Practical 1 Review Cards
1/438
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
439 Terms
Girdles
Structures that connect limbs to the axial skeleton.
Pectoral Girdle
Composed of scapula and clavicle; connects upper limbs to the torso.
Pelvic Girdle
Formed by coxal bones and sacrum; supports lower limbs.
Scapula
Shoulder blade; provides attachment for muscles and articulates with the humerus.
Acromion Process
Part of the scapula; forms a protective cover and attaches to the clavicle.
Scapular Spine
Divides the posterior surface of the scapula into supra and infraspinous fossae.
Coracoid Process
A projection on the scapula; serves as an attachment point for muscles.
Glenoid Cavity
A shallow socket in the scapula that articulates with the head of the humerus.
Clavicle
Bone that articulates with the acromion and manubrium of the sternum; connects the arm to the body.
Humerus
The bone of the upper arm; articulates with the shoulder and elbow.
Tubercles
Projections on the humerus; include greater and lesser tubercles for muscle attachment.
Intertubercular Groove
A groove on the humerus that houses the tendon of the biceps brachii.
Capitulum
Rounded part of the humerus that articulates with the radius.
Trochlea
Spool-shaped part of the humerus that articulates with the ulna.
Epicondyles
Projections on the humerus for ligament attachment.
Radius
Forearm bone on the thumb side; involved in wrist movement.
Ulna
Forearm bone on the little finger side; forms the elbow joint.
Trochlear Notch
A notch on the ulna that fits over the trochlea of the humerus.
Olecranon Process
The bony prominence of the elbow, part of the ulna.
Carpal Bones
Eight bones in the wrist; arranged in two rows.
Carpal Tunnel
A passageway in the wrist; contains tendons and nerves.
Metacarpals
Five bones that form the palm of the hand.
Pelvic Girdle
Composed of coxal bones and sacrum; supports the lower limbs.
Acetabulum
A socket in the pelvic girdle that articulates with the head of the femur.
Femur
The thigh bone; the longest bone in the body.
Trochanters
Projections on the femur for muscle attachment; include greater and lesser.
Patella
The kneecap; a sesamoid bone that protects the knee joint.
Tibia
The larger bone of the lower leg; supports most of the body's weight.
Fibula
The smaller bone of the lower leg; stabilizes the ankle.
Tarsals
Seven bones in the foot; include the navicular, talus, and calcaneus.
Metatarsals
Five bones that form the middle part of the foot.
Phalanges
Bones of the toes; each toe has three phalanges except for the big toe, which has two.
Margin/Border
Edge
Ramus
Branch off body
Condyle
Smooth rounded articular surface
Facet
Small flattened articular surface
Process
Prominent projection
Tubercle
Small rounded bump
Tuberosity
Knob
Trochanter
Tuberosities on proximal femur
Epicondyle
Near or above condyle
Line/Linea
Low ridge
Crest/Crista
Prominent ridge
Spine
Very high ridge
Foramen
Hole used for nerves, blood vessels, etc.
Canal/Meatus
Tunnel
Fissure
Cleft
Sinus/Labyrinth
Cavity
Fossa
Depression
Fovea
Little point
Groove/Sulcus
Deeper, narrow depression
Fontanel
Becomes sutures after ossification in fetal skulls
Articular
Movement/Attachment
Paranasal Sinuses
Named for bones in which they are found (Frontal, Maxillary, Ethmoidal, Sphenoidal)
Fontanels
Membranous areas in same suture between bones; may ossify completely in adults and become synostosis
Intervertebral Disks
Located between adjacent vertebrae; filled with water to prevent collapse
Annulus fibrosus
External part of intervertebral disks
Nucleus pulposus
Internal and gelatinous part of intervertebral disks
Kyphosis
Outward curve in spine
Lordosis
Inward curve in spine
Thoracic Vertebrae
Long thin spinous processes directed inferiorly
Lumbar Vertebrae
Large thick bodies with rectangular transverse and spinous processes
Median Sacral Crest
Partially fused spinous process of the sacrum
Sacral Foramina
Intervertebral foramina in the sacrum
Coccyx
Tailbone
True/Vertebrosternal Ribs
Superior 7 ribs that attach directly to sternum via costal cartilages
False Ribs
Interior five ribs, including vertebrochondral (3) and floating (2) ribs
Manubrium
Part of the sternum that articulates with the first rib and clavicle
Jugular Notch
Superior notch of the manubrium
Sternal Angle
Point where manubrium joins body; second rib articulates here
Body of Sternum
Articulates with third through seventh ribs; also known as gladiolus
Xiphoid Process
Inferior tip of the sternum
Osteo...
Related to bones
Functions of Skeleton
Support, Protection, Movement, Electrolyte balance, Acid-Base balance, Blood formation
Osteoclast
Bone dissolving cells.
Osteocytes
mature Osteoblasts trapped in matrix they deposited. Reside in lacunae.
Osteoblast
Bone forming cells..
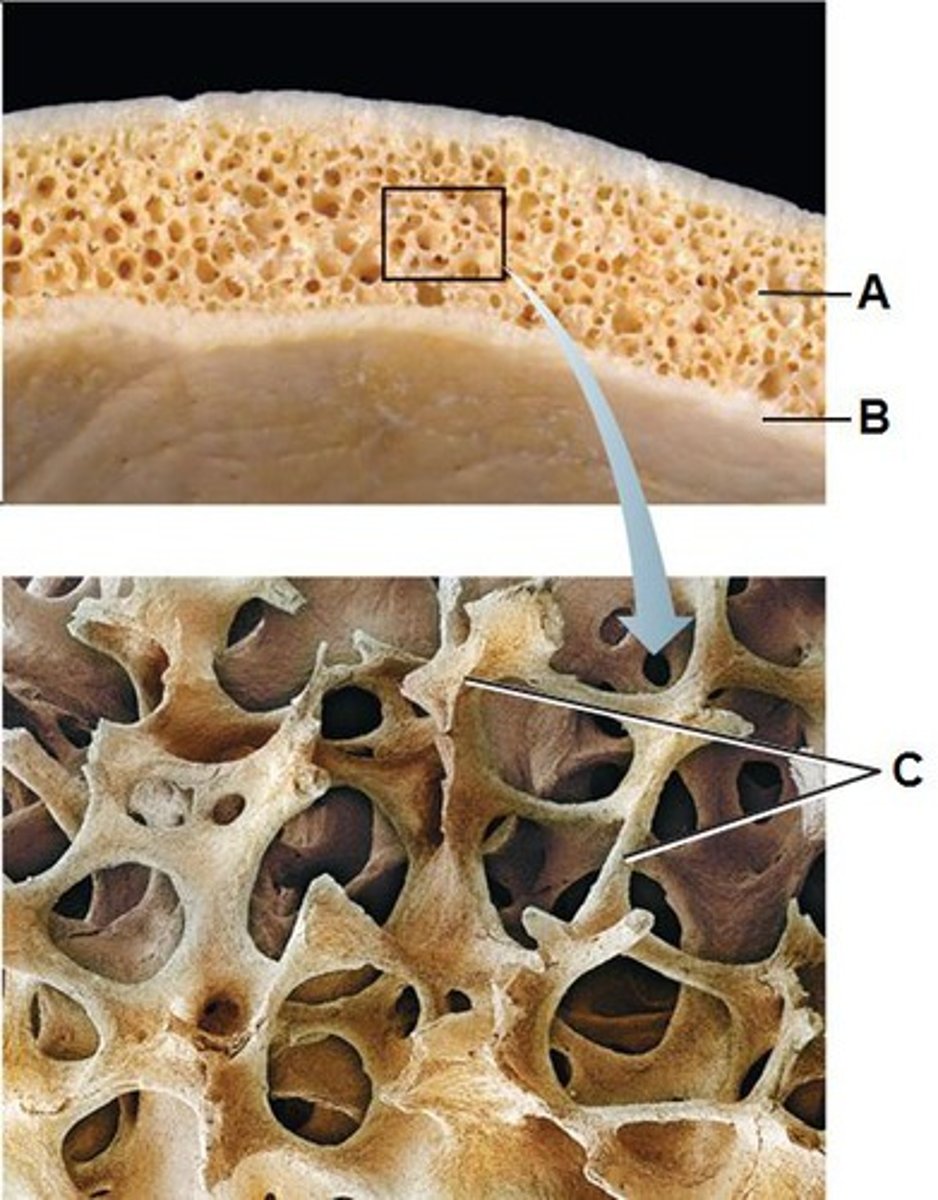
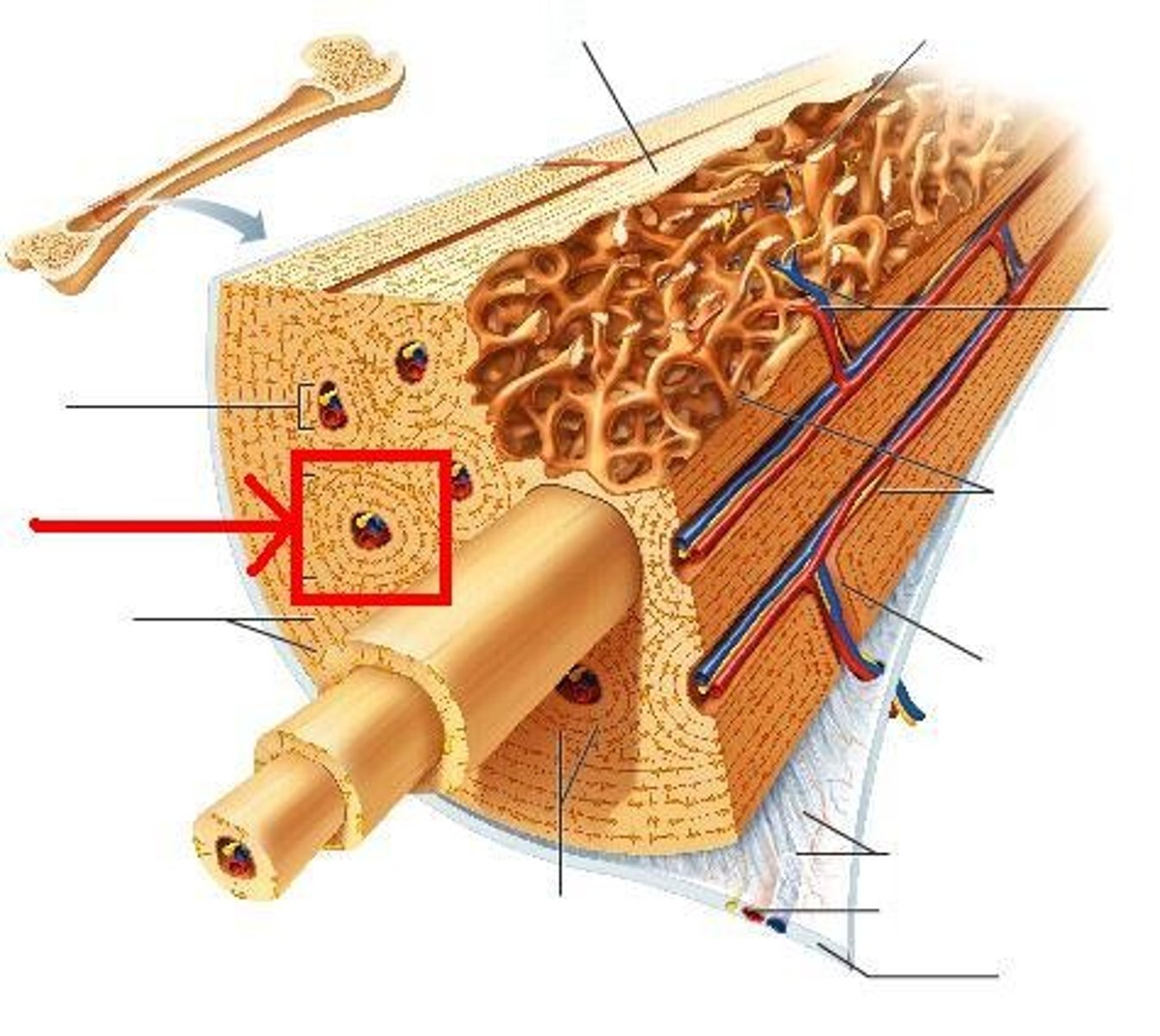
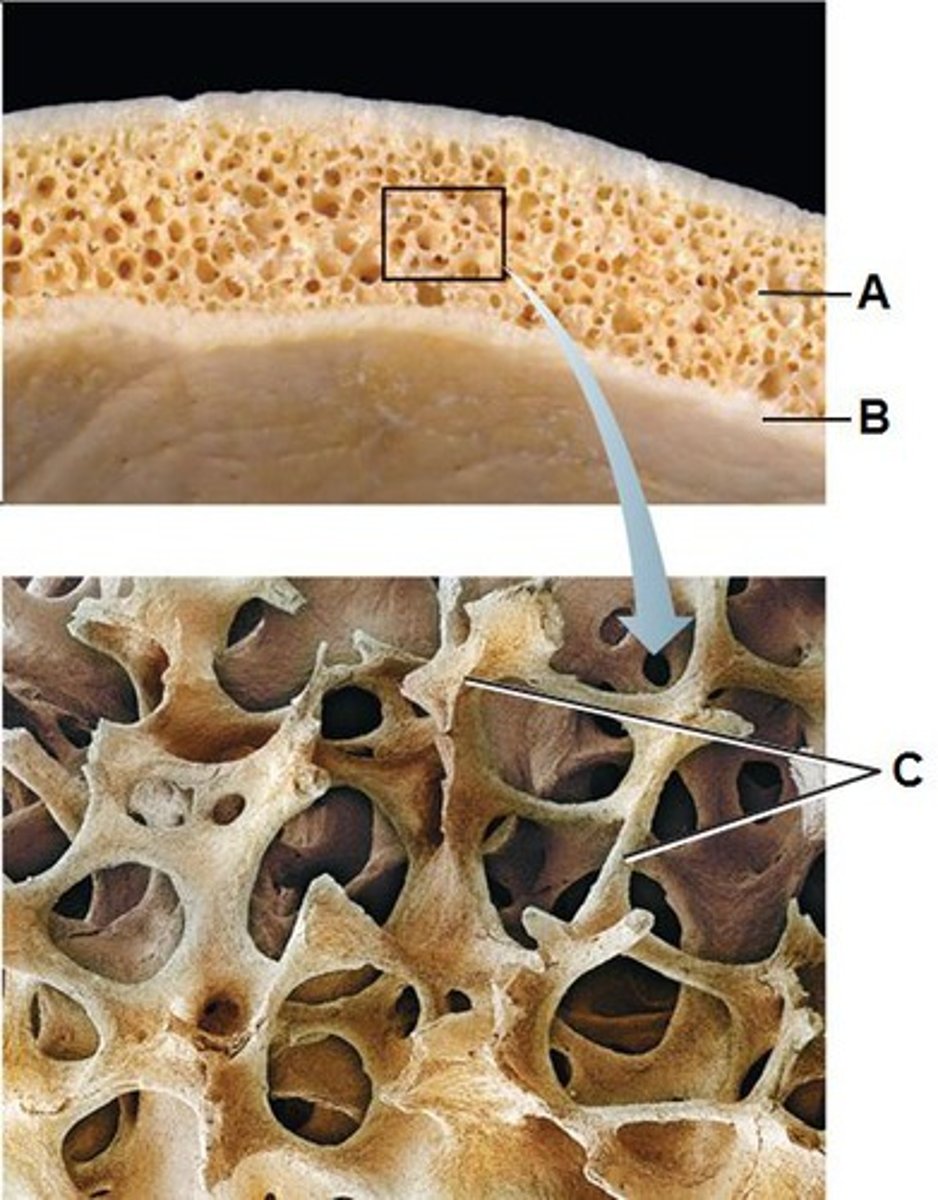
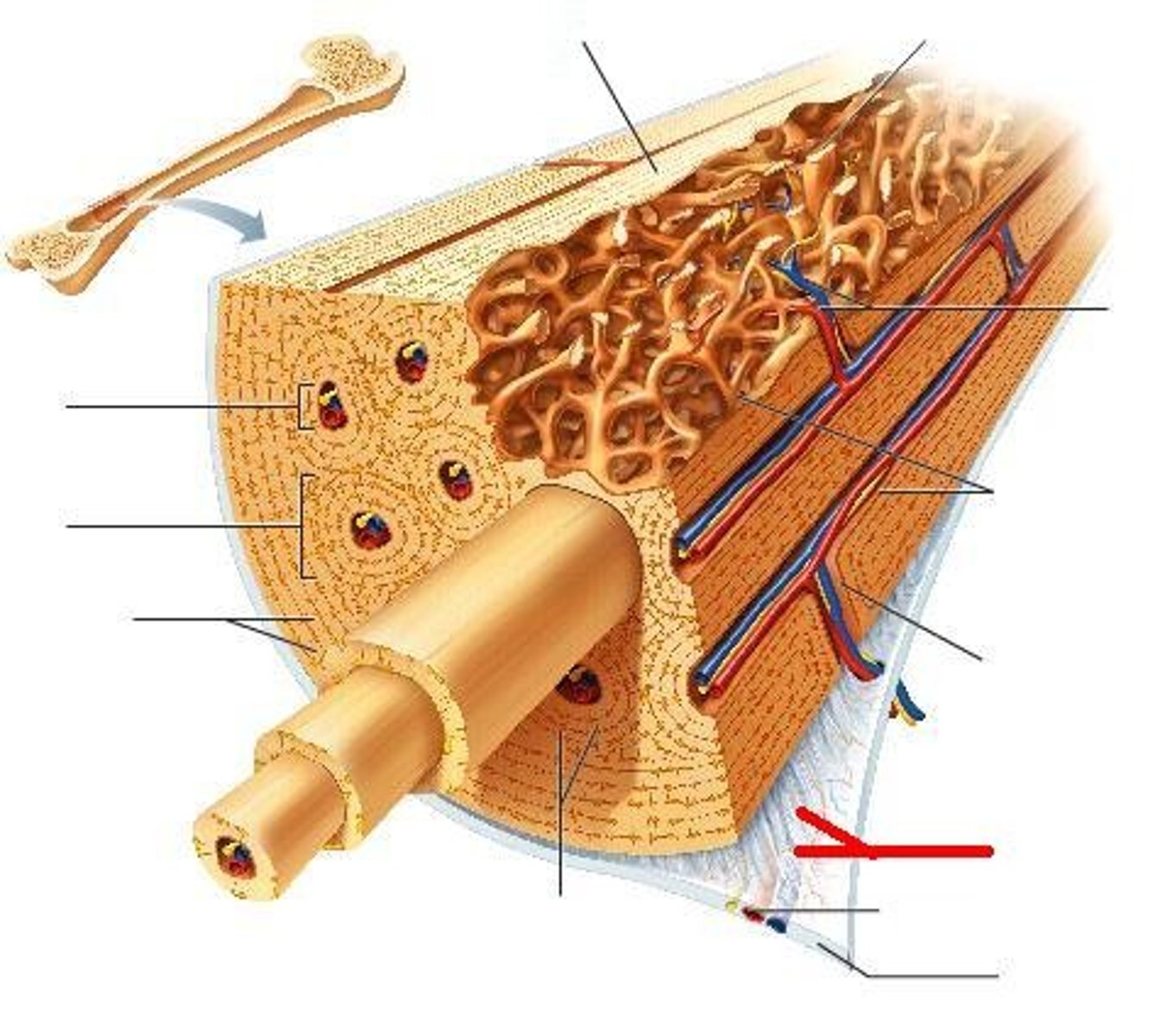
Compact (cortical) bone
Structure shown in B
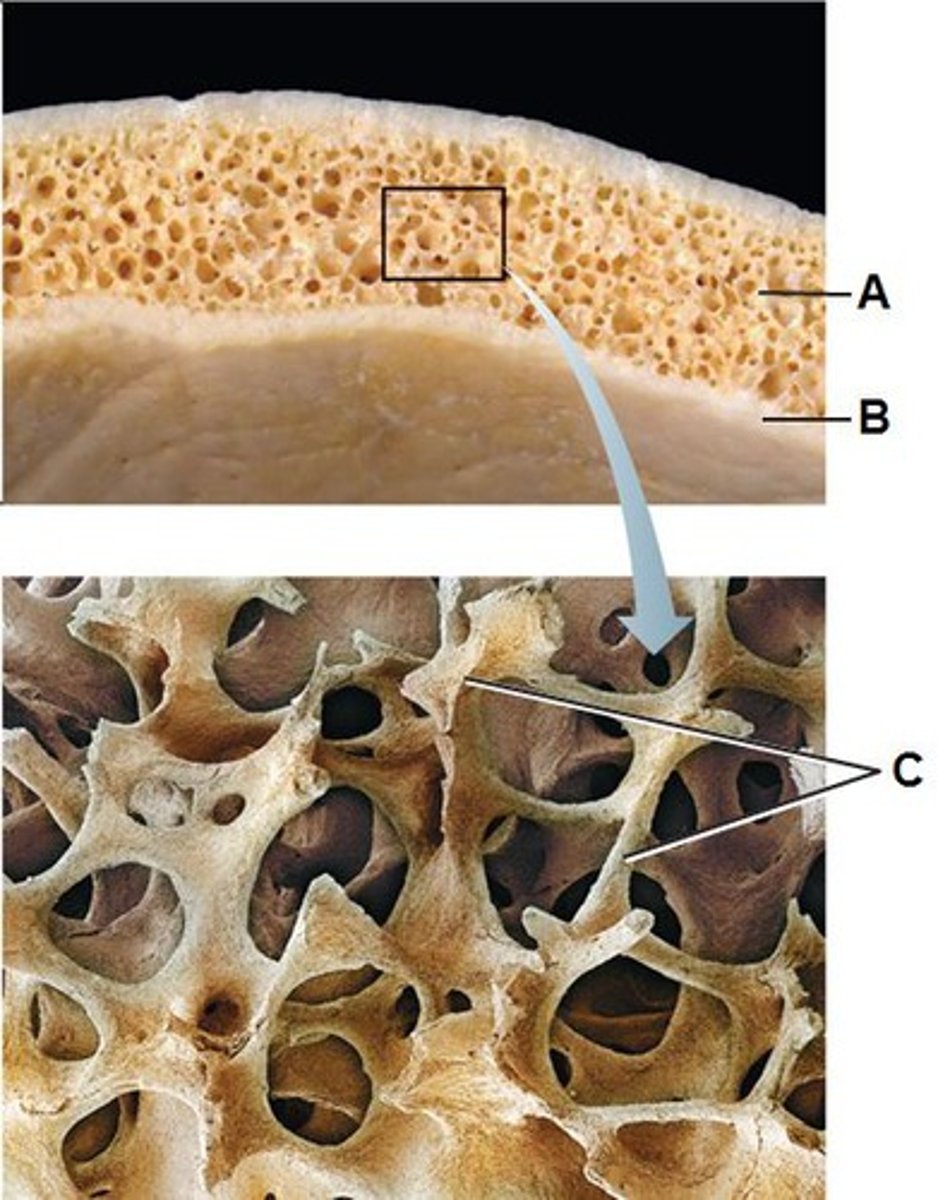
Spongy (trabecular) bone
Structure shown in A
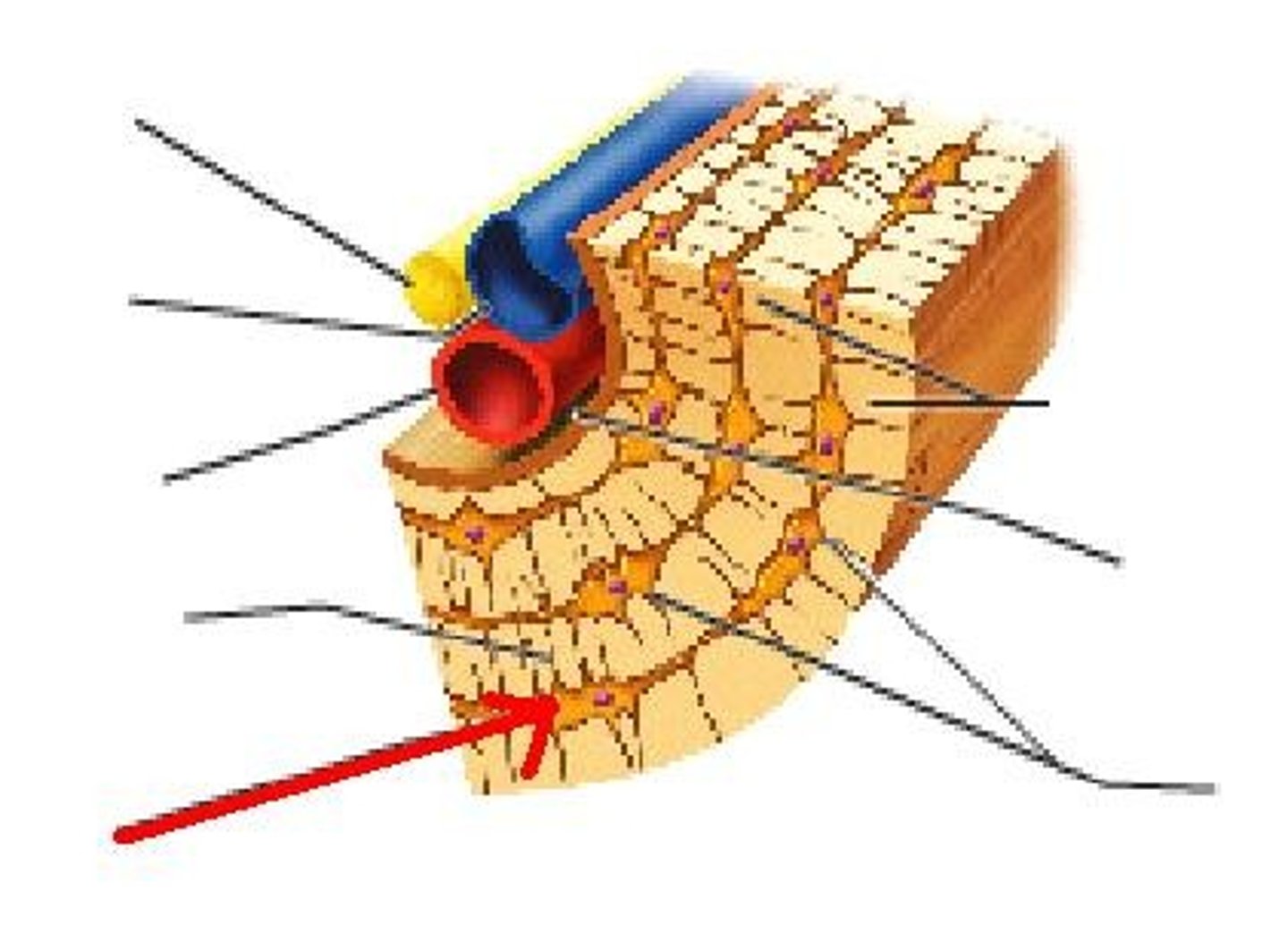
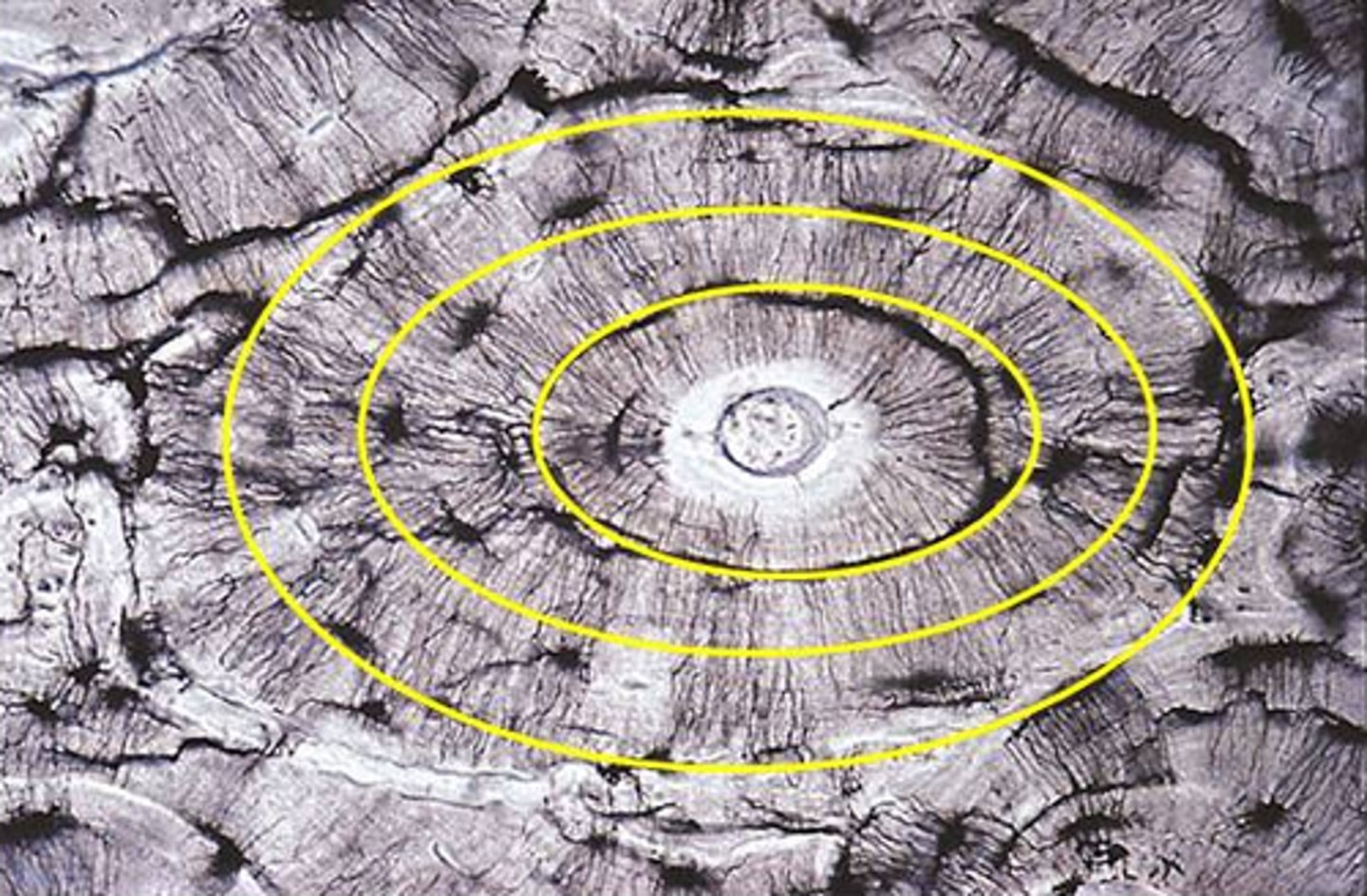
Osteon
Basic unit of compact bone
Central (Haversian) Canal
see image - lengthwise
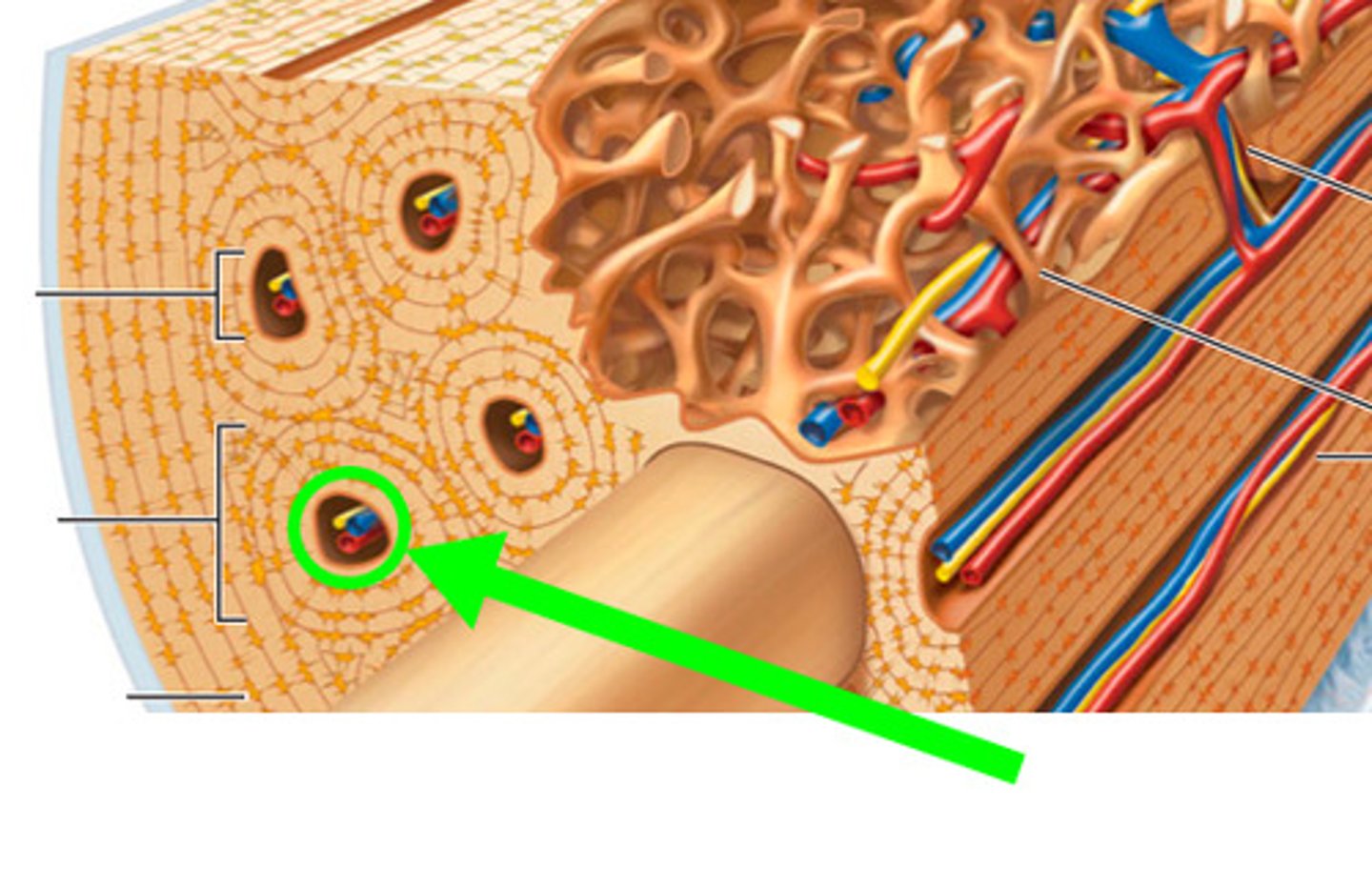
Lacuna
see image - holes in ring
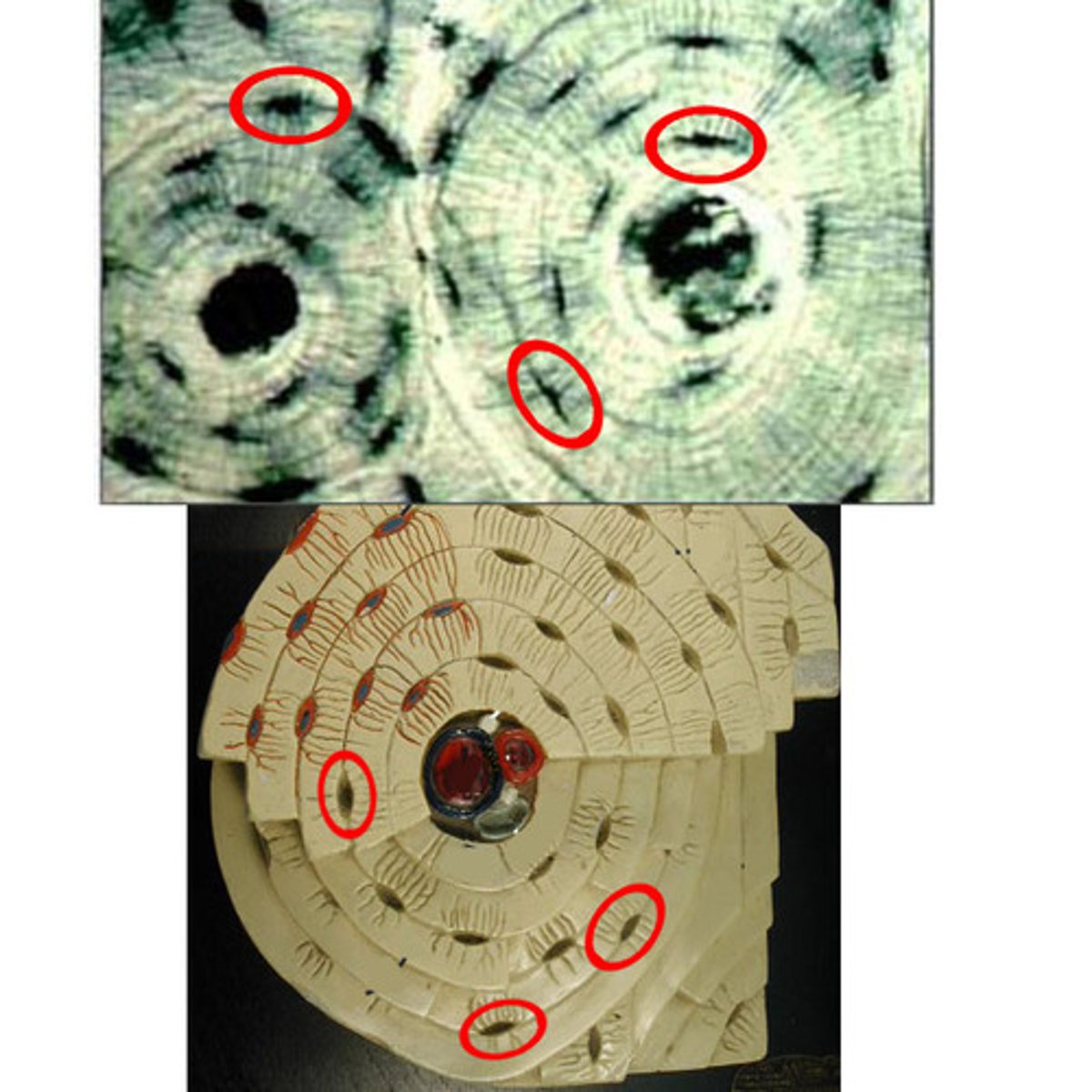
Concentric Lamellae
see image - rings
Trabeculae of spongy bone
structure seen in C
Flat bones
Cranial bones, scapula, sternum, ribs, and hip bones
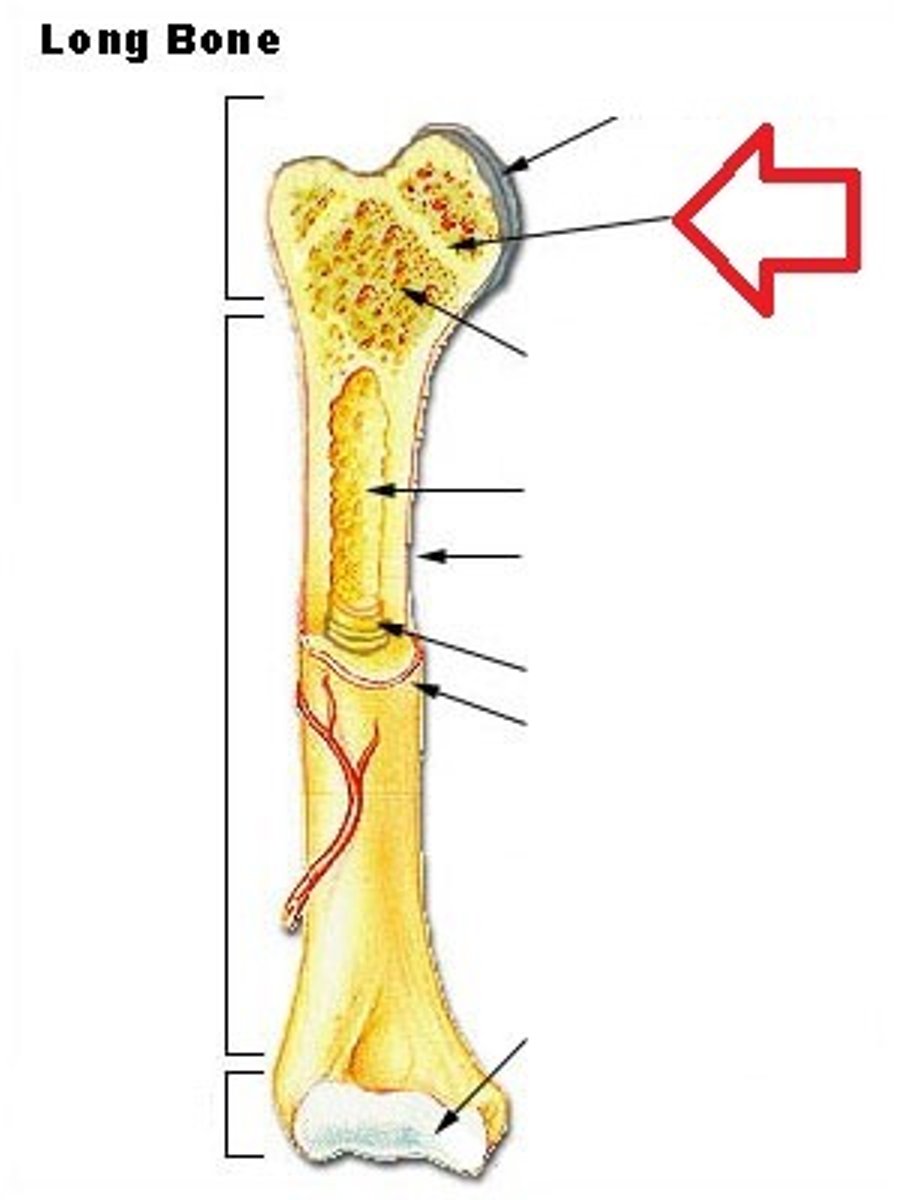
Long bones
Bones of the limbs and hands/feet (NOT wrists and ankles)
Short bones
Carpal and tarsal and patella.
Irregular bones
Vertebrae, middle-ear bones
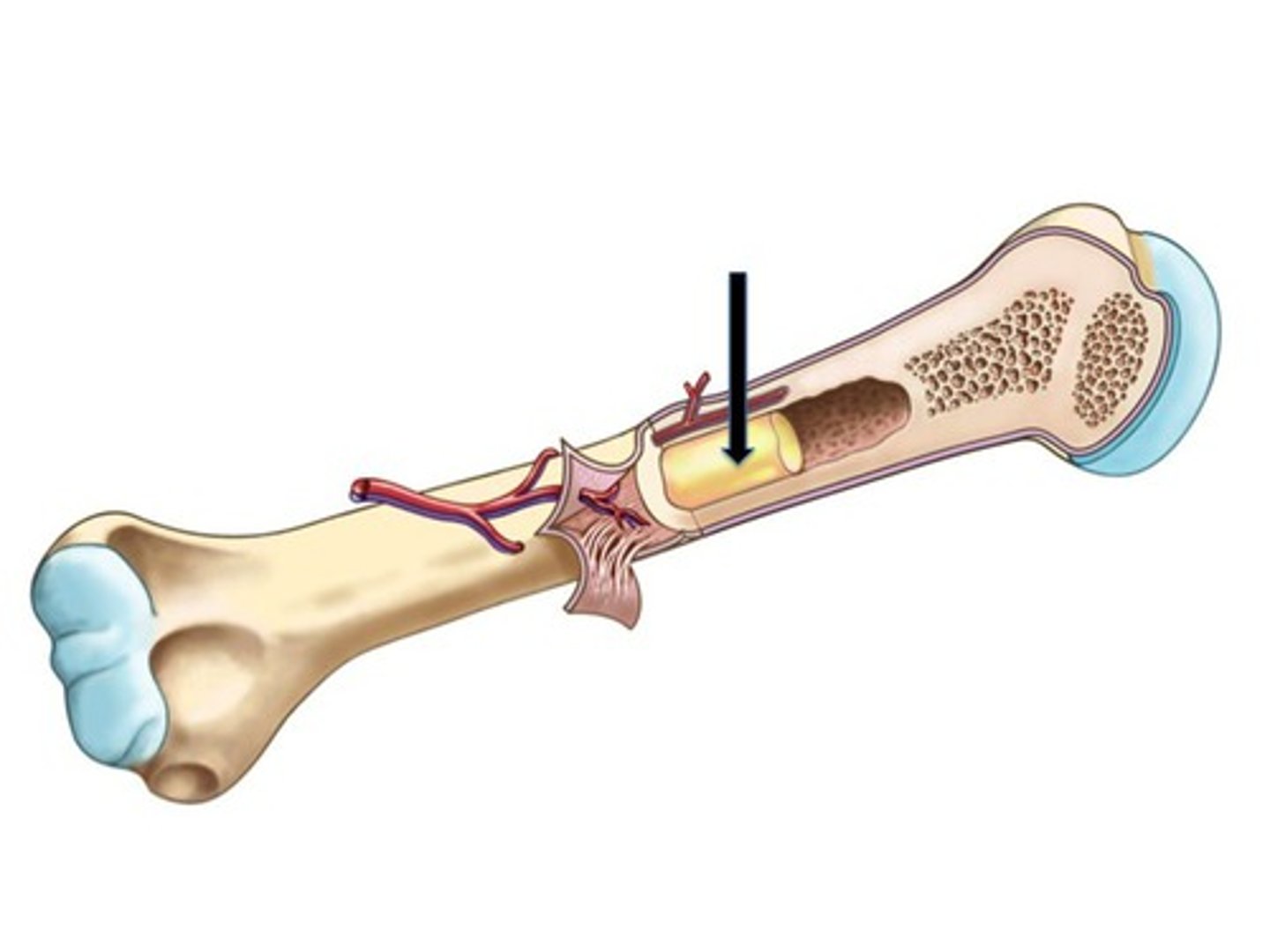
Medullary Cavity
Also known as marrow cavity, contains bone marrow.
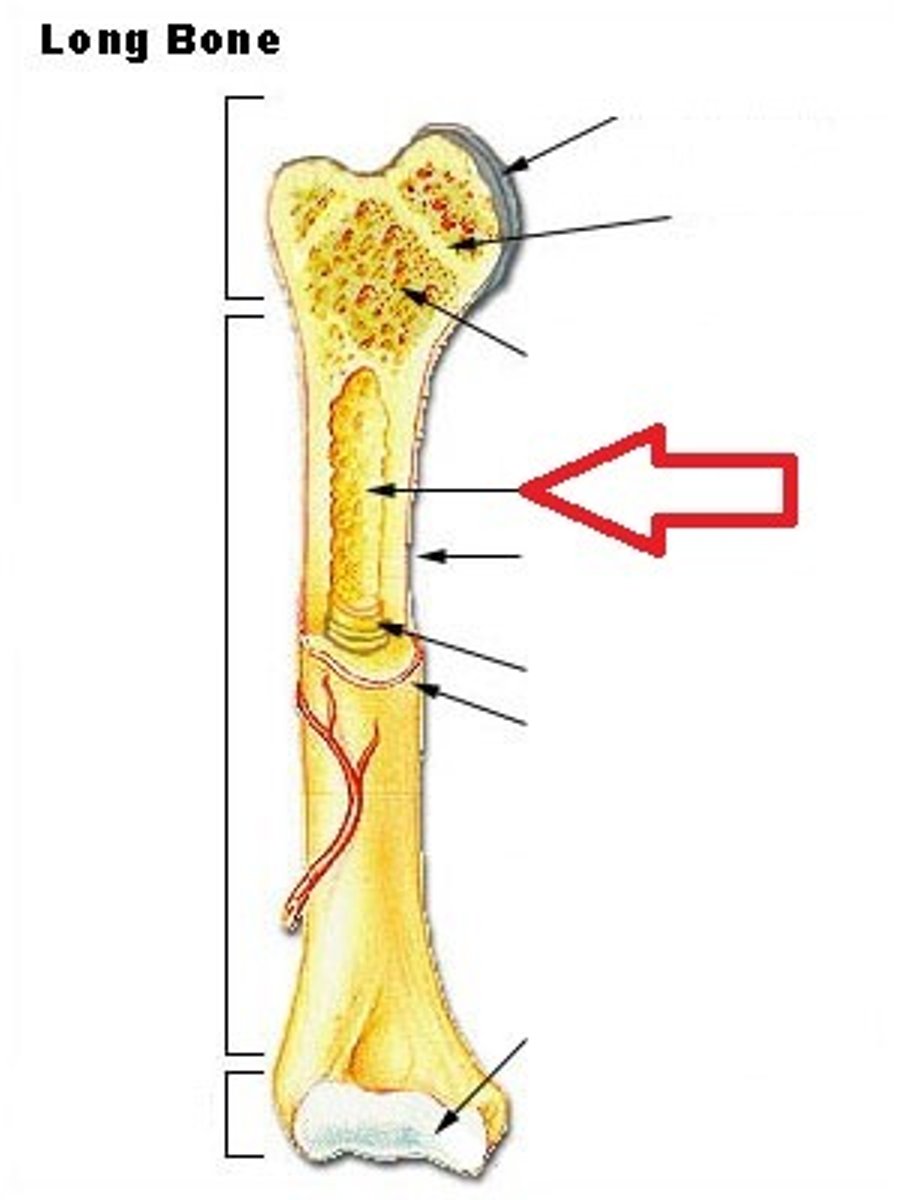
Diaphysis
Shaft of bone. (Leverage)
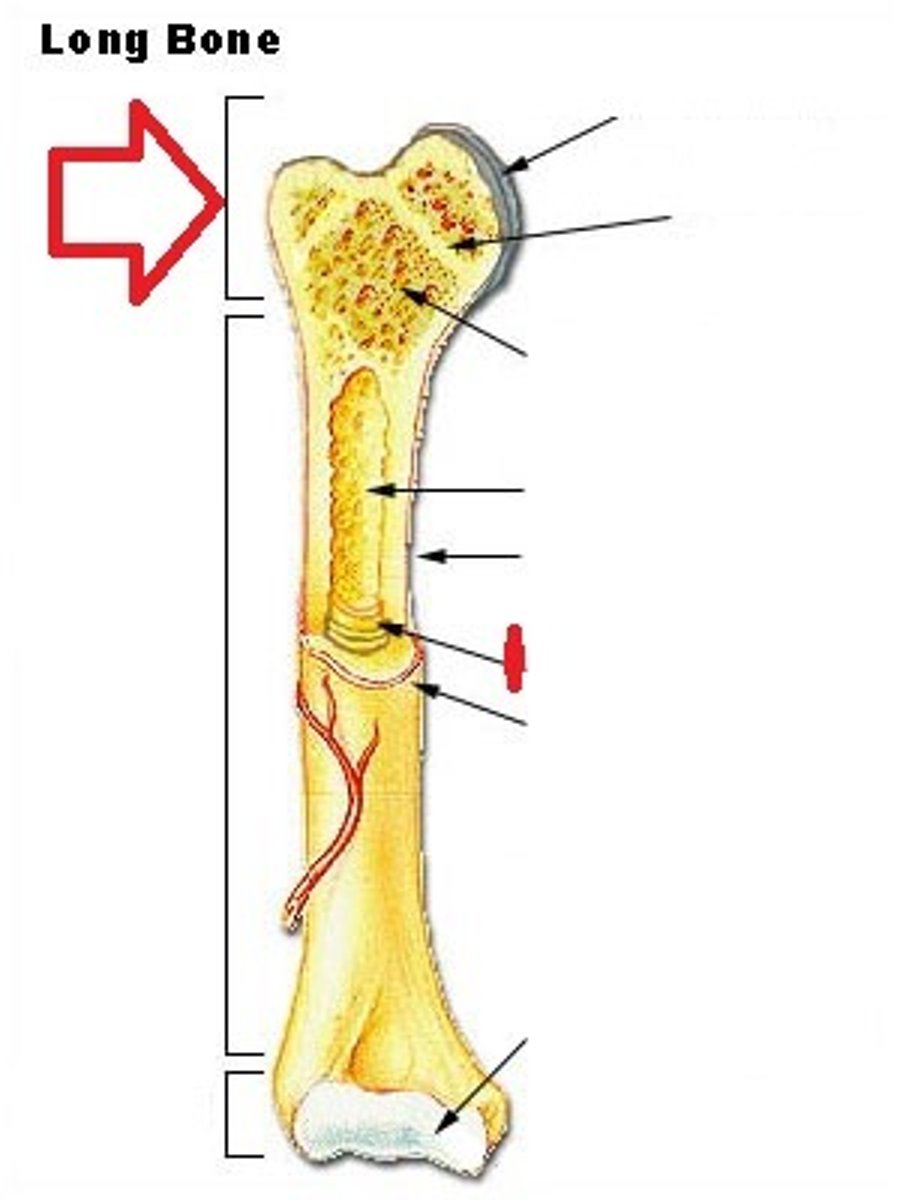
Epiphysis
Enlarged head of bone. (strength joint/provide muscle attachments) Proximal and Distal.
Articular Cartilage
Type of hyaline cartilage found at the articulation (joint) of bones.
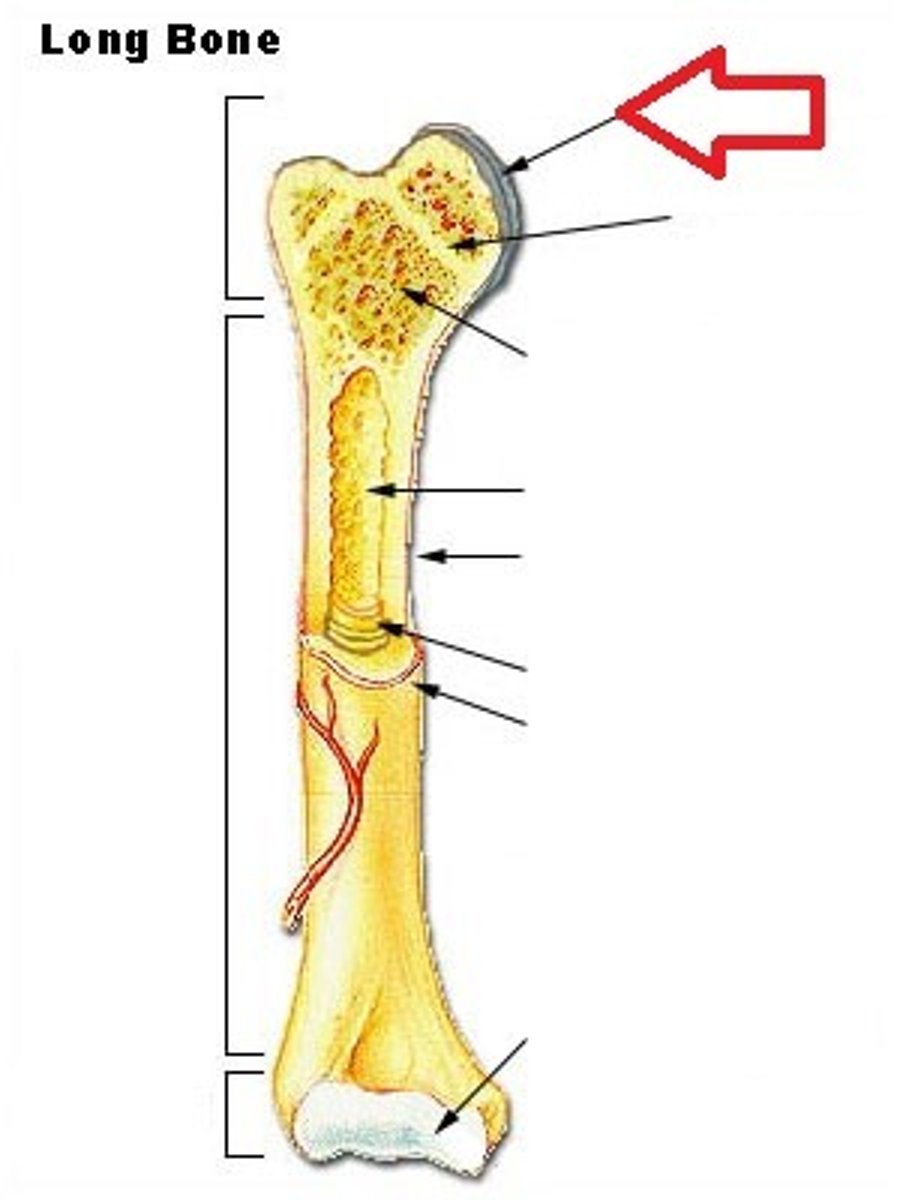
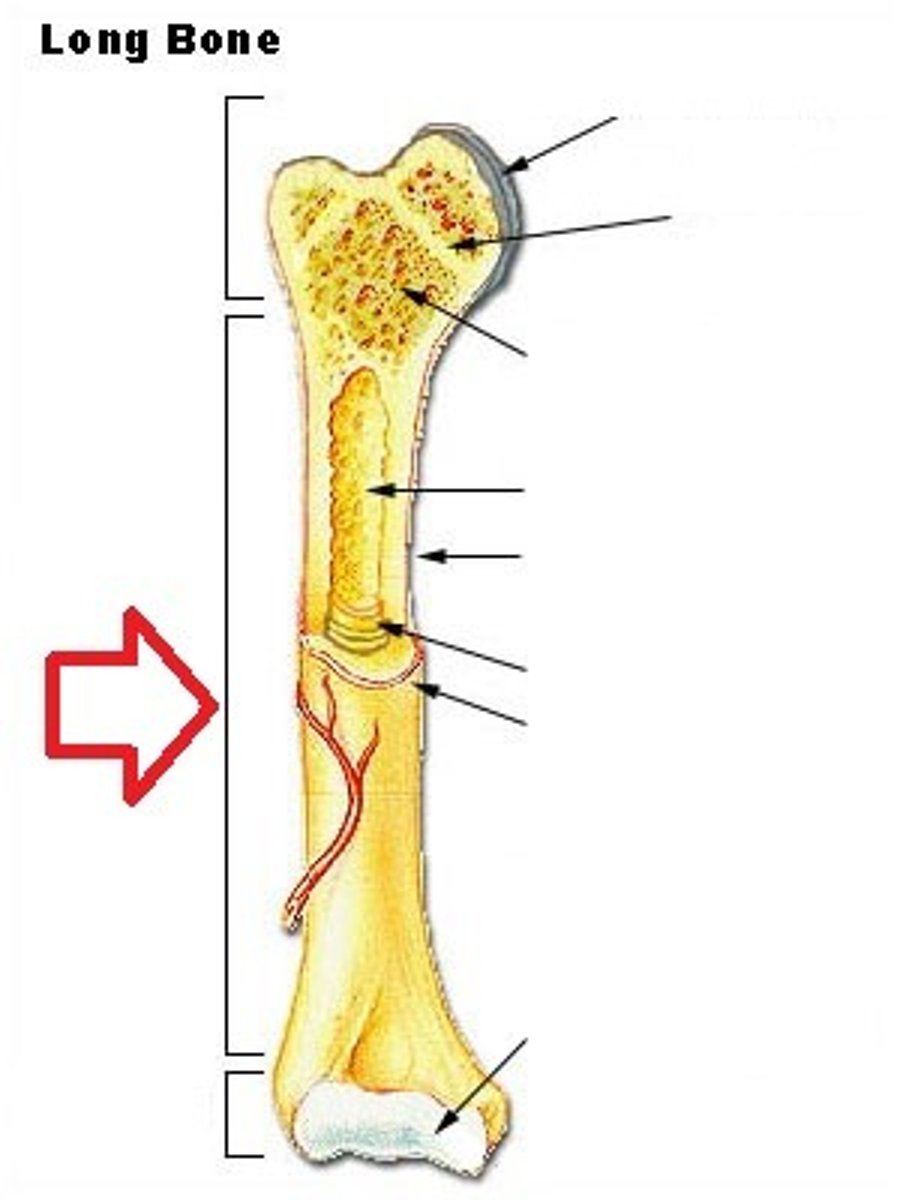
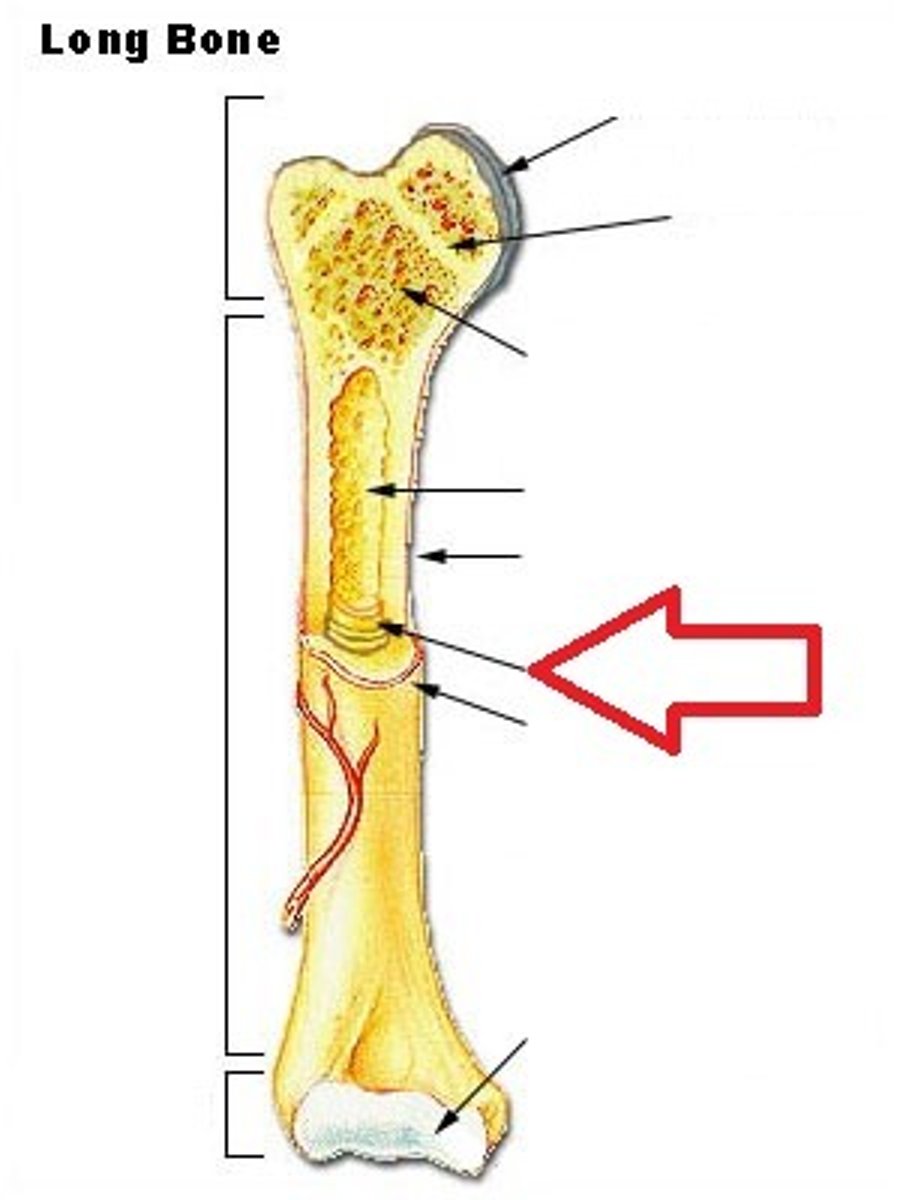
Metaphysis
In between Epiphysis and Diaphysis.
Periosteum
Sheath of outer fibrous collagen and inner osteogenic layer of bone forming cells.
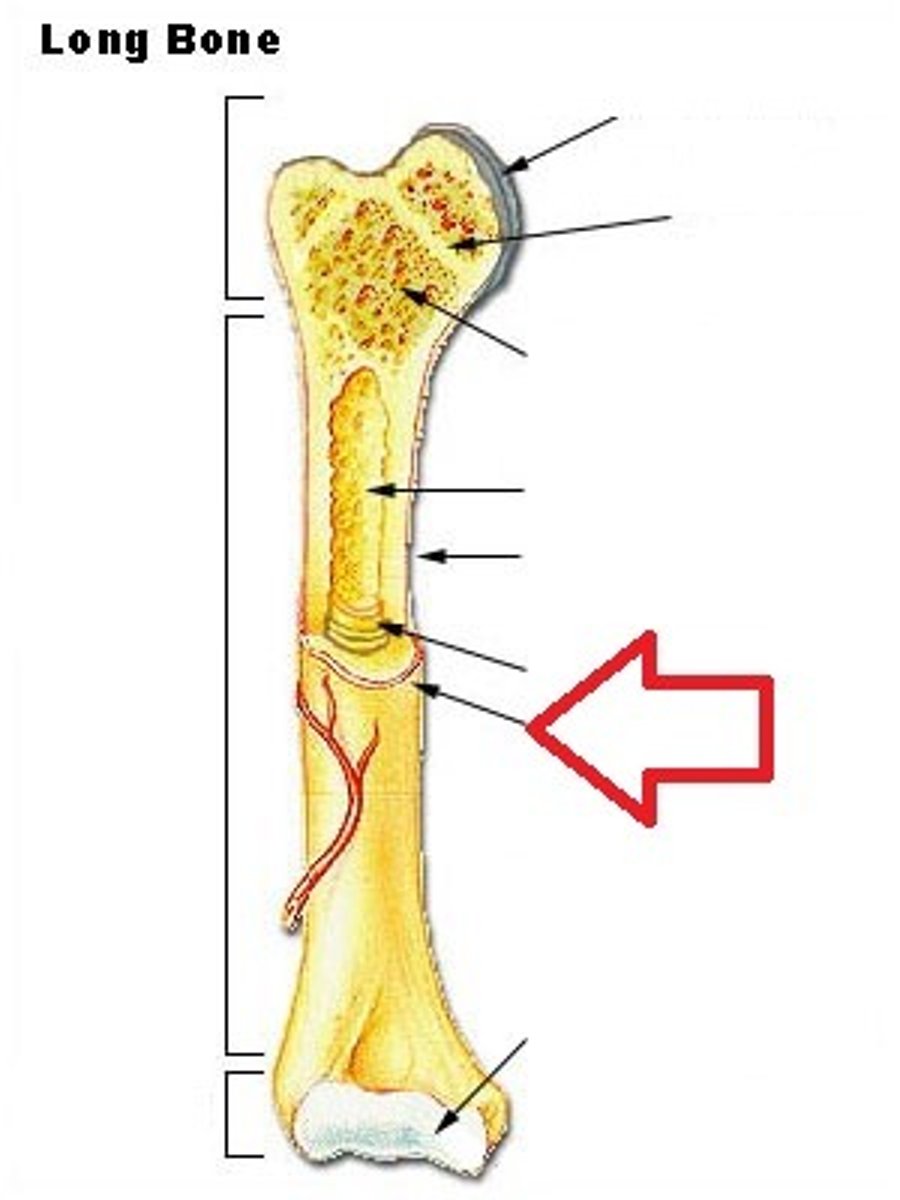
Sharpey's fibers
Anchors the periosteum to the bone matrix.
Endosteum
Thin layer of reticular CT lining internal marrow cavity. Also covers honeycomb surfaces of spongy bones and has many osteoclasts.
Epiphyseal plate
Hyaline cartilage separating the marrow spaces in children. Where the bones grow in length. Is just an /epiphyseal line/ in adults.
Bone Marrow
soft tissue that occupies marrow cavity of long bones, spaces amid trabeculae of spongy bone, and larger central canals.
Red Bone Marrow
Produces blood cells.
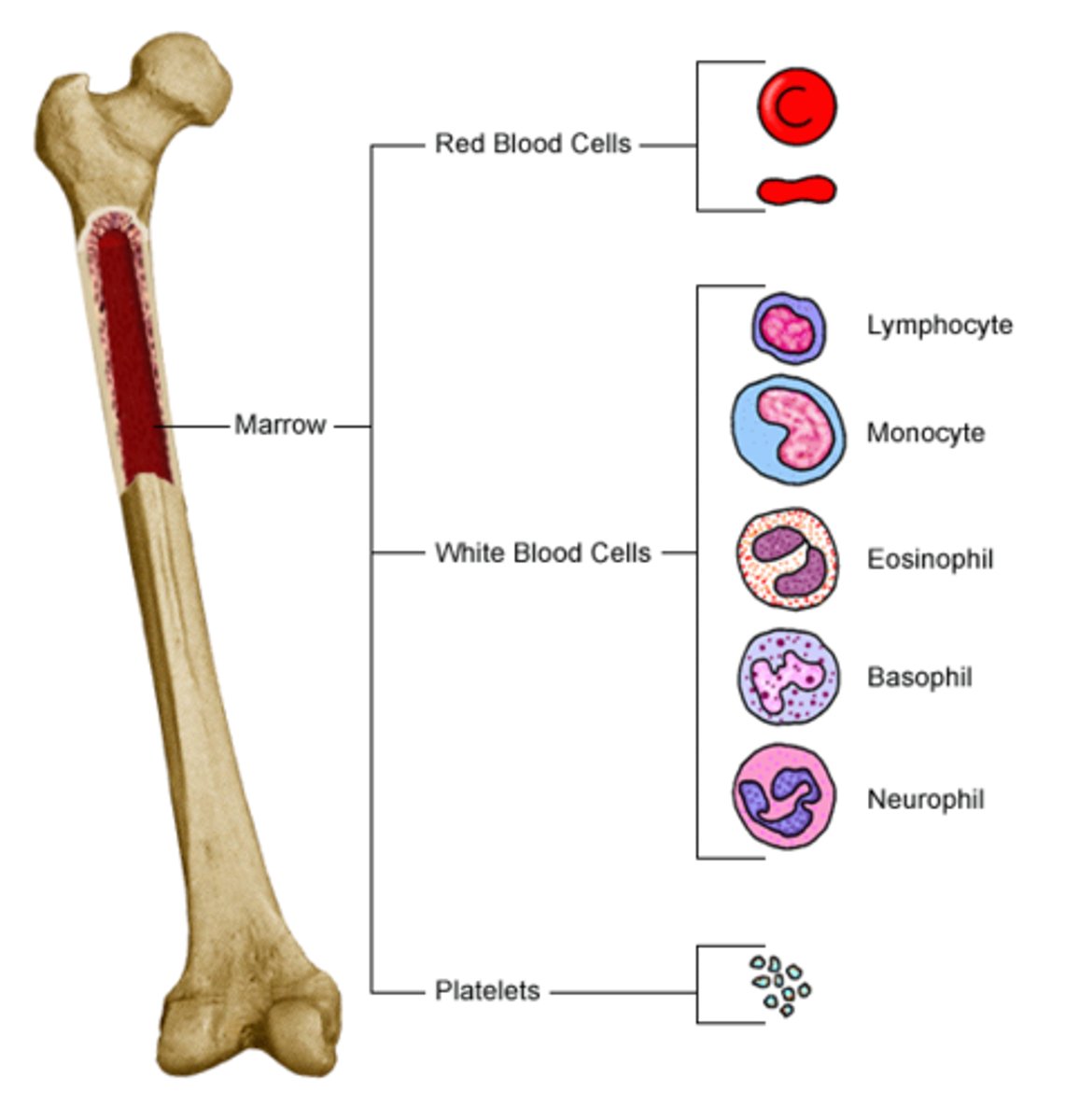
Yellow Bone Marrow
Red marrow of bones in limbs turns into this in adults.