AP Micro CRAM
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
shutdown rule
shutdown when P < AVC
—> firms should shut down when TR is insufficient to cover VC. If they continue to produce, they will end up with more losses than if they decide to shut down and just incur FC.
Short run production costs
AFC: decreasing into asymptote
AVC: above AFC, below ATC, cuts MC at min
ATC: above AVC, cuts MC at min
economies of scale
the cost advantages a firm gains by increasing its production output (lower per-unit costs)
—> ATC decreases as output increases
—> long run production cost
diseconomies of scale
the cost disadvantages a firm faces when increasing production (higher per-unit costs)
—> ATC increases as output increases
—> long run production cost
constant returns to scale
proportional increase in all inputs leads to a proportional increase in output
economic profit
revenue - explicit cost - implicit cost
accounting profit - implicit cost
accounting profit
revenue - explicit cost
implicit costs
opportunity costs
explicit costs
costs that involve spending money
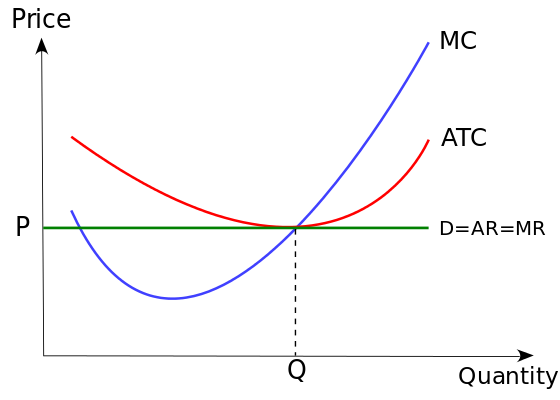
perfect competition
many competitors
identical products
no barriers to entry
no price control (price takers)
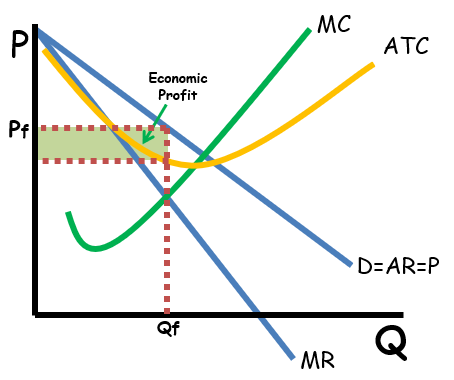
monopoly
1 firm
unique products
high barriers to entry
100% price control (price makers)
monopolistic competition
many firms
differentiated products
no barriers to entry
limited price control
oligopoly
few firms
identical or differentiated goods
has barriers to entry
significant price control
oligopoly cartels
group of firms that cooperate to set prices or production levels to maximize collective profits
oligopoly collusion
act of firms cooperating to set prices or output levels, acting collectively to increase profits
antitrust policy
government regulations aimed at promoting competition to prevent monopolies
monopsony
a market with 1 buyer
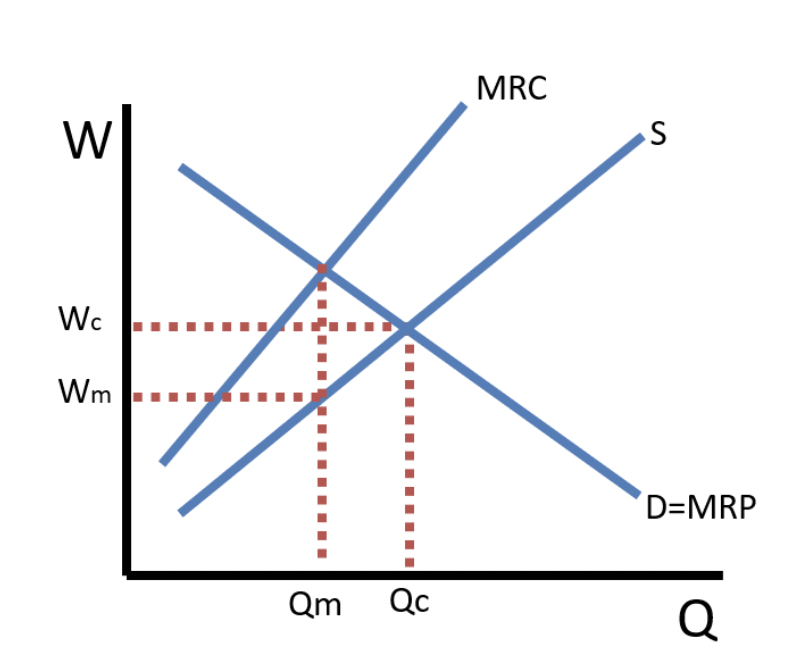
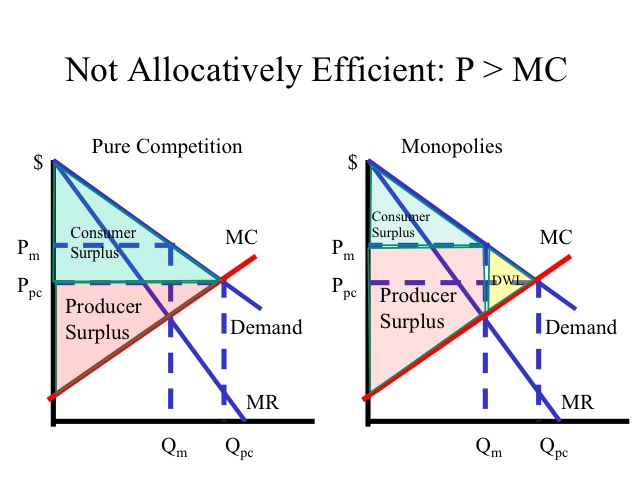
producer/consumer surplus on competitions
maximizing revenue
MR = 0
determinants of DL (factor market)
Productivity of workers
Produce price
Product demand
determinants of SL
anything impacting number of workers: age, population, availability…
marginal revenue product (MRP)
MR x P
marginal resource cost (MRC)
change in TRC (total resource cost)
total resource cost (TRC)
wage x QL
marginal product (MP)
change in total output/change in input
—> change in Q / change in # of workers
least cost rule
marginal product per $: MP / P
choose input with higher marginal product per $
factor market profit maximization
MRP = MRC
allocative efficiency
MB = MC
D = MC
productive efficiency
ATC = MC
lorenz curve
measures the distribution of income equality
(want to be as close to the perfect equality line)
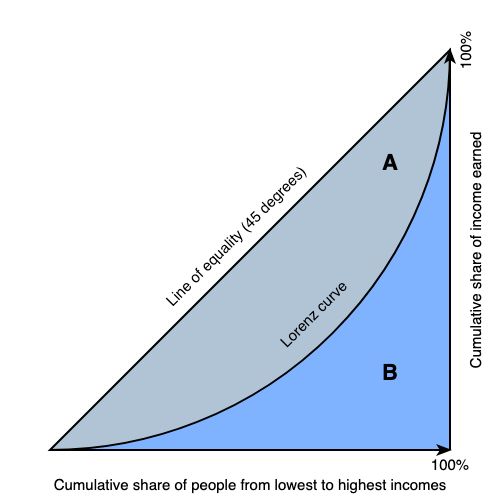
gini coefficient
A/(A+B)
Closer to 0, more equality (smaller A area)
Closer to 1, more inequality (bigger A area)
elasticity calculation
(% change in Qd) / (% change in P)
marginal revenue (MR)
change in the TR/change in Q
Marginal cost (MC)
change in TC / change in Q