Blood supply to the Brain W1 L0
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
What is the Circle of Willis and why is it significant in cerebral circulation?
The Circle of Willis is a circular network of arteries at the base of the brain that connects the anterior and posterior blood supply, allowing for collateral circulation. It is significant because it provides alternative routes for blood flow in case of occlusion.
Explain the difference between ischemic stroke and hemorrhagic stroke.
Ischemic stroke occurs due to a blockage in a blood vessel supplying the brain, while hemorrhagic stroke occurs due to the rupture of a blood vessel, leading to bleeding within or around the brain.
What are the implications of Broca’s area damage in a patient?
Damage to Broca's area, located in the dominant hemisphere, generally results in expressive aphasia, where the patient has difficulty producing speech but may still comprehend language.
Describe lacunar stroke and what causes it.
Lacunar stroke is the occlusion of small penetrating arteries that supply deep structures of the brain, often caused by chronic hypertension or diabetes, leading to specific deficits based on the affected area.
What role do vertebral arteries play in brain circulation?
Vertebral arteries supply blood to the posterior circulation of the brain, including the cerebellum and brainstem.
What condition is characterized by oxygen deprivation in the brain, and what are its effects?
Anoxic condition is characterized by oxygen deprivation in the brain, leading to potential unconsciousness after approximately 20 seconds without oxygen.
Define collateral circulation and why it is important in cases of vascular obstruction.
Collateral circulation refers to alternate pathways for blood flow that occur if a primary vessel becomes occluded, helping to maintain blood supply to the affected areas of the brain.
What is the consequence of a saccular aneurysm if it ruptures?
If a saccular aneurysm ruptures, it can lead to a hemorrhagic stroke, causing bleeding into the surrounding brain tissue and potentially resulting in serious neurological deficits or death.
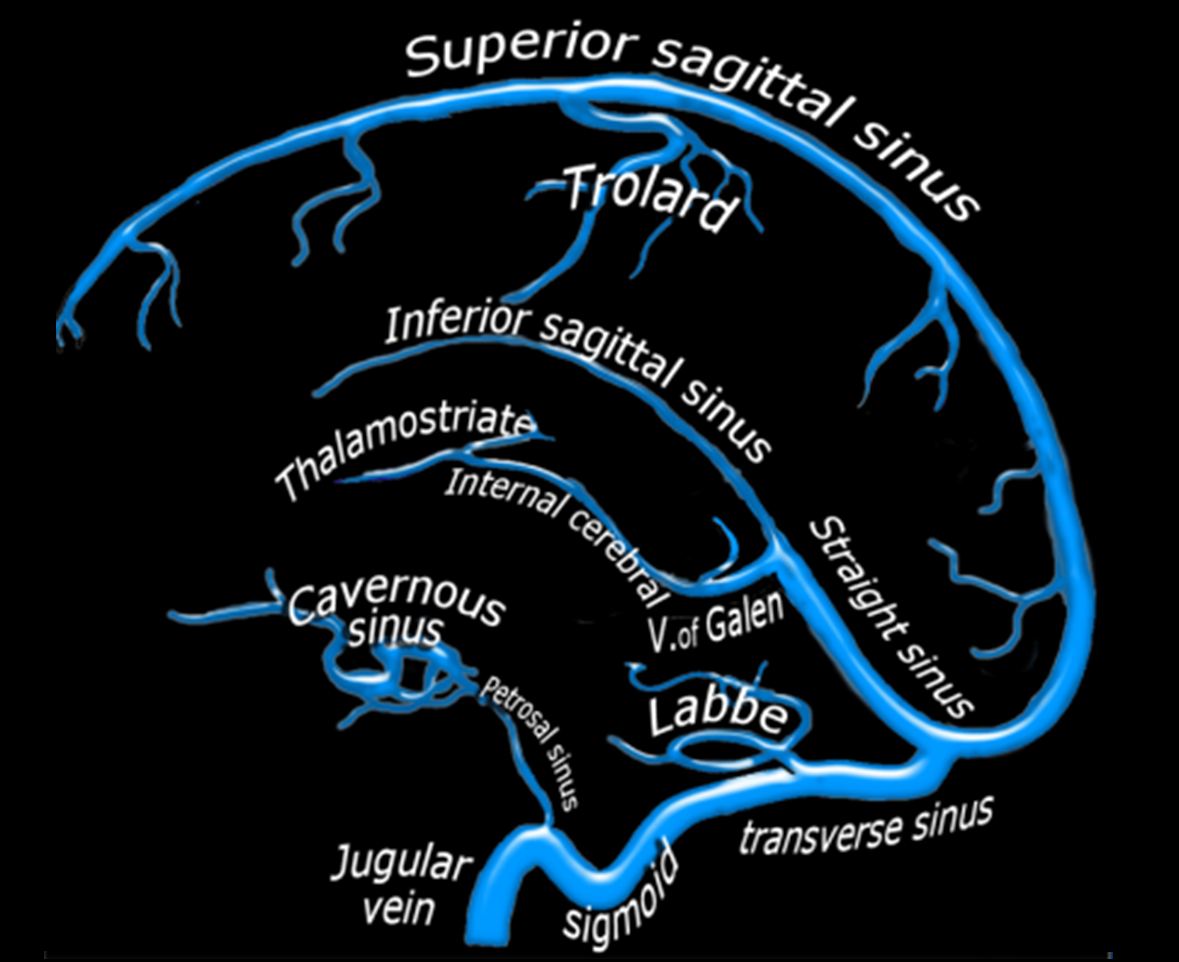
What is the role of the dural venous sinuses in brain venous drainage?
Dural venous sinuses are channels formed between the layers of the dura mater, responsible for draining deoxygenated blood from the brain back to the heart.
What are the major risk factors for atherosclerosis, and how does it affect cerebrovascular health?
Major risk factors for atherosclerosis include high cholesterol, hypertension, smoking, and diabetes. Atherosclerosis can lead to the narrowing of arteries, increasing the risk for cerebrovascular accidents (strokes).
explain the pathway of the posterior blood supply - so vertebrobasilar into the brain
first begins as vertebral artery - then up through the transverse foramina at C6-C1 - then through foramen magnum - then changes into the basilar artery.
Basilar artery, which supplies blood to the brainstem and cerebellum, and branches into the posterior cerebral arteries that provide blood to the occipital lobe and inferior portions of the temporal lobes.
explain pathway of anterior blood supply of internal carotid arteries
so right common carotid , then carotid sinus, then carotid canal then cavernous sinus.
what does ACA provide
medial portions of frontal and parietal lobes. so motor and sensory cortex.
what will aneurysm to the ACA cause >
motor and sensory issues. and since frontal lobe is affected, it will cause apathy
what does MCA supply
lateral aspect of the frontal, parietal, and temporal lobes.
Also goes to caudate and lentiform nucleus and internal capsule
what does an aneurism to MCA cause
contralateral motor and sensory deficits, and possible language deficits if the dominant hemisphere is affected.
if its non dominant than hemisptial neglect is caused , which is neglect on one side. It may also lead to visual field cuts and impairment in spatial awareness.
what does vertebral and basilar arteries supply ?
brainstem, cerebellum and medial temporal lobes
what does the PCA supply ?
`what will an aneurysm cause ?
supplies the occipital lobe and the inferior part of the temporal lobe.
An aneurysm in this area can lead to visual field deficits, specifically homonymous hemianopia, and potential memory issues due to involvement of the temporal lobe.
what does PICA and AICA supply
the lateral medulla and cerebellum;
an aneurysm may cause dizziness, ataxia, and swallowing difficulties.
go over where the sinuses are,
superior saggiato, straight sinus, inferior sagittal sinus, vein of Gallen , transverse sinus, jugular vein