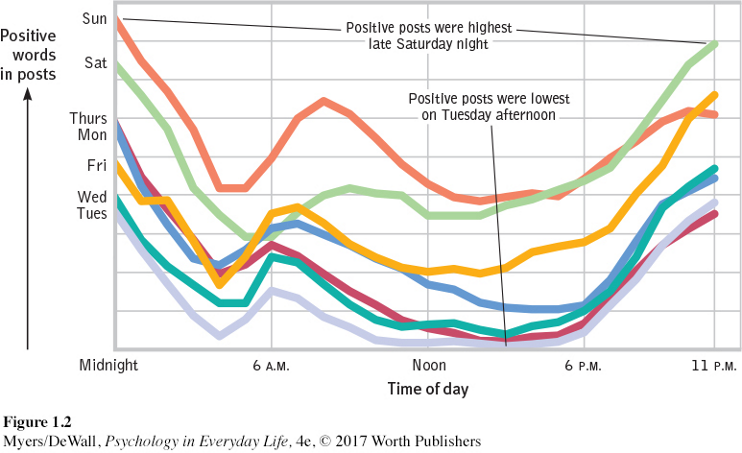
A natural observer
“observations, made in the natural habitat, helped to show that the societies and behavior of animals are far more complex than previously supposed” Jane Goodall. 1998
Survey
a descriptive technique for obtaining the self-reported attitudes or behaviors of a particular group, usually by questioning a representative random sample of the group.
Wording Effects
subtle changes in wording can have major effects. Examples., People prefer aid to the needy rather than welfare. Gun safety laws rather than gun control laws.
Sampling bias
a flawed sampling process that produces an unrepresentative sample.
Population
all those in a group being studied, from which sample may be drawn. (Note: except for national studies, this does not refer to a country’s whole population)/
Random Sample
a sample that fairly represents a population because each member has an equal chance of inclusion
Sampling Bias
a flawed sampling process that produces unrepresentative sample
Social Desirability Bias
bias when people report their behavior inaccurately
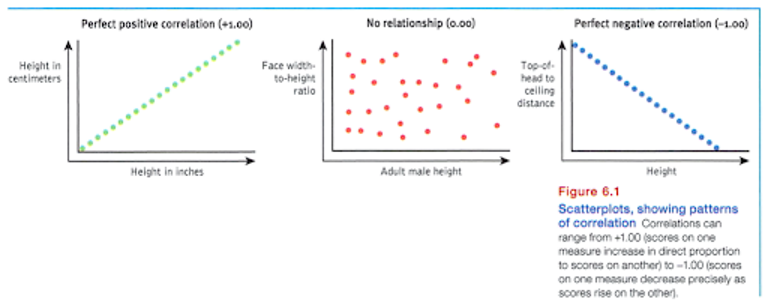
Correlation
a measure of the event to which two factors vary together, and thus of how well either factor predicts the other.
Correlation Coefficient
a statistical index of the relationship between two things ( from -1:00 to +1.00_
Variable
anything that can vary and is feasible and ethical to measure
Scatterplot
a graphed cluster of dots, each of which represents two variable. The amount of scatter suggest the strength of the correlation (little scatter indicates high correlation).
Illusory Correlation
perceiving a relationship where none exits, or perceiving a stronger than actual relationship
Regression toward the mean
the tendency for extreme or unusual scores to fall back (regress) toward the average
Experimentation
Different from description… the uses manipulation of a variable
can Isolate cause and effect
Control of factors (variable)
What you need to set up an experiment
Hypothesis, Operational definition, population sample
Experimental Group
Receive the treatment (the variable)
Control Group
Does not receive the treatment
Random assignment
Eliminated alternative explanations different from random sample
Blind
Uninformed
Single-Blind Procedure
the person being experimented is unaware the person doesn’t know the circumstances
Double-Blind procedure
neither subjects nor people in direct contact with subjects know
Placebo
Experimental results cause by expectation alone; any effect on behavior caused by the administration of an inert substance or condition, which the recipient assumes is an active agent.
Independent Varibale
It’s what is being manipulated
Confounding variable
a factor other than the factor being studied that might influence a study’s result
Experimenter Bias
bias caused when researchers may unintentionally influence results to confirm their own beliefs
Dependent Variable
what is being measured
Validity
the extent to which a test or experiment measures or predicts what it is supposed to
Qualitive Research
a research method that relies on in-depth, narrative data that are not translated into numbers
Quantitative Research
a research method that relies on quantifiable, numerical data.
How do psychologist predict everyday behavior?
They intend to make a simplified reality environment. this environment should stimulate and control important everyday life features and researches principles to help explain many behaviors
Confederates
People who pretend to be fellow participants but are actually part of the experiment
Placebo effect
“I took a pill so I’ll get better”
What to do to watch out for placebo effect
Write it up…get it peer reviewed…watch people replicate it
Mode
the most frequently occurring score in a distribution
Range
difference between highest minus lowest (can be misleading)
Mean
the arithmetic average of a distribution; obtained by addding the scores and then dividing by the number of scores
median
the middle score in a distribution’; half the scores are above it and half are below it
Standard Deviation
a computed measure of how much scores vary around the mean score
Skewed Distribution
a representation of scores that lack symmetry around their average value
Percentile Rank
the percentage of scores that are lower than a given scores
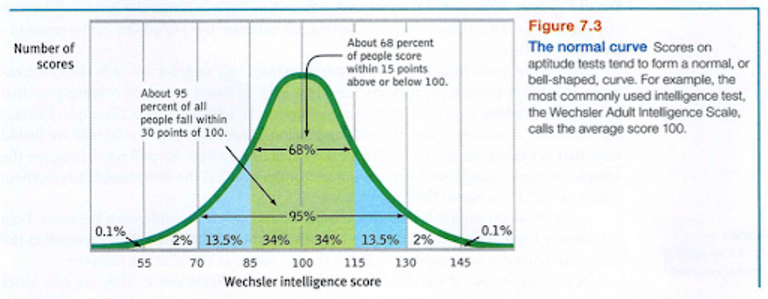
Normal curve
a symmetrical, bell-shaped cure that describes the distribution of many types of data; most scores fall near the mean (about 68 percent fall within one standard deviation of it) and fewer and fewer near the extremes
What does statistical significance mean in psychology
The odds need to be at least 5%
Informed consent
Know enough to participation
Debriefing
The post experimental explanation of a study’ including its purpose and any deceptions, to its participants.
Ensuring Scientific Integrity
Honesty often cited as most important scientific value. Fraud and fake science can do enormous harm. Example the discredited Lancet article that purported to link the MMR vaccine to autism. Despite retraction and disbarment of the physician, the damage has led to declining vaccine rates
Values in Psychology
Values inform psychological science and psychological science has the power to persuade.

Statistical Reasoning in Everyday life
Use critical thinking when presented with big, round, undocumented numbers
Descriptive Statistics
numerical data used to measure and describe characteristics of groups. Includes the measure of central tendency and measures of variation
Histograms
a bar graph depicting a frequency distribution
What are parts of ethics in human research
Informed consent, Protect from harm and discomfort, maintain confidentiality, Debriefing
Descriptive Methods
describe behaviors - methods are the Case Study, Naturalistic Observation and Surveys
Case Study
a descriptive technique in which one individual or group is studied in depth in the hope of revealing universal principles
Interferential Statistics
numerical data that allows one to generalize - to infer from sample data the probability of something being true of a population
Meta-Analysis-
a statistical procedure for analyzing the results of multiple studies to reach an overall conclusion. When deciding whether it is safe to infer a population difference from a sample difference, keep three points in mind:
Representative Sample are better than biased samples. more bigger samples are better than smaller ones
More estimates are better than fewer estimates
Statistical Significance
a statistical statement of how likely it is that an obtained result occurred by chance
Effect Size
the strength of the relationship between two variables. The larger the effect size, the more on variable can be explained by the other.