Lecture 3 Polymer Materials - Chemistry
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
What is a polymer?
A polymer is a substance composed of molecules which have long sequences of one or more species of atoms or groups of atoms linked to each other by primary, usually covalent, bonds.

How are polymer molecules formed?
Polymer molecules are formed by linking together monomer molecules through polymerization.
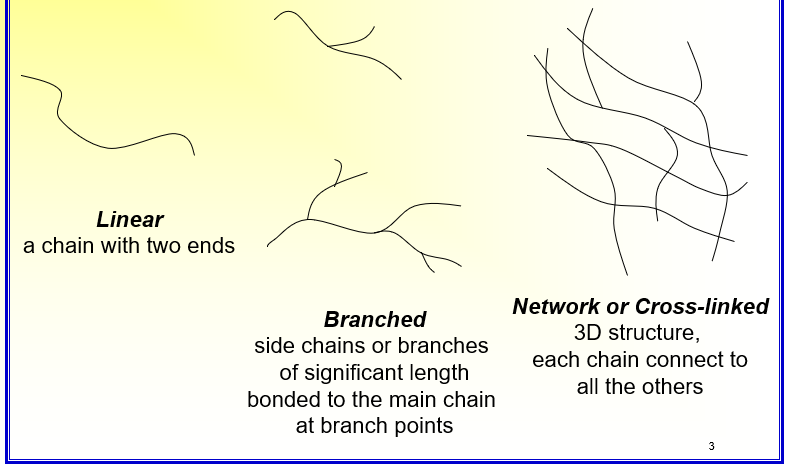
What are the different classes of skeletal structures for polymers?
Linear: Chain with two ends
Branched: Side chains or branches of significant length bonded to the main chain at branch points
Network or Cross-linked: 3D structure, each chain connects to all the others
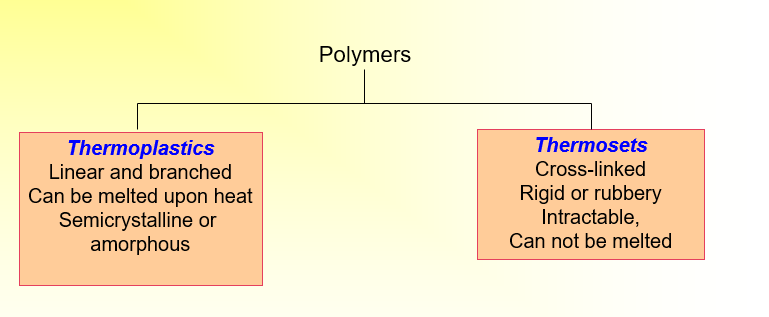
Thermoplastics vs. Thermosets
What is a homopolymer?
•A polymer resulting from the polymerization of a single monomer; a polymer consisting substantially of a single type of repeating unit.
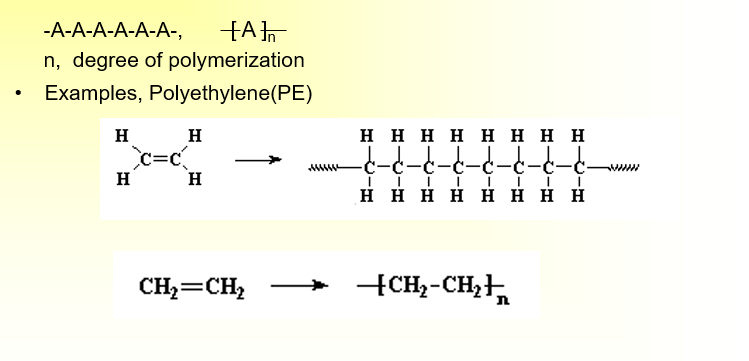
-A-A-A-A-A-A-,
n, degree of polymerization
•Examples, Polyethylene(PE)
What is a copolymer?
Definition: Polymers whose molecules contain more than one type of repeat unit.
What are statistical copolymers?
•Statistical copolymers: the sequential distribution of the repeat units obeys known statistical laws
–Random copolymer, a special type of statistical copolymer, true random

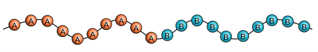
What is an alternating copolymer?

What is a graft copolymer?
branched polymers with branch having different chemical structure from the main chain
Graft and block copolymers may have unique properties that are not intermediate to those of the corresponding homopolymers
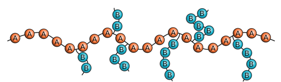
What is a block copolymer?
Repeat units exist in long sequences or blocks of the same type
Graft and block copolymers may have unique properties that are not intermediate to those of the corresponding homopolymers
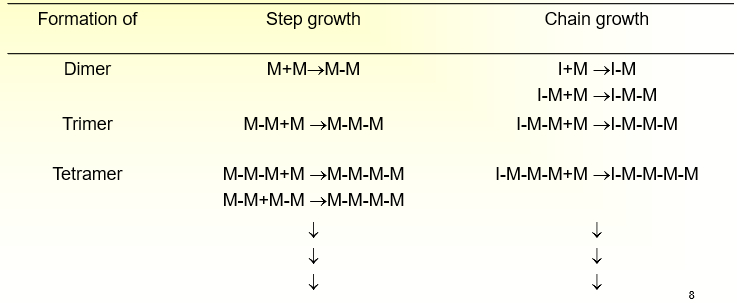
What are the two methods of Synthesis?
Step-growth Polymerization
Polymerization in which the polymer chains grow step-wise by reactions that can occur between any two molecular species
Chain-growth Polymerization
Polymerization in which a polymer chain grows only by reaction of monomers with a reactive end-group on the growing chain
How does the step-growth polymerization reaction, Condensation, work?
2n-1 H2O’s for polyester and polyamides
some medical materials based on polyester: vessel made from polyester material
an example of polyamide use in medicine is nylon-based sutures

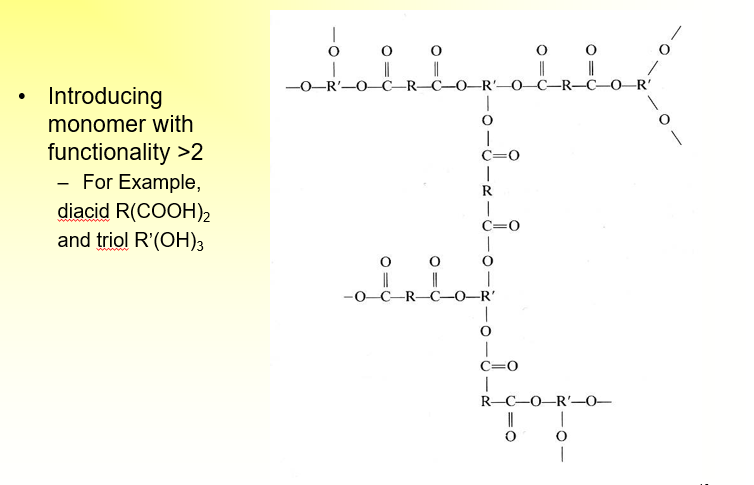
What is the significance of branching and Crosslinking in a Condensation
If you introduce more than two reactive groups, you can get crosslinks and/or branches
What are the two categories of chain-growth polymerization?
•Free Radical Polymerization
–Free radical: independently-existing species with unpaired electron and are normally highly reactive
–Polymer molecule grows by addition of monomer to a terminal free-radical reactive site known as active center
•Ionic Polymerization
–Anionic
–Cationic
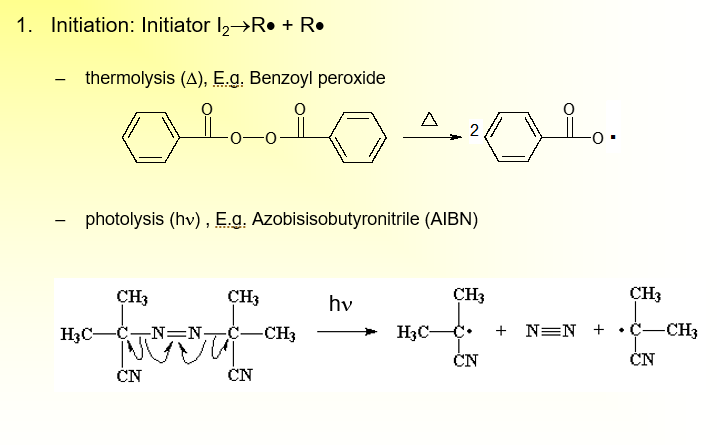
Method for Free-Radical Polymerization: Initiation
Initiator: Starts formation of radical in presence of some catalyst
Initiation: Initiator I2→R· + R·
•R · + M → RM ·
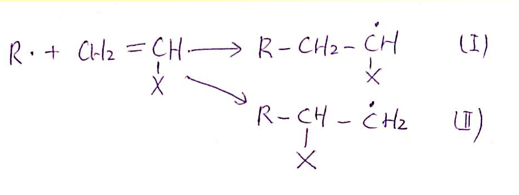
Which radical is more likely to perform
Mode (I) predominates because attack at the methylene carbon is less
sterically-hindered and yields a product free radical that’s more stable.
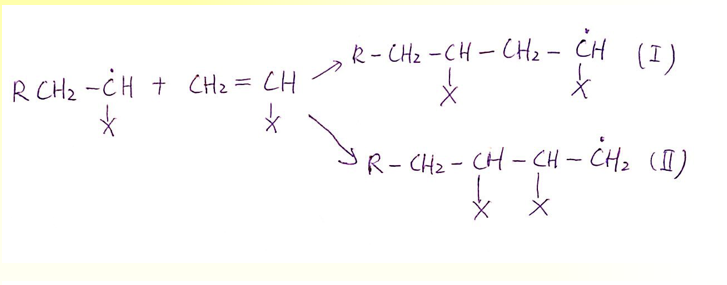
Free Radical Polymerization: What is propagation
The growing of a chain
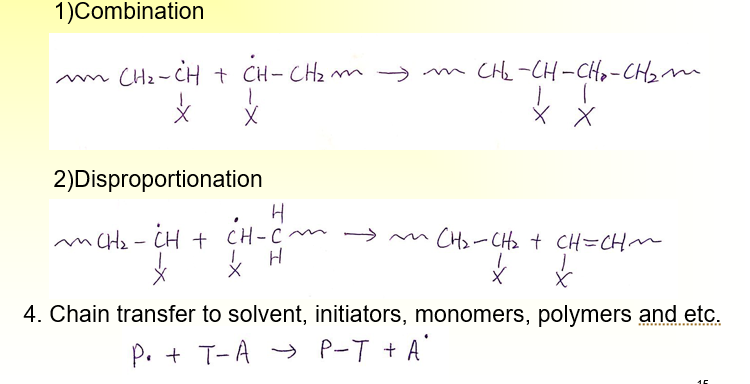
Free Radical Polymerization: What is Termination
The method of termination is pretty random, nothing is dominant, and it varies based on the X you have
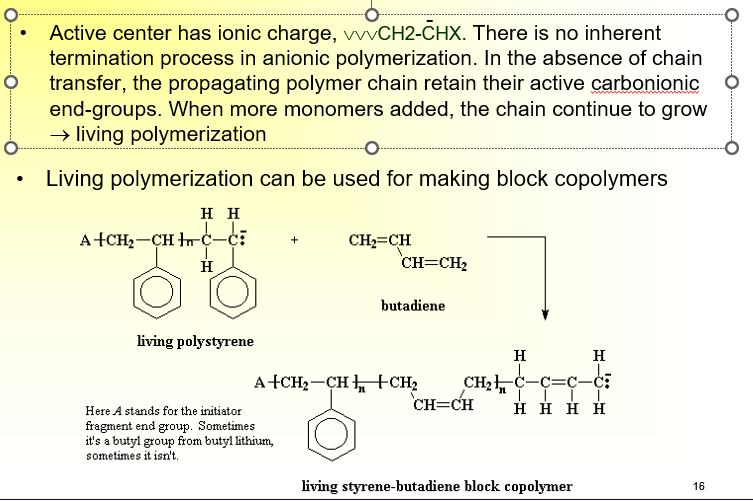
What is Anionic Polymerization?
Active center has ionic charge, \/\/\/CH2-CHX. There is no inherent termination process in anionic polymerization.
In the absence of chain transfer, the propagating polymer chain retain their active carbonionic end-groups.
When more monomers added, the chain continue to grow
→ living polymerization
Can be used for making block copolymers
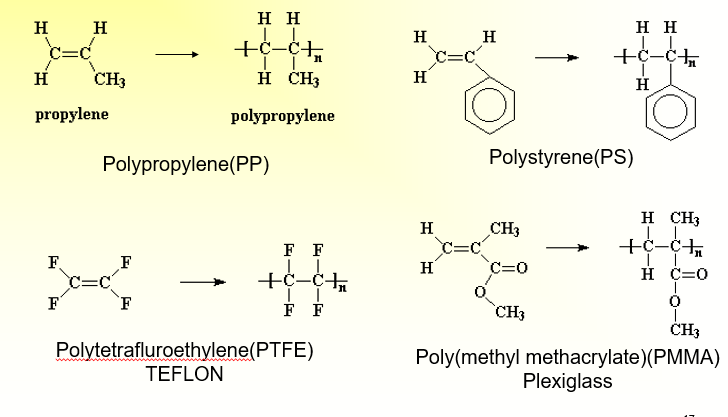
Nomenclature for polymers: Examples
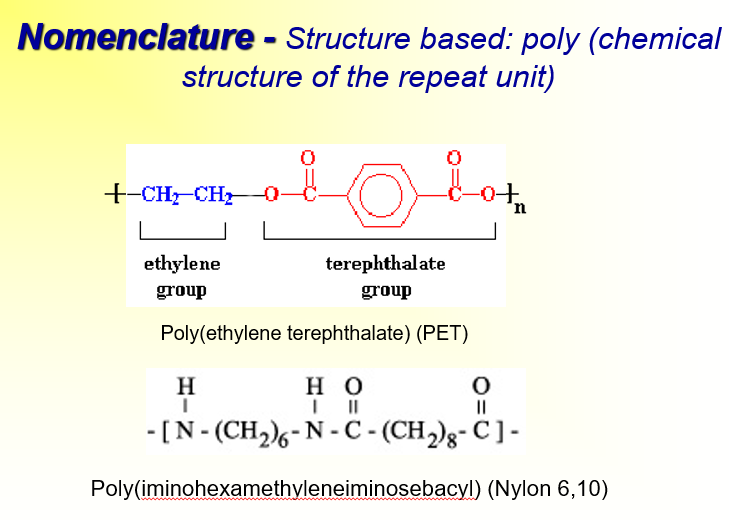
How to name polymers based on chemical structure of the repeat unit>
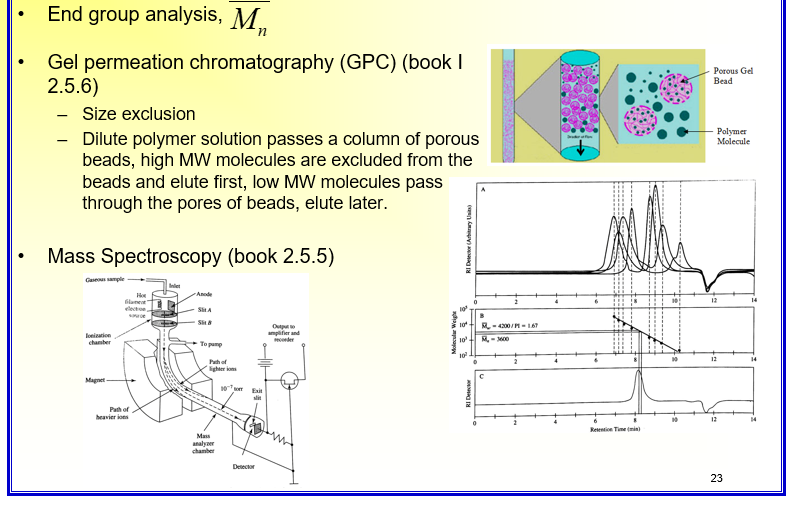
Molar Mass, Degree of Polymerization & Molar Mass Distribution
•Molar Mass M=nM0
–n, degree of polymerization, number of repeat units
–M0, molar mass of the repeat unit
•Molar Mass Distribution
–With very few exceptions, polymers consist of macromolecules with a range of molar mass.
Polyethylene’s number of repeat unit is n=100, what is the molar mass of the polymer?
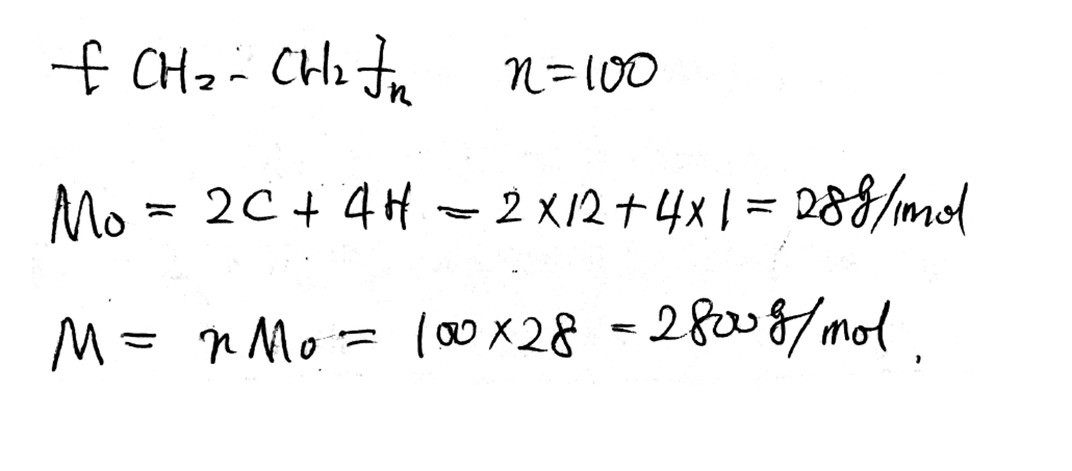
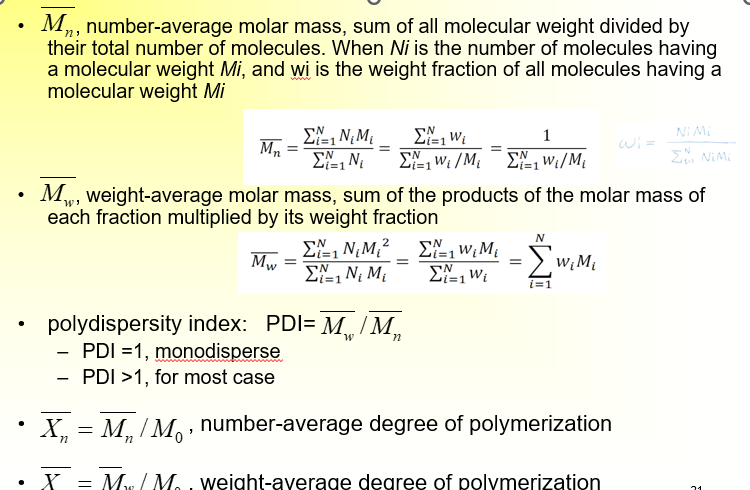
Average Molar Mass (Molecular Weight)
small n is degree of polymerization
big N is number of molecules
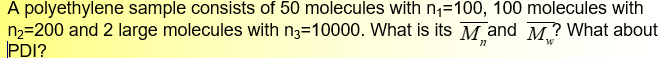
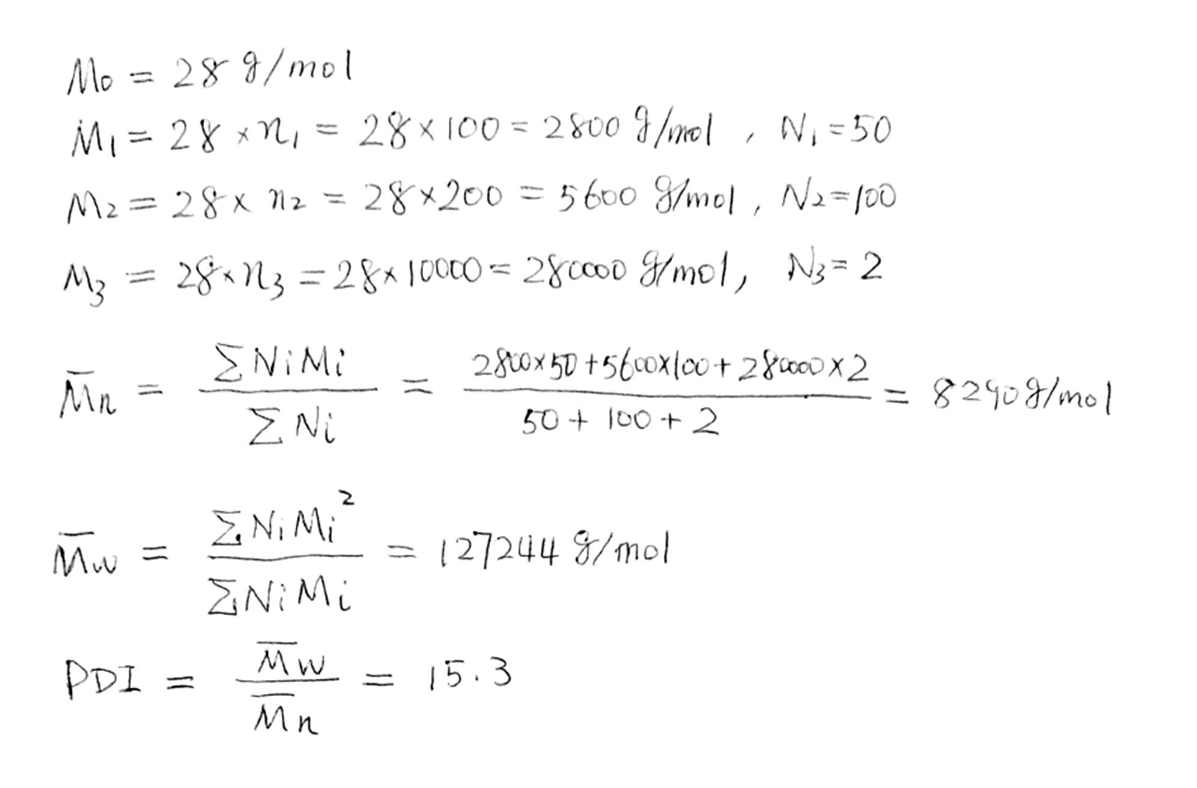
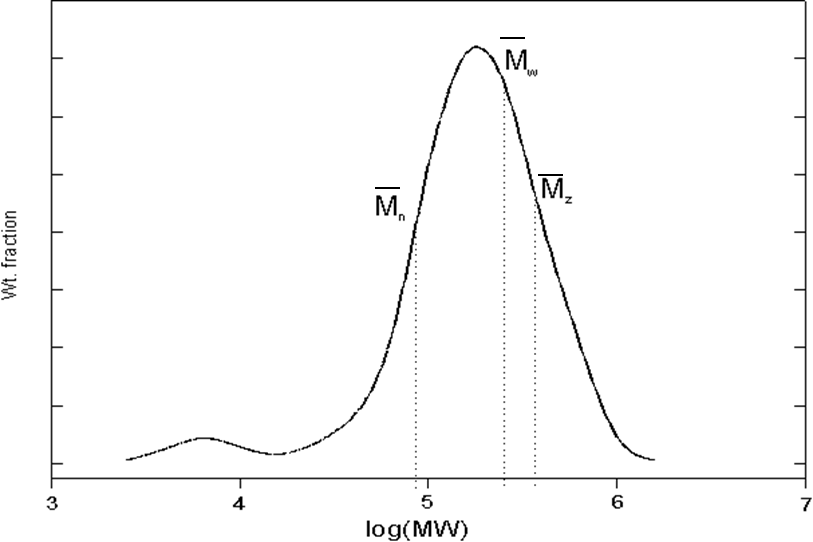
Molecular Weight Distribution