BIO 80 Exam 2
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
111 Terms
Species
Group of populations that can inbreed and produce viable fertile offspring
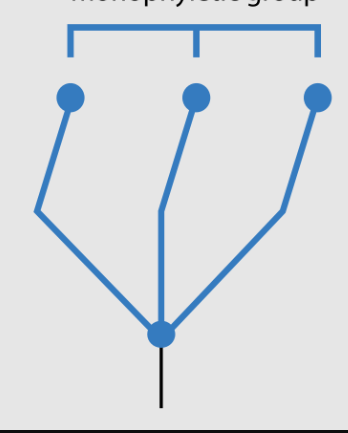
monophyletic
Grouping that includes 1 ancestor and its decendants
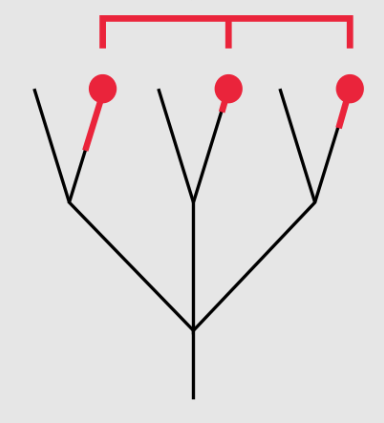
Polyphyletic
Grouping of descendants what come from a common ancestor (but not the ancestor themselves)
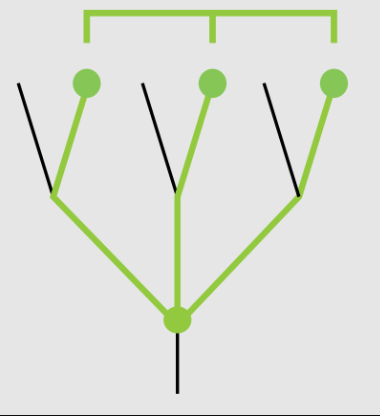
Paraphyletic
Grouping of Some (not all) decendants
Phenetics
classification method that groups organisms based on overall similarity in observable traits
Phylogeny
The study of evolutionary relatedness among groups
taxonomy
System of Naming and clasifying organisms
Donald Kills people coming from greater Syria + subspecies
Gause’s Principle
No two species can make use of the same niche in one habitat
if they do one or both will not be able to survive
Direct competition
When organisms physically interact (fighting) for resources (harms both)
Indirect (exploitative) Competition
Struggle for common resources due to resources being used (passive) (benefits one harms another)
intraspecific competition
between A species
population
The amount of a certain species in one area
Biotic Potential
Max reproduction capacity in a population without environmental resistance
Environmental resistance
Ecological features that halt/ minimize reproduction
Density dependent
influence that impacts population size an a result of the density of a population
Such as: less resources due to high population levels.
Biological
Density Independent
influence that impacts population growth not dependent on the Populus
Environmental
such as natural disasters
Carrying Capacity
The max amount of individuals an environment is able to carry for a prolonged period of time
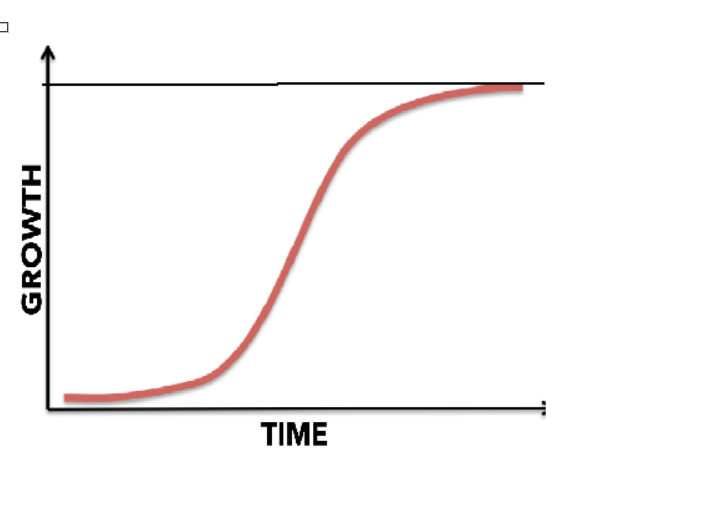
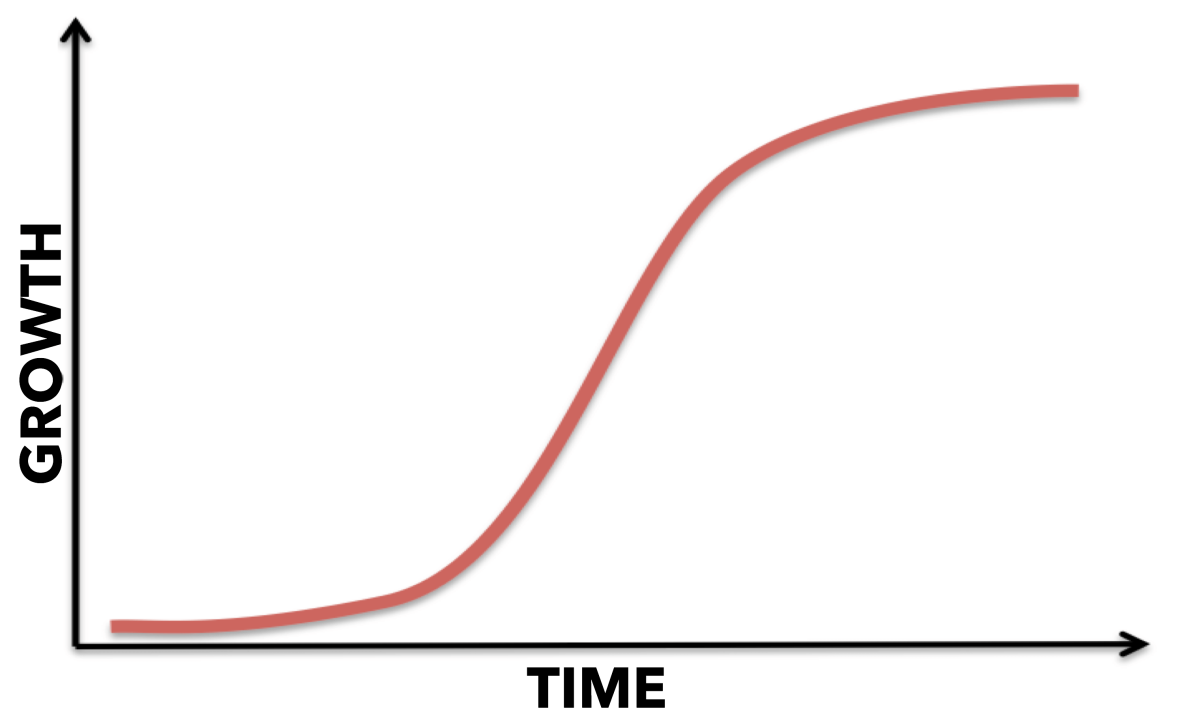
S shaped curve
Logistic
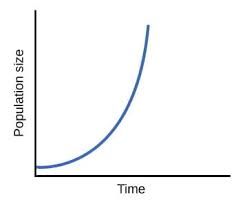
J shaped curve
Exponential
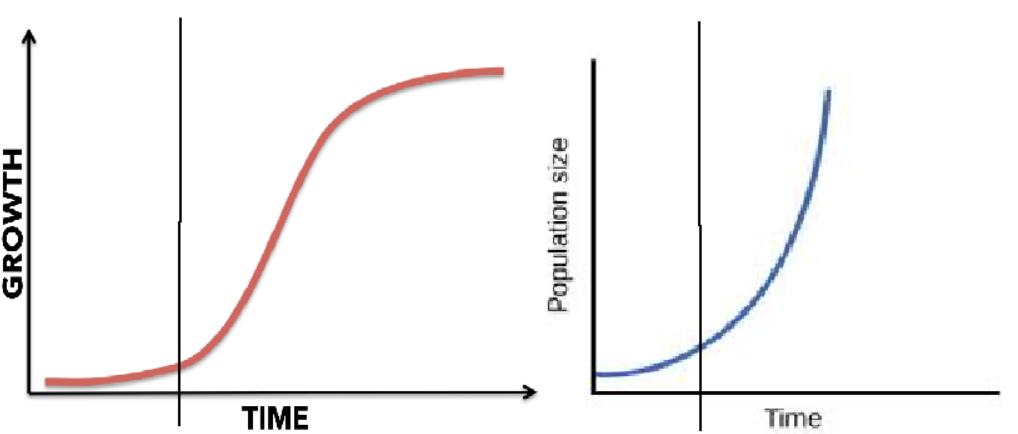
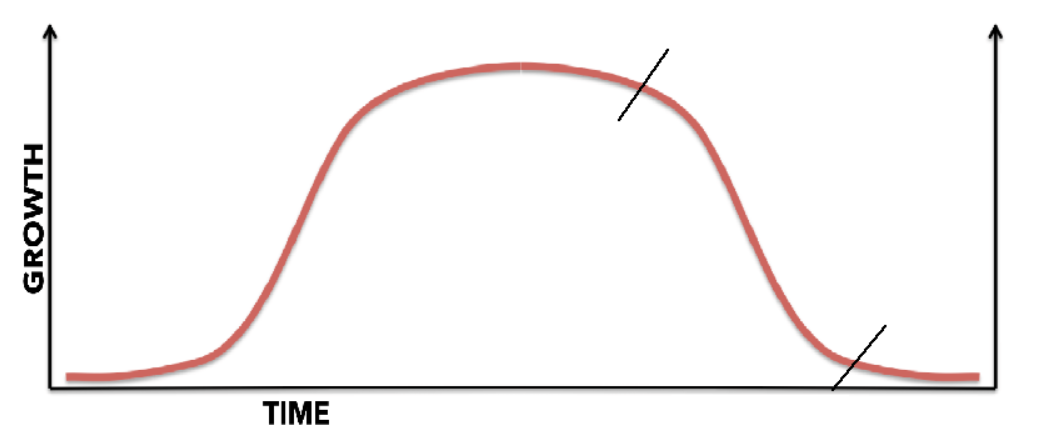
Lag phase
initial phase
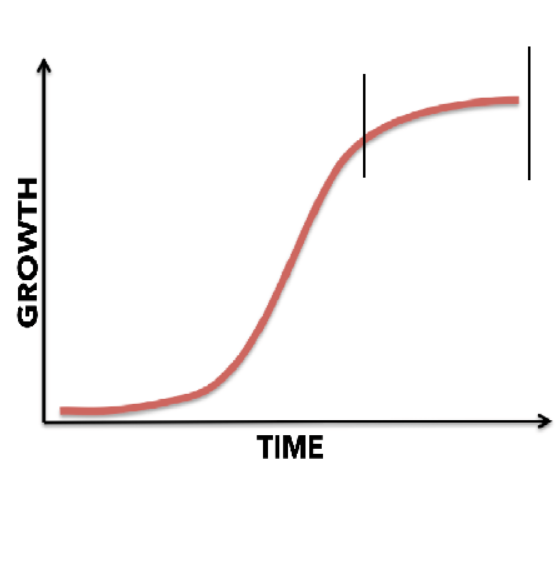
Acceleration and Deceleration phase
rapid growth followed by it slowing down

Equilibrium stage
Nearing Max capacity
Maximum stationary phase
When Organisms can survive but not reproduce
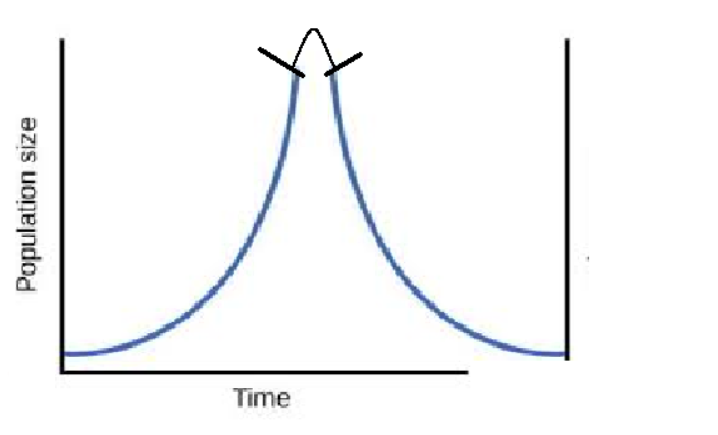
Crash phase
decline
Allele/gene frequency
Numeric rate of which a gene occurs in a group of gene pairs
Genetic drift
the change in frequency do to an event (migration ect)
Gene flow
The movement of genes from one population from another
Environmental selection
The favorability of certain traits leading to higher rates of survival (survival of the fittest)
Mutation
a permanent change in an organism's DNA
Evolutionary fitness
The ability for an organism/alleles to survive and reproduce in comparison to organisms of similar species.
Evolution
A change in genes over a period of time
Biological species concept
Group of organisms that can produce viable offspring w/ one another
Morphological species concept
Classification of species bas on anatomical similarities
ecological species concept
Classification or organisms that share a set niche
Allopatric speciation
Speciation in two separate areas
Parapatric speciation
Speciation that occurs in two adjacent regions
sympatric speciation
Organisms w/ the same ancestor diverge into two species despite having no mating barriers.
Antheridia
Spore/sperm producing
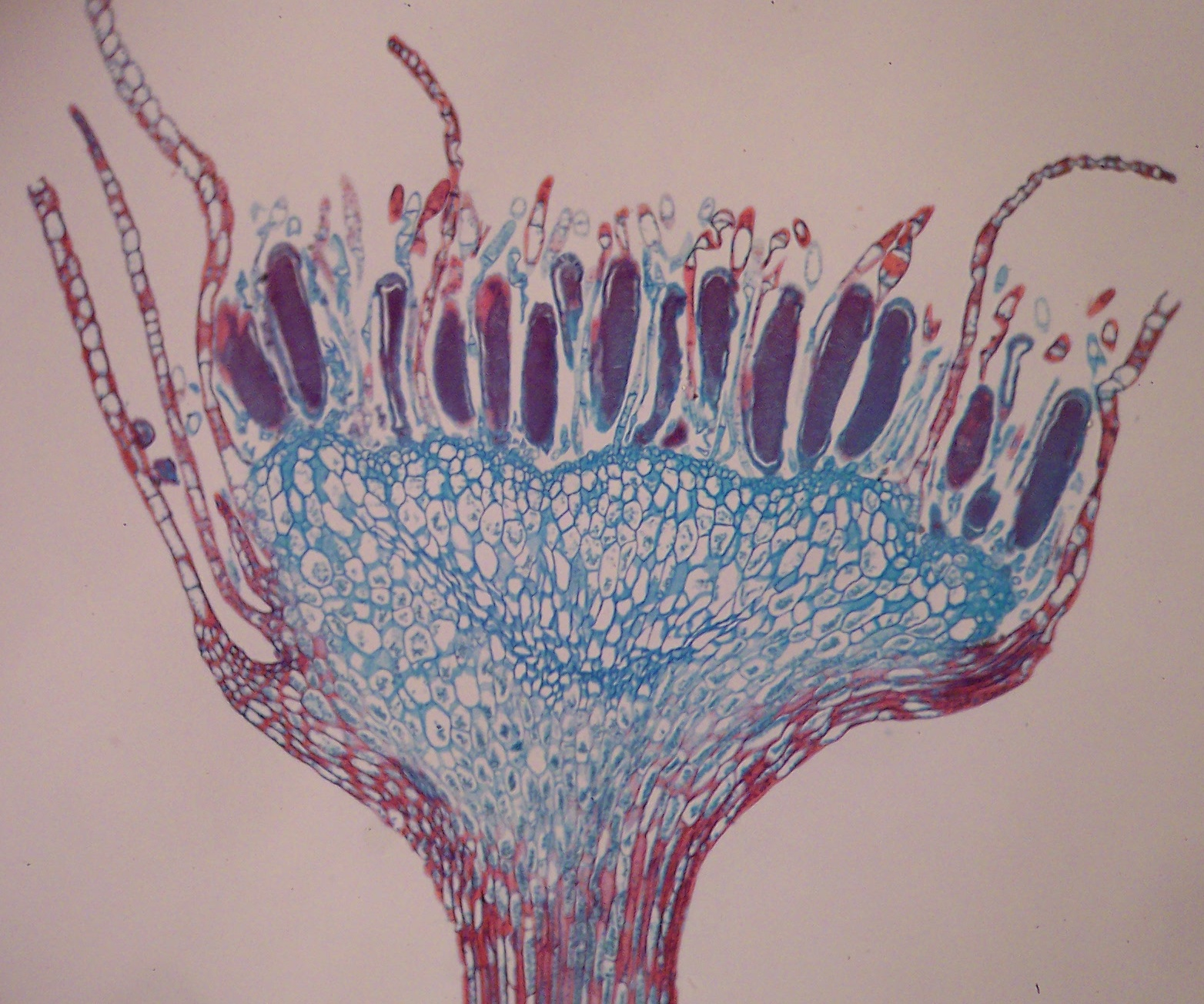
archegonia
Egg bareing,

Leaves
flat structure
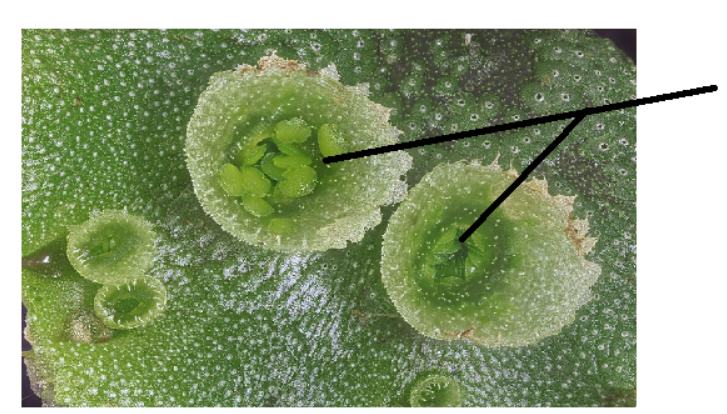
gemma cups
Cups on liverworts- for reproduction; haploid cells in the cups that get dispersed by water.
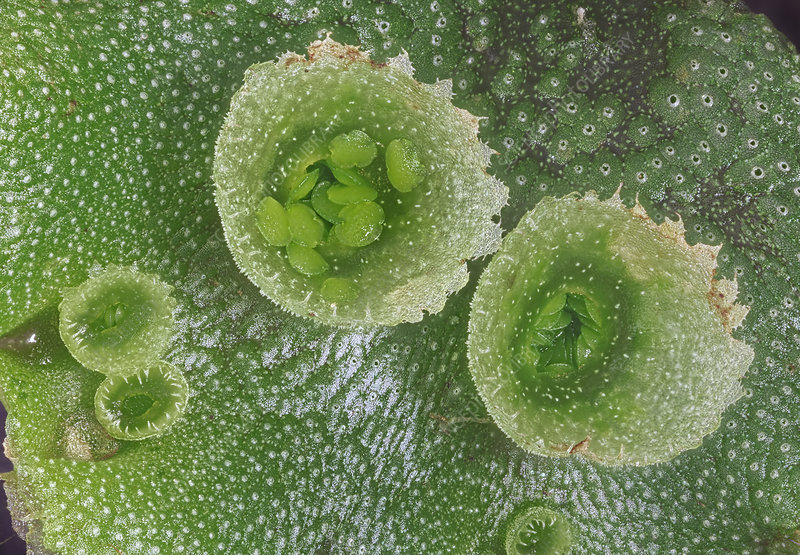

gemmae
Haploid cells within liverwort cups that are moved around via water

lignin
microphylls
megaphylls
phloem
Rhizoid
Rhizome
Roots
Sori

Sporophylls
Stem
Stomata
Strobilus
Tracheids
Vascular Bundle
Waxy Cuticle
waxy layer around epidermis to retain water
Xylem
Dioecious
Male and female reproductive systems are on different bodies
Evapotranspiration
Upward movement of water (in plants)
Monoecious
Male and female reproductive systems are on the same body
Spore
Syngamy
The fertilization of zygotes
Zygote
time period when plants began to colonize terrestrial environments.
about 500 million years ago
Terrestrial adaptations of Bryophytes
Terrestrial adaptations of ferns
Terrestrial adaptations of gymnosperms
Terrestrial adaptations of angiosperms

nutrients for seed
Food store
True endosperm
pericarp
conifer adaptations to cold
Dicots
Flower petals in multiples of 4 or 5
● Branching/net-like vascular system/ leaf veins leaves
Cotyledon Count:2
● A tap root (usually
Monocots
Flower petals in multiples of 3
Cotyledon Count: 1
Parallel vascular system/viens
● A fibrous root ball
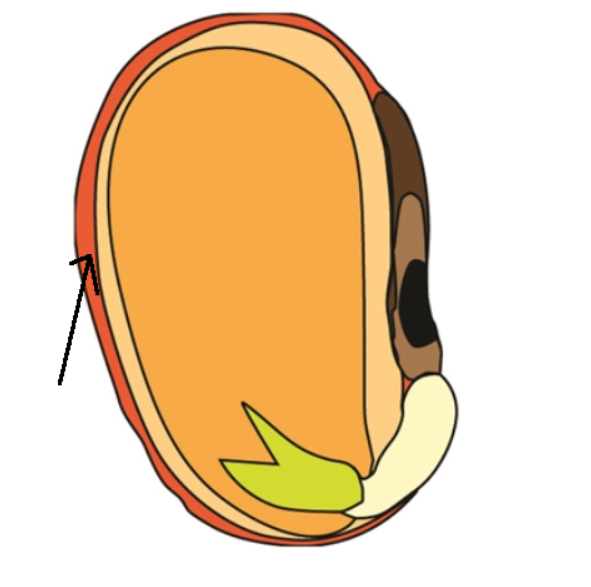
protective coating
Seed coat
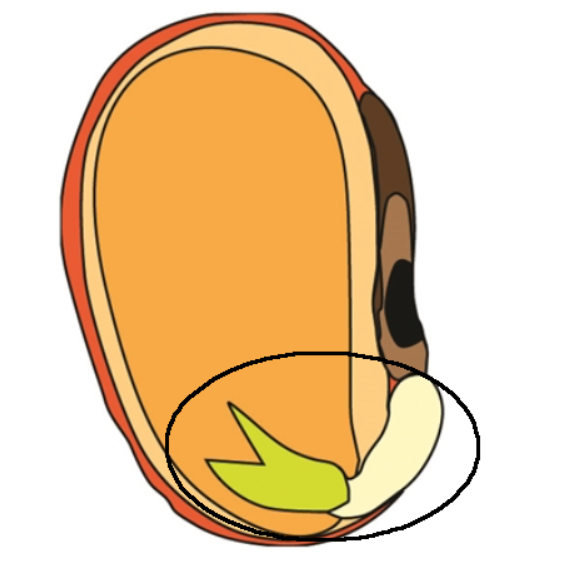
Embryo
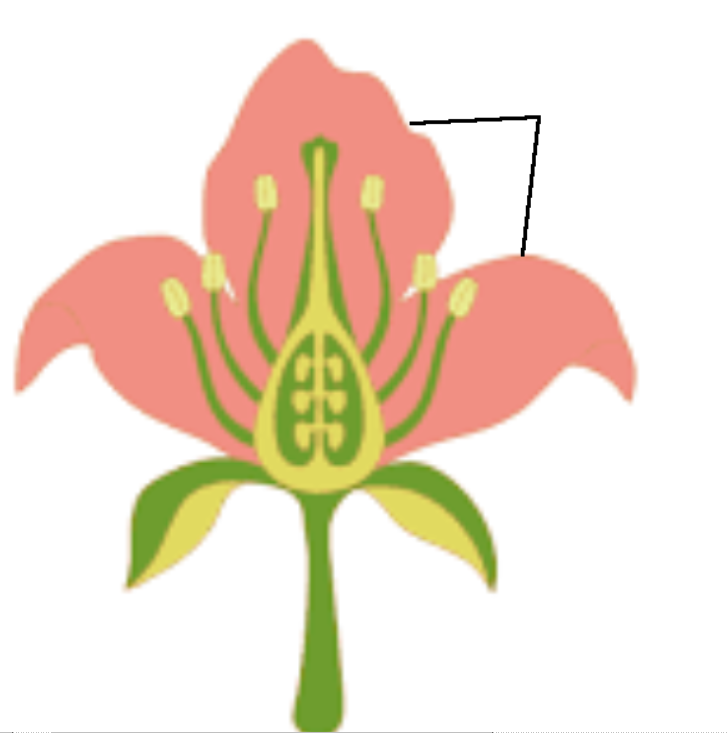
Petal(singular)/ Corolla(Multiple)
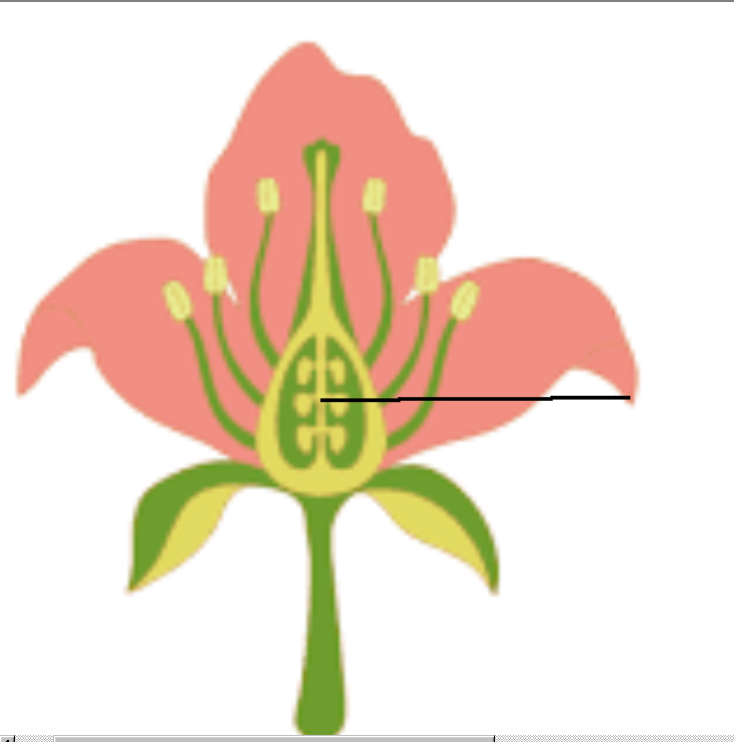
Ovary

anther
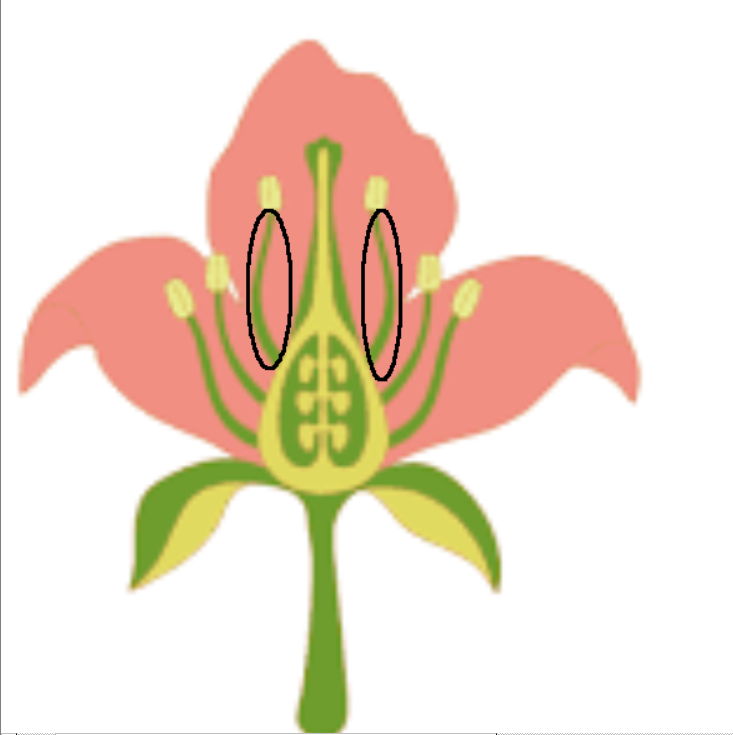

filament
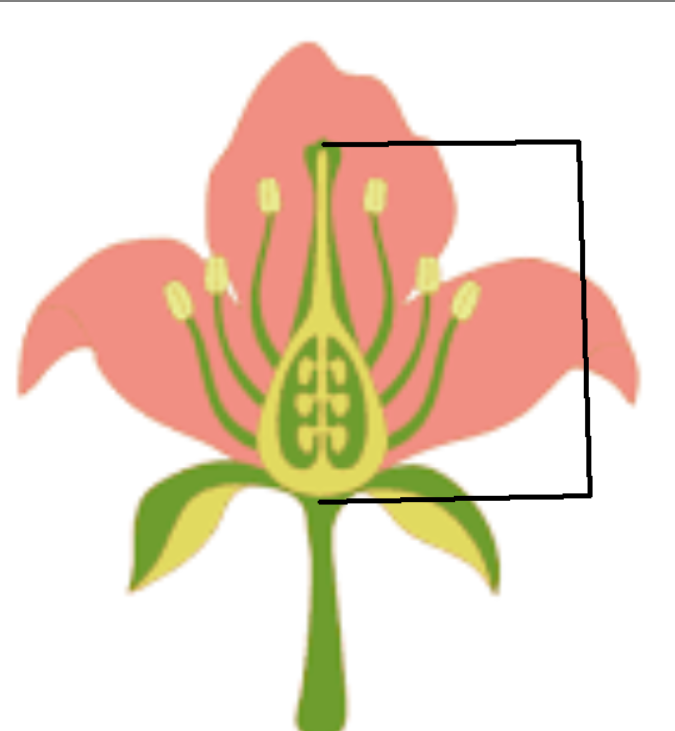
Pistil/carpal
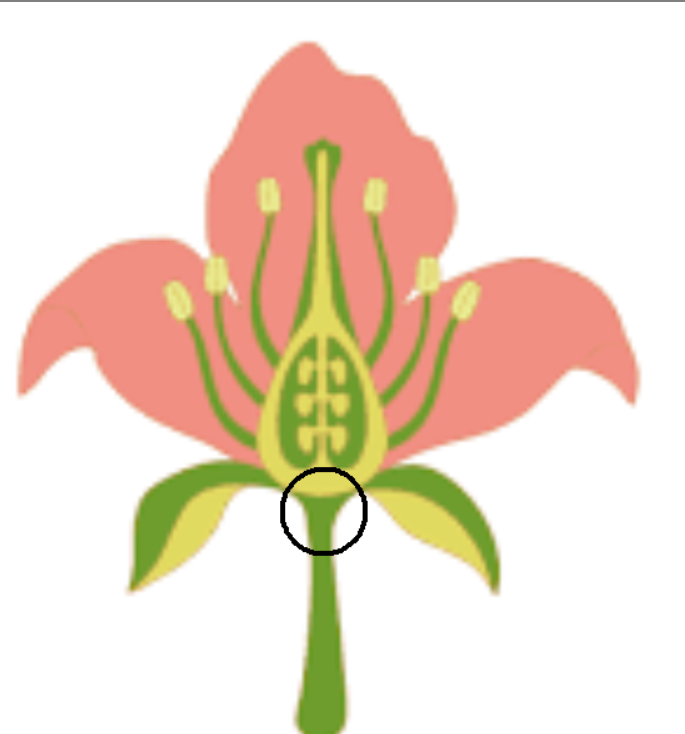
receptical
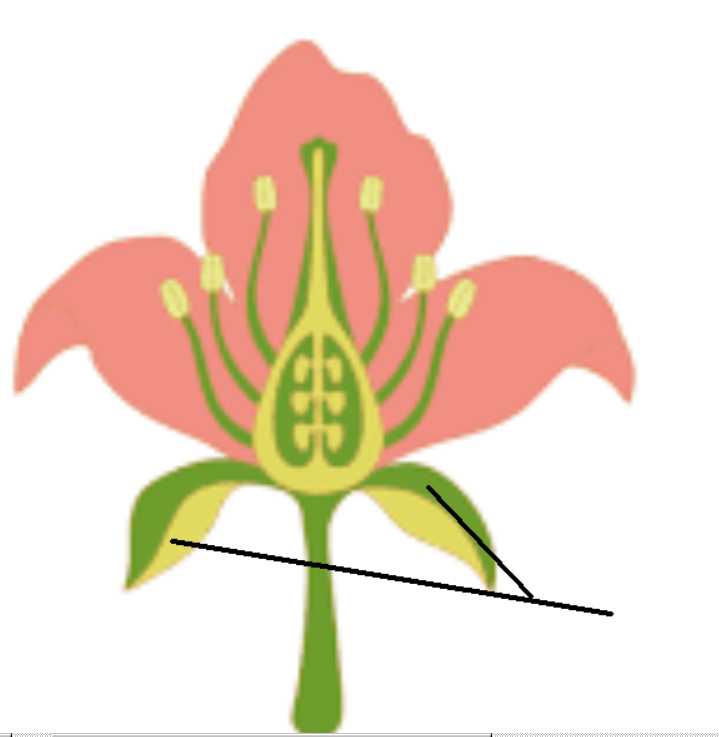
sepal (singular)/ Calyx (both)
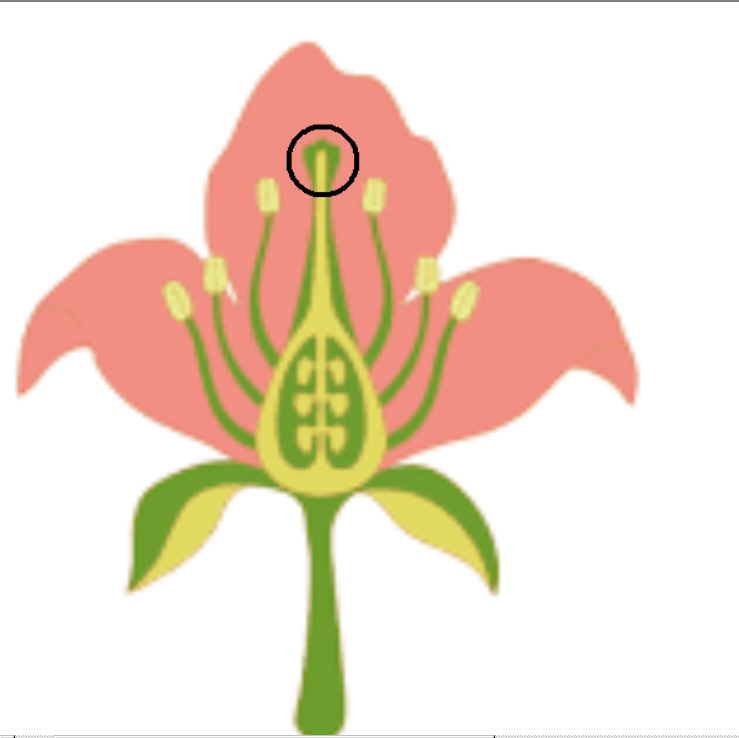
Stigma
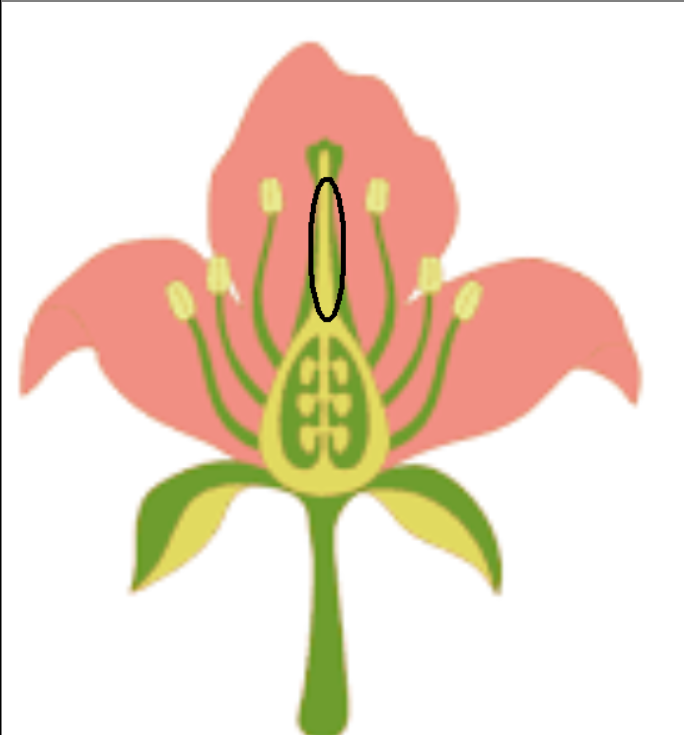

Style
Interspecific Competition
Between two differing species
Describe the five conditions that must be met for a population to undergo no change in the frequency 1)
No random events that eliminate alelles
Describe the five conditions that must be met for a population to undergo no change in the frequency 2)
No movement(migration) in or out of a population
Describe the five conditions that must be met for a population to undergo no change in the frequency 3)
no reproductive or survival advantages
Describe the five conditions that must be met for a population to undergo no change in the frequency 4)
All mating must be random (mates can not be selected)
Describe the five conditions that must be met for a population to undergo no change in the frequency 5)
No mutations can occur
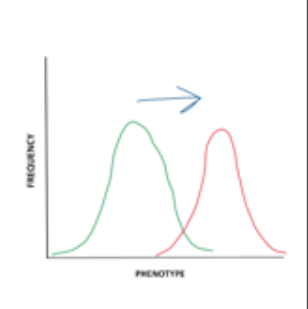
Pattern of natural selection likely to lead to biological speciation.
Disruptive
stabilizing
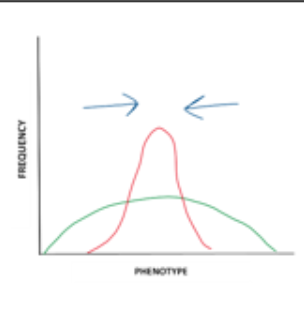
Disruptive
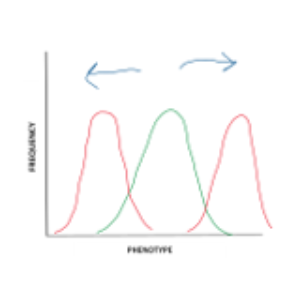
directional
Angiosperm
Have: xylem, phloem, roots, stems, megaphylls, flowers, fruits, seeds
Bryophytes/ Mosses
Have: embryo retention, waxy cuticle, stomata, rhizoids, simple leaves
Do NOT have: xylem, phloem, roots, seeds, flowers, fruits
Lycophytes
Have: xylem, phloem, roots, microphylls, stems, sporophylls
Do NOT have: seeds, flowers, fruits
Ferns
Have: xylem, phloem, roots, megaphylls, sori, rhizomes, sporophylls
Do NOT have: seeds, flowers, fruits