Geology Final Exam
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/99
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
1
New cards
earthquake intensity
-a representation of the strength of an earthquake
-based on the amount of damage due to the event and on people's perception of ground shaking during the event
-intensity is measured with the Mercalli scale; intensity decreases with increasing distance from the epicenter
-based on the amount of damage due to the event and on people's perception of ground shaking during the event
-intensity is measured with the Mercalli scale; intensity decreases with increasing distance from the epicenter
2
New cards
Modified Mercalli Intensity (MMI) Scale
an earthquake characterization scale based on the amount of damage that the earthquake causes.
3
New cards
earthquake magnitude
-a representation of the energy released by an earthquake
-as indicated by the amplitude of specific seismic waves as they would be recorded by a seismometer at a set distance from the epicenter
-as indicated by the amplitude of specific seismic waves as they would be recorded by a seismometer at a set distance from the epicenter
4
New cards
earthquake amplitude
the amount of up-and-down or back-and-forth motion of the ground—the larger the amplitude
-the greater the deflection of a seismometer pen or needle as it traces out a seismogram
-the greater the deflection of a seismometer pen or needle as it traces out a seismogram
5
New cards
richter scale
a scale that defines earthquakes on the basis of the amplitude of the largest ground motion recorded on a seismogram
6
New cards
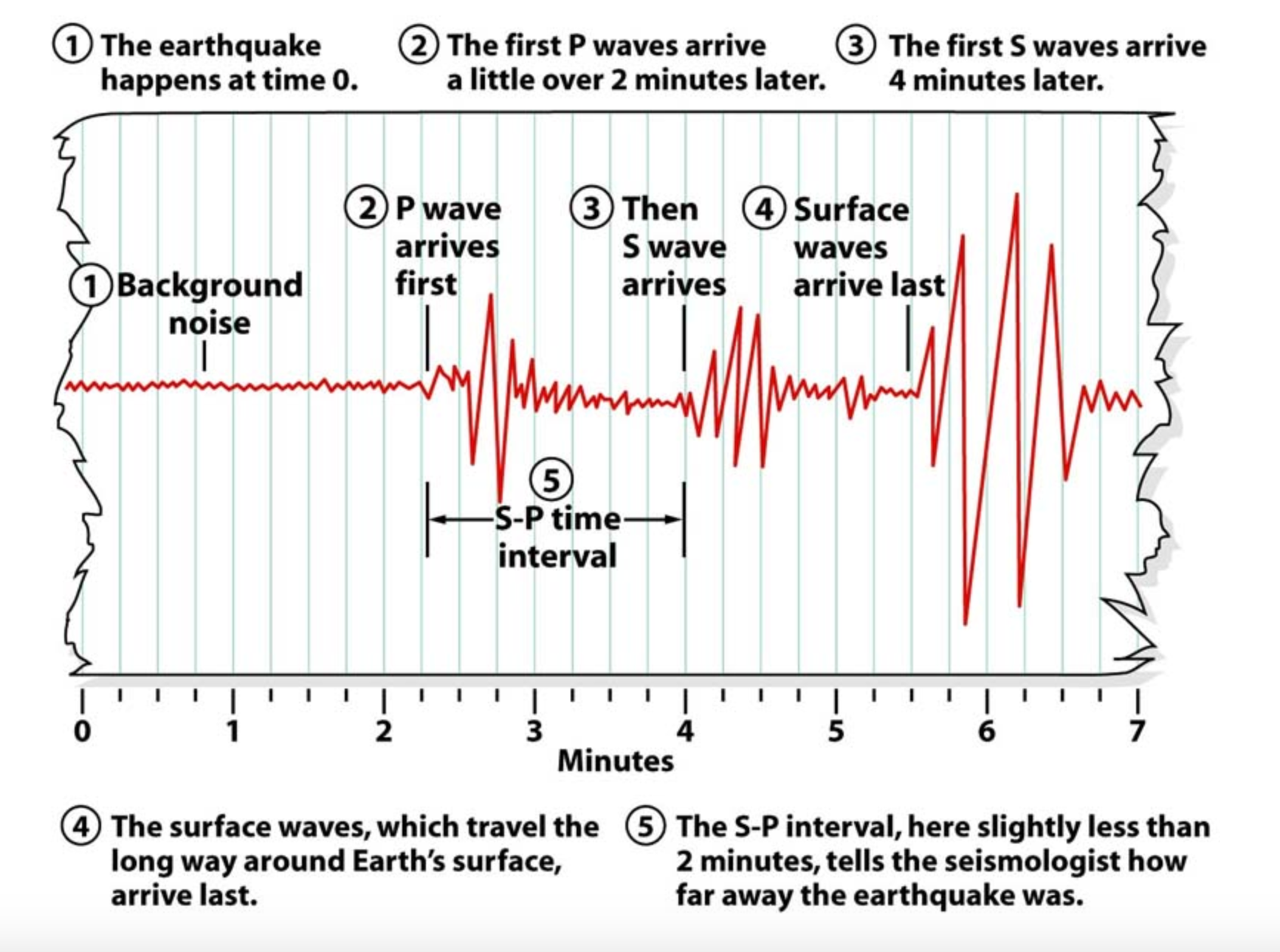
seismogram
The record of an earthquake produced by a seismometer
7
New cards
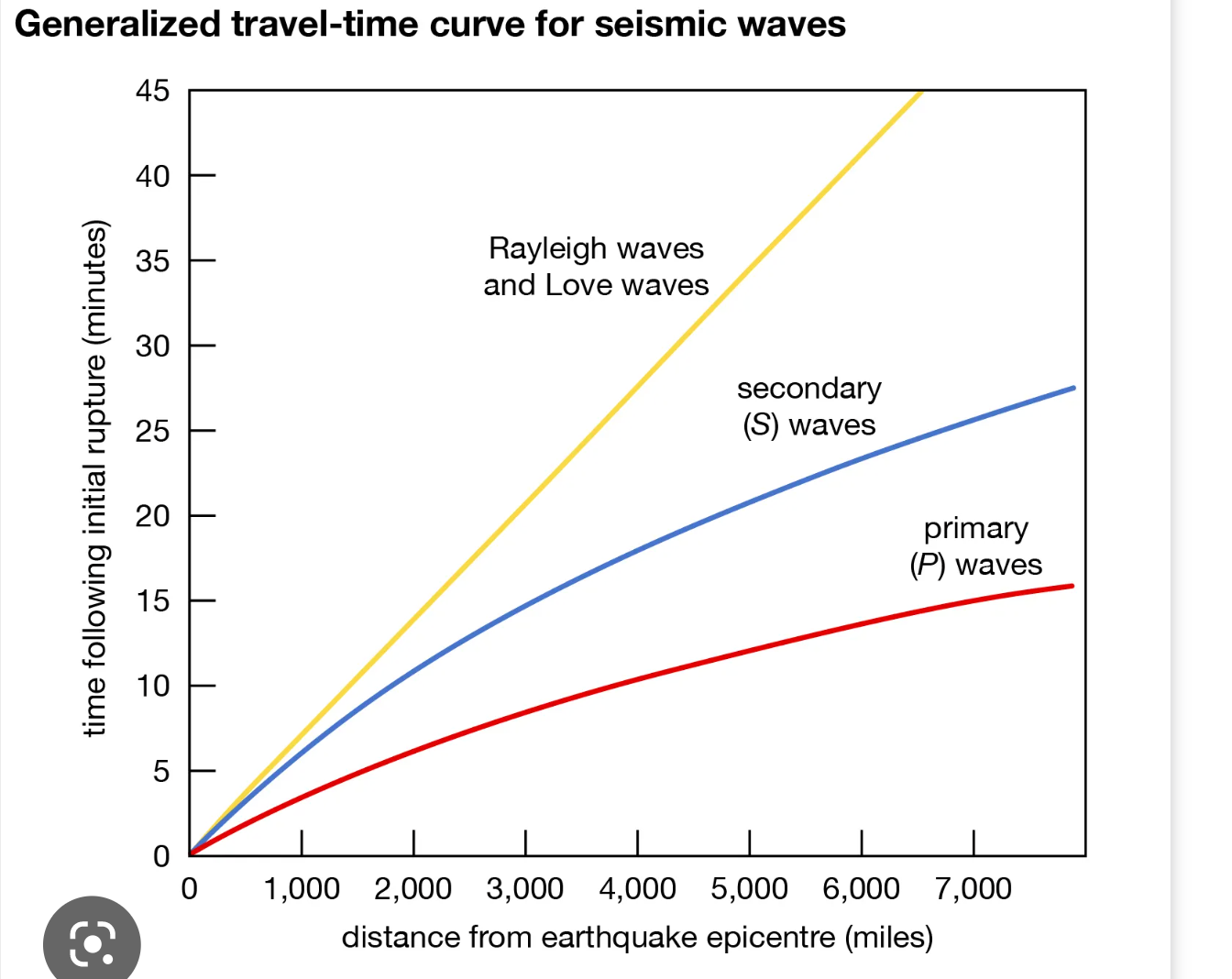
travel-time curve
a graph that plots the time since an earthquake began on the vertical axis and the distance to the epicenter on the horizontal axis
8
New cards
Seismologists find that earthquakes take place on
most seismic belts or seismic zones
9
New cards
The majority of earthquakes happen on faults along plate boundaries because
the relative motion between plates causes slip on faults
10
New cards
damaging effects of earthquakes
-building collapse
-buried pipes break
-fires
-liquifaction
-tsunami
-sanitation
-buried pipes break
-fires
-liquifaction
-tsunami
-sanitation
11
New cards
fire during earthquakes occurs when
leaked fuel and electrical transmission lines mix
12
New cards
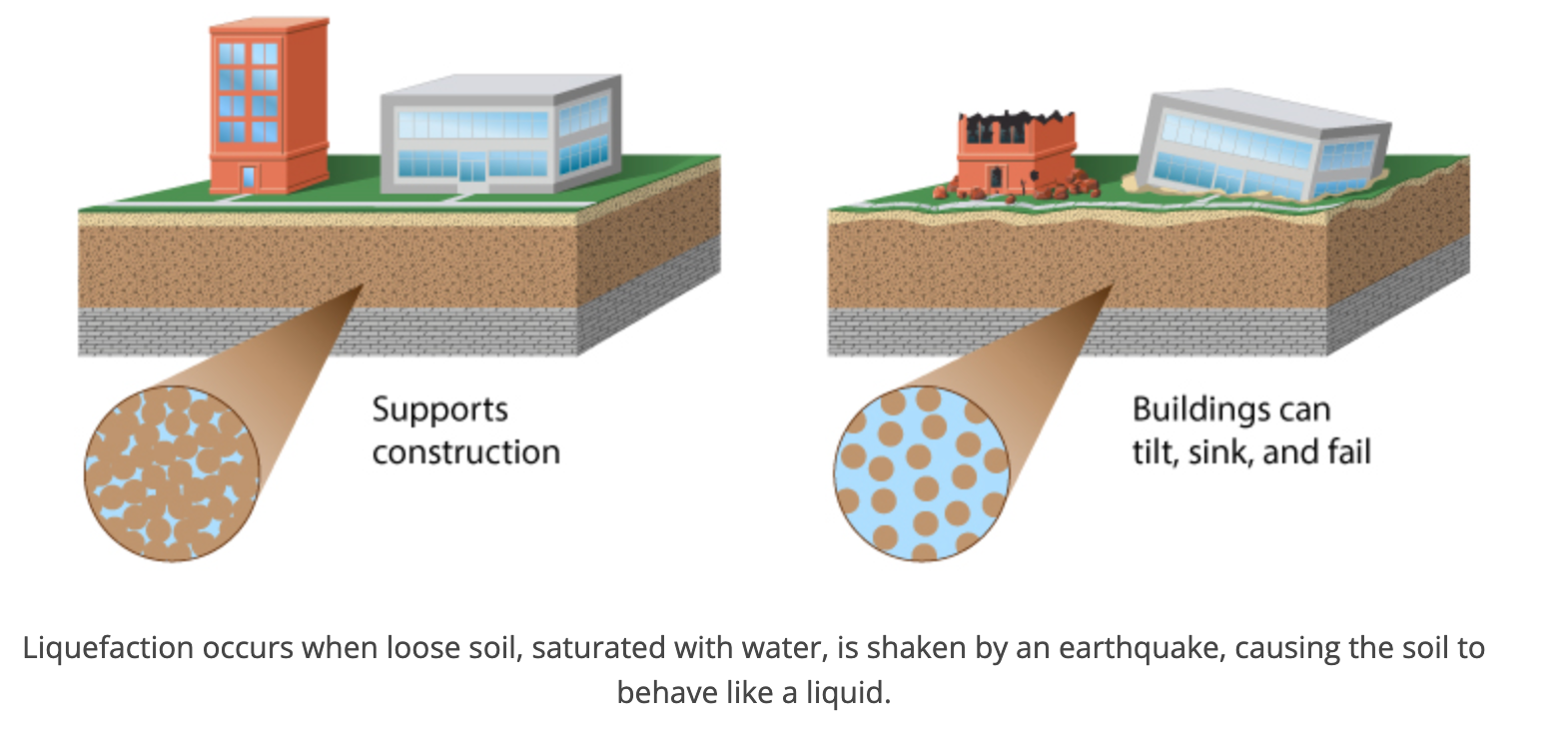
liquifaction
occurs when an earthquake's violent shaking suddenly turns loose, soft soil into liquid mud
13
New cards
tsunami
a giant wave usually caused by an earthquake beneath the ocean floor
14
New cards
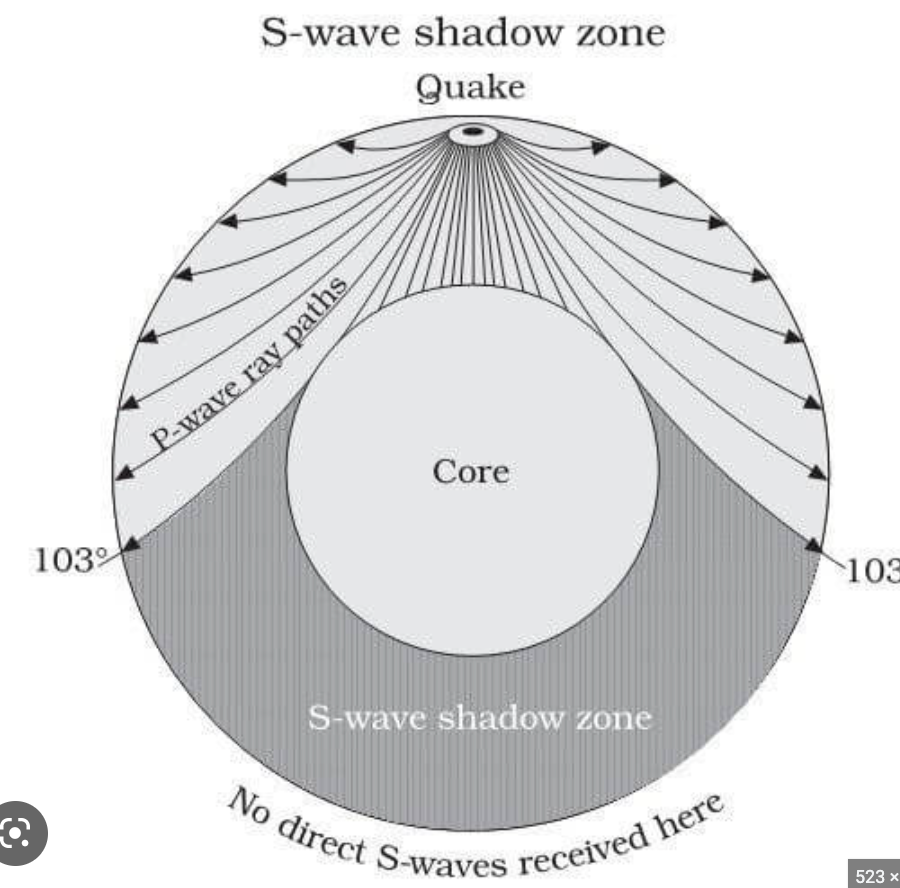
S-wave shadow zone
A band between 103° and 180° from the epicenter of an earthquake inside of which S-waves do not arrive at seismograph stations
15
New cards
seismic topography
analysis by sophisticated computers of global seismic data in order to create a three-dimensional image of variations in seismic-wave velocities within the Earth
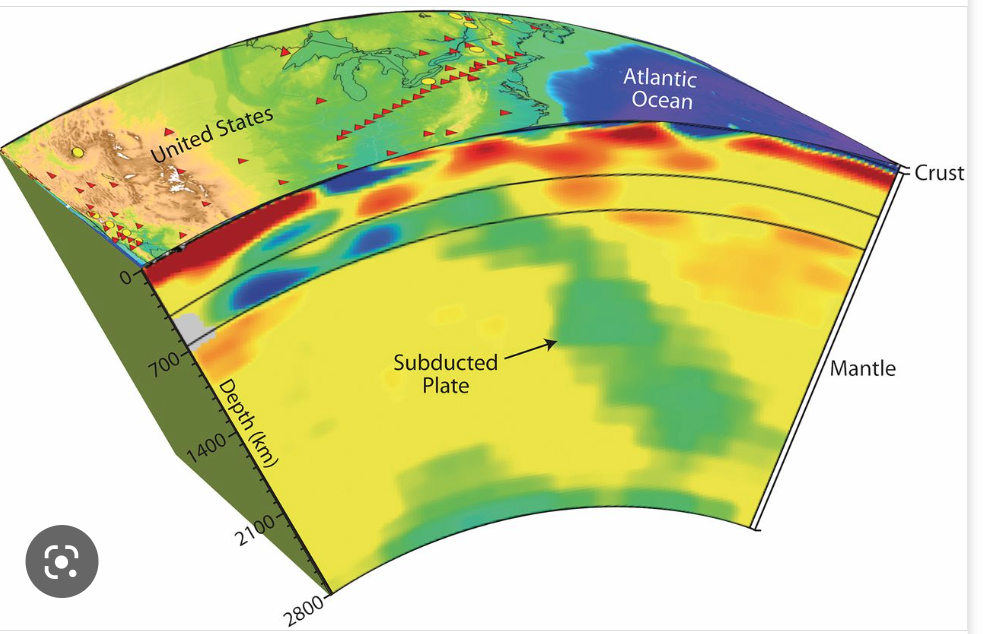
16
New cards
seismic velocity
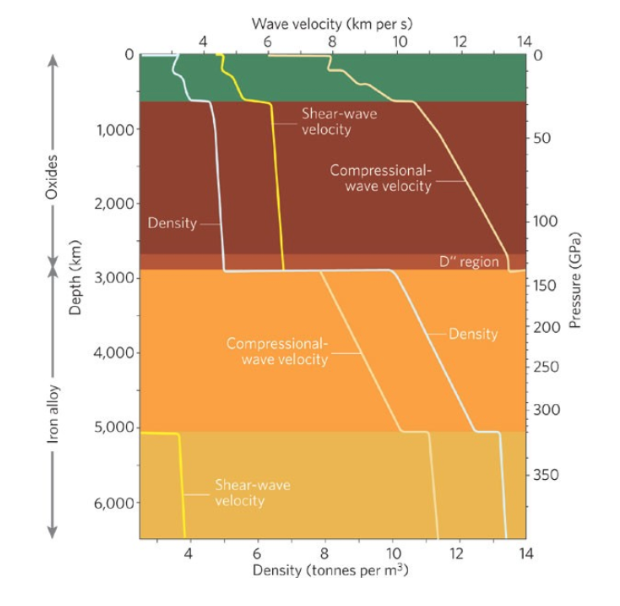
17
New cards
velocity
the speed of an object in a particular direction
18
New cards
depth
downward measurement from a surface
19
New cards
crust
The thin and solid outermost layer of the Earth above the mantle
20
New cards
mantle
The layer of hot, solid material between Earth's crust and core
21
New cards
lithosphere
the solid, outer layer of the earth that consists of the crust and the rigid upper part of the mantle
-100- 150 km
-100- 150 km
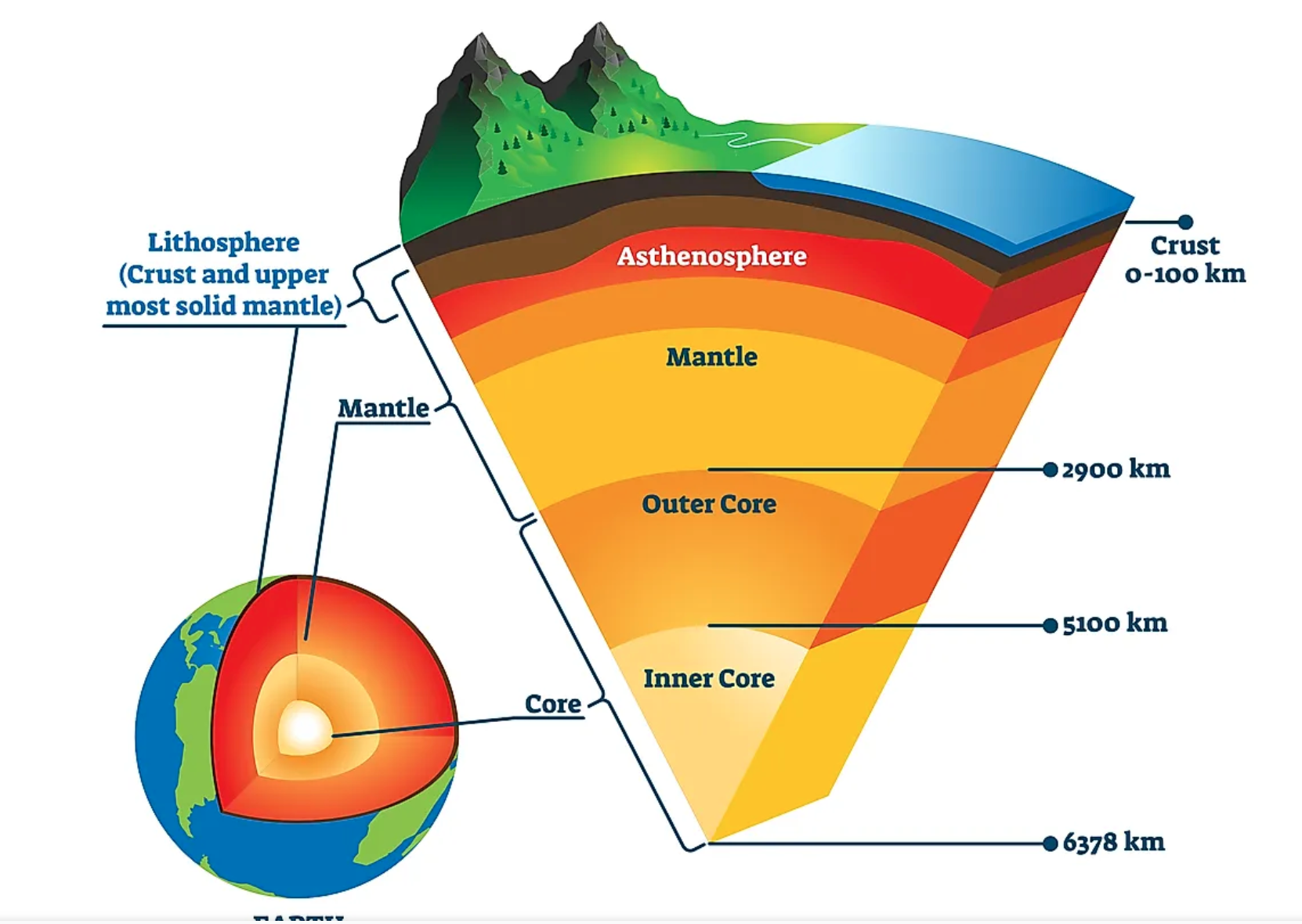
22
New cards
asthenosphere
upper mantle and below the lithosphere (200- 500 km); "weak" (soft) sphere
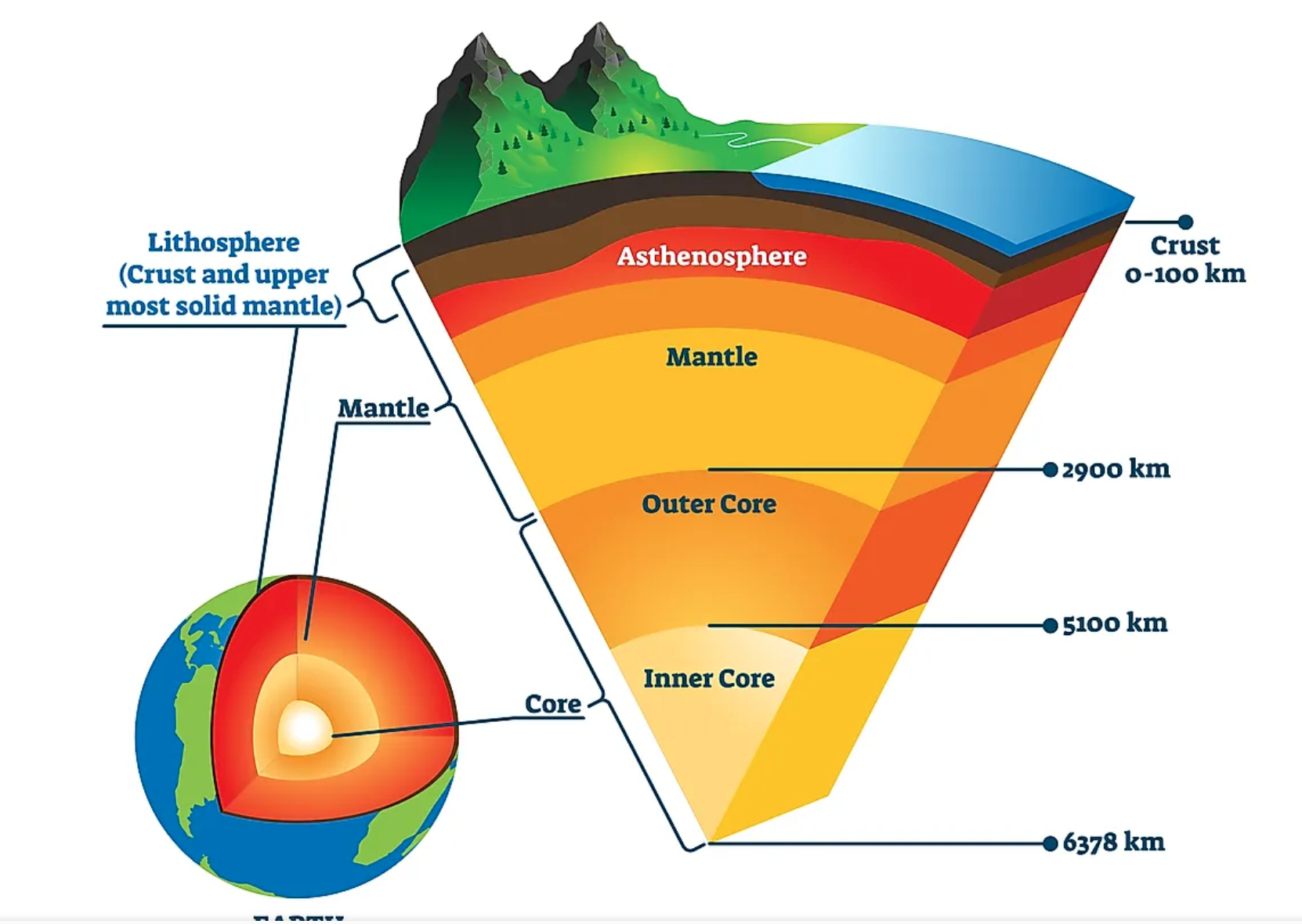
23
New cards
lithostatic pressure
-pressure exerted on rocks by the weight of overlying rocks
-uniform pressure that "feels" the same from all directions
-uniform pressure that "feels" the same from all directions
24
New cards
differential stress
stress applied unequally in different directions
25
New cards
force
A push or pull exerted on an object
26
New cards
surface area
the sum of all the areas of all surfaces of a solid
27
New cards
stress
-the push, pull, or shear that a material feels when subjected to a force
-formally, the force applied per unit area over which the force acts
-formally, the force applied per unit area over which the force acts
28
New cards
types of stress
compressive, tensile, shear
29
New cards
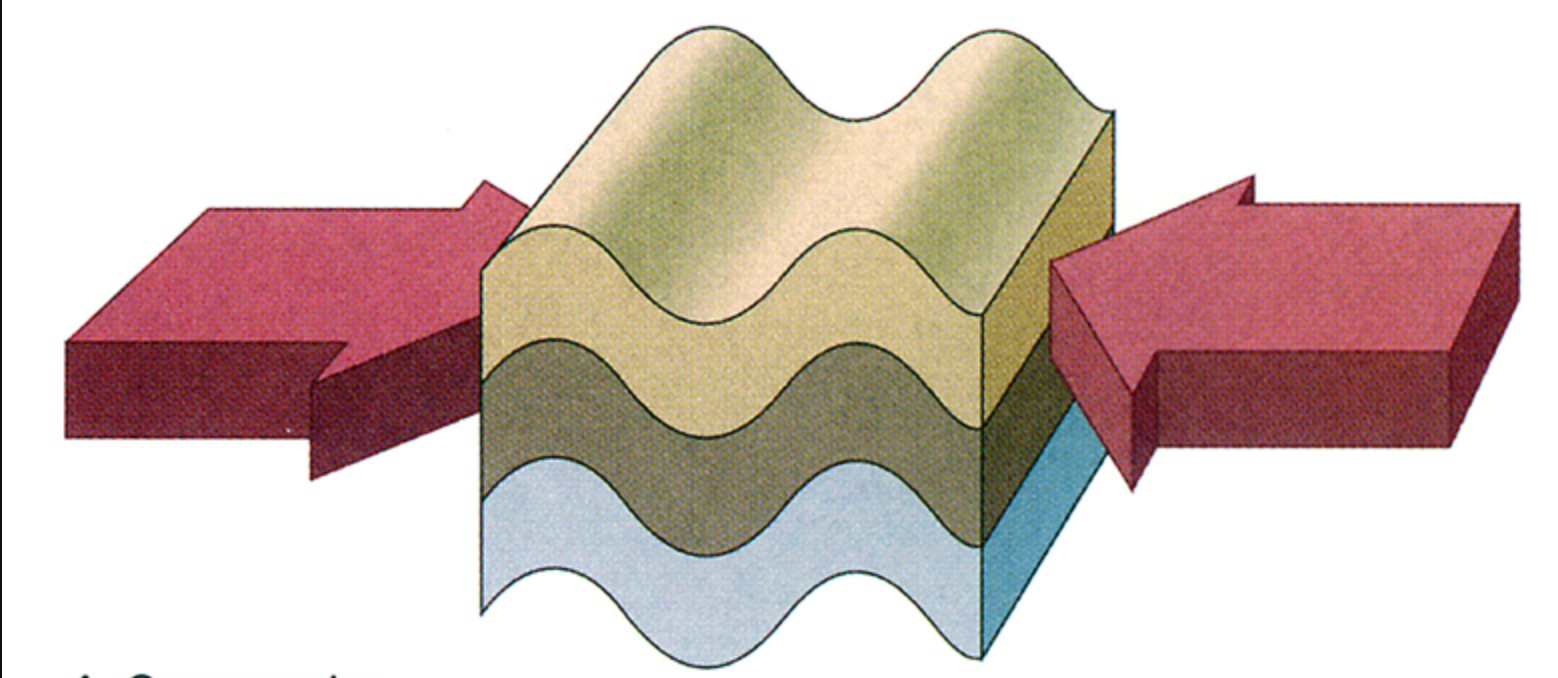
compressive stress
A stress due to a force pushing together on a rock
30
New cards
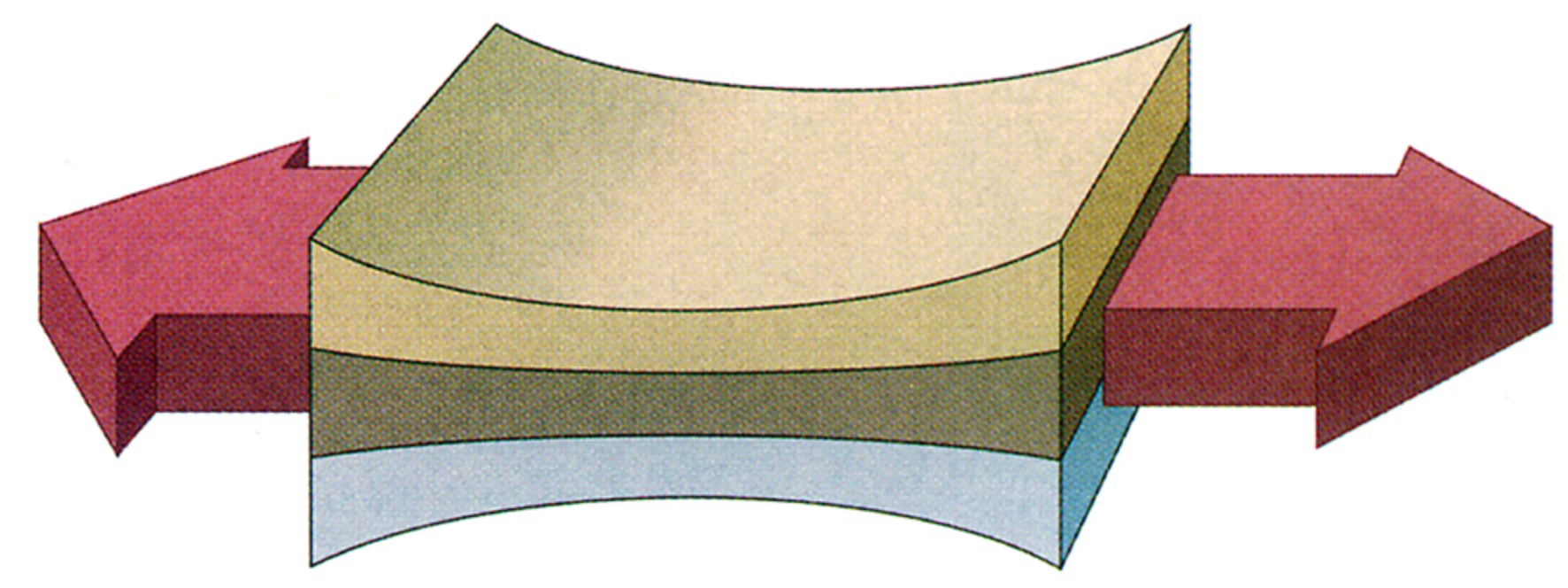
tensional stress
occurs when a rock is pulled apart
31
New cards
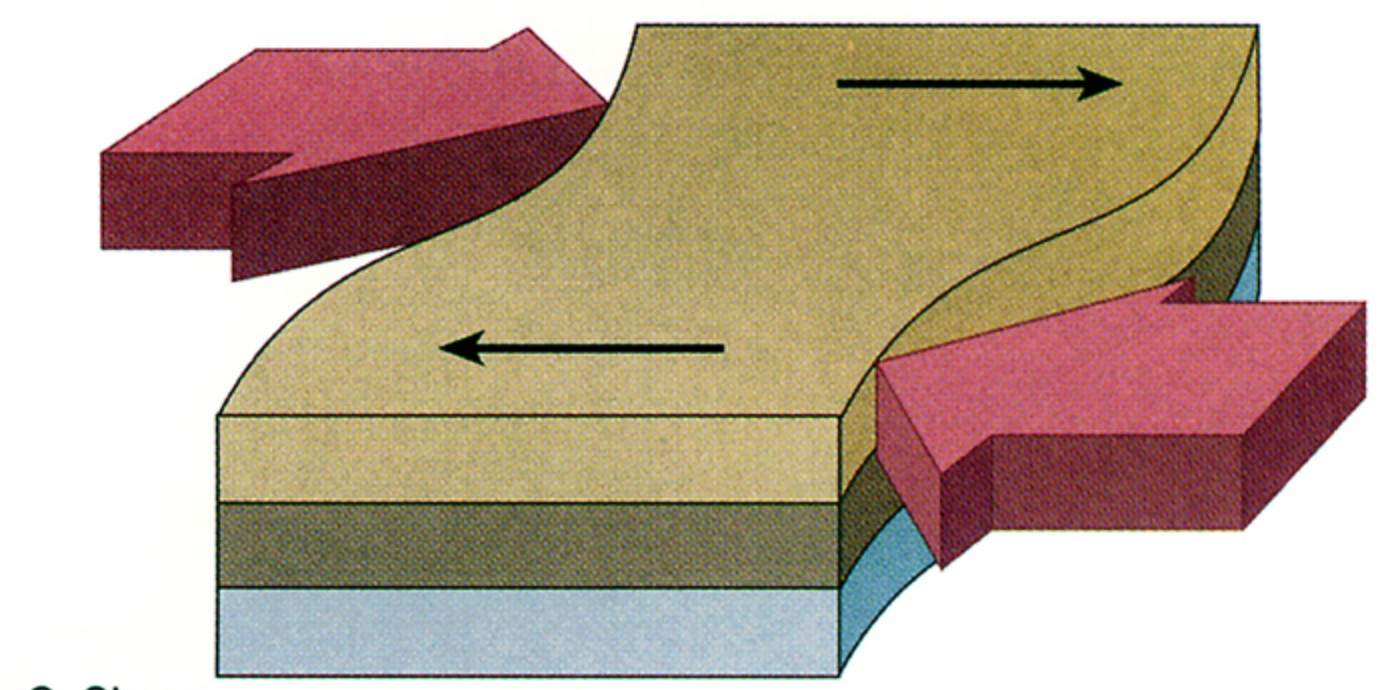
shear stress
develops when one part of a rock body moves sideways past another
-in general, the stress acting in one direction is not the same magnitude as the stress acting in another direction
-in general, the stress acting in one direction is not the same magnitude as the stress acting in another direction
32
New cards
deformation
the bending, tilting, and breaking of Earth's crust
-the change in the shape of rock in response to stress
-the change in the shape of rock in response to stress
33
New cards
types of deformation
displacement, rotation, change of shape (strain)
34
New cards
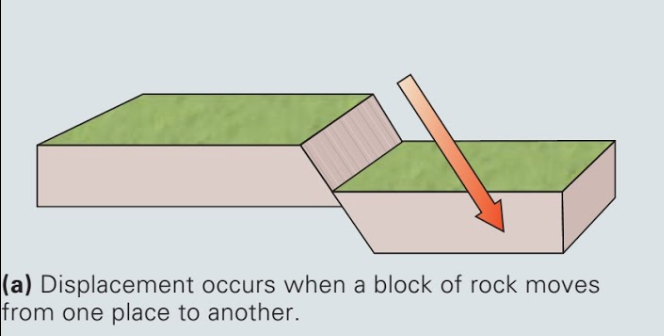
displacement
the amount of movement or slip across a fault plane
-a change in location
-a change in location
35
New cards
rotation
change in orientation or position
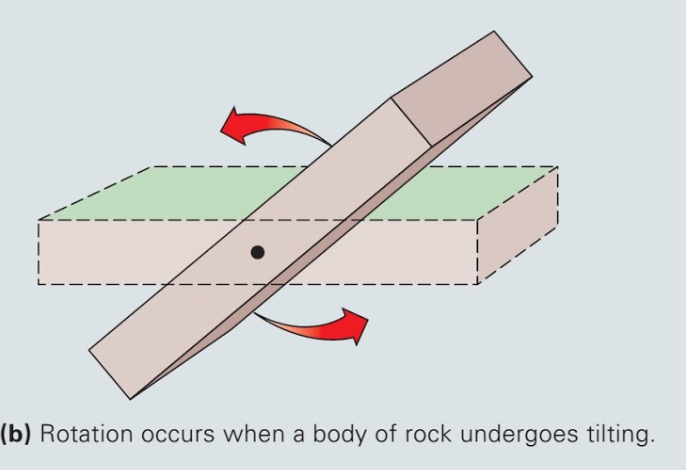
36
New cards
change of shape (strain) (distortion)
change in shape of a rock
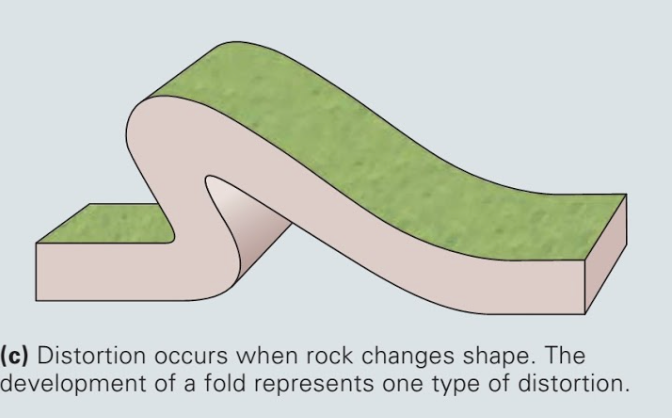
37
New cards
strain
the change in shape of an object in response to deformation
-response to stress
-response to stress
38
New cards
type of strain
elastic, brittle, ductile
39
New cards
elastic strain
change in rock that is not permanent
-when stress is removed rock goes back to original shape
-does not break
-spontaneous recovery
-w/o loss of cohesion
-delta shape
-when stress is removed rock goes back to original shape
-does not break
-spontaneous recovery
-w/o loss of cohesion
-delta shape
40
New cards
plastic (ductile) strain
the deformational process in which mineral grains behave like plastic
-when compressed or sheared, become flattened or elongated without cracking or breaking
-permanent form after strain
-w/o loss of cohesion
-delta shape
-when compressed or sheared, become flattened or elongated without cracking or breaking
-permanent form after strain
-w/o loss of cohesion
-delta shape
41
New cards
brittle strain
the cracking and fracturing of a material subjected to stress
-loss of cohesion
-permanent
-loss of cohesion
-permanent
42
New cards
factors that effect type of strain
-heat (temp)
-pressure
-rate (time)
-water
-pressure
-rate (time)
-water
43
New cards
heat
hot - plastic (ductile)
cold - elastic and brittle
cold - elastic and brittle
44
New cards
pressure
high pressure - plastic (ductile)
low pressure - elastic and brittle
low pressure - elastic and brittle
45
New cards
rate (time)
slow - plastic (ductile)
rapid - elastic and brittle
rapid - elastic and brittle
46
New cards
water
weakens rock
47
New cards
vein
-a seam of minerals that forms when dissolved ions carried by water solutions precipitate in cracks
-a mineral filled crack
-a mineral filled crack
48
New cards
strike
The compass orientation of a horizontal line on a plane
-an imaginary horizontal line on the plane and the direction to true north
-an imaginary horizontal line on the plane and the direction to true north
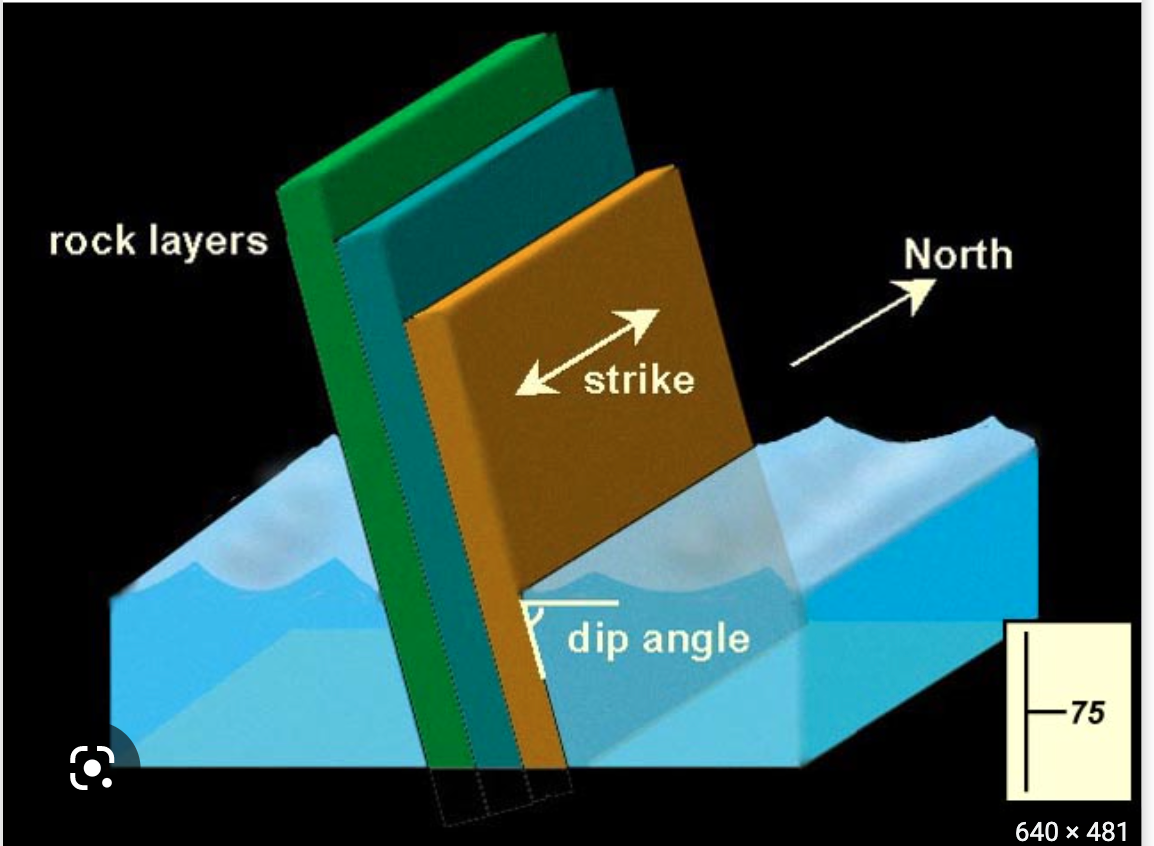
49
New cards
dip
The angle of a plane's slope as measured in a vertical plane perpendicular to the strike
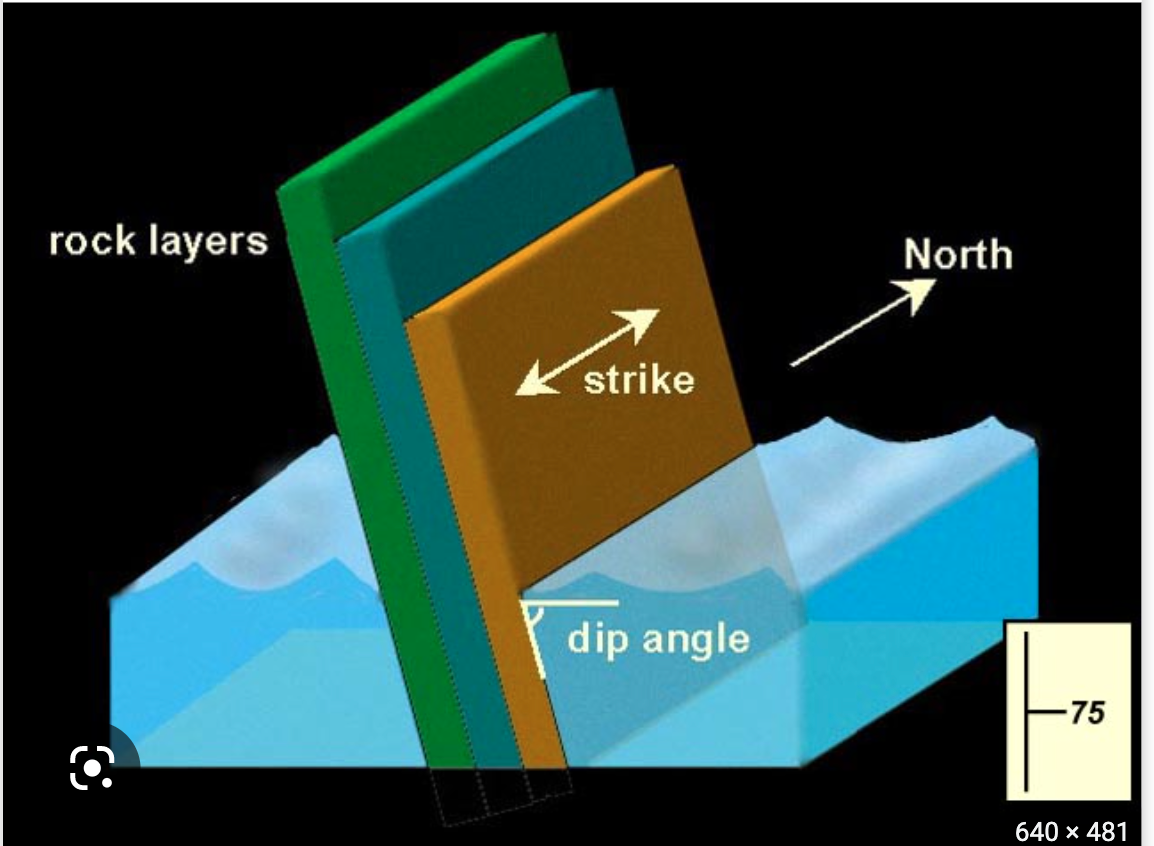
50
New cards
dip direction
the compass direction of the dip measured at right angles to the strike
-always perpendicular to the line of strike
-always perpendicular to the line of strike
51
New cards
types of faults
normal, reverse, strike-slip, dip-slip
52
New cards
strike-slip fault
a fault in which one block slides horizontally past another (and therefore parallel to the strike line), so there is no relative vertical motion
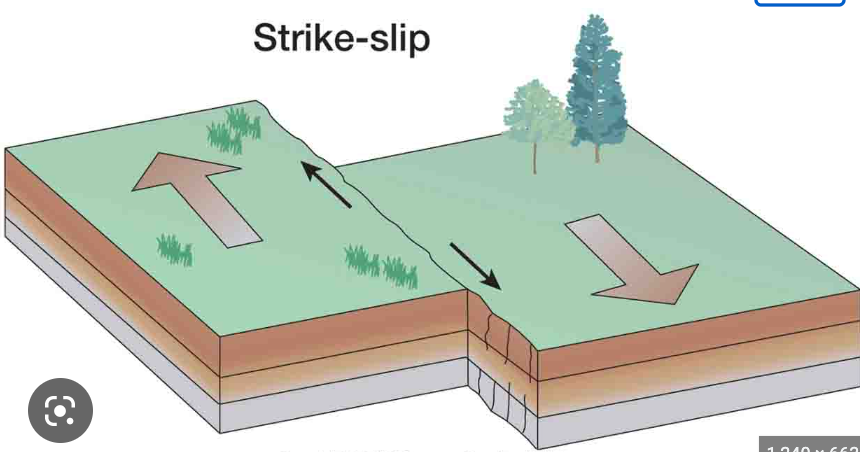
53
New cards
left-lateral (sinistral)
left-lateral (sinistral)
used in describing strike-slip faults if the rock of the other side of the fault moves to the left
-If the block on the far side slipped to your left
used in describing strike-slip faults if the rock of the other side of the fault moves to the left
-If the block on the far side slipped to your left

54
New cards
right-lateral (dextral)
used in describing strike-slip faults if the rock on the other side of the fault moves to the right
-If the block on the far side slipped to your right
-If the block on the far side slipped to your right

55
New cards
dip-slip fault
movement parallels the dip line, a line going down the slope of the fault surface
-normal and reverse fault
-normal and reverse fault
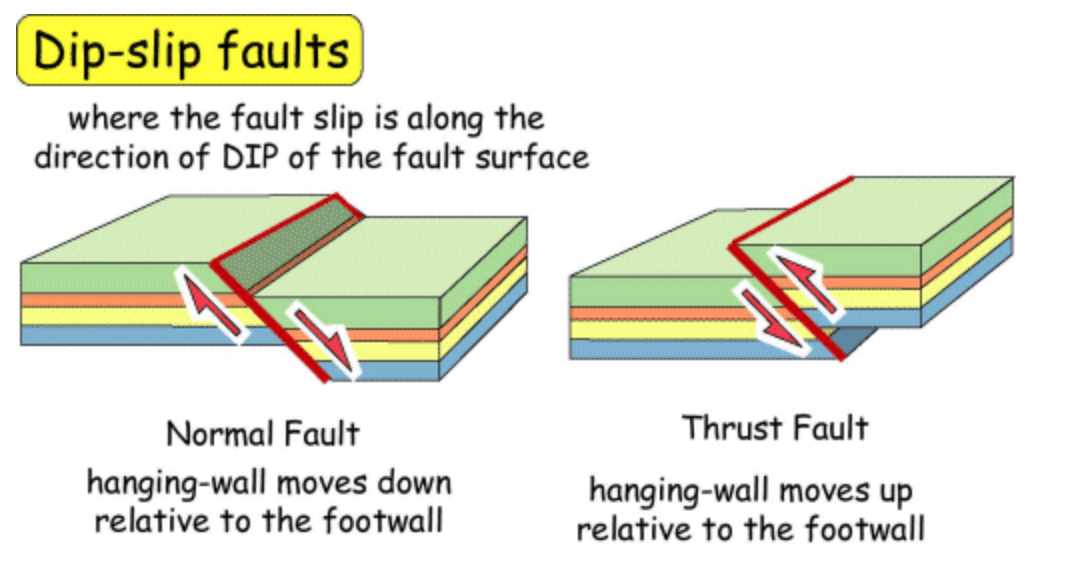
56
New cards
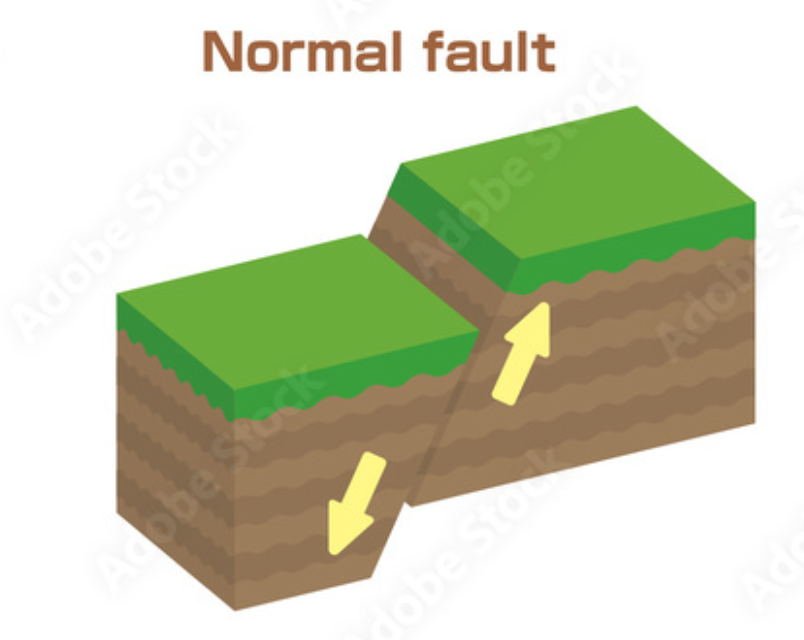
normal fault
A fault in which the hanging-wall block moves down the slope of the fault
57
New cards
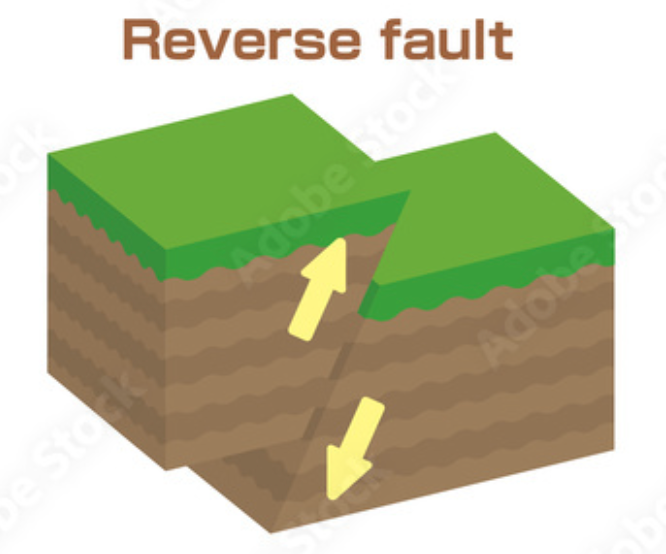
reverse fault
a steeply dipping fault on which the hanging-wall block slides up
58
New cards
oblique-slip fault
a fault with both strike-slip and dip-slip components
59
New cards
A horizontal plane has a dip of 0 degrees and
a vertical plane has a dip of 90 degree
60
New cards
fold types
anticline and syncline
61
New cards
thrust fault
a gently dipping reverse fault
62
New cards
anticline
Folds that have an archlike shape in which the limbs dip away from the hinge
-represents an arch-like shape
-compression causes anticlines
-represents an arch-like shape
-compression causes anticlines
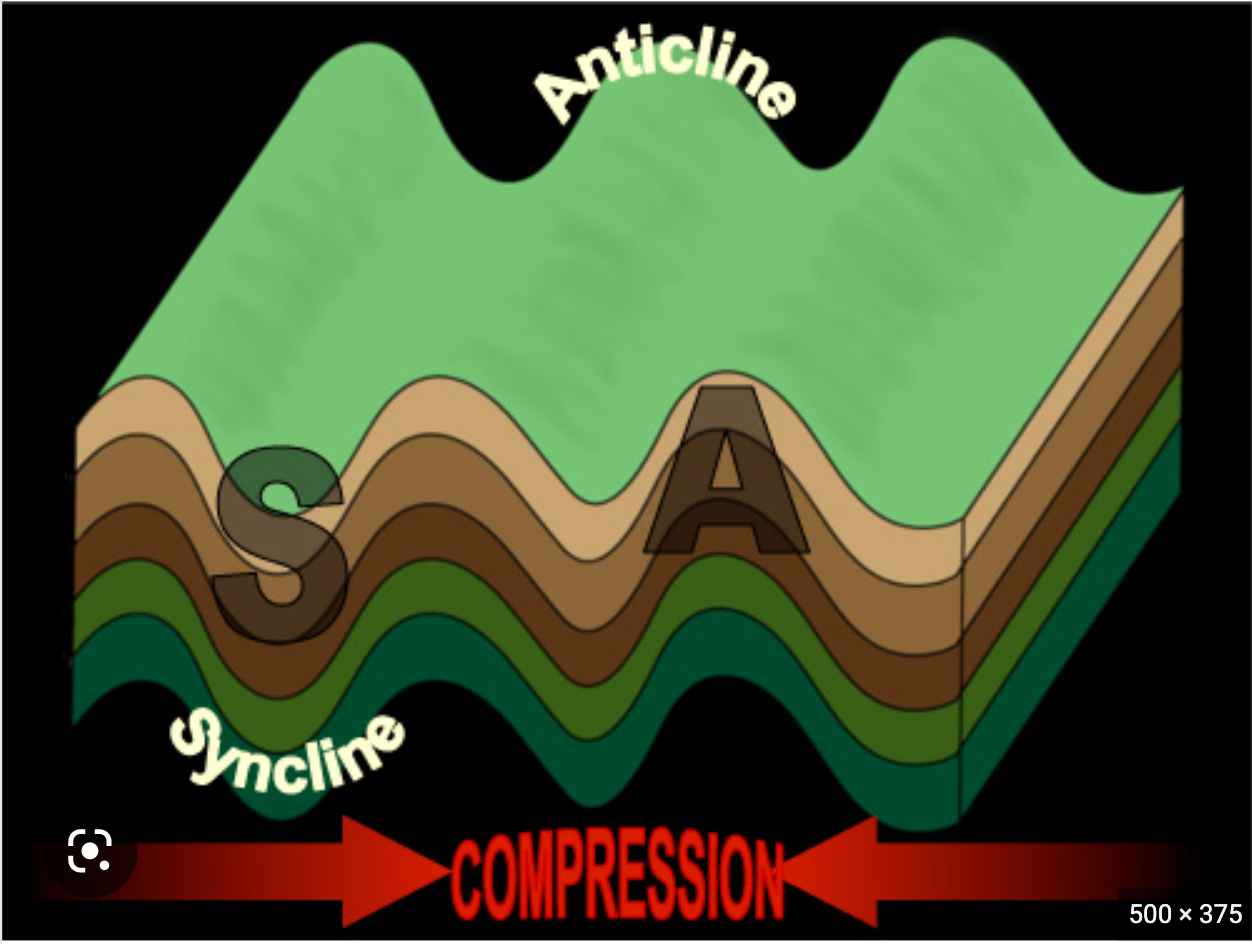
63
New cards
syncline
A trough-shaped fold whose limbs dip toward the hinge
-represents a trough
-compression causes synclines
-represents a trough
-compression causes synclines
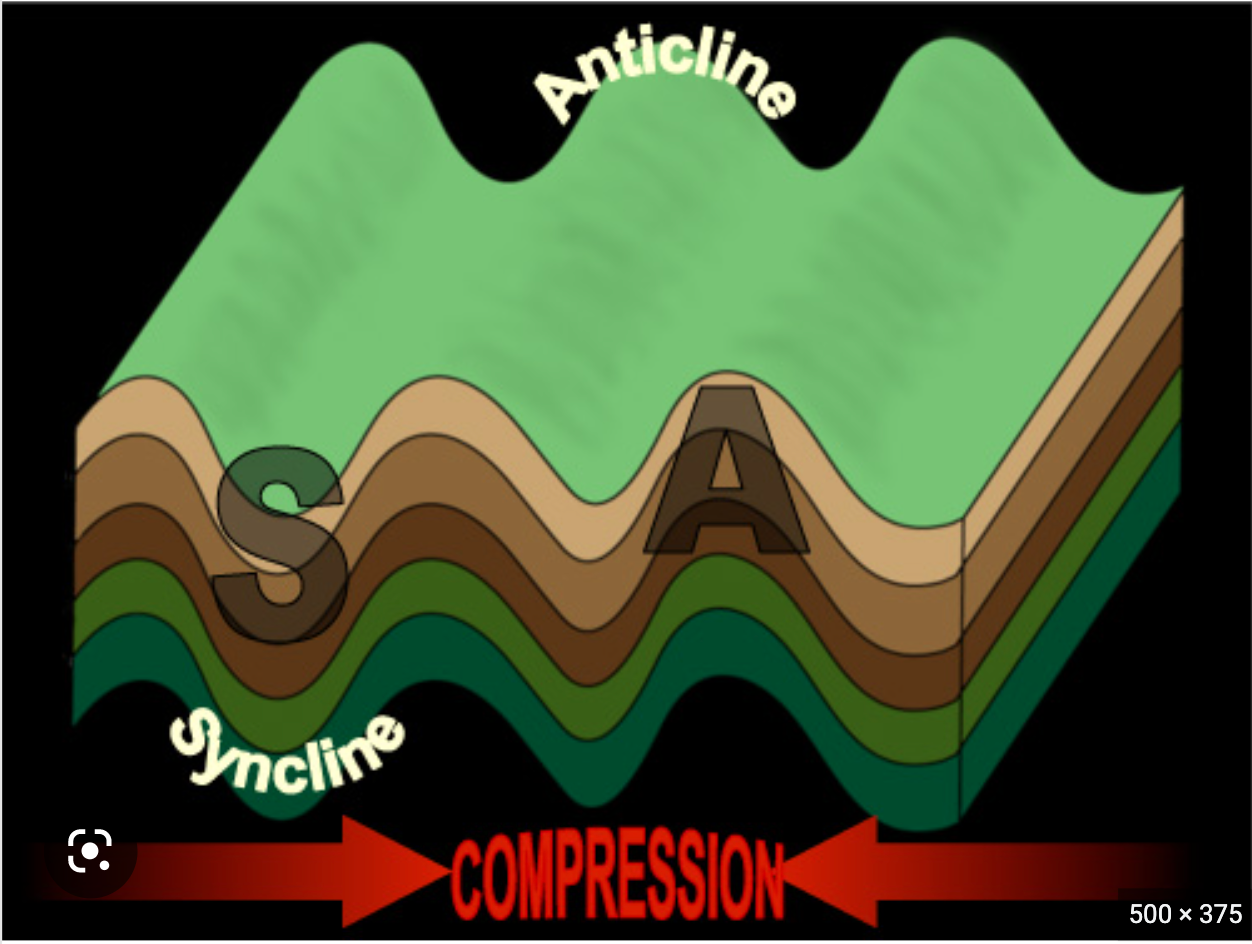
64
New cards
relative age (time)
a sequence of events
65
New cards
numerical (absolute) age (time)
The age of a feature given in years
-carbon dating (radiometric dating)
-tree rings
-lichenometry
-carbon dating (radiometric dating)
-tree rings
-lichenometry
66
New cards
radiometric dating
method used to determine the age of rocks using the rate of decay of radioactive isotopes
67
New cards
geologic time scale
represents the duration of this history
-scale used by paleontologists to represent evolutionary time
-scale used by paleontologists to represent evolutionary time
68
New cards
geologic principles for determining relative age
-created by Charles Lyell
uniformitarianism, cross-cutting relations, superposition
uniformitarianism, cross-cutting relations, superposition
69
New cards
uniformitarianism
-created by James Hutton; Lyell made it popular
-means that physical processes we observe operating today also operated in the past, at roughly comparable rates
-means that physical processes we observe operating today also operated in the past, at roughly comparable rates
70
New cards
cross-cutting relations
If one geologic feature cuts across another, the feature that has been cut is older
-if a layer of sediment buries a fault, the layer must be younger than the fault
-if a layer of sediment buries a fault, the layer must be younger than the fault
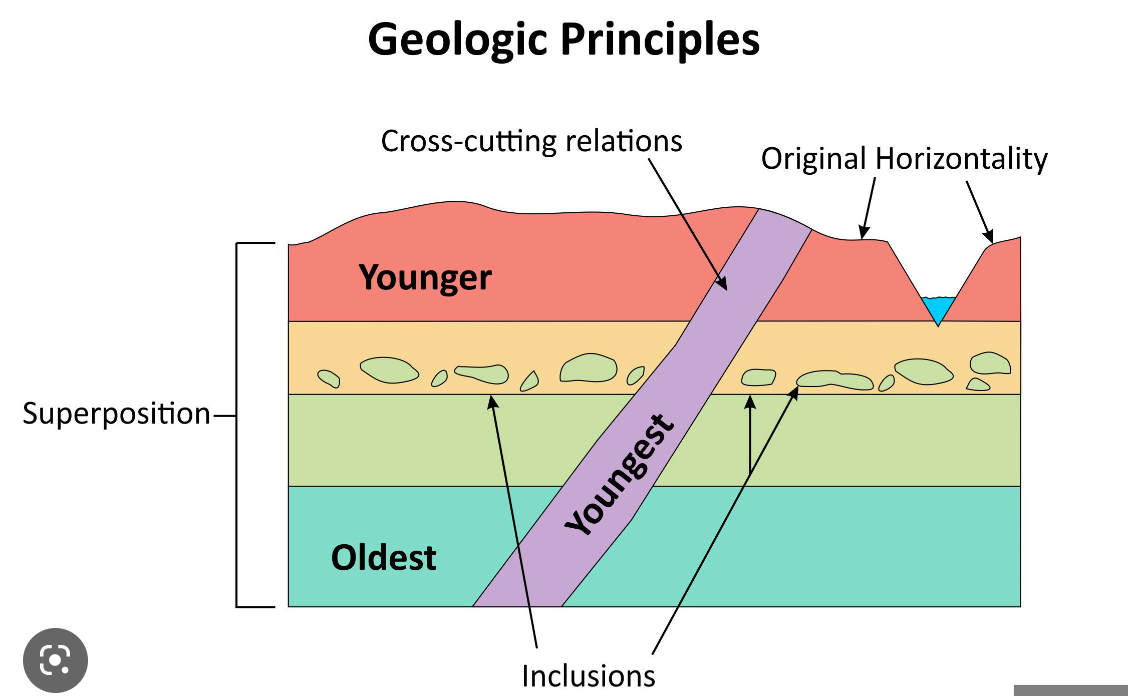
71
New cards
The principle of superposition:
the principle that in a series of stratified sedimentary rocks the lowest stratum is the oldest
-the layer at the bottom of a sequence is the oldest, and the layer at the top is the youngest
-the layer at the bottom of a sequence is the oldest, and the layer at the top is the youngest
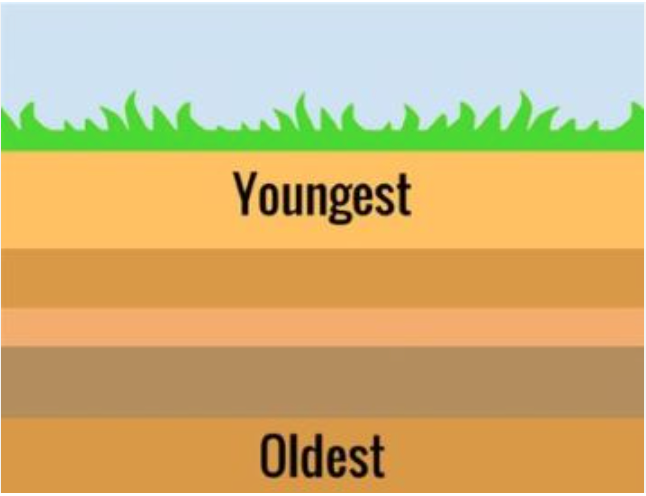
72
New cards
fossil succession
states that the assemblage of fossils in strata changes from base to top of a sequence
-created by William Smith
-created by William Smith
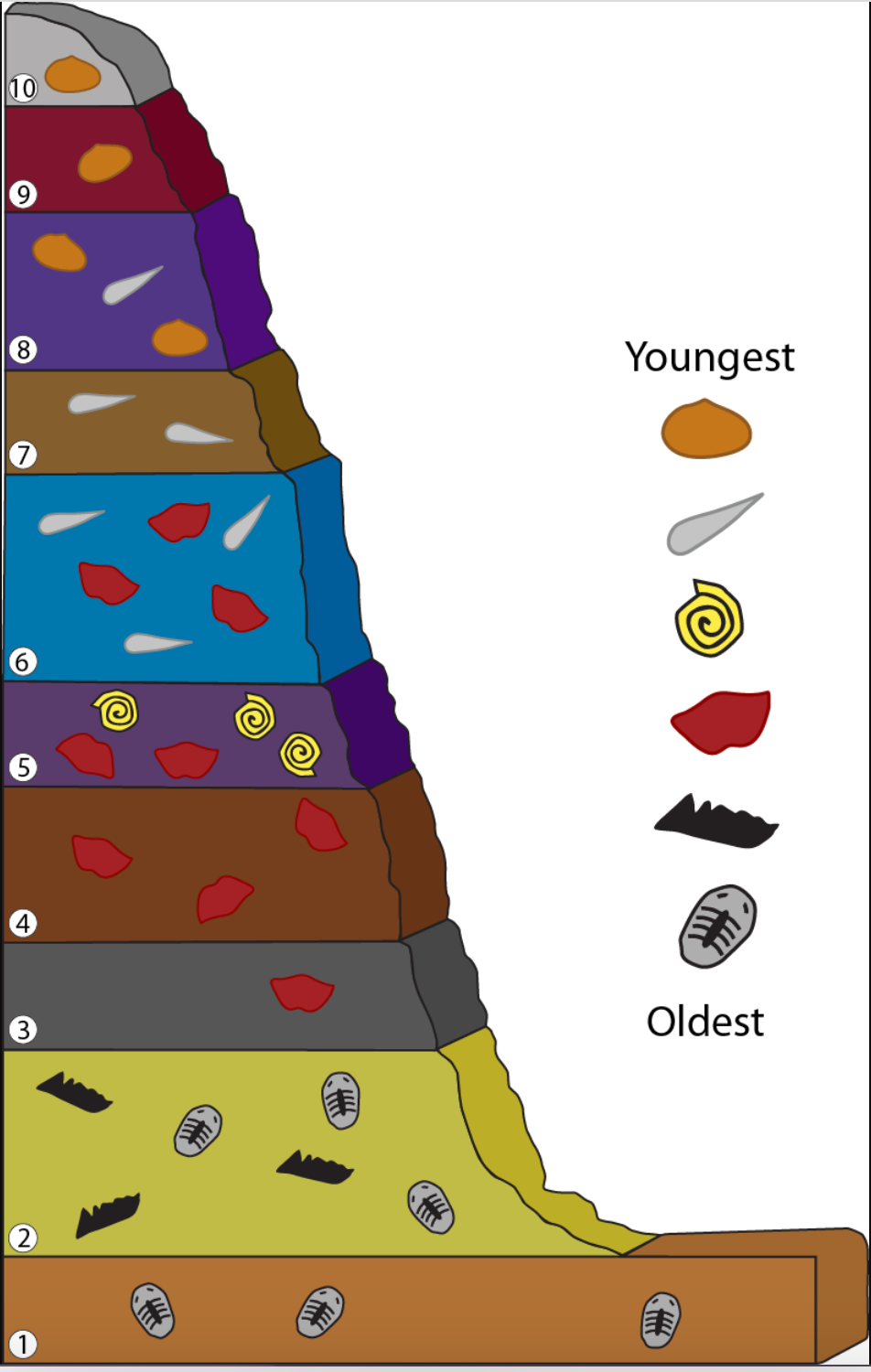
73
New cards

geologic time scale diagram
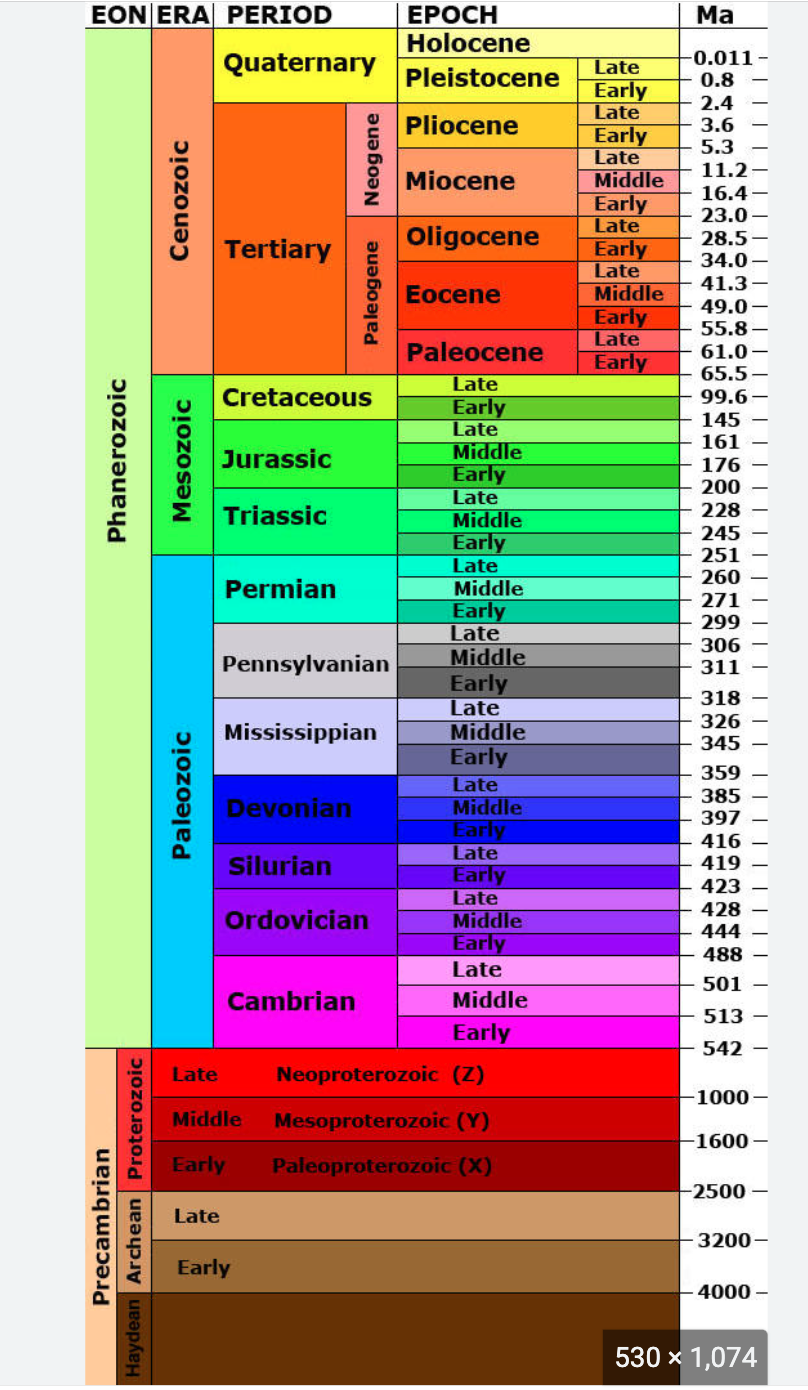
74
New cards
era
An interval of geologic time representing the largest subdivision of the Phanerozoic Eon
-paleozoic, mesozoic, cenozoic
-paleozoic, mesozoic, cenozoic
75
New cards
period
An interval of geologic time representing a subdivision of a geologic era
-ex: triassic
-ex: triassic
76
New cards
epoch
An interval of geologic time representing the largest subdivision of a period
ex: holocene of the quaternary period
ex: holocene of the quaternary period
77
New cards
K-T boundary
the Cretaceous period and rocks of the Paleogene period that provides evidence of a meteorite impact
T= also equals tertiary
T= also equals tertiary
78
New cards
Phanerozoic Eon
most recent eon, include the past 542 million years, divided into 3 eras
-paleozoic, mesozoic, cenozoic
-paleozoic, mesozoic, cenozoic
79
New cards
Paleozoic Era
the part of geologic time 570-245 million years ago ; invertebrates, fishes, amphibians, reptiles, ferns, and cone-bearing trees were dominant
80
New cards
Cambrian explosion (part of paleozoic era)
A burst of evolutionary origins when most of the major body plans of animals appeared in a relatively brief time in geologic history; recorded in the fossil record about 545 to 525 million years ago
-big animals evolved
-big animals evolved
81
New cards
Devonian Period
The Paleozoic age of fishes
82
New cards
silurian period (part of paleozoic era)
The period with the first plants
-rapid evolution of plants
-rapid evolution of plants
83
New cards
unconformity
a boundary between two different rock sequences representing an interval of time during which new strata were not deposited and/or were eroded
84
New cards
types of unconformities
angular, disconformity, nonconformity
85
New cards
Strata
layers of sedimentary rock
86
New cards
angular unconformity
the strata below were tilted or folded before the unconformity developed
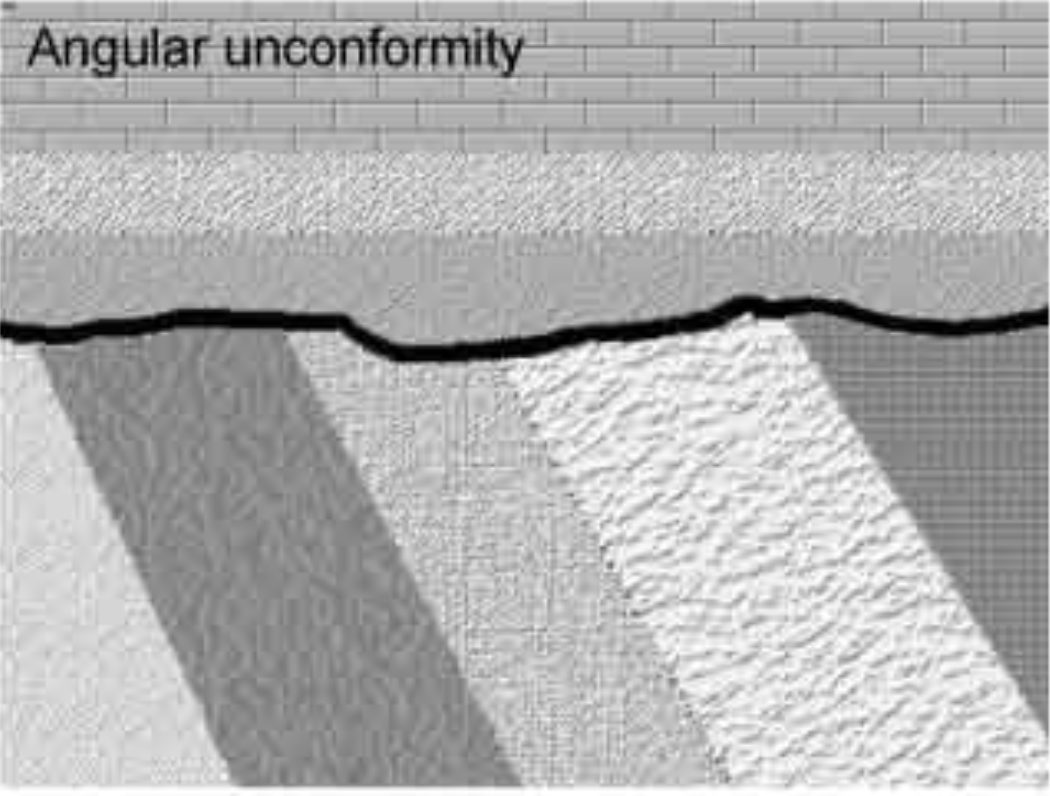
87
New cards
disconformity
an unconformity parallel to the two sedimentary sequences it separates
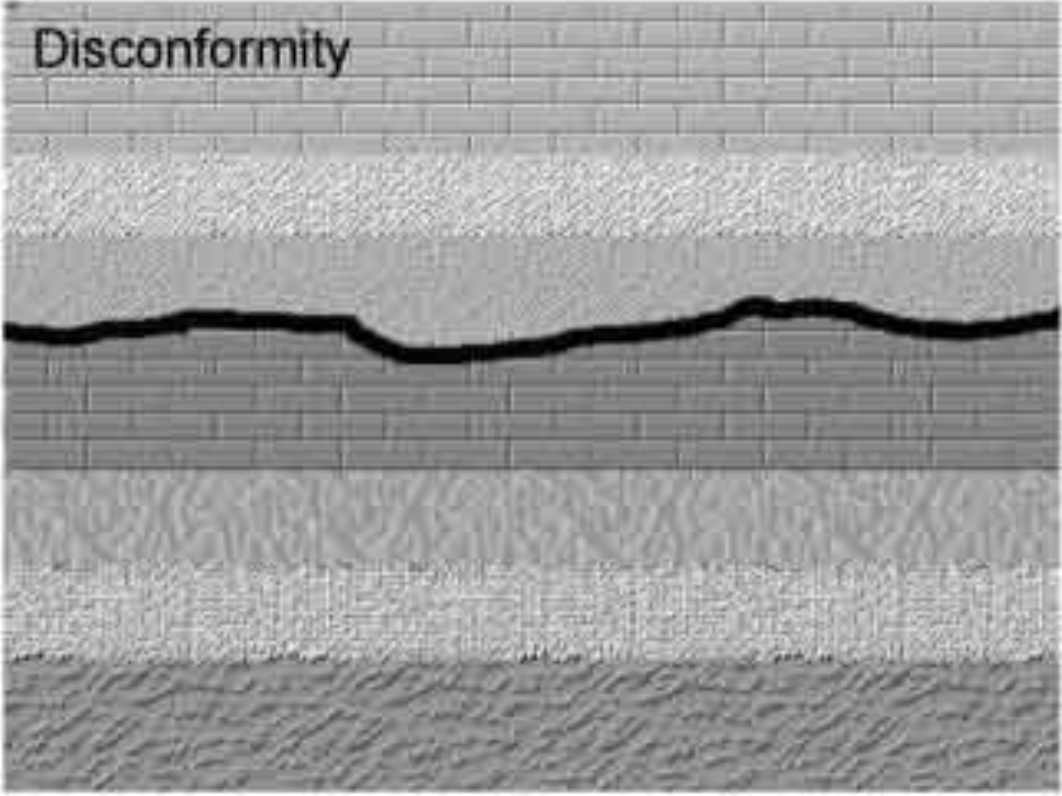
88
New cards
nonconformity
sedimentary rocks overlie generally much older intrusive igneous rocks or metamorphic rocks
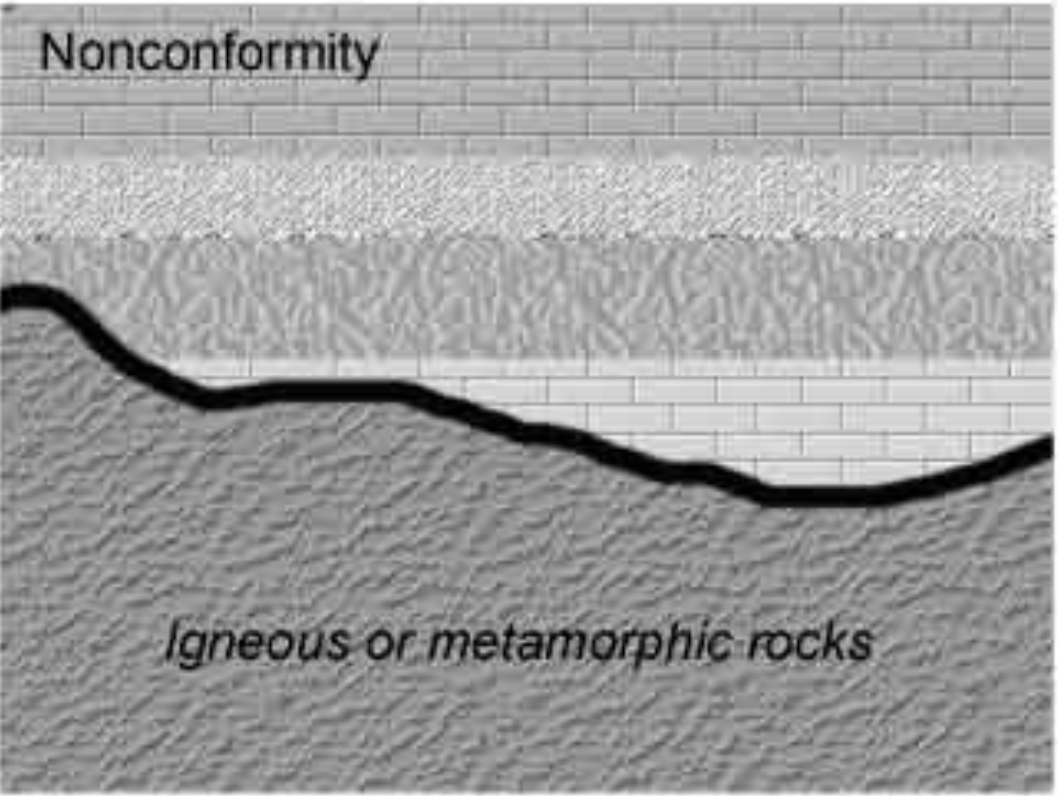
89
New cards
the grand staircase
grand canyon, zion canyon, and bryce canyon
90
New cards
radioactive decay
The process by which a radioactive isotope undergoes fission or releases particles, thereby being transformed into a new element
91
New cards
radioactive parent
an atom of a radioactive isotope that has not yet decayed
92
New cards
radiogenic daughter
the product of a radioactive decay
93
New cards
half life
the time it takes for half of a group of a radioactive element's isotopes to decay
94
New cards
Graphic representation of parent and daughter atoms vs. half life
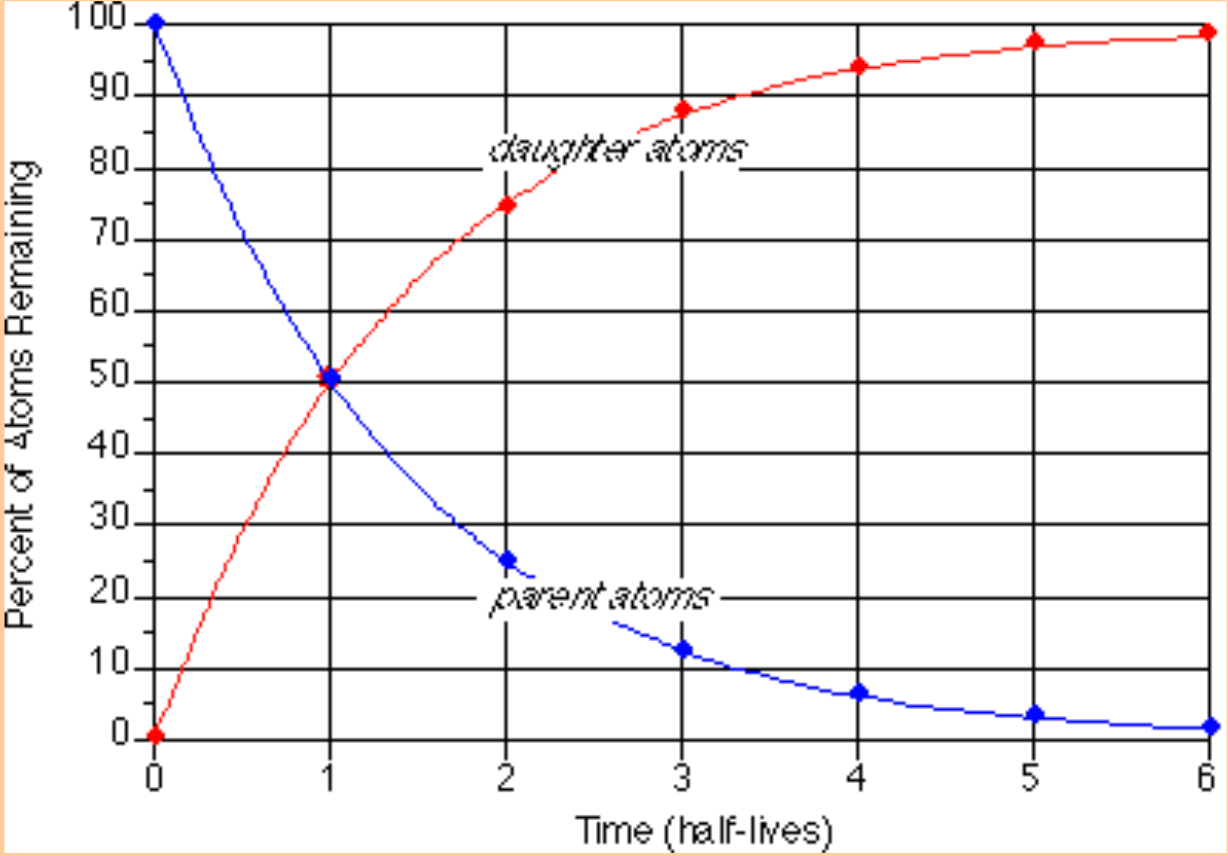
95
New cards
half life equation
t1/2 = 0.693/k
k= number of atoms/number of decays
k= number of atoms/number of decays
96
New cards
2,500 parent atoms and 17,500 daughter atoms requires
3 half lives
t1/2= 20 MY
age= 60 MY
t1/2= 20 MY
age= 60 MY
97
New cards
isotope systems
Carbon-14, C^14 Nitrogen-14, N^14
Potassium-40, K^40 Argon-40, Ar^40
Uranium-238, U^238 Lead-206, Pb^206
Rubidium-87, Rb^87 Strontium-87, Sr^87
Potassium-40, K^40 Argon-40, Ar^40
Uranium-238, U^238 Lead-206, Pb^206
Rubidium-87, Rb^87 Strontium-87, Sr^87
98
New cards
Determining numerical (absolute) age of sedimentary rocks
-Studying cross cutting relationships between sedimentary rocks and datable igneous or metamorphic rocks.
-The Geologic Time Scale: A scale that describes the intervals of geologic time
-The Geologic Time Scale: A scale that describes the intervals of geologic time
99
New cards
age of earth
4.56 Ga
100
New cards
Lord Kelvin (William Thomson)
-1862- 1897
calculated earth was 20 MY old
calculated earth was 20 MY old